Mitigation of PFOA-Induced Developmental Toxicity in Danio rerio by Bacillus subtilis var. natto: Focus on Growth and Ossification
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
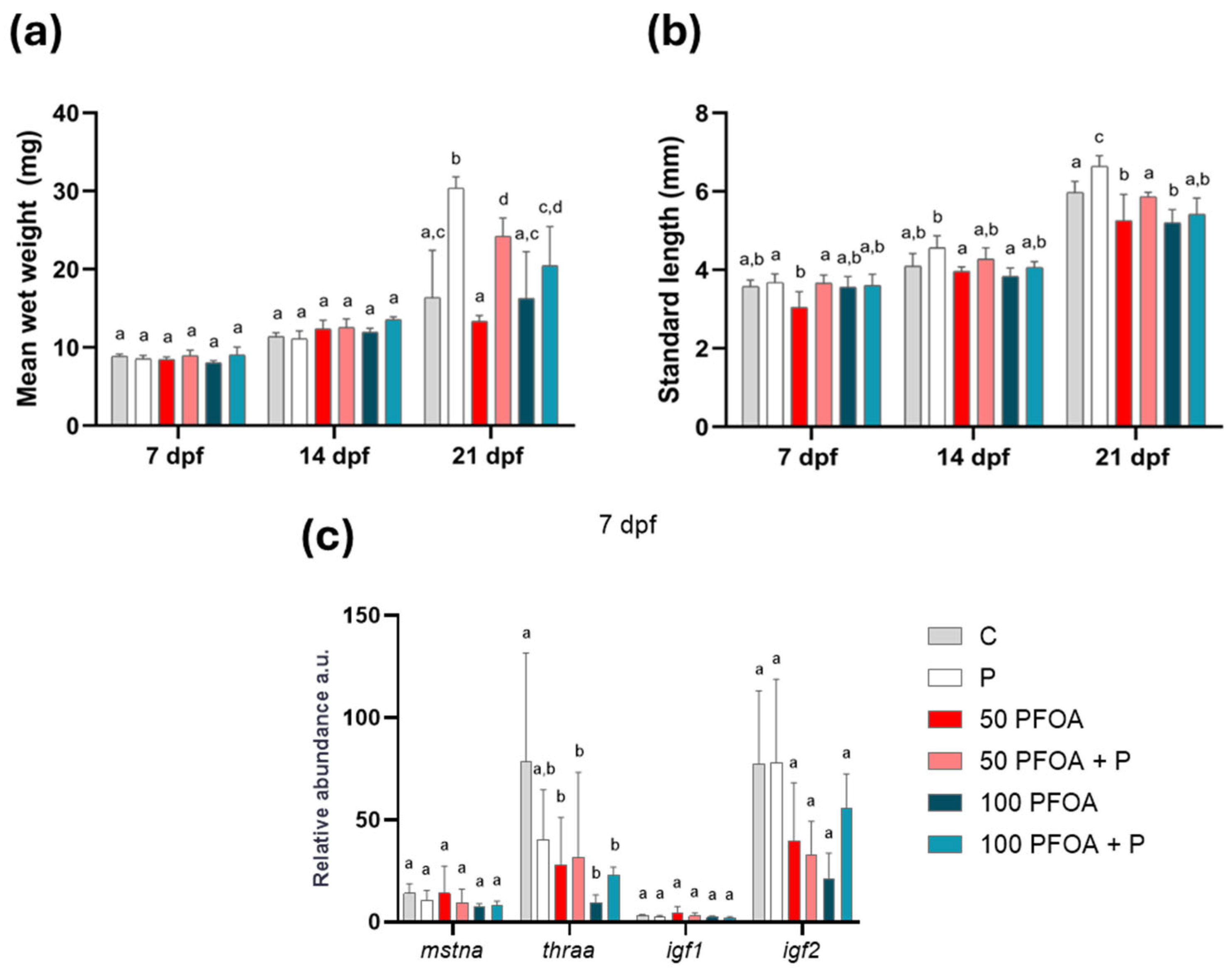
2.1. Impact of PFOA Exposure and Probiotic Treatment on Zebrafish Growth
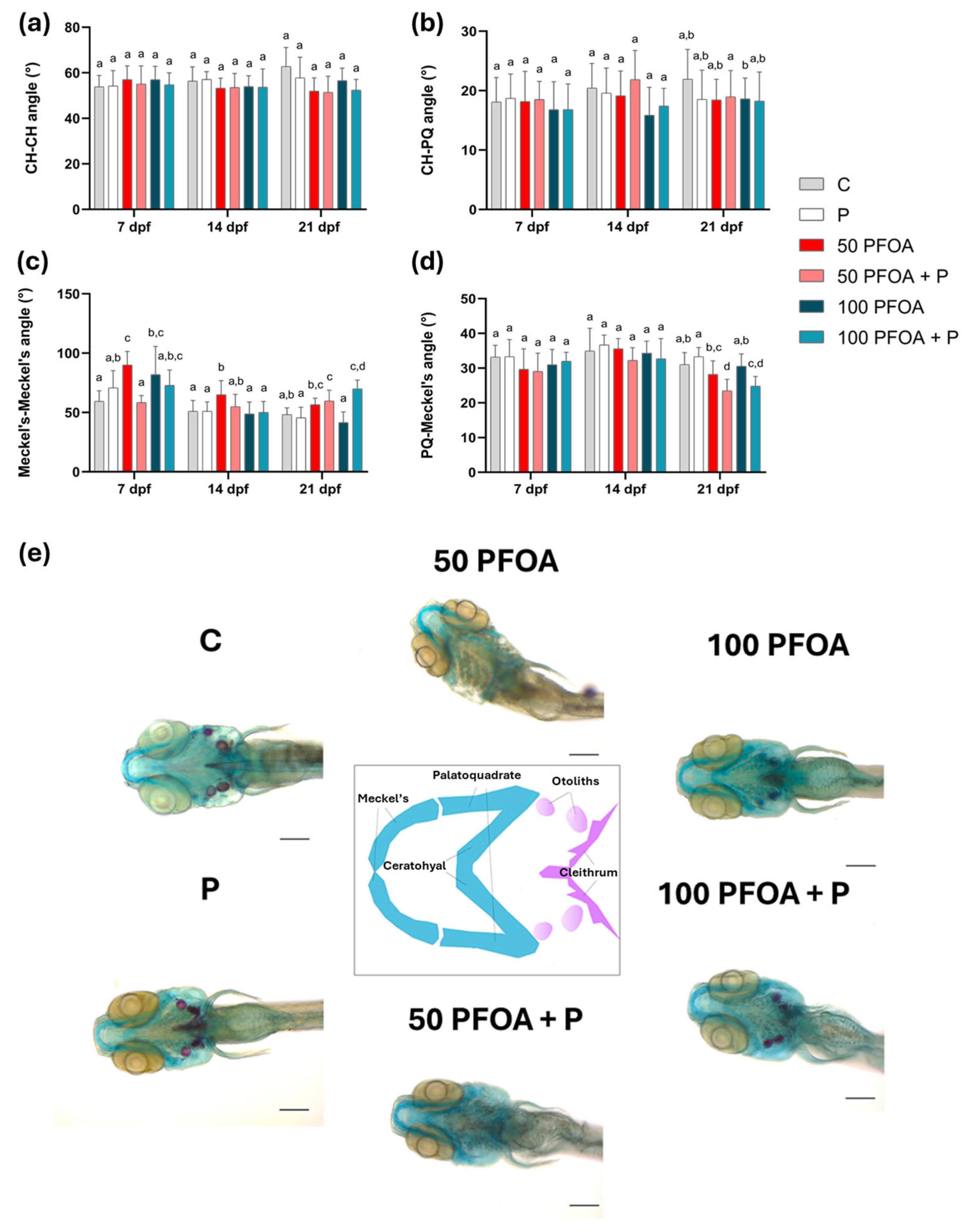
2.2. Effects of PFOA Exposure and Probiotic Treatments on Zebrafish Larval Morphology
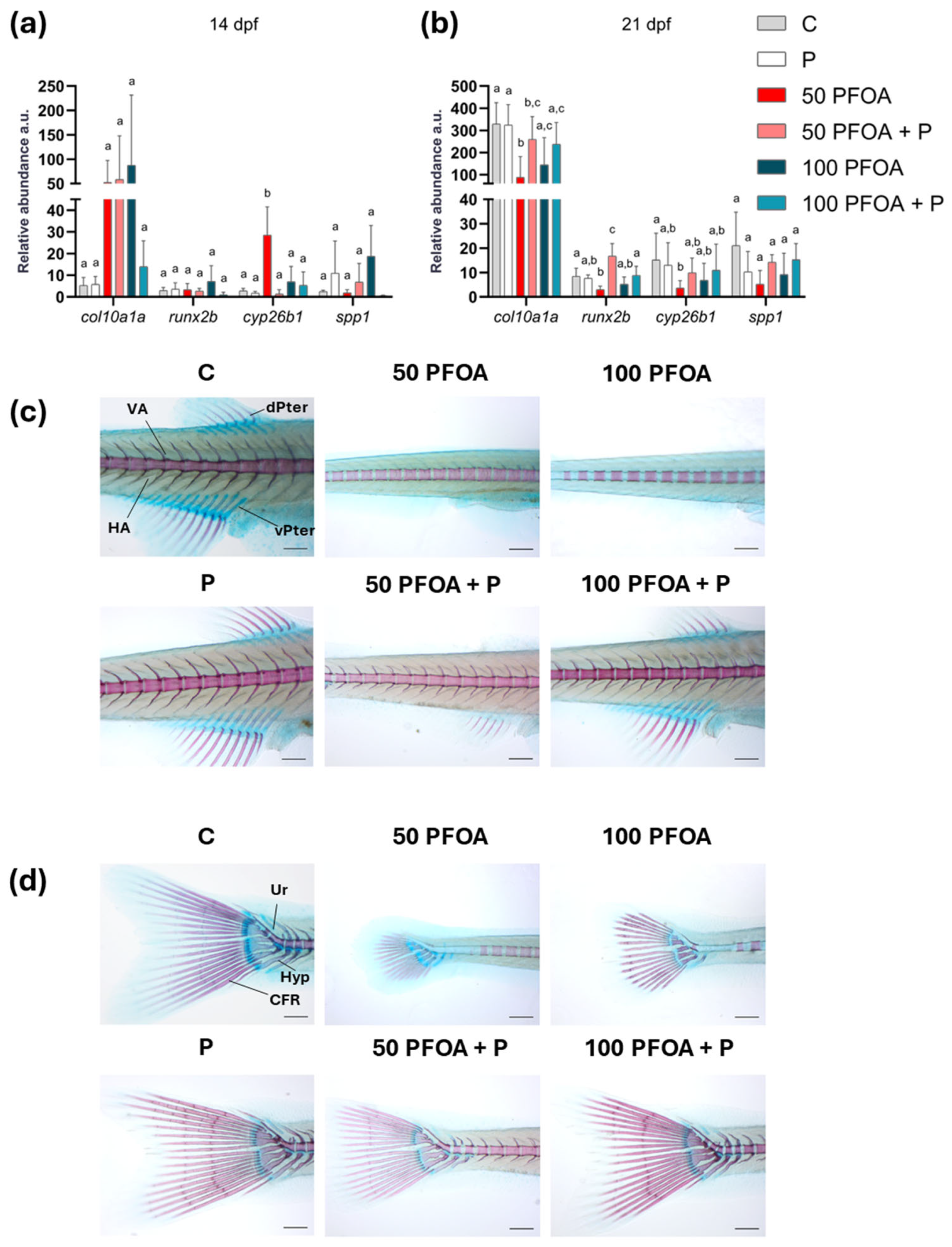
2.3. Effects of PFOA Exposure and Probiotic Treatment on Zebrafish Larval Ossification
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Zebrafish Husbandry and Treatment
4.2. Biometric Evaluation
4.3. Alcian Blue and Alizarin Red Staining
4.4. Morphological Studies
4.5. Gene Expression Analysis
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- PFOA. Available online: https://chm.pops.int/Implementation/Alternatives/AlternativestoPOPs/ChemicalslistedinAnnexA/PFOA/tabid/8292/Default.aspx?utm (accessed on 7 February 2025).
- Sostanze Per-e Polifluoroalchiliche (PFAS)—ECHA. Available online: https://echa.europa.eu/hot-topics/perfluoroalkyl-chemicals-pfas (accessed on 7 February 2025).
- Jantzen, C.E.; Toor, F.; Annunziato, K.A.; Cooper, K.R. Effects of chronic perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) at low concentration on morphometrics, gene expression, and fecundity in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Reprod. Toxicol. 2017, 69, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Shi, G.; Yao, J.; Sheng, N.; Cui, R.; Su, Z.; Guo, Y.; Dai, J. Perfluoropolyether carboxylic acids (novel alternatives to PFOA) impair zebrafish posterior swim bladder development via thyroid hormone disruption. Environ. Int. 2020, 134, 105317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gui, W.; Guo, H.; Wang, C.; Li, M.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, K.; Dai, J.; Zhao, Y. Comparative developmental toxicities of zebrafish towards structurally diverse per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 902, 166569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rericha, Y.; Simonich, M.T.; Truong, L.; Tanguay, R.L. Review of the zebrafish as a model to investigate per- and polyfluoroalkyl substance toxicity. Toxicol. Sci. 2023, 194, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, K.; Mao, W.; Fan, Z.; Liu, T.; Hong, R.; Chen, H.; Pan, C. Emerging perfluoroalkyl substances retard skeletal growth by accelerating osteoblasts senescence via ferroptosis. Environ. Res. 2024, 258, 119483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan Bassett, J.H.; Williams, G.R. Role of Thyroid Hormones in Skeletal Development and Bone Maintenance. Endocr. Rev. 2016, 37, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Pang, Y.; Xu, J.; Chen, X.; Zhang, C.; Wu, B.; Gao, J. Endocrine Regulation on Bone by Thyroid. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 873820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Chen, C.; Zhou, G.; Cai, Z.; Man, Q.; Liu, B.; Wang, W.C. Perfluorooctanoic acid disrupts thyroid-specific genes expression and regulation via the TSH-TSHR signaling pathway in thyroid cells. Environ. Res. 2023, 239, 117372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Chen, K.; Li, W.; Chai, Y.; Zhu, J.; Chu, B.; Li, N.; Yan, J.; Zhang, S.; Yang, Y. Varied thyroid disrupting effects of perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and its novel alternatives hexafluoropropylene-oxide-dimer-acid (GenX) and ammonium 4,8-dioxa-3H-perfluorononanoate (ADONA) in vitro. Environ. Int. 2021, 156, 106745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, K.; Fiedler, I.A.K.; Kurzyukova, A.; López-Delgado, A.C.; McGowan, L.M.; Geurtzen, K.; Hammond, C.L.; Busse, B.; Knopf, F. Skeletal Biology and Disease Modeling in Zebrafish. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2021, 36, 436–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Pabic, P.; Dranow, D.B.; Hoyle, D.J.; Schilling, T.F. Zebrafish endochondral growth zones as they relate to human bone size, shape and disease. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1060187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergen, D.J.M.; Kague, E.; Hammond, C.L. Zebrafish as an Emerging Model for Osteoporosis: A Primary Testing Platform for Screening New Osteo-Active Compounds. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masiero, C.; Aresi, C.; Forlino, A.; Tonelli, F. Zebrafish Models for Skeletal and Extraskeletal Osteogenesis Imperfecta Features: Unveiling Pathophysiology and Paving the Way for Drug Discovery. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2024, 115, 931–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veldman, M.B.; Lin, S. Zebrafish as a Developmental Model Organism for Pediatric Research. Pediatr. Res. 2008, 64, 470–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonelli, F.; Bek, J.W.; Besio, R.; De Clercq, A.; Leoni, L.; Salmon, P.; Coucke, P.J.; Willaert, A.; Forlino, A. Zebrafish: A Resourceful Vertebrate Model to Investigate Skeletal Disorders. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heubel, B.P.; Bredesen, C.A.; Schilling, T.F.; Le Pabic, P. Endochondral growth zone pattern and activity in the zebrafish pharyngeal skeleton. Dev. Dyn. 2021, 250, 74–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, R.; Antony, M.; Nivelle, R.; Lavergne, A.; Zappia, J.; Guerrero-Limón, G.; Caetano da Silva, C.; Kumari, P.; Sojan, J.M.; Degueldre, C.; et al. The Osteoblast Transcriptome in Developing Zebrafish Reveals Key Roles for Extracellular Matrix Proteins Col10a1a and Fbln1 in Skeletal Development and Homeostasis. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, C.H.; Wan, S.M.; Chen, Y.L.; Huysseune, A.; Wu, Y.M.; Zhou, J.J.; Hilsdorf, A.W.S.; Wang, W.M.; Witten, P.E.; Lin, Q.; et al. Single-cell transcriptomes and runx2b−/− mutants reveal the genetic signatures of intermuscular bone formation in zebrafish. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2022, 9, nwac152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galea, G.L.; Zein, M.R.; Allen, S.; Francis-West, P. Making and shaping endochondral and intramembranous bones. Dev. Dyn. 2020, 250, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spoorendonk, K.M.; Peterson-Maduro, J.; Renn, J.; Trowe, T.; Kranenbarg, S.; Winkler, C.; Schulte-Merker, S. Retinoic acid and Cyp26b1 are critical regulators of osteogenesis in the axial skeleton. Development 2008, 135, 3765–3774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira, K.C.; Fonseca, I.C.; Oborn, C.; Wengryn, P.; Ghafoor, S.; Beke, A.; Dreseris, E.S.; Wong, C.; Iacovone, A.; Soltys, C.L.; et al. CYP26B1-related disorder: Expanding the ends of the spectrum through clinical and molecular evidence. Hum. Genet. 2023, 142, 1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maclean, G.; Dollé, P.; Petkovich, M. Genetic disruption of CYP26B1 severely affects development of neural crest derived head structures, but does not compromise hindbrain patterning. Dev. Dyn. 2009, 238, 732–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laue, K.; Jänicke, M.; Plaster, N.; Sonntag, C.; Hammerschmidt, M. Restriction of retinoic acid activity by Cyp26b1 is required for proper timing and patterning of osteogenesis during zebrafish development. Development 2008, 135, 3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sojan, J.M.; Gioacchini, G.; Giorgini, E.; Orlando, P.; Tiano, L.; Maradonna, F.; Carnevali, O. Zebrafish caudal fin as a model to investigate the role of probiotics in bone regeneration. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laue, K.; Pogoda, H.M.; Daniel, P.B.; Van Haeringen, A.; Alanay, Y.; Von Ameln, S.; Rachwalski, M.; Morgan, T.; Gray, M.J.; Breuning, M.H.; et al. Craniosynostosis and Multiple Skeletal Anomalies in Humans and Zebrafish Result from a Defect in the Localized Degradation of Retinoic Acid. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2011, 89, 595–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Hu, C.; Zhao, B.; Li, J.; Chen, L. Proteomic and cardiac dysregulation by representative perfluoroalkyl acids of different chemical speciation during early embryogenesis of zebrafish. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 926, 172000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britton, K.N.; Judson, R.S.; Hill, B.N.; Jarema, K.A.; Olin, J.K.; Knapp, B.R.; Lowery, M.; Feshuk, M.; Brown, J.; Padilla, S. Using Zebrafish to Screen Developmental Toxicity of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS). Toxics 2024, 12, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Yang, D.; Hu, B.; Zai, W.; Li, W.; Wang, Y.; Liu, F.; Liao, X.; Li, H.; Tao, Q.; et al. Perfluorodecanoic acid induces the increase of innate cells in zebrafish embryos by upregulating oxidative stress levels. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2025, 287, 110037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, S.; Lu, C.; Wang, X.; Du, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, B.; Wang, J.; Zhu, L. Comparison of the combined toxicity of PFOA and emerging alternatives: A comprehensive evaluation of oxidative damage, apoptosis and immunotoxicity in embryonic and adult zebrafish. Water Res. 2025, 273, 123028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yang, X.; Lu, C.; Zhang, J.; Li, B.; Du, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Juhasz, A.; Yang, Y.; et al. Are HFPO-TA and HFPO-DA safe substitutes for PFOA? A comprehensive toxicity study using zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos and adults. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 484, 136718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seely, K.D.; Kotelko, C.A.; Douglas, H.; Bealer, B.; Brooks, A.E. The Human Gut Microbiota: A Key Mediator of Osteoporosis and Osteogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schepper, J.D.; Irwin, R.; Kang, J.; Dagenais, K.; Lemon, T.; Shinouskis, A.; Parameswaran, N.; McCabe, L.R. Probiotics in Gut-Bone Signaling. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 1033, 225–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibáñez, L.; Rouleau, M.; Wakkach, A.; Blin-Wakkach, C. Gut microbiome and bone. Jt. Bone Spine 2019, 86, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goudarzi, F.; Kiani, A.; Nami, Y.; Shahmohammadi, A.; Mohammadalipour, A.; Karami, A.; Haghshenas, B. Potential probiotic Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. lactis KUMS-Y33 suppresses adipogenesis and promotes osteogenesis in human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 9689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sojan, J.M.; Licini, C.; Marcheggiani, F.; Carnevali, O.; Tiano, L.; Mattioli-Belmonte, M.; Maradonna, F. Bacillus subtilis Modulated the Expression of Osteogenic Markers in a Human Osteoblast Cell Line. Cells 2023, 12, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvaneh, K.; Ebrahimi, M.; Sabran, M.R.; Karimi, G.; Hwei, A.N.M.; Abdul-Majeed, S.; Ahmad, Z.; Ibrahim, Z.; Jamaluddin, R. Probiotics (Bifidobacterium longum) Increase Bone Mass Density and Upregulate Sparc and Bmp-2 Genes in Rats with Bone Loss Resulting from Ovariectomy. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 897639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Liu, H.; Yu, Y.; Zhu, X.; Xie, H.; Wei, C.; Mei, C.; Shi, Y.; Zhou, N.; Qin, K.; et al. Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG ameliorates osteoporosis in ovariectomized rats by regulating the Th17/Treg balance and gut microbiota structure. Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2190304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avella, M.A.; Olivotto, I.; Silvi, S.; Place, A.R.; Carnevali, O. Effect of dietary probiotics on clownfish: A molecular approach to define how lactic acid bacteria modulate development in a marine fish. Am. J. Physiol.-Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2010, 298, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palermo, F.A.; Mosconi, G.; Avella, M.A.; Carnevali, O.; Verdenelli, M.C.; Cecchini, C.; Polzonetti-Magni, A.M. Modulation of cortisol levels, endocannabinoid receptor 1A, proopiomelanocortin and thyroid hormone receptor alpha mRNA expressions by probiotics during sole (Solea solea) larval development. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2011, 171, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maradonna, F.; Gioacchini, G.; Falcinelli, S.; Bertotto, D.; Radaelli, G.; Olivotto, I.; Carnevali, O. Probiotic Supplementation Promotes Calcification in Danio rerio Larvae: A Molecular Study. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e83155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avella, M.A.; Place, A.; Du, S.J.; Williams, E.; Silvi, S.; Zohar, Y.; Carnevali, O. Lactobacillus rhamnosus accelerates zebrafish backbone calcification and gonadal differentiation through effects on the GnRH and IGF systems. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carnevali, O.; Avella, M.A.; Gioacchini, G. Effects of probiotic administration on zebrafish development and reproduction. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2012, 188, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sojan, J.M.; Raman, R.; Muller, M.; Carnevali, O.; Renn, J. Probiotics Enhance Bone Growth and Rescue BMP Inhibition: New Transgenic Zebrafish Lines to Study Bone Health. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giommi, C.; Maradonna, F.; Ladisa, C.; Habibi, H.R.; Carnevali, O. Probiotics as Potential Tool to Mitigate Nucleotide Metabolism Alterations Induced by DiNP Dietary Exposure in Danio rerio. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 11151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giommi, C.; Lombó, M.; Habibi, H.R.; Rossi, G.; Basili, D.; Mangiaterra, S.; Ladisa, C.; Chemello, G.; Carnevali, O.; Maradonna, F. The probiotic SLAB51 as agent to counteract BPA toxicity on zebrafish gut microbiota -liver-brain axis. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 169303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giommi, C.; Habibi, H.R.; Candelma, M.; Carnevali, O.; Maradonna, F. Probiotic Administration Mitigates Bisphenol A Reproductive Toxicity in Zebrafish. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, L.; Ma, Y.; Huang, W.; Ling, Y.; Sun, L.; Wang, X.; Zeng, A.; Dahlgren, R.A.; Wang, C.; Wang, H. Dietary Lactobacillus plantarum ST-III alleviates the toxic effects of triclosan on zebrafish (Danio rerio) via gut microbiota modulation. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 84, 1157–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Liu, M.; Tang, L.; Liu, H.; Sun, B.; Chen, L. Probiotic intervention mitigates the metabolic disturbances of perfluorobutanesulfonate along the gut-liver axis of zebrafish. Chemosphere 2021, 284, 131374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Lam, J.C.W.; Tang, L.; Tang, L.; Hu, C.; Liu, M.; Liu, M.; Lam, P.K.S.; Zhou, B. Probiotic Modulation of Lipid Metabolism Disorders Caused by Perfluorobutanesulfonate Pollution in Zebrafish. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 7494–7503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Tang, L.; Hu, C.; Huang, Z.; Sun, B.; Lam, J.C.W.; Lam, P.K.S.; Chen, L. Antagonistic interaction between perfluorobutanesulfonate and probiotic on lipid and glucose metabolisms in the liver of zebrafish. Aquat. Toxicol. 2021, 237, 105897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Liu, M.; Tang, L.; Hu, C.; Huang, Z.; Chen, L. Probiotics inhibit the stunted growth defect of perfluorobutanesulfonate via stress and thyroid axes in zebrafish larvae. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 290, 118013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, B.; Liu, M.; Tang, L.; Hu, C.; Huang, Z.; Zhou, X.; Chen, L. Probiotic supplementation mitigates the developmental toxicity of perfluorobutanesulfonate in zebrafish larvae. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 799, 149458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Tang, L.; Hu, C.; Sun, B.; Huang, Z.; Chen, L. Interaction between probiotic additive and perfluorobutanesulfonate pollutant on offspring growth and health after parental exposure using zebrafish. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 214, 112107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Meng, X.; Yang, D.; Dong, S.; Xu, J.; Chen, D.; Shi, Y.; Sun, Y.; Ding, G. Thyroid disrupting effects and the developmental toxicity of hexafluoropropylene oxide oligomer acids in zebrafish during early development. Chemosphere 2024, 361, 142462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, M.; Vats, A.; Lim, I.E.; Sapkota, B.; Abdelmoneim, A. Effects of developmental exposure to individual and combined PFAS on development and behavioral stress responses in larval zebrafish. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 349, 123912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Guo, X.; Lu, S.; He, J.; Wu, Q.; Liu, X.; Han, Z.; Xie, P. Perfluorohexanoic acid caused disruption of the hypothalamus-pituitary-thyroid axis in zebrafish larvae. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 232, 113283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godfrey, A.; Hooser, B.; Abdelmoneim, A.; Horzmann, K.A.; Freemanc, J.L.; Sepúlveda, M.S. Thyroid disrupting effects of halogenated and next generation chemicals on the swim bladder development of zebrafish. Aquat. Toxicol. 2017, 193, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gioacchini, G.; Giorgini, E.; Merrifield, D.L.; Hardiman, G.; Borini, A.; Vaccari, L.; Carnevali, O. Probiotics Can Induce Follicle Maturational Competence: The Danio rerio Case. Biol. Reprod. 2012, 86, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutfi, E.; Basili, D.; Falcinelli, S.; Morillas, L.; Carnevali, O.; Capilla, E.; Navarro, I. The probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus mimics the dark-driven regulation of appetite markers and melatonin receptors’ expression in zebrafish (Danio rerio) larvae: Understanding the role of the gut microbiome. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2021, 256, 110634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnevali, O.; Miccoli, A.; Gioacchini, G.; Maradonna, F.; Benato, F.; Skobo, T. Beneficial Bacteria Affect Danio rerio Development by the Modulation of Maternal Factors Involved in Autophagic, Apoptotic and Dorsalizing Processes. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 35, 1706–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Power, D.M.; Llewellyn, L.; Faustino, M.; Nowell, M.A.; Björnsson, B.T.; Einarsdottir, I.E.; Canario, A.V.M.; Sweeney, G.E. Thyroid hormones in growth and development of fish. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2001, 130, 447–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazcano, I.; Pech-Pool, S.M.; Olvera, A.; García-Martínez, I.; Palacios-Pérez, S.; Orozco, A. The importance of thyroid hormone signaling during early development: Lessons from the zebrafish model. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2023, 334, 114225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.; Wang, M.; Gui, W.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, L.; Zhu, G. Changes in Thyroid Hormone Levels during Zebrafish Development. Zool. Sci. 2012, 29, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazcano, I.; Rodríguez-Ortiz, R.; Villalobos, P.; Martínez-Torres, A.; Solís-Saínz, J.C.; Orozco, A. Knock-down of specific thyroid hormone receptor isoforms impairs body plan development in zebrafish. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 441653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, G.; Lee, Y.M.; Zoh, K.D.; Choi, K. Thyroid disrupting effects of perfluoroundecanoic acid and perfluorotridecanoic acid in zebrafish (Danio rerio) and rat pituitary (GH3) cell line. Chemosphere 2021, 262, 128012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deveau, C.; Jiao, X.; Suzuki, S.C.; Krishnakumar, A.; Yoshimatsu, T.; Hejtmancik, J.F.; Nelson, R.F. Thyroid hormone receptor beta mutations alter photoreceptor development and function in Danio rerio (zebrafish). PLOS Genet. 2020, 16, e1008869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farre, A.A.; Thomas, P.; Huang, J.; Poulsen, R.A.; Owusu Poku, E.; Stenkamp, D.L. Plasticity of cone photoreceptors in adult zebrafish revealed by thyroid hormone exposure. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 15697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, A.; Popowitz, J.; Delbridge-Perry, M.; Rowe, C.J.; Connaughton, V.P. The Role of Estrogen and Thyroid Hormones in Zebrafish Visual System Function. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 837687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, E.N. Endocrine Disruptors and Thyroid Health. Endocr. Pract. 2024, 30, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannetier, P.; Poulsen, R.; Gölz, L.; Coordes, S.; Stegeman, H.; Koegst, J.; Reger, L.; Braunbeck, T.; Hansen, M.; Baumann, L. Reversibility of Thyroid Hormone System–Disrupting Effects on Eye and Thyroid Follicle Development in Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Embryos. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2023, 42, 1276–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Wei, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Ru, S.; Zhang, X. Mechanism of thyroid hormone and its structurally similar contaminant bisphenol S exposure on retinoid metabolism in zebrafish larval eyes. Environ. Int. 2023, 180, 108217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volz, S.N.; Poulsen, R.; Hansen, M.; Holbech, H. Bisphenol A alters retinal morphology, visually guided behavior, and thyroid hormone levels in zebrafish larvae. Chemosphere 2023, 348, 140776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraft, M.; Gölz, L.; Rinderknecht, M.; Koegst, J.; Braunbeck, T.; Baumann, L. Developmental exposure to triclosan and benzophenone-2 causes morphological alterations in zebrafish (Danio rerio) thyroid follicles and eyes. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 33711–33724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Wang, X.; Zheng, S.; Wu, R.; Liu, C.; Wu, K. Effect of bisphenol A on craniofacial cartilage development in zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos: A morphological study. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 212, 111991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenberg, L.N. Non-Monotonic Dose Responses in Studies of Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals: Bisphenol A as a Case Study. Dose-Response 2013, 12, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astuto, M.C.; Benford, D.; Bodin, L.; Cattaneo, I.; Halldorsson, T.; Schlatter, J.; Sharpe, R.M.; Tarazona, J.; Younes, M. Applying the adverse outcome pathway concept for assessing non-monotonic dose responses: Biphasic effect of bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP) on testosterone levels. Arch. Toxicol. 2022, 97, 313–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Han, L.; Qiu, L.; Zhao, B.; Gao, Y.; Chu, Z.; Dai, X. Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA) Exposure Compromises Fertility by Affecting Ovarian and Oocyte Development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 25, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.H. Perfluorooctanoic acid induces peroxisomal fatty acid oxidation and cytokine expression in the liver of male Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes). Chemosphere 2010, 81, 548–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, A.J.; De Silva, A.O.; Schissler, D.M.; Hedges, A.M.; Brown, L.R.; Shires, K.; Miller, J.; Sullivan, C.; Spencer, C.; Parrott, J.L. Lethal and sublethal toxicity of perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) in chronic tests with Hyalella azteca (amphipod) and early-life stage tests with Pimephales promelas (fathead minnow). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 207, 111250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.; Huang, L.; Wang, H.; Tao, C.; Ran, Z.; Xu, J.; Sun, H.; Wang, P. Effects of Lactobacillus acidophilus AC on the growth, intestinal flora and metabolism of zebrafish (Danio rerio). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2024, 149, 109570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Jin, G.; Tang, Q.; Huang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Liu, T.; Guo, Z.; Yang, C.; Wang, B.; et al. Early life Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG colonisation inhibits intestinal tumour formation. Br. J. Cancer 2022, 126, 1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhat, M.I.; Singh, V.K.; Sharma, D.; Kapila, S.; Kapila, R. Adherence capability and safety assessment of an indigenous probiotic strain Lactobacillus rhamnosus MTCC-5897. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 130, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.W.; Jung, B.H.; Lee, J.H.; Yoo, K.Y.; Lee, H.; Kang, M.S.; Lee, J.K. Effect of Weissella cibaria on the reduction of periodontal tissue destruction in mice. J. Periodontol. 2020, 91, 1367–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, S.; Lv, D.; Yang, F.; Lou, L.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, S.; Zhang, N.; et al. Immunomodulatory effect of Bifidobacterium breve on experimental allergic rhinitis in BALB/c mice. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 16, 3996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarantoniello, M.; Bruni, L.; Randazzo, B.; Vargas, A.; Gioacchini, G.; Truzzi, C.; Annibaldi, A.; Riolo, P.; Parisi, G.; Cardinaletti, G.; et al. Partial Dietary Inclusion of Hermetia illucens (Black Soldier Fly) Full-Fat Prepupae in Zebrafish Feed: Biometric, Histological, Biochemical, and Molecular Implications. Zebrafish 2018, 15, 519–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, M.B.; Kimmel, C.B. A two-color acid-free cartilage and bone stain for zebrafish larvae. Biotech. Histochem. 2007, 82, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damiani, E.; Sella, F.; Astolfi, P.; Galeazzi, R.; Carnevali, O.; Maradonna, F. First In Vivo Insights on the Effects of Tempol-Methoxycinnamate, a New UV Filter, as Alternative to Octyl Methoxycinnamate, on Zebrafish Early Development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Gene Name | Gene Symbol | Primer Sequence (5′-3′) | Accession Number | Tm (C°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ribosomal protein large P0 | rplp0 | F: CTGAACATCTCGCCCTTCTC R: TAGCCGATCTGCAGACACAC | NM_131580.2 | 60 |
| Ribosomal protein L13a | rpl13a | F: TCTGGAGGACTGTAAGAGGTATGC R: AGACGCACAATCTTGAGAGCAG | NM_212784.1 | 59 |
| Insulin-like growth factor 1 | igf1 | F: GGCAAATCTCCACGATCTCTAC R: GGCAAATCTCCACGATCTCTA | NM_131825.2 | 53 |
| Insulin-like growth factor 2 | igf2 | F: TCCTTTGTTTGTTGCCATTTG R: GAGTCCCATCCATTCTGTTG | NM_131433.1 | 59 |
| Myostatin a | mstna | F: GGACTGGACTGCGATGAG R: GATGGGTGTGGGGATACTTC | AF019626.1 | 58 |
| Thyroid hormone receptor alpha a | thraa | F: GGAAACAGAAGCGCAAGTTC R: TCTTCACAAGGCAGCTCTGA | NM_131396.1 | 52 |
| BCL2 associated X apoptosis regulator a | baxa | F: CAACAAGATGGCATCACACC R: TGAACCCGCTCGTATATGAAA | NM_131562.2 | 60 |
| Bcl-2 apoptosis regulator a | bcl2a | F: CCTTCAATAAAGCAGTGGAGGAA R: CGGGCTATCAGGCATTCAGA | NM_001030253.2 | 60 |
| caspase 3, apoptosis-related cysteine peptidase a | casp3a | F: GTGCCAGTCAACAAACAAAG R: CATCTCCAACCGCTTAACG | NM_131877.3 | 60 |
| Collagen type X alpha 1a | col10a1a | F: CCCATCCACATCACATCAAA R: GCGTGCATTTCTCAGAACAA | NM_001083827.1 | 60 |
| Secreted phosphoprotein 1 | spp1 | F: GAGCCTACACAGACCACGCCAACAG R: GGTAGCCCAAACTGTCTCCCCG | NM_001002308.1 | 60 |
| RUNX family transcription factor b | runx2b | F: GTGGCCACTTACCACAGAGC R: TCGGAGAGTCATCCAGCTT | NM_212862.2 | 60 |
| Cytochrome P450, family 26 subfamily b polypeptide 1 | cyp26b1 | F: GCTGTCAACCAGAACATTCCC R: GGTTCTGATTGGAGTCGAGGC | NM_212666.1 | 60 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Giommi, C.; Lombó, M.; Francioni, F.; Sella, F.; Habibi, H.R.; Maradonna, F.; Carnevali, O. Mitigation of PFOA-Induced Developmental Toxicity in Danio rerio by Bacillus subtilis var. natto: Focus on Growth and Ossification. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4261. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094261
Giommi C, Lombó M, Francioni F, Sella F, Habibi HR, Maradonna F, Carnevali O. Mitigation of PFOA-Induced Developmental Toxicity in Danio rerio by Bacillus subtilis var. natto: Focus on Growth and Ossification. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(9):4261. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094261
Chicago/Turabian StyleGiommi, Christian, Marta Lombó, Francesca Francioni, Fiorenza Sella, Hamid R. Habibi, Francesca Maradonna, and Oliana Carnevali. 2025. "Mitigation of PFOA-Induced Developmental Toxicity in Danio rerio by Bacillus subtilis var. natto: Focus on Growth and Ossification" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 9: 4261. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094261
APA StyleGiommi, C., Lombó, M., Francioni, F., Sella, F., Habibi, H. R., Maradonna, F., & Carnevali, O. (2025). Mitigation of PFOA-Induced Developmental Toxicity in Danio rerio by Bacillus subtilis var. natto: Focus on Growth and Ossification. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(9), 4261. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094261







