Sex Differences in the Regulation of Interleukins in Chronic Pain: A Widely Recognized but Difficult-to-Tackle Factor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Influences of Sex Differences in Pain Processing and the Diversity of Estrogen Action
3. The Influences of Sex Differences in Interleukin Production and Reactivity in the Nervous System
4. Sex Differences-Associated ILs in Chronic Pain
4.1. IL-1β
4.2. IL-6
4.3. IL-18
4.4. IL-23/IL-17
4.5. IL-33
4.6. IL-10
4.7. IL-35
5. Therapeutic Strategy of IL Family
6. The Change in Pain Threshold in Klinefelter Syndrome
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kennedy, J.; Roll, J.M.; Schraudner, T.; Murphy, S.; McPherson, S. Prevalence of persistent pain in the U.S. adult population: New data from the 2010 national health interview survey. J. Pain 2014, 15, 979–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberg, D.S.; McGee, S.J. Pain as a global public health priority. BMC Public Health 2011, 11, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Hecke, O.; Austin, S.K.; Khan, R.A.; Smith, B.H.; Torrance, N. Neuropathic pain in the general population: A systematic review of epidemiological studies. Pain 2014, 155, 654–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamood, R.; Hamood, H.; Merhasin, I.; Keinan-Boker, L. Chronic pain and other symptoms among breast cancer survivors: Prevalence, predictors, and effects on quality of life. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 167, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.H.; Fu, Q.C.; Shi, D.; Bu, H.L.; Song, Z.P.; Xiong, B.R.; Shu, B.; Xiang, H.B.; Xu, B.; Manyande, A.; et al. Activation of spinal chemokine receptor CXCR3 mediates bone cancer pain through an Akt-ERK crosstalk pathway in rats. Exp. Neurol. 2015, 263, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Li, X.; Jian, W.; Xue, Q.; Liu, Z. Roles of Long Non-coding RNAs in the Development of Chronic Pain. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2021, 14, 760964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glare, P.; Aubrey, K.R.; Myles, P.S. Transition from acute to chronic pain after surgery. Lancet 2019, 393, 1537–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.Y.; Song, Z.W.; Guo, S.W.; He, J.S.; Wang, S.Y.; Zhu, J.G.; Yang, H.L.; Liu, J.B. CXCL12/CXCR4 signaling contributes to neuropathic pain via central sensitization mechanisms in a rat spinal nerve ligation model. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2019, 25, 922–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, M.M.; Davoli-Ferreira, M.; Santa-Cecília, F.; Guimarães, R.M.; Oliveira, F.F.B.; Kusuda, R.; Ferreira, D.W.; Alves-Filho, J.C.; Cunha, F.Q.; Cunha, T.M. IL-27 Counteracts Neuropathic Pain Development Through Induction of IL-10. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogil, J.S.; Chanda, M.L. The case for the inclusion of female subjects in basic science studies of pain. Pain 2005, 117, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogil, J.S. Qualitative sex differences in pain processing: Emerging evidence of a biased literature. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2020, 21, 353–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buse, D.C.; Loder, E.W.; Gorman, J.A.; Stewart, W.F.; Reed, M.L.; Fanning, K.M.; Serrano, D.; Lipton, R.B. Sex differences in the prevalence, symptoms, and associated features of migraine, probable migraine and other severe headache: Results of the American Migraine Prevalence and Prevention (AMPP) Study. Headache 2013, 53, 1278–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fillingim, R.B.; King, C.D.; Ribeiro-Dasilva, M.C.; Rahim-Williams, B.; Riley, J.L., 3rd. Sex, gender, and pain: A review of recent clinical and experimental findings. J. Pain 2009, 10, 447–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogil, J.S. Sex differences in pain and pain inhibition: Multiple explanations of a controversial phenomenon. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2012, 13, 859–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chesterton, L.S.; Barlas, P.; Foster, N.E.; Baxter, D.G.; Wright, C.C. Gender differences in pressure pain threshold in healthy humans. Pain 2003, 101, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frot, M.; Feine, J.S.; Bushnell, C.M. Sex differences in pain perception and anxiety. A psychophysical study with topical capsaicin. Pain 2004, 108, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarlani, E.; Farooq, N.; Greenspan, J.D. Gender and laterality differences in thermosensation throughout the perceptible range. Pain 2003, 106, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignali, D.A.; Kuchroo, V.K. IL-12 family cytokines: Immunological playmakers. Nat. Immunol. 2012, 13, 722–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Huang, L.; Zhao, H.; Yan, Y.; Lu, J. The Role of Interleukins in Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 16, 2323–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvador, A.F.; de Lima, K.A.; Kipnis, J. Neuromodulation by the immune system: A focus on cytokines. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 21, 526–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchheit, T.; Huh, Y.; Maixner, W.; Cheng, J.; Ji, R.R. Neuroimmune modulation of pain and regenerative pain medicine. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 2164–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binshtok, A.M.; Wang, H.; Zimmermann, K.; Amaya, F.; Vardeh, D.; Shi, L.; Brenner, G.J.; Ji, R.R.; Bean, B.P.; Woolf, C.J.; et al. Nociceptors are interleukin-1beta sensors. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 14062–14073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richter, F.; Natura, G.; Ebbinghaus, M.; von Banchet, G.S.; Hensellek, S.; König, C.; Bräuer, R.; Schaible, H.G. Interleukin-17 sensitizes joint nociceptors to mechanical stimuli and contributes to arthritic pain through neuronal interleukin-17 receptors in rodents. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 4125–4134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Li, F.; Maixner, D.W.; Yadav, R.; Gao, M.; Ali, M.W.; Hooks, S.B.; Weng, H.R. Interleukin-1beta released by microglia initiates the enhanced glutamatergic activity in the spinal dorsal horn during paclitaxel-associated acute pain syndrome. Glia 2019, 67, 482–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, R.R.; Kronfli, T.; Haythornthwaite, J.A.; Smith, M.T.; McGuire, L.; Page, G.G. Association of catastrophizing with interleukin-6 responses to acute pain. Pain 2008, 140, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, H.; Liu, H.Z.; Zhang, W.W.; Matsuda, M.; Lv, N.; Chen, G.; Xu, Z.Z.; Zhang, Y.Q. Interleukin-17 Regulates Neuron-Glial Communications, Synaptic Transmission, and Neuropathic Pain after Chemotherapy. Cell Rep. 2019, 29, 2384–2397.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruse, J.L.; Olmstead, R.; Hellemann, G.; Breen, E.C.; Tye, S.J.; Brooks, J.O., 3rd; Wade, B.; Congdon, E.; Espinoza, R.; Narr, K.L.; et al. Interleukin-8 and lower severity of depression in females, but not males, with treatment-resistant depression. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2021, 140, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouihate, A.; Kalakh, S. Maternal Interleukin-6 Hampers Hippocampal Neurogenesis in Adult Rat Offspring in a Sex-Dependent Manner. Dev. Neurosci. 2021, 43, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keckstein, S.; Pritz, S.; Amann, N.; Meister, S.; Beyer, S.; Jegen, M.; Kuhn, C.; Hutter, S.; Knabl, J.; Mahner, S.; et al. Sex Specific Expression of Interleukin 7, 8 and 15 in Placentas of Women with Gestational Diabetes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Chen, O.; Wang, Z.; Bang, S.; Ji, J.; Lee, S.H.; Huh, Y.; Furutani, K.; He, Q.; Tao, X.; et al. IL-23/IL-17A/TRPV1 axis produces mechanical pain via macrophage-sensory neuron crosstalk in female mice. Neuron 2021, 109, 2691–2706.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; He, Q.; Luo, X.; Bang, S.; Matsuoka, Y.; McGinnis, A.; Nackley, A.G.; Ji, R.R. IL-23 Enhances C-Fiber-Mediated and Blue Light-Induced Spontaneous Pain in Female Mice. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 787565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craft, R.M. Modulation of pain by estrogens. Pain 2007, 132 (Suppl. S1), S3–S12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, K.; Wei, F.; Dubner, R.; Murphy, A.; Hoffman, G.E. Progesterone attenuates persistent inflammatory hyperalgesia in female rats: Involvement of spinal NMDA receptor mechanisms. Brain Res. 2000, 865, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hau, M.; Dominguez, O.A.; Evrard, H.C. Testosterone reduces responsiveness to nociceptive stimuli in a wild bird. Horm. Behav. 2004, 46, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoffel, E.C.; Ulibarri, C.M.; Folk, J.E.; Rice, K.C.; Craft, R.M. Gonadal hormone modulation of mu, kappa, and delta opioid antinociception in male and female rats. J. Pain 2005, 6, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuba, T.; Wu, H.B.; Nazarian, A.; Festa, E.D.; Barr, G.A.; Jenab, S.; Inturrisi, C.E.; Quinones-Jenab, V. Estradiol and progesterone differentially regulate formalin-induced nociception in ovariectomized female rats. Horm. Behav. 2006, 49, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nag, S.; Mokha, S.S. Testosterone is essential for alpha(2)-adrenoceptor-induced antinociception in the trigeminal region of the male rat. Neurosci. Lett. 2009, 467, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, A.D.; Angelotti, T.; Nag, S.; Mokha, S.S. Sex-specific modulation of spinal nociception by alpha2-adrenoceptors: Differential regulation by estrogen and testosterone. Neurosci. 2008, 153, 1268–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, K.P.; Nag, S.; Thompson, A.D.; Mokha, S.S. Sex-specificity and estrogen-dependence of kappa opioid receptor-mediated antinociception and antihyperalgesia. Pain 2010, 151, 806–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zhang, W.; Sadana, N.; Chen, X. Estrogen receptors in pain modulation: Cellular signaling. Biol. Sex Differ. 2021, 12, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.N.; McFarland, K.; Olsson, R.; Burstein, E.S. Estrogen Receptor Beta Selective Agonists as Agents to Treat Chemotherapeutic-Induced Neuropathic Pain. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2016, 7, 1180–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Fan, X.; Warner, M.; Xu, X.J.; Gustafsson, J.A.; Wiesenfeld-Hallin, Z. Ablation of estrogen receptor alpha or beta eliminates sex differences in mechanical pain threshold in normal and inflamed mice. Pain 2009, 143, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, S.N.; Green, A.R.; Debner, E.K.; Ramos Freitas, L.E.; Abdelhadi, H.M.K.; Szabo-Pardi, T.A.; Burton, M.D. The influence of sex on neuroimmune communication, pain, and physiology. Biol. Sex Differ. 2024, 15, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papka, R.E.; Storey-Workley, M.; Shughrue, P.J.; Merchenthaler, I.; Collins, J.J.; Usip, S.; Saunders, P.T.; Shupnik, M. Estrogen receptor-alpha and beta-immunoreactivity and mRNA in neurons of sensory and autonomic ganglia and spinal cord. Cell Tissue Res. 2001, 304, 193–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shughrue, P.J.; Lane, M.V.; Merchenthaler, I. Comparative distribution of estrogen receptor-alpha and -beta mRNA in the rat central nervous system. J. Comp. Neurol. 1997, 388, 507–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdi, J.; Jafari-Sabet, M.; Mokhtari, R.; Mesdaghinia, A.; Banafshe, H.R. The effect of progesterone on expression and development of neuropathic pain in a rat model of peripheral neuropathy. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 699, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claiborne, J.; Nag, S.; Mokha, S.S. Activation of opioid receptor like-1 receptor in the spinal cord produces sex-specific antinociception in the rat: Estrogen attenuates antinociception in the female, whereas testosterone is required for the expression of antinociception in the male. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 13048–13053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, C.; Leinders, M.; Üçeyler, N. Inflammation in the pathophysiology of neuropathic pain. Pain 2018, 159, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, P.A.; Arora, V.K.; Sawyers, C.L. Emerging mechanisms of resistance to androgen receptor inhibitors in prostate cancer. Nature reviews. Cancer 2015, 15, 701–711. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Xing, X.; Jin, Q.; Wang, X.M.; Dai, P.; Han, M.; Shi, H.; Zhang, Z.; Shao, X.; Peng, Y.; et al. Sex differences orchestrated by androgens at single-cell resolution. Nature 2024, 629, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.Z.; Ding, Q.; Hu, J.; He, S.M.; Shi, F.; Ma, L.T. GPER expressed on microglia mediates the anti-inflammatory effect of estradiol in ischemic stroke. Brain Behav. 2016, 6, e00449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Hou, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, M.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, Y.; Hou, W. Estrogen Attenuates Traumatic Brain Injury by Inhibiting the Activation of Microglia and Astrocyte-Mediated Neuroinflammatory Responses. Mol. Neurobiol. 2021, 58, 1052–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, T.; Iwasaki, A. Sex differences in immune responses. Science 2021, 371, 347–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, C.; Liu, B.; Li, Y.; Li, K.; Li, P.; Song, C. The comparison of sex differences in depression-like behaviors and neuroinflammatory changes in a rat model of depression induced by chronic stress. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 1059594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parekh, S.V.; Adams, L.O.; Barkell, G.A.; Lysle, D.T. Sex-differences in anxiety, neuroinflammatory markers, and enhanced fear learning following chronic heroin withdrawal. Psychopharmacology 2023, 240, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnard, D.F.; Gabella, K.M.; Kulp, A.C.; Parker, A.D.; Dugan, P.B.; Johnson, J.D. Sex differences in the regulation of brain IL-1β in response to chronic stress. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2019, 103, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonaizan, R.; Alotaibi, W.K.; Alsulami, A.; Alkhulaifi, F.M.; Alomar, S. Sex-Differences Influence Depressive-Like Behaviour via Alterations in Microglial Expression of GIF-1, TREM2, and IL-1β in an Acute Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Murine Neuroinflammation Model. Immunol. Investig. 2025, 54, 317–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholz, J.; Finnerup, N.B.; Attal, N.; Aziz, Q.; Baron, R.; Bennett, M.I.; Benoliel, R.; Cohen, M.; Cruccu, G.; Davis, K.D.; et al. The IASP classification of chronic pain for ICD-11: Chronic neuropathic pain. Pain 2019, 160, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treede, R.D.; Rief, W.; Barke, A.; Aziz, Q.; Bennett, M.I.; Benoliel, R.; Cohen, M.; Evers, S.; Finnerup, N.B.; First, M.B.; et al. Chronic pain as a symptom or a disease: The IASP Classification of Chronic Pain for the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-11). Pain 2019, 160, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Q.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, J. IL-10 and IL-1β mediate neuropathic-pain like behavior in the ventrolateral orbital cortex. Neurochem. Res. 2015, 40, 733–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mailhot, B.; Christin, M.; Tessandier, N.; Sotoudeh, C.; Bretheau, F.; Turmel, R.; Pellerin, È.; Wang, F.; Bories, C.; Joly-Beauparlant, C.; et al. Neuronal interleukin-1 receptors mediate pain in chronic inflammatory diseases. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 217, e20191430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Krukowski, K.; Laumet, G.O.; Weis, D.; Alexander, J.F.; Heijnen, C.J.; Kavelaars, A. CD8+ T cell-derived IL-13 increases macrophage IL-10 to resolve neuropathic pain. JCI Insight 2022, 7, e154194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.M.; Jeong, C.W.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, Y.O.; Cui, J.H.; Yoon, M.H. The intrathecally administered kappa-2 opioid agonist GR89696 and interleukin-10 attenuate bone cancer-induced pain through synergistic interaction. Anesth. Analg. 2011, 113, 934–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helyes, Z.; Tékus, V.; Szentes, N.; Pohóczky, K.; Botz, B.; Kiss, T.; Kemény, Á.; Környei, Z.; Tóth, K.; Lénárt, N.; et al. Transfer of complex regional pain syndrome to mice via human autoantibodies is mediated by interleukin-1-induced mechanisms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 13067–13076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirabelli, E.; Ni, L.; Li, L.; Acioglu, C.; Heary, R.F.; Elkabes, S. Pathological pain processing in mouse models of multiple sclerosis and spinal cord injury: Contribution of plasma membrane calcium ATPase 2 (PMCA2). J. Neuroinflammation 2019, 16, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, T.; Qu, X.; Sun, G.; Fu, Q.; Han, G. Stress/cell death pathways, neuroinflammation, and neuropathic pain. Immunol. Rev. 2024, 321, 33–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vergne-Salle, P.; Bertin, P. Chronic pain and neuroinflammation. Jt. Bone Spine 2021, 88, 105222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, A.L.; Lim, M.; Doshi, T.L. Targeting cytokines for treatment of neuropathic pain. Scand. J. Pain 2017, 17, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Zhou, R.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, T.; Li, Q.; Zhang, W. Interleukin-17 as a potential therapeutic target for chronic pain. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 999407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.Q.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Z.H.; Chen, S.P.; Li, M.; Shahveranov, A.; Ye, D.W.; Tian, Y.K. Interleukin-6: An emerging regulator of pathological pain. J. Neuroinflamm. 2016, 13, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillarisetti, S. Targeting interleukin-1β for pain. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2011, 10, 571–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, J.; Li, Z.; Jia, X.; Peng, X.; Wang, J.; Gao, F. Interleukin-18 in chronic pain: Focus on pathogenic mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets. Pharmacol. Res. 2024, 201, 107089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.M.; Sherlock, J.P.; Hamilton, J.A. The role of interleukin (IL)-23 in regulating pain in arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2022, 24, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milligan, E.D.; Penzkover, K.R.; Soderquist, R.G.; Mahoney, M.J. Spinal interleukin-10 therapy to treat peripheral neuropathic pain. Neuromodulation. 2012, 15, 520–526, discussion 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Yu, Q.; Nie, H.; Yin, C.; Liu, B. IL-33/ST2 signaling in pain and itch: Cellular and molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potentials. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 165, 115143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.; Ren, Y.; Luo, X.; Mirando, A.J.; Long, J.T.; Leinroth, A.; Ji, R.R.; Hilton, M.J. Interleukin-6 signaling mediates cartilage degradation and pain in posttraumatic osteoarthritis in a sex-specific manner. Sci. Signal. 2022, 15, eabn7082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Luo, X.; Qadri, M.Y.; Berta, T.; Ji, R.R. Sex-Dependent Glial Signaling in Pathological Pain: Distinct Roles of Spinal Microglia and Astrocytes. Neurosci. Bull. 2018, 34, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorge, R.E.; Mapplebeck, J.C.; Rosen, S.; Beggs, S.; Taves, S.; Alexander, J.K.; Martin, L.J.; Austin, J.S.; Sotocinal, S.G.; Chen, D.; et al. Different immune cells mediate mechanical pain hypersensitivity in male and female mice. Nat. Neurosci. 2015, 18, 1081–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorge, R.E.; Mapplebeck, J.C.; Rosen, S.; Beggs, S.; Taves, S.; Alexander, J.K.; Martin, L.J.; Austin, J.S.; Sotocinal, S.G.; Chen, D.; et al. Interleukin-1beta and inflammasome expression in spinal cord following chronic constriction injury in male and female rats. Brain Behav. Immun. 2024, 115, 157–168. [Google Scholar]
- Khariv, V.; Ni, L.; Ratnayake, A.; Sampath, S.; Lutz, B.M.; Tao, X.X.; Heary, R.F.; Elkabes, S. Impaired sensitivity to pain stimuli in plasma membrane calcium ATPase 2 (PMCA2) heterozygous mice: A possible modality-and sex-specific role for PMCA2 in nociception. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 224–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.N.; Zhong, L.Q.; Xu, C.X.; Wang, T.T.; Wu, H.; Wang, L.; Traub, R.J.; Chen, X.; Cao, D.Y. Up-regulation of IL-1β and sPLA2-III in the medial prefrontal cortex contributes to orofacial and somatic hyperalgesia induced by malocclusion via glial-neuron crosstalk. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2024, 982, 176933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AboTaleb, H.A.; Alturkistani, H.A.; Abd El-Aziz, G.S.; Hindi, E.A.; Halawani, M.M.; Al-Thepyani, M.A.; Alghamdi, B.S. The Antinociceptive Effects and Sex-Specific Neurotransmitter Modulation of Metformin in a Mouse Model of Fibromyalgia. Cells 2024, 13, 1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Deng, N.; Liu, K.; Zhou, N.; Sun, Y.; Zeng, W. CNTF-STAT3-IL-6 Axis Mediates Neuroinflammatory Cascade across Schwann Cell-Neuron-Microglia. Cell Rep. 2020, 31, 107657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, Y.A.; Liao, H.Y.; Hsiao, I.H.; Hsu, H.C.; Lin, Y.W. Electroacupuncture Reduced Fibromyalgia-Pain-like Behavior through Inactivating Transient Receptor Potential V1 and Interleukin-17 in Intermittent Cold Stress Mice Model. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakabayashi, H.; Kato, S.; Nagao, N.; Miyamura, G.; Naito, Y.; Sudo, A. Interleukin-6 Inhibitor Suppresses Hyperalgesia Without Improvement in Osteoporosis in a Mouse Pain Model of Osteoporosis. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2019, 104, 658–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ochoa Bernal, M.A.; Song, Y.; Joshi, N.; Burns, G.W.; Paul, E.N.; Vegter, E.; Hrbek, S.; Sempere, L.F.; Fazleabas, A.T. The Regulation of MicroRNA-21 by Interleukin-6 and Its Role in the Development of Fibrosis in Endometriotic Lesions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, D.; Kong, L.Y.; Cai, J.; Li, S.; Liu, X.D.; Han, J.S.; Xing, G.G. Interleukin-6-mediated functional upregulation of TRPV1 receptors in dorsal root ganglion neurons through the activation of JAK/PI3K signaling pathway: Roles in the development of bone cancer pain in a rat model. Pain 2015, 156, 1124–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serizawa, K.; Tomizawa-Shinohara, H.; Magi, M.; Yogo, K.; Matsumoto, Y. Anti-IL-6 receptor antibody improves pain symptoms in mice with experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2018, 319, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baggio, D.F.; da Luz, F.M.R.; Lopes, R.V.; Ferreira, L.E.N.; Araya, E.I.; Chichorro, J.G. Sex Dimorphism in Resolvin D5-induced Analgesia in Rat Models of Trigeminal Pain. J. Pain 2023, 24, 717–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, H.; Li, T.T.; Luo, H.; Gu, X.Y.; Lü, N.; Ji, R.R.; Zhang, Y.Q. Delayed activation of spinal microglia contributes to the maintenance of bone cancer pain in female Wistar rats via P2X7 receptor and IL-18. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 7950–7963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viatchenko-Karpinski, V.; Kong, L.; Weng, H.R. Activation of microglial GPR109A alleviates thermal hyperalgesia in female lupus mice by suppressing IL-18 and glutamatergic synaptic activity. Glia 2022, 70, 634–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.M.; Zhang, Z.; Achuthan, A.; Fleetwood, A.J.; Smith, J.E.; Hamilton, J.A.; Cook, A.D. IL-23 in arthritic and inflammatory pain development in mice. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2020, 22, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, R.; Dong, C.; Jiao, L.; Xu, L.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Lao, L. Transient Receptor Potential Channel and Interleukin-17A Involvement in LTTL Gel Inhibition of Bone Cancer Pain in a Rat Model. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2015, 14, 381–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Huang, F.; Wang, Z.J. CaMKIIα Mediates the Effect of IL-17 To Promote Ongoing Spontaneous and Evoked Pain in Multiple Sclerosis. J. Neurosci. 2018, 38, 232–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verri, W.A., Jr.; Guerrero, A.T.; Fukada, S.Y.; Valerio, D.A.; Cunha, T.M.; Xu, D.; Ferreira, S.H.; Liew, F.Y.; Cunha, F.Q. IL-33 mediates antigen-induced cutaneous and articular hypernociception in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 2723–2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarpelon, A.C.; Cunha, T.M.; Alves-Filho, J.C.; Pinto, L.G.; Ferreira, S.H.; McInnes, I.B.; Xu, D.; Liew, F.Y.; Cunha, F.Q.; Verri, W.A., Jr. IL-33/ST2 signalling contributes to carrageenin-induced innate inflammation and inflammatory pain: Role of cytokines, endothelin-1 and prostaglandin E2. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 169, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durante, M.; Squillace, S.; Lauro, F.; Giancotti, L.A.; Coppi, E.; Cherchi, F.; Di Cesare Mannelli, L.; Ghelardini, C.; Kolar, G.; Wahlman, C.; et al. Adenosine A3 agonists reverse neuropathic pain via T cell-mediated production of IL-10. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e139299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Doyle, T.M.; Luongo, L.; Largent-Milnes, T.M.; Giancotti, L.A.; Kolar, G.; Squillace, S.; Boccella, S.; Walker, J.K.; Pendleton, A.; et al. Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 activation in astrocytes contributes to neuropathic pain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 10557–10562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Peng, S.; Wei, J.; Zhao, M.; Ahmad, K.A.; Chen, J.; Wang, Y.X. Spinal microglial β-endorphin signaling mediates IL-10 and exenatide-induced inhibition of synaptic plasticity in neuropathic pain. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2021, 27, 1157–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankaranarayanan, I.; Tavares-Ferreira, D.; Mwirigi, J.M.; Mejia, G.L.; Burton, M.D.; Price, T.J. Inducible co-stimulatory molecule (ICOS) alleviates paclitaxel-induced neuropathic pain via an IL-10-mediated mechanism in female mice. J. Neuroinflamm. 2023, 20, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willemen, H.L.; Eijkelkamp, N.; Garza Carbajal, A.; Wang, H.; Mack, M.; Zijlstra, J.; Heijnen, C.J.; Kavelaars, A. Monocytes/Macrophages control resolution of transient inflammatory pain. J. Pain 2014, 15, 496–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiore, N.T.; Hayes, J.P.; Williams, S.I.; Moalem-Taylor, G. Interleukin-35 alleviates neuropathic pain and induces an anti-inflammatory shift in spinal microglia in nerve-injured male mice. Brain Behav. Immun. 2024, 122, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, S.S.; Keating, B.A.; Perera, C.J.; Lees, J.G.; Tonkin, R.S.; Makker, P.G.S.; Carrive, P.; Butovsky, O.; Moalem-Taylor, G. Regulatory T Cells and Their Derived Cytokine, Interleukin-35, Reduce Pain in Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. J. Neurosci. 2019, 39, 2326–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, H.C.; Lin, L.X.; Hu, X.F.; Zhu, H.; Li, H.P.; Zhang, R.Y.; Hu, L.; Liu, W.T.; Zhao, Y.L.; Shu, Y.; et al. AMPK activation attenuates inflammatory pain through inhibiting NF-κB activation and IL-1β expression. J. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 16, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morishita, M.; Miyagi, M.; Iwamoto, Y. Effects of sex hormones on production of interleukin-1 by human peripheral monocytes. J. Periodontol. 1999, 70, 757–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilat, D.; Rojewska, E.; Jurga, A.M.; Piotrowska, A.; Makuch, W.; Przewlocka, B.; Mika, J. IL-1 receptor antagonist improves morphine and buprenorphine efficacy in a rat neuropathic pain model. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 764, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souter, A.J.; Garry, M.G.; Tanelian, D.L. Spinal interleukin-1beta reduces inflammatory pain. Pain 2000, 86, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Fan, X.; Bu, H.; Ma, L.; Kong, C.; Huang, C.; Xu, Y. Downregulation of lncRNA FIRRE relieved the neuropathic pain of female mice by suppressing HMGB1 expression. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2021, 476, 841–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cesare Mannelli, L.; Micheli, L.; Cervetto, C.; Toti, A.; Lucarini, E.; Parisio, C.; Marcoli, M.; Ghelardini, C. Neuronal alarmin IL-1α evokes astrocyte-mediated protective signals: Effectiveness in chemotherapy-induced neuropathic pain. Neurobiol. Dis. 2022, 168, 105716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mika, J.; Korostynski, M.; Kaminska, D.; Wawrzczak-Bargiela, A.; Osikowicz, M.; Makuch, W.; Przewlocki, R.; Przewlocka, B. Interleukin-1 alpha has antiallodynic and antihyperalgesic activities in a rat neuropathic pain model. Pain 2008, 138, 587–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goebel, A. Complex regional pain syndrome in adults. Rheumatology 2011, 50, 1739–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queiroz, L.P. Worldwide epidemiology of fibromyalgia. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2013, 17, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garbers, C.; Rose-John, S. Dissecting Interleukin-6 Classic-and Trans-Signaling in Inflammation and Cancer. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1725, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- de Hooge, A.S.; van de Loo, F.A.; Bennink, M.B.; Arntz, O.J.; de Hooge, P.; van den Berg, W.B. Male IL-6 gene knock out mice developed more advanced osteoarthritis upon aging. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2005, 13, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, C.; Chen, M.; Huang, H.; Lin, J. Testosterone enhances lipopolysaccharide-induced interleukin-6 and macrophage chemotactic protein-1 expression by activating the extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2/nuclear factor-κB signalling pathways in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankord, R.; Turk, J.R.; Schadt, J.C.; Casati, J.; Ganjam, V.K.; Price, E.M.; Keisler, D.H.; Laughlin, M.H. Sex difference in link between interleukin-6 and stress. Endocrinology 2007, 148, 3758–3764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, A.D.; Wardlaw, S.L. Testosterone suppresses the response of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis to interleukin-6. Neuroimmunomodulation 2000, 8, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgellaie, A.; Thomas, S.J.; Kaelle, J.; Bartschi, J.; Larkin, T. Pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-1α, IL-6 and TNF-α in major depressive disorder: Sex-specific associations with psychological symptoms. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2023, 57, 1913–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, V.M.; Lawrence, D.A.; Coccaro, G.A.; Mondal, T.K.; Andrews, K.; Dreiem, A.; Seegal, R.F. Sex effects of interleukin-6 deficiency on neuroinflammation in aged C57Bl/6 mice. Brain Res. 2010, 1318, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, C.; Ines, L.S.; Nour, D.; Straub, R.H.; da Silva, J.A. Differential male and female adrenal cortical steroid hormone and cortisol responses to interleukin-6 in humans. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2002, 966, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serizawa, K.; Tomizawa-Shinohara, H.; Miyake, S.; Yogo, K.; Matsumoto, Y. Interleukin-6: Evolving role in the management of neuropathic pain in neuroimmunological disorders. Inflamm. Regen. 2021, 41, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atzeni, F.; Nucera, V.; Masala, I.F.; Sarzi-Puttini, P.; Bonitta, G. Il-6 Involvement in pain, fatigue and mood disorders in rheumatoid arthritis and the effects of Il-6 inhibitor sarilumab. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 149, 104402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srikanth, V.K.; Fryer, J.L.; Zhai, G.; Winzenberg, T.M.; Hosmer, D.; Jones, G. A meta-analysis of sex differences prevalence, incidence and severity of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2005, 13, 769–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mun, C.J.; Letzen, J.E.; Nance, S.; Smith, M.T.; Khanuja, H.S.; Sterling, R.S.; Bicket, M.C.; Haythornthwaite, J.A.; Jamison, R.N.; Edwards, R.R.; et al. Sex Differences in Interleukin-6 Responses Over Time Following Laboratory Pain Testing Among Patients With Knee Osteoarthritis. J. Pain 2020, 21, 731–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, T.; Chen, T.; Qiu, J.; Gao, W.; Qiu, X.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, H.; Deng, Z.; et al. Inhibition of nuclear receptor RORα attenuates cartilage damage in osteoarthritis by modulating IL-6/STAT3 pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makabe, K.; Okada, H.; Tachibana, N.; Ishikura, H.; Ito, N.; Tanaka, M.; Chijimatsu, R.; Terashima, A.; Yano, F.; Asaka, M.; et al. Baricitinib ameliorates inflammatory and neuropathic pain in collagen antibody-induced arthritis mice by modulating the IL-6/JAK/STAT3 pathway and CSF-1 expression in dorsal root ganglion neurons. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2024, 26, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mima, Z.; Wang, K.; Liang, M.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; Wei, X.; Luo, F.; Nie, P.; Chen, X.; Xu, Y.; et al. Blockade of JAK2 retards cartilage degeneration and IL-6-induced pain amplification in osteoarthritis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 113, 109340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossù, P.; Ciaramella, A.; Moro, M.L.; Bellincampi, L.; Bernardini, S.; Federici, G.; Trequattrini, A.; Macciardi, F.; Spoletini, I.; Di Iulio, F.; et al. Interleukin 18 gene polymorphisms predict risk and outcome of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2007, 78, 807–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zendedel, A.; Mönnink, F.; Hassanzadeh, G.; Zaminy, A.; Ansar, M.M.; Habib, P.; Slowik, A.; Kipp, M.; Beyer, C. Estrogen Attenuates Local Inflammasome Expression and Activation after Spinal Cord Injury. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 1364–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregg, C.; Zhang, J.; Butler, J.E.; Haig, D.; Dulac, C. Sex-specific parent-of-origin allelic expression in the mouse brain. Science 2010, 329, 682–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyoshi, K.; Obata, K.; Kondo, T.; Okamura, H.; Noguchi, K. Interleukin-18-mediated microglia/astrocyte interaction in the spinal cord enhances neuropathic pain processing after nerve injury. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 12775–12787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilat, D.; Piotrowska, A.; Rojewska, E.; Jurga, A.; Ślusarczyk, J.; Makuch, W.; Basta-Kaim, A.; Przewlocka, B.; Mika, J. Blockade of IL-18 signaling diminished neuropathic pain and enhanced the efficacy of morphine and buprenorphine. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2016, 71, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parham, C.; Chirica, M.; Timans, J.; Vaisberg, E.; Travis, M.; Cheung, J.; Pflanz, S.; Zhang, R.; Singh, K.P.; Vega, F.; et al. A receptor for the heterodimeric cytokine IL-23 is composed of IL-12Rbeta1 and a novel cytokine receptor subunit, IL-23R. J. Immunol. 2002, 168, 5699–5708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schinocca, C.; Rizzo, C.; Fasano, S.; Grasso, G.; La Barbera, L.; Ciccia, F.; Guggino, G. Role of the IL-23/IL-17 Pathway in Rheumatic Diseases: An Overview. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 637829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Janabi, A.; Alabas, O.A.; Yiu, Z.Z.N.; Foulkes, A.C.; Eyre, S.; Khan, A.R.; Reynolds, N.J.; Smith, C.H.; Griffiths, C.E.M.; Warren, R.B.; et al. Risk of Paradoxical Eczema in Patients Receiving Biologics for Psoriasis. JAMA Dermatol. 2024, 160, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lubberts, E. The IL-23-IL-17 axis in inflammatory arthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2015, 11, 415–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ljosaa, T.M.; Mork, C.; Stubhaug, A.; Moum, T.; Wahl, A.K. Skin pain and skin discomfort is associated with quality of life in patients with psoriasis. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2012, 26, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elewski, B.; Alexis, A.F.; Lebwohl, M.; Stein Gold, L.; Pariser, D.; Del Rosso, J.; Yosipovitch, G. Itch: An under-recognized problem in psoriasis. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2019, 33, 1465–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, A.; Honda, T.; Egawa, G.; Kanameishi, S.; Takimoto, R.; Miyake, T.; Hossain, M.R.; Komine, M.; Ohtsuki, M.; Gunzer, M.; et al. Estradiol suppresses psoriatic inflammation in mice by regulating neutrophil and macrophage functions. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2022, 150, 909–919.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deodhar, A.; Helliwell, P.S.; Boehncke, W.H.; Kollmeier, A.P.; Hsia, E.C.; Subramanian, R.A.; Xu, X.L.; Sheng, S.; Agarwal, P.; Zhou, B.; et al. Guselkumab in patients with active psoriatic arthritis who were biologic-naive or had previously received TNFα inhibitor treatment (DISCOVER-1): A double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet 2020, 395, 1115–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mease, P.J.; Rahman, P.; Gottlieb, A.B.; Kollmeier, A.P.; Hsia, E.C.; Xu, X.L.; Sheng, S.; Agarwal, P.; Zhou, B.; Zhuang, Y.; et al. Guselkumab in biologic-naive patients with active psoriatic arthritis (DISCOVER-2): A double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet 2020, 395, 1126–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McInnes, I.B.; Rahman, P.; Gottlieb, A.B.; Hsia, E.C.; Kollmeier, A.P.; Chakravarty, S.D.; Xu, X.L.; Subramanian, R.A.; Agarwal, P.; Sheng, S.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Guselkumab, an Interleukin-23p19-Specific Monoclonal Antibody, Through One Year in Biologic-Naive Patients With Psoriatic Arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021, 73, 604–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Zhao, S.; Shi, H.; Li, X.; Ran, L.; Cao, J.; He, Y. Effects on peripheral and central nervous system of key inflammatory intercellular signalling peptides and proteins in psoriasis. Exp. Dermatol. 2024, 33, e15104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, J.; Owyang, A.; Oldham, E.; Song, Y.; Murphy, E.; McClanahan, T.K.; Zurawski, G.; Moshrefi, M.; Qin, J.; Li, X.; et al. IL-33, an interleukin-1-like cytokine that signals via the IL-1 receptor-related protein ST2 and induces T helper type 2-associated cytokines. Immunity 2005, 23, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boraschi, D.; Tagliabue, A. The interleukin-1 receptor family. Semin. Immunol. 2013, 25, 394–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macari, S.; Madeira, M.F.M.; Lima, I.L.A.; Pereira, T.S.F.; Dias, G.J.; Cirelli, J.A.; de Molon, R.S.; Fukada, S.Y.; Szawka, R.E.; Garlet, G.P.; et al. ST2 regulates bone loss in a site-dependent and estrogen-dependent manner. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 8511–8521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, T.; Yasuda, K.; Matsushita, K.; Ishii, K.J.; Hirota, S.; Yoshimoto, T.; Shibahara, H. Interleukin-1/-33 Signaling Pathways as Therapeutic Targets for Endometriosis. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- York, A.G.; Skadow, M.H.; Oh, J.; Qu, R.; Zhou, Q.D.; Hsieh, W.Y.; Mowel, W.K.; Brewer, J.R.; Kaffe, E.; Williams, K.J.; et al. IL-10 constrains sphingolipid metabolism to limit inflammation. Nature 2024, 627, 628–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, W.; Rutz, S.; Crellin, N.K.; Valdez, P.A.; Hymowitz, S.G. Regulation and functions of the IL-10 family of cytokines in inflammation and disease. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 29, 71–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraiva, M.; O’Garra, A. The regulation of IL-10 production by immune cells. Nature reviews. Immunology 2010, 10, 170–181. [Google Scholar]
- Pinzan, C.F.; Ruas, L.P.; Casabona-Fortunato, A.S.; Carvalho, F.C.; Roque-Barreira, M.C. Immunological basis for the gender differences in murine Paracoccidioides brasiliensis infection. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahlke, V.; Angele, M.K.; Ayala, A.; Schwacha, M.G.; Cioffi, W.G.; Bland, K.I.; Chaudry, I.H. Immune dysfunction following trauma-haemorrhage: Influence of gender and age. Cytokine 2000, 12, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chistyakov, D.V.; Azbukina, N.V.; Astakhova, A.A.; Goriainov, S.V.; Chistyakov, V.V.; Sergeeva, M.G. Sex-Mediated Differences in LPS Induced Alterations of TNFα, IL-10 Expression, and Prostaglandin Synthesis in Primary Astrocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesquita, A.R.; Correia-Neves, M.; Roque, S.; Castro, A.G.; Vieira, P.; Pedrosa, J.; Palha, J.A.; Sousa, N. IL-10 modulates depressive-like behavior. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2008, 43, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloane, E.; Ledeboer, A.; Seibert, W.; Coats, B.; van Strien, M.; Maier, S.F.; Johnson, K.W.; Chavez, R.; Watkins, L.R.; Leinwand, L.; et al. Anti-inflammatory cytokine gene therapy decreases sensory and motor dysfunction in experimental Multiple Sclerosis: MOG-EAE behavioral and anatomical symptom treatment with cytokine gene therapy. Brain Behav. Immun. 2009, 23, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orhan, C.; Tuzcu, M.; Durmus, A.S.; Sahin, N.; Ozercan, I.H.; Deeh, P.B.D.; Morde, A.; Bhanuse, P.; Acharya, M.; Padigaru, M.; et al. Protective effect of a novel polyherbal formulation on experimentally induced osteoarthritis in a rat model. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 151, 113052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groth, K.A.; Skakkebæk, A.; Høst, C.; Gravholt, C.H.; Bojesen, A. Clinical review: Klinefelter syndrome--a clinical update. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, H.; Xia, L. IL-35 alleviates inflammation progression in a rat model of diabetic neuropathic pain via inhibition of JNK signaling. J. Inflamm. 2019, 16, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, L.C.; Mezzaroma, E.; Van Tassell, B.W.; Marchetti, C.; Carbone, S.; Abbate, A.; Toldo, S. Interleukin-18 as a therapeutic target in acute myocardial infarction and heart failure. Mol. Med. 2014, 20, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbate, A.; Toldo, S.; Marchetti, C.; Kron, J.; Van Tassell, B.W.; Dinarello, C.A. Interleukin-1 and the Inflammasome as Therapeutic Targets in Cardiovascular Disease. Circ. Res. 2020, 126, 1260–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doberer, K.; Duerr, M.; Halloran, P.F.; Eskandary, F.; Budde, K.; Regele, H.; Reeve, J.; Borski, A.; Kozakowski, N.; Reindl-Schwaighofer, R.; et al. A Randomized Clinical Trial of Anti-IL-6 Antibody Clazakizumab in Late Antibody-Mediated Kidney Transplant Rejection. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2021, 32, 708–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narazaki, M.; Tanaka, T.; Kishimoto, T. The role and therapeutic targeting of IL-6 in rheumatoid arthritis. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2017, 13, 535–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golebski, K.; Layhadi, J.A.; Sahiner, U.; Steveling-Klein, E.H.; Lenormand, M.M.; Li, R.C.Y.; Bal, S.M.; Heesters, B.A.; Vilà-Nadal, G.; Hunewald, O.; et al. Induction of IL-10-producing type 2 innate lymphoid cells by allergen immunotherapy is associated with clinical response. Immunity 2021, 54, 291–307.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelsen, S.G.; Agache, I.O.; Soong, W.; Israel, E.; Chupp, G.L.; Cheung, D.S.; Theess, W.; Yang, X.; Staton, T.L.; Choy, D.F.; et al. Astegolimab (anti-ST2) efficacy and safety in adults with severe asthma: A randomized clinical trial. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 148, 790–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avci, A.B.; Feist, E.; Burmester, G.R. Targeting IL-6 or IL-6 Receptor in Rheumatoid Arthritis: What Have We Learned? BioDrugs 2024, 38, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGonagle, D.; Watad, A.; Sharif, K.; Bridgewood, C. Why Inhibition of IL-23 Lacked Efficacy in Ankylosing Spondylitis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 614255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, T.; Puig, L.; Vender, R.; Lynde, C.; Piaserico, S.; Carrascosa, J.M.; Gisondi, P.; Daudén, E.; Conrad, C.; Mendes-Bastos, P.; et al. Drug Survival of IL-12/23, IL-17 and IL-23 Inhibitors for Psoriasis Treatment: A Retrospective Multi-Country, Multicentric Cohort Study. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2021, 22, 567–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorge, R.E.; LaCroix-Fralish, M.L.; Tuttle, A.H.; Sotocinal, S.G.; Austin, J.S.; Ritchie, J.; Chanda, M.L.; Graham, A.C.; Topham, L.; Beggs, S.; et al. Spinal cord Toll-like receptor 4 mediates inflammatory and neuropathic hypersensitivity in male but not female mice. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 15450–15454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McInnis, C.M.; Thoma, M.V.; Gianferante, D.; Hanlin, L.; Chen, X.; Breines, J.G.; Hong, S.; Rohleder, N. Measures of adiposity predict interleukin-6 responses to repeated psychosocial stress. Brain Behav. Immun. 2014, 42, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Känel, R.; Kudielka, B.M.; Preckel, D.; Hanebuth, D.; Fischer, J.E. Delayed response and lack of habituation in plasma interleukin-6 to acute mental stress in men. Brain Behav. Immun. 2006, 20, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanfranco, F.; Kamischke, A.; Zitzmann, M.; Nieschlag, E. Klinefelter’s syndrome. Lancet 2004, 364, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakkas, L.I.; Chikanza, I.C. Sex bias in immune response: It is time to include the sex variable in studies of autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Rheumatol. Int. 2024, 44, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fish, E.N. The X-files in immunity: Sex-based differences predispose immune responses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 737–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalayci Yigin, A.; Alay, M.T.; Uğurlu, S.; Seven, M. The First Case Report of 47,XXY/46,XX/46,XY Mosaic Klinefelter Syndrome Patient With Mixed Connective Tissue Disorder. Am. J. Men’s Health 2023, 17, 15579883231165173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panimolle, F.; Tiberti, C.; Spaziani, M.; Riitano, G.; Lucania, G.; Anzuini, A.; Lenzi, A.; Gianfrilli, D.; Sorice, M.; Radicioni, A.F. Non-organ-specific autoimmunity in adult 47,XXY Klinefelter patients and higher-grade X-chromosome aneuploidies. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2021, 205, 316–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yığman, M.; Yığman, F.; Tangal, S.; Haliloğlu, A.H.; Çağlar, G.S. Pre-test anxiety levels and postoperative pain in non-obstructive azoospermic patients: Is klinefelter syndrome a predisposing factor? Urol. J. 2022, 89, 280–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
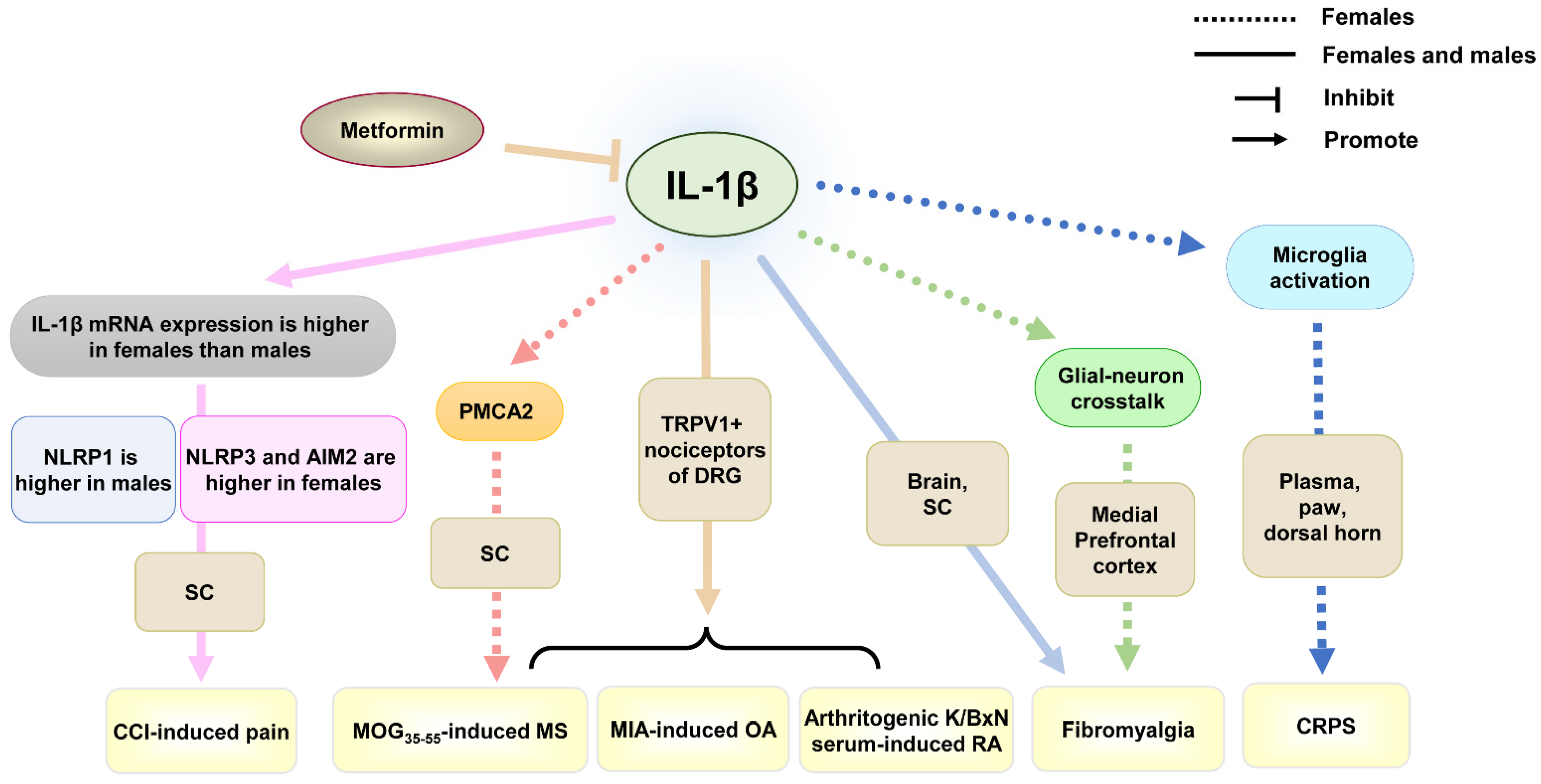
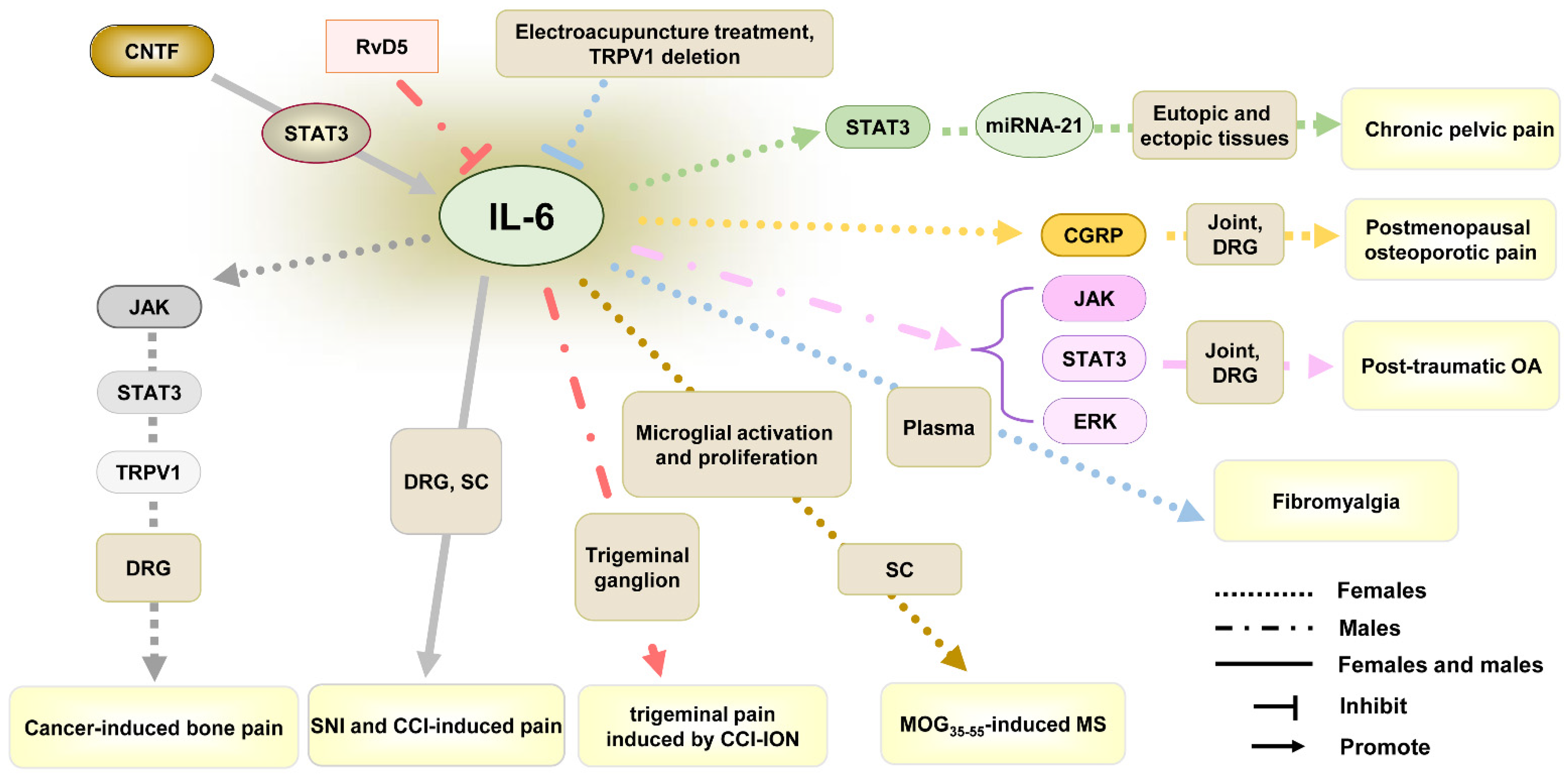

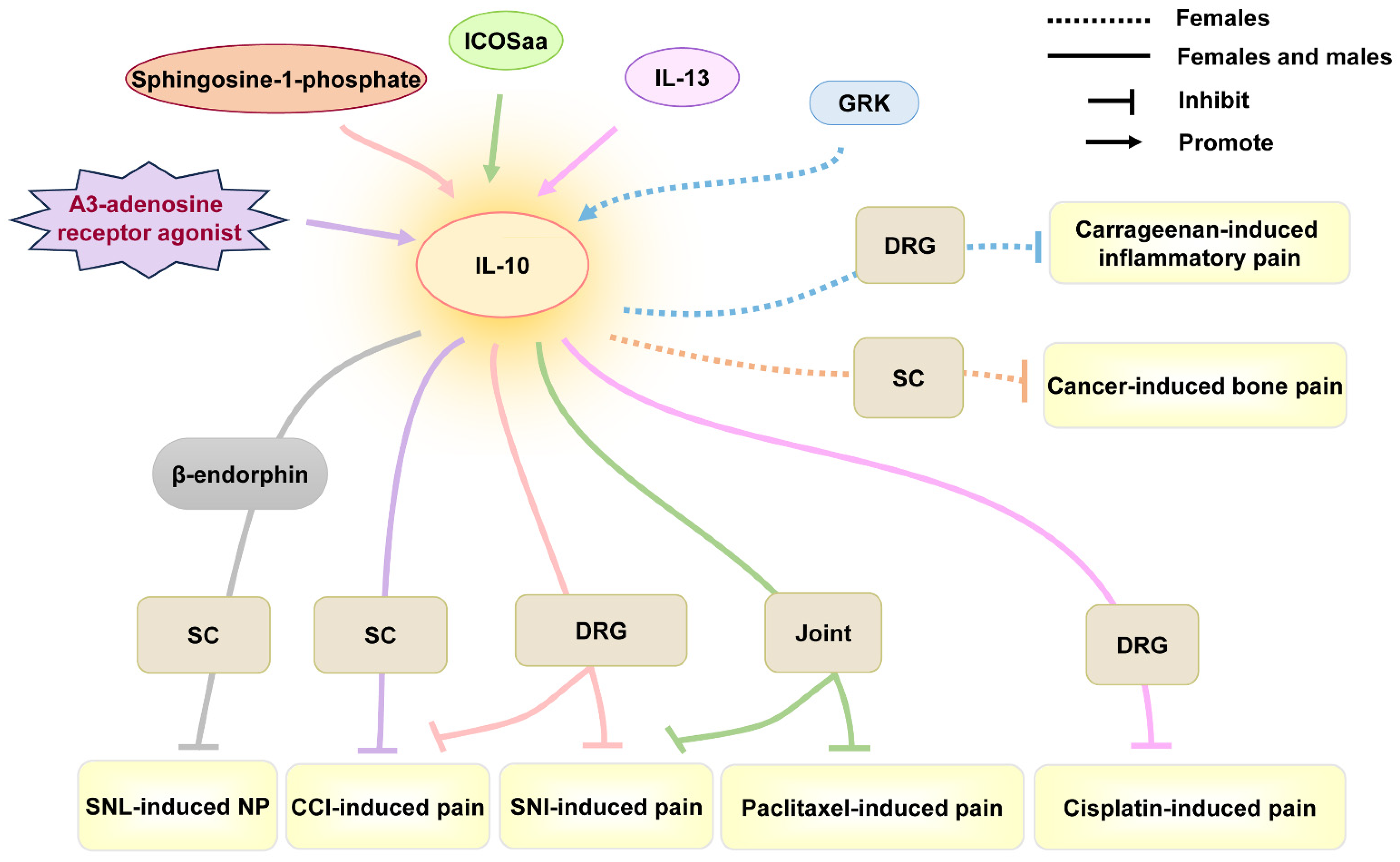
| Sex | Interleukin | Mechanism | Effect on Pain | Type of Pain Model | Type of Pain-Like Behavior | Location | Expression Patterns | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female and male | IL-1β | Knockout of IL-1 receptor in TRPV1+ nociceptors of DRG prevents the development of inflammatory pain. | Promote | MOG35–55-induced MS, arthritogenic K/BxN serum-induced RA, and MIA-induced OA | Mechanical allodynia | TRPV1+ nociceptors of DRG | Up-regulation | [61] |
| Female and male | IL-1β | Total mRNA expression of IL-1β is higher in females than in males after CCI. NLRP3 and AIM2 are more highly expressed in females, but NLRP1 expression is higher in males. | Promote | CCI-induced pain | Mechanical allodynia | SC | Up-regulation | [79] |
| Female, but not male | IL-1β | IL-1β increases mechanical and thermal pain responsiveness by decreasing PMCA2 levels. | Promote | MOG35–55-induced MS | Mechanical and thermal hyperalgesia | SC | Up-regulation | [65,80] |
| Female | IL-1β | IL-1 receptor antagonists prevent the development of CRPS and reverse the established CRPS by inhibiting microglia activation of dorsal horn. | Promote | CRPS | Mechanical allodynia | plasma, paw, dorsal horn | Up-regulation | [64] |
| Female | IL-1β | IL-1β-mediated glial-neuron crosstalk contributes to the development of fibromyalgia. | Promote | Fibromyalgia | Thermal hyperalgesia, mechanical allodynia | medial prefrontal cortex | Up-regulation | [81] |
| Female and male | IL-1β | Metformin ameliorates fibromyalgia by reducing the increased IL-1β levels in males, but partially decreasing IL-1β levels in the brain of females. | Promote | Fibromyalgia | Thermal hyperalgesia, mechanical allodynia | Brain, SC | Up-regulation | [82] |
| Female and male | IL-6 | CNTF-STAT3-IL-6 axis. | Promote | SNI or CCI-induced pain | Mechanical allodynia, thermal hyperalgesia | DRG, SC | Up-regulation | [83] |
| Male, but not female | IL-6 | IL-6/JAK signaling is a critical mediator of IL-6-induced cartilage catabolism and pain signaling in nociceptive neurons; IL-6/STAT3 signaling is a potent driver of cartilage catabolism; IL-6/ERK signaling is essential for IL-6-induced neurite outgrowth and pain signaling in DRG neurons. | Promote | Post-traumatic OA induced by destabilization of the medial meniscus | Mechanical allodynia | Joint, DRG | Up-regulation | [76] |
| Female | IL-6 | Electroacupuncture treatment and TRPV1 deletion reduce chronic pain by reversing the increase in IL-6. | Promote | fibromyalgia induced by ICS | Mechanical allodynia, thermal hyperalgesia | plasma | Up-regulation | [84] |
| Female | IL-6 | IL-6 induces postmenopausal osteoporotic pain by regulating calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) expression. | Promote | Postmenopausal osteoporotic pain | Mechanical allodynia | Joint, DRG | Up-regulation | [85] |
| Female | IL-6 | IL-6 regulates miRNA-21 expression by STAT3 pathway and results in chronic pelvic pain induced by endometriosis | Promote | Chronic pelvic pain | / | Eutopic and ectopic tissues | Up-regulation | [86] |
| Female | IL-6 | IL-6 upregulates TRPV1 expression and function through JAK/PI3K signaling pathway. | Promote | Cancer-induced bone pain | Mechanical allodynia, thermal hyperalgesia | DRG | Up-regulation | [87] |
| Female | IL-6 | Anti-IL-6 receptor antibody decreases mechanical allodynia by inhibiting microglial activation and proliferation. | Promote | MOG35–55-induced MS | Mechanical allodynia | SC | Up-regulation | [88] |
| Male, but not female | IL-6 | RvD5 can inhibit trigeminal pain by reducing level of IL-6. | Promote | Trigeminal pain induced by CCI-ION | Mechanical allodynia, thermal hyperalgesia | Trigeminal ganglion | Up-regulation | [89] |
| Female | IL-18 | Microglia can maintain advanced-phase cancer pain by producing the proinflammatory cytokine IL-18 to enhance synaptic transmission. | Promote | Cancer-induced bone pain | Mechanical allodynia, thermal hyperalgesia | Microglia in SC | Up-regulation | [90] |
| Female | IL-18 | Gi protein-coupled receptor (GPR109A) attenuates thermal hyperalgesia via suppressing p38 MAPK activity and production of IL-18. | Promote | SLE | Thermal hyperalgesia | Microglia in SC | Up-regulation | [91] |
| Female and male | IL-23 | IL-23 promotes arthritic inflammatory pain induced by GM-CSF, TNF, or CCL17 via COX. | Promote | Zymosan-driven arthritic pain | Pain-like behavior (incapacitance meter) | Joint | Up-regulation | [73,92] |
| Female, but not male | IL-23/IL-17A | Under expression of ERα, IL-23 requires IL-17A release from macrophages to evoke mechanical pain through TRPV1 nociceptor. | Promote | IL-23-induced pain, chemotherapy (paclitaxel)-induced pain, CCI-induced pain, streptozotoxin-induced diabetic neuropathy, formalin-induced pain | Mechanical allodynia, but not thermal hyperalgesia, or cold allodynia | IL-23 in macrophages of DRG, IL-17A in C-fiber nociceptors of DRG | Up-regulation | [30] |
| Female, but not male | IL-23 | Estrogen and IL-23 co-application increases IL-17A release in THP-1 human macrophages and promotes C-fiber-mediated spontaneous pain. | Promote | Blue light-induced spontaneous Pain | Mechanical allodynia | C-fiber nociceptors of DRG | Up-regulation | [31] |
| Female | IL-17A | Chinese medicated gel Long-Teng-Tong-Luo inhibits bone cancer pain by decreasing transient receptor potential channel expression in DRG and spinal astrocyte IL-17A. | Promote | Cancer-induced bone pain | Mechanical allodynia, thermal hyperalgesia | SC | Up-regulation | [93] |
| Female | IL-17 | Electroacupuncture treatment and TRPV1 deletion reduce heat and mechanical hyperalgesia by decreasing IL-17 and IL-17-related signaling pathways (PI3K/Akt, p38, JNK, NF-κB) levels. | Promote | Fibromyalgia induced by ICS | Mechanical allodynia, thermal hyperalgesia | Somatosensory cortex, cerebellum lobe V-VII | Up-regulation | [84] |
| Female | IL-17 | IL-17 promotes the occurrence of MS-associated chronic pain by improving CaMKIIα activation. | Promote | MOG35–55-induced MS | Mechanical allodynia, thermal hyperalgesia | SC | Up-regulation | [94] |
| Female and male | IL-33 | IL-33-TNFα-IL-1β-IFNγ-endothelin 1-prostaglandin (PG) E2 signaling cascade participates in antigen-induced cutaneous and articular hypernociception. | Promote | Antigen-induced pain | Mechanical allodynia | Skin of paw | Up-regulation | [95,96] |
| Female and male | IL-10 | A3-adenosine receptor agonist reverses mechanical allodynia by promoting the IL-10 release of CD4+ T cells in DRG. | Reverse | CCI-induced pain | Mechanical allodynia | CD4+ T cells in DRG | / | [97] |
| Female and male | IL-10 | Sphingosine-1-phosphate antagonists attenuate and reverse neuropathic pain by promoting IL-10 production in astrocytes of spinal cord. | Alleviate, reverse | SNI- and CCI-induced pain | Mechanical allodynia, thermal anti-nociception | Astrocytes in SC | / | [98] |
| Female and male | IL-10 | IL-10 inhibits spinal abnormal synaptic plasticity through β-endorphin expression in microglia. | Alleviate | SNL-induced pain | Mechanical allodynia, thermal hyperalgesia | SC | / | [99] |
| Female and male | IL-10 | Inducible co-stimulatory molecule agonist antibody (ICOSaa) shows a more rapid resolution of mechanical hypersensitivity in females by recruiting T cells and driving IL-10 production. | Alleviate | Chemotherapy (paclitaxel)-induced pain, SNI-induced pain | Mechanical allodynia | T cell in DRG | / | [100] |
| Female and male | IL-10 | IL-13 produced by CD8+ T cells promotes IL-10 release in macrophages of DRG, ameliorating cisplatin-induced mechanical allodynia. | Alleviate | Chemotherapy (cisplatin)-induced pain | Mechanical allodynia | Macrophages of DRG | Up-regulation | [62] |
| Female | IL-10 | Intrathecal IL-10 can effectively reduce cancer-induced bone pain behavior. | Alleviate | Cancer-induced bone pain | Mechanical allodynia | SC | / | [63] |
| Female | IL-10 | IL-10 from GRK+ macrophages promotes resolution of carrageenan-induced mechanical allodynia and thermal hyperalgesia. | Alleviate | Carrageenan-induced pain | Mechanical allodynia, thermal hyperalgesia | Peripheral monocytes/macrophages in DRG | Up-regulation | [101] |
| Male | IL-35 | Intrathecal recombinant IL-35 treatment alleviates mechanical pain by inhibiting microglia activation. | Alleviate | CCI-induced pain | Mechanical allodynia | SC | / | [102] |
| Female | IL-35 | IL-35 reduces mechanical allodynia and spontaneous pain by increasing myelination, upregulating IL-10 expression, and reducing monocyte infiltration. | Alleviate | MOG35–55-induced MS | Mechanical allodynia, spontaneous pain | SC | Down-regulation | [103] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, J.; Li, Z.; Ju, J.; Chu, T.; Gao, F. Sex Differences in the Regulation of Interleukins in Chronic Pain: A Widely Recognized but Difficult-to-Tackle Factor. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3835. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083835
Liu J, Li Z, Ju J, Chu T, Gao F. Sex Differences in the Regulation of Interleukins in Chronic Pain: A Widely Recognized but Difficult-to-Tackle Factor. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(8):3835. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083835
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Jie, Zheng Li, Jie Ju, Tiantian Chu, and Feng Gao. 2025. "Sex Differences in the Regulation of Interleukins in Chronic Pain: A Widely Recognized but Difficult-to-Tackle Factor" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 8: 3835. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083835
APA StyleLiu, J., Li, Z., Ju, J., Chu, T., & Gao, F. (2025). Sex Differences in the Regulation of Interleukins in Chronic Pain: A Widely Recognized but Difficult-to-Tackle Factor. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(8), 3835. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083835





