Correlations of the Specific Rates of Solvolysis of Aromatic Carbamoyl Chlorides, Chloroformates, Chlorothionoformates, and Chlorodithioformates Revisited
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1 Solvolyses of N-Aryl-N-Methylcarbamoyl Chlorides
2.2 Solvolyses of N, N-Diphenylcarbamoyl Chloride
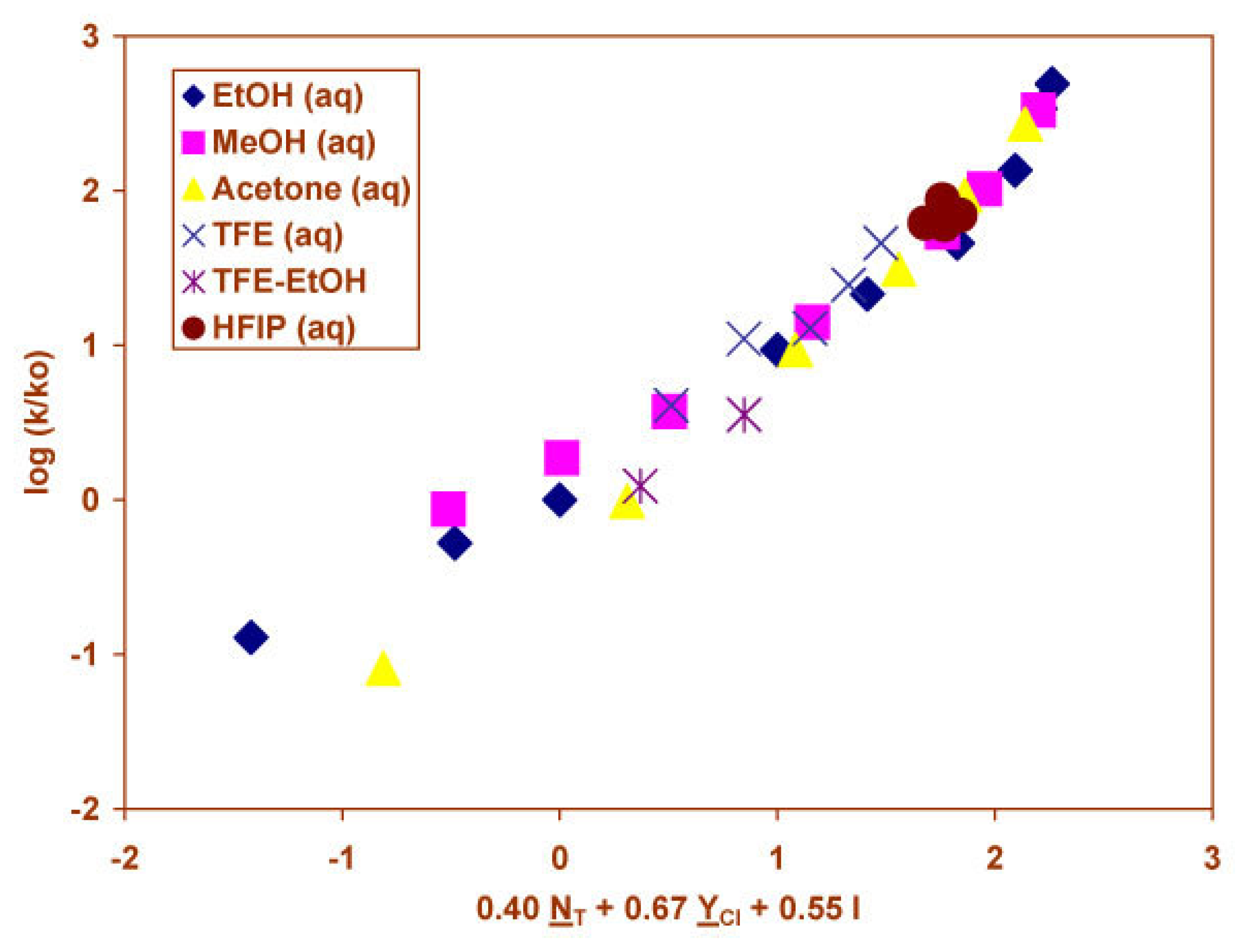
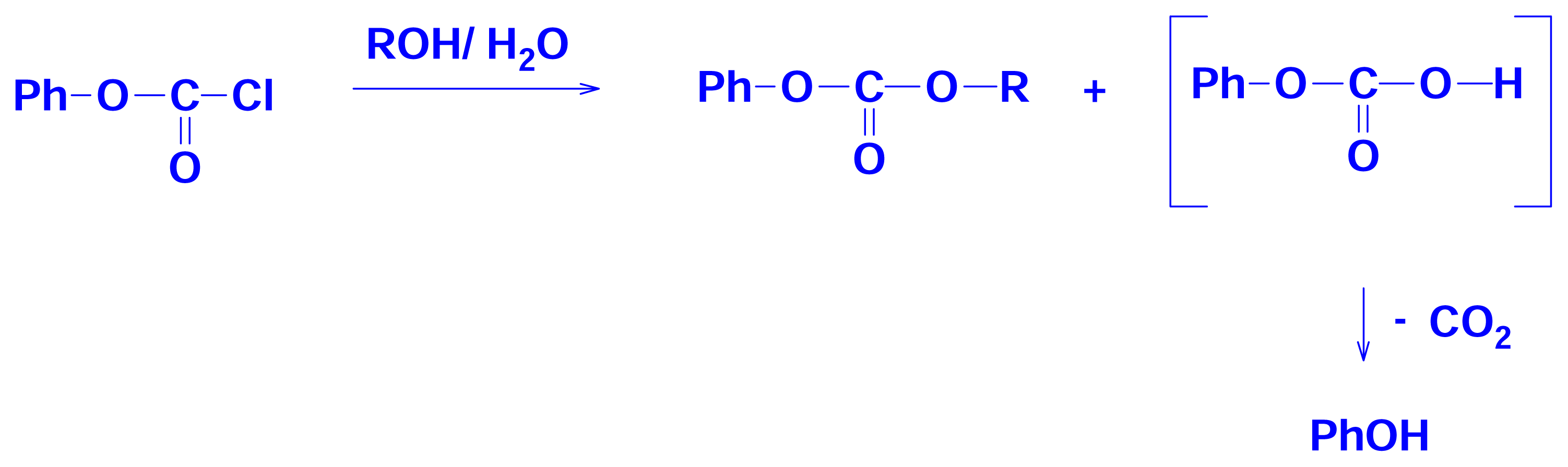
2.3 Solvolyses of Phenyl and p-Methoxyphenyl Chloroformates
2.4 Solvolyses of Phenyl Chlorothionoformate and Chlorodithioformate
3. Conclusions
3. Experimental Section






| Substrate | T°C | nb | ℓc | mc | hc | cc | Rd | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MePhNCOClf | 25.0 | 32 | 0.55±0.03 | −0.10±0.08 | 0.965 | 408 | ||
| 0.51±0.03 | −0.62±0.20 (0.004)g | −0.08±0.07 | 0.974 | 269 | ||||
| 0.44±0.04 | 0.68±0.02 | 0.01±0.03 | 0.994 | 1290 | ||||
| 0.50±0.05 | 0.71±0.02 | 0.23±0.12 (0.068)g | 0.02±0.03 | 0.995 | 939 | |||
| Me(4-ClC6H4)NCOClf | 25.0 | 32 | 0.53±0.04 | 0.02±0.10 | 0.936 | 213 | ||
| 0.46±0.04 | −0.73±0.19 | 0.13±0.09 | 0.958 | 163 | ||||
| 0.44±0.06 | 0.66±0.03 | 0.13±0.06 | 0.980 | 347 | ||||
| 0.47±0.09 | 0.68±0.05 | 0.11±0.20 (0.591)g | 0.13±0.06 | 0.980 | 226 | |||
| Me(4-NO2C6H4) NCOClf | 25.0 | 20 | 0.55±0.09 | −1.86±0.28 | 0.831 | 40 | ||
| 0.39±0.07 | −1.56±0.32 | −1.71±0.19 | 0.934 | 58 | ||||
| 0.58±0.06 | 0.69±0.04 | −1.68±0.12 | 0.974 | 154 | ||||
| 0.51±0.10 | 0.64±0.07 | −0.29±0.33 (0.395)g | −1.68±0.12 | 0.975 | 102 | |||
| Ph2NCOClh | 62.5 | 33 | 0.48±0.03 | 0.00±0.09 | 0.942 | 249 | ||
| 0.47±0.03 | −0.33±0.15 (0.034)g | 0.04±0.09 | 0.951 | 140 | ||||
| 0.23±0.04 | 0.58±0.03 | 0.08±0.07 | 0.969 | 234 | ||||
| 0.40±0.07 | 0.67±0.04 | 0.55±0.19 (0.007)g | 0.07±0.06 | 0.976 | 197 | |||
| MePhNCOCli | 62.5 | 19 | 0.30±0.04 | −0.16±0.07 | 0.869 | 52 | ||
| 0.31±0.04 | −0.31±0.25 (0.216)g | −0.10±0.08 | 0.882 | 28 | ||||
| 0.40±0.08 | 0.51±0.05 | 0.01±0.06 | 0.948 | 70 | ||||
| 0.43±0.10 | 0.53±0.06 | 0.13±0.20 (0.514)g | 0.00±0.06 | 0.949 | 45 |
| Solvent (%)a | 104k(s−1)b | NTc | YCld | Ie |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 90% Acetone (v/v) | 2.38±0.14 | −0.35 | −2.22 | −0.17 |
| 80% TFE (w/w) | 0.702±0.028 | −2.22 | 2.90 | 0.28 |
| 70% TFE (w/w) | 1.74±0.13 | −1.98 | 2.96 | 0.25 |
| 50% TFE (w/w) | 6.35±0.30 | −1.73 | 3.16 | 0.09 |
| 60T-40E(v/v) | 1.99±0.05f | −0.94 | 0.63 | 0.59 |
| 50T-50E (v/v) | 4.21±0.17 | −0.64 | 0.16 | 0.51 |
| 40T-60E (v/v) | 5.77±0.19 | −0.34 | −0.48 | 0.43 |
| 20T-80E(v/v) | 16.9±0.9 | 0.08 | −1.42 | 0.31 |
| 97%HFIP (w/w) | 1.48(±0.20)x10−4 | −5.26 | 5.17 | 0.73 |
| Substrate | nb | ℓc | mc | hc | cc | Rd | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PhOCOClf | 49g | −0.07±0.11 | −0.46±0.31 | 0.093 | 0.4 | ||
| 1.66±0.05 | 0.56±0.03 | 0.15±0.07 | 0.980 | 568 | |||
| 1.77±0.08 | 0.61±0.04 | 0.35±0.19 (0.068)h | 0.16±0.06 | 0.982 | 400 | ||
| 21i | 1.68±0.10 | 0.57±0.06 | 0.12±0.13 | 0.973 | 159 | ||
| 4-MeO C6H4OCOClj | 31g | 0.06±0.07 | −0.02±0.21 | 0.153 | 0.7 | ||
| 1.46±0.08 | 0.53±0.03 | 0.18±0.06 | 0.964 | 182 | |||
| 1.75±0.07 | 0.66±0.03 | 0.85±0.15 | 0.22±0.04 | 0.984 | 274 | ||
| PhOCSClk | 40g | 0.16±0.06 | −0.23±0.18 | 0.393 | 6.9 | ||
| 0.49±0.10 | 0.37±0.06 | −0.12±0.14 | 0.706 | 18 | |||
| 0.69±0.16 | 0.48±0.09 | 0.65±0.43 (0.135)h | −0.10±0.14 | 0.727 | 13 | ||
| 9ℓ | −0.25±0.23 | −0.34±0.29 | 0.376 | 1.2 | |||
| 1.88±0.28 | 0.56±0.15 | 0.38±0.15 | 0.950 | 28 | |||
| 18m | 0.90±0.18 | −3.14±0.68 | 0.784 | 26 | |||
| 0.34±0.05 | 0.93±0.09 | −2.54±0.34 | 0.955 | 77 | |||
| 0.50±0.12 | 1.01±0.10 | 0.51±0.36 (0.181)h | −2.53±0.34 | 0.961 | 56 | ||
| 12n | 0.93±0.15 | −3.50±0.56 | 0.898 | 41 | |||
| 0.26±0.04 | 0.94±0.07 | −2.88±0.29 | 0.980 | 107 | |||
| PhSCSClo | 31g | 0.66±0.06 | −0.05±0.12 | 0.896 | 118 | ||
| 0.69±0.05 | 0.95±0.03 | 0.18±0.05 | 0.987 | 521 | |||
| 0.80±0.06 | 1.02±0.04 | 0.42±0.15 (0.009)h | 0.16±0.04 | 0.990 | 485 |
Acknowledgements
References and Notes
- Grunwald, E.; Winstein, S. The Correlation of Solvolysis Rates. J. Am. Chem. Soc 1948, 70, 846–854. [Google Scholar]
- Bentley, T.W.; Carter, G.E. The SN2-SN1 Spectrum. 4. Mechanism for Solvolyses of tert-Butyl Chloride: A Revised Y Scale of Solvent Ionizing Power based on Solvolyses of 1-Adamantyl Chloride. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1982, 104, 5741–5747. [Google Scholar]
- Bentley, T.W.; Llewellyn, G. Yx Scales of Solvent Ionizing Power. Prog. Phys. Org. Chem 1990, 17, 121–158. [Google Scholar]
- Winstein, S.; Grunwald, E.; Jones, H.W. The Correlation of Solvolyses Rates and the Classification of Solvolysis Reactions into Mechanistic Categories. J. Am. Chem. Soc 1951, 73, 2700–2707. [Google Scholar]
- Schadt, F.L.; Bentley, T.W.; Schleyer, P.v.R. The SN2-SN1 Spectrum. 2. Quantitative Treatments of Nucleophilic Solvent Assistance. A Scale of Solvent Nucleophilicities. J. Am. Chem. Soc 1976, 98, 7667–7674. [Google Scholar]
- Kevill, D.N.; Anderson, S.W. An Improved Scale of Solvent Nucleophilicity Based on the Solvolysis of the S-Methyldibenzothiophenium Ion. J. Org. Chem 1991, 56, 1845. [Google Scholar]
- Kaspi, J.; Rappoport, Z. Nucleophilicity and Ionizing Power in Binary Solvent Mixtures. Tetrahedron Lett 1977, 2035–2038. [Google Scholar]
- Kevill, D.N.; Park, B.-C.; Park, K.-H.; D’Souza, M.J.; Yaakoubd, L.; Mlynarski, S.L.; Kyong, J.B. Rate and Product Studies in the Solvolyses of N,N-Dimethylsulfamoyl and 2-Propanesulfonyl Chlorides. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2006, 4, 1580–1586, , and referenced therein.. [Google Scholar]
- Kevill, D.N.; Ryu, Z.H. Additional Solvent Ionizing Power Values for Binary Water – 1,1,1,3,3,3,-Hexafluoro-2-propanol Solvents. Int. J. Mol. Sci 2006, 7, 451–455. [Google Scholar]
- Kevill, D.N.; Ismail, N.HJ.; D’Souza, M.J. Solvolysis of the (p-Methoxybenzyl)dimethylsulfonium Ion. Development and Use of a Scale to Correct for Dispersion in Grunwald-Winstein Plots. J. Org. Chem. 1994, 59, 6303–6312. [Google Scholar]
- Kevill, D.N.; D’Souza, M.J. Application of the Aromatic Ring Parameter (I) to the Grunwald-Winstein Treatment of the Specific Rates of Solvolysis of Substituted Naphthylmethyl and Anthrylmethyl Sufonates. Org. React. (Tartu) 1995, 29, 55. [Google Scholar]
- Kevill, D.N.; D’Souza, M.J. Considerably Improved Grunwald-Winstein Correlations for Solvolyses of Several Secondary and Tertiary Benzylic Derivatives upon Inclusion of a Term Governed by the Aromatic Ring Parameter (I). J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 2 1995, 973–980. [Google Scholar]
- Kevill, D.N.; D’Souza, M.J. Incorporation of a Term Governed by the Aromatic Ring Parameter (I) into Grunwald-Winstein Correlations of the Solvolyses of Diarylmethyl, Naphthylmethyl and Arylmethyl Bromides. J. Chem. Res. Synop 1996, 286–287. [Google Scholar]Miniprint 1996, 1649.
- Bentley, T.W.; Koo, I.S.; Norman, S.J. Distinguishing Between Solvation Effects and Mechanistic Changes. Effects Due to Differences in Solvation of Aromatic Rings and Alkyl Groups. J. Org. Chem 1991, 56, 1604–1609. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, K.-T; Sheu, H.-C. Solvolysis of 2-Aryl-2-Chloroadamantanes. A New Y Scale for Benzylic Chlorides. J. Org. Chem. 1991, 56, 3021–3025. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, K.-T; Lin, Y.-S.; Duann, Y.-F. Solvent Effects on the Solvolysis of Some Secondary Tosylates. Applications of YBnOTs and YxBnOTs Scales to Mechanistic Studies. J. Phys. Org. Chem. 2002, 15, 750–757. [Google Scholar]
- Kevill, D.N.; Anderson, S.W.; Ismail, N.HJ. Correlation of the Rates of Solvolysis of the Benzhydryldimethylsulfonium Ion. Application of the Aromatic Ring Parameter. J. Org. Chem. 1996, 61, 7256–7262. [Google Scholar]
- Kevill, D.N.; D’Souza, M.J. Application of the Aromatic Ring Parameter (I) to Solvolyses of β-Arylalkyl Toluene-p-sulfonates. J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 2 1997, 257–264. [Google Scholar]
- Kevill, D.N.; D’Souza, M.J. Correlation of the Rates of Solvolysis of Benzoyl Chloride and Derivatives Using Extended Forms of the Grunwald-Winstein Equation. J. Phys. Org. Chem 2002, 15, 881–888. [Google Scholar]
- Kevill, D.N.; D’Souza, M.J. Correlation of the Rates of Solvolysis of Benzoyl Fluoride. J. Org. Chem 2004, 69, 7044–7050. [Google Scholar]
- Kevill, D.N.; D’Souza, M.J. Correlation of the Rates of Solvolysis of Phenyl Chloroformate. J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 2 1997, 1721–1724. [Google Scholar]
- Kyong, J.B.; Park, B.-C.; Kim, C.-B.; Kevill, D.N. Rate and Product Studies with Benzyl and p-Nitrobenzyl Chloroformates Under Solvolytic Conditions. J. Org. Chem 2000, 65, 8051–8058. [Google Scholar]
- Kyong, J.B.; Won, H.; Kevill, D.N. Application of the Extended Grunwald-Winstein Equation to Solvolyses of n-Propyl Chloroformate. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2005, 6, 87–96. [Google Scholar]
- D’Souza, M.J.; Boggs, M.E.; Kevill, D.N. Correlation of the Rates of Solvolysis of 2-Furancarbonyl Chloride and Three Naphthoyl Chlorides. J. Phys. Org. Chem 2006, 19, 173–178. [Google Scholar]
- Kevill, D.N.; D’Souza, M.J. Correlation of the Rates of Solvolyses of n-Octyl Fluoroformate and a Comparison with n-Octyl Chloroformate Solvolyses. J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 2 2002, 240–243. [Google Scholar]
- Kyong, J.B.; Ryu, S.H.; Kevill, D.N. Rate and Product Studies of Solvolyses of Benzyl Fluoroformate. Int. J. Mol. Sci 2006, 7, 186–196. [Google Scholar]
- D’Souza, M.J.; Kevill, D.N.; Bentley, T.W.; Devaney, A.C. Kinetics and Selectivities for the Solvolyses of N, N-Diphenylcarbamoyl Chloride. J. Org. Chem 1995, 60, 1632–1637. [Google Scholar]
- Kevill, D.N.; Oldfield, A.J.; D’Souza, M.J. Correlation of the Rates of Solvolyses of N, N-Dimethylcarbamoyl Chloride. J. Chem. Res. Synop. 1996, 122–123. [Google Scholar]
- Kevill, D.N.; Best, B.J.; D’Souza, M.J. Correlation of the Rates of Solvolyses of N-Methyl-N-phenylcarbamoyl Chloride. Org. React. (Tartu) 1997, 31, 55–58. [Google Scholar]
- Kevill, D.N.; Carver, J.S. Rate and Product Studes with Dimethyl Phosphorochloridate and Dimethyl Phosphorochloridothionate Under Solvolytic Conditions. Org. Biomol. Chem 2004, 2, 2040–2043, , and references therein.. [Google Scholar]
- Kevill, D.N.; Koh, H.J. Correlation of the Rates of Solvolyses of Diphenylphosphinyl Chloride Using an Extended Form of the Grunwald-Winstein Equation. J. Phys. Org. Chem 2007, 20, 88–92. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, K.–T.; Chen, H.–I.; Lin, Y.–S.; Jin, B.-Y. Solvolysis of N,N-Diphenylcarbamoyl Chloride Revisted. Extended Positive Charge Delocalizaiton on Phenyl Rings in the Transition State and Possible Contribution of Non-Canonical Resonance Structure. J. Phys. Org. Chem. 2000, 13, 322–329. [Google Scholar]
- Kevill, D.N. Development and Uses of Scales of Solvent Nucleophilicity. In Advances in Quantitative Structure-Property Relationships; Volume 1, Charton, M., Ed.; JAI Press: Greenwich, CT, 1996; pp. 81–115. [Google Scholar]
- Kevill, D.N.; D’Souza, M.J. Additional YClValues and Correlation of the Specific Rates of Solvolysis of tert-Butyl Chloride in Terms of NTand YClScales. J. Chem. Res. Synop 1993, 174–175. [Google Scholar]
- Kevill, D.N.; Anderson, S.W. Essentially Solvent-Independent Rates of Solvolysis of the 1-Adamantyldimethylsulfonium Ion. Implications Regarding Nucleophilic Assistance in Solvolyses of tert-Butyl Derivatives and the NKL Sovlent Nucleophilicity Scale. J. Am. Chem. Soc 1986, 108, 1579–1581. [Google Scholar]
- Koo, I.S.; An, S.K.; Yang, K.; Koh, H.J.; Choi, M.H.; Lee, I. Solvolyses of N-Methyl-N-phenylcarbamoyl Chlorides with Electron Acceptor Substituents in Aqueous Binary Mixtures. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc 2001, 22, 842–846. [Google Scholar]
- There should be no 80% acetone value, the value given within Table 1 is actually the value for 70% acetone, as can be deduced by comparison with Figure 2 of the publication.
- Yew, K.H.; Koh, H.J.; Lee, H.W.; Lee, I. Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions of Phenyl Chloroformate. J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 2 1995, 2263–2268. [Google Scholar]
- Koo, I.S.; Yang, K.; Kang, K.; Lee, I. Transition-State Variation in the Solvolyses of para-Substituted Phenyl Chloroformates in Alcohol-Water Mixtures. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc 1998, 19, 968–972. [Google Scholar]
- McKinnon, D.M.; Queen, A. Kinetics and Mechanism for the Hydrolysis of Chlorothionoformate and Chlorodithioformate Esters in Water and Aqueous Acetone. Can. J. Chem 1972, 50, 1401–1406. [Google Scholar]
- Csunderlik, C.; Bacaloglu, R.; Ostrogovich, G. Nucleophilic Substitutions in Carbonic Acid Derivatives. IV. Kinetics and Mechanism of Hydrolysis of O-Aryl Chlorothiocarbonates. J. Prakt. Chem (Leipzig) 1975, 317, 73. [Google Scholar]
- Kevill, D.N.; D’Souza, M.J. Correlation of the Rates of Solvolysis of Phenyl Chlorothionoformate and Phenyl Chlorodithioformate. Can. J. Chem 1999, 77, 1118–1122. [Google Scholar]
- Koo, I.S.; Yang, K.; Kang, D.H.; Park, H.J.; Kang, K.; Lee, I. Transition-State Variation in the Solvolyses of Phenyl Chlorothionoformate in Alcohol-Water Mixtures. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc 1999, 20, 577–580. [Google Scholar]
- Queen, A. Kinetics of the Hydrolysis of the Acyl Chlorides in Pure Water. Can J. Chem 1967, 45, 1619–1629. [Google Scholar]
- Queen, A.; McKinnon, D.M.; Bell, A.W. The Kinetics of the Reactions of Chlorodithioformate Esters with Azide Ions in 70% Acetone. Can J. Chem 1976, 54, 1906–1909. [Google Scholar]
- An, S.K.; Yang, J.S.; Cho, J.M.; Yang, K.; Lee, P.L.; Bentley, T.W.; Lee, I.; Koo, I.S. Correlation of the Rates Solvolysis of Phenyl Chlorodithioformate. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc 2002, 23, 1445. [Google Scholar]
- This statement is accurate after the values in TFE-water within Table 2 of ref. 46 are reduced by a factor of ten to allow for an order of magnitude error. Unfortunately, the reported values were also used in the correlations presented within the reference.
© 2007 by MDPI Reproduction is permitted for noncommercial purposes.
Share and Cite
Kevill, D.N.; Koyoshi, F.; D’Souza, M.J. Correlations of the Specific Rates of Solvolysis of Aromatic Carbamoyl Chlorides, Chloroformates, Chlorothionoformates, and Chlorodithioformates Revisited. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2007, 8, 346-362. https://doi.org/10.3390/i8040346
Kevill DN, Koyoshi F, D’Souza MJ. Correlations of the Specific Rates of Solvolysis of Aromatic Carbamoyl Chlorides, Chloroformates, Chlorothionoformates, and Chlorodithioformates Revisited. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2007; 8(4):346-362. https://doi.org/10.3390/i8040346
Chicago/Turabian StyleKevill, Dennis N., Fumie Koyoshi, and Malcolm J. D’Souza. 2007. "Correlations of the Specific Rates of Solvolysis of Aromatic Carbamoyl Chlorides, Chloroformates, Chlorothionoformates, and Chlorodithioformates Revisited" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 8, no. 4: 346-362. https://doi.org/10.3390/i8040346
APA StyleKevill, D. N., Koyoshi, F., & D’Souza, M. J. (2007). Correlations of the Specific Rates of Solvolysis of Aromatic Carbamoyl Chlorides, Chloroformates, Chlorothionoformates, and Chlorodithioformates Revisited. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 8(4), 346-362. https://doi.org/10.3390/i8040346




