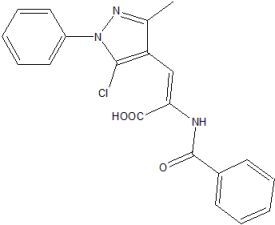
2-(Benzoylamino)-3-(5-chloro-3-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)acrylic acid
Abstract
:Introduction
Experimental
Synthesis of 2-benzamido-3-(5-chloro-3-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl) acrylic acid (2)
Supplementary materials
Supplementary File 1Supplementary File 2Supplementary File 3Supplementary File 4Acknowledgements
References
- BAMM. Monograph of Acrylic Acid; Basic Acrylic Monomer Manufacturers, Inc.: Hamilton, VA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Isozaki, T.; Kurokawa, M.; Honma, A. Process for producing glycidyl ester of acrylic acid or methacrylic acid. U.S. Patent 5,750,739, 12 May 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Butyl Acrylate, Technical Data Sheet (TDS); Dow Chemical Company: Midland, MI, USA, 9 February 2007; Form no. 745-00109-1004AA.
- IARC Monographs on the other data relevant to an evaluation of carcinogenicity and its mechanisms, Acrylic acid. IARC Monographs 1999, 71, 1223–1230.
- Kaushik, D.; Khan, S.A.; Chawla, G. Design & synthesis of 2-(substituted aryloxy)-5-(substituted benzylidene)-3-phenyl-2, 5-dihydro-1H-[1,2,4] triazin-6-one as potential anticonvulsant agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 3960–3969. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]

© 2011 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Kaushik, D.; Verma, T.; Madaan, K. 2-(Benzoylamino)-3-(5-chloro-3-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)acrylic acid. Molbank 2011, 2011, M726. https://doi.org/10.3390/M726
Kaushik D, Verma T, Madaan K. 2-(Benzoylamino)-3-(5-chloro-3-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)acrylic acid. Molbank. 2011; 2011(2):M726. https://doi.org/10.3390/M726
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaushik, Darpan, Tarawanti Verma, and Kapish Madaan. 2011. "2-(Benzoylamino)-3-(5-chloro-3-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)acrylic acid" Molbank 2011, no. 2: M726. https://doi.org/10.3390/M726
APA StyleKaushik, D., Verma, T., & Madaan, K. (2011). 2-(Benzoylamino)-3-(5-chloro-3-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)acrylic acid. Molbank, 2011(2), M726. https://doi.org/10.3390/M726