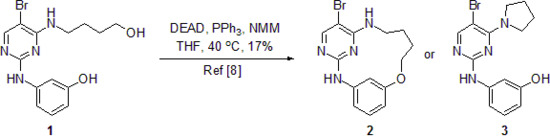
3-({5-Bromo-4-[pyrrolidin-1-yl]pyrimidin-2-yl}amino)phenol
Abstract
:Experimental Section
General Information
Synthesis of 3-((5-Bromo-4-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)pyrimidin-2-yl)amino)phenol (3)
Supplementary materials
Supplementary File 1Supplementary File 2Supplementary File 3Supplementary File 4Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References and Notes
- Driggers, E.M.; Hale, S.P.; Lee, J.; Terrett, N.K. The exploration of macrocycles for drug discovery—an underexploited structural class. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 608–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peña, S.; Scarone, L.; Serra, G. Macrocycles as potential therapeutic agents in neglected diseases. Future Med. Chem. 2015, 7, 355–382. [Google Scholar]
- Mallinson, J.; Collins, I. Macrocycles in New Drug Discovery. Future Med. Chem. 2012, 4, 1409–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yudin, A.K. Macrocycles: Lessons from the distant past, recent developments, and future directions. Chem. Sci. 2015, 6, 30–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.; Yousuf, S.K.; Mukherjee, D. Importance and synthesis of benzannulated medium-sized and macrocyclic rings (BMRs). RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 43241–43257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dakas, P.-Y.; Barluenga, S.; Totzke, F.; Zirrgiebel, U.; Winssinger, N. Modular synthesis of radicicol A and related resorcylic acid lactones, potent kinase inhibitors. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2007, 46, 6899–6902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dakas, P.-Y.; Jogireddy, R.; Valot, G.; Barluenga, S.; Winssinger, N. Divergent syntheses of resorcylic acid lactones: L-783277, LL-Z1640– 2, and hypothemycin. Chem. Eur. J. 2009, 15, 11490–11497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lücking, U.; Siemeister, G.; Schäfer, M.; Briem, H.; Krüger, M.; Lienau, P.; Jautelat, R. Macrocyclic Aminopyrimidines as Multitarget CDK and VEGF-R Inhibitors with Potent Antiproliferative Activities. ChemMedChem 2007, 2, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The water signal in d6-DMSO occurs as a broad singlet at 3.33 ppm. Gottlieb, H.E.; Kotlyar, V.; Nudelman, A. NMR Chemical Shifts of Common Laboratory Solvents as Trace Impurities. J. Org. Chem. 1997, 62, 7512–7515. [Google Scholar]
- Data obtained for 5-Bromo-2-chloro-4-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)pyrimidine (5). 1H-NMR (400 MHz, d6-DMSO) δ 8.24 (s, 1H), 3.75–3.69 (m, 4 H), 1.89–1.85 (m, 4H); 13C-NMR (100 MHz, d6-DMSO) δ 159.9, 157.8, 157.4, 100.0, 50.0, 25.1; LC-MS (TOF, 2.0 min) Rt = 0.173 min; m/z (ESI) 262 (M79Br+H), 264 (M81Br+H). Hi-Res LC-MS (ESI) m/z calcd for C8H979BrClN3 (M+H) 261.9747, found 261.9743.


© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jones, A.M. 3-({5-Bromo-4-[pyrrolidin-1-yl]pyrimidin-2-yl}amino)phenol. Molbank 2015, 2015, M859. https://doi.org/10.3390/M859
Jones AM. 3-({5-Bromo-4-[pyrrolidin-1-yl]pyrimidin-2-yl}amino)phenol. Molbank. 2015; 2015(2):M859. https://doi.org/10.3390/M859
Chicago/Turabian StyleJones, Alan M. 2015. "3-({5-Bromo-4-[pyrrolidin-1-yl]pyrimidin-2-yl}amino)phenol" Molbank 2015, no. 2: M859. https://doi.org/10.3390/M859
APA StyleJones, A. M. (2015). 3-({5-Bromo-4-[pyrrolidin-1-yl]pyrimidin-2-yl}amino)phenol. Molbank, 2015(2), M859. https://doi.org/10.3390/M859