Genome-Wide Investigation of CPK-Related Kinase (CRK) Gene Family in Arabidopsis thaliana
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
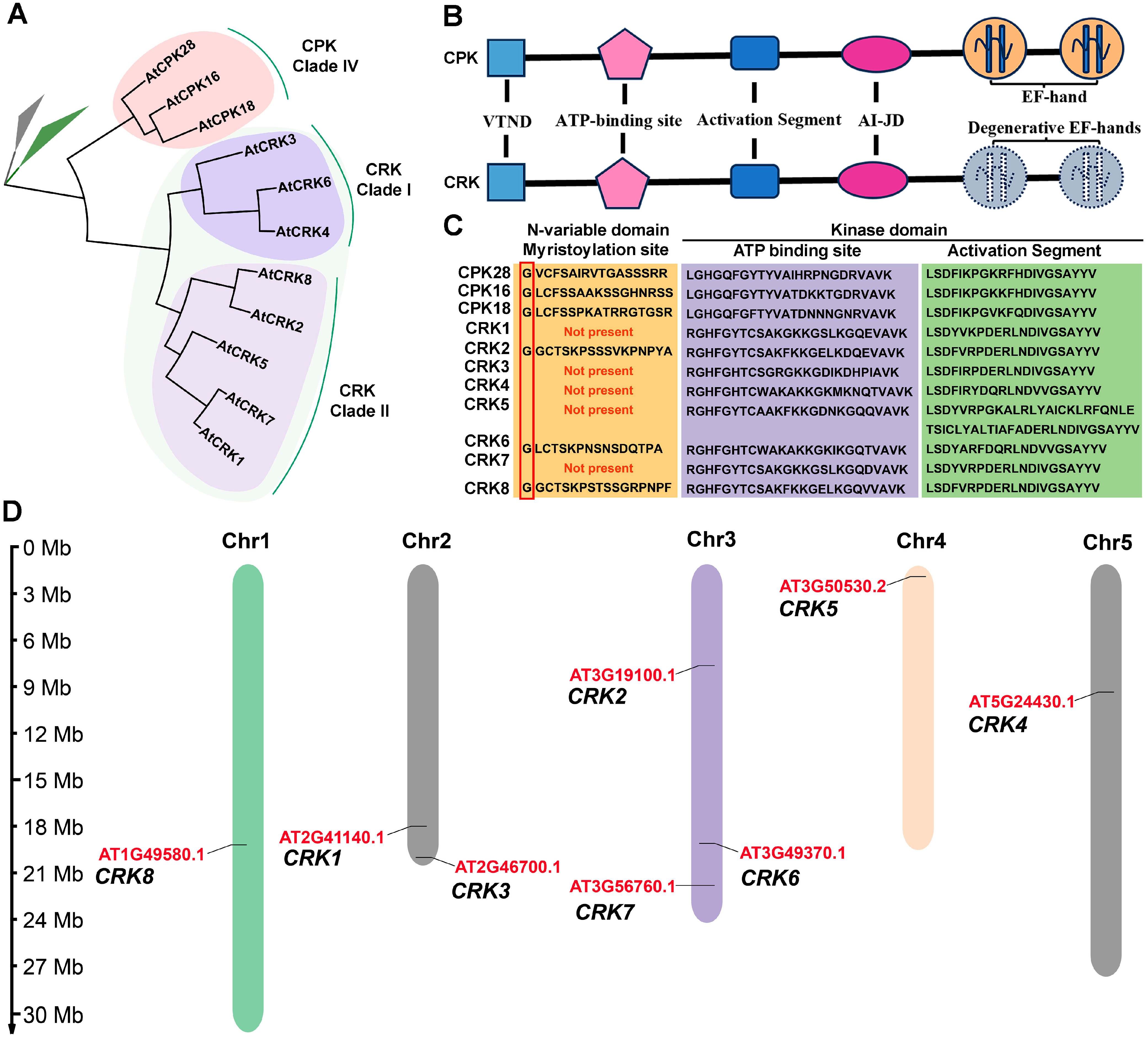
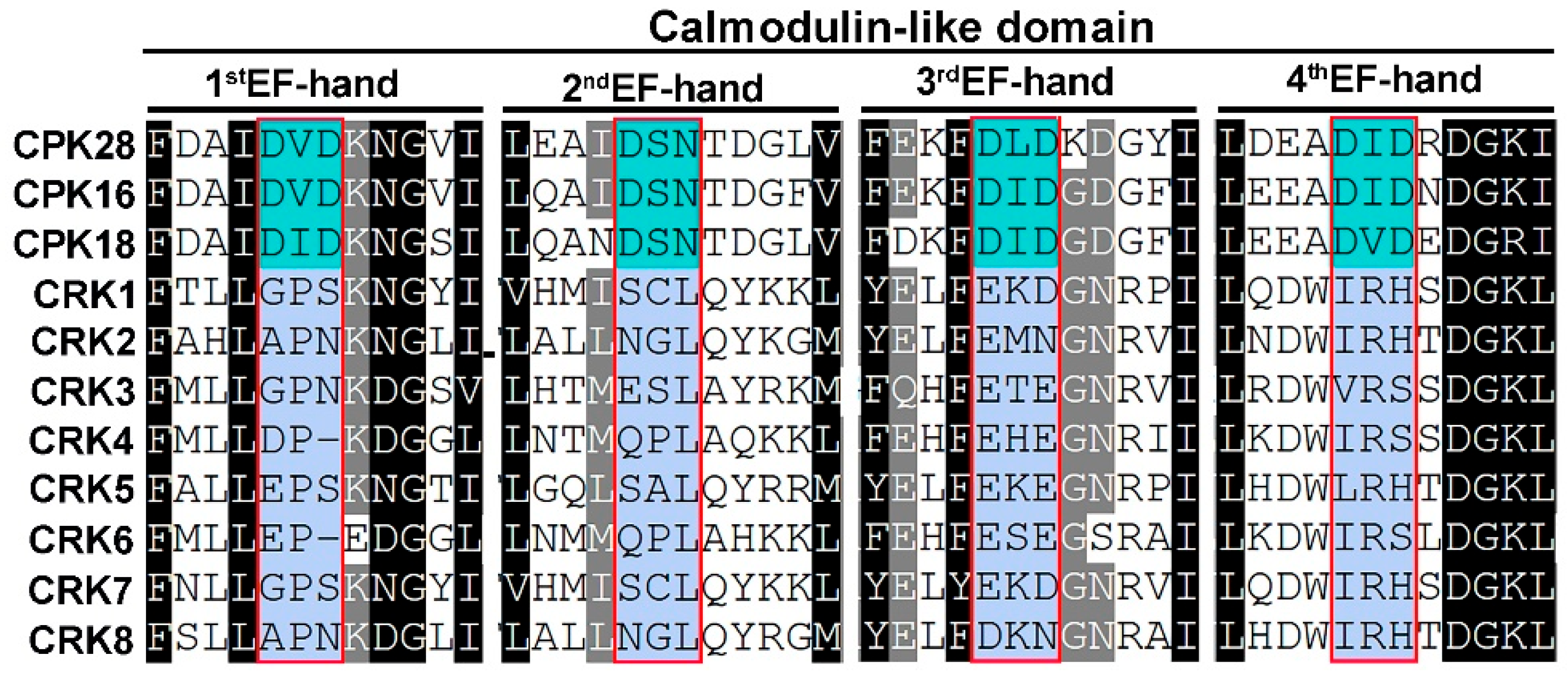
2.1. CRK Represents a Group of CPK-like Kinase That Contains Degenerative EF-Hands
2.2. Distribution of CRK Genes and Analysis of the Physicochemical Properties of CRK Proteins
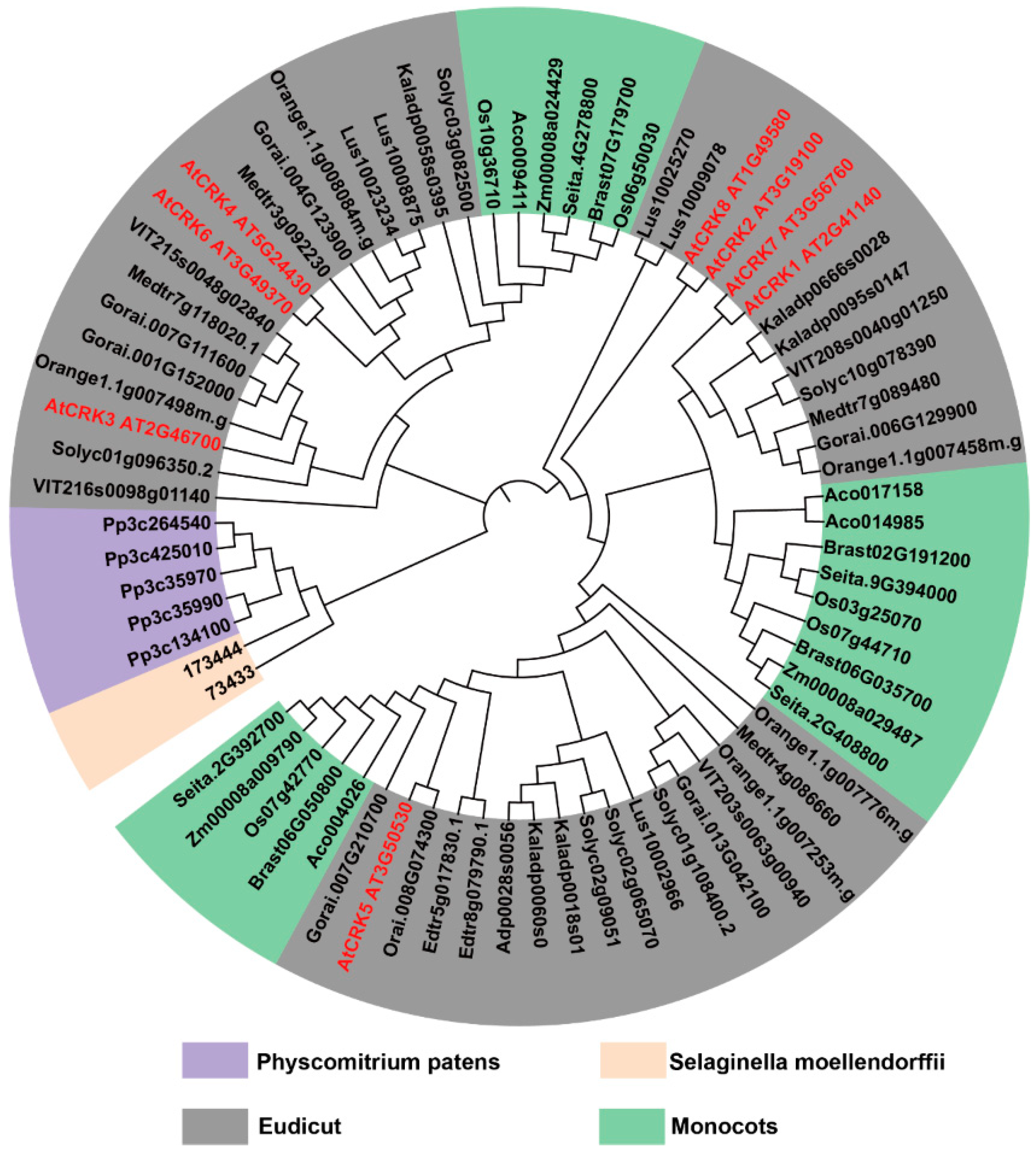
2.3. CRK Widely Exists in Land Plants
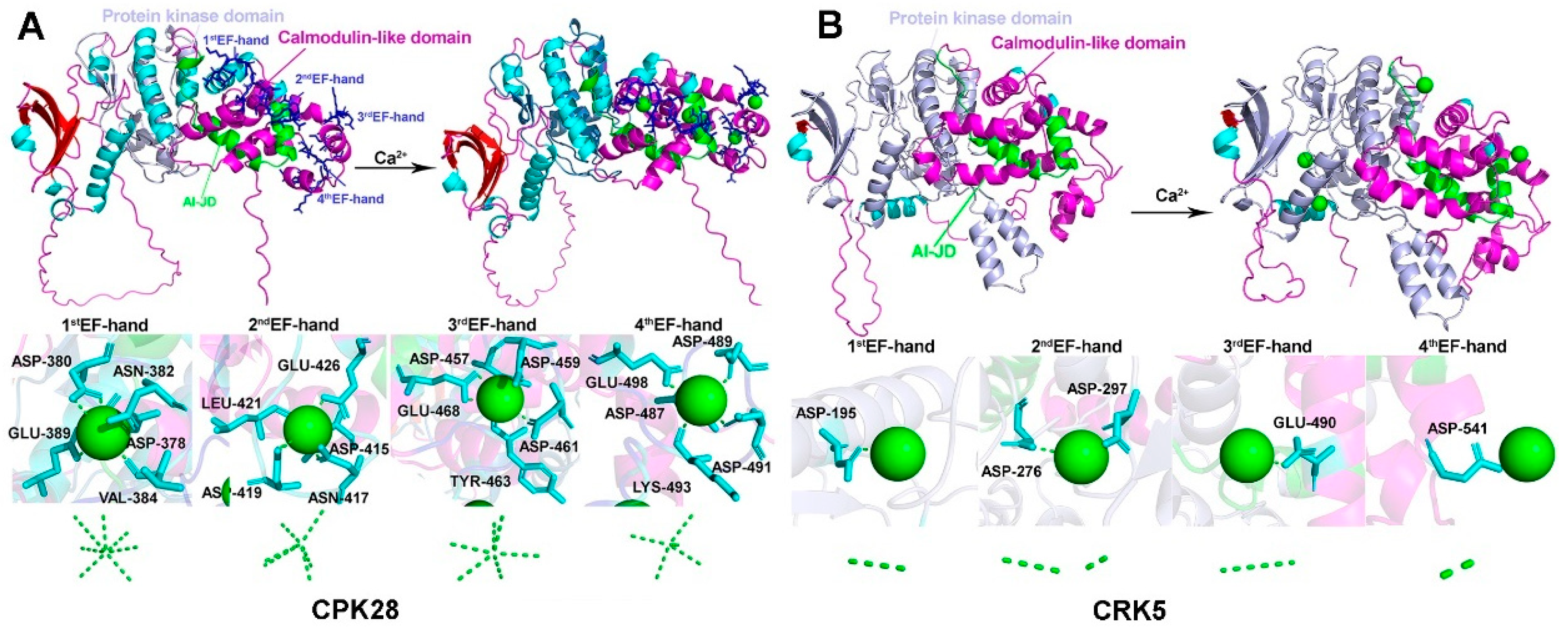
2.4. CRK Loses the Ability to Associate with Ca2+
2.5. The Subcellular Localizations of CRK
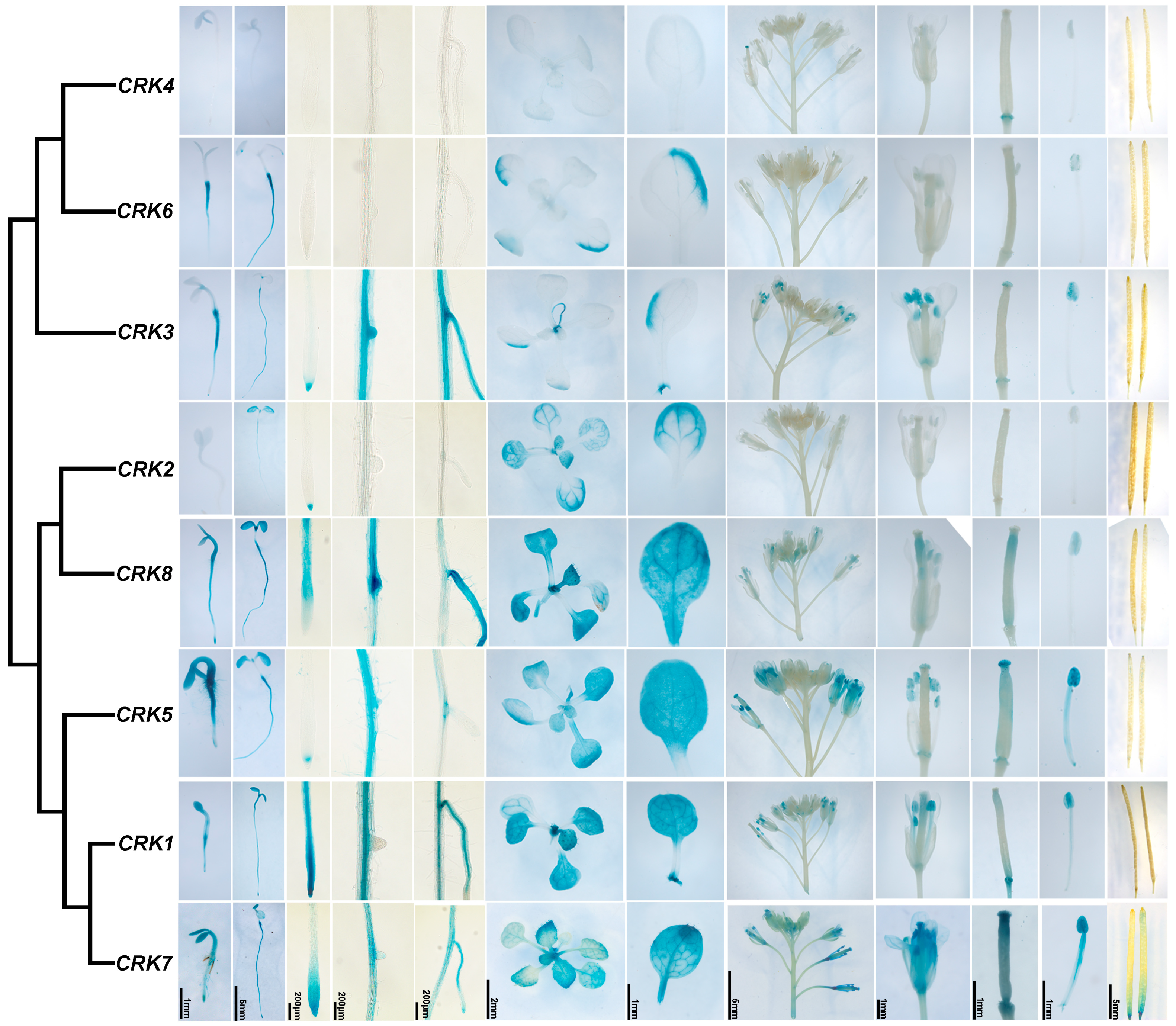
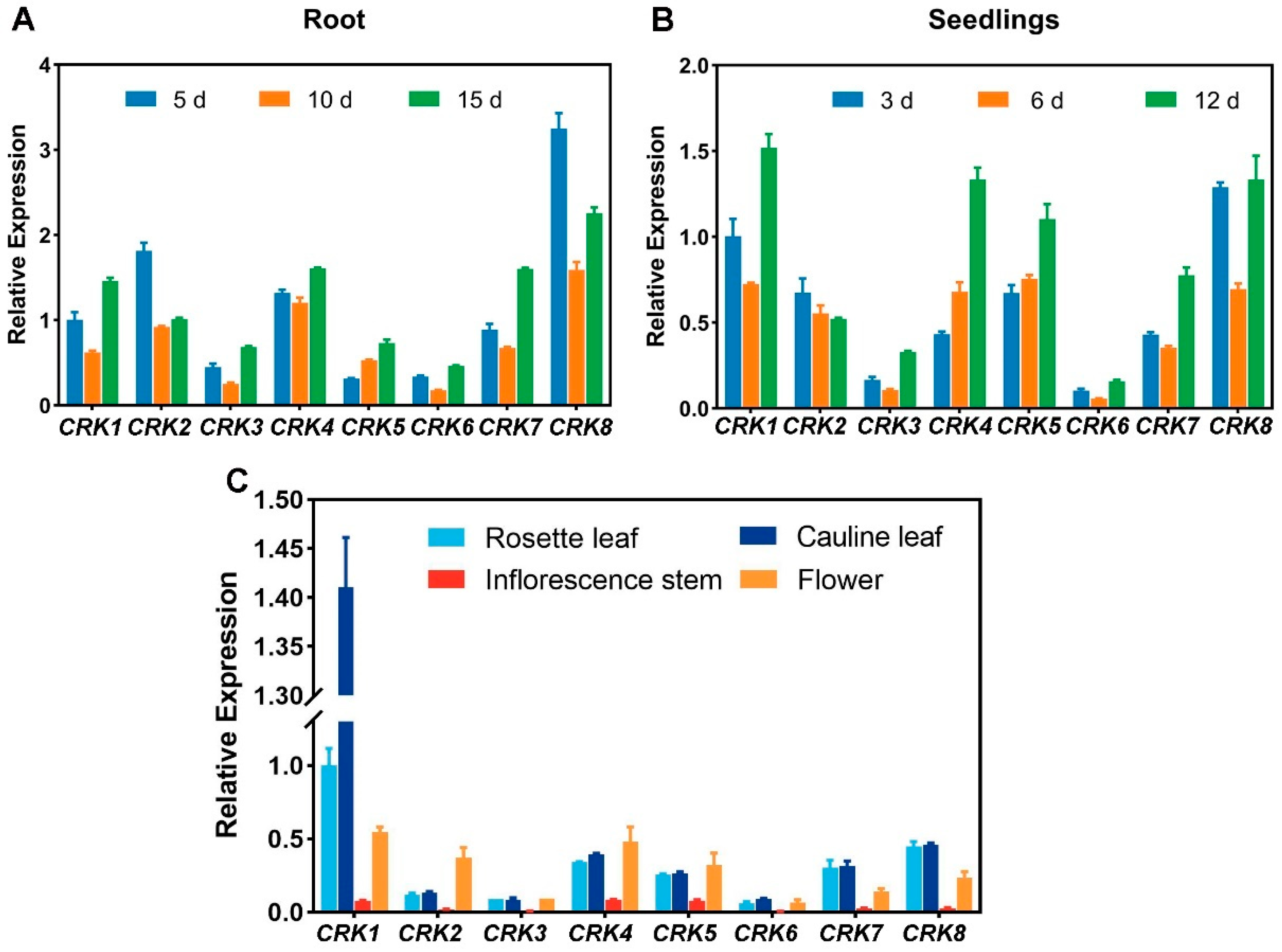
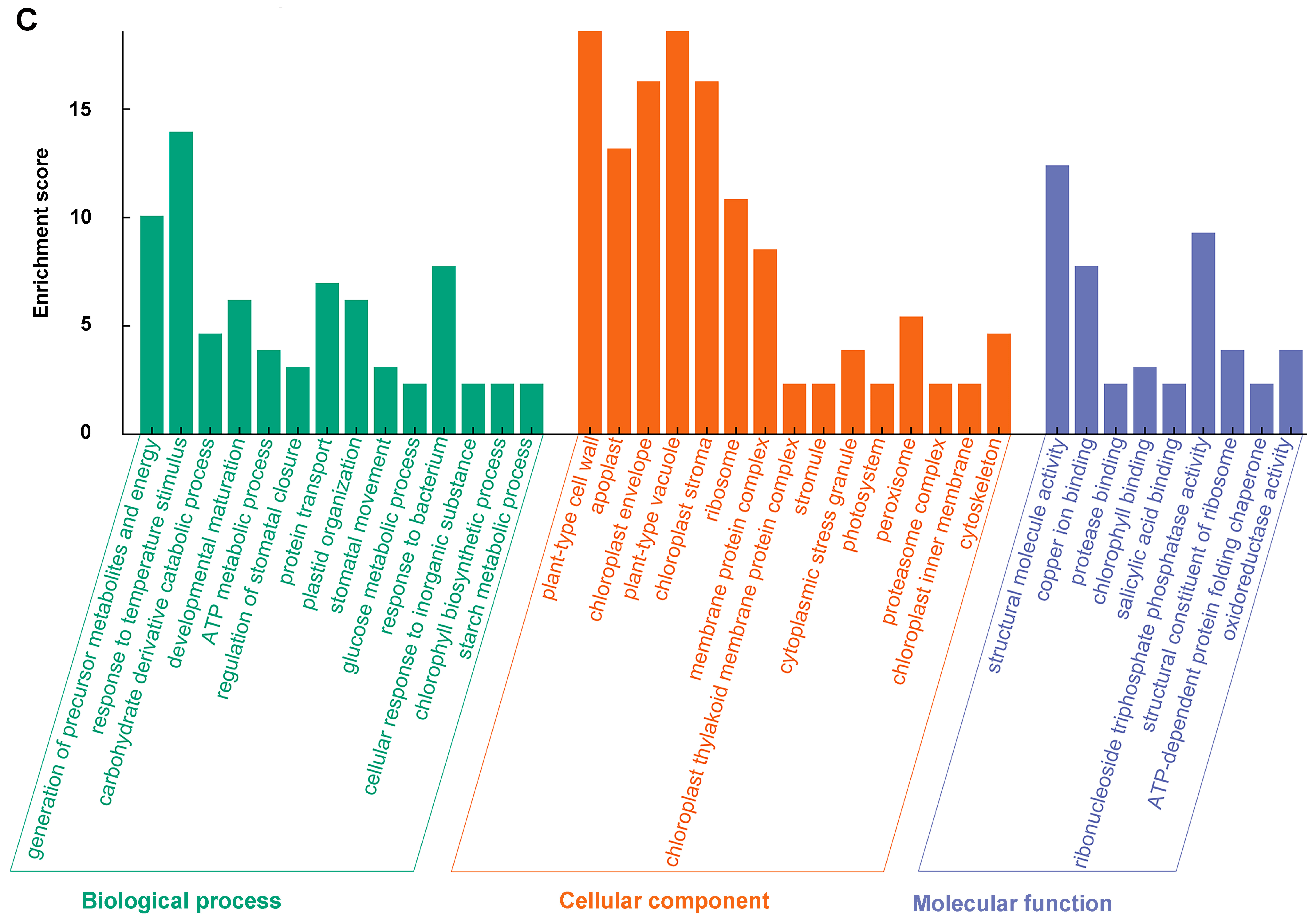
2.6. The Expression Patterns of CRK Genes in Arabidopsis
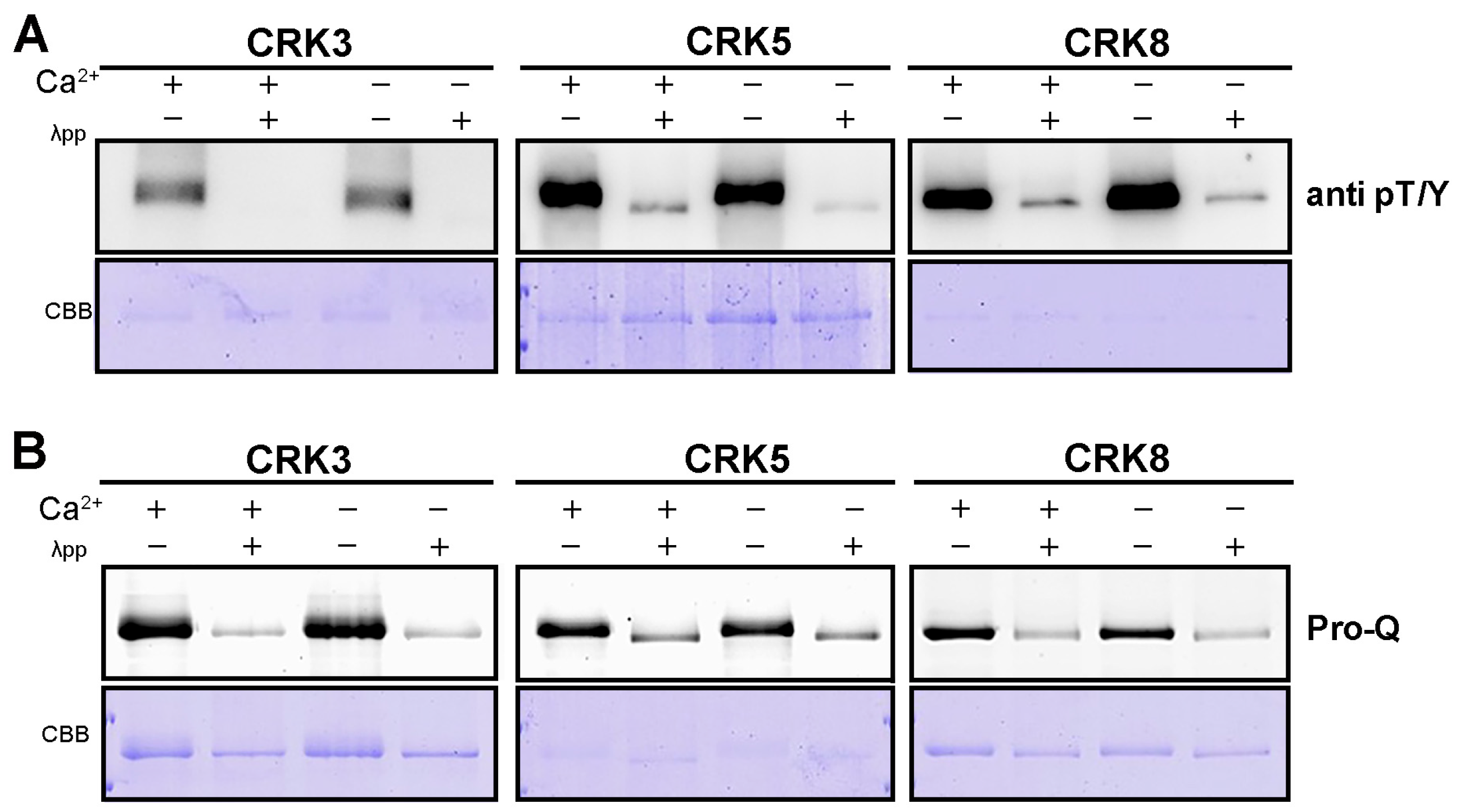
2.7. The Kinase Activity of Arabidopsis CRK Is Ca2+-Independent
2.8. The Analysis of Cis-Elements of the Promoters of CRK
2.9. The Expression of CRK Genes Is in Response to Biotic and Abiotic Stresses
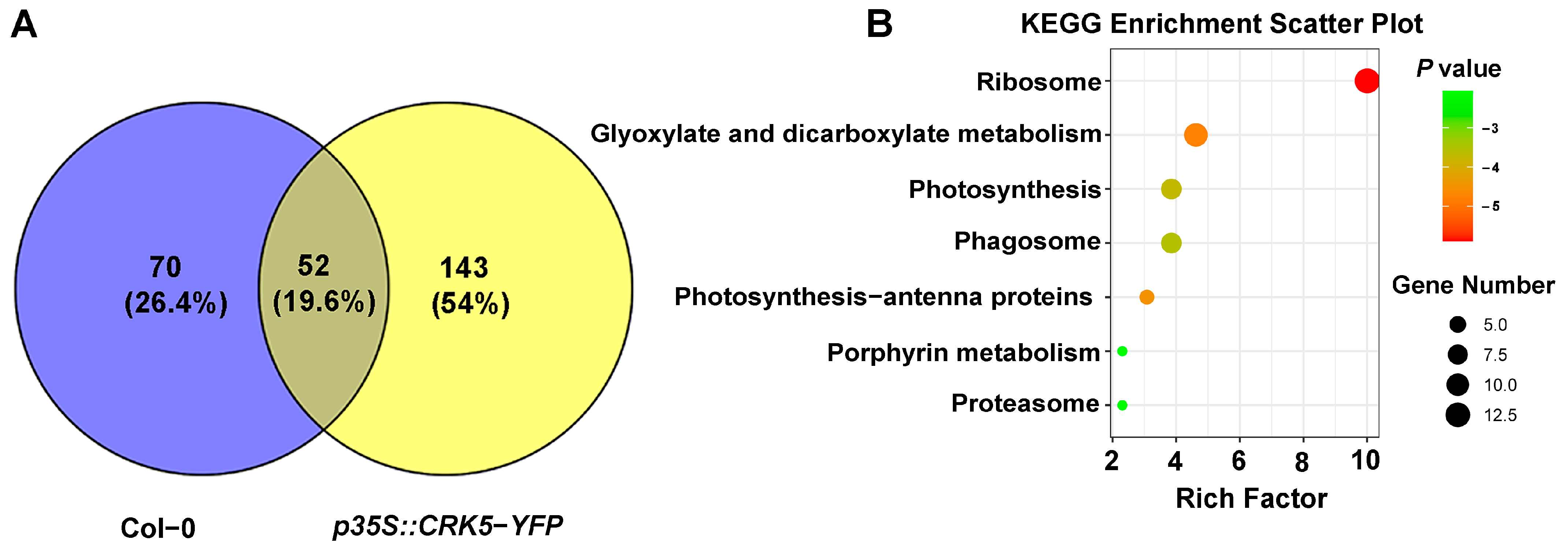
2.10. Identification of CRK-Interacting Proteins by IP-MS
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials and Growth Conditions
4.2. Molecular Cloning and Construction of Transgenic Plants
4.3. Database Search and Sequence Retrieval
4.4. Phylogenetic Analysis and Chromosomal Distributions of CRK Genes
4.5. Multiple Sequence Alignment and Myristoylation Site Prediction
4.6. Model Performance Analysis and Visualization
4.7. Promoter Sequence Analysis and Physicochemical Properties of CRK Proteins
4.8. Subcellular Localization Assay
4.9. Expression and Purification of Recombinant CRK in Escherichia coli
4.10. In Vitro Kinase Assays
4.11. GUS Staining
4.12. RT-qPCR
4.13. Mass Spectrometry Analysis
4.14. Data Acquisition and Statistics
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Friso, G.; van Wijk, K.J. Posttranslational Protein Modifications in Plant Metabolism. Plant Physiol. 2015, 169, 1469–1487. [Google Scholar]
- Matte, A.; Tari, L.W.; Delbaere, L.T. How do kinases transfer phosphoryl groups? Structure 1998, 6, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Su, Y.H.; Xu, T. Protein phosphorylation: A molecular switch in plant signaling. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 112729. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Luan, S.; Wang, C. Calcium Signaling Mechanisms Across Kingdoms. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 37, 311–340. [Google Scholar]
- Mohanta, T.K.; Yadav, D.; Khan, A.L.; Hashem, A.; Abd Allah, E.F.; Al-Harrasi, A. Molecular Players of EF-hand Containing Calcium Signaling Event in Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrabak, E.M.; Chan, C.W.; Gribskov, M.; Harper, J.F.; Choi, J.H.; Halford, N.; Kudla, J.; Luan, S.; Nimmo, H.G.; Sussman, M.R.; et al. The Arabidopsis CDPK-SnRK superfamily of protein kinases. Plant Physiol. 2003, 132, 666–680. [Google Scholar]
- Polge, C.; Thomas, M. SNF1/AMPK/SnRK1 kinases, global regulators at the heart of energy control? Trends Plant Sci. 2007, 12, 20–28. [Google Scholar]
- Jossier, M.; Bouly, J.P.; Meimoun, P.; Arjmand, A.; Lessard, P.; Hawley, S.; Grahame, H.D.; Thomas, M. SnRK1 (SNF1-related kinase 1) has a central role in sugar and ABA signalling in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 2009, 59, 316–328. [Google Scholar]
- Baena-Gonzalez, E.; Rolland, F.; Thevelein, J.M.; Sheen, J. A central integrator of transcription networks in plant stress and energy signalling. Nature 2007, 448, 938–942. [Google Scholar]
- Margalha, L.; Confraria, A.; Baena-Gonzalez, E. SnRK1 and TOR: Modulating growth-defense trade-offs in plant stress responses. J. Exp. Bot. 2019, 70, 2261–2274. [Google Scholar]
- Fujii, H.; Verslues, P.E.; Zhu, J.K. Identification of two protein kinases required for abscisic acid regulation of seed germination, root growth, and gene expression in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Ma, L.; Zhang, Z.; Mu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, L.; Xie, S.; et al. Initiation and amplification of SnRK2 activation in abscisic acid signaling. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2456. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Luan, S. The CBL-CIPK network in plant calcium signaling. Trends Plant Sci. 2009, 14, 37–42. [Google Scholar]
- Luan, S.; Kudla, J.; Rodriguez-Concepcion, M.; Yalovsky, S.; Gruissem, W. Calmodulins and calcineurin B-like proteins: Calcium sensors for specific signal response coupling in plants. Plant Cell 2002, 14, 389–400. [Google Scholar]
- Harper, J.F.; Breton, G.; Harmon, A. Decoding Ca2+ signals through plant protein kinases. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2004, 55, 263–288. [Google Scholar]
- Lindzen, E.; Choi, J.H. A carrot cDNA encoding an atypical protein kinase homologous to plant calcium-dependent protein kinases. Plant Mol. Biol. 1995, 28, 785–797. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, B.F.; Liang, S.; Jones, R.L.; Lu, Y.T. Molecular and biochemical characterization of a calcium/calmodulin-binding protein kinase from rice. Biochem. J. 2002, 368, 145–157. [Google Scholar]
- Furumoto, T.; Ogawa, N.; Hata, S.; Izui, K. Plant calcium-dependent protein kinase-related kinases (CRKs) do not require calcium for their activities. FEBS Lett. 1996, 396, 147–151. [Google Scholar]
- Hua, W.; Zhang, L.; Liang, S.; Jones, R.L.; Lu, Y.T. A tobacco calcium/calmodulin-binding protein kinase functions as a negative regulator of flowering. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 31483–31494. [Google Scholar]
- Leclercq, J.; Ranty, B.; Sanchez-Ballesta, M.T.; Li, Z.; Jones, B.; Jauneau, A.; Pech, J.C.; Latche, A.; Ranjeva, R.; Bouzayen, M. Molecular and biochemical characterization of LeCRK1, a ripening-associated tomato CDPK-related kinase. J. Exp. Bot. 2005, 56, 25–35. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.P.; Xu, Y.P.; Munyampundu, J.P.; Liu, T.Y.; Cai, X.Z. Calcium-dependent protein kinase (CDPK) and CDPK-related kinase (CRK) gene families in tomato: Genome-wide identification and functional analyses in disease resistance. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2016, 291, 661–676. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Li, X.D.; Jia, D.; Qi, L.; Jing, R.; Hao, J.; Wang, Z.; Cheng, J.; Chen, L.M. ZmCRK1 negatively regulates maize’s response to drought stress by phosphorylating plasma membrane H+-ATPase ZmMHA2. N. Phytol. 2024, 244, 1362–1376. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, X.C.; Lu, Y.T. Loss of AtCRK1 gene function in Arabidopsis thaliana decreases tolerance to salt. J. Plant Biol. 2013, 56, 306–314. [Google Scholar]
- Baba, A.I.; Rigó, G.; Ayaydin, F.; Rehman, A.U.; Andrási, N.; Zsigmond, L.; Valkai, I.; Urbancsok, J.; Vass, I.; Pasternak, T.; et al. Functional Analysis of the Arabidopsis thaliana CDPK-Related Kinase Family: AtCRK1 Regulates Responses to Continuous Light. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemoto, K.; Takemori, N.; Seki, M.; Shinozaki, K.; Sawasaki, T. Members of the Plant CRK Superfamily Are Capable of Trans and Autophosphorylation of Tyrosine Residues. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 16665–16677. [Google Scholar]
- Nemoto, K.; Ramadan, A.; Arimura, G.I.; Imai, K.; Tomii, K.; Shinozaki, K.; Sawasaki, T. Tyrosine phosphorylation of the GARU E3 ubiquitin ligase promotes gibberellin signalling by preventing GID1 degradation. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1004. [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto, T.; Uemura, T.; Nemoto, K.; Daito, M.; Nozawa, A.; Sawasaki, T.; Arimura, G.I. Tyrosine Kinase-Dependent Defense Responses Against Herbivory in Arabidopsis. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 776. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.J.; Hua, W.; Lu, Y.T. Arabidopsis cytosolic glutamine synthetase AtGLN1;1 is a potential substrate of AtCRK3 involved in leaf senescence. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 342, 119–126. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.T.; Gao, F.; Li, G.L.; Han, J.L.; Liu, D.L.; Sun, D.Y.; Zhou, R.G. The calmodulin-binding protein kinase 3 is part of heat-shock signal transduction in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 2008, 55, 760–773. [Google Scholar]
- Rigó, G.; Ayaydin, F.; Tietz, O.; Zsigmond, L.; Kovács, H.; Páy, A.; Salchert, K.; Darula, Z.; Medzihradszky, K.F.; Szabados, L.; et al. Inactivation of plasma membrane-localized CDPK-RELATED KINASE5 decelerates PIN2 exocytosis and root gravitropic response in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 2013, 25, 1592–1608. [Google Scholar]
- Baba, A.I.; Valkai, I.; Labhane, N.M.; Koczka, L.; Andrási, N.; Klement, É.; Darula, Z.; Medzihradszky, K.F.; Szabados, L.; Fehér, A.; et al. CRK5 Protein Kinase Contributes to the Progression of Embryogenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cséplő, Á.; Zsigmond, L.; Andrási, N.; Baba, A.I.; Labhane, N.M.; Pető, A.; Kolbert, Z.; Kovács, H.E.; Steinbach, G.; Szabados, L.; et al. The AtCRK5 Protein Kinase Is Required to Maintain the ROS NO Balance Affecting the PIN2-Mediated Root Gravitropic Response in Arabidopsis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, H.J.; Guo, Y.; Wang, J.Q.; Li, R.; Lu, Y.T.; Zhang, L. WDRP, a DWD protein component of CUL4-based E3 ligases, acts as a receptor of CDPK-related protein kinase 5 to mediate kinase degradation in Arabidopsis. J. Plant Biol. 2016, 59, 627–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, J.; Shan, L. SERKs. Curr. Biol. 2020, 30, R293–R294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villalobo, A.; Gonzalez-Munoz, M.; Berchtold, M.W. Proteins with calmodulin-like domains: Structures and functional roles. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2019, 76, 2299–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, C.; Xu, Y.; Kirberger, M.; Yang, J.J. Structural aspects and prediction of calmodulin-binding proteins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 22, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.N.; Shen, L.K.; Zhang, W.Z.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; Wu, W.H. Ca2+-dependent protein kinase11 and 24 modulate the activity of the inward rectifying K+ channels in Arabidopsis pollen tubes. Plant Cell. 2013, 25, 649–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaghan, J.; Matschi, S.; Shorinola, O.; Rovenich, H.; Matei, A.; Segonzac, C.; Malinovsky, F.G.; Rathjen, J.P.; MacLean, D.; Romeis, T.; et al. The calcium-dependent protein kinase CPK28 buffers plant immunity and regulates BIK1 turnover. Cell Host Microbe 2014, 16, 605–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaghan, J.; Matschi, S.; Romeis, T.; Zipfel, C. The calcium-dependent protein kinase CPK28 negatively regulates the BIK1-mediated PAMP-induced calcium burst. Plant Signal Behav. 2015, 10, e1018497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bredow, M.; Bender, K.W.; Dingee, J.A.; Holmes, D.R.; Thomson, A.; Ciren, D.; Tanney, C.A.S.; Dunning, K.E.; Trujillo, M.; Huber, S.C.; et al. Phosphorylation-dependent subfunctionalization of the calcium-dependent protein kinase CPK28. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2024272118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hailemariam, S.; Liao, C.J.; Mengiste, T. Receptor-like cytoplasmic kinases: Orchestrating plant cellular communication. Trends Plant Sci. 2024, 29, 1113–1130. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wen, J.; Lease, K.A.; Doke, J.T.; Tax, F.E.; Walker, J.C. BAK1, an Arabidopsis LRR receptor-like protein kinase, interacts with BRI1 and modulates brassinosteroid signaling. Cell 2002, 110, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nam, K.H.; Li, J. BRI1/BAK1, a receptor kinase pair mediating brassinosteroid signaling. Cell 2002, 110, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, K.; Gou, X.; Yuan, T.; Lin, H.; Asami, T.; Yoshida, S.; Russell, S.D.; Li, J. BAK1 and BKK1 Regulate Brassinosteroid-Dependent Growth and Brassinosteroid-Independent Cell-Death Pathways. Curr. Biol. 2007, 17, 1109–1115. [Google Scholar]
- Chinchilla, D.; Zipfel, C.; Robatzek, S.; Kemmerling, B.; Nurnberger, T.; Jones, J.D.; Felix, G.; Boller, T. A flagellin-induced complex of the receptor FLS2 and BAK1 initiates plant defence. Nature 2007, 448, 497–500. [Google Scholar]
- Heese, A.; Hann, D.R.; Gimenez-Ibanez, S.; Jones, A.M.; He, K.; Li, J.; Schroeder, J.I.; Peck, S.C.; Rathjen, J.P. The receptor-like kinase SERK3/BAK1 is a central regulator of innate immunity in plants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 12217–12222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhan, Y.; Kui, H.; Liu, H.; Yan, L.; Kemmerling, B.; Zhou, J.M.; He, K.; Li, J. Loss of the common immune coreceptor BAK1 leads to NLR-dependent cell death. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 27044–27053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liese, A.; Eichstädt, B.; Lederer, S.; Schulz, P.; Oehlschläger, J.; Matschi, S.; Feijó, J.A.; Schulze, W.X.; Konrad, K.R.; Romeis, T. Imaging of plant calcium-sensor kinase conformation monitors real time calcium-dependent decoding in planta. Plant Cell 2024, 36, 276–297. [Google Scholar]
- Delormel, Y.T.; Boudsocq, M. Properties and functions of calcium-dependent protein kinases and their relatives in Arabidopsis thaliana. N. Phytol. 2019, 224, 585–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Ding, Y.; Yang, Y.; Song, C.; Wang, B.; Yang, S.; Guo, Y.; Gong, Z. Protein kinases in plant responses to drought, salt, and cold stress. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2021, 63, 53–78. [Google Scholar]
- Clough, S.J.; Bent, A.F. Floral dip: A simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 1998, 16, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sievers, F.; Wilm, A.; Dineen, D.; Gibson, T.J.; Karplus, K.; Li, W.; Lopez, R.; McWilliam, H.; Remmert, M.; Soding, J.; et al. Fast, scalable generation of high-quality protein multiple sequence alignments using Clustal Omega. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2011, 7, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Peterson, D.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. MEGA6: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, J.; Li, Z.; Sun, Y.; Aluko, O.O.; Wu, X.; Wang, Q.; Liu, G. MG2C: A user-friendly online tool for drawing genetic maps. Mol. Hortic. 2021, 1, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramson, J.; Adler, J.; Dunger, J.; Evans, R.; Green, T.; Pritzel, A.; Ronneberger, O.; Willmore, L.; Ballard, A.J.; Bambrick, J. Accurate structure prediction of biomolecular interactions with AlphaFold3. Nature 2024, 630, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Zeng, Z.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Feng, J.; Chen, H.; He, Y.; et al. TBtools-II: A “one for all, all for one” bioinformatics platform for biological big-data mining. Mol. Plant 2023, 16, 1733–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Liu, B.; Kong, H.; Zeng, J.; Feng, Y.; Xiao, C.; Shao, Q.; Huang, X.; Wu, Y.; Bao, A.; et al. Two calcium sensor-activated kinases function in root hair growth. Plant Physiol. 2024, 196, 1534–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Hu, C.; Zhu, Y.; Cheng, K.; Li, X.; Wei, Z.; Xue, L.; Lin, F.; Shi, H.; Yi, J.; et al. CIK Receptor Kinases Determine Cell Fate Specification during Early Anther Development in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2018, 30, 2383–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Fang, X.; Xiao, C.; Ma, Z.; Huang, X.; Su, J.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Luan, S.; et al. Kinase SnRK1.1 regulates nitrate channel SLAH3 engaged in nitrate-dependent alleviation of ammonium toxicity. Plant Physiol. 2021, 186, 731–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Protein Name | Number of Amino Acid | Molecular Weight | Theoretical pI | Instability Index | Aliphatic Index | Grand Average of Hydropathicity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CRK1 | 576 | 64,315.06 | 8.76 | 47.87 | 84.97 | −0.232 |
| CRK2 | 599 | 67,207.07 | 9.06 | 53.91 | 86.49 | −0.340 |
| CRK3 | 595 | 66,600.05 | 8.96 | 47.04 | 82.64 | −0.395 |
| CRK4 | 594 | 66,513.96 | 8.46 | 49.52 | 79.33 | −0.369 |
| CRK5 | 632 | 70,478.64 | 9.01 | 47.31 | 81.99 | −0.312 |
| CRK6 | 594 | 66,371.73 | 8.33 | 52.60 | 81.99 | −0.328 |
| CRK7 | 577 | 64,547.31 | 8.84 | 51.55 | 88.54 | −0.245 |
| CRK8 | 606 | 67,972.80 | 9.15 | 51.59 | 81.65 | −0.352 |
| EF-Hand | CPK | CRK |
|---|---|---|
| 1st | D-x-D, D-x-N, D | None |
| 2nd | D-x-D, D-x-N, D | None |
| 3rd | D-x-D, D-x-N | None |
| 4th | D-x-D, D-x-N | None |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, S.; Fang, Y.; Fang, X.; He, J.; He, K. Genome-Wide Investigation of CPK-Related Kinase (CRK) Gene Family in Arabidopsis thaliana. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3297. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073297
Yang S, Fang Y, Fang X, He J, He K. Genome-Wide Investigation of CPK-Related Kinase (CRK) Gene Family in Arabidopsis thaliana. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(7):3297. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073297
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Shiquan, Yuan Fang, Xianming Fang, Jingwen He, and Kai He. 2025. "Genome-Wide Investigation of CPK-Related Kinase (CRK) Gene Family in Arabidopsis thaliana" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 7: 3297. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073297
APA StyleYang, S., Fang, Y., Fang, X., He, J., & He, K. (2025). Genome-Wide Investigation of CPK-Related Kinase (CRK) Gene Family in Arabidopsis thaliana. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(7), 3297. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073297








