Targeting the Hippo Pathway in Breast Cancer: A Proteomic Analysis of Yes-Associated Protein Inhibition
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
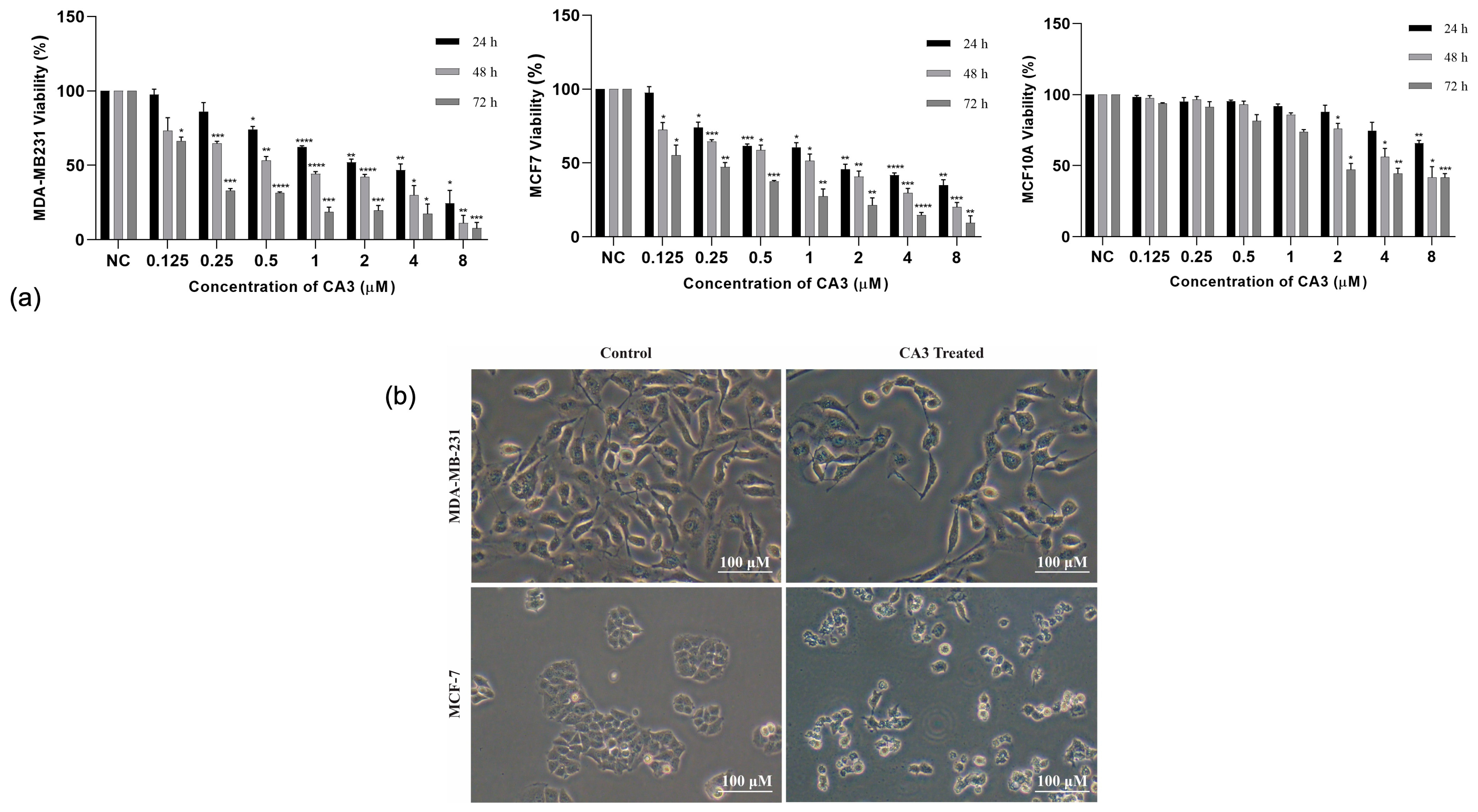
2.1. CA3-Induced Cytotoxicity and Selectivity
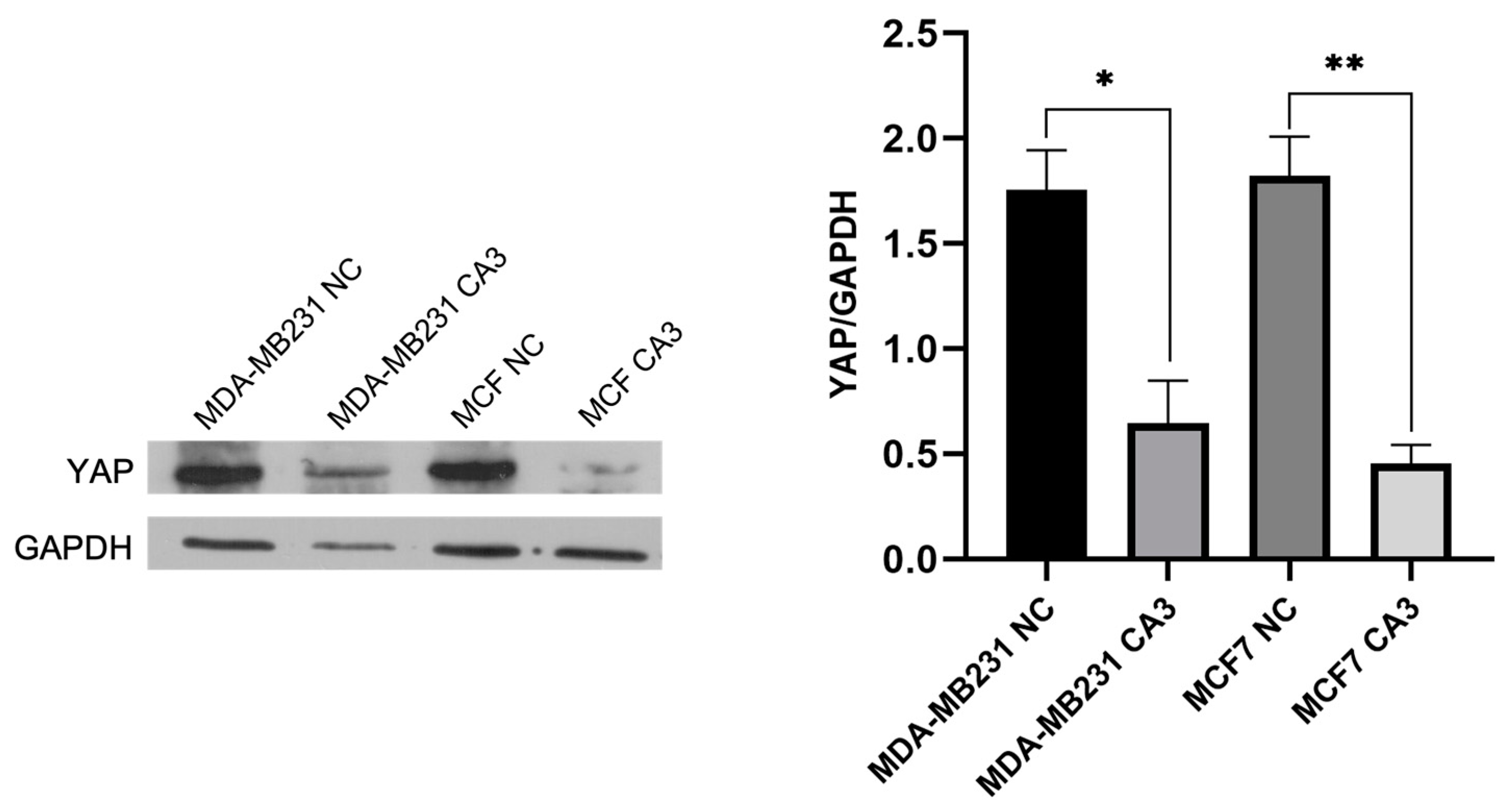
2.2. YAP Inhibition by CA3 in Breast Cancer Cells
2.3. Label-Free Quantification and Protein Identification
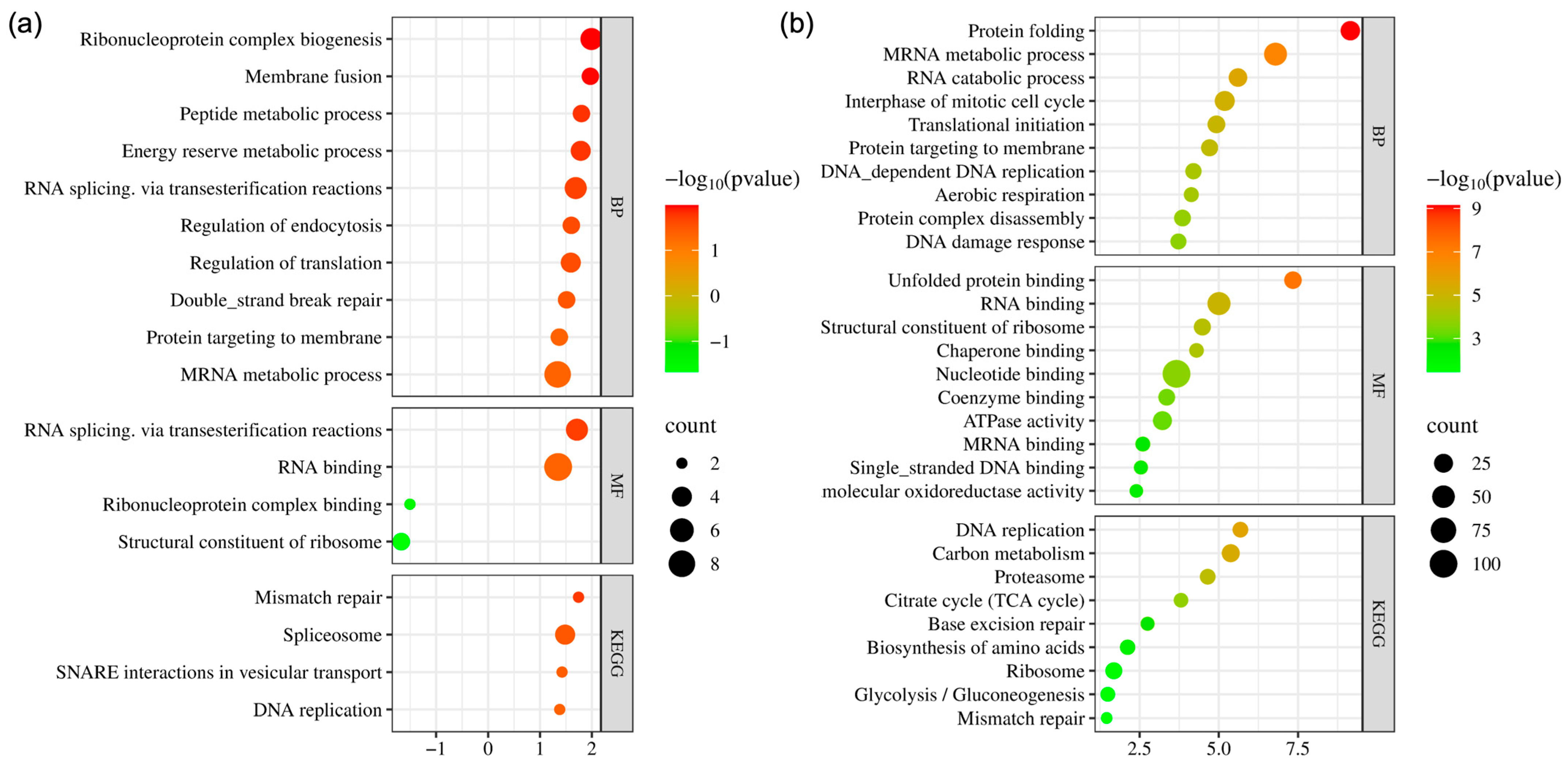
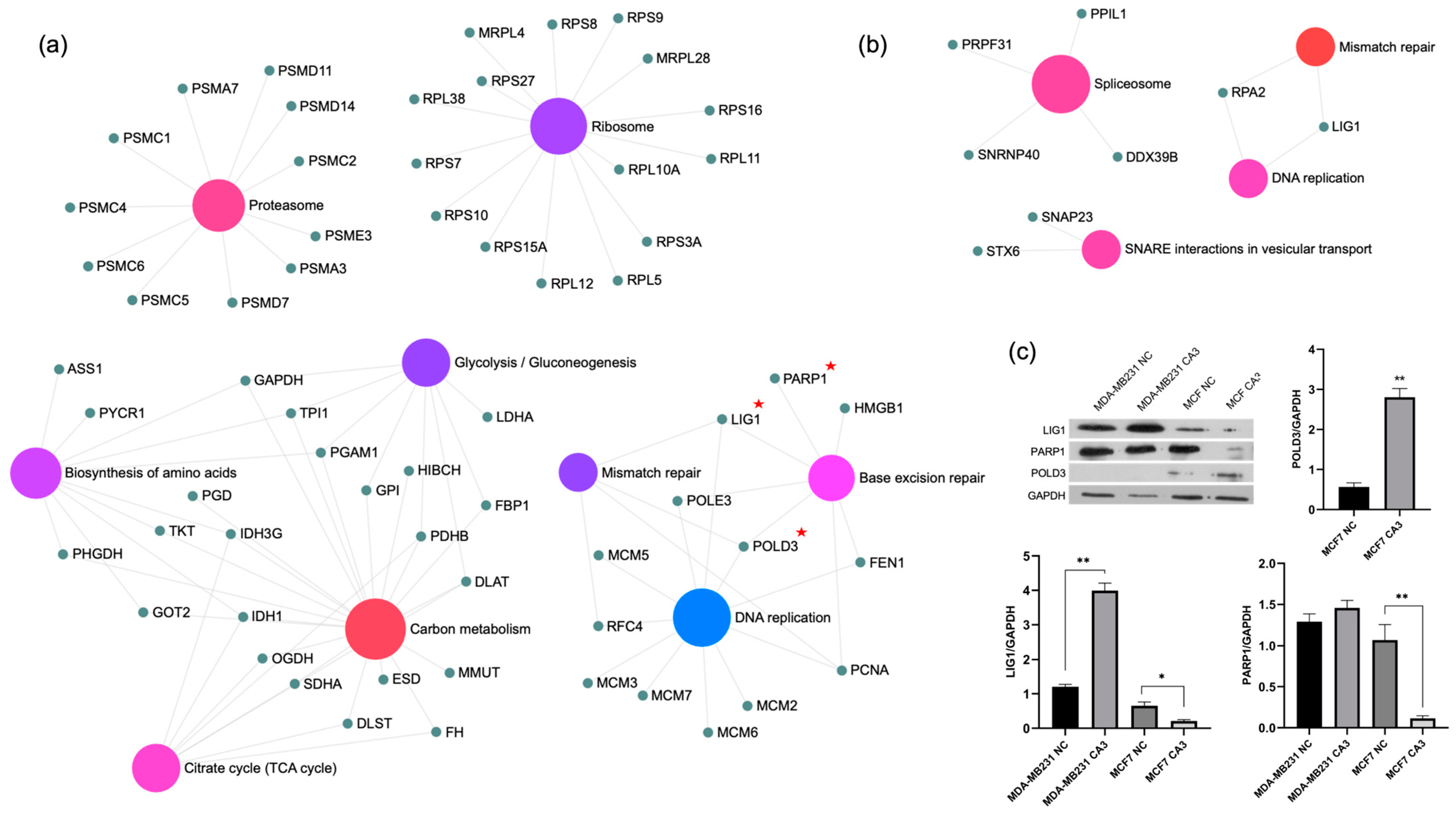
2.4. Bioinformatics Analysis and Validation of Differentially Expressed Proteins
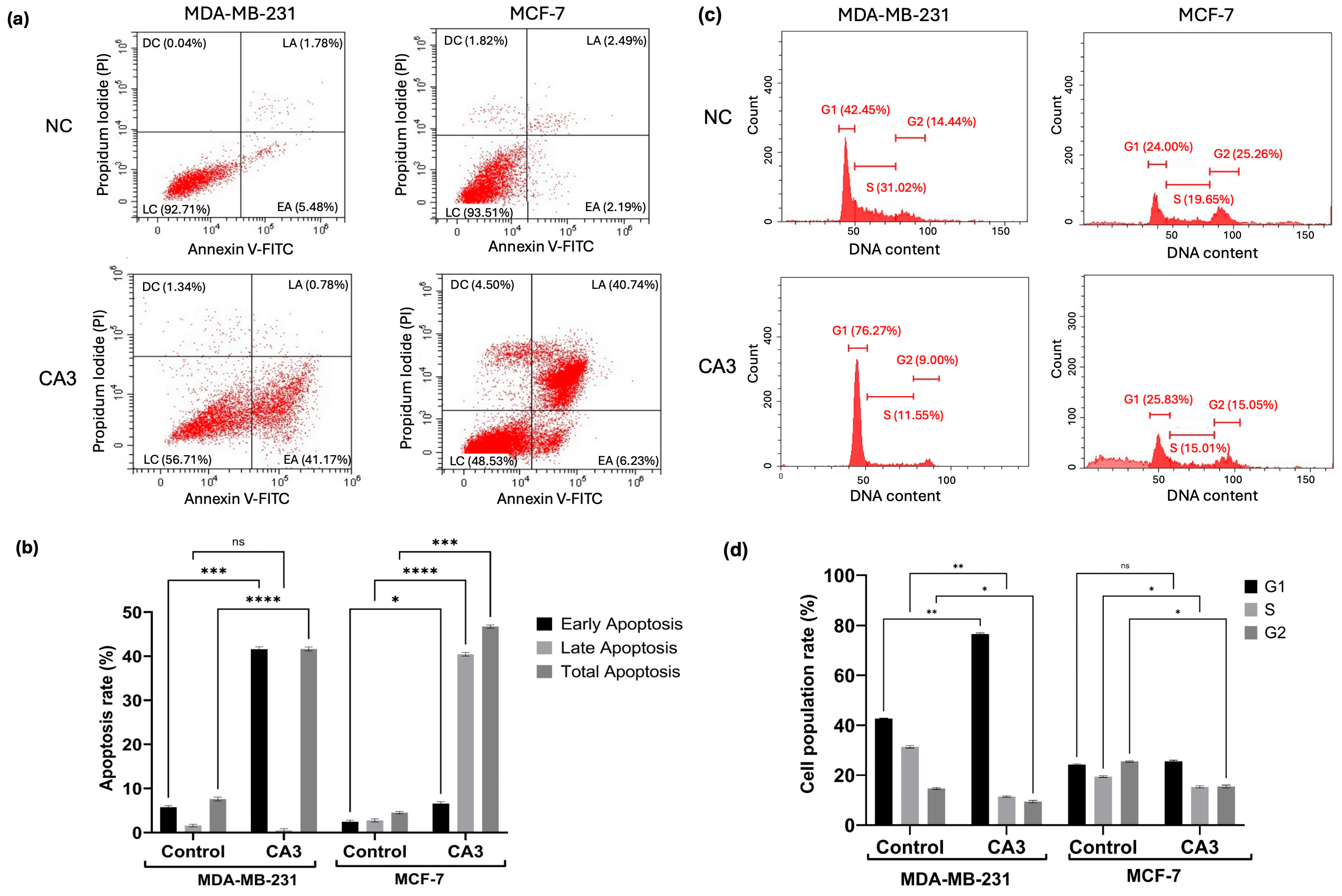
2.5. Induction of Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Modulation
2.6. Autophagic Markers Following YAP Inhibition
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cytotoxicity Assessment of CA3 in Breast Cancer Cells
4.2. Protein Isolation and Proteomic Identification Through Nano-LC-MS/MS
4.3. Functional and Network Analysis of Proteomic Data
4.4. Protein Expression Profiling by Western Blot
4.5. Flow Cytometric Assessment of Apoptosis and Cell Cycle
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perou, C.M.; Sørlie, T.; Eisen, M.B.; van de Rijn, M.; Jeffrey, S.S.; Rees, C.A.; Pollack, J.R.; Ross, D.T.; Johnsen, H.; Akslen, L.A.; et al. Molecular Portraits of Human Breast Tumours. Nature 2000, 406, 747–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.-X.; Zhao, B.; Guan, K.-L. Hippo Pathway in Organ Size Control, Tissue Homeostasis, and Cancer. Cell 2015, 163, 811–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Wang, W.; Zhang, S.; Stewart, R.A.; Yu, W. Identifying Tumor Suppressors in Genetic Mosaics: The Drosophila Lats Gene Encodes a Putative Protein Kinase. Development 1995, 121, 1053–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Wei, X.; Li, W.; Udan, R.S.; Yang, Q.; Kim, J.; Xie, J.; Ikenoue, T.; Yu, J.; Li, L.; et al. Inactivation of YAP Oncoprotein by the Hippo Pathway Is Involved in Cell Contact Inhibition and Tissue Growth Control. Genes Dev. 2007, 21, 2747–2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, B.; Ye, X.; Yu, J.; Li, L.; Li, W.; Li, S.; Yu, J.; Lin, J.D.; Wang, C.-Y.; Chinnaiyan, A.M.; et al. TEAD Mediates YAP-Dependent Gene Induction and Growth Control. Genes Dev. 2008, 22, 1962–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Z.; Moroishi, T.; Guan, K.-L. Mechanisms of Hippo Pathway Regulation. Genes Dev. 2016, 30, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanconato, F.; Cordenonsi, M.; Piccolo, S. YAP/TAZ at the Roots of Cancer. Cancer Cell 2016, 29, 783–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, K.F.; Zhang, X.; Thomas, D.M. The Hippo Pathway and Human Cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moroishi, T.; Hansen, C.G.; Guan, K.-L. The Emerging Roles of YAP and TAZ in Cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2015, 15, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Wang, M.; Cai, M.; Zhang, C.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, H.; Wang, J.; Zhao, W.; et al. Transcriptional Co-Activators YAP/TAZ: Potential Therapeutic Targets for Metastatic Breast Cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 133, 110956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, F.; Ding, X.-Y.; Li, T.-E.; Wang, H.-Y.; Gao, Y.-H.; Wang, W.-J.; Liu, Y.-F.; Chen, X.-S.; Shen, K.-W. Hippo/YAP Signaling Choreographs the Tumor Immune Microenvironment to Promote Triple Negative Breast Cancer Progression via TAZ/IL-34 Axis. Cancer Lett. 2022, 527, 174–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu-Chittenden, Y.; Huang, B.; Shim, J.S.; Chen, Q.; Lee, S.-J.; Anders, R.A.; Liu, J.O.; Pan, D. Genetic and Pharmacological Disruption of the TEAD–YAP Complex Suppresses the Oncogenic Activity of YAP. Genes Dev. 2012, 26, 1300–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Zou, H.; Guo, Y.; Tong, T.; Chen, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Pan, Y.; Li, P. The Oncogenic Roles and Clinical Implications of YAP/TAZ in Breast Cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2023, 128, 1611–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alva-Ruiz, R.; Yonkus, J.; Watkins, R.; Abdelrahman, A.; Conboy, C.; Truty, M.; Smoot, R. Novel YAP Inhibitor, CA3, Demonstrates Antitumoral Activity in Vitro and in Vivo Model of Cholangiocarcinoma. HPB 2021, 23, S510–S511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Xie, M.; Scott, A.W.; Jin, J.; Ma, L.; Dong, X.; Skinner, H.D.; Johnson, R.L.; Ding, S.; Ajani, J.A. A Novel YAP1 Inhibitor Targets CSCs-Enriched Radiation Resistant Cells and Exerts Strong Antitumor Activity in Esophageal Adenocarcinoma. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2017, 17, 443–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandasamy, S.; Adhikary, G.; Rorke, E.A.; Friedberg, J.S.; Mickle, M.B.; Alexander, H.R.; Eckert, R.L. The YAP1 Signaling Inhibitors, Verteporfin and CA3, Suppress the Mesothelioma Cancer Stem Cell Phenotype. Mol. Cancer Res. 2020, 18, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.; Lim, J.Y.; Cho, K.; Lee, H.W.; Park, J.Y.; Ro, S.W.; Kim, K.S.; Seo, H.R.; Kim, D.Y. Anti-Cancer Effects of YAP Inhibitor (CA3) in Combination with Sorafenib against Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) in Patient-Derived Multicellular Tumor Spheroid Models (MCTS). Cancers 2022, 14, 2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alva-Ruiz, R.; Watkins, R.D.; Tomlinson, J.L.; Yonkus, J.A.; Abdelrahman, A.M.; Conboy, C.B.; Jessen, E.; Werneburg, N.W.; Kuipers, H.; Sample, J.W.; et al. YAP-TEAD Inhibition Is Associated with Upregulation of an Androgen Receptor Mediated Transcription Program Providing Therapeutic Escape. FEBS Open Bio 2024, 14, 1873–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witt, B.L.; Tollefsbol, T.O. Molecular, Cellular, and Technical Aspects of Breast Cancer Cell Lines as a Foundational Tool in Cancer Research. Life 2023, 13, 2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimei, M.; Alrouh, S.; Saber-Ayad, M.; Hafezi, S.A.; Vinod, A.; Rawat, S.; Wardeh, Y.; Bakkour, T.M.; El-Serafi, A.T. Inhibition of Yes-Associated Protein-1 (YAP1) Enhances the Response of Invasive Breast Cancer Cells to the Standard Therapy. Breast Cancer Targets Ther. 2020, 12, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade, D.; Mehta, M.; Griffith, J.; Panneerselvam, J.; Srivastava, A.; Kim, T.-D.; Janknecht, R.; Herman, T.; Ramesh, R.; Munshi, A. YAP1 Inhibition Radiosensitizes Triple Negative Breast Cancer Cells by Targeting the DNA Damage Response and Cell Survival Pathways. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 98495–98508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; He, Y.; Yang, S.; Zeng, T.; Hua, Y.; Bao, S.; Yang, F.; Duan, N.; Sun, C.; Liang, Y.; et al. A Positive Feedback Loop: RAD18-YAP-TGF-β between Triple-Negative Breast Cancer and Macrophages Regulates Cancer Stemness and Progression. Cell Death Discov. 2022, 8, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anurag, M.; Jaehnig, E.J.; Krug, K.; Lei, J.T.; Bergstrom, E.J.; Kim, B.-J.; Vashist, T.D.; Huynh, A.M.T.; Dou, Y.; Gou, X.; et al. Proteogenomic Markers of Chemotherapy Resistance and Response in Triple Negative Breast Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2022, 12, 2586–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dueva, R.; Iliakis, G. Replication Protein A: A Multifunctional Protein with Roles in DNA Replication, Repair and Beyond. NAR Cancer 2020, 2, zcaa022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, D.; Baek, S.; Chang, J.; Seol, T.; Ku, B.; Ha, H.; Lee, H.; Cho, S.; Roh, T.-Y.; Kim, Y.K.; et al. YAP Promotes Global MRNA Translation to Fuel Oncogenic Growth despite Starvation. Exp. Mol. Med. 2024, 56, 2202–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, X.; Peng, X.; Guo, Y.; Dai, Z.; Cui, L.; Yu, W.; Liu, Y.; Liu, C.-Y. YAP/TAZ Enhances P-Body Formation to Promote Tumorigenesis. eLife 2024, 12, RP88573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alli, N.; Lou-Hing, A.; Bolt, E.L.; He, L. POLD3 as Controller of Replicative DNA Repair. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirota, K.; Yoshikiyo, K.; Guilbaud, G.; Tsurimoto, T.; Murai, J.; Tsuda, M.; Phillips, L.G.; Narita, T.; Nishihara, K.; Kobayashi, K.; et al. The POLD3 Subunit of DNA Polymerase δ Can Promote Translesion Synthesis Independently of DNA Polymerase ζ. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 1671–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhou, T.; Wang, Z.; Yi, F.; Li, C.; Guo, W.; Xu, H.; Cui, H.; Dong, X.; Liu, J.; et al. Post-Translational Modifications of PCNA in Control of DNA Synthesis and DNA Damage Tolerance-the Implications in Carcinogenesis. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 17, 4047–4059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, C.; Ketchen, A.-M.; Redhead, N.J.; O’Sullivan, M.J.; Melton, D.W. Replication Failure, Genome Instability, and Increased Cancer Susceptibility in Mice with a Point Mutation in the DNA Ligase I Gene. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 4065–4074. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tang, Q.; Kamble, P.; Çağlayan, M. DNA Ligase I Variants Fail in the Ligation of Mutagenic Repair Intermediates with Mismatches and Oxidative DNA Damage. Mutagenesis 2020, 35, 391–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summa, S.D.; Pinto, R.; Pilato, B.; Sambiasi, D.; Porcelli, L.; Guida, G.; Mattioli, E.; Paradiso, A.; Merla, G.; Micale, L.; et al. Expression of Base Excision Repair Key Factors and MiR17 in Familial and Sporadic Breast Cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tufail, M.; Jiang, C.-H.; Li, N. Altered Metabolism in Cancer: Insights into Energy Pathways and Therapeutic Targets. Mol. Cancer 2024, 23, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, L.; Yang, S.; Zhu, Y.; Zhai, X.; Li, S.; Tao, X.; Dong, D. Relationship between Metabolic Reprogramming and Drug Resistance in Breast Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 942064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Shay, C.; Saba, N.F.; Teng, Y. Cancer Metabolism and Carcinogenesis. Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 2024, 13, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Deng, L.; Zou, H.; Guo, Y.; Tong, T.; Huang, M.; Ling, G.; Li, P. New Insights into the Ambivalent Role of YAP/TAZ in Human Cancers. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. CR 2023, 42, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baroja, I.; Kyriakidis, N.C.; Halder, G.; Moya, I.M. Expected and Unexpected Effects after Systemic Inhibition of Hippo Transcriptional Output in Cancer. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriazoglou, A.; Liontos, M.; Zakopoulou, R.; Kaparelou, M.; Tsiara, A.; Papatheodoridi, A.M.; Georgakopoulou, R.; Zagouri, F. The Role of the Hippo Pathway in Breast Cancer Carcinogenesis, Prognosis, and Treatment: A Systematic Review. Breast Care 2021, 16, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, G.; Mckinley, J.; Wang, W. MAP4K2 Connects the Hippo Pathway to Autophagy in Response to Energy Stress. Autophagy 2024, 20, 704–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.; Christofori, G. The Cross-Talk between the Hippo Signaling Pathway and Autophagy:Implications on Physiology and Cancer. Cell Cycle 2020, 19, 2563–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, K.; Wang, X.; Zhou, D.; Wang, Y.; Yu, R.; Zhou, X. YAP Promotes Autophagy and Progression of Gliomas via Upregulating HMGB1. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 40, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Zhang, M.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, K.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, R.; Song, W.; Huang, Q.; Zhao, W.; et al. YAP Manipulates Proliferation via PTEN/AKT/MTOR-Mediated Autophagy in Lung Adenocarcinomas. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, L.; Chen, Y.; Cheng, D.; He, Z.; Shi, X.; Du, B.; Xi, X.; Gao, Y.; Guo, Y. YAP Inhibits Autophagy and Promotes Progression of Colorectal Cancer via Upregulating Bcl-2 Expression. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, R.; Zeh, H.J.; Lotze, M.T.; Tang, D. The Beclin 1 Network Regulates Autophagy and Apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2011, 18, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runwal, G.; Stamatakou, E.; Siddiqi, F.H.; Puri, C.; Zhu, Y.; Rubinsztein, D.C. LC3-Positive Structures Are Prominent in Autophagy-Deficient Cells. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korak, T.; Albayrak, M.G.B.; Yanar, S.; Akpınar, G.; Kasap, M. Decreased Autophagic Activity in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells upon Hydroxychloroquine and Thymoquinone Combination Treatment. Hitit Méd. J. 2024, 6, 246–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanar, S.; Albayrak, M.G.B.; Kasap, M.; Akpinar, G. From Androgen Dependence to Independence in Prostate Cancer: Unraveling Therapeutic Potential and Proteomic Landscape of Hydroxychloroquine as an Autophagy Inhibitor. OMICS J. Integr. Biol. 2024, 28, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yanar, S.; Bal Albayrak, M.G.; Korak, T.; Deveci Ozkan, A.; Arabacı Tamer, S.; Kasap, M. Targeting the Hippo Pathway in Breast Cancer: A Proteomic Analysis of Yes-Associated Protein Inhibition. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3943. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26093943
Yanar S, Bal Albayrak MG, Korak T, Deveci Ozkan A, Arabacı Tamer S, Kasap M. Targeting the Hippo Pathway in Breast Cancer: A Proteomic Analysis of Yes-Associated Protein Inhibition. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(9):3943. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26093943
Chicago/Turabian StyleYanar, Sevinc, Merve Gulsen Bal Albayrak, Tuğcan Korak, Asuman Deveci Ozkan, Sevil Arabacı Tamer, and Murat Kasap. 2025. "Targeting the Hippo Pathway in Breast Cancer: A Proteomic Analysis of Yes-Associated Protein Inhibition" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 9: 3943. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26093943
APA StyleYanar, S., Bal Albayrak, M. G., Korak, T., Deveci Ozkan, A., Arabacı Tamer, S., & Kasap, M. (2025). Targeting the Hippo Pathway in Breast Cancer: A Proteomic Analysis of Yes-Associated Protein Inhibition. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(9), 3943. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26093943





