Phylogenetic Analysis and Expression Patterns of Triterpenoid Saponin Biosynthesis Genes in 19 Araliaceae Plants
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Assembly and Characterization of Transcriptome of Araliaceae Plants
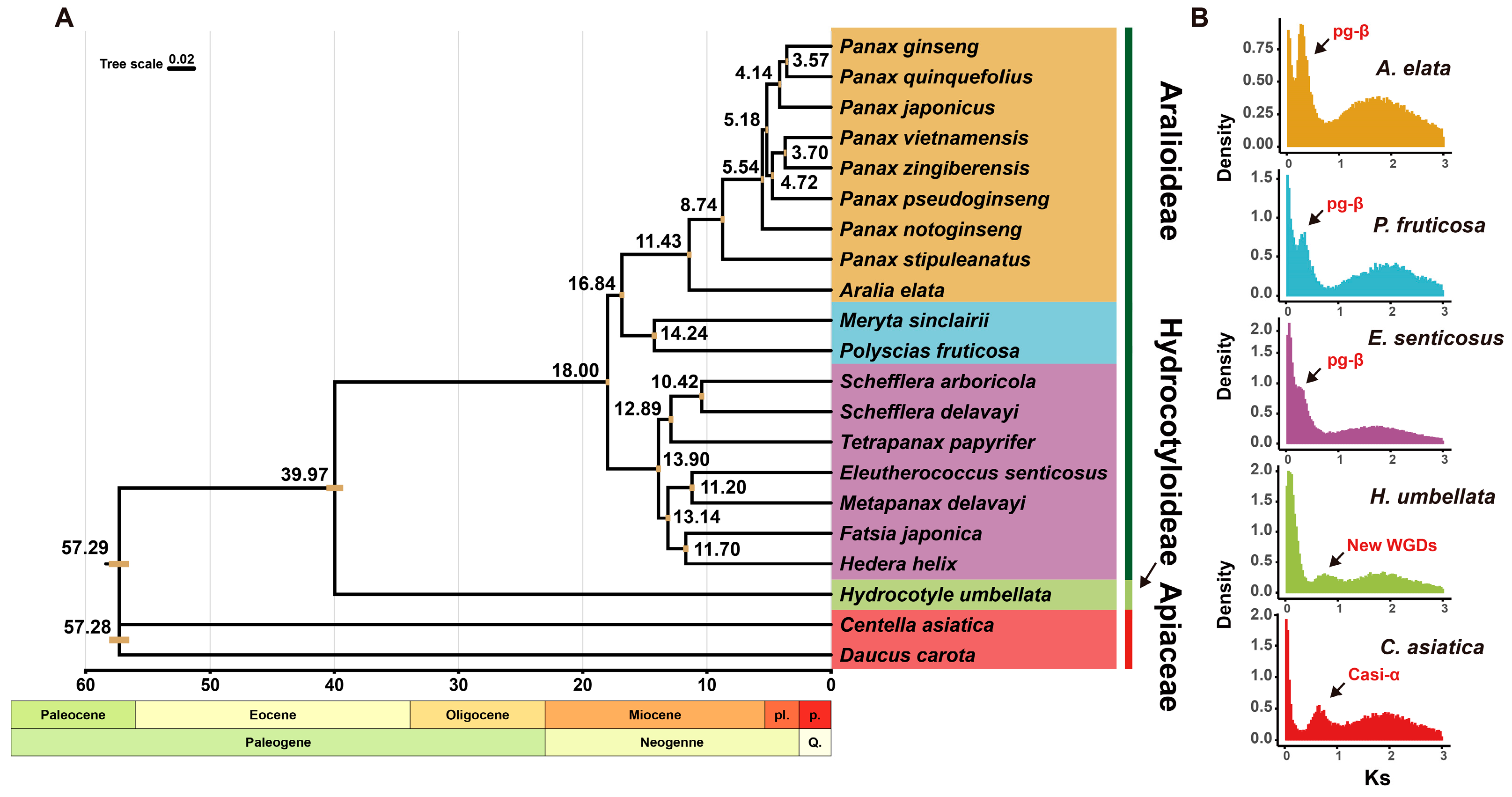
2.2. Phylogenetic Trees and Divergence Times of Araliaceae Plants Based on Comparative Transcriptomic Analysis
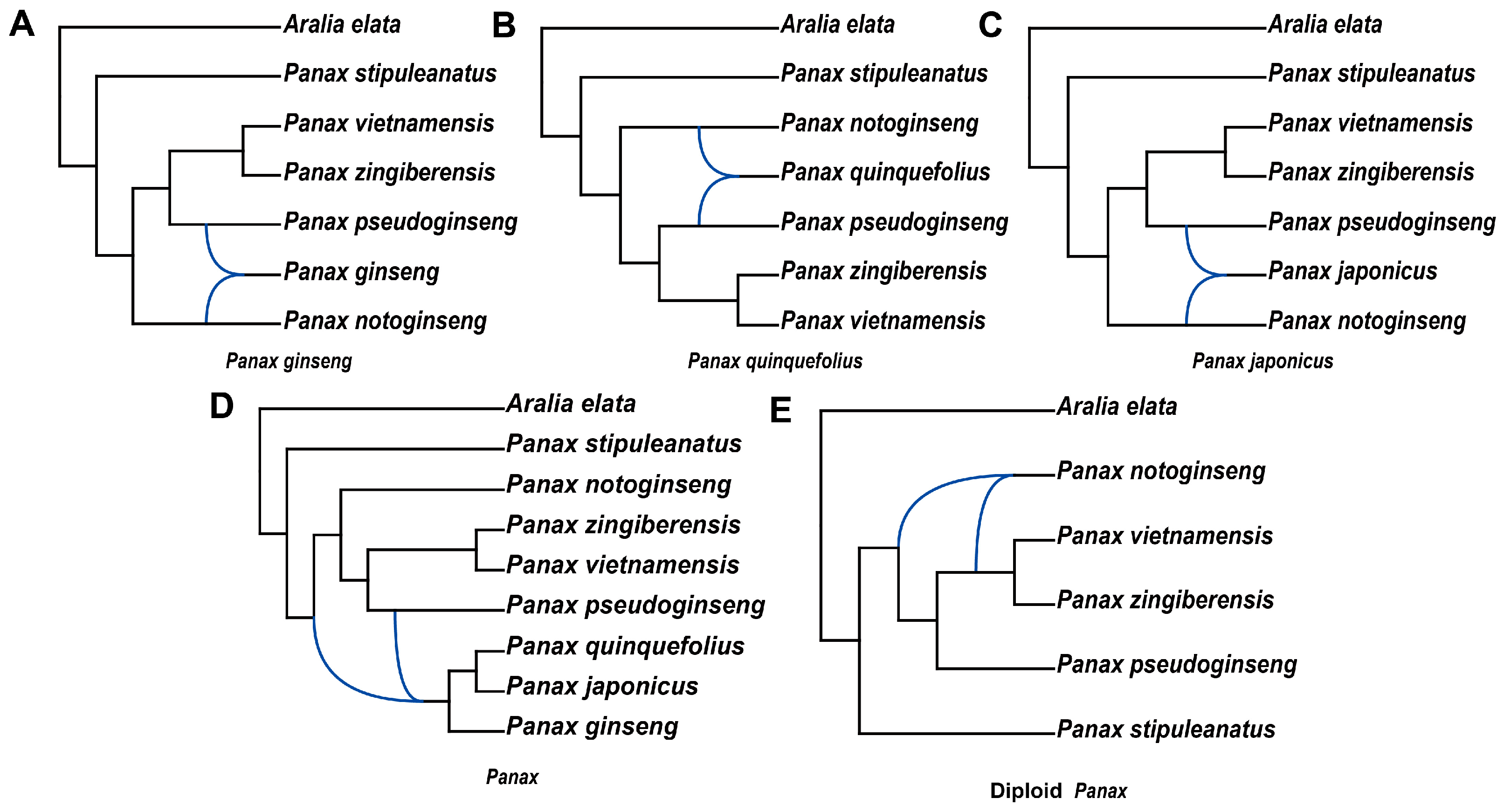
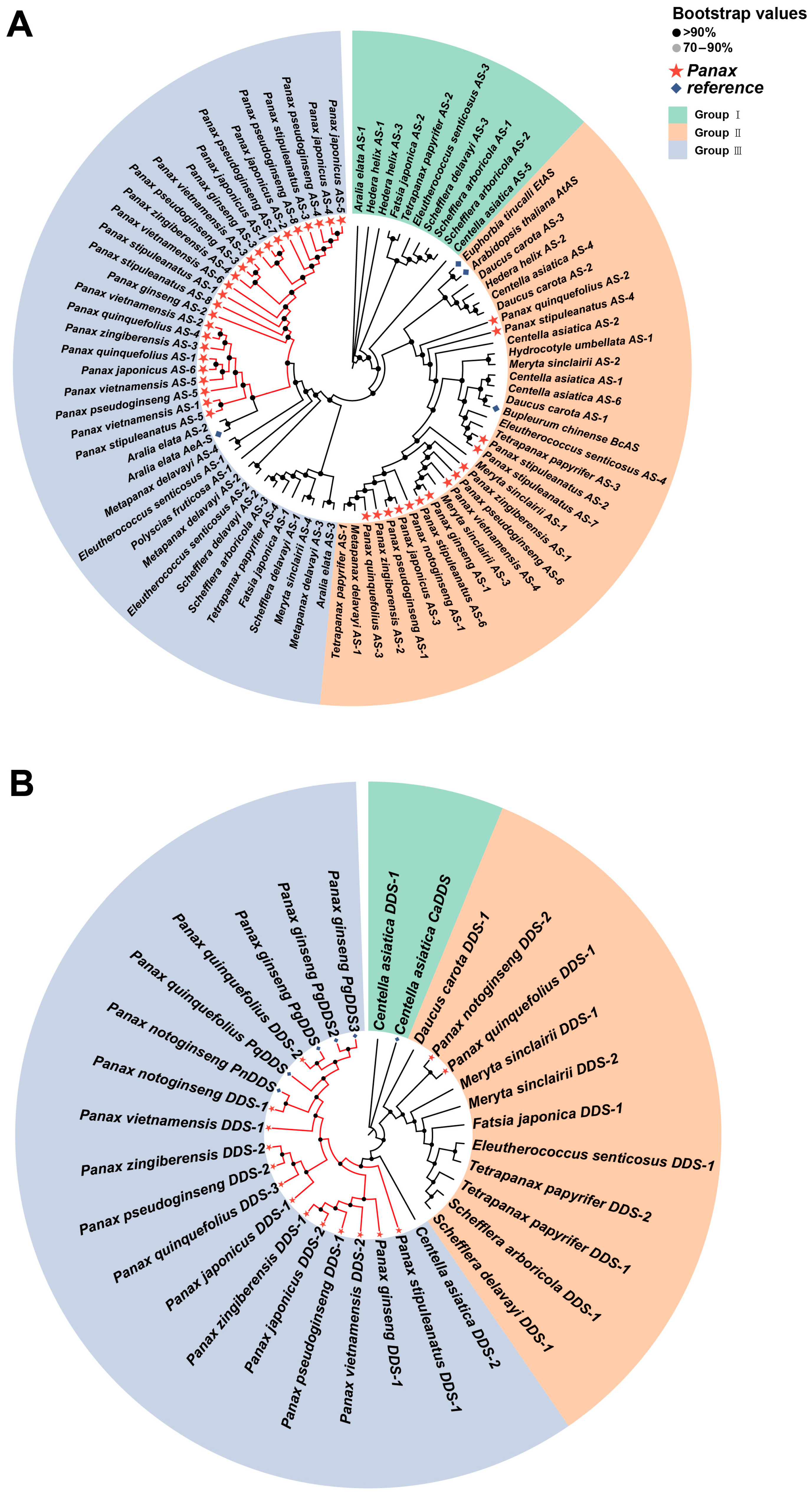
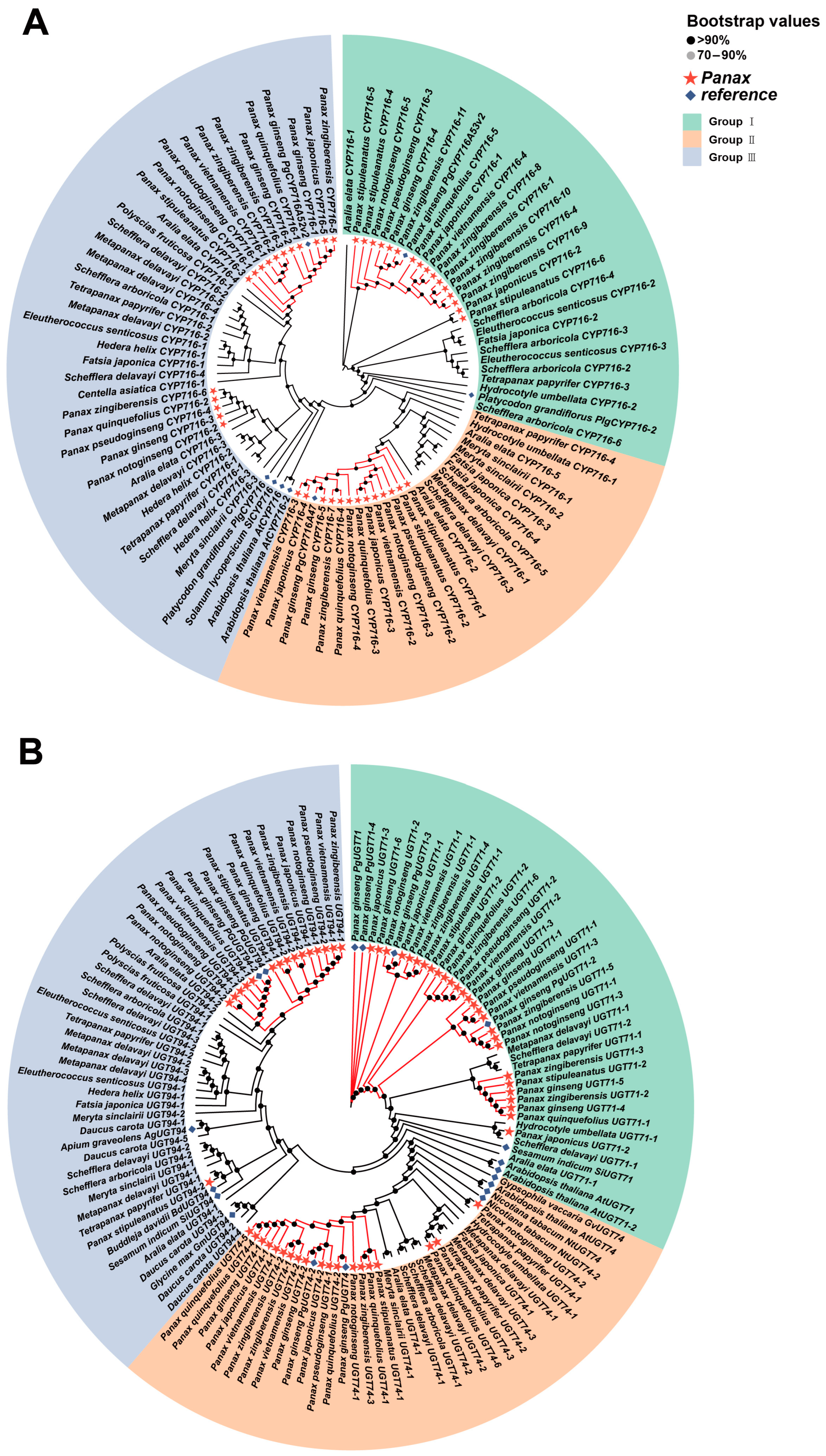
2.3. The Evolutionary Origin of Polyploid Panax Species
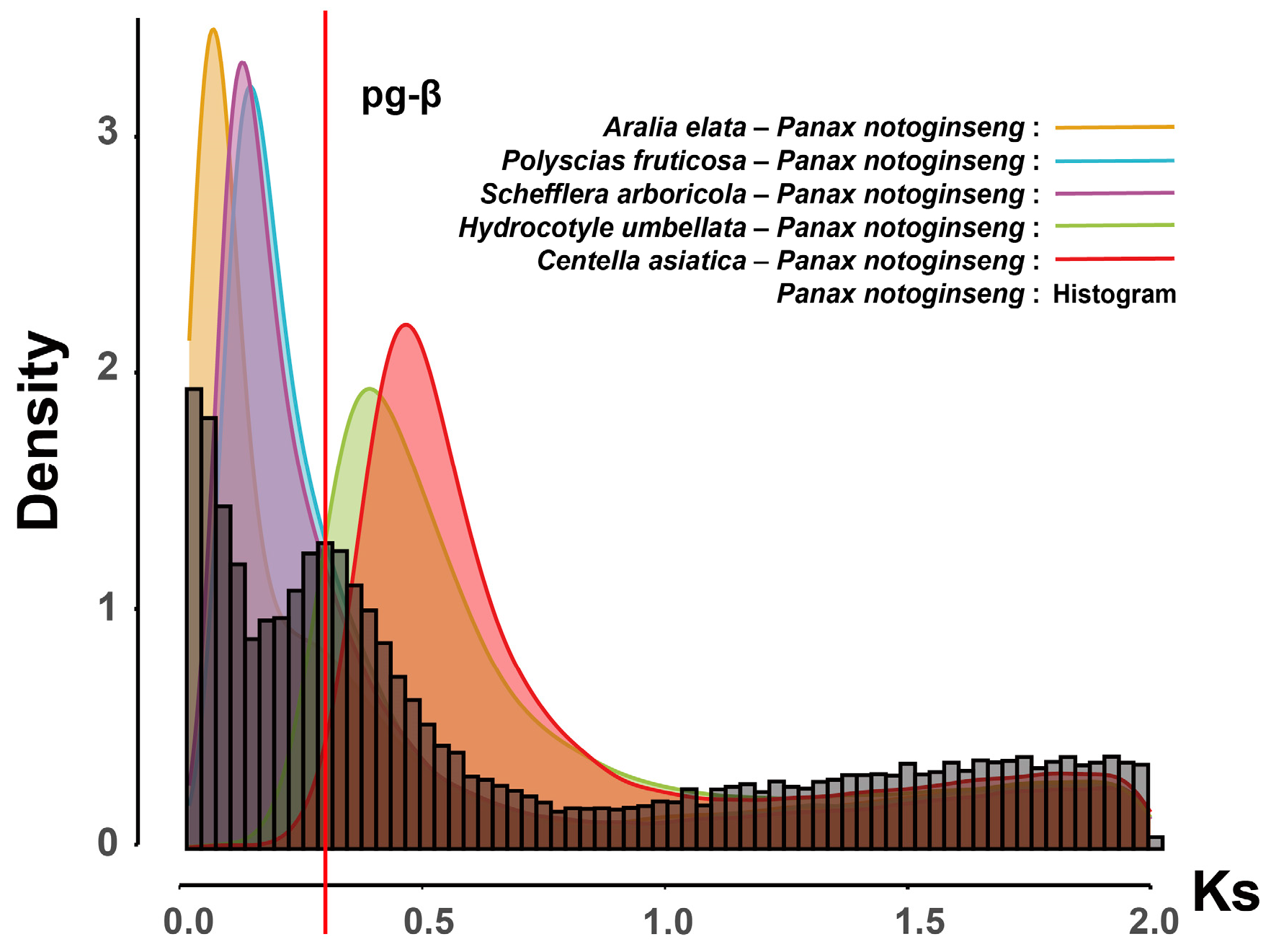
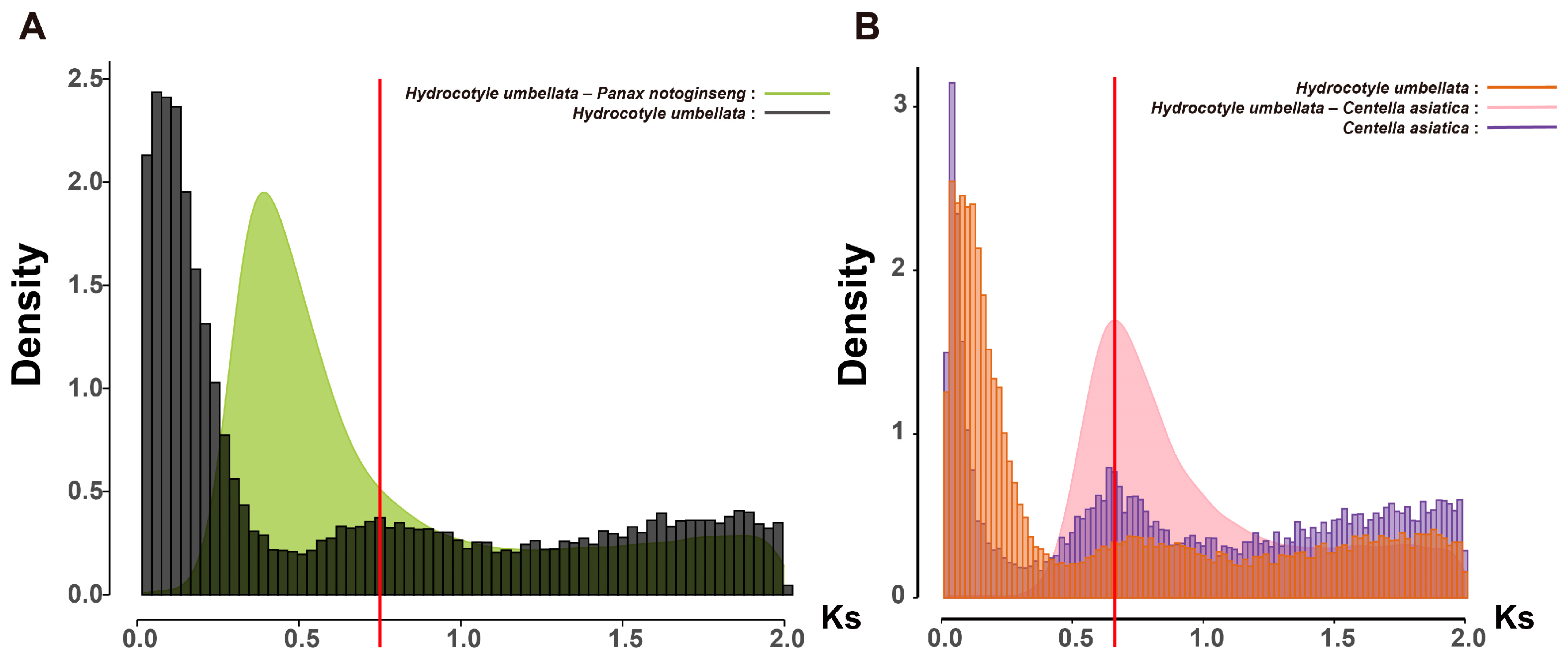
2.4. Whole-Genome Duplication Events in Araliaceae
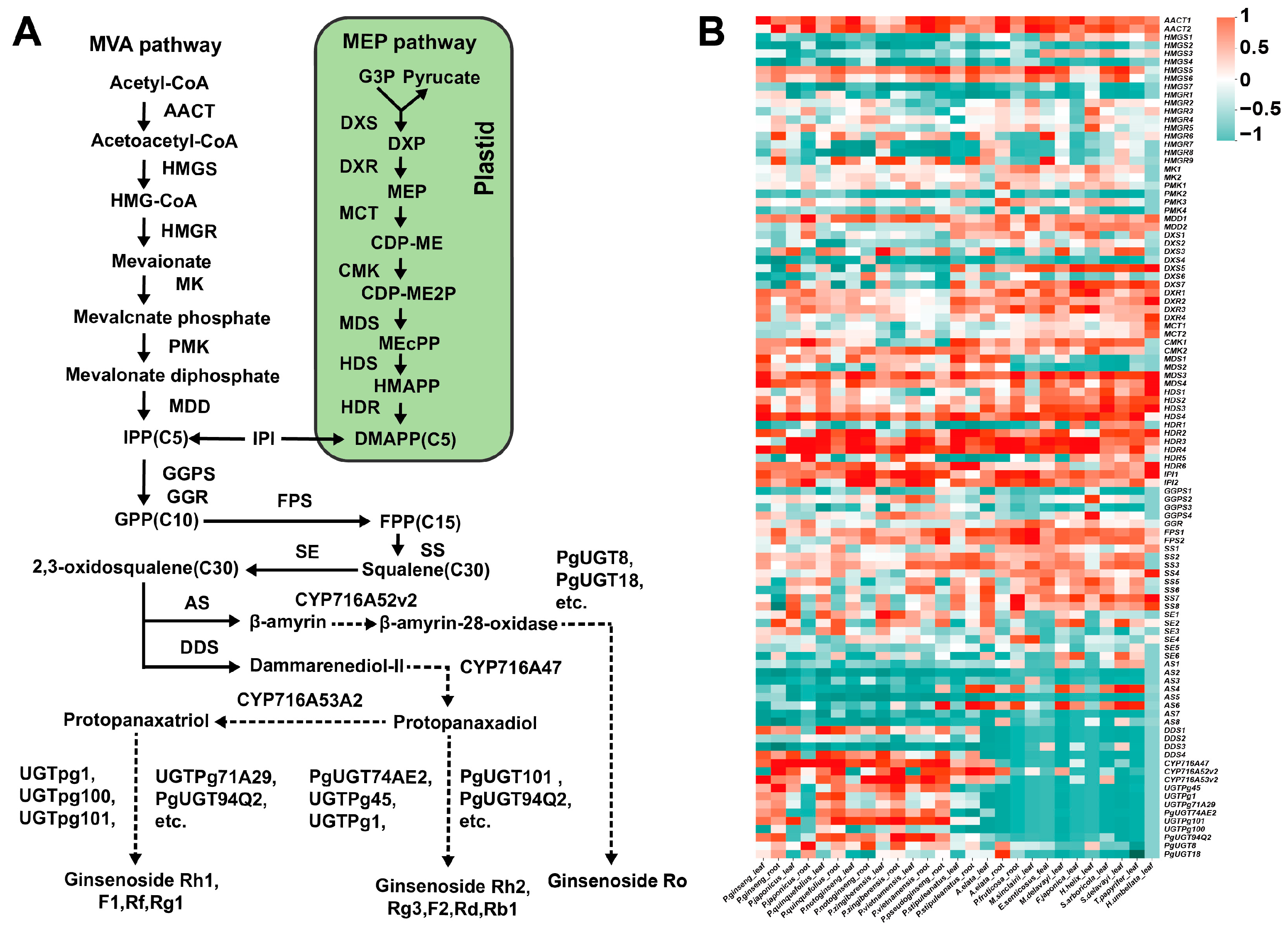
2.5. Gene Expression Patterns in the Ginsenoside Biosynthesis Pathway
3. Discussion
3.1. Resolution of the Phylogeny of Araliaceae Plants
3.2. The Expression Patterns and Evolutionary Relationships of Key Enzyme-Coding Genes in Ginsenoside Biosynthesis of Araliaceae Plants
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Data Sources and Transcriptome Assembly
4.2. Gene Functional Annotation and Single-Copy Orthologue Identification
4.3. Phylogeny Construction and Divergence Time Estimation
4.4. Inferring the Origin of Allopolyploidy in the Panax Genus
4.5. Identification of Whole-Genome Duplication Events in Araliaceae
4.6. Analysis of Expression Patterns of Key Genes in the Ginsenoside Biosynthesis Pathway
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, R.; Wen, J. Phylogeny and diversification of Chinese Araliaceae based on nuclear and plastid DNA sequence data. J. Syst. Evol. 2016, 54, 453–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.S.; Giang, V.N.L.; Park, H.S.; Park, Y.S.; Cho, W.H.Y.; Nguyen, V.; Shim, H.; Waminal, N.E.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, H.H.; et al. Evolution of the Araliaceae family involved rapid diversification of the Asian Palmate group and Hydrocotyle specific mutational pressure. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.T.; Zhang, Y.T.; Wang, X.; Yu, X.K.; Liao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, L.F.; Wang, Y.P.; Liu, B.; Li, W. Telomere-to-telomere reference genome for Panax ginseng highlights the evolution of saponin biosynthesis. Hortic. Res. 2024, 11, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Guo, R.X.; Zhou, G.H.; Zhou, X.D.; Kou, Z.Z.; Sui, F.; Li, C.; Tang, L.Y.; Wang, Z.J. Traditional uses, botany, phytochemistry, pharmacology and toxicology of Panax notoginseng (Burk.) FH Chen: A review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 188, 234–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Hou, A.J.; Zhang, J.X.; Wang, S.; Man, W.J.; Yu, H.; Zheng, S.W.; Wang, X.J.; Liu, S.T.; Jiang, H. Panacis Quinquefolii Radix: A Review of the Botany, Phytochemistry, Quality Control, Pharmacology, Toxicology and Industrial Applications Research Progress. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, M.Q.; Wang, R.F.; Zhao, S.J.; Wang, Z.T. Ginsenosides in Panax genus and their biosynthesis. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 11, 1813–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.L.; Hu, Z.F.; Zhang, T.T.; Gu, A.D.; Gong, T.; Zhu, P. Progress on the Studies of the Key Enzymes of Ginsenoside Biosynthesis. Molecules 2018, 23, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pena, R.D.; Hodgson, H.; Liu, J.C.T.; Stephenson, M.J.; Martin, A.C.; Owen, C.; Harkess, A.; Leebens-Mack, J.; Jimenez, L.E.; Osbourn, A.; et al. Complex scaffold remodeling in plant triterpene biosynthesis. Science 2023, 379, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Ma, K. The state’s will, scientific decision and citizen participation: In memory of the first provincial species red list in China. Biodivers. Sci. 2017, 25, 794–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fang, X.X.; Wang, M.Q.; Zhou, X.T.; Wang, H.; Wang, H.Y.; Xiao, H.X. Effects of growth years on ginsenoside biosynthesis of wild ginseng and cultivated ginseng. BMC Genom. 2022, 23, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harms, H. Araliaceae. In Die Natürlichen Pflanzenfamilien; Teil 3; Engler, A., Prantl, K., Eds.; Wilhelm Engelmann: Leipzig, Germany, 1898; Volume 8, pp. 1–62. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, J.; Plunkett, G.M.; Mitchell, A.D.; Wagstaff, S.J. The Evolution of Araliaceae: A Phylogenetic Analysis Based on ITS Sequences of Nuclear Ribosomal DNA. Syst. Bot. 2001, 26, 144–167. [Google Scholar]
- Plunkett, G.M.; Wen, J.; Lowry, P.P., II. Infrafamilial classifications and characters in Araliaceae: Insights from the phylogenetic analysis of nuclear (ITS) and plastid (trnL-trnF) sequence data. Plant Syst. Evol. 2004, 245, 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Nie, Z.L.; Ren, C.; Su, C.; Wen, J. Phylogenomics of Aralia sect. Aralia (Araliaceae): Signals of hybridization and insights into its species delimitations and intercontinental biogeography. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2023, 181, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.H.; Nie, Z.L.; Fairbanks, R.A.; Liu, J.; Literman, R.; Johnson, G.; Handy, S.; Wen, J. Phylogenomic insights into species relationships, reticulate evolution, and biogeographic diversification of the ginseng genus Panax (Araliaceae), with an emphasis on the diversification in the Himalayan-Hengduan Mountains. J. Syst. Evol. 2025, 63, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Tong, W.; Zhao, H.J.; Ge, R.H.; Li, R.P.; Huang, J.; Li, F.D.; Wang, Y.L.; Mallano, A.I.; Deng, W.W.; et al. Comparative transcriptomic analysis unveils the deep phylogeny and secondary metabolite evolution of 116 Camellia plants. Plant J. 2022, 111, 406–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leebens-Mack, J.H.; Barker, M.S.; Carpenter, E.J.; Deyholos, M.K.; Gitzendanner, M.A.; Graham, S.W.; Grosse, I.; Li, Z.; Melkonian, M.; Mirarab, S.; et al. One thousand plant transcriptomes and the phylogenomics of green plants. Nature 2019, 574, 679–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, G.L.; Zhou, C.R.; Liu, S.L.; Zhou, X. Phylogenomics based on transcriptomics and short-read sequences. Bio-101 2021, e1010649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.Y.; Zhang, R.; Jiang, K.W.; Qi, J.; Hu, Y.; Guo, J.; Zhu, R.B.; Zhang, T.K.; Egan, A.N.; Yi, T.S.; et al. Nuclear phylotranscriptomics and phylogenomics support numerous polyploidization events and hypotheses for the evolution of rhizobial nitrogen-fixing symbiosis in Fabaceae. Mol. Plant 2021, 14, 748–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.F.; Huang, C.H.; Liu, M.; Hu, Y.; Panero, J.L.; Luebert, F.; Gao, T.G.; Ma, H. Phylotranscriptomic insights into Asteraceae diversity, polyploidy, and morphological innovation. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2021, 63, 1273–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Won, S.Y.; Kwon, S.J.; Lee, T.H.; Jung, J.A.; Kim, J.S.; Kang, S.H.; Sohn, S.H. Comparative transcriptome analysis reveals whole-genome duplications and gene selection patterns in cultivated and wild Chrysanthemum species. Plant Mol. Biol. 2017, 95, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.B.; Gao, J.P.; Li, Z.W.; Chen, K.; Pu, W.X.; Feng, C. Phylotranscriptomics supports numerous polyploidization events and phylogenetic relationships in Nicotiana. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Lyu, R.; Luo, Y.K.; Xiao, J.M.; Xie, L.; Wen, J.; Li, W.H.; Pei, L.Y.; Cheng, J. A phylotranscriptome study using silica gel-dried leaf tissues produces an updated robust phylogeny of Ranunculaceae. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2022, 174, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, D.F.; Xie, C.A.; Ren, T.; Song, B.N.; Zhou, S.D.; He, X.J. Plastid phylogenomic insights into relationships, divergence, and evolution of Apiales. Planta 2022, 256, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.I.; Waminal, N.E.; Park, H.M.; Kim, N.H.; Choi, B.S.; Park, M.; Choi, D.; Lim, Y.P.; Kwon, S.J.; Park, B.S.; et al. Major repeat components covering one-third of the ginseng (Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer) genome and evidence for allotetraploidy. Plant J. 2014, 77, 906–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, D.Q.; Yu, Y.; Zhu, J.F.; Nakhleh, L. Inferring Phylogenetic Networks Using PhyloNet. Syst. Biol. 2018, 67, 735–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.H.; Wang, X.F.; Lu, T.Y.; Li, M.R.; Jiang, P.; Zhao, J.; Liu, S.T.; Fu, X.Q.; Wendel, J.F.; Van de Peer, Y.; et al. Reshuffling of the ancestral core-eudicot genome shaped chromatin topology and epigenetic modification in Panax. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.J.; Chen, S.S.; Wang, S.F.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, G.H.; Dong, Y.; Yang, S.C.; Miao, J.H.; Chen, W.; Sheng, J. Chromosomal-scale genome assembly of Eleutherococcus senticosus provides insights into chromosome evolution in Araliaceae. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2021, 21, 2204–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Li, W.; Xia, E.H.; Zhang, Q.J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tong, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Niu, Y.C.; Xu, J.H.; et al. The Medicinal Herb Panax notoginseng Genome Provides Insights into Ginsenoside Biosynthesis and Genome Evolution. Mol. Plant 2017, 10, 903–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.X.; Guo, W.H.; Chen, S.; Xu, H.H.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, S.; You, X.L. A High-Quality Reference Genome Sequence and Genetic Transformation System of Aralia elata. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallego-Narbón, A.; Wen, J.; Liu, J.; Valcárcel, V. Hybridization and genome duplication for early evolutionary success in the Asian Palmate group of Araliaceae. J. Syst. Evol. 2022, 60, 1303–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Ri, H.C.; An, Z.Y.; Wang, X.; Zhou, J.N.; Zheng, D.R.; Wu, H.; Wang, P.C.; Yang, J.F.; et al. Deletion and tandem duplications of biosynthetic genes drive the diversity of triterpenoids in Aralia elata. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.Y.; Kwon, Y.S.; Yang, D.C.; Jung, Y.R.; Choi, Y.E. Expression and RNA interference-induced silencing of the dammarenediol synthase gene in Panax ginseng. Plant Cell Physiol. 2006, 47, 1653–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Kwon, Y.S.; Choi, Y.E. The Cyt P450 Enzyme CYP716A47 Catalyzes the Formation of Protopanaxadiol from Dammarenediol-II During Ginsenoside Biosynthesis in Panax ginseng. Plant Cell Physiol. 2011, 52, 2062–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kushiro, T.; Shibuya, M.; Ebizuka, Y. Beta-amyrin synthase—cloning of oxidosqualene cyclase that catalyzes the formation of the most popular triterpene among higher plants. Eur. J. Biochem. 1998, 256, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Li, W.; Chen, Z.J.; Wei, F.G.; Liu, Y.L.; Gao, L.Z. SMRT- and Illumina-based RNA-seq analyses unveil the ginsinoside biosynthesis and transcriptomic complexity in Panax notoginseng. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanan, P.; Yang, T.-J.; Song, Y.H. Genes and Regulatory Mechanisms for Ginsenoside Biosynthesis. J. Plant Biol. 2023, 66, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.J.; Li, X.B.; Yang, L.; Peng, S.F.; Song, W.L.; Lin, Y.; Xiang, G.S.; Li, Y.; Ye, S.; Ma, C.H.; et al. Comparative genomics reveals the diversification of triterpenoid biosynthesis and origin of ocotillol- type triterpenes in Panax. Plant Commun. 2023, 4, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.Y.; Hwang, H.S.; Choi, S.W.; Kim, H.J.; Choi, Y.E. Cytochrome P450 CYP716A53v2 Catalyzes the Formation of Protopanaxatriol from Protopanaxadiol During Ginsenoside Biosynthesis in Panax ginseng. Plant Cell Physiol. 2012, 53, 1535–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.X.; Li, R.Q.; He, W.S.; Xu, W.; Xu, W.; Yan, G.H.; Xu, S.H.; Chen, L.X.; Feng, Y.Q.; Li, H. Progress in Identification of UDP-Glycosyltransferases for Ginsenoside Biosynthesis. J. Nat. Prod. 2024, 87, 1246–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.Y.; Kim, M.J.; Ban, Y.W.; Hwang, H.S.; Choi, Y.E. The Involvement of β-Amyrin 28-Oxidase (CYP716A52v2) in Oleanane-Type Ginsenoside Biosynthesis in Panax ginseng. Plant Cell Physiol. 2013, 54, 2034–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Liu, J.Y.; Zeng, Y.L.; Jin, S.R.; Liu, W.T.; Li, Z.L.; Qin, X.H.; Bai, Y.L. Traditional uses, phytochemistry, pharmacology, toxicity and quality control of medicinal genus Aralia: A review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 284, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Huang, L.J.; Scheller, H.; Keasling, J.D. Medicinal terpenoid UDP-glycosyltransferases in plants: Recent advances and research strategies. J. Exp. Bot. 2023, 74, 1343–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Sena Brandine, G.; Smith, A.D. Falco: High-speed FastQC emulation for quality control of sequencing data. F1000Research 2019, 8, 1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, B.J.; Papanicolaou, A.; Yassour, M.; Grabherr, M.; Blood, P.D.; Bowden, J.; Couger, M.B.; Eccles, D.; Li, B.; Lieber, M.; et al. De novo transcript sequence reconstruction from RNA-seq using the Trinity platform for reference generation and analysis. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 1494–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.M.; Niu, B.F.; Zhu, Z.W.; Wu, S.T.; Li, W.Z. CD-HIT: Accelerated for clustering the next-generation sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 3150–3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simao, F.A.; Waterhouse, R.M.; Ioannidis, P.; Kriventseva, E.V.; Zdobnov, E.M. BUSCO: Assessing genome assembly and annotation completeness with single-copy orthologs. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3210–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.Y.; Krishnakumar, V.; Chan, A.P.; Thibaud-Nissen, F.; Schobel, S.; Town, C.D. Araport11: A complete reannotation of the Arabidopsis thaliana reference genome. Plant J. 2017, 89, 789–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Madden, T.L.; Schaffer, A.A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Miller, W.; Lipman, D.J. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 3389–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Jiao, C.; Sun, H.H.; Rosli, H.G.; Pombo, M.A.; Zhang, P.F.; Banf, M.; Dai, X.B.; Martin, G.B.; Giovannoni, J.J.; et al. iTAK: A Program for Genome-wide Prediction and Classification of Plant Transcription Factors, Transcriptional Regulators, and Protein Kinases. Mol. Plant. 2016, 9, 1667–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emms, D.M.; Kelly, S. OrthoFinder: Phylogenetic orthology inference for comparative genomics. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: Multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capella-Gutiérrez, S.; Silla-Martínez, J.M.; Gabaldón, T. trimAl: A tool for automated alignment trimming in large-scale phylogenetic analyses. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1972–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, B.Q.; Schmidt, H.A.; Chernomor, O.; Schrempf, D.; Woodhams, M.D.; von Haeseler, A.; Lanfear, R. IQ-TREE 2: New Models and Efficient Methods for Phylogenetic Inference in the Genomic Era. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 1530–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huelsenbeck, J.P.; Ronquist, F. MRBAYES: Bayesian inference of phylogenetic trees. Bioinformatics 2001, 17, 754–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirarab, S.; Warnow, T. ASTRAL-II: Coalescent-based species tree estimation with many hundreds of taxa and thousands of genes. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, i44–i52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.A.; Moore, M.J.; Brown, J.W.; Yang, Y. Analysis of phylogenomic datasets reveals conflict, concordance, and gene duplications with examples from animals and plants. BMC Evol. Biol. 2015, 15, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z. PAML 4: Phylogenetic analysis by maximum likelihood. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2007, 24, 1586–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.-I.; Kim, N.-H.; Lee, J.; Choi, B.S.; Kim, K.D.; Park, J.Y.; Lee, S.-C.; Yang, T.J. Evolutionary relationship of Panax ginseng and Panax quinquefolius inferred from sequencing and comparative analysis of expressed sequence tags. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2013, 60, 1377–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.M.; Chen, Y.R.; Cai, G.J.; Cai, R.L.; Hu, Z.; Wang, H. Tree Visualization by One Table (tvBOT): A web application for visualizing, modifying and annotating phylogenetic trees. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, W587–W592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huson, D.H.; Scornavacca, C. Dendroscope 3: An Interactive Tool for Rooted Phylogenetic Trees and Networks. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 1061–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Yang, Y.; Moore, M.J.; Brockington, S.F.; Walker, J.F.; Brown, J.W.; Liang, B.; Feng, T.; Edwards, C.; Mikenas, J.; et al. Evolution of Portulacineae Marked by Gene Tree Conflict and Gene Family Expansion Associated with Adaptation to Harsh Environments. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2019, 36, 112–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.Q.; Tu, L.C.; Yang, W.F.; Zhang, Y.F.; Hu, T.Y.; Ma, B.W.; Lu, Y.; Cui, X.M.; Gao, J.; Wu, X.Y.; et al. The chromosome-level reference genome assembly for Panax notoginseng and insights into ginsenoside biosynthesis. Plant Commun. 2021, 2, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Landmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. HISAT: A fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danecek, P.; Bonfield, J.K.; Liddle, J.; Marshall, J.; Ohan, V.; Pollard, M.O.; Whitwham, A.; Keane, T.; McCarthy, S.A.; Davies, R.M.; et al. Twelve years of SAMtools and BCFtools. Gigascience 2021, 10, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.; Smyth, G.K.; Shi, W. featureCounts: An efficient general purpose program for assigning sequence reads to genomic features. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eddy, S.R. Profile hidden Markov models. Bioinformatics 1998, 14, 755–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayers, E.W.; Beck, J.; Bolton, E.E.; Brister, J.R.; Chan, J.; Comeau, D.C.; Connor, R.; DiCuccio, M.; Farrell, C.M.; Feldgarden, M.; et al. Database resources of the National Center for Biotechnology Information. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, D33–D43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Y.; Chitsaz, F.; Derbyshire, M.K.; Gonzales, N.R.; Gwadz, M.; Lu, S.N.; Marchler, G.H.; Song, J.S.; Thanki, N.; Yamashita, R.A.; et al. The conserved domain database in 2023. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D384–D388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
 ”. Otherwise, the support values are indicated in the format of IQTREE (bootstrap support)/ASTRAL (local posterior probability)/MrBayes (posterior probability). The subfamilies and groups to which the Araliaceae plants belong are marked on the right side.
”. Otherwise, the support values are indicated in the format of IQTREE (bootstrap support)/ASTRAL (local posterior probability)/MrBayes (posterior probability). The subfamilies and groups to which the Araliaceae plants belong are marked on the right side.
 ”. Otherwise, the support values are indicated in the format of IQTREE (bootstrap support)/ASTRAL (local posterior probability)/MrBayes (posterior probability). The subfamilies and groups to which the Araliaceae plants belong are marked on the right side.
”. Otherwise, the support values are indicated in the format of IQTREE (bootstrap support)/ASTRAL (local posterior probability)/MrBayes (posterior probability). The subfamilies and groups to which the Araliaceae plants belong are marked on the right side.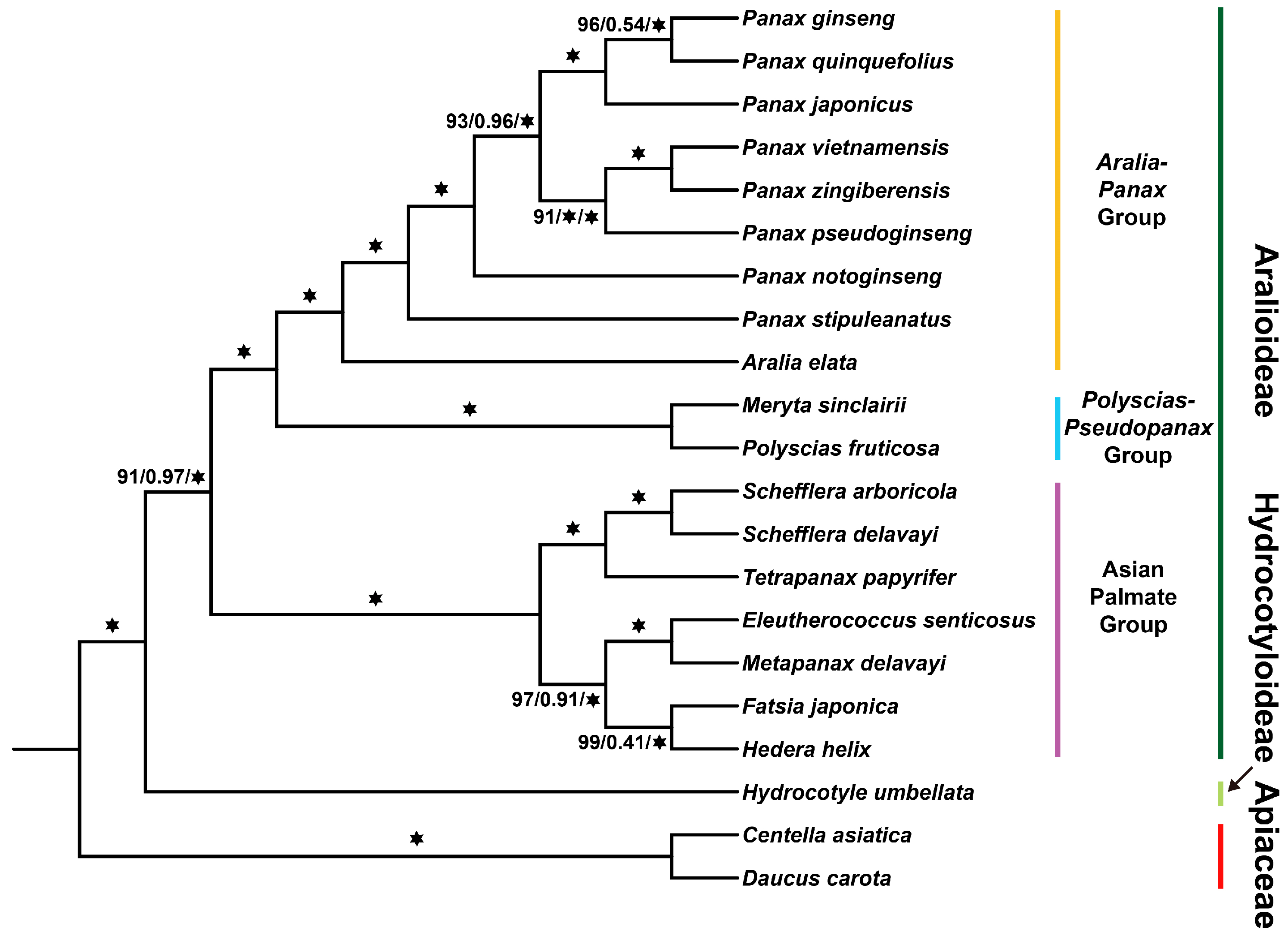

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, C.; Lin, Y.; Yin, J.; Zhu, L.; Fang, J.; Zhang, D. Phylogenetic Analysis and Expression Patterns of Triterpenoid Saponin Biosynthesis Genes in 19 Araliaceae Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3439. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073439
Ma C, Lin Y, Yin J, Zhu L, Fang J, Zhang D. Phylogenetic Analysis and Expression Patterns of Triterpenoid Saponin Biosynthesis Genes in 19 Araliaceae Plants. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(7):3439. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073439
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Chi, Yu Lin, Junjun Yin, Lijuan Zhu, Jinkai Fang, and Dan Zhang. 2025. "Phylogenetic Analysis and Expression Patterns of Triterpenoid Saponin Biosynthesis Genes in 19 Araliaceae Plants" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 7: 3439. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073439
APA StyleMa, C., Lin, Y., Yin, J., Zhu, L., Fang, J., & Zhang, D. (2025). Phylogenetic Analysis and Expression Patterns of Triterpenoid Saponin Biosynthesis Genes in 19 Araliaceae Plants. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(7), 3439. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073439




