Role of Toxoplasma gondii p24δ in Regulating the Transition from Tachyzoite to Bradyzoite Development
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
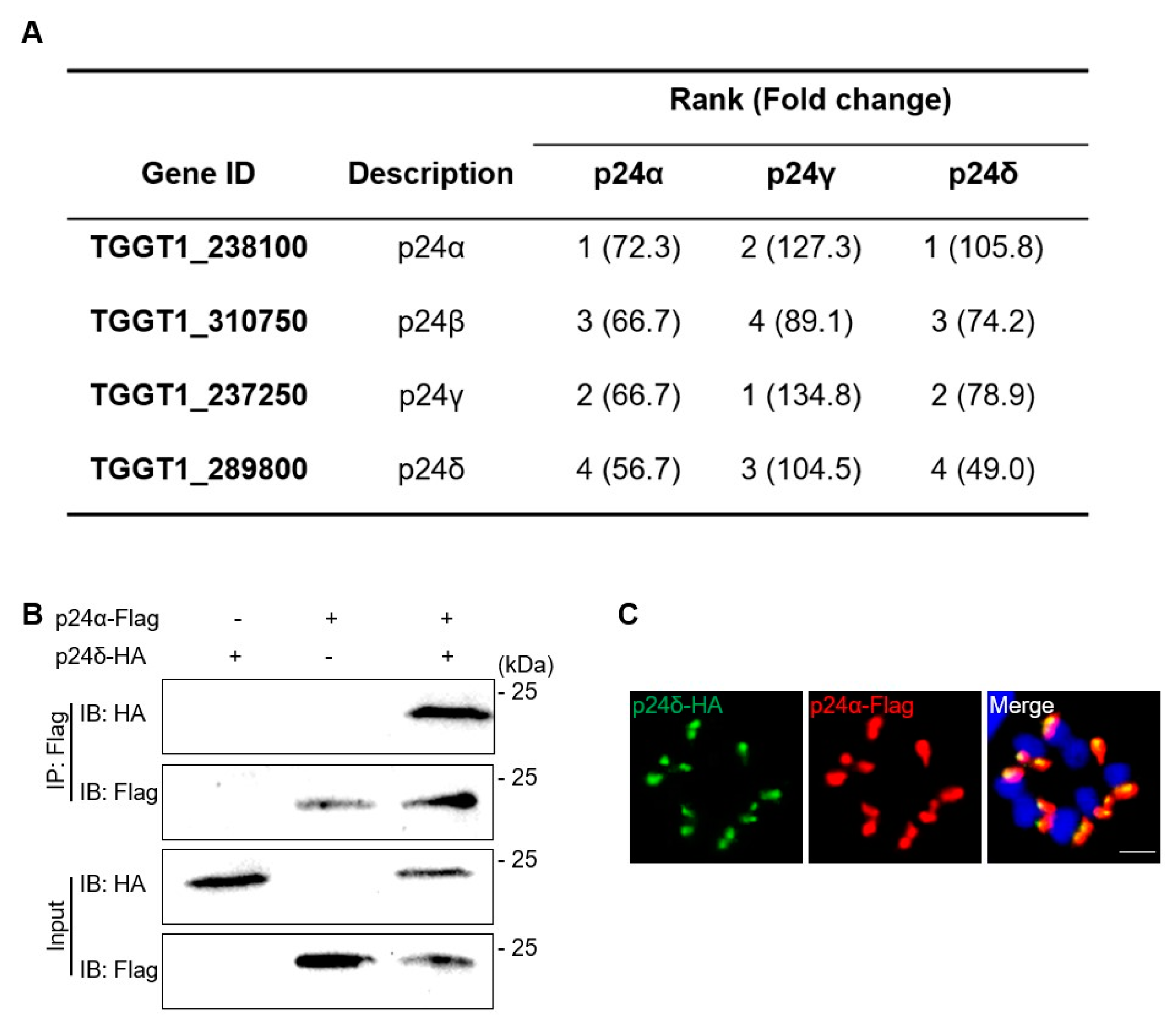
2.1. Characterization of p24 Protein in T. gondii
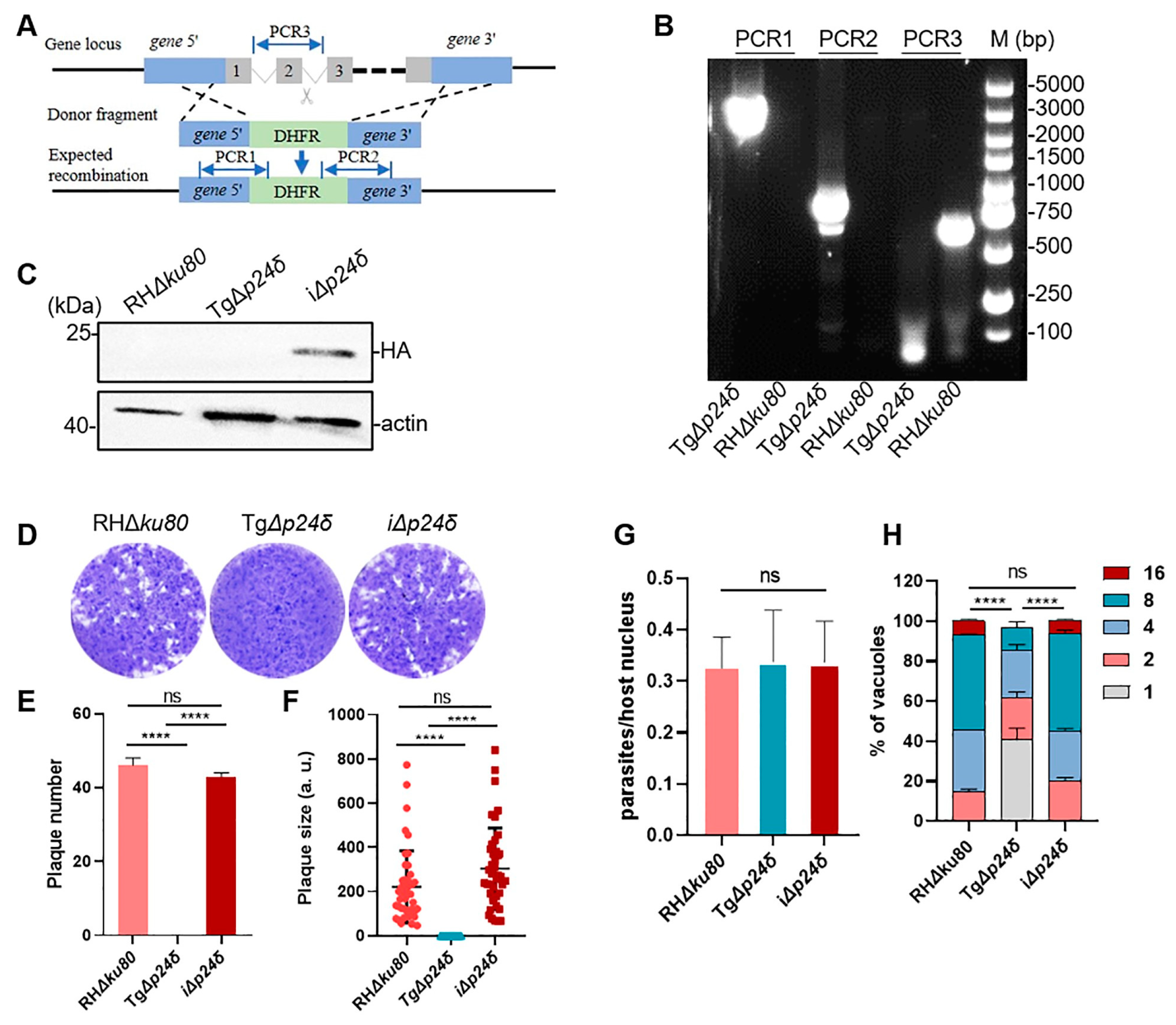
2.2. Tgp24δ Plays Important Roles in Parasite Growth
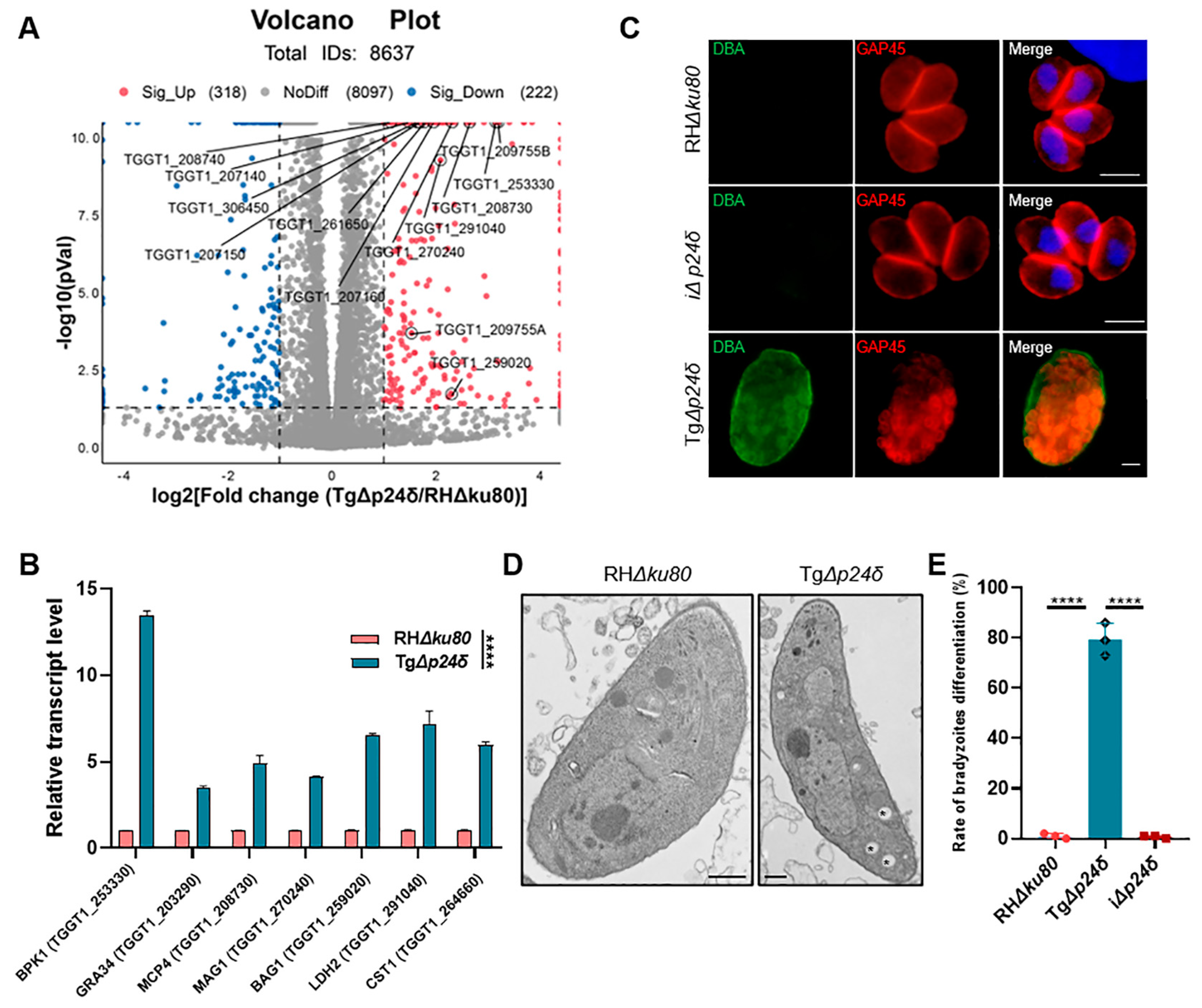
2.3. Tgp24δ Knockout Influences the Differenation from Tachyzoite to Bradyzoite in Type I T. gondii
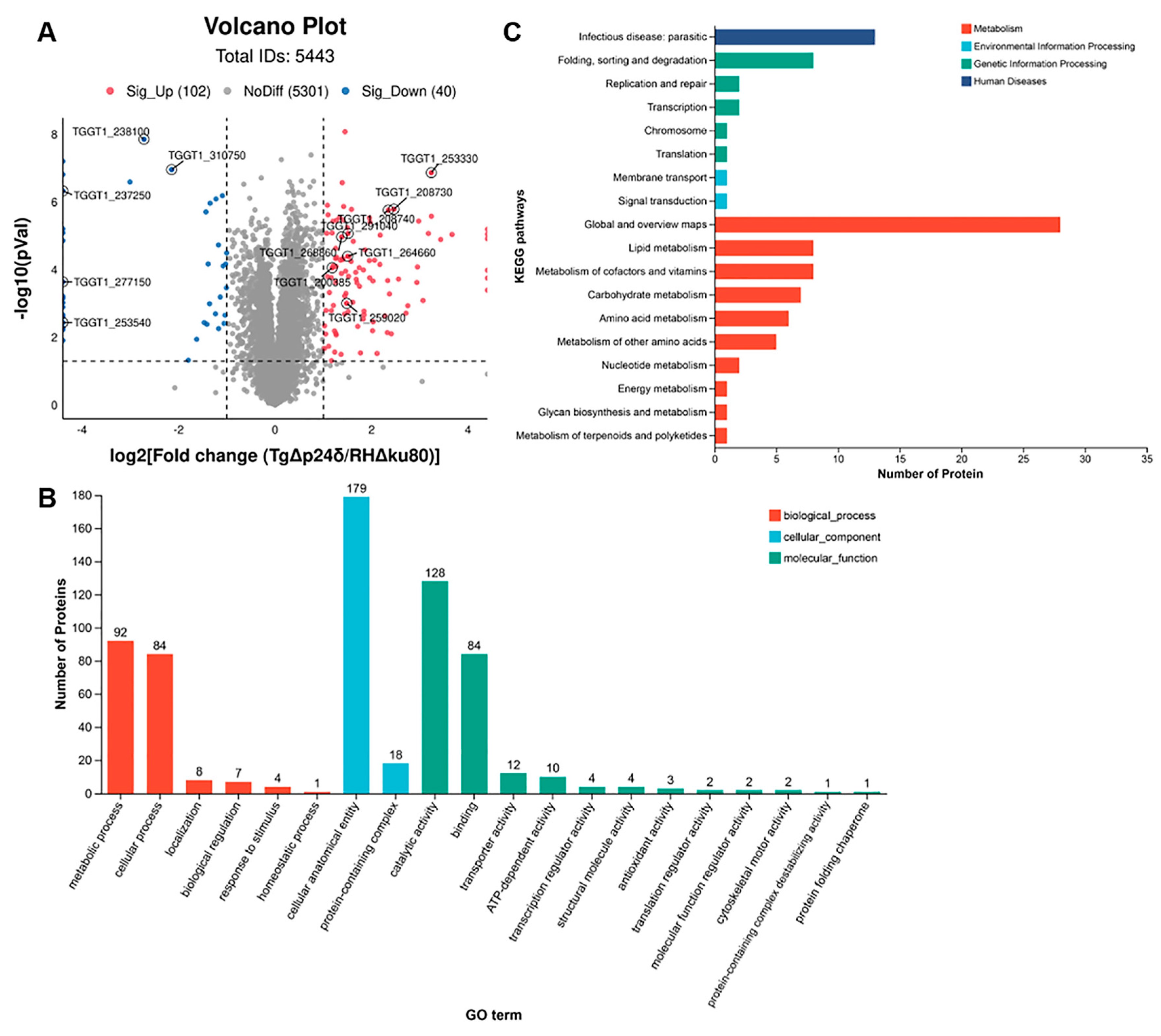
2.4. Comparative Proteomic Analysis Reveals Upregulated Expression of Bradyzoite-Specific Proteins in TgΔp24δ Parasites
2.5. Tgp24δ Is an Essential Virulence Factor
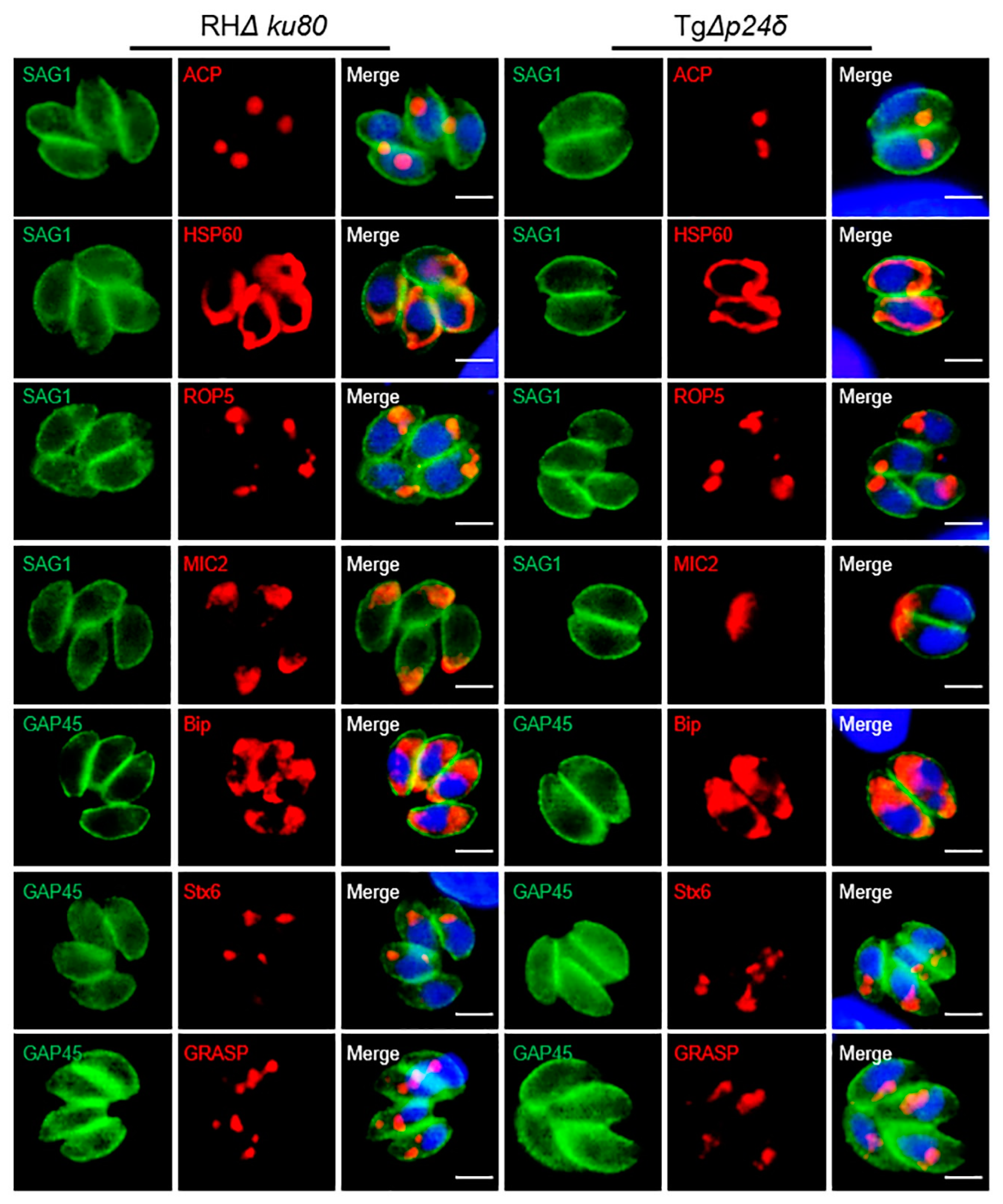
2.6. Influence of Tgp24δ Deletion on Protein Transport in Parasites
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Proteins and Phylogenetic Analysis
4.2. Parasite and Cell Cultures
4.3. Generation of Transgenic Strains
4.4. Indirect Immunofluorescence Assay (IFA) Staining and Western Blotting
4.5. Plaque Assay
4.6. Invasion Assay
4.7. Intracellular Replication Assay
4.8. Co-Immunoprecipitation and Mass Spectrometry
4.9. RNA-Seq Analysis and DIA Quantitative Proteomic Analysis
4.10. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
4.11. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
4.12. Assessment of Virulence
4.13. Statistical Analyses
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dubey, J.P. Toxoplasmosis—A waterborne zoonosis. Vet. Parasitol. 2004, 126, 57–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, J.L.; Dubey, J.P. Foodborne toxoplasmosis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 55, 845–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, R.E.; McLeod, R.; Roberts, C.W. Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoite-bradyzoite interconversion. Trends Parasitol. 2002, 18, 198–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pappas, G.; Roussos, N.; Falagas, M.E. Toxoplasmosis snapshots: Global status of Toxoplasma gondii seroprevalence and implications for pregnancy and congenital toxoplasmosis. Int. J. Parasitol. 2009, 39, 1385–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soête, M.; Camus, D.; Dubremetz, J.F. Experimental induction of bradyzoite-specific antigen expression and cyst formation by the RH strain of Toxoplasma gondii in vitro. Exp. Parasitol. 1994, 78, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohne, W.; Roos, D.S. Stage-specific expression of a selectable marker in Toxoplasma gondii permits selective inhibition of either tachyzoites or bradyzoites. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 1997, 88, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, B.A.; Gigley, J.P.; Bzik, D.J. Toxoplasma gondii lacks the enzymes required for de novo arginine biosynthesis and arginine starvation triggers cyst formation. Int. J. Parasitol. 2004, 34, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihara, F.; Nishikawa, Y. Starvation of low-density lipoprotein-derived cholesterol induces bradyzoite conversion in Toxoplasma gondii. Parasit. Vectors. 2014, 7, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohne, W.; Heesemann, J.; Gross, U. Reduced replication of Toxoplasma gondii is necessary for induction of bradyzoite-specific antigens: A possible role for nitric oxide in triggering stage conversion. Infect. Immun. 1994, 62, 1761–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffers, V.; Tampaki, Z.; Kim, K.; Sullivan, W.J., Jr. A latent ability to persist: Differentiation in Toxoplasma gondii. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 2355–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.; Ge, C.C.; Fan, Y.M.; Jin, Q.W.; Shen, B.; Huang, S.Y. The determinants regulating Toxoplasma gondii bradyzoite development. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1027073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugi, T.; Ma, Y.F.; Tomita, T.; Murakoshi, F.; Eaton, M.S.; Yakubu, R.; Han, B.; Tu, V.; Kato, K.; Kawazu, S.; et al. Toxoplasma gondii cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase subunit 3 is involved in the switch from tachyzoite to bradyzoite development. mBio 2016, 7, e00755-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Liu, J.; Wu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Sun, X.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Q. Requirement of Toxoplasma gondii metacaspases for IMC1 maturation, endodyogeny and virulence in mice. Parasit. Vectors. 2021, 14, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strating, J.R.; Martens, G.J. The p24 family and selective transport processes at the ER-Golgi interface. Biol. Cell 2009, 101, 495–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contreras, I.; Yang, Y.; Robinson, D.G.; Aniento, F. Sorting signals in the cytosolic tail of plant p24 proteins involved in the interaction with the COPII coat. Plant Cell Physiol. 2004, 45, 1779–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor-Cantizano, N.; Montesinos, J.C.; Bernat-Silvestre, C.; Marcote, M.J.; Aniento, F. p24 family proteins: Key players in the regulation of trafficking along the secretory pathway. Protoplasma 2016, 253, 967–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belden, W.J.; Barlowe, C. Deletion of yeast p24 genes activates the unfolded protein response. Mol. Biol. Cell 2001, 12, 957–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schimmöller, F.; Singer-Krüger, B.; Schröder, S.; Krüger, U.; Barlowe, C.; Riezman, H. The absence of Emp24p, a component of ER-derived COPII-coated vesicles, causes a defect in transport of selected proteins to the Golgi. EMBO J. 1995, 14, 1329–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belden, W.J.; Barlowe, C. Erv25p, a component of COPII-coated vesicles, forms a complex with Emp24p that is required for efficient endoplasmic reticulum to Golgi transport. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 26939–26946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, M.; Watanabe, R.; Jaensch, N.; Romanova-Michaelides, M.; Satoh, T.; Kato, M.; Riezman, H.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Maeda, Y.; Kinoshita, T. Sorting of GPI-anchored proteins into ER exit sites by p24 proteins is dependent on remodeled GPI. J. Cell Biol. 2011, 194, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Yang, F.; Heng, Y.; Zhou, S.; Wang, G.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Chen, X.; Yao, Z.P.; Wu, Z.; et al. TMED10 mediates the trafficking of insulin-like growth factor 2 along the secretory pathway for myoblast differentiation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2215285120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, B.A.; Ristuccia, J.G.; Gigley, J.P.; Bzik, D.J. Efficient gene replacements in Toxoplasma gondii strains deficient for nonhomologous end joining. Eukaryot. Cell 2009, 8, 520–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hager, K.M.; Striepen, B.; Tilney, L.G.; Roos, D.S. The nuclear envelope serves as an intermediary between the ER and Golgi complex in the intracellular parasite Toxoplasma gondii. J. Cell Sci. 1999, 112, 2631–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, S.; Yang, J.; Fu, J.; Chen, H.; Jia, H. The dissection of SNAREs reveals key factors for vesicular trafficking to the endosome-like compartment and apicoplast via the secretory system in Toxoplasma gondii. mBio 2021, 12, e0138021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelletier, L.; Stern, C.A.; Pypaert, M.; Sheff, D.; Ngô, H.M.; Roper, N.; He, C.Y.; Hu, K.; Toomre, D.; Coppens, I.; et al. Golgi biogenesis in Toxoplasma gondii. Nature 2002, 418, 548–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, A.J.; Clucas, C.; Mamczur, N.J.; Ferguson, D.J.; Meissner, M. Toxoplasma gondii Syntaxin 6 is required for vesicular transport between endosomal-like compartments and the Golgi complex. Traffic 2013, 14, 1166–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, K.; Charvat, R.; Arrizabalaga, G. Identification of Fis1 interactors in Toxoplasma gondii reveals a novel protein required for peripheral distribution of the mitochondrion. mBio 2020, 11, e02732-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidik, S.M.; Huet, D.; Ganesan, S.M.; Huynh, M.H.; Wang, T.; Nasamu, A.S.; Thiru, P.; Saeij, J.P.J.; Carruthers, V.B.; Niles, J.C.; et al. A genome-wide CRISPR screen in Toxoplasma identifies essential apicomplexan genes. Cell 2016, 166, 1423–1435.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Fu, Y.; Huang, W.; Uddin, T.; Sibley, L.D. Constitutive upregulation of transcription factors underlies permissive bradyzoite differentiation in a natural isolate of Toxoplasma gondii. mBio. 2024, 15, e0064124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldman, B.S.; Schwarz, D.; Wadsworth, M.H.; Saeij, J.P., II; Shalek, A.K.; Lourido, S. Identification of a master regulator of differentiation in Toxoplasma. Cell 2020, 180, 359–372.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seizova, S.; Ferrel, A.; Boothroyd, J.; Tonkin, C.J. Toxoplasma protein export and effector function. Nat. Microbiol. 2024, 9, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belden, W.J.; Barlowe, C. Distinct roles for the cytoplasmic tail sequences of Emp24p and Erv25p in transport between the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi complex. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 43040–43048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzioch, M.; Henthorn, D.C.; Herrmann, J.M.; Wilson, R.; Thomas, D.Y.; Bergeron, J.J.; Solari, R.C.; Rowley, A. Erp1p and Erp2p, partners for Emp24p and Erv25p in a yeast p24 complex. Mol. Biol. Cell 1999, 10, 1923–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Feng, Z.; Pastor-Pareja, J.C. p24-Tango1 interactions ensure ER-Golgi interface stability and efficient transport. J. Cell Biol. 2024, 223, e202309045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, K.G.; Chamberlin, H.M. Genetic characterization of C. elegans TMED genes. Dev. Dyn. 2023, 252, 1149–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montesinos, J.C.; Pastor-Cantizano, N.; Robinson, D.G.; Marcote, M.J.; Aniento, F. Arabidopsis p24δ5 and p24δ9 facilitate Coat Protein I-dependent transport of the K/HDEL receptor ERD2 from the Golgi to the endoplasmic reticulum. Plant J. 2014, 80, 1014–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knöckel, J.; Dundas, K.; Yang, A.S.P.; Galaway, F.; Metcalf, T.; Gemert, G.V.; Sauerwein, R.W.; Rayner, J.C.; Billker, O.; Wright, G.J. Systematic identification of Plasmodium falciparum sporozoite membrane protein interactions reveals an essential role for the p24 complex in host infection. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2021, 20, 100038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomavo, S.; Slomianny, C.; Meissner, M.; Carruthers, V.B. Protein trafficking through the endosomal system prepares intracellular parasites for a home invasion. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, L.; Lin, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Guo, Q.; Li, S.; Sun, Y.; Tao, X.; Zhang, D.; et al. A translocation pathway for vesicle-mediated unconventional protein secretion. Cell 2020, 181, 637–652.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piersimoni, L.; Kastritis, P.L.; Arlt, C.; Sinz, A. Cross-linking mass spectrometry for investigating protein conformations and protein-protein interactions—A method for all seasons. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 7500–7531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeninga, M.D.; Quinn, J.E.; Petter, M. ApiAP2 transcription factors in Apicomplexan parasites. Pathogens 2019, 8, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Liu, J.; Zhang, H.; Sun, Z.; Ying, Z.; Wu, Y.; Xu, J.; Liu, Q. Toxoplasma gondii glutathione S-transferase 2 plays an important role in partial secretory protein transport. FASEB J. 2021, 35, e21352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, J.; Ying, Z.; Li, S.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Q. Toxoplasma gondii UBL-UBA shuttle proteins contribute to the degradation of ubiquitinylated proteins and are important for synchronous cell division and virulence. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 13711–13725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Sui, M.; Yu, J.; Wu, J.; Gu, Z.; Zhou, X. Linking proteomic function and structure to electroactive biofilms development across electrode orientations. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 412, 131375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Tang, T.; He, K.; Long, S. TBC9, an essential TBC-domain protein, regulates early vesicular transport and IMC formation in Toxoplasma gondii. Commun. Biol. 2024, 7, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, Z.; Ying, Z.; Pei, Y.; Shan, Z.; Peng, J.; Sun, M.; Liu, Q.; Liu, J. Role of Toxoplasma gondii p24δ in Regulating the Transition from Tachyzoite to Bradyzoite Development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3331. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073331
Zhu Z, Ying Z, Pei Y, Shan Z, Peng J, Sun M, Liu Q, Liu J. Role of Toxoplasma gondii p24δ in Regulating the Transition from Tachyzoite to Bradyzoite Development. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(7):3331. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073331
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Zifu, Zhu Ying, Yanqun Pei, Zhili Shan, Jing Peng, Ming Sun, Qun Liu, and Jing Liu. 2025. "Role of Toxoplasma gondii p24δ in Regulating the Transition from Tachyzoite to Bradyzoite Development" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 7: 3331. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073331
APA StyleZhu, Z., Ying, Z., Pei, Y., Shan, Z., Peng, J., Sun, M., Liu, Q., & Liu, J. (2025). Role of Toxoplasma gondii p24δ in Regulating the Transition from Tachyzoite to Bradyzoite Development. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(7), 3331. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073331




