Dried Spot Paradigm: Problems and Prospects in Proteomics
Abstract
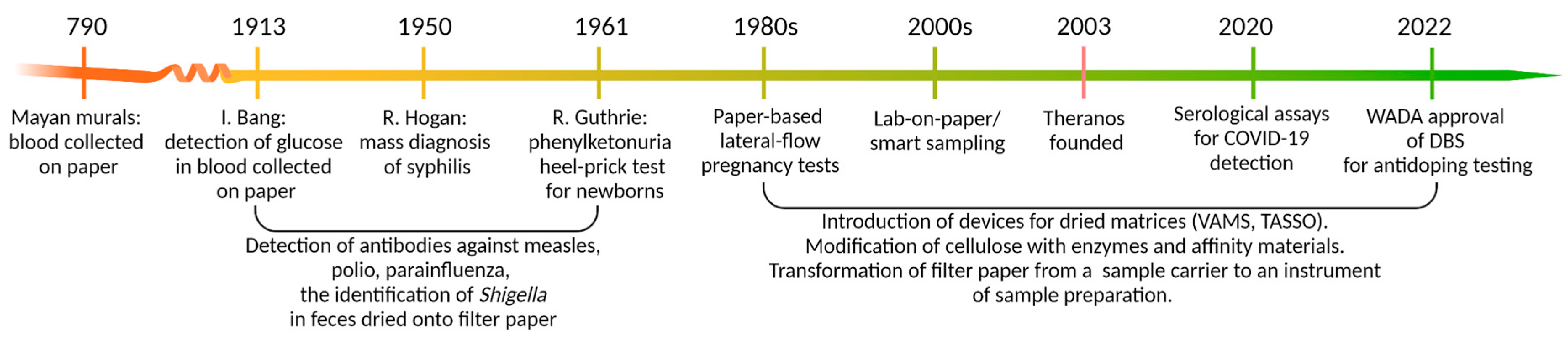
:1. Dried Matrices: Long Story Short
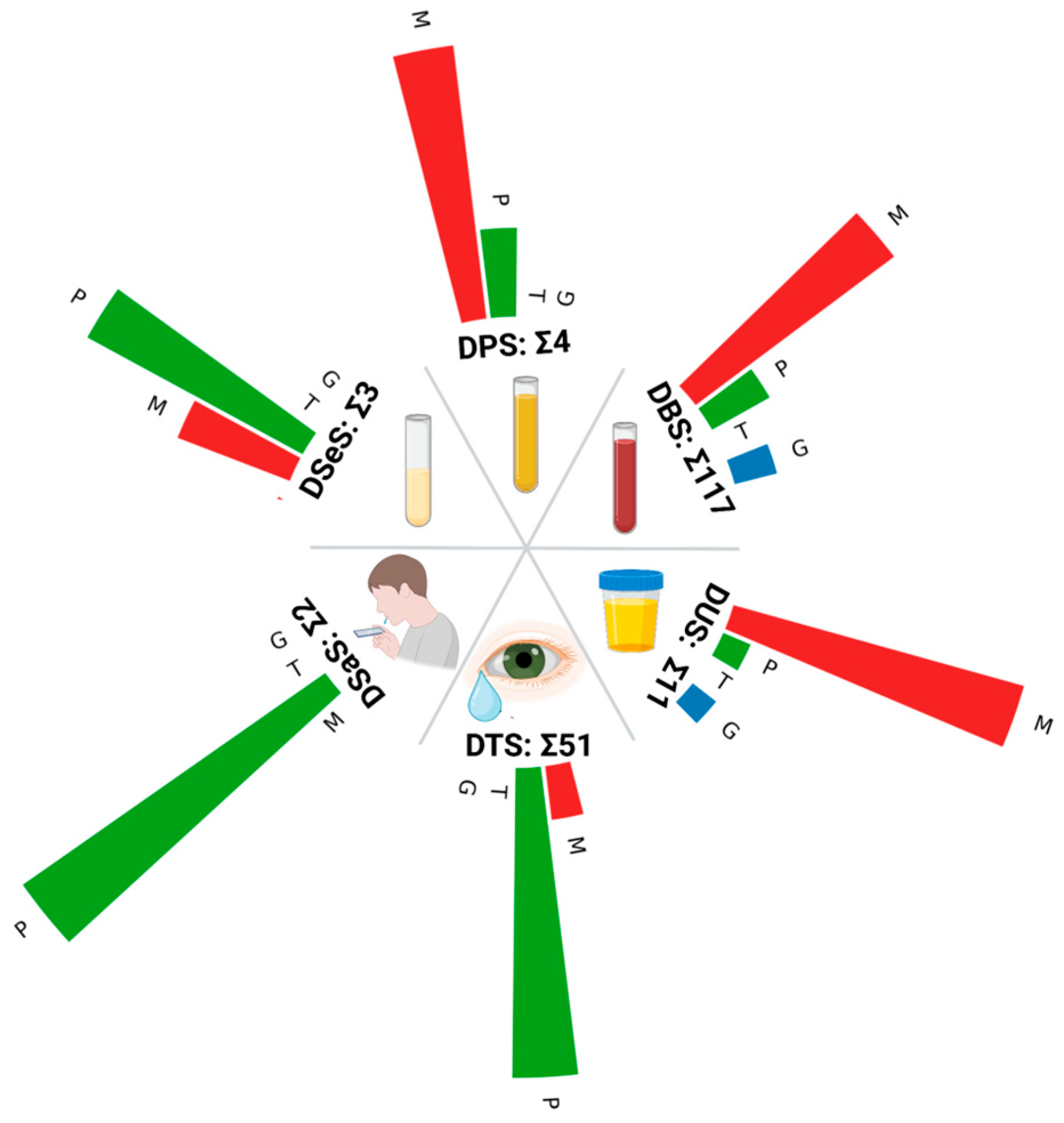
2. Types of Biological Liquids to Apply
2.1. Blood and Its Components
2.2. Saliva
2.3. Tears
2.4. Urine
3. Considerations on Sample Preparation and Analysis Techniques
4. Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DBS | Dried blood spot |
| DSeS | Dried serum spot |
| DSaS | Dried saliva spot |
| DDA | Data-dependent proteomic analysis |
| DIA | Data-independent proteomic analysis |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| PKU | Phenylketonuria |
| SPMA | Syringe-push nitrocellulose membrane absorption |
| VAMS | Volumetric absorptive microsamplers |
References
- Hannon, W.H.; Therrell, B.L. Overview of the History and Applications of Dried Blood Samples. In Dried Blood Spots; Li, W., Lee, M.S., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 1–15. ISBN 978-1-118-05469-7. [Google Scholar]
- Levy, H.L. Robert Guthrie and the Trials and Tribulations of Newborn Screening. Int. J. Neonatal Screen. 2021, 7, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Farrell, B. Evolution in Lateral Flow–Based Immunoassay Systems. In Lateral Flow Immunoassay; Wong, R., Tse, H., Eds.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 1–33. ISBN 978-1-58829-908-6. [Google Scholar]
- Johannsen, C.; Mrsa, A.; Halvorsen, T.G.; Reubsaet, L. Smart Sampling as the “Spot-on” Method for LC-MS Protein Analysis from Dried Blood Spots. J. Sep. Sci. 2023, 46, 2300394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiyaga, C.; Makoha, C.; Nkugwa, I.; Okiira, C.; Okwir, R.; Gebreab, S.Z.; Suarez, P.R.-V.; LaBrot, B.; Durán, A.C. The Plasma Separation Card as a Novel Solution for Enhancing Central Laboratory Capability for HIV-1 Viral Load Monitoring in Limited-Access Settings. PLoS Glob. Public Health 2023, 3, e0002099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baillargeon, K.R.; Morbioli, G.G.; Brooks, J.C.; Miljanic, P.R.; Mace, C.R. Direct Processing and Storage of Cell-Free Plasma Using Dried Plasma Spot Cards. ACS Meas. Sci. Au 2022, 2, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halvorsen, T.G.; Reubsaet, L. Is This the End of Dried Blood Spots as We Know It? Anal. Sci. Adv. 2023, 4, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangavelu, M.U.; Wouters, B.; Kindt, A.; Reiss, I.K.M.; Hankemeier, T. Blood Microsampling Technologies: Innovations and Applications in 2022. Anal. Sci. Adv. 2023, 4, 154–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Use of Volumetric Absorptive Microsampling (VAMS) for the Quantification of Novel Blood Markers of EAAS Doping. Available online: https://www.wada-ama.org/en/resources/scientific-research/use-volumetric-absorptive-microsampling-vams-quantification-novel (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- COVID-19: How DBS Is Supporting the Fight Against Coronavirus. Available online: https://www.gov.uk/guidance/covid-19-how-dbs-is-supporting-the-fight-against-coronavirus (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- Mazer, B. Theranos Exploited Black Box Medicine. BMJ 2022, 379, o3003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easterbrook, P.J.; WHO Guidelines Development Group. Who to Test and How to Test for Chronic Hepatitis C Infection—2016 WHO Testing Guidance for Low- and Middle-Income Countries. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, S46–S66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Huang, A.; Wen, S.; Yang, R.; Liu, X. Temporal Assessment of Protein Stability in Dried Blood Spots. J. Proteome Res. 2024, 23, 3585–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, J.; Mahler, H.-C.; Friess, W. Drying for Stabilization of Protein Formulations. In Drying Technologies for Biotechnology and Pharmaceutical Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 91–119. ISBN 978-3-527-80210-4. [Google Scholar]
- Björkesten, J.; Enroth, S.; Shen, Q.; Wik, L.; Hougaard, D.M.; Cohen, A.S.; Sörensen, L.; Giedraitis, V.; Ingelsson, M.; Larsson, A.; et al. Stability of Proteins in Dried Blood Spot Biobanks. Mol. Cell. Proteom. MCP 2017, 16, 1286–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, J.Y. Enzyme Immobilization on Cellulose Matrixes. J. Bioact. Compat. Polym. 2016, 31, 553–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, D.; Kawashima, Y.; Shibata, H.; Yasumi, T.; Isa, M.; Izawa, K.; Nishikomori, R.; Heike, T.; Ohara, O. Simple and Sensitive Analysis for Dried Blood Spot Proteins by Sodium Carbonate Precipitation for Clinical Proteomics. J. Proteome Res. 2020, 19, 2821–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ignjatovic, V.; Geyer, P.E.; Palaniappan, K.K.; Chaaban, J.E.; Omenn, G.S.; Baker, M.S.; Deutsch, E.W.; Schwenk, J.M. Mass Spectrometry-Based Plasma Proteomics: Considerations from Sample Collection to Achieving Translational Data. J. Proteome Res. 2019, 18, 4085–4097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, J.D.; Rosman, L.M.; Ratcliff, J.D.; Strickland, P.T.; Graham, D.R.; Silbergeld, E.K. State of the Science in Dried Blood Spots. Clin. Chem. 2018, 64, 656–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skogvold, H.B.; Rootwelt, H.; Reubsaet, L.; Elgstøen, K.B.P.; Wilson, S.R. Dried Blood Spot Analysis with Liquid Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry: Trends in Clinical Chemistry. J. Sep. Sci. 2023, 46, e2300210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.; Whiteaker, J.R.; Zhao, L.; Yoo, H.-W.; Paulovich, A.G.; Hahn, S.H. Quantification of ATP7B Protein in Dried Blood Spots by Peptide Immuno-SRM as a Potential Screen for Wilson’s Disease. J. Proteome Res. 2017, 16, 862–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredolini, C.; Dodig-Crnković, T.; Bendes, A.; Dahl, L.; Dale, M.; Albrecht, V.; Mattsson, C.; Thomas, C.E.; Torinsson Naluai, Å.; Gisslen, M.; et al. Proteome Profiling of Home-Sampled Dried Blood Spots Reveals Proteins of SARS-CoV-2 Infections. Commun. Med. 2024, 4, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spooner, N.; Denniff, P.; Michielsen, L.; De Vries, R.; Ji, Q.C.; Arnold, M.E.; Woods, K.; Woolf, E.J.; Xu, Y.; Boutet, V.; et al. A Device for Dried Blood Microsampling in Quantitative Bioanalysis: Overcoming The Issues Associated Blood Hematocrit. Bioanalysis 2015, 7, 653–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daousani, C.; Karalis, V.; Malenović, A.; Dotsikas, Y. Hematocrit Effect on Dried Blood Spots in Adults: A Computational Study and Theoretical Considerations. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 2019, 79, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daily, A.; Ravishankar, P.; Harms, S.; Klimberg, V.S. Using Tears as a Non-Invasive Source for Early Detection of Breast Cancer. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0267676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, A.G.; Percy, A.J.; Yang, J.; Borchers, C.H. Multiple Reaction Monitoring Enables Precise Quantification of 97 Proteins in Dried Blood Spots. Mol. Cell. Proteom. MCP 2015, 14, 3094–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malsagova, K.A.; Stepanov, A.A.; Kopylov, A.T.; Enikeev, D.V.; Potoldykova, N.V.; Izotov, A.A.; Butkova, T.V.; Kaysheva, A.L. Stability of Plasma Protein Composition in Dried Blood Spot during Storage. Processes 2020, 8, 1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyers, E.; Coen, A.; Padalko, E.; Cools, P. Short- and Long-Term Stability of SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies on Dried Blood Spots under Different Storage Conditions. Microbiol. Spectr. 2024, 12, e01113-24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amini, F.; Auma, E.; Hsia, Y.; Bilton, S.; Hall, T.; Ramkhelawon, L.; Heath, P.T.; Le Doare, K. Reliability of Dried Blood Spot (DBS) Cards in Antibody Measurement: A Systematic Review. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0248218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, R.; Hill, C.; Rudge, J.; Herbert, B.; Karsten, E. Stability of Inflammation Markers in Human Blood Collected Using Volumetric Absorptive Microsampling (VAMS) under Typical Laboratory Storage Temperatures. Cytokine 2023, 171, 156355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Protti, M.; Cirrincione, M.; Mandrioli, R.; Rudge, J.; Regazzoni, L.; Valsecchi, V.; Volpi, C.; Mercolini, L. Volumetric Absorptive Microsampling (VAMS) for Targeted LC-MS/MS Determination of Tryptophan-Related Biomarkers. Molecules 2022, 27, 5652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SYSTEM AND PROCEDURE FOR STABILIZING, STORING AND RECOVERING BLOOD SAMPLES—Patent 3639005. Available online: https://data.epo.org/publication-server/rest/v1.0/publication-dates/20200422/patents/EP3639005NWA1/document.html (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- Eshghi, A.; Pistawka, A.J.; Liu, J.; Chen, M.; Sinclair, N.J.T.; Hardie, D.B.; Elliott, M.; Chen, L.; Newman, R.; Mohammed, Y.; et al. Concentration Determination of >200 Proteins in Dried Blood Spots for Biomarker Discovery and Validation. Mol. Cell. Proteom. MCP 2020, 19, 540–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Broin, S.D.; Kelleher, B.P. A Dried Serum Spot Assay for Vitamin B(12). Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2008, 46, 354–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karvaly, G.; Molnár-Világos, G.; Kovács, K.; Mészáros, K.; Patócs, A.; Vásárhelyi, B. Evaluation of the Analytical and Clinical Concordance of 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Levels in Dried Blood Spots, Dried Serum Spots, and Serum as Potential Biorepository Specimens. Biopreservation Biobanking 2017, 15, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osteresch, B.; Viegas, S.; Cramer, B.; Humpf, H.-U. Multi-Mycotoxin Analysis Using Dried Blood Spots and Dried Serum Spots. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 3369–3382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocur, A.; Czajkowska, A.; Moczulski, M.; Kot, B.; Rubik, J.; Pawiński, T. Assessment of Dried Serum Spots (DSS) and Volumetric-Absorptive Microsampling (VAMS) Techniques in Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of (Val)Ganciclovir-Comparative Study in Analytical and Clinical Practice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercatali, L.; Serra, P.; Miserocchi, G.; Spadazzi, C.; Liverani, C.; De Vita, A.; Marisi, G.; Bongiovanni, A.; Recine, F.; Pangan, A.; et al. Dried Blood and Serum Spots As A Useful Tool for Sample Storage to Evaluate Cancer Biomarkers. J. Vis. Exp. JoVE 2018, 136, 57113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Würsch, D.; Rojas-Montes, O.; Maldonado-Rodríguez, A.; Sevilla-Reyes, E.; Cevallos, A.M.; Sánchez-Burgos, G.; Chávez-Negrete, A.; Lira, R. Dried Serum Samples for Antibody Detection in Arthropod-Borne Virus Infections Are an Effective Alternative to Serum Samples. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2023, 109, 933–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billinger, K.; Okai, C.A.; Russ, M.; Koy, C.; Röwer, C.; Opuni, K.F.M.; Illges, H.; Pecks, U.; Glocker, M.O. Dried Serum Spots on Pre-Punched Filter Paper Discs Are Ready-to-Use Storage and Shipping Devices for Blood-Borne Antigens and Antibodies. J. Immunol. Methods 2023, 519, 113519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desbois, D.; Roque-Afonso, A.-M.; Lebraud, P.; Dussaix, E. Use of Dried Serum Spots for Serological and Molecular Detection of Hepatitis a Virus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2009, 47, 1536–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abad, P.; Coronado, M.; Vincelle-Nieto, Á.; Pérez-Benavente, S.; Fobil, J.N.; Puyet, A.; Diez, A.; Reyes-Palomares, A.; Azcárate, I.G.; Bautista, J.M. Shotgun Characterization of the Circulating IgM Antigenome of an Infectious Pathogen by Immunocapture-LC-MS/MS from Dried Serum Spots. J. Proteome Res. 2024, 23, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barin, F.; Plantier, J.-C.; Brand, D.; Brunet, S.; Moreau, A.; Liandier, B.; Thierry, D.; Cazein, F.; Lot, F.; Semaille, C.; et al. Human Immunodeficiency Virus Serotyping on Dried Serum Spots as a Screening Tool for the Surveillance of the AIDS Epidemic. J. Med. Virol. 2006, 78 (Suppl. 1), S13–S18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chambers, A.G.; Percy, A.J.; Hardie, D.B.; Borchers, C.H. Comparison of Proteins in Whole Blood and Dried Blood Spot Samples by LC/MS/MS. J. Am. Soc. Mass. Spectrom. 2013, 24, 1338–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahluwalia, N.; Lönnerdal, B.; Lorenz, S.G.; Allen, L.H. Spot Ferritin Assay for Serum Samples Dried on Filter Paper. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1998, 67, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahluwalia, N.; Bulux, J.; Solomons, N.W.; Romero-Abal, M.-E.; Mercedes Hernández, M.; Boy, E. Ferritin Concentrations in Dried Serum Spots Prepared by Standard Compared with Simplified Approaches: A Validation Study in Guatemala City. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 81, 1366–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahluwalia, N.; de Silva, A.; Atukorala, S.; Weaver, V.; Molls, R. Ferritin Concentrations in Dried Serum Spots from Capillary and Venous Blood in Children in Sri Lanka: A Validation Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2002, 75, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, J.D.; Flowers, C.H.; Skikne, B.S. An Assessment of Dried Blood-Spot Technology for Identifying Iron Deficiency. Blood 1998, 92, 1807–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flowers, C.H.; Cook, J.D. Dried Plasma Spot Measurements of Ferritin and Transferrin Receptor for Assessing Iron Status. Clin. Chem. 1999, 45, 1826–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koehler, K.; Marks-Nelson, E.; Braga, C.P.; Beckford, S.; Adamec, J. Validity of Plasma Collection Cards for Ferritin Assessment-A Proof-of-Concept Study. Eur. J. Haematol. 2020, 104, 554–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Woenker, T.; Adamec, J.; Regnier, F.E. Simple, Miniaturized Blood Plasma Extraction Method. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 11501–11508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cvetko, A.; Tijardović, M.; Bilandžija-Kuš, I.; Gornik, O. Comparison of Self-Sampling Blood Collection for N-Glycosylation Analysis. BMC Res. Notes 2022, 15, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serventi, F.; Musyoka, A.; Saunders, J.; Mremi, A.; Mmbaga, B.T.; Patrick, E.; Mwakyembe, T.; Jones, M.; Lucas, F.L.; Miesfeldt, S.; et al. NOHA: A Promising Biomarker for Determining Estrogen Receptor Status Among Patients With Breast Cancer in Resource-Constrained Settings. JCO Glob. Oncol. 2022, 8, e2200192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollard, S.; Anderson, J.C.; Bah, F.; Mateus, M.; Sidhu, M.; Simmons, D. Non-Lethal Blood Sampling of Fish in the Lab and Field With Methods for Dried Blood Plasma Spot Omic Analyses. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 795348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona, S.; Seiverth, B.; Magubane, D.; Hans, L.; Hoppler, M. Separation of Plasma from Whole Blood by Use of the Cobas Plasma Separation Card: A Compelling Alternative to Dried Blood Spots for Quantification of HIV-1 Viral Load. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2019, 57, e01336-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picchio, C.A.; Nicolàs, A.; Ayemfouo Fofou, I.V.; Kasone, V.; Guewo-Fokeng, M.; Tagny, C.T.; Nanyonjo, T.; Nansumba, H.; Kouongni, Y.N.; Sezawo Kamdjeu, R.G.E.; et al. Acceptability and Feasibility of the Plasma Separation Card for an Integrated Model of Care for HBV and HCV Screening Among People Attending HIV Clinics in Cameroon and Uganda. J. Epidemiol. Glob. Heal. 2024, 14, 827–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanroye, F.; Van den Bossche, D.; Vercauteren, K. Prospective Laboratory Evaluation of the Cobas Plasma Separation Card for HIV and Treponema Pallidum Antibody Analysis. Sex. Transm. Dis. 2023, 50, 764–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colucci, G.; Uceda Renteria, S.; Ceriotti, F.; Lampertico, P. Clinical Evaluation of Plasma Separation Cards as a Tool to Collect, Store, and Test Blood Samples for Hepatitis B and C Serological Markers. Clin. Chem. 2021, 68, 214–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nichols, B.E.; Girdwood, S.J.; Shibemba, A.; Sikota, S.; Gill, C.J.; Mwananyanda, L.; Noble, L.; Stewart-Isherwood, L.; Scott, L.; Carmona, S.; et al. Cost and Impact of Dried Blood Spot Versus Plasma Separation Card for Scale-up of Viral Load Testing in Resource-Limited Settings. Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2020, 70, 1014–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lombardi, V.; Carassiti, D.; Giovannoni, G.; Lu, C.-H.; Adiutori, R.; Malaspina, A. The Potential of Neurofilaments Analysis Using Dry-Blood and Plasma Spots. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Protein Profiling from Dried Serum Spots—2016—Wiley Analytical Science. Available online: https://analyticalscience.wiley.com/content/article-do/protein-profiling-dried-serum-spots (accessed on 29 March 2025).
- Cao, H.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, S.; Cao, H.; Li, Y.; Huang, J. Dried Plasma Spot Based LC-MS/MS Method for Monitoring of Meropenem in the Blood of Treated Patients. Molecules 2022, 27, 1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagan, A.S.; Jones, D.R.; Agarwal, R. Use of Dried Plasma Spots for the Quantification of Iothalamate in Clinical Studies. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. CJASN 2013, 8, 909–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Broek, I.; Sparidans, R.W.; Schellens, J.H.M.; Beijnen, J.H. Quantitative Bioanalysis of Peptides by Liquid Chromatography Coupled to (Tandem) Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life. Sci. 2008, 872, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosypal, A.C.; Pick, L.D.; Hernandez, J.O.E.; Lindsay, D.S. Evaluation of a Novel Dried Blood Spot Collection Device (HemaSpotTM) to Test Blood Samples Collected from Dogs for Antibodies to Leishmania Infantum. Vet. Parasitol. 2014, 205, 338–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Cai, X.; Wang, R.-Q.; Xiao, J. Immobilized Trypsin on Hydrophobic Cellulose Decorated Nanoparticles Shows Good Stability and Reusability for Protein Digestion. Anal. Biochem. 2015, 477, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzu-Nascimento, T.; Morbioli, G.G.; Milan, L.A.; Donofrio, F.C.; Mestriner, C.A.; Carrilho, E. Development and Statistical Assessment of a Paper-Based Immunoassay for Detection of Tumor Markers. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 950, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannsen, C.; Haq, A.U.; Reubsaet, L.; Halvorsen, T.G. On the Spot Immunocapture in Targeted Biomarker Analysis Using Paper-Bound Streptavidin as Anchor for Biotinylated Antibodies. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2022, 414, 5979–5989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaduskar, O.; Bhatt, V.; Prosperi, C.; Hayford, K.; Hasan, A.Z.; Deshpande, G.R.; Tilekar, B.; Vivian Thangaraj, J.W.; Kumar, M.S.; Gupta, N.; et al. Optimization and Stability Testing of Four Commercially Available Dried Blood Spot Devices for Estimating Measles and Rubella IgG Antibodies. mSphere 2021, 6, e0049021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, K.; DeLong, A.; Balamane, M.; Schreier, L.; Orido, M.; Chepkenja, M.; Kemboi, E.; D’Antuono, M.; Chan, P.A.; Emonyi, W.; et al. HemaSpot, a Novel Blood Storage Device for HIV-1 Drug Resistance Testing. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2016, 54, 223–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denniff, P.; Spooner, N. Volumetric Absorptive Microsampling: A Dried Sample Collection Technique for Quantitative Bioanalysis. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 8489–8495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodeja, P.; Giannoutsos, S.; Caritis, S.; Venkataramanan, R. Applications of Volumetric Absorptive Microsampling Technique: A Systematic Critical Review. Ther. Drug Monit. 2023, 45, 431–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amado, F.; Calheiros-Lobo, M.J.; Ferreira, R.; Vitorino, R. Sample Treatment for Saliva Proteomics. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1073, 23–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esser, D.; Alvarez-Llamas, G.; de Vries, M.P.; Weening, D.; Vonk, R.J.; Roelofsen, H. Sample Stability and Protein Composition of Saliva: Implications for Its Use as a Diagnostic Fluid. Biomark. Insights 2008, 3, 25–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomadaki, K.; Helmerhorst, E.J.; Tian, N.; Sun, X.; Siqueira, W.L.; Walt, D.R.; Oppenheim, F.G. Whole-Saliva Proteolysis and Its Impact on Salivary Diagnostics. J. Dent. Res. 2011, 90, 1325–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, H.; Nakajima, D.; Ishikawa, M.; Konno, R.; Nakamura, R.; Ohara, O.; Kawashima, Y. Evaluation of the Suitability of Dried Saliva Spots for In-Depth Proteome Analyses for Clinical Applications. J. Proteome Res. 2022, 21, 1340–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christianson, C.D.; Laine, D.F.; Zimmer, J.S.; Johnson, C.J.; Sheaff, C.N.; Carpenter, A.; Needham, S.R. Development and Validation of an HPLC–MS/MS Method for The Analysis of Dexamethasone from Pig Synovial Fluid Using Dried Matrix Spotting. Bioanalysis 2010, 2, 1829–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, Y.-C.; Lin, S.-Y.; Chien, K.-Y.; Chen, S.-F.; Wu, C.-C.; Chang, Y.-T.; Chi, L.-M.; Chu, L.J.; Chiang, W.-F.; Chien, C.-Y.; et al. An Immuno-MALDI Mass Spectrometry Assay for the Oral Cancer Biomarker, Matrix Metalloproteinase-1, in Dried Saliva Spot Samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1100, 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulte, F.; Hasturk, H.; Hardt, M. Mapping Relative Differences in Human Salivary Gland Secretions by Dried Saliva Spot Sampling and nanoLC-MS/MS. Proteomics 2019, 19, e1900023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Zhao, S.Z.; Koh, S.K.; Chen, L.; Vaz, C.; Tanavde, V.; Li, X.R.; Beuerman, R.W. In-Depth Analysis of the Human Tear Proteome. J. Proteom. 2012, 75, 3877–3885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagan, S.; Martin, E.; Enríquez-de-Salamanca, A. Tear Fluid Biomarkers in Ocular and Systemic Disease: Potential Use for Predictive, Preventive and Personalised Medicine. EPMA J. 2016, 7, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieragostino, D.; D’Alessandro, M.; di Ioia, M.; Di Ilio, C.; Sacchetta, P.; Del Boccio, P. Unraveling the Molecular Repertoire of Tears as a Source of Biomarkers: Beyond Ocular Diseases. Proteom. Clin. Appl. 2015, 9, 169–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Thun Und Hohenstein-Blaul, N.; Funke, S.; Grus, F.H. Tears as a Source of Biomarkers for Ocular and Systemic Diseases. Exp. Eye Res. 2013, 117, 126–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebrecht, A.; Boehm, D.; Schmidt, M.; Koelbl, H.; Schwirz, R.L.; Grus, F.H. Diagnosis of Breast Cancer by Tear Proteomic Pattern. Cancer Genom. Proteom. 2009, 6, 177–182. [Google Scholar]
- Lebrecht, A.; Boehm, D.; Schmidt, M.; Koelbl, H.; Grus, F.H. Surface-Enhanced Laser Desorption/Ionisation Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry to Detect Breast Cancer Markers in Tears and Serum. Cancer Genom. Proteom. 2009, 6, 75–83. [Google Scholar]
- Böhm, D.; Keller, K.; Pieter, J.; Boehm, N.; Wolters, D.; Siggelkow, W.; Lebrecht, A.; Schmidt, M.; Kölbl, H.; Pfeiffer, N.; et al. Comparison of Tear Protein Levels in Breast Cancer Patients and Healthy Controls Using a De Novo Proteomic Approach. Oncol. Rep. 2012, 28, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchoo, S.; Havanapan, P.-O.; Phungthanom, N.; Rucksaken, R.; Muikaew, R.; Sussadee, M. Analysis and Comparison of Tear Protein Profiles in Dogs Using Different Tear Collection Methods. BMC Vet. Res. 2022, 18, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tham, M.L.; Mahmud, A.; Abdullah, M.; Md Saleh, R.; Mohammad Razali, A.; Cheah, Y.K.; Mohd Taib, N.; Ho, K.L.; Mahmud, M.; Mohd Isa, M. Tear Samples for Protein Extraction: Comparative Analysis of Schirmer’s Test Strip and Microcapillary Tube Methods. Cureus 2023, 15, e50972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posa, A.; Bräuer, L.; Schicht, M.; Garreis, F.; Beileke, S.; Paulsen, F. Schirmer Strip vs. Capillary Tube Method: Non-Invasive Methods of Obtaining Proteins from Tear Fluid. Ann. Anat. Anat. Anz. Off. Organ. Anat. Ges. 2013, 195, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, W.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, L.; Wang, T.; Gao, Y. A Dry Method for Preserving Tear Protein Samples. Biopreservation Biobanking 2017, 15, 417–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gijs, M.; Arumugam, S.; van de Sande, N.; Webers, C.A.B.; Sethu, S.; Ghosh, A.; Shetty, R.; Vehof, J.; Nuijts, R.M.M.A. Pre-Analytical Sample Handling Effects on Tear Fluid Protein Levels. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponzini, E.; Santambrogio, C.; De Palma, A.; Mauri, P.; Tavazzi, S.; Grandori, R. Mass Spectrometry-based Tear Proteomics for Noninvasive Biomarker Discovery. Mass. Spectrom. Rev. 2022, 41, 842–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, S.; Altman, J.; Jones, G.; Lee, T.J.; Robertson, D.M.; Zhi, W.; Sharma, S.; Sharma, A. Mass Spectrometric Detection of Keratins in Tear Fluid. Exp. Eye Res. 2025, 251, 110231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choy, C.K.; Cho, P.; Chung, W.Y.; Benzie, I.F. Water-Soluble Antioxidants in Human Tears: Effect of the Collection Method. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2001, 42, 3130–3134. [Google Scholar]
- Bachhuber, F.; Huss, A.; Senel, M.; Tumani, H. Diagnostic Biomarkers in Tear Fluid: From Sampling to Preanalytical Processing. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, N.; Garapati, K.; Ghose, V.; Kandasamy, R.K.; Pandey, A. Recent Progress in Mass Spectrometry-Based Urinary Proteomics. Clin. Proteom. 2024, 21, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betz, D.; Fane, K. Human Chorionic Gonadotropin. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Ecke, T.H.; Meisl, C.J.; Schlomm, T.; Rabien, A.; Labonté, F.; Rong, D.; Hofbauer, S.; Friedersdorff, F.; Sommerfeldt, L.; Gagel, N.; et al. BTA Stat®, NMP22® BladderChek®, UBC® Rapid Test, and CancerCheck® UBC® Rapid VISUAL as Urinary Marker for Bladder Cancer: Final Results of a German Multicenter Study. Urol. Oncol. Semin. Orig. Investig. 2023, 41, 484.e17–484.e26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Fan, C.; Su, M.; Wang, Q.; Bao, H. Use of the Nuclear Matrix Protein 22 BladderChek Test for the Detection of Primary and Recurrent Urothelial Carcinoma. Dis. Markers 2020, 1, 3424039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M. Effects of Extrinsic Factors on the Urinary Proteome. In Urine: Promising Biomarker Source for Early Disease Detection; Gao, Y., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 197–225. ISBN 9789811391095. [Google Scholar]
- Santucci, L.; Candiano, G.; Petretto, A.; Bruschi, M.; Lavarello, C.; Inglese, E.; Righetti, P.G.; Ghiggeri, G.M. From Hundreds to Thousands: Widening the Normal Human Urinome (1). J. Proteom. 2015, 112, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okendo, J.; Musanabaganwa, C.; Mwangi, P.; Nyaga, M.; Onywera, H. SARS-CoV-2-Positive Patients Display Considerable Differences in Proteome Diversity in Urine, Nasopharyngeal, Gargle Solution and Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid Sample. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0271870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, J.; Lindemann, V.; Olsen, M.; Cramer, B.; Humpf, H.-U. Dried Urine Spots as Sampling Technique for Multi-Mycotoxin Analysis in Human Urine. Mycotoxin Res. 2021, 37, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Protti, M.; Marasca, C.; Cirrincione, M.; Sberna, A.E.; Mandrioli, R.; Mercolini, L. Dried Urine Microsampling Coupled to Liquid Chromatography—Tandem Mass Spectrometry (LC–MS/MS) for the Analysis of Unconjugated Anabolic Androgenic Steroids. Molecules 2020, 25, 3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chutipongtanate, S.; Changtong, C.; Weeraphan, C.; Hongeng, S.; Srisomsap, C.; Svasti, J. Syringe-Push Membrane Absorption as a Simple Rapid Method of Urine Preparation for Clinical Proteomics. Clin. Proteom. 2015, 12, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Protti, M.; Sberna, P.M.; Sberna, A.E.; Ferrante, R.; Mandrioli, R.; Mercolini, L. Enhanced Urinary Stability of Peptide Hormones and Growth Factors by Dried Urine Microsampling. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 204, 114234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashirina, D.N.; Brzhozovskiy, A.G.; Sun, W.; Pastushkova, L.K.; Popova, O.V.; Rusanov, V.B.; Nikolaev, E.N.; Larina, I.M.; Kononikhin, A.S. Proteomic Characterization of Dry Blood Spots of Healthy Women During Simulation the Microgravity Effects Using Dry Immersion. Front. Physiol. 2022, 12, 837–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimakawa, Y.; Vernoux, L.; Gabassi, A.; Mercier-Delarue, S.; Vincent, J.P.; Simon, F.; Maylin, S. Analytical Validation of Hepatitis B Core-related Antigen (HBcrAg) Using Dried Blood Spots (DBS). J. Viral Hepat. 2021, 28, 837–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, K.; Holgate, T.; Tekoaua, R.; Nicholson, S.; Littlejohn, M.; Locarnini, S. Evaluation of Dried Blood Spots for Hepatitis B and D Serology and Nucleic Acid Testing. J. Med. Virol. 2022, 94, 642–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omosule, C.L.; Conklin, J.; Seck, S.; Howell, R.; Hock, K.G.; Ballman, C.; Freeman, J.; Du Toit, L.; Dubberke, E.; Farnsworth, C.W. Qualitative and Quantitative Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies from Dried Blood Spots. Clin. Biochem. 2023, 117, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whittaker, K.; Mao, Y.-Q.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, S.; Peck, H.; Huang, R.-P. Dried Blood Sample Analysis by Antibody Array across the Total Testing Process. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 20549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, N.Y.; Hwang, H.; Ji, E.S.; Park, G.W.; Lee, J.Y.; Lee, H.K.; Kim, J.Y.; Yoo, J.S. Direct Analysis of Site-Specific N-Glycopeptides of Serological Proteins in Dried Blood Spot Samples. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 4971–4981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iuraşcu, M.-I.; Balla, Z.; Pereira, C.; Andrási, N.; Varga, L.; Csuka, D.; Szilágyi, Á.; Tripolszki, K.; Khan, S.; Susnea, I.; et al. Application of a Dried Blood Spot Based Proteomic and Genetic Assay for Diagnosing Hereditary Angioedema. Clin. Transl. Allergy 2023, 13, e12317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vialaret, J.; Vignon, M.; Hirtz, C.; Badiou, S.; Baptista, G.; Fichter, L.; Dupuy, A.-M.; Maceski, A.M.; Fayolle, M.; Brousse, M.; et al. Use of Dried Blood Spots for Monitoring Inflammatory and Nutritional Biomarkers in the Elderly. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. CCLM 2024, 62, 881–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedes, S.; Perpétuo, L.; Veloso, J.; Lima, T.; Ferreira, A.F.; Pires, I.; Savaiva, F.; Lourenço, A.; Moreira-Costa, L.; Leite-Moreira, A.; et al. Comprehensive Characterization of Protein Modifications Using Mass Spectrometry and Dry Blood Spots. Proteom. Clin. Appl. 2024, 18, e2300102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, C.S.; Moggridge, S.; Müller, T.; Sorensen, P.H.; Morin, G.B.; Krijgsveld, J. Single-Pot, Solid-Phase-Enhanced Sample Preparation for Proteomics Experiments. Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 68–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashirina, D.N.; Pastushkova, L.K.; Brzhozovskiy, A.G.; Kononikhin, A.S.; Rusanov, V.B.; Kukanov, V.Y.; Popova, O.V.; Tyuzhin, M.G.; Nikolaev, E.N.; Larina, I.M.; et al. A Study on the Protein Composition of Dry Blood Spots of Healthy Volunteers in an Experiment with Hypomagnetic Conditions. Hum. Physiol. 2023, 49, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimer, R.M.; Sumaily, K.M.; Almuslat, A.; Abdel Jabar, M.; Sabi, E.M.; Al-Muhaizea, M.A.; Abdel Rahman, A.M. Dystrophin Protein Quantification as a Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Diagnostic Biomarker in Dried Blood Spots Using Multiple Reaction Monitoring Tandem Mass Spectrometry: A Preliminary Study. Molecules 2022, 27, 3662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumaily, K.M.; Nimer, R.; Alzahrani, M.; Abdel Jabar, M.; Alodib, A.; Sabi, E.M.; Nizami, I.; Abdel Rahman, A.M. CFTR Protein Quantification as a Cystic Fibrosis Diagnostic Biomarker in Dried Blood Spots Using Multiple Reaction Monitoring Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2022, 216, 114801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, C.J.; Chang, I.J.; Jung, S.; Dayuha, R.; Whiteaker, J.R.; Segundo, G.R.S.; Torgerson, T.R.; Ochs, H.D.; Paulovich, A.G.; Hahn, S.H. Rapid Multiplexed Proteomic Screening for Primary Immunodeficiency Disorders From Dried Blood Spots. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Huo, L.; Liu, Z.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; He, Q.; Wang, X.; Liang, S. Sodium Laurate, a Novel Protease- and Mass Spectrometry-Compatible Detergent for Mass Spectrometry-Based Membrane Proteomics. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Zheng, H.; Tan, Z.; Kang, E.; Xue, P.; Li, X.; Guan, F. Optimizing and Integrating Depletion and Precipitation Methods for Plasma Proteomics through Data-Independent Acquisition-Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2024, 1235, 124046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakajima, D.; Ohara, O.; Kawashima, Y. Toward Proteome-wide Exploration of Proteins in Dried Blood Spots Using Liquid Chromatography-coupled Mass Spectrometry. Proteomics 2021, 21, 2100019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viode, A.; van Zalm, P.; Smolen, K.K.; Fatou, B.; Stevenson, D.; Jha, M.; Levy, O.; Steen, J.; Steen, H. A Simple, Time- and Cost-Effective, High-Throughput Depletion Strategy for Deep Plasma Proteomics. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadf9717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Huan, T. Comparison of Full-Scan, Data-Dependent, and Data-Independent Acquisition Modes in Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry Based Untargeted Metabolomics. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 8072–8080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, B.; Pyr dit Ruys, S.; Balligand, J.-L.; Belkhir, L.; Cani, P.D.; Collet, J.-F.; De Greef, J.; Dewulf, J.P.; Gatto, L.; Haufroid, V.; et al. Deep Plasma Proteomics with Data-Independent Acquisition: Clinical Study Protocol Optimization with a COVID-19 Cohort. J. Proteome Res. 2024, 23, 3806–3822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metatla, I.; Roger, K.; Chhuon, C.; Ceccacci, S.; Chapelle, M.; Pierre-Olivier Schmit; Demichev, V.; Guerrera, I.C. Neat Plasma Proteomics: Getting the Best out of the Worst. Clin. Proteom. 2024, 21, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosting, C.; Yu, J.; Cooper, H.J. High Field Asymmetric Waveform Ion Mobility Spectrometry in Nontargeted Bottom-up Proteomics of Dried Blood Spots. J. Proteome Res. 2018, 17, 1997–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-J.; Hwang, J.; Seo, Y.; Lee, G.; Lee, H.J.; Min, H. Simultaneous Detection of Myostatin-Targeting Monoclonal Antibodies in Dried Blood Spots and Plasma Using Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry with Field Asymmetric Ion Mobility Spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2025, 252, 116518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijakowski, K.; Surdacka, A. Salivary Biomarkers for Diagnosis of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nättinen, J.; Aapola, U.; Nukareddy, P.; Uusitalo, H. Clinical Tear Fluid Proteomics—A Novel Tool in Glaucoma Research. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meikopoulos, T.; Begou, O.; Gika, H.; Theodoridis, G. Dried Urine Spot (DUS) Applied for Sampling Prior to the Accurate HILIC-MS/MS Determination of 14 Amino Acids. Talanta 2024, 269, 125489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretti, M.; Freni, F.; Carelli, C.; Previderé, C.; Grignani, P.; Vignali, C.; Cobo-Golpe, M.; Morini, L. Analysis of Cannabinoids and Metabolites in Dried Urine Spots (DUS). Molecules 2021, 26, 5334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decramer, S.; Peredo, A.G.de.; Breuil, B.; Mischak, H.; Monsarrat, B.; Bascands, J.-L.; Schanstra, J.P. Urine in Clinical Proteomics. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2008, 7, 1850–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, W.W.; Hardt, M.; Zhang, Y.H.; Freire, M.; Ruhl, S. The Human Salivary Proteome Wiki: A Community-Driven Research Platform. J. Dent. Res. 2021, 100, 1510–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Numako, M.; Takayama, T.; Noge, I.; Kitagawa, Y.; Todoroki, K.; Mizuno, H.; Min, J.Z.; Toyo’oka, T. Dried Saliva Spot (DSS) as a Convenient and Reliable Sampling for Bioanalysis: An Application for the Diagnosis of Diabetes Mellitus. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 635–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Shi, Q.; Xu, C.-Y.; Di, L.; Zhao, L.-L.; Jin, W.; Min, J.Z. A Convenient Sampling and Noninvasive Dried Spot Method of Uric Acid in Human Saliva: Comparison of Serum Uric Acid Value and Salivary Uric Acid in Healthy Volunteers and Hyperuricemia Patients. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life. Sci. 2021, 1164, 122528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, M.V.; Raymundo, S.; Cezimbra da Silva, A.C.; Muller, V.V.; Vicente Neto, O.J.; Schwartsmann, G.; Linden, R. Determination of Endogenous Concentrations of Uracil and Dihydrouracil in Dried Saliva Spots by LC-MS/MS: Method Development, Validation, and Clinical Application. Ther. Drug Monit. 2019, 41, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nättinen, J.; Aapola, U.; Jylhä, A.; Vaajanen, A.; Uusitalo, H. Comparison of Capillary and Schirmer Strip Tear Fluid Sampling Methods Using SWATH-MS Proteomics Approach. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2020, 9, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.-J.; Mangwiro, Y.; Wake, M.; Saffery, R.; Greaves, R.F. Multi-Omics Analysis from Archival Neonatal Dried Blood Spots: Limitations and Opportunities. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. CCLM 2022, 60, 1318–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kiseleva, O.I.; Ikhalaynen, Y.A.; Kurbatov, I.Y.; Arzumanian, V.A.; Kryukova, P.A.; Poverennaya, E.V. Dried Spot Paradigm: Problems and Prospects in Proteomics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3857. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083857
Kiseleva OI, Ikhalaynen YA, Kurbatov IY, Arzumanian VA, Kryukova PA, Poverennaya EV. Dried Spot Paradigm: Problems and Prospects in Proteomics. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(8):3857. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083857
Chicago/Turabian StyleKiseleva, Olga I., Yuriy A. Ikhalaynen, Ilya Y. Kurbatov, Viktoriia A. Arzumanian, Polina A. Kryukova, and Ekaterina V. Poverennaya. 2025. "Dried Spot Paradigm: Problems and Prospects in Proteomics" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 8: 3857. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083857
APA StyleKiseleva, O. I., Ikhalaynen, Y. A., Kurbatov, I. Y., Arzumanian, V. A., Kryukova, P. A., & Poverennaya, E. V. (2025). Dried Spot Paradigm: Problems and Prospects in Proteomics. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(8), 3857. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083857







