Air Pollution-Induced Neurotoxicity: The Relationship Between Air Pollution, Epigenetic Changes, and Neurological Disorders
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Air Pollutants
3. Gaseous Air Pollutants
3.1. Ozone
3.2. Sulfur Dioxide
3.3. Nitrogen Oxides
3.4. Carbon Monoxide
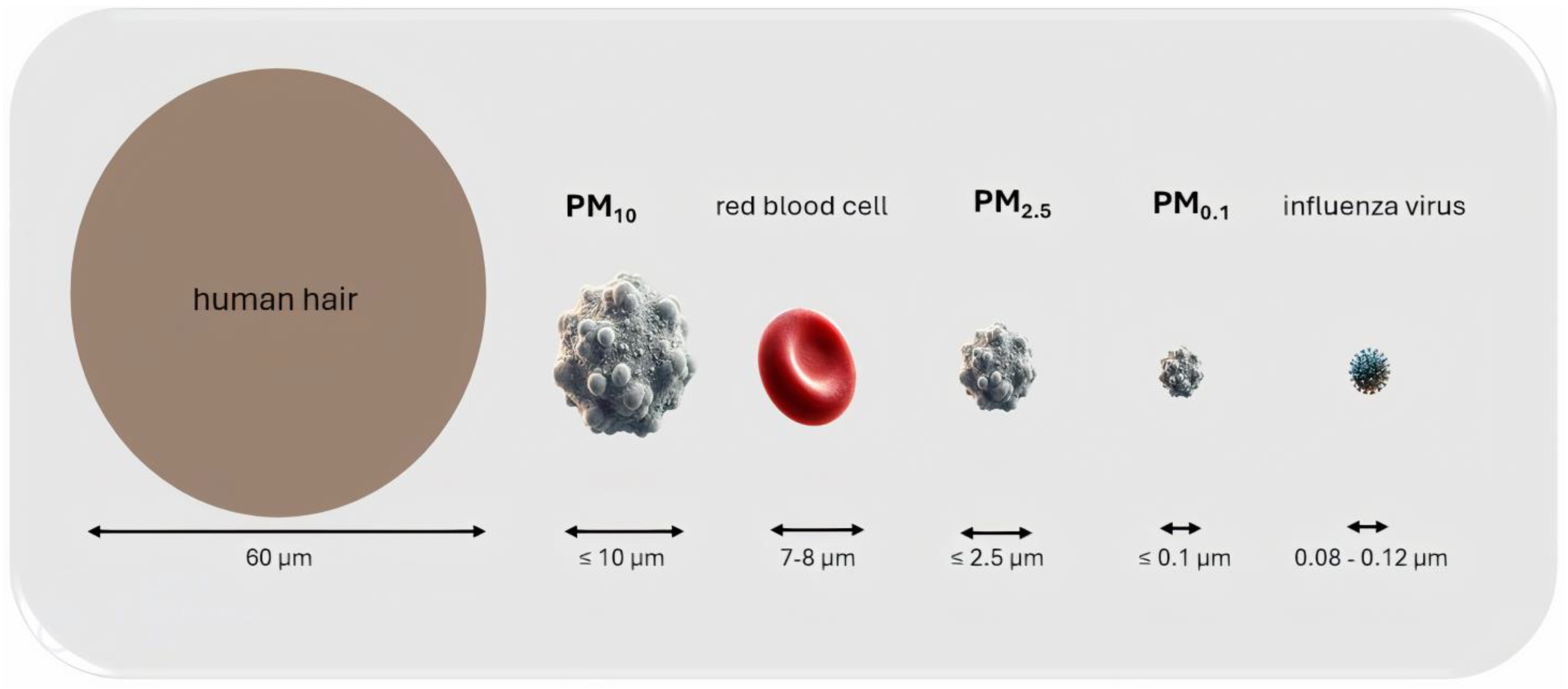
4. Particulate Matter—The Most Dangerous Air Pollutant
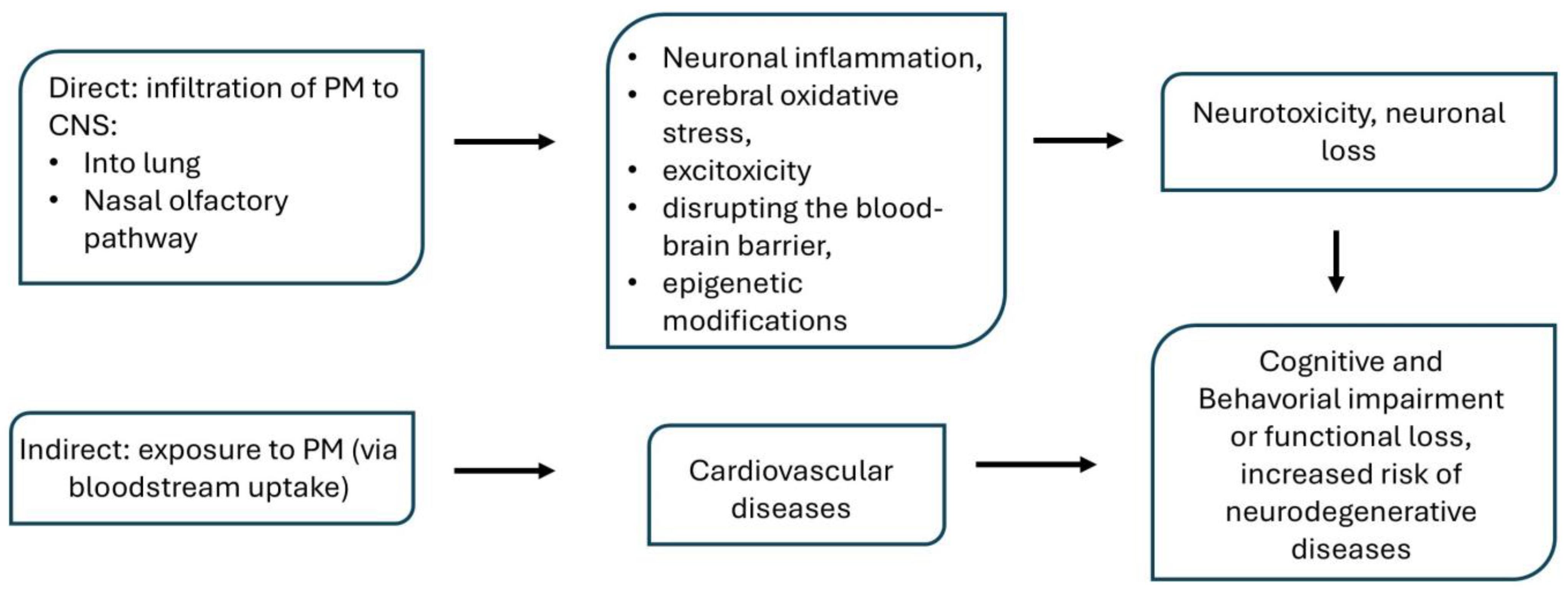
Routes of PM Entry
5. The Role of Particulate Matter in the Development of Brain Disorders and Diseases
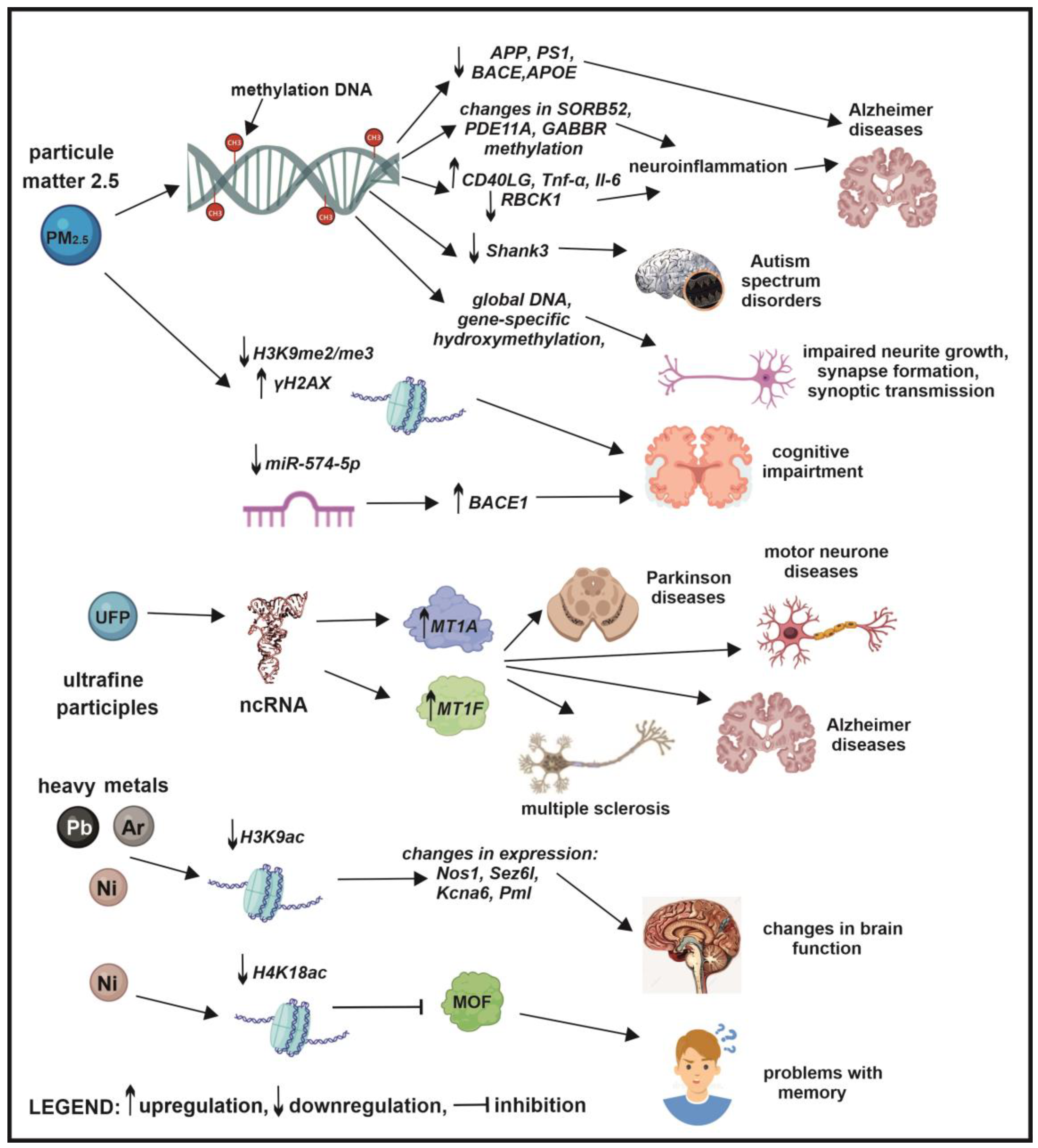
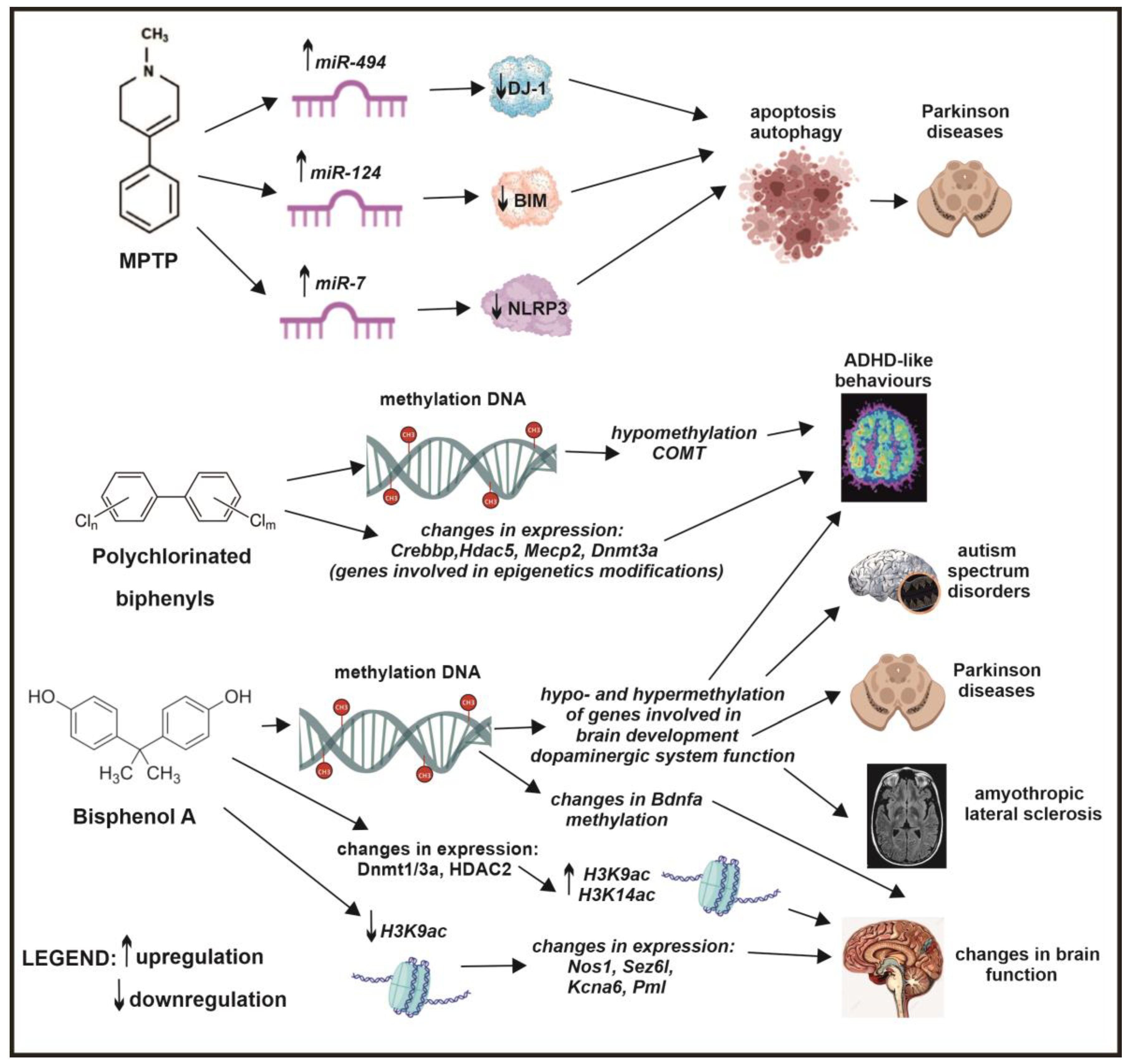
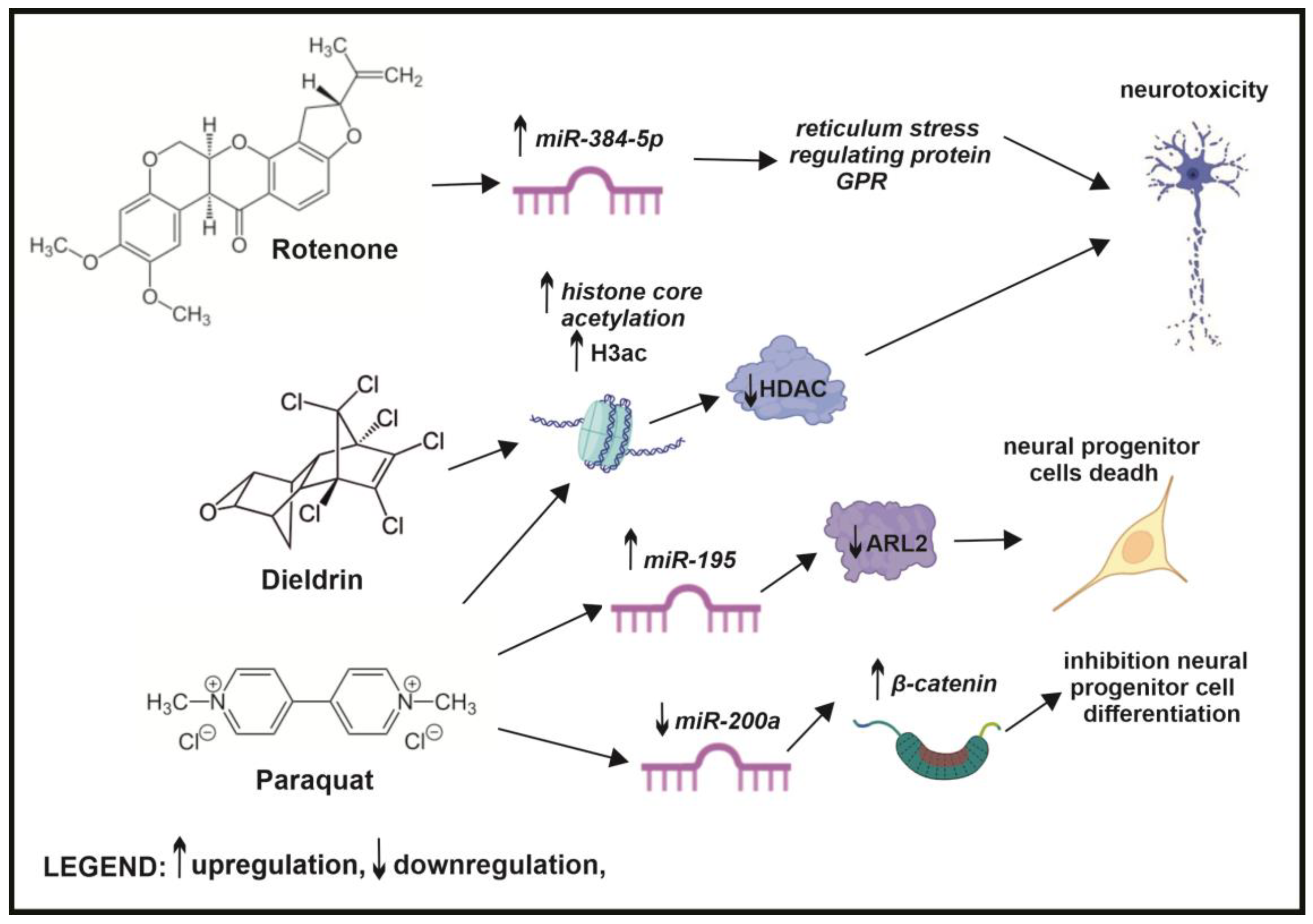
6. The Role of Epigenetics in Air Pollution-Induced Neurodegenerative Diseases
7. Future Perspectives and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Health Effects Institute. State of Global Air 2024. Special Report; Health Effects Institute: Boston, MA, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X. Air pollution: A global problem needs local fixes. Nature 2019, 570, 437–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Chen, X.; Chen, J.; Zhang, F.; He, C.; Zhao, J.; Yin, L. Seasonal Variations and Chemical Compositions of PM 2.5 Aerosol in the Urban Area of Fuzhou, China. Atmos. Res. 2012, 104–105, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juda-Rezler, K.; Zajusz-Zubek, E.; Reizer, M.; Maciejewska, K.; Kurek, E.; Bulska, E.; Klejnowski, K. Bioavailability of Elements in Atmospheric PM2.5 during Winter Episodes at Central Eastern European Urban Background Site. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 245, 117993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacciottolo, M.; Wang, X.; Driscoll, I.; Woodward, N.; Saffari, A.; Reyes, J.; Serre, M.L.; Vizuete, W.; Sioutas, C.; Morgan, T.E.; et al. Particulate Air Pollutants, APOE Alleles and Their Contributions to Cognitive Impairment in Older Women and to Amyloidogenesis in Experimental Models. Transl. Psychiatry 2017, 7, e1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casanova, R.; Wang, X.; Reyes, J.; Akita, Y.; Serre, M.L.; Vizuete, W.; Chui, H.C.; Driscoll, I.; Resnick, S.M.; Espeland, M.A.; et al. A Voxel-Based Morphometry Study Reveals Local Brain Structural Alterations Associated with Ambient Fine Particles in Older Women. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Kwong, J.C.; Copes, R.; Tu, K.; Villeneuve, P.J.; van Donkelaar, A.; Hystad, P.; Martin, R.V.; Murray, B.J.; Jessiman, B.; et al. Living near Major Roads and the Incidence of Dementia, Parkinson’s Disease, and Multiple Sclerosis: A Population-Based Cohort Study. Lancet 2017, 389, 718–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, A.J.; Brauer, M.; Burnett, R.; Anderson, H.R.; Frostad, J.; Estep, K.; Balakrishnan, K.; Brunekreef, B.; Dandona, L.; Dandona, R.; et al. Estimates and 25-Year Trends of the Global Burden of Disease Attributable to Ambient Air Pollution: An Analysis of Data from the Global Burden of Diseases Study 2015. Lancet 2017, 389, 1907–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosselman, K.E.; Navas-Acien, A.; Kaufman, J.D. Environmental Factors in Cardiovascular Disease. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2015, 12, 627–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heusinkveld, H.J.; Wahle, T.; Campbell, A.; Westerink, R.H.S.; Tran, L.; Johnston, H.; Stone, V.; Cassee, F.R.; Schins, R.P.F. Neurodegenerative and Neurological Disorders by Small Inhaled Particles. Neurotoxicology 2016, 56, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kioumourtzoglou, M.A.; Schwartz, J.D.; Weisskopf, M.G.; Melly, S.J.; Wang, Y.; Dominici, F.; Zanobetti, A. Long-Term PM2.5 Exposure and Neurological Hospital Admissions in the Northeastern United States. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krewski, D.; Jerrett, M.; Burnett, R.T.; Ma, R.; Hughes, E.; Shi, Y.; Turner, M.C.; Newbold, B.; Ramsay, T.; Ross, Z.; et al. Extended Follow−Up and Spatial Analysis of the American Cancer Society Study Linking Particulate Air Pollution and Mortality; Health Effects Institute: Boston, MA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Meo, S.A.; Memon, A.N.; Sheikh, S.A.; Rouq, F.A.; Usmani, A.M.; Hassan, A.; Arian, S.A. Effect of environmental air pollution on type 2 diabetes mellitus. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 19, 123–128. [Google Scholar]
- Loomis, D.; Grosse, Y.; Lauby-Secretan, B.; El Ghissassi, F.; Bouvard, V.; Benbrahim-Tallaa, L.; Guha, N.; Baan, R.; Mattock, H.; Straif, K. The Carcinogenicity of Outdoor Air Pollution. Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, 1262–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malley, C.S.; Kuylenstierna, J.C.I.; Vallack, H.W.; Henze, D.K.; Blencowe, H.; Ashmore, M.R. Preterm Birth Associated with Maternal Fine Particulate Matter Exposure: A Global, Regional and National Assessment. Environ. Int. 2017, 101, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, F.P.; Chang, H.W.; Tang, D.; Roen, E.L.; Herbstman, J.; Margolis, A.; Huang, T.J.; Miller, R.L.; Wang, S.; Rauh, V. Early-Life Exposure to Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and ADHD Behavior Problems. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thurston, G.; Lippmann, M. Ambient Particulate Matter Air Pollution and Cardiopulmonary Diseases. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 36, 422–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khreis, H.; Bredell, C.; Wai Fung, K.; Hong, L.; Szybka, M.; Phillips, V.; Abbas, A.; Lim, Y.H.; Jovanovic Andersen, Z.; Woodcock, J.; et al. Impact of Long-Term Air Pollution Exposure on Incidence of Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Protocol for a Systematic Review and Exposure-Response Meta-Analysis. Environ. Int. 2022, 170, 107596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Weerasinghe-Mudiyanselage, P.D.E.; Kim, B.; Kang, S.; Kim, J.S.; Moon, C. Particulate Matter Exposure and Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Comprehensive Update on Toxicity and Mechanisms. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 266, 115565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadzadeh, M.; Khoshakhlagh, A.H.; Grafman, J. Air Pollution: A Latent Key Driving Force of Dementia. BMC Public Health 2024, 24, 2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.A.; Nakanishi, E.; Lee, M. Association between Exposure to Air Pollution and Late-Life Neurodegenerative Disorders: An Umbrella Review. Environ. Int. 2022, 158, 106956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da, L.; Song, X.; Jia, Z.; Myers, N.G.L.; Sun, J.; Wei, J.; Jung, D.; Li, F.; Song, S. Objectively Measured Environmental Features and Their Association with Cognition and Dementia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Ageing Res. Rev. 2024, 104, 102630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchesne, J.; Gutierrez, L.A.; Carrière, I.; Mura, T.; Chen, J.; Vienneau, D.; de Hoogh, K.; Helmer, C.; Jacquemin, B.; Berr, C.; et al. Exposure to Ambient Air Pollution and Cognitive Decline: Results of the Prospective Three-City Cohort Study. Environ. Int. 2022, 161, 107118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulick, E.R.; Wellenius, G.A.; Boehme, A.K.; Joyce, N.R.; Schupf, N.; Kaufman, J.D.; Mayeux, R.; Sacco, R.L.; Manly, J.J.; Elkind, M.S.V. Long-Term Exposure to Air Pollution and Trajectories of Cognitive Decline among Older Adults. Neurology 2020, 94, e1782–e1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLachlan, J.; Cox, S.R.; Pearce, J.; Valdés Hernández, M.D.C. Long-Term Exposure to Air Pollution and Cognitive Function in Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Environ. Health 2023, 2, 1205443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, D.; Evangelopoulos, D.; Beevers, S.; Kitwiroon, N.; Demakakos, P.; Katsouyanni, K. Exposure to Ambient Air Pollution and Cognitive Function: An Analysis of the English Longitudinal Study of Ageing Cohort. Environ. Health 2024, 23, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nováková, Z.; Novák, J.; Kitanovski, Z.; Kukučka, P.; Smutná, M.; Wietzoreck, M.; Lammel, G.; Hilscherová, K. Toxic Potentials of Particulate and Gaseous Air Pollutant Mixtures and the Role of PAHs and Their Derivatives. Environ. Int. 2020, 139, 105634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, R.; Chen, H.; Szyszkowicz, M.; Fann, N.; Hubbell, B.; Pope, C.A.; Apte, J.S.; Brauer, M.; Cohen, A.; Weichenthal, S.; et al. Global Estimates of Mortality Associated with Longterm Exposure to Outdoor Fine Particulate Matter. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci USA 2018, 115, 9592–9597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamanaka, R.B.; Mutlu, G.M. Particulate Matter Air Pollution: Effects on the Cardiovascular System. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villányi, V.; Turk, B.; Csintalan, Z. Ozone Pollution and its Bioindication. In Air Pollution; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manisalidis, I.; Stavropoulou, E.; Stavropoulos, A.; Bezirtzoglou, E. Environmental and Health Impacts of Air Pollution: A Review. Front. Public Health 2020, 8, 505570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farfán-García, E.D.; Castillo-Hernández, M.C.; Pinto-Almazán, R.; Rivas-Arancibia, S.; Gallardo, J.M.; Guerra-Araiza, C. Tibolone Prevents Oxidation and Ameliorates Cholinergic Deficit Induced by Ozone Exposure in the Male Rat Hippocampus. Neurochem. Res. 2014, 39, 1776–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad Ganai, S.; Ramadoss, M.; Mahadevan, V. Histone Deacetylase (HDAC) Inhibitors-Emerging Roles in Neuronal Memory, Learning, Synaptic Plasticity and Neural Regeneration. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2016, 14, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.T. Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Dysfunction-Linked Neurodegenerative Disorders. Neurol. Res. 2017, 39, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello-Medina, P.C.; Rodríguez-Martínez, E.; Prado-Alcalá, R.A.; Rivas-Arancibia, S. Ozone Pollution, Oxidative Stress, Synaptic Plasticity, and Neurodegeneration. Neurologia 2022, 37, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas-Arancibia, S.; Guevara-Guzmán, R.; López-Vidal, Y.; Rodríguez-Martínez, E.; Zanardo-Gomes, M.; Angoa-Pérez, M.; Raisman-Vozari, R. Oxidative Stress Caused by Ozone Exposure Induces Loss of Brain Repair in the Hippocampus of Adult Rats. Toxicol. Sci. 2009, 113, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colín-Barenque, L.; Dorado-Martinez, C.; Rivas-Arancibia, S.; Avila-Costa, M.R.; Fortoul, T.I. Morphological Recovery of the Granule Cells from the Olfactory Bulb after the Cessation of Acute Ozone Exposure. Int. J. Neurosci. 2005, 115, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, C.; Greve, H.J.; Garza-Lombo, C.; Malley, J.A.; Johnson, J.A.; Oblak, A.L.; Block, M.L. Peripheral HMGB1 Is Linked to O3 Pathology of Disease-Associated Astrocytes and Amyloid. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2024, 20, 3551–3566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Markevych, I.; Romanos, M.; Nowak, D.; Heinrich, J. Ambient Ozone Exposure and Mental Health: A Systematic Review of Epidemiological Studies. Environ. Res. 2018, 165, 459–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Lu, Y.; Cheng, H.; Wang, C.; Chan, P. The Impact of Long-Term Exposure to Ambient Air Pollution and Second-Hand Smoke on the Onset of Parkinson Disease: A Review and Meta-Analysis. Public Health 2020, 179, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasdagli, M.I.; Katsouyanni, K.; Dimakopoulou, K.; Samoli, E. Air Pollution and Parkinson’s Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis up to 2018. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2019, 222, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.Y.; Fang, Y.; Li, F.L.; Dong, B.; Hua, X.G.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, H.; Lyu, Y.; Zhang, X.J. Association between Ambient Air Pollution and Parkinson’s Disease: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Environ. Res. 2019, 168, 448–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Pinault, L.; Toyib, O.; Vanos, J.; Tjepkema, M.; Cakmak, S. Long-Term Ozone Exposure and Mortality from Neurological Diseases in Canada. Environ. Int. 2021, 157, 106817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szyszkowicz, M.; Zemek, R.; Colman, I.; Gardner, W.; Kousha, T.; Smith-Doiron, M. Air Pollution and Emergency Department Visits for Mental Disorders among Youth. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, G.; Yue, H.; Yun, Y.; Sang, N. Chronic SO2 Inhalation above Environmental Standard Impairs Neuronal Behavior and Represses Glutamate Receptor Gene Expression and Memory-Related Kinase Activation via Neuroinflammation in Rats. Environ. Res. 2015, 137, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sang, N.; Yun, Y.; Yao, G.Y.; Li, H.Y.; Guo, L.; Li, G.K. SO2-Induced Neurotoxicity Is Mediated by Cyclooxygenases-2-Derived Prostaglandin E 2 and Its Downstream Signaling Pathway in Rat Hippocampal Neurons. Toxicol. Sci. 2011, 124, 400–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, G.; Yun, Y.; Sang, N. Differential Effects between One Week and Four Weeks Exposure to Same Mass of SO2 on Synaptic Plasticity in Rat Hippocampus. Environ. Toxicol. 2016, 31, 820–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, F.C.; Chen, C.Y.; Lin, C.W.; Wu, M.T.; Chen, H.Y.; Huang, P. Air Pollution Is Associated with Cognitive Deterioration of Alzheimer’s Disease. Gerontology 2022, 68, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.C.; Wang, C.F.; Lai, B.C.; Hsieh, S.W.; Chen, S.C.; Hung, C.H.; Kuo, C.H. Air Pollution Is Associated with Poor Cognitive Function in Taiwanese Adults. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavery, A.M.; Waubant, E.; Casper, T.C.; Roalstad, S.; Candee, M.; Rose, J.; Belman, A.; Weinstock-Guttman, B.; Aaen, G.; Tillema, J.M.; et al. Urban Air Quality and Associations with Pediatric Multiple Sclerosis. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2018, 5, 1146–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaducci, A.; Downs, J.W. Nitrogen Dioxide Toxicity. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Tampa, FL, USA, 2023. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK554539/ (accessed on 21 February 2024).
- Gorguner, M.; Akgun, M. Acute Inhalation Injury. Eurasian J. Med. 2010, 42, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Yun, Y.; Ku, T.; Li, G.; Sang, N. NO2 Inhalation Promotes Alzheimer’s Disease-like Progression: Cyclooxygenase-2-Derived Prostaglandin E2 Modulation and Monoacylglycerol Lipase Inhibition-Targeted Medication. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xin, X. Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2) Pollution as a Potential Risk Factor for Developing Vascular Dementia and Its Synaptic Mechanisms. Chemosphere 2013, 92, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crous-Bou, M.; Gascon, M.; Gispert, J.D.; Cirach, M.; Sánchez-Benavides, G.; Falcon, C.; Arenaza-Urquijo, E.M.; Gotsens, X.; Fauria, K.; Sunyer, J.; et al. Impact of Urban Environmental Exposures on Cognitive Performance and Brain Structure of Healthy Individuals at Risk for Alzheimer’s Dementia. Environ. Int. 2020, 138, 105546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotter, D.L.; Campbell, C.E.; Sukumaran, K.; McConnell, R.; Berhane, K.; Schwartz, J.; Hackman, D.A.; Ahmadi, H.; Chen, J.C.; Herting, M.M. Effects of Ambient Fine Particulates, Nitrogen Dioxide, and Ozone on Maturation of Functional Brain Networks across Early Adolescence. Environ. Int. 2023, 177, 108001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.Y.; Cheng, Y.Y.; Guo, H.R.; Tseng, Y.C. Air Pollution during Pregnancy and Childhood Autism Spectrum Disorder in Taiwan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 9784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fania, A.; Monaco, A.; Amoroso, N.; Bellantuono, L.; Cazzolla Gatti, R.; Firza, N.; Lacalamita, A.; Pantaleo, E.; Tangaro, S.; Velichevskaya, A.; et al. Machine Learning and XAI Approaches Highlight the Strong Connection between O3 and NO2 Pollutants and Alzheimer’s Disease. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 5385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritz, B.; Lee, P.C.; Hansen, J.; Lassen, C.F.; Ketzel, M.; Sørensen, M.; Raaschou-Nielsen, O. Traffic-Related Air Pollution and Parkinson’s Disease in Denmark: A Case–Control Study. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleury, V.; Himsl, R.; Joost, S.; Nicastro, N.; Bereau, M.; Guessous, I.; Burkhard, P.R. Geospatial Analysis of Individual-Based Parkinson’s Disease Data Supports a Link with Air Pollution: A Case-Control Study. Park. Relat. Disord. 2021, 83, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mureşan, C.O.; Zavoi, R.E.; Dumache, R.O.; Precup, C.V.; Ciocan, V.; Bulzan, O.Ş.; Florou, C.; Enache, A. Co-Morbidities in the Multiple Victims of the Silent Killer in Carbon Monoxide Poisoning. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2019, 60, 125–131. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, C.; Kuang, D.; Zhang, H.; Ren, J.; Chen, J. Different components of air pollutants and neurological disorders. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 959921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, J.J.; Wang, L.; Xu, Q.; McTiernan, C.F.; Shiva, S.; Tejero, J.; Gladwin, M.T. Carbon Monoxide Poisoning: Pathogenesis, Management, and Future Directions of Therapy. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 195, 596–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwierzyńska, E.; Miłkowska, E.; Furmanek, M.; Holak-Puczyńska, A.; Laskowska, A.; Pniewski, J. Zatrucie tlenkiem wę-gla-problemy diagnostyczne. Pol. Przegląd Neurol. 2014, 10, 127–134. [Google Scholar]
- Alonso, J.R.; Cardellach, F.; López, S.; Casademont, J.; Miró, Ò. Carbon Monoxide Specifically Inhibits Cytochrome C Oxidase of Human Mitochondrial Respiratory Chain. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2003, 93, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kośmider, P.; Gorczyca-Michta, I.; Wożakowska-Kapłon, B. Zawał Serca w Przebiegu Zatrucia Tlenkiem Węgla. Folia Cardiol. 2017, 12, 394–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overfelt, C. Carbon Monoxide Poisoning: Diagnosis and Management. J. Am. Acad. Physician Assist. 2023, 36, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Guo, Y.; Li, W.; Li, G.; Chen, Y. The Efficacy of N-Butylphthalide and Dexamethasone Combined with Hyperbaric Oxygen on Delayed Encephalopathy after Acute Carbon Monoxide Poisoning. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2020, 14, 1333–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.O.; Thundiyil, J.G.; Stolbach, A. Clearing the Air: A Review of the Effects of Particulate Matter Air Pollution on Human Health. J. Med. Toxicol. 2012, 8, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sielicki, P.; Janik, H.; Guzman, A.; Namieśnik, J. The Progress in Electron Microscopy Studies of Particulate Matters to Be Used as a Standard Monitoring Method for Air Dust Pollution. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2011, 41, 314–334. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- You, R.; Ho, Y.S.; Chang, R.C.C. The pathogenic effects of particulate matter on neurodegeneration: A review. J. BioMed. Sci. 2022, 29, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, L.G.; Cole, T.B.; Dao, K.; Chang, Y.C.; Garrick, J.M. Developmental Impact of Air Pollution on Brain Function. Neurochem. Int. 2019, 131, 104580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilian, J.; Kitazawa, M. The Emerging Risk of Exposure to Air Pollution on Cognitive Decline and Alzheimer’s Disease–Evidence from Epidemiological and Animal Studies. Biomed. J. 2018, 41, 141–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankowska-Kieltyka, M.; Roman, A.; Nalepa, I. The Air We Breathe: Air Pollution as a Prevalent Proinflammatory Stimulus Contributing to Neurodegeneration. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2021, 15, 647643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberdörster, G.; Sharp, Z.; Atudorei, V.; Elder, A.; Gelein, R.; Kreyling, W.; Cox, C. Translocation of inhaled ultrafine particles to the brain. Inhal. Toxicol. 2004, 16, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutlu, E.A.; Comba, I.Y.; Cho, T.; Engen, P.A.; Yazıcı, C.; Soberanes, S.; Hamanaka, R.B.; Niğdelioğlu, R.; Meliton, A.Y.; Ghio, A.J.; et al. Inhalational Exposure to Particulate Matter Air Pollution Alters the Composition of the Gut Microbiome. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 240, 817–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kish, L.; Hotte, N.; Kaplan, G.G.; Vincent, R.; Tso, R.; Gänzle, M.; Rioux, K.P.; Thiesen, A.; Barkema, H.W.; Wine, E.; et al. Environmental Particulate Matter Induces Murine Intestinal Inflammatory Responses and Alters the Gut Microbiome. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, S.R.; Chaudhari, V.B.; Ahmed, S.; Kwatra, M.; Jala, A.; Ponneganti, S.; Pawar, S.D.; Borkar, R.M.; Sharma, P.; Naidu, V.G.M. Ambient Particulate Matter (PM2.5) Exposure Contributes to Neurodegeneration through the Microbiome-Gut-Brain Axis: Therapeutic Role of Melatonin. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2023, 101, 104183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, K.; Wu, Z.X.; Chen, X.Y.; Wang, J.Q.; Zhang, D.; Xiao, C.; Zhu, D.; Koya, J.B.; Wei, L.; Li, J.; et al. Microbiota in health and diseases. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy 2022, 7, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.C.; Chiu, C.C.; Lee, P.Y.; Chen, K.J.; He, C.X.; Hsu, S.K.; Cheng, K.C. The Adverse Effects of Air Pollution on the Eye: A Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Li, M.; Zou, T.; Chen, X.; Li, Q.; Li, Y.; Ge, L.; Chen, S.; Xu, H. The Impact of Particulate Matter (PM2.5) on Human Retinal Development in HESC-Derived Retinal Organoids. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 607341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, S.Y.L.; Khawaja, A.P.; Morgan, J.; Strouthidis, N.; Reisman, C.; Dick, A.D.; Khaw, P.T.; Patel, P.J.; Foster, P.J. The Relationship between Ambient Atmospheric Fine Particulate Matter (PM2.5) and Glaucoma in a Large Community Cohort. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2019, 60, 4915–4923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, S.Y.L.; Khawaja, A.P.; Dick, A.D.; Morgan, J.; Dhillon, B.; Lotery, A.J.; Strouthidis, N.G.; Reisman, C.; Peto, T.; Khaw, P.T.; et al. Ambient Air Pollution Associations with Retinal Morphology in the UK Biobank. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2020, 61, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crüts, B.; van Etten, L.; Törnqvist, H.; Blomberg, A.; Sandström, T.; Mills, N.L.; Borm, P.J. Exposure to Diesel Exhaust Induces Changes in EEG in Human Volunteers. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2008, 5, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderón-Garcidueñas, L.; González-Maciel, A.; Reynoso-Robles, R.; Hammond, J.; Kulesza, R.; Lachmann, I.; Torres-Jardón, R.; Mukherjee, P.S.; Maher, B.A. Quadruple Abnormal Protein Aggregates in Brainstem Pathology and Exogenous Metal-Rich Magnetic Nanoparticles (and Engineered Ti-Rich Nanorods). The Substantia Nigrae Is a Very Early Target in Young Urbanites and the Gastrointestinal Tract a Key Brainstem Portal. Environ. Res. 2020, 191, 110139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, B.A.; Ahmed, I.A.M.; Karloukovski, V.; MacLaren, D.A.; Foulds, P.G.; Allsop, D.; Mann, D.M.A.; Torres-Jardón, R.; Calderon-Garciduenas, L. Magnetite Pollution Nanoparticles in the Human Brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 10797–10801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pankhurst, Q.; Hautot, D.; Khan, N.; Dobson, J. Increased Levels of Magnetic Iron Compounds in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2008, 13, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Weerd, L.; Lefering, A.; Webb, A.; Egli, R.; Bossoni, L. Effects of Alzheimer’s Disease and Formalin Fixation on the Different Mineralised-Iron Forms in the Human Brain. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, R.J.; Zucca, F.A.; Duyn, J.H.; Crichton, R.R.; Zecca, L. The Role of Iron in Brain Ageing and Neurodegenerative Disorders. Lancet Neurol. 2014, 13, 1045–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamasb, S. Extension of the Neuronal Membrane Model to Account for Suppression of the Action Potential by a Constant Magnetic Field. Biophysics 2017, 62, 428–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrò, E.; Condello, S.; Currò, M.; Ferlazzo, N.; Caccamo, D.; Magazù, S.; Ientile, R. Effects of Low Intensity Static Magnetic Field on FTIR Spectra and ROS Production in SH-SY5Y Neuronal-like Cells. Bioelectromagnetics 2013, 34, 618–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everett, J.; Collingwood, J.F.; Tjendana-Tjhin, V.; Brooks, J.; Lermyte, F.; Plascencia-Villa, G.; Hands-Portman, I.; Dobson, J.; Perry, G.; Telling, N.D. Nanoscale Synchrotron X-Ray Speciation of Iron and Calcium Compounds in Amyloid Plaque Cores from Alzheimer’s Disease Subjects. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 11782–11796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plascencia-Villa, G.; Ponce, A.; Collingwood, J.F.; Josefina Arellano-Jiménez, M.; Zhu, X.; Rogers, J.T.; Betancourt, I.; José-Yacamán, M.; Perry, G. High-Resolution Analytical Imaging and Electron Holography of Magnetite Particles in Amyloid Cores of Alzheimer’s Disease. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teller, S.; Tahirbegi, I.B.; Mir, M.; Samitier, J.; Soriano, J. Magnetite-Amyloid-β Deteriorates Activity and Functional Organization in an in Vitro Model for Alzheimer’s Disease. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ailshire, J.A.; Clarke, P. Fine Particulate Matter Air Pollution and Cognitive Function among U.S. Older Adults. J. Gerontol. Ser. B Psychol. Sci. Soc. Sci. 2015, 70, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.J.; Tan, H.Y.; Lee, C.Y.; Cho, H. An Air Particulate Pollutant Induces Neuroinflammation and Neurodegeneration in Human Brain Models. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2101251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, B.; Mackos, A.R.; Floden, A.M.; Wold, L.E.; Combs, C.K. Particulate Matter Exposure Exacerbates Amyloid-β Plaque Deposition and Gliosis in APP/PS1 Mice. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2021, 80, 761–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saveleva, L.; Vartiainen, P.; Górová, V.; Chew, S.; Belaya, I.; Konttinen, H.; Zucchelli, M.; Korhonen, P.; Kaartinen, E.; Kortelainen, M.; et al. Subacute Inhalation of Ultrafine Particulate Matter Triggers Inflammation without Altering Amyloid Beta Load in 5xFAD Mice. Neurotoxicology 2022, 89, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, M.; Tang, M.; Xue, Y. Neurodevelopmental Toxicity Induced by Airborne Particulate Matter. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2023, 43, 167–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youyou, Z.; Zhaoyang, L.; Chen, L.; Shuquan, Z.; Hui, W. Effects of Prenatal Methcathinone Exposure on the Neurological Behavior of Adult Offspring. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2024, 22, 2256–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Xie, P.; Yong, T.; Huang, W.; Liu, J.; Wu, D.; Ji, F.; Li, M.; Zhang, D.; Li, R.; et al. Airborne Fine Particulate Matter Induces Cognitive and Emotional Disorders in Offspring Mice Exposed during Pregnancy. Sci. Bull. 2021, 66, 578–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehsanifar, M.; Yavari, Z.; Rafati, M. Exposure to Urban Air Pollution Particulate Matter: Neurobehavioral Alteration and Hippocampal Inflammation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 50856–50866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajipour, S.; Farbood, Y.; Gharib-Naseri, M.K.; Goudarzi, G.; Rashno, M.; Maleki, H.; Bakhtiari, N.; Nesari, A.; Khoshnam, S.E.; Dianat, M.; et al. Exposure to Ambient Dusty Particulate Matter Impairs Spatial Memory and Hippocampal LTP by Increasing Brain Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Rats. Life Sci. 2020, 242, 117210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.; Lee, G.; Kim, K.H.; Bae, H. Particulate Matter Exacerbates the Death of Dopaminergic Neurons in Parkinson’s Disease through an Inflammatory Response. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, P.; Guo, X.; Qu, Q.; Li, R. Exploring the Association between Air Pollution and Parkinson’s Disease or Alzheimer’s Disease: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 123939–123947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.Y.; Hu, H.Y.; Sun, Y.; Ou, Y.N.; Ma, Y.H.; Li, M.; Li, Q.Y.; Tan, L. Association between Air Pollution and Cerebrospinal Fluid Alpha-Synuclein in Urban Elders: The CABLE Study. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2024, 16, 1422772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Wan, W.; Yu, C.; Xuan, C.; Zheng, P.; Yan, J. Associations between PM2.5 Exposure and Alzheimer’s Disease Prevalence Among Elderly in Eastern China. Environ. Health 2022, 21, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, X.; Yang, Y.; Liu, C.; Tian, Y.; Xia, D.; Liu, Z.; Pan, L.; Xiong, M.; Xiong, J.; Meng, L.; et al. Fine Particulate Matter Triggers α-Synuclein Fibrillization and Parkinson-like Neurodegeneration. Mov. Disord. 2022, 37, 1817–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvi, S. Health Effects of Ambient Air Pollution in Children. Paediatr. Respir. Rev. 2007, 8, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; Ma, H.; Li, D.; Pan, L.; Wang, T.; Li, R.; Ren, X. Prenatal Exposure to Fine Particulate Matter Chemical Constituents and the Risk of Stillbirth and the Mediating Role of Pregnancy Complications: A Cohort Study. Chemosphere 2024, 349, 140858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Wu, L.; Wang, H.; Zhang, L.; Yin, W.; Tao, R.; Tao, F.; Zhu, P. Prenatal Air Pollution, Fetal β-Cell Dysfunction and Neurodevelopmental Delay. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 268, 115705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miodovnik, A. Environmental Neurotoxicants and Developing Brain. Mt. Sinai J. Med. 2011, 78, 58–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehab, M.A.; Pope, F.D. Effects of Short-Term Exposure to Particulate Matter Air Pollution on Cognitive Performance. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, J.I.; Byun, G.; Lee, J.T. Exposure to Particulate Matter as a Potential Risk Factor for Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder in Korean Children and Adolescents (KNHANES 2008–2018). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 13966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodward, N.C.; Haghani, A.; Johnson, R.G.; Hsu, T.M.; Saffari, A.; Sioutas, C.; Kanoski, S.E.; Finch, C.E.; Morgan, T.E. Prenatal and Early Life Exposure to Air Pollution Induced Hippocampal Vascular Leakage and Impaired Neurogenesis in Association with Behavioral Deficits. Transl. Psychiatry 2018, 8, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brokamp, C.; Strawn, J.R.; Beck, A.F.; Ryan, P. Pediatric Psychiatric Emergency Department Utilization and Fine Particulate Matter: A Case-Crossover Study. Environ. Health Perspect. 2019, 127, 97006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.J.; Wang, F.; Liu, H.; Wei, Y.B.; Li, H.; Yue, J.; Que, J.; Degenhardt, L.; Lappin, J.; Lu, L.; et al. Ambient Fine Particulate Matter Is Associated with Increased Emergency Ambulance Dispatches for Psychiatric Emergencies. Environ. Res. 2019, 177, 108611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota-Bertran, A.; Coenders, G.; Plaja, P.; Saez, M.; Barceló, M.A. Air Pollution and Children’s Mental Health in Rural Areas: Compositional Spatio-Temporal Model. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 19363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, M.H.; Gold, D.R.; Rifas-Shiman, S.L.; Melly, S.J.; Zanobetti, A.; Coull, B.A.; Schwartz, J.D.; Gryparis, A.; Kloog, I.; Koutrakis, P.; et al. Prenatal and Childhood Traffic-Related Air Pollution Exposure and Childhood Executive Function and Behavior. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2016, 57, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calderón-Garcidueñas, L.; Gónzalez-Maciel, A.; Reynoso-Robles, R.; Delgado-Chávez, R.; Mukherjee, P.S.; Kulesza, R.J.; Torres-Jardón, R.; Ávila-Ramírez, J.; Villarreal-Ríos, R. Hallmarks of Alzheimer Disease Are Evolving Relentlessly in Metropolitan Mexico City Infants, Children and Young Adults. APOE4 Carriers Have Higher Suicide Risk and Higher Odds of Reaching NFT Stage V at ≤ 40 Years of Age. Environ. Res. 2018, 164, 475–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daiber, A.; Kuntic, M.; Hahad, O.; Delogu, L.G.; Rohrbach, S.; Di Lisa, F.; Schulz, R.; Münzel, T. Effects of Air Pollution Particles (Ultrafine and Fine Particulate Matter) on Mitochondrial Function and Oxidative Stress–Implications for Cardiovascular and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2020, 696, 108662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Januel, E.; Dessimond, B.; Colette, A.; Annesi-Maesano, I.; Stankoff, B. Fine Particulate Matter Related to Multiple Sclerosis Relapse in Young Patients. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 651084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunez, Y.; Boehme, A.K.; Weisskopf, M.G.; Re, D.B.; Navas-Acien, A.; van Donkelaar, A.; Martin, R.V.; Kioumourtzoglou, M.A. Fine Particle Exposure and Clinical Aggravation in Neurodegenerative Diseases in New York State. Environ. Health Perspect. 2021, 129, 27003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semmens, E.O.; Leary, C.S.; Fitzpatrick, A.L.; Ilango, S.D.; Park, C.; Adam, C.E.; DeKosky, S.T.; Lopez, O.; Hajat, A.; Kaufman, J.D. Air Pollution and Dementia in Older Adults in the Ginkgo Evaluation of Memory Study. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2023, 19, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangwar, R.S.; Bevan, G.H.; Palanivel, R.; Das, L.; Rajagopalan, S. Oxidative Stress Pathways of Air Pollution Mediated Toxicity: Recent Insights. Redox Biol. 2020, 34, 101545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Chen, Y.H.; Chien, C.C.; Yan, Y.H.; Chen, H.C.; Chuang, H.C.; Hsieh, H.I.; Cho, K.H.; Kuo, L.W.; Chou, C.C.K.; et al. Three Month Inhalation Exposure to Low-Level PM2.5 Induced Brain Toxicity in an Alzheimer’s Disease Mouse Model. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0254587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Liu, Q.; Xu, Z.; Guo, X.; Wu, S. Association between Short-Term Exposure to Ambient Particulate Air Pollution and Biomarkers of Oxidative Stress: A Meta-Analysis. Environ. Res. 2020, 191, 110105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobley, J.N.; Fiorello, M.L.; Bailey, D.M. 13 Reasons Why the Brain Is Susceptible to Oxidative Stress. Redox Biol 2018, 15, 490–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Kukreti, R.; Saso, L.; Kukreti, S. Oxidative Stress: A Key Modulator in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Molecules 2019, 24, 1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagundes, L.S.; Fleck, A.D.S.; Zanchi, A.C.; Saldiva, P.H.N.; Rhoden, C.R. Direct Contact with Particulate Matter Increases Oxidative Stress in Different Brain Structures. Inhal. Toxicol. 2015, 27, 462–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Lin, C.Y.; Chen, T.F.; Chou, C.C.; Chiu, M.J.; Tee, B.L.; Liang, H.J.; Cheng, T.J. Distinct Brain Lipid Signatures in Response to Low-Level PM2.5 Exposure in a 3xTg-Alzheimer’s Disease Mouse Inhalation Model. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838 Pt 4, 156456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Lee, P.H.; Liang, H.J.; Tang, C.H.; Chen, T.F.; Cheng, T.J.; Lin, C.Y. Brain Lipid Profiles in the Spontaneously Hypertensive Rat after Subchronic Real-World Exposure to Ambient Fine Particulate Matter. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 707, 135603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liu, S.; Zhang, W.; Wu, C.; Liu, H.; Zhang, F.; Lu, Z.; Ding, W. Nrf2 Deficiency Exacerbates PM2.5-Induced Olfactory Bulb Injury. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 505, 1154–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Childs, R.; Karamacoska, D.; Lim, C.K.; Steiner-Lim, G.Z. “Let’s Talk about Sex, Inflammaging, and Cognition, Baby”: A Meta-Analysis and Meta-Regression of 106 Case-Control Studies on Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer’s Disease. Brain Behav. Immun. Health 2024, 40, 100819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, T.B.; Coburn, J.; Dao, K.; Roqué, P.; Chang, Y.C.; Kalia, V.; Guilarte, T.R.; Dziedzic, J.; Costa, L.G. Sex and Genetic Differences in the Effects of Acute Diesel Exhaust Exposure on Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Mouse Brain. Toxicology 2016, 374, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehsanifar, M.; Montazeri, Z.; Taheri, M.A.; Rafati, M.; Behjati, M.; Karimian, M. Hippocampal Inflammation and Oxidative Stress Following Exposure to Diesel Exhaust Nanoparticles in Male and Female Mice. Neurochem. Int. 2021, 145, 104989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jetton, T.L.; Galbraith, O.T.; Peshavaria, M.; Bonney, E.A.; Holmén, B.A.; Fukagawa, N.K. Sex-Specific Metabolic Adaptations from in Utero Exposure to Particulate Matter Derived from Combustion of Petrodiesel and Biodiesel Fuels. Chemosphere 2023, 346, 140480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, T.; Sun, L.; Li, W.; Zhang, C.; Yu, L.; Guan, Y. Gestational B-Vitamin Supplementation Alleviates PM2.5-Induced Autism-like Behavior and Hippocampal Neurodevelopmental Impairment in Mice Offspring. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 185, 109686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wang, T.; Sun, L.; Zhang, H.; Liu, C.; Zhang, C.; Yu, L. B-Vitamin Supplementation Ameliorates Anxiety- and Depression-like Behavior Induced by Gestational Urban PM2.5 Exposure through Suppressing Neuroinflammation in Mice Offspring. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266, 115146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanchi, A.C.; Venturini, C.D.; Saiki, M.; Nascimento Saldiva, P.H.; Tannhauser Barros, H.M.; Rhoden, C.R. Chronic Nasal Instillation of Residual-Oil Fly Ash (ROFA) Induces Brain Lipid Peroxidation and Behavioral Changes in Rats. Inhal. Toxicol. 2008, 20, 795–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, W.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.; Qin, Y.; Xu, Y. Neurodevelopmental Toxicity Induced by Maternal PM2.5 Exposure and Protective Effects of Quercetin and Vitamin C. Chemosphere 2018, 213, 182–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, M.V.; McGavern, D.B. Inflammatory Neuroprotection Following Traumatic Brain Injury. Science 2016, 353, 783–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irrsack, E.; Aydin, S.; Bleckmann, K.; Schuller, J.; Dringen, R.; Koch, M. Local Administrations of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles in the Prefrontal Cortex and Caudate Putamen of Rats Do Not Compromise Working Memory and Motor Activity. Neurotox. Res. 2024, 42, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickard, M.R.; Chari, D.M. Robust Uptake of Magnetic Nanoparticles (MNPs) by Central Nervous System (CNS) Microglia: Implications for Particle Uptake in Mixed Neural Cell Populations. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2010, 11, 967–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Mello, C.; Le, T.; Swain, M.G. Cerebral Microglia Recruit Monocytes into the Brain in Response to Tumor Necrosis Factora Signaling during Peripheral Organ Inflammation. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 2089–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czyżewski, W.; Mazurek, M.; Sakwa, L.; Szymoniuk, M.; Pham, J.; Pasierb, B.; Litak, J.; Czyżewska, E.; Turek, M.; Piotrowski, B.; et al. Astroglial Cells: Emerging Therapeutic Targets in the Management of Traumatic Brain Injury. Cells 2024, 13, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotoh, M.; Miyamoto, Y.; Ikeshima-Kataoka, H. Astrocytic Neuroimmunological Roles Interacting with Microglial Cells in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruol, D.L. The Neuroimmune System and the Cerebellum. Cerebellum 2024, 23, 2511–2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Block, M.L.; Calderón-Garcidueñas, L. Air Pollution: Mechanisms of Neuroinflammation and CNS Disease. Trends Neurosci. 2009, 32, 506–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calderón-Garcidueñas, L.; Engle, R.; Antonieta Mora-Tiscareño, A.M.; Styner, M.; Gómez-Garza, G.; Zhu, H.; Jewells, V.; Torres-Jardón, R.; Romero, L.; Monroy-Acosta, M.E.; et al. Exposure to Severe Urban Air Pollution Influences Cognitive Outcomes, Brain Volume and Systemic Inflammation in Clinically Healthy Children. Brain Cogn. 2011, 77, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calderón-Garcidueñas, L.; Leray, E.; Heydarpour, P.; Torres-Jardón, R.; Reis, J. Air Pollution, a Rising Environmental Risk Factor for Cognition, Neuroinflammation and Neurodegeneration: The Clinical Impact on Children and Beyond. Rev. Neurol. 2016, 172, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderón-Garcidueñas, L.; Reynoso-Robles, R.; Vargas- Martínez, J.; Gómez-Maqueo-Chew, A.; Pérez-Guillé, B.; Mukherjee, P.S.; Torres-Jardón, R.; Perry, G.; Gónzalez-Maciel, A. Prefrontal White Matter Pathology in Air Pollution Exposed Mexico City Young Urbanites and Their Potential Impact on Neurovascular Unit Dysfunction and the Development of Alzheimer’s Disease. Environ. Res. 2016, 146, 404–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderón-Garcidueñas, L.; Solt, A.C.; Henríquez-Roldán, C.; Torres-Jardón, R.; Nuse, B.; Herritt, L.; Villarreal-Calderón, R.; Osnaya, N.; Stone, I.; García, R.; et al. Long-Term Air Pollution Exposure Is Associated with Neuroinflammation, an Altered Innate Immune Response, Disruption of the Blood-Brain Barrier, Ultrafine Particulate Deposition, and Accumulation of Amyloid β-42 and α-Synuclein in Children and Young Adults. Toxicol. Pathol. 2008, 36, 289–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeffer, P.E.; Ho, T.R.; Mann, E.H.; Kelly, F.J.; Sehlstedt, M.; Pourazar, J.; Dove, R.E.; Sandstrom, T.; Mudway, I.S.; Hawrylowicz, C.M. Urban Particulate Matter Stimulation of Human Dendritic Cells Enhances Priming of Naive CD8 T Lymphocytes. Immunology 2018, 153, 502–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Domenico, M.; de Menezes Benevenuto, S.G.; Tomasini, P.P.; Yariwake, V.Y.; de Oliveira Alves, N.; Rahmeier, F.L.; da Cruz Fernandes, M.; Moura, D.J.; Nascimento Saldiva, P.H.; Veras, M.M. Concentrated Ambient Fine Particulate Matter (PM2.5) Exposure Induce Brain Damage in Pre and Postnatal Exposed Mice. Neurotoxicology 2020, 79, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roqué, P.J.; Dao, K.; Costa, L.G. Microglia Mediate Diesel Exhaust Particle-Induced Cerebellar Neuronal Toxicity through Neuroinflammatory Mechanisms. Neurotoxicology 2016, 56, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, A.; Daher, N.; Solaimani, P.; Mendoza, K.; Sioutas, C. Human Brain Derived Cells Respond in a Type-Specific Manner after Exposure to Urban Particulate Matter (PM). Toxicol. Vitr. 2014, 28, 1290–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.F.; Lee, S.H.; Zheng, W.R.; Hsu, C.C.; Cho, K.H.; Kuo, L.W.; Chou, C.C.K.; Chiu, M.J.; Tee, B.L.; Cheng, T.J. White Matter Pathology in Alzheimer’s Transgenic Mice with Chronic Exposure to Low-Level Ambient Fine Particulate Matter. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2022, 19, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Yu, Y.; Sun, Z.; Duan, J. A Comprehensive Understanding of Ambient Particulate Matter and Its Components on the Adverse Health Effects Based from Epidemiological and Laboratory Evidence. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2022, 19, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, B.; Yang, H.; Cui, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Sun, H.; Meng, Q.; Wu, S.; et al. Activation of NLRP3 in Microglia Exacerbates Diesel Exhaust Particles-Induced Impairment in Learning and Memory in Mice. Environ. Int. 2020, 136, 105487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, C.H.; Chen, J.K.; Kuo, L.W.; Cho, K.H.; Hsiao, T.C.; Lin, Z.W.; Lin, Y.S.; Kang, J.H.; Lo, Y.C.; Chuang, K.J.; et al. Chronic Pulmonary Exposure to Traffic-Related Fine Particulate Matter Causes Brain Impairment in Adult Rats. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2018, 15, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.Y.; Lee, D.H.; Park, S.; Kim, B.G.; Jang, A.S.; Oh, S.H.; Lee, J.H.; Suh, M.W.; Park, M.K. Neuronal and Perineuronal Changes of Cerebral Cortex after Exposure to Inhaled Particulate Matter. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Chen, Q.; Wu, B.; Rui, W.; Zheng, J.C.; Ding, W. Macrophages Treated with Particulate Matter PM2.5 Induce Selective Neurotoxicity through Glutaminase-Mediated Glutamate Generation. J. Neurochem. 2015, 134, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehsanifar, M.; Jafari, A.J.; Nikzad, H.; Zavareh, M.S.; Atlasi, M.A.; Mohammadi, H.; Tameh, A.A. Prenatal Exposure to Diesel Exhaust Particles Causes Anxiety, Spatial Memory Disorders with Alters Expression of Hippocampal pro-Inflammatory Cytokines and NMDA Receptor Subunits in Adult Male Mice Offspring. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 176, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Ji, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Li, S.; Qi, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cai, Y.; et al. Atmospheric particulate matter impairs cognition by modulating synaptic function via the nose-to-brain route. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 857 Pt 3, 159600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.; Guo, Y.; Yan, W.; Wei, F.; Ding, J.; Hong, W.; Wu, X.; Ku, T.; Yue, H.; Sang, N. PM2.5 Exposure Contributes to Anxiety and Depression-like Behaviors via Phenyl-Containing Compounds Interfering with Dopamine Receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidari Nejad, S.; Takechi, R.; Mullins, B.J.; Giles, C.; Larcombe, A.N.; Bertolatti, D.; Rumchev, K.; Dhaliwal, S.; Mamo, J. The Effect of Diesel Exhaust Exposure on Blood-Brain Barrier Integrity and Function in a Murine Model. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2015, 35, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huuskonen, M.T.; Liu, Q.; Lamorie-Foote, K.; Shkirkova, K.; Connor, M.; Patel, A.; Montagne, A.; Baertsch, H.; Sioutas, C.; Morgan, T.E.; et al. Air Pollution Particulate Matter Amplifies White Matter Vascular Pathology and Demyelination Caused by Hypoperfusion. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 785519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aquino, G.V.; Dabi, A.; Odom, G.J.; Lavado, R.; Nunn, K.; Thomas, K.; Schackmuth, B.; Shariff, N.; Jarajapu, M.; Pluto, M.; et al. Evaluating the Effect of Acute Diesel Exhaust Particle Exposure on P-Glycoprotein Efflux Transporter in the Blood–Brain Barrier Co-Cultured with Microglia. Curr. Res. Toxicol. 2023, 4, 100107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jablonka, E.; Lamb, M.J. The changing concept of epigenetics. Ann. New York Acad. Sci. 2002, 981, 82–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skinner, M.K. Environmental Epigenetics and a Unified Theory of the Molecular Aspects of Evolution: A Neo-Lamarckian Concept That Facilitates Neo-Darwinian Evolution. Genome Biol Evol 2015, 7, 1296–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skinner, M.K. Environmental epigenetic transgenerational inheritance and somatic epigenetic mitotic stability. Epigenetics 2011, 6, 838–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babenko, O.; Kovalchuk, I.; Metz, G.A. Epigenetic Programming of Neurodegenerative Diseases by an Adverse Environment. Brain Res. 2012, 1444, 96–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berson, A.; Nativio, R.; Berger, S.L.; Bonini, N.M. Epigenetic Regulation in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Trends Neurosci. 2018, 41, 587–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.C.; Lockwood, A.H.; Sonawane, B.R. Neurodegenerative Diseases: An Overview of Environmental Risk Factors. Environ. Health Perspect. 2005, 113, 1250–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin-Chan, M.; Navarro-Yepes, J.; Quintanilla-Vega, B. Environmental Pollutants as Risk Factors for Neurodegenerative Disorders: Alzheimer and Parkinson Diseases. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppedè, F.; Mancuso, M.; Siciliano, G.; Migliore, L.; Murri, L. Genes and the Environment in Neurodegeneration. Biosci. Rep. 2006, 26, 341–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqubal, A.; Ahmed, M.; Ahmad, S.; Ranjan Sahoo, C.; Kashif Iqubal, M.; Ehtaishamul Haque, S. Environmental Neurotoxic Pollutants: Review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 41175–41198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Liu, M.; Mei, X.; Li, Q.; Zhang, W.; Deng, P.; He, Z.; Xi, Y.; Tong, T.; Pi, H.; et al. Histone Hypoacetylation Contributes to Neurotoxicity Induced by Chronic Nickel Exposure in Vivo and in Vitro. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 783, 147014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Guo, Z.; Li, H. Analyses of Epigenetic Modification in Environmental Pollutants-Induced Neurotoxicity. Environmental Toxicology and Toxicogenomics. Methods in Molecular Biology 2021, 2326, 123–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Tian, Y.; Xu, C.; Wang, J.; Jin, Y. Prenatal and Postnatal Traffic Pollution Exposure, DNA Methylation in Shank3 and MeCP2 Promoter Regions, H3K4me3 and H3K27me3 and Sociability in Rats’ Offspring. Clin. Epigenet. 2021, 13, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forster, V.J.; McDonnell, A.; Theobald, R.; McKay, J.A. Effect of Methotrexate/Vitamin B12 on DNA Methylation as a Potential Factor in Leukemia Treatment-Related Neurotoxicity. Epigenomics 2017, 9, 1205–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, C.; Wen, Y.; Wu, L.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Q.; Wang, D.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, J. Arsenite-Induced Transgenerational Glycometabolism Is Associated with up-Regulation of H3K4me2 via Inhibiting Spr-5 in Caenorhabditis Elegans. Toxicol. Lett. 2020, 326, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, S.; Jiang, C.; Yan, Y.; Inagaki, Y.; Arzua, T.; Bai, X. Propofol Alters Long Non-Coding RNA Profiles in the Neonatal Mouse Hippocampus: Implication of Novel Mechanisms in Anesthetic-Induced Developmental Neurotoxicity. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 49, 2496–2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, M.; Richardson, J.R. Epigenetic Regulation of Astrocyte Function in Neuroinflammation and Neurodegeneration. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2018, 1864, 432–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jose, C.C.; Wang, Z.; Tanwar, V.S.; Zhang, X.; Zang, C.; Cuddapah, S. Nickel-Induced Transcriptional Changes Persist Post Exposure through Epigenetic Reprogramming. Epigenet. Chromatin 2019, 12, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blennow, K.; De Leon, M.J.; Zetterberg, H. Alzheimer’s Disease. Lancet 2006, 368, 387–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qureshi, I.A.; Mehler, M.F. Epigenetic Mechanisms Governing the Process of Neurodegeneration. Mol. Asp. Med. 2013, 34, 875–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuso, A.; Seminara, L.; Cavallaro, R.A.; D’Anselmi, F.; Scarpa, S. S-Adenosylmethionine/Homocysteine Cycle Alterations Modify DNA Methylation Status with Consequent Deregulation of PS1 and BACE and Beta-Amyloid Production. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2005, 28, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwata, A.; Nagata, K.; Hatsuta, H.; Takuma, H.; Bundo, M.; Iwamoto, K.; Tamaoka, A.; Murayama, S.; Saido, T.; Tsuji, S. Altered CpG Methylation in Sporadic Alzheimer’s Disease Is Associated with APP and MAPT Dysregulation. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014, 23, 648–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmo, S.D.; Hanzel, C.E.; Jacobs, M.L.; MacHnes, Z.; Iulita, M.F.; Yang, J.; Yu, L.; Ducatenzeiler, A.; Danik, M.; Breuillaud, L.S.; et al. Rescue of Early Bace-1 and Global DNA Demethylation by S-Adenosylmethionine Reduces Amyloid Pathology and Improves Cognition in an Alzheimer’s Model. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarantini, L.; Bonzini, M.; Apostoli, P.; Pegoraro, V.; Bollati, V.; Marinelli, B.; Cantone, L.; Rizzo, G.; Hou, L.; Schwartz, J.; et al. Effects of Particulate Matter on Genomic DNA Methylation Content and INOS Promoter Methylation. Environ. Health Perspect. 2009, 117, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shou, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Liu, C.; Hu, Y.; Wang, H. A Review of the Possible Associations between Ambient PM2.5 Exposures and the Development of Alzheimer’s Disease. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 174, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liang, D.; Ebelt, S.; Gearing, M.; Kobor, M.S.; Konwar, C.; Maclsaac, J.L.; Dever, K.; Wingo, A.P.; Levey, A.I.; et al. Differential DNA Methylation in the Brain as Potential Mediator of the Association between Traffic-Related PM2.5 and Neuropathology Markers of Alzheimer’s Disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2024, 20, 2538–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, S.; Carlson, A.K.; Suresh, A.; Rim, J.; Mays, M.A.; Ontaneda, D.; Dhawan, A. Impacts of Climate Change and Air Pollution on Neurologic Health, Disease, and Practice: A Scoping Review. Neurology 2023, 100, 474–483. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Li, L.; Cui, B.; Gai, Z.; Li, Q.; Wang, S.; Yan, J.; Lin, B.; Tian, L.; Liu, H.; et al. Early Postnatal Exposure to Airborne Fine Particulate Matter Induces Autism-like Phenotypes in Male Rats. Toxicol. Sci. 2018, 162, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, H.; Liang, F.; Meng, G.; Nie, Z.; Zhou, R.; Cheng, W.; Wu, X.; Feng, Y.; Wang, Y. Redox/Methylation Mediated Abnormal DNA Methylation as Regulators of Ambient Fine Particulate Matter-Induced Neurodevelopment Related Impairment in Human Neuronal Cells. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebolledo-Solleiro, D.; Castillo Flores, L.Y.; Solleiro-Villavicencio, H. Impact of BPA on Behavior, Neurodevelopment and Neurodegeneration. Front. Biosci. 2021, 26, 363–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasbanerjee, T.; Middleton, F.A.; Berger, D.F.; Lombardo, J.P.; Sagvolden, T.; Faraone, S.V. A Comparison of Molecular Alterations in Environmental and Genetic Rat Models of ADHD: A Pilot Study. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2008, 147, 1554–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Li, S.S.L. Epigenetic Effects of Environmental Chemicals Bisphenol A and Phthalates. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 10143–10153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheong, A.; Johnson, S.A.; Howald, E.C.; Ellersieck, M.R.; Camacho, L.; Lewis, S.M.; Vanlandingham, M.M.; Ying, J.; Ho, S.M.; Rosenfeld, C.S. Gene Expression and DNA Methylation Changes in the Hypothalamus and Hippocampus of Adult Rats Developmentally Exposed to Bisphenol A or Ethinyl Estradiol: A CLARITY-BPA Consortium Study. Epigenetics 2018, 13, 704–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayan, N.M.; Husin, A.; Siran, R. The Risk of Prenatal Bisphenol A Exposure in Early Life Neurodevelopment: Insights from Epigenetic Regulation. Early Hum. Dev. 2024, 198, 106120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, T.; Chen, M.; Li, B.; Yun, Y.; Li, G.; Sang, N. Synergistic Effects of Particulate Matter (PM2.5) and Sulfur Dioxide (SO2) on Neurodegeneration via the MicroRNA-Mediated Regulation of Tau Phosphorylation. Toxicol. Res. 2017, 6, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Feng, Y.; Liang, F.; Cheng, W.; Wu, X.; Zhou, R.; Wang, Y. Role of Oxidative Stress and DNA Hydroxymethylation in the Neurotoxicity of Fine Particulate Matter. Toxicology 2017, 380, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basavarajappa, B.S.; Subbanna, S. Histone Methylation Regulation in Neurodegenerative Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Wang, R.; Yang, X.; Tang, K.; Jing, N. Dual Roles of Histone H3 Lysine 9 Acetylation in Human Embryonic Stem Cell Pluripotency and Neural Differentiation. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 2508–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gjoneska, E.; Pfenning, A.R.; Mathys, H.; Quon, G.; Kundaje, A.; Tsai, L.H.; Kellis, M. Conserved Epigenomic Signals in Mice and Humans Reveal Immune Basis of Alzheimer’s Disease. Nature 2015, 518, 365–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benito, E.; Urbanke, H.; Ramachandran, B.; Barth, J.; Halder, R.; Awasthi, A.; Jain, G.; Capece, V.; Burkhardt, S.; Navarro-Sala, M.; et al. HDAC Inhibitor-Dependent Transcriptome and Memory Reinstatement in Cognitive Decline Models. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 3572–3584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Cassel, R.; Schneider-Anthony, A.; Merienne, K.; Cosquer, B.; Tzeplaeff, L.; Halder Sinha, S.; Kumar, M.; Chaturbedy, P.; Eswaramoorthy, M.; et al. Reinstating Plasticity and Memory in a Tauopathy Mouse Model with an Acetyltransferase Activator. EMBO Mol. Med. 2018, 10, e8587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvi, B.R.; Cassel, J.C.; Kundu, T.K.; Boutillier, A.L. Tuning Acetylation Levels with HAT Activators: Therapeutic Strategy in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gene Regul. Mech. 2010, 1799, 840–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, J.V.; de Freitas, B.S.; Antoniazzi, V.; Dos Santos, C.D.S.; Vedovelli, K.; Pires, V.N.; Paludo, L.; de Lima, M.N.M.; Bromberg, E. Social Isolation and Social Support at Adulthood Affect Epigenetic Mechanisms, Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Levels and Behavior of Chronically Stressed Rats. Behav. Brain Res. 2019, 366, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mews, P.; Donahue, G.; Drake, A.M.; Luczak, V.; Abel, T.; Berger, S.L. Acetyl-CoA Synthetase Regulates Histone Acetylation and Hippocampal Memory. Nature 2017, 546, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, S.D.; Mifsud, K.R.; Reul, J.M.H.M. Acute Stress Enhances Epigenetic Modifications but Does Not Affect the Constitutive Binding of PCREB to Immediate-Early Gene Promoters in the Rat Hippocampus. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godino, A.; Jayanthi, S.; Cadet, J.L. Epigenetic Landscape of Amphetamine and Methamphetamine Addiction in Rodents. Epigenetics 2015, 10, 574–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latusz, J.; Maćkowiak, M. Early-Life Blockade of NMDA Receptors Induces Epigenetic Abnormalities in the Adult Medial Prefrontal Cortex: Possible Involvement in Memory Impairment in Trace Fear Conditioning. Psychopharmacology 2020, 237, 231–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cronican, A.A.; Fitz, N.F.; Carter, A.; Saleem, M.; Shiva, S.; Barchowsky, A.; Koldamova, R.; Schug, J.; Lefterov, I. Genome-Wide Alteration of Histone H3K9 Acetylation Pattern in Mouse Offspring Prenatally Exposed to Arsenic. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Huang, X.; Ye, D.; Han, M.; Wang, H.L. Regulatory Roles of Histone Deacetylases 1 and 2 in Pb-Induced Neurotoxicity. Toxicol. Sci. 2018, 162, 688–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeo, M.; Berglund, K.; Hanna, M.; Guo, J.U.; Kittur, J.; Torres, M.D.; Abramowitz, J.; Busciglio, J.; Gao, Y.; Birnbaumer, L.; et al. Bisphenol A Delays the Perinatal Chloride Shift in Cortical Neurons by Epigenetic Effects on the Kcc2 Promoter. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 4315–4320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, K.; Martinez, L.A.; Tejada-Simon, M.V. Impaired Cognitive Function and Reduced Anxiety-Related Behavior in a Promyelocytic Leukemia (PML) Tumor Suppressor Protein-Deficient Mouse. Genes Brain Behav. 2013, 12, 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dachtler, J.; Hardingham, N.R.; Fox, K. The Role of Nitric Oxide Synthase in Cortical Plasticity Is Sex Specific. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 14994–14999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.M.; Kim, J.E.; Sohn, J.H.; Choi, H.C.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, M.J.; Choi, I.G.; Kang, T.C. Down-Regulation of Delayed Rectifier K+ Channels in the Hippocampus of Seizure Sensitive Gerbils. Brain Res. Bull. 2009, 80, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, A.; Aumann, T.D.; Pigoni, M.; Lichtenthaler, S.F.; Takeshima, H.; Munro, K.M.; Gunnersen, J.M. Lack of Sez6 Family Proteins Impairs Motor Functions, Short-Term Memory, and Cognitive Flexibility and Alters Dendritic Spine Properties. Cereb. Cortex 2020, 30, 2167–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaidery, N.A.; Tarannum, S.; Thomas, B. Epigenetic Landscape of Parkinson’s Disease: Emerging Role in Disease Mechanisms and Therapeutic Modalities. Neurotherapeutics 2013, 10, 698–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, A.; Costa, M. Nuclear Protein 1 Imparts Oncogenic Potential and Chemotherapeutic Resistance in Cancer. Cancer Lett. 2020, 494, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broday, L.; Peng, W.; Kuo, M.-H.; Salnikow, K.; Zoroddu, M.; Costa, M. Nickel compounds are novel inhibitors of histone H4 acetylation. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 238–241. [Google Scholar]
- Song, C.; Kanthasamy, A.; Anantharam, V.; Sun, F.; Kanthasamy, A.G. Environmental Neurotoxic Pesticide Increases Histone Acetylation to Promote Apoptosis in Dopaminergic Neuronal Cells: Relevance to Epigenetic Mechanisms of Neurodegeneration. Mol. Pharmacol. 2010, 77, 621–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Kanthasamy, A.; Jin, H.; Anantharam, V.; Kanthasamy, A.G. Paraquat Induces Epigenetic Changes by Promoting Histone Acetylation in Cell Culture Models of Dopaminergic Degeneration. Neurotoxicology 2011, 32, 586–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calderón-Garcidueñas, L.; Herrera-Soto, A.; Jury, N.; Maher, B.A.; González-Maciel, A.; Reynoso-Robles, R.; Ruiz-Rudolph, P.; van Zundert, B.; Varela-Nallar, L. Reduced Repressive Epigenetic Marks, Increased DNA Damage and Alzheimer’s Disease Hallmarks in the Brain of Humans and Mice Exposed to Particulate Urban Air Pollution. Environ. Res. 2020, 183, 109226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivashkevich, A.; Redon, C.E.; Nakamura, A.J.; Martin, R.F.; Martin, O.A. Use of the γ-H2AX Assay to Monitor DNA Damage and Repair in Translational Cancer Research. Cancer Lett. 2012, 327, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Ebadi, M. Significance of Metallothioneins in Aging Brain. Neurochem. Int. 2014, 65, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solaimani, P.; Saffari, A.; Sioutas, C.; Bondy, S.C.; Campbell, A. Exposure to Ambient Ultrafine Particulate Matter Alters the Expression of Genes in Primary Human Neurons. Neurotoxicology 2017, 58, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fénelon, K.; Mukai, J.; Xu, B.; Hsu, P.K.; Drew, L.J.; Karayiorgou, M.; Fischbach, G.D.; MacDermott, A.B.; Gogos, J.A. Deficiency of Dgcr8, a Gene Disrupted by the 22q11.2 Microdeletion, Results in Altered Short-Term Plasticity in the Prefrontal Cortex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 4447–4452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleck, B.; Grunig, G.; Chiu, A.; Liu, M.; Gordon, T.; Kazeros, A.; Reibman, J. MicroRNA-375 Regulation of Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin by Diesel Exhaust Particles and Ambient Particulate Matter in Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 3757–3763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourdon, J.A.; Saber, A.T.; Halappanavar, S.; Jackson, P.A.; Wu, D.; Hougaard, K.S.; Jacobsen, N.R.; Williams, A.; Vogel, U.; Wallin, H.; et al. Carbon Black Nanoparticle Intratracheal Installation Results in Large and Sustained Changes in the Expression of MiR-135b in Mouse Lung. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2012, 53, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, D.P.; Puig, K.L.; Gorr, M.W.; Wold, L.E.; Combs, C.K. A Pilot Study to Assess Effects of Long-Term Inhalation of Airborne Particulate Matter on Early Alzheimer-like Changes in the Mouse Brain. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, T.; Li, B.; Gao, R.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, W.; Ji, X.; Li, G.; Sang, N. NF-ΚB-Regulated MicroRNA-574-5p Underlies Synaptic and Cognitive Impairment in Response to Atmospheric PM2.5 Aspiration. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2017, 14, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, T.; Yadav, S. Role of MicroRNAs in Neurodegeneration Induced by Environmental Neurotoxicants and Aging. Ageing Res. Rev. 2020, 60, 101068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, M.; Yun, Q.; Shi, F.; Niu, G.; Gao, Y.; Xie, S.; Yu, S. Downregulation of MiR-384-5p Attenuates Rotenone-Induced Neurotoxicity in Dopaminergic SH-SY5Y Cells through Inhibiting Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2016, 310, C755–C763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Jiang, H.; Gu, J.; Tang, Y.; Shen, N.; Jin, Y. MicroRNA-195 Targets ADP-Ribosylation Factor-like Protein 2 to Induce Apoptosis in Human Embryonic Stem Cell-Derived Neural Progenitor Cells. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, M.; Lou, D.; Wang, Y.P.; Cai, Q.; Li, H.H. Paraquat Inhibited Differentiation in Human Neural Progenitor Cells (HNPCs) and down Regulated MiR-200a Expression by Targeting CTNNB1. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2016, 42, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, R.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Li, H.; Chen, W.; Zhang, B.; Wang, L.; Wu, L.; Li, W.; Ding, J.; et al. MicroRNA-494 Reduces DJ-1 Expression and Exacerbates Neurodegeneration. Neurobiol. Aging 2014, 35, 705–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Z.; Lu, M.; Qiao, C.; Zhou, Y.; Ding, J.H.; Hu, G. MicroRNA-7 Enhances Subventricular Zone Neurogenesis by Inhibiting NLRP3/Caspase-1 Axis in Adult Neural Stem Cells. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 7057–7069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Ye, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Mo, L.; Lin, C.; Wang, Q.; Wang, H.; Gong, X.; He, X.; Lu, G.; et al. MiR-124 Regulates Apoptosis and Autophagy Process in MPTP Model of Parkinson’s Disease by Targeting to Bim. Brain Pathol. 2016, 26, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saenen, N.D.; Martens, D.S.; Neven, K.Y.; Alfano, R.; Bové, H.; Janssen, B.G.; Roels, H.A.; Plusquin, M.; Vrijens, K.; Nawrot, T.S. Air Pollution-Induced Placental Alterations: An Interplay of Oxidative Stress, Epigenetics, and the Aging Phenotype? Clin. Epigenet. 2019, 11, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kalenik, S.; Zaczek, A.; Rodacka, A. Air Pollution-Induced Neurotoxicity: The Relationship Between Air Pollution, Epigenetic Changes, and Neurological Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3402. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073402
Kalenik S, Zaczek A, Rodacka A. Air Pollution-Induced Neurotoxicity: The Relationship Between Air Pollution, Epigenetic Changes, and Neurological Disorders. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(7):3402. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073402
Chicago/Turabian StyleKalenik, Sebastian, Agnieszka Zaczek, and Aleksandra Rodacka. 2025. "Air Pollution-Induced Neurotoxicity: The Relationship Between Air Pollution, Epigenetic Changes, and Neurological Disorders" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 7: 3402. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073402
APA StyleKalenik, S., Zaczek, A., & Rodacka, A. (2025). Air Pollution-Induced Neurotoxicity: The Relationship Between Air Pollution, Epigenetic Changes, and Neurological Disorders. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(7), 3402. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073402





