GTPLM-GO: Enhancing Protein Function Prediction Through Dual-Branch Graph Transformer and Protein Language Model Fusing Sequence and Local–Global PPI Information
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- We propose a novel protein function prediction method, GTPLM-GO, which effectively utilizes the functional semantic encoding of sequences, as well as local and global information of PPI networks. GTPLM-GO enhances protein function prediction accuracy by leveraging the complementarity of this information.
- We develop a dual-branch Graph Transformer that integrates both local and global information from PPI networks. The local information is extracted using a two-layer GCN branch, while the global information is captured through a linear attention-based Transformer encoder. This design effectively mitigates the over-smoothing problem commonly found in traditional graph networks and achieves collaborative modeling of local and global information.
- Experimental results on PPI network datasets of varying scales show that GTPLM-GO outperforms advanced network-based and sequence-based methods. This confirms its ability to extract valuable information from PPI networks and validate information complementation. Furthermore, GTPLM-GO exhibits notable advantages in species-specific protein function prediction, indicating its good generalization capabilities.
2. Results
2.1. Experimental Setup
2.2. Evaluation Metrics
2.3. Comparison with Advanced Methods on PPI Networks of Varying Scales
2.4. Generalization on Proteins Within the PPI Network
2.5. Generalization on Specific Species
2.6. Ablation Studies
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Datasets
3.2. Methods
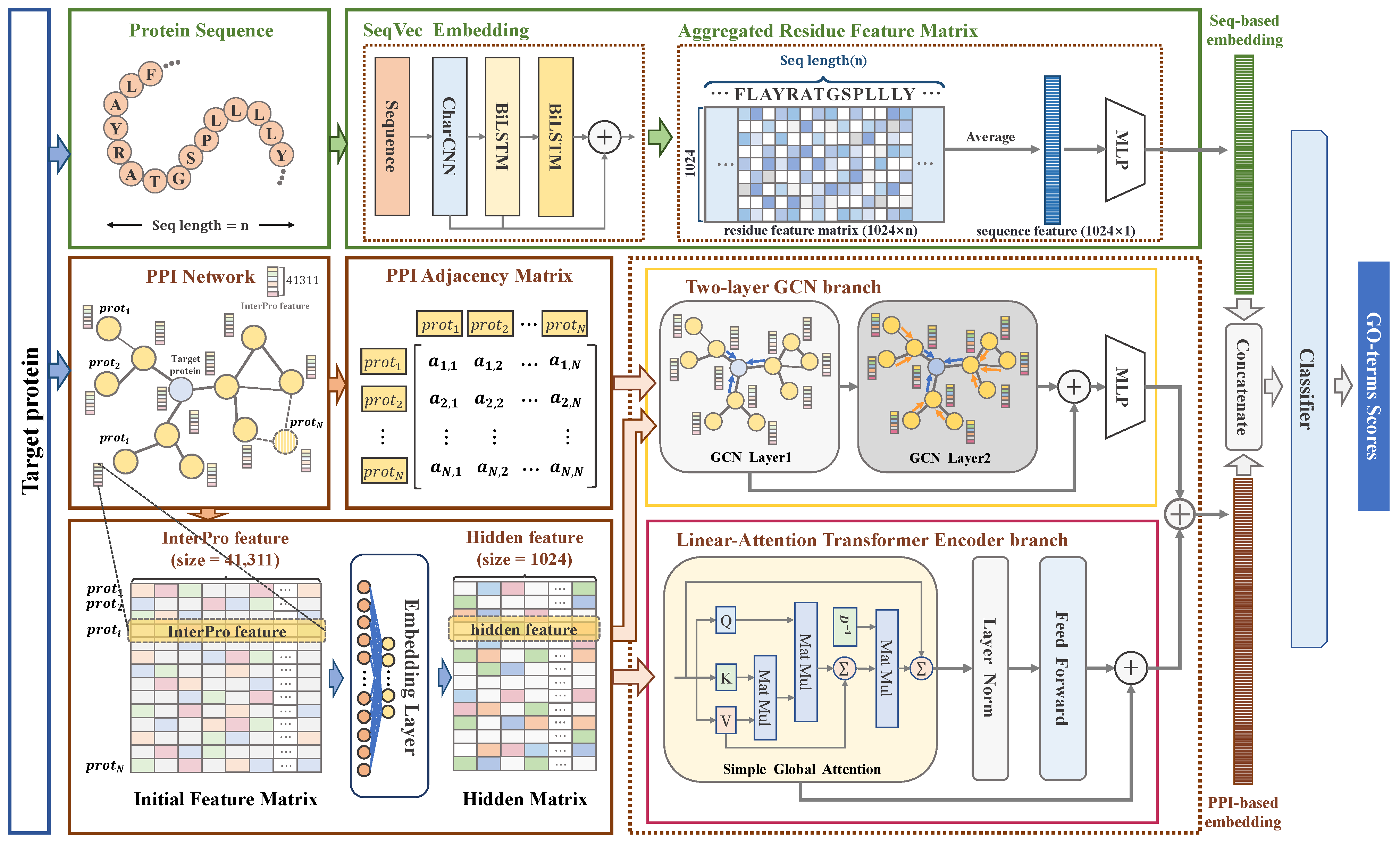
3.2.1. Overview
3.2.2. Linear Attention-Based Transformer Encoder for Extracting Global PPI Information
3.2.3. Two-Layer GCN for Extracting Local PPI Information
3.2.4. Generating Functional Semantic Encoding Through Protein Language Model
3.2.5. Protein Function Classifier Based on Sequence and Local–Global PPI Information
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eisenberg, D.; Marcotte, E.M.; Xenarios, I.; Yeates, T.O. Protein function in the post-genomic era. Nature 2000, 405, 823–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashburner, M.; Ball, C.A.; Blake, J.A.; Botstein, D.; Butler, H.; Cherry, J.M.; Davis, A.P.; Dolinski, K.; Dwight, S.S.; Eppig, J.T.; et al. Gene ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. Nat. Genet. 2000, 25, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boutet, E.; Lieberherr, D.; Tognolli, M.; Schneider, M.; Bairoch, A. UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot: The manually annotated section of the UniProt KnowledgeBase. In Plant bioinformatics: Methods and protocols; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2007; pp. 89–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The UniProt Consortium. UniProt: The Universal Protein Knowledgebase in 2023. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 51, D523–D531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanzo, M.; VanderSluis, B.; Koch, E.N.; Baryshnikova, A.; Pons, C.; Tan, G.; Wang, W.; Usaj, M.; Hanchard, J.; Lee, S.D.; et al. A global genetic interaction network maps a wiring diagram of cellular function. Science 2016, 353, aaf1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radivojac, P.; Clark, W.T.; Oron, T.R.; Schnoes, A.M.; Wittkop, T.; Sokolov, A.; Graim, K.; Funk, C.; Verspoor, K.; Ben-Hur, A.; et al. A large-scale evaluation of computational protein function prediction. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, N.; Jiang, Y.; Bergquist, T.R.; Lee, A.J.; Kacsoh, B.Z.; Crocker, A.W.; Lewis, K.A.; Georghiou, G.; Nguyen, H.N.; Hamid, M.N.; et al. The CAFA challenge reports improved protein function prediction and new functional annotations for hundreds of genes through experimental screens. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Madden, T.L.; Schäffer, A.A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Miller, W.; Lipman, D.J. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 3389–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conesa, A.; Götz, S.; García-Gómez, J.M.; Terol, J.; Talón, M.; Robles, M. Blast2GO: A universal tool for annotation, visualization and analysis in functional genomics research. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 3674–3676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Xie, J.; Xie, J.; Zhao, H.; Yang, Y. Fast and accurate protein function prediction from sequence through pretrained language model and homology-based label diffusion. Briefings Bioinform. 2023, 24, bbad117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulmanov, M.; Khan, M.A.; Hoehndorf, R. DeepGO: Predicting protein functions from sequence and interactions using a deep ontology-aware classifier. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 660–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulmanov, M.; Hoehndorf, R. DeepGOPlus: Improved protein function prediction from sequence. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Shen, Y. TALE: Transformer-based protein function Annotation with joint sequence–Label Embedding. Bioinformatics 2021, 37, 2825–2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; pp. 6000–6010. [Google Scholar]
- Heinzinger, M.; Elnaggar, A.; Wang, Y.; Dallago, C.; Nechaev, D.; Matthes, F.; Rost, B. Modeling aspects of the language of life through transfer-learning protein sequences. BMC Bioinform. 2019, 20, 723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elnaggar, A.; Heinzinger, M.; Dallago, C.; Rehawi, G.; Wang, Y.; Jones, L.; Gibbs, T.; Feher, T.; Angerer, C.; Steinegger, M.; et al. Prottrans: Toward understanding the language of life through self-supervised learning. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 44, 7112–7127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rives, A.; Meier, J.; Sercu, T.; Goyal, S.; Lin, Z.; Liu, J.; Guo, D.; Ott, M.; Zitnick, C.L.; Ma, J.; et al. Biological structure and function emerge from scaling unsupervised learning to 250 million protein sequences. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2016239118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, M.; Neumann, M.; Iyyer, M.; Gardner, M.; Zettlemoyer, L. Deep Contextualized Word Representations. In Proceedings of the 2018 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, New Orleans, LA, USA, 1–6 June 2018; Volume 1 (Long Papers). Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2018; pp. 2227–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. Bert: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. In Proceedings of the 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2–7 June 2019; Volume 1 (Long and Short Papers). Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2019; pp. 4171–4186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Luo, X.; Liu, Y.; Jin, X. A comprehensive review and comparison of existing computational methods for protein function prediction. Briefings Bioinform. 2024, 25, bbae289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Nastou, K.; Koutrouli, M.; Kirsch, R.; Mehryary, F.; Hachilif, R.; Hu, D.; Peluso, M.E.; Huang, Q.; Fang, T.; et al. The STRING database in 2025: Protein networks with directionality of regulation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025, 53, D730–D737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spirin, V.; Mirny, L.A. Protein complexes and functional modules in molecular networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 12123–12128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A. Protein Interaction Networks: Computational Analysis; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, P.; Wang, X.; Pei, J.; Zhu, W. A survey on network embedding. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2018, 31, 833–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perozzi, B.; Al-Rfou, R.; Skiena, S. Deepwalk: Online learning of social representations. In Proceedings of the 20th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, New York, NY, USA, 24–27 August 2014; pp. 701–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikolov, T.; Sutskever, I.; Chen, K.; Corrado, G.S.; Dean, J. Distributed representations of words and phrases and their compositionality. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2013, 3111–3119. [Google Scholar]
- Alshahrani, M.; Khan, M.A.; Maddouri, O.; Kinjo, A.R.; Queralt-Rosinach, N.; Hoehndorf, R. Neuro-symbolic representation learning on biological knowledge graphs. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 2723–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gligorijević, V.; Barot, M.; Bonneau, R. deepNF: Deep network fusion for protein function prediction. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 3873–3881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Pan, S.; Chen, F.; Long, G.; Zhang, C.; Philip, S.Y. A comprehensive survey on graph neural networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2020, 32, 4–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.; Lv, H.; Guo, Y.; Peng, W.; Liu, B. sAMPpred-GAT: Prediction of antimicrobial peptide by graph attention network and predicted peptide structure. Bioinformatics 2022, 39, btac715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, R.; Yao, S.; Mamitsuka, H.; Zhu, S. DeepGraphGO: Graph neural network for large-scale, multispecies protein function prediction. Bioinformatics 2021, 37, i262–i271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kipf, T.N.; Welling, M. Semi-supervised classification with graph convolutional networks. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1609.02907. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Guo, H.; Zhang, F.; Wang, X.; Wu, K.; Qiu, S.; Liu, B.; Wang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Li, J. HNetGO: Protein function prediction via heterogeneous network transformer. Briefings Bioinform. 2023, 24, bbab556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Han, Z.; Wu, X.M. Deeper insights into graph convolutional networks for semi-supervised learning. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 2018, 32, 3438–3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Lin, Y.; Li, W.; Li, P.; Zhou, J.; Sun, X. Measuring and relieving the over-smoothing problem for graph neural networks from the topological view. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 2020, 34, 3438–3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, C.; Cai, T.; Luo, S.; Zheng, S.; Ke, G.; He, D.; Shen, Y.; Liu, T.Y. Do transformers really perform badly for graph representation? Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 28877–28888. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Q.; Zhao, W.; Li, Z.; Wipf, D.; Yan, J. NodeFormer: A Scalable Graph Structure Learning Transformer for Node Classification. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), New Orleans, LA, USA, 28 November–9 December 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Q.; Yang, C.; Zhao, W.; He, Y.; Wipf, D.; Yan, J. DIFFormer: Scalable (Graph) Transformers Induced by Energy Constrained Diffusion. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), Kigali, Rwanda, 1–5 May 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Q.; Zhao, W.; Yang, C.; Zhang, H.; Nie, F.; Jiang, H.; Bian, Y.; Yan, J. SGFormer: Simplifying and Empowering Transformers for Large-Graph Representations. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), New Orleans, LA, USA, 10–16 December 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Guo, M.; Jin, X.; Chen, J.; Liu, B. CFAGO: Cross-fusion of network and attributes based on attention mechanism for protein function prediction. Bioinformatics 2023, 39, btad123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Batra, D.; Parikh, D.; Lee, S. ViLBERT: Pretraining Task-Agnostic Visiolinguistic Representations for Vision-and-Language Tasks. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Curran Associates, Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2019; Volume 32. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Z.; Huang, W.; Gu, S.; Xie, L.; Wang, Y.; Jiao, J.; Ye, Q. Conformer: Local features coupling global representations for visual recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 367–376. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, P.; Wang, B.; Wang, X.; Liu, B.; Wang, Y.; Li, J. Struct2GO: Protein function prediction based on graph pooling algorithm and AlphaFold2 structure information. Bioinformatics 2023, 39, btad637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Shuai, Y.; Li, Y.; Zeng, M.; Li, M. Enhancing Protein Function Prediction Through the Fusion of Multi-Type Biological Knowledge With Protein Language Model and Graph Neural Network. IEEE Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2025, 22, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Gligorijević, V.; Renfrew, P.D.; Kosciolek, T.; Leman, J.K.; Berenberg, D.; Vatanen, T.; Chandler, C.; Taylor, B.C.; Fisk, I.M.; Vlamakis, H.; et al. Structure-based protein function prediction using graph convolutional networks. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, R.; Zhang, Z.; Xiong, Y.; Sun, F.; Mamitsuka, H.; Zhu, S. GOLabeler: Improving sequence-based large-scale protein function prediction by learning to rank. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 2465–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, R.; Yao, S.; Xiong, Y.; Huang, X.; Sun, F.; Mamitsuka, H.; Zhu, S. NetGO: Improving large-scale protein function prediction with massive network information. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W379–W387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verkuil, R.; Kabeli, O.; Du, Y.; Wicky, B.I.; Milles, L.F.; Dauparas, J.; Baker, D.; Ovchinnikov, S.; Sercu, T.; Rives, A. Language models generalize beyond natural proteins. BioRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Gable, A.L.; Nastou, K.C.; Lyon, D.; Kirsch, R.; Pyysalo, S.; Doncheva, N.T.; Legeay, M.; Fang, T.; Bork, P.; et al. The STRING database in 2021: Customizable protein–protein networks, and functional characterization of user-uploaded gene/measurement sets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 49, D605–D612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Gable, A.L.; Lyon, D.; Junge, A.; Wyder, S.; Huerta-Cepas, J.; Simonovic, M.; Doncheva, N.T.; Morris, J.H.; Bork, P.; et al. STRING v11: Protein–protein association networks with increased coverage, supporting functional discovery in genome-wide experimental datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D607–D613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huntley, R.P.; Sawford, T.; Mutowo-Meullenet, P.; Shypitsyna, A.; Bonilla, C.; Martin, M.J.; O’Donovan, C. The GOA database: Gene ontology annotation updates for 2015. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D1057–D1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, A.L.; Attwood, T.K.; Babbitt, P.C.; Blum, M.; Bork, P.; Bridge, A.; Brown, S.D.; Chang, H.Y.; El-Gebali, S.; Fraser, M.I.; et al. InterPro in 2019: Improving coverage, classification and access to protein sequence annotations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D351–D360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, P.; Binns, D.; Chang, H.Y.; Fraser, M.; Li, W.; McAnulla, C.; McWilliam, H.; Maslen, J.; Mitchell, A.; Nuka, G.; et al. InterProScan 5: Genome-scale protein function classification. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1236–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, W.; Ohue, M. SpatialPPIv2: Enhancing protein–protein interaction prediction through graph neural networks with protein language models. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2025, 27, 508–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holm, L.; Sander, C. Mapping the protein universe. Science 1996, 273, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krissinel, E. On the relationship between sequence and structure similarities in proteomics. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 717–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O.; Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Bates, R.; Žídek, A.; Potapenko, A.; et al. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

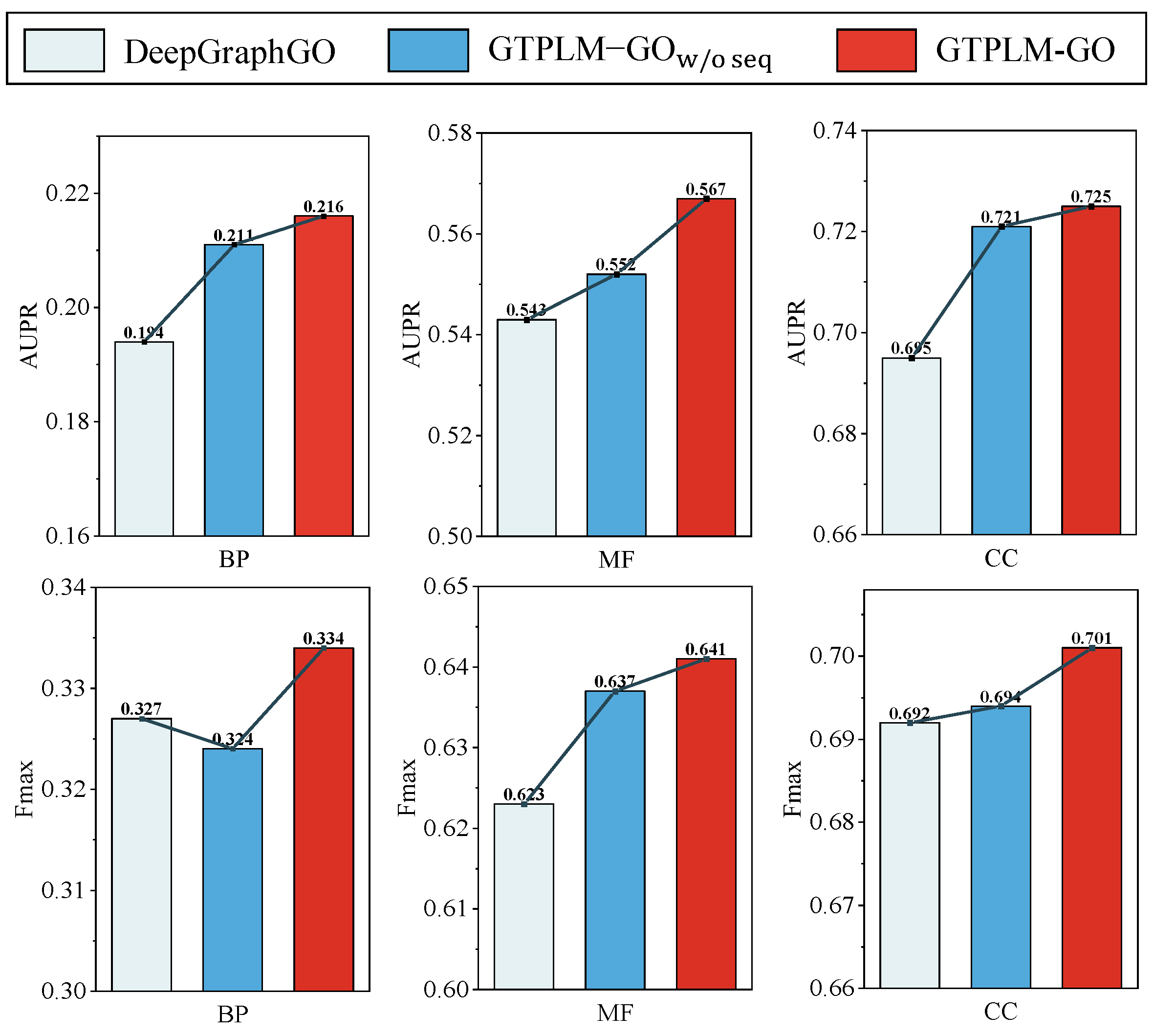

| Method | Fmax | AUPR | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MFO | BPO | CCO | MFO | BPO | CCO | |
| BLAST-KNN 1 [48] | 0.590 | 0.274 | 0.650 | 0.455 | 0.113 | 0.570 |
| LR-InterPro 1 [48] | 0.617 | 0.278 | 0.661 | 0.530 | 0.144 | 0.672 |
| Net-KNN 1 [49] | 0.426 | 0.305 | 0.667 | 0.276 | 0.157 | 0.641 |
| DeepGOCNN 1 [13] | 0.434 | 0.248 | 0.632 | 0.306 | 0.101 | 0.573 |
| DeepGOPlus 2 [13] | 0.593 | 0.290 | 0.672 | 0.398 | 0.108 | 0.595 |
| DeepGraphGO 1 [32] | 0.623 | 0.327 | 0.692 | 0.543 | 0.194 | 0.695 |
| GTPLM-GO 2 | 0.641 | 0.334 | 0.701 | 0.567 | 0.216 | 0.725 |
| Method | AUPR | Fmax | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MFO | BPO | CCO | MFO | BPO | CCO | |
| STRING | ||||||
| BLAST-KNN 1 [48] | 0.466 | 0.122 | 0.438 | 0.608 | 0.291 | 0.570 |
| LR-InterPro 1 [48] | 0.562 | 0.162 | 0.598 | 0.630 | 0.293 | 0.627 |
| Net-KNN 1 [49] | 0.297 | 0.177 | 0.607 | 0.443 | 0.314 | 0.617 |
| DeepGOCNN 1 [13] | 0.173 | 0.036 | 0.136 | 0.432 | 0.258 | 0.588 |
| DeepGOPlus 2 [13] | 0.423 | 0.118 | 0.489 | 0.602 | 0.306 | 0.617 |
| DeepGraphGO 1 [32] | 0.582 | 0.209 | 0.663 | 0.642 | 0.348 | 0.665 |
| GTPLM-GO 2 | 0.607 | 0.245 | 0.662 | 0.653 | 0.350 | 0.655 |
| HOMO | ||||||
| BLAST-KNN 1 [48] | 0.456 | 0.104 | 0.652 | 0.583 | 0.248 | 0.704 |
| LR-InterPro 1 [48] | 0.501 | 0.114 | 0.720 | 0.602 | 0.256 | 0.689 |
| Net-KNN 1 [49] | 0.253 | 0.128 | 0.675 | 0.422 | 0.300 | 0.709 |
| DeepGOCNN 1 [13] | 0.349 | 0.088 | 0.613 | 0.456 | 0.231 | 0.662 |
| DeepGOPlus 2 [13] | 0.438 | 0.100 | 0.656 | 0.582 | 0.257 | 0.710 |
| DeepGraphGO 1 [32] | 0.475 | 0.157 | 0.736 | 0.619 | 0.306 | 0.726 |
| GTPLM-GO 2 | 0.517 | 0.192 | 0.781 | 0.641 | 0.323 | 0.738 |
| Method | AUPR | Fmax | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MFO | BPO | CCO | MFO | BPO | CCO | |
| HUMAN | ||||||
| BLAST-KNN 1 [48] | 0.296 | 0.074 | 0.384 | 0.471 | 0.241 | 0.555 |
| LR-InterPro 1 [48] | 0.496 | 0.138 | 0.603 | 0.593 | 0.282 | 0.650 |
| Net-KNN 1 [49] | 0.358 | 0.143 | 0.620 | 0.485 | 0.261 | 0.615 |
| DeepGOCNN 1 [13] | 0.327 | 0.114 | 0.552 | 0.468 | 0.263 | 0.594 |
| DeepGOPlus 2 [13] | 0.246 | 0.088 | 0.479 | 0.501 | 0.277 | 0.625 |
| DeepGraphGO 1 [32] | 0.520 | 0.178 | 0.642 | 0.633 | 0.320 | 0.655 |
| GTPLM-GO 2 | 0.471 | 0.185 | 0.777 | 0.588 | 0.327 | 0.732 |
| MOUSE | ||||||
| BLAST-KNN 1 [48] | 0.593 | 0.105 | 0.441 | 0.681 | 0.289 | 0.593 |
| LR-InterPro 1 [48] | 0.625 | 0.175 | 0.569 | 0.628 | 0.312 | 0.592 |
| Net-KNN 1 [49] | 0.319 | 0.167 | 0.569 | 0.420 | 0.302 | 0.588 |
| DeepGOCNN 1 [13] | 0.405 | 0.129 | 0.495 | 0.475 | 0.258 | 0.574 |
| DeepGOPlus 2 [13] | 0.550 | 0.132 | 0.488 | 0.634 | 0.306 | 0.598 |
| DeepGraphGO 1 [32] | 0.651 | 0.201 | 0.634 | 0.650 | 0.329 | 0.638 |
| GTPLM-GO 2 | 0.653 | 0.203 | 0.679 | 0.701 | 0.334 | 0.682 |
| Method | Fmax | AUPR | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MFO | BPO | CCO | MFO | BPO | CCO | |
| 0.573 | 0.263 | 0.676 | 0.485 | 0.139 | 0.689 | |
| 0.637 | 0.324 | 0.694 | 0.552 | 0.211 | 0.721 | |
| GTPLM-GO | 0.641 | 0.334 | 0.701 | 0.567 | 0.216 | 0.725 |
| Variant | Protein Language Model (pLM) | Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| GTPLM-GO | SeqVec | 93 M |
| ProtBert | 420 M | |
| esm1b_t33_650M_UR50S | 650 M | |
| esm2_t33_650M_UR50D | 650 M | |
| ProtT5-XL-UniRef50 | 3B |
| Train | Valid | Test | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MFO | BPO | CCO | MFO | BPO | CCO | MFO | BPO | CCO | |
| All Data | 51,549 | 85,104 | 76,098 | 490 | 1570 | 923 | 426 | 925 | 1224 |
| Data used by GTPLM-GO | 35,092 | 54,276 | 48,093 | 490 | 1570 | 923 | 426 | 925 | 1224 |
| HUMAN (9606) | 9208 | 12,095 | 18,842 | 86 | 138 | 137 | 41 | 87 | 767 |
| MOUSE (10090) | 6138 | 9927 | 8482 | 103 | 299 | 228 | 65 | 156 | 130 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Y.; Luo, X.; Liu, Y.; Chen, B.; Jin, X.; Zhu, D. GTPLM-GO: Enhancing Protein Function Prediction Through Dual-Branch Graph Transformer and Protein Language Model Fusing Sequence and Local–Global PPI Information. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4088. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094088
Zhang H, Sun Y, Wang Y, Luo X, Liu Y, Chen B, Jin X, Zhu D. GTPLM-GO: Enhancing Protein Function Prediction Through Dual-Branch Graph Transformer and Protein Language Model Fusing Sequence and Local–Global PPI Information. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(9):4088. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094088
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Haotian, Yundong Sun, Yansong Wang, Xiaoling Luo, Yumeng Liu, Bin Chen, Xiaopeng Jin, and Dongjie Zhu. 2025. "GTPLM-GO: Enhancing Protein Function Prediction Through Dual-Branch Graph Transformer and Protein Language Model Fusing Sequence and Local–Global PPI Information" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 9: 4088. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094088
APA StyleZhang, H., Sun, Y., Wang, Y., Luo, X., Liu, Y., Chen, B., Jin, X., & Zhu, D. (2025). GTPLM-GO: Enhancing Protein Function Prediction Through Dual-Branch Graph Transformer and Protein Language Model Fusing Sequence and Local–Global PPI Information. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(9), 4088. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094088





