Empagliflozin Alleviates Hepatic Steatosis and Oxidative Stress via the NRF1 Pathway in High-Fat Diet-Induced Mouse Model of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
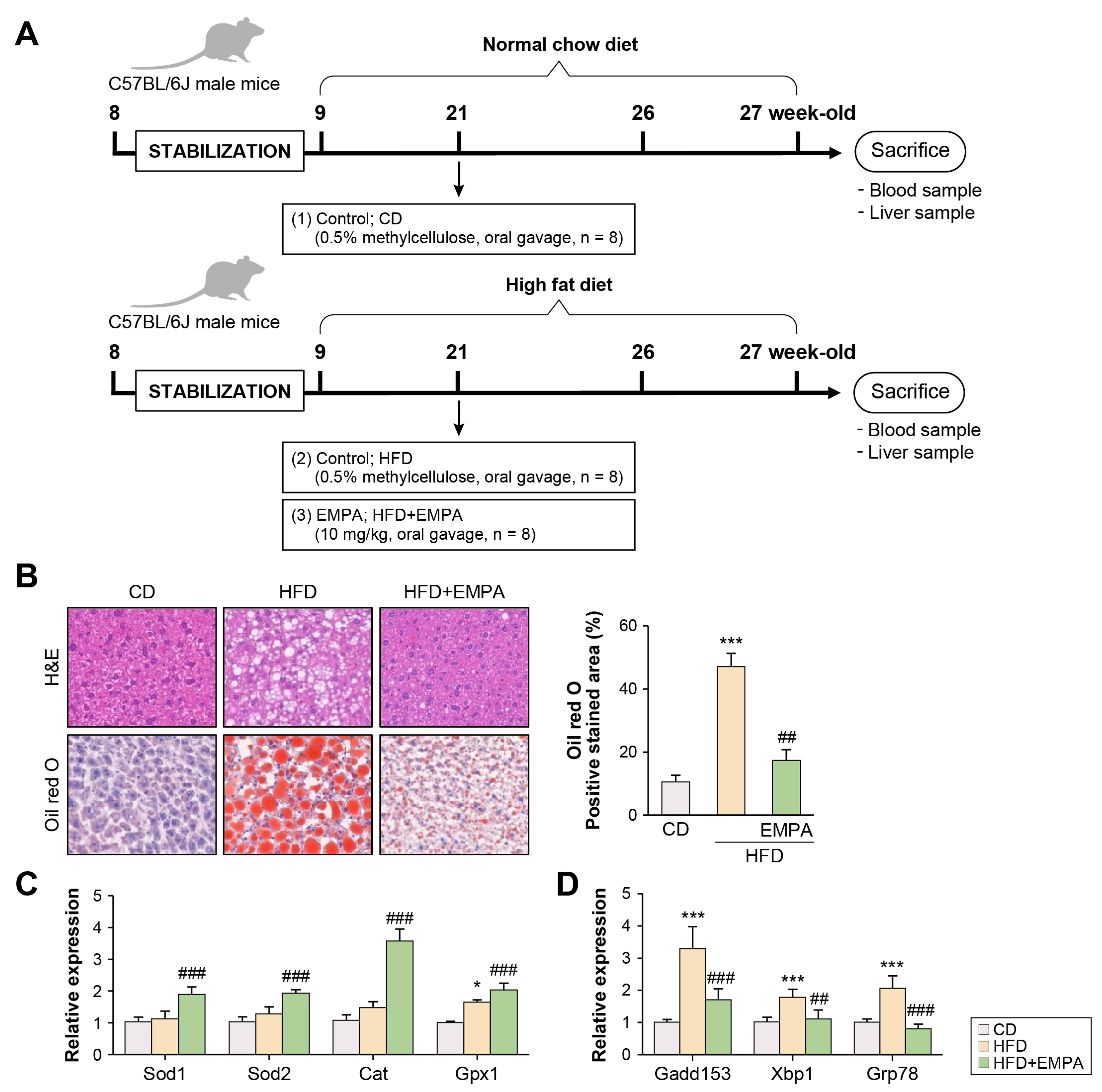
2.1. Empagliflozin Attenuates HFD-Induced Liver Oxidative Stress and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress
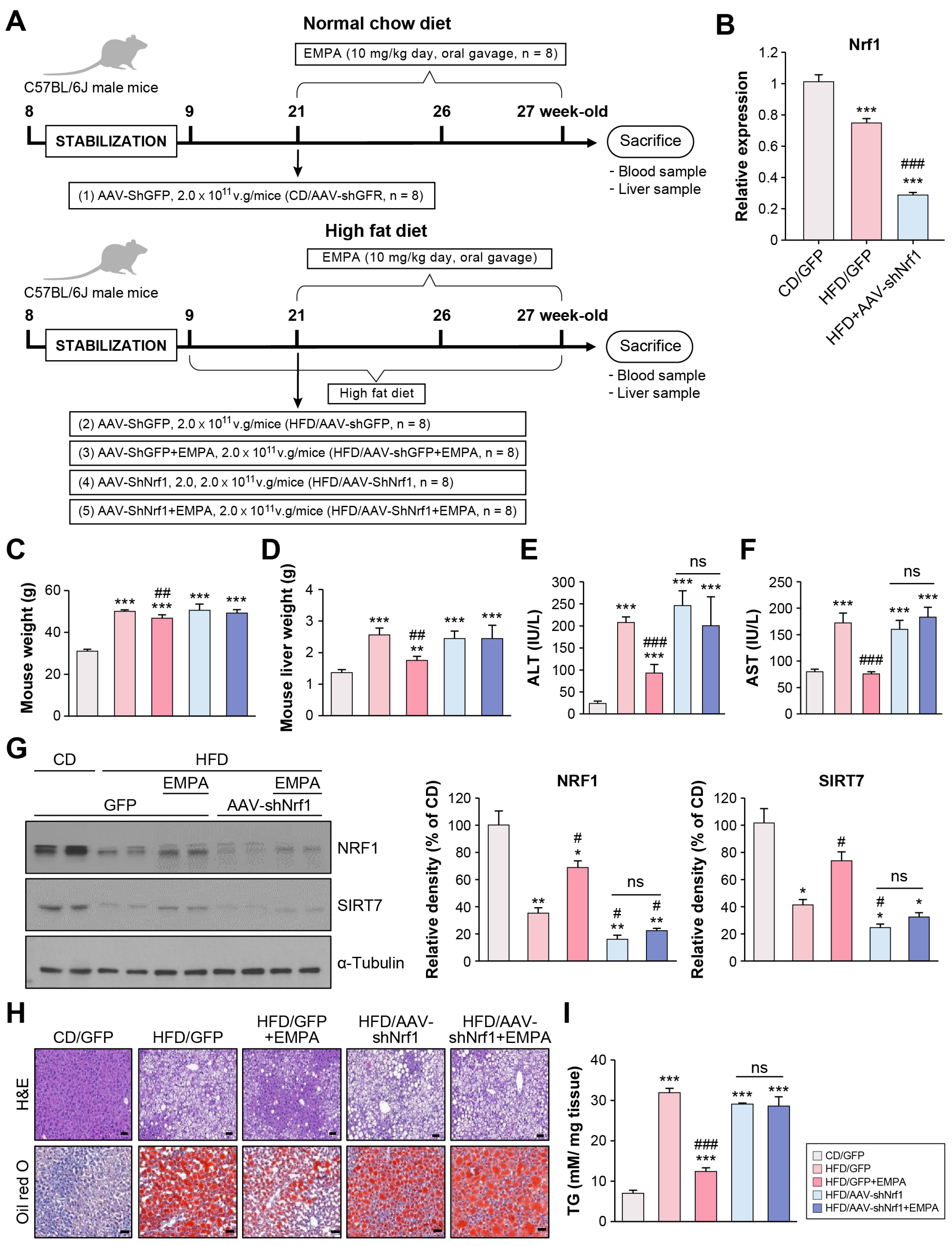
2.2. Empagliflozin Modulates NRF1 and SIRT7 Signaling Pathways in the Liver of HFD-Fed Mice
2.3. Empagliflozin Attenuates Hepatic Steatosis Through NRF1 in the Liver of HFD-Fed Mice
2.4. Empagliflozin Alleviates HFD-Induced Insulin Resistance and Lipid Synthesis via NRF1 in the Liver
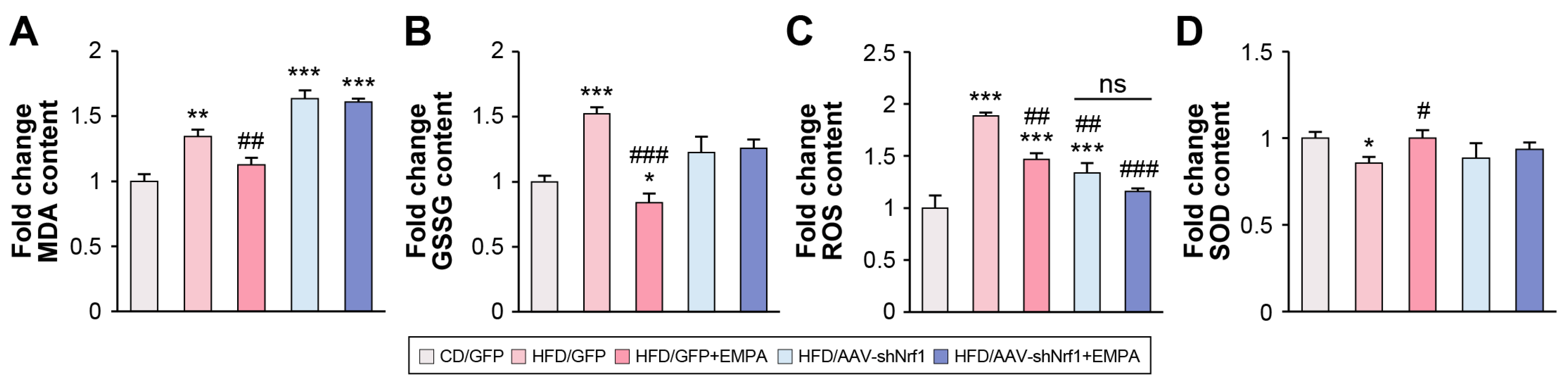
2.5. Empagliflozin Attenuates HFD-Induced Liver ER Stress and Oxidative Stress via NRF1
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animal Study
4.2. Construction of a shNrf1-Expressing AAV (AAV-shNrf1)
4.3. Glucose and Insulin Tolerance Test
4.4. Histological Analysis
4.5. Measurement of TG Levels and Hepatic Biochemical Analysis
4.6. RNA Isolation and Real-Time PCR
4.7. Western Blotting
4.8. Biochemical Analysis
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALT | Alanine aminotransferase |
| ANOVA | Analysis of variance |
| AST | Aspartate aminotransferase |
| ARE | Antioxidant response element |
| CAT | Catalase |
| CD | Control diet |
| CLI | Cholestatic liver injury |
| CPT2 | Carnitine palmitoyltransferase 2 |
| EHHADH | Enoyl-CoA hydratase and 3-hydroxyacyl CoA dehydrogenase |
| EMPA | Empagliflozin |
| ER | Endoplasmic reticulum |
| GADD153 | DNA damage-inducible gene-153 |
| GFP | Green fluorescent protein |
| GPX-1 | Glutathione peroxidase-1 |
| GRP | Glucose-regulated protein |
| GSSG | Oxidized glutathione |
| HCC | Hepatocellular carcinoma |
| H&E | Hematoxylin and eosin |
| HFD | High-fat diet |
| HO-1 | Heme oxygenase-1 |
| IRE1 | Inositol-requiring enzyme 1 |
| MASH | Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis |
| MASLD | Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease |
| MDA | Malondialdehyde |
| NRF-1 | Nuclear respiratory factor 1 |
| ORO | Oil Red O |
| PPAR | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| SCD1 | Stearyl CoA desaturase 1 |
| SGLT2i | Sodium–glucose transport protein 2 inhibitor |
| SIRT | Sirtuin |
| SOD | Superoxide dismutase |
| SREBF | Sterol regulatory element-binding transcription factor |
| XBP-1 | X-box binding protein 1 |
| T2DM | Type 2 diabetes mellitus |
| TG | Triglyceride |
| TFAM | Mitochondrial transcription factor A |
| UPR | Unfolded protein response |
References
- Foglia, B.; Sutti, S.; Cannito, S.; Rosso, C.; Maggiora, M.; Casalino, A.; Bocca, C.; Novo, E.; Protopapa, F.; Ramavath, N.N.; et al. Histidine-rich glycoprotein in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis-related disease progression and liver carcinogenesis. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1342404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, G.A.; Heisel, W.E.; Afshin, A.; Jensen, M.D.; Dietz, W.H.; Long, M.; Kushner, R.F.; Daniels, S.R.; Wadden, T.A.; Tsai, A.G.; et al. The science of obesity management: An endocrine society scientific statement. Endocr. Rev. 2018, 39, 79–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, U.J.; Choi, M.S. Obesity and its metabolic complications: The role of adipokines and the relationship between obesity, inflammation, insulin resistance, dyslipidemia and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 6184–6223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, C.P.; James, O.F. Steatohepatitis: A tale of two “hits”? Gastroenterology 1998, 114, 842–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroyave-Ospina, J.C.; Wu, Z.; Geng, Y.; Moshage, H. Role of oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Implications for prevention and therapy. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolo, A.P.; Teodoro, J.S.; Palmeira, C.M. Role of oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2012, 52, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinman, B.; Wanner, C.; Lachin, J.M.; Fitchett, D.; Bluhmki, E.; Hantel, S.; Mattheus, M.; Devins, T.; Johansen, O.E.; Woerle, H.J.; et al. Empagliflozin, cardiovascular outcomes, and mortality in type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 2117–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuire, D.K.; Shih, W.J.; Cosentino, F.; Charbonnel, B.; Cherney, D.Z.I.; Dagogo-Jack, S.; Pratley, R.; Greenberg, M.; Wang, S.; Huyck, S.; et al. Association of SGLT2 inhibitors with cardiovascular and kidney outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis. JAMA Cardiol. 2021, 6, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gastaldelli, A.; Cusi, K. From NASH to diabetes and from diabetes to NASH: Mechanisms and treatment options. JHEP Rep. 2019, 1, 312–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, C.K.; Zinman, B. Sodium–glucose cotransporter–2 (SGLT-2) inhibitors and the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Annu. Rev. Med. 2019, 70, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiang, J.C.; Wong, V.W. SGLT2 inhibitors in liver patients. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 18, 2168–2172.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, M.; Chan, J.Y. Role of Nrf1 in antioxidant response element-mediated gene expression and beyond. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2010, 244, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsujita, T.; Peirce, V.; Baird, L.; Matsuyama, Y.; Takaku, M.; Walsh, S.V.; Griffin, J.L.; Uruno, A.; Yamamoto, M.; Hayes, J.D. Transcription factor Nrf1 negatively regulates the cystine/glutamate transporter and lipid-metabolizing enzymes. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2014, 34, 3800–3816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.-J.; Zhang, T.-N.; Chen, H.-H.; Yu, X.-F.; Lv, J.-L.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Liu, Y.-S.; Zheng, G.; Zhao, J.-Q.; Wei, Y.-F.; et al. The sirtuin family in health and disease. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohrin, M.; Shin, J.; Liu, Y.; Brown, K.; Luo, H.; Xi, Y.; Haynes, C.M.; Chen, D. Stem cell aging. A mitochondrial UPR-mediated metabolic checkpoint regulates hematopoietic stem cell aging. Science 2015, 347, 1374–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akl, M.G.; Li, L.; Widenmaier, S.B. Protective effects of hepatocyte stress defenders, Nrf1 and Nrf2, against MASLD progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.; Chen, M. Progress in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: SIRT family regulates mitochondrial biogenesis. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Digaleh, H.; Kiaei, M.; Khodagholi, F. Nrf2 and Nrf1 signaling and ER stress crosstalk: Implication for proteasomal degradation and autophagy. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2013, 70, 4681–4694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Li, Y.; Zhu, K.S.; Wang, H.; Zhu, W.G. Advances in cellular characterization of the sirtuin isoform, SIRT7. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuru, H.; Osaka, M.; Hiraoka, Y.; Yoshida, M. HFD-induced hepatic lipid accumulation and inflammation are decreased in Factor D deficient mouse. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hüttl, M.; Markova, I.; Miklankova, D.; Zapletalova, I.; Poruba, M.; Haluzik, M.; Vaněčkova, I.; Malinska, H. In a prediabetic model, empagliflozin improves hepatic lipid metabolism independently of obesity and before onset of hyperglycemia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mone, P.; Varzideh, F.; Jankauskas, S.S.; Pansini, A.; Lombardi, A.; Frullone, S.; Santulli, G. SGLT2 inhibition via empagliflozin improves endothelial function and reduces mitochondrial oxidative stress: Insights from frail hypertensive and diabetic patients. Hypertension 2022, 79, 1633–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasiri-Ansari, N.; Nikolopoulou, C.; Papoutsi, K.; Kyrou, I.; Mantzoros, C.S.; Kyriakopoulos, G.; Chatzigeorgiou, A.; Kalotychou, V.; Randeva, M.S.; Chatha, K.; et al. Empagliflozin Attenuates Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) in High Fat Diet Fed ApoE(-/-) Mice by Activating Autophagy and Reducing ER Stress and Apoptosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsuoka, F.; Motohashi, H.; Ishii, T.; Aburatani, H.; Engel, J.D.; Yamamoto, M. Genetic evidence that small maf proteins are essential for the activation of antioxidant response element-dependent genes. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 25, 8044–8051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinkova-Kostova, A.T.; Kostov, R.V.; Kazantsev, A.G. The role of Nrf2 signaling in counteracting neurodegenerative diseases. FEBS J. 2018, 285, 3576–3590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.M.; Maltagliati, A.J. Nrf2 at the heart of oxidative stress and cardiac protection. Physiol. Genom. 2018, 50, 77–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimta, A.-A.; Cenariu, D.; Irimie, A.; Magdo, L.; Nabavi, S.M.; Atanasov, A.G.; Berindan-Neagoe, I. The role of Nrf2 activity in cancer development and progression. Cancers 2019, 11, 1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Chen, L.; Leung, L.; Yen, T.S.; Lee, C.; Chan, J.Y. Liver-specific inactivation of the Nrf1 gene in adult mouse leads to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and hepatic neoplasia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 4120–4125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Feng, J.; Wang, M.; Wufuer, R.; Liu, K.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Nrf1 is an indispensable redox-determining factor for mitochondrial homeostasis by integrating multi-hierarchical regulatory networks. Redox Biol. 2022, 57, 102470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galehdar, Z.; Swan, P.; Fuerth, B.; Callaghan, S.M.; Park, D.S.; Cregan, S.P. Neuronal apoptosis induced by endoplasmic reticulum stress is regulated by ATF4-CHOP-mediated induction of the Bcl-2 homology 3-only member PUMA. J. Neurosci. 2010, 15, 16938–16948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Huang, A.; Tong, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, S.; Yu, X. Nobiletin protects against alcohol-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and liver injury by regulating the hepatic NRF1-TFAM signaling pathway. Redox Rep. 2024, 29, 2395779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gleyzer, N.; Vercauteren, K.; Scarpulla, R.C. Control of mitochondrial transcription specificity factors (TFB1M and TFB2M) by nuclear respiratory factors (NRF-1 and NRF-2) and PGC-1 family coactivators. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 25, 1354–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piantadosi, C.A.; Suliman, H.B. Mitochondrial transcription factor A induction by redox activation of nuclear respiratory factor 1. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, L.; Zhong, W.; Dong, H.; Guo, W.; Sun, X.; Zhang, W.; Yue, R.; Li, T.; Griffiths, A.; Ahmadi, A.R.; et al. ATF4 activation promotes hepatic mitochondrial dysfunction by repressing NRF1-TFAM signalling in alcoholic steatohepatitis. Gut 2021, 70, 1933–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Yi, W.; Tang, J.; Sun, Y.; Huang, J.; Lan, T.; Dai, X.; Xu, S.; Jin, Z.-G.; Wu, X. Urolithin A protects against acetaminophen-induced liver injury in mice via sustained activation of Nrf2. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 18, 2146–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, M.J.; Sabaj, M.; Tolosa, G.; Vielma, F.H.; Zúñiga, M.J.; González, D.R.; Zúñiga-Hernández, J. Maresin-1 prevents liver fibrosis by targeting Nrf2 and NF-κB, reducing oxidative stress and inflammation. Cells 2021, 10, 3406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Fu, X.; Zeng, L.; Hu, Y.; Gao, R.; Xian, S.; Liao, S.; Huang, J.; Yang, Y.; Liu, J.; et al. Activation of Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway exacerbates cholestatic liver injury. Commun. Biol. 2024, 7, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Ding, C.; Yu, T.; Liu, B.; Tang, W.; Wang, Z.; Tang, X.; Liang, G.; Peng, J.; Zhang, X.; et al. SIRT7 promotes Hippo/YAP activation and cancer cell proliferation in hepatocellular carcinoma via suppressing MST1. Cancer Sci. 2024, 115, 1209–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.; He, M.; Liu, Y.; Paredes, S.; Villanova, L.; Brown, K.; Qiu, X.; Nabavi, N.; Mohrin, M.; Wojnoonski, K.; et al. SIRT7 represses Myc activity to suppress ER stress and prevent fatty liver disease. Cell Rep. 2013, 5, 654–665, Erratum in: Cell Rep. 2013, 5, 1479. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2013.11.036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carli, F.; Della Pepa, G.; Sabatini, S.; Puig, A.V.; Gastaldelli, A. Lipid metabolism in MASLD and MASH: From mechanism to the clinic. JHEP Rep. 2024, 6, 101185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, G.; Kuang, Z.; Xu, Q.; Ye, T.; Li, X.; Qu, N.; Han, F.; Kan, C.; Sun, X. Empagliflozin activates Sestrin2-mediated AMPK/mTOR pathway and ameliorates lipid accumulation in obesity-related nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 944886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Gene | Primer Forward | Primer Reverse |
|---|---|---|
| Sod1 | GCTCCCAGCATTTCCAGTCT | TAACTGAAGGCCAGCATGGG |
| Sod2 | GCTTGATAGCCTCCAGCAAC | CCGAGGAGAAGTACCACGAG |
| Cat | GAGTGTCCGGGTAGGCAAAA | TTCGTCCCGAGTCTCTCCAT |
| GPx1 | TGTCGATGGTACGAAAGCGG | CAGTCCACCGTGTATGCCTT |
| Gadd153 | CAGGGTCAAGAGTAGTGAAGGT | CTGGAAGCCTGGTATGAGGAT |
| Xbp1 | ACAGGGTCCAACTTGTCCAG | TCCGCAGCACTCAGACTATG |
| Grp78 | CTTCATAGTCCTGCCCATTG | CGAAGGGATCATCTGCTATTAC |
| Nrf1 | AGGTGGTGACCTTGGAACAG | GGCTTTTTGGGACAGTGAAA |
| Nrf2 | TTCGTTAAAGGGGAGGGACT | GGAAAGGCACAGAGAGCATC |
| Sirt1 | TCCACGGTGCTGAGGTATAC | GCCACTGTCACTGTTACTGC |
| Sirt2 | AGCCAACCATCTGCCACTAC | CACTCGTTCCAGCGTGTCTA |
| Sirt3 | TTTCTTTCACAACCCCAAGC | TGGAGGAGCCTCAGGAAGTA |
| Sirt4 | CATCCAGCACATTGATTTCG | GTTGGGTTGGTGAGAGGAGA |
| Sirt5 | CCACCGACAGATTCAGGTTT | GGGCGGTTAAGAAGTCCTTT |
| Sirt6 | CCCAAGTTTGACACCACCTT | CTGACCAGGAAGCTGAGGAA |
| Sirt7 | GACTGAGCGTACTGCCCTTC | ACAATGGTATCCCGAAGCTG |
| Pparg | TTCAGAAGTGCCTTGCTGTG | CCAACAGCTTCTCCTTCTCG |
| Ppara | CGAGGTGAAAGATTCGGAAA | GGCCTTGACCTTGTTCATGT |
| Srebf | GCTGTTGGCATCCTGCTATC | AGCTGGAAGTGACGGTGGT |
| Cpt2 | GGATTTTGAGAACGGCATTGG | TCATCACGACTGGGTTTGGGT |
| Ehhadh | CTGGCTATGATCCGCCTCTG | CTGCGGGGTTCTATGGGTTT |
| Scd1 | CACACGCCGACCCTCACAAT | TTTGACAGCCGGGTGTTTGC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Heo, Y.J.; Park, J.; Lee, N.; Choi, S.-E.; Jeon, J.Y.; Han, S.J.; Kim, D.J.; Lee, K.W.; Kim, H.J. Empagliflozin Alleviates Hepatic Steatosis and Oxidative Stress via the NRF1 Pathway in High-Fat Diet-Induced Mouse Model of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4054. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094054
Heo YJ, Park J, Lee N, Choi S-E, Jeon JY, Han SJ, Kim DJ, Lee KW, Kim HJ. Empagliflozin Alleviates Hepatic Steatosis and Oxidative Stress via the NRF1 Pathway in High-Fat Diet-Induced Mouse Model of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(9):4054. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094054
Chicago/Turabian StyleHeo, Yu Jung, Jieun Park, Nami Lee, Sung-E Choi, Ja Young Jeon, Seung Jin Han, Dae Jung Kim, Kwan Woo Lee, and Hae Jin Kim. 2025. "Empagliflozin Alleviates Hepatic Steatosis and Oxidative Stress via the NRF1 Pathway in High-Fat Diet-Induced Mouse Model of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 9: 4054. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094054
APA StyleHeo, Y. J., Park, J., Lee, N., Choi, S.-E., Jeon, J. Y., Han, S. J., Kim, D. J., Lee, K. W., & Kim, H. J. (2025). Empagliflozin Alleviates Hepatic Steatosis and Oxidative Stress via the NRF1 Pathway in High-Fat Diet-Induced Mouse Model of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(9), 4054. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094054






