(S)-N-(N-(((2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-Amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-3,4-dihydroxytetrahydrofuran-2-yl)methyl)sulfamoyl)-5-oxopyrrolidine-2-carboxamide
Abstract
:


Experimental Section
General Procedures
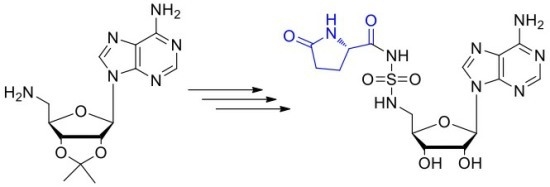
Direct Synthesis of pGlu-SA 4
Indirect Synthesis of pGlu-SA 4
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ibba, M.; Soll, D. Aminoacyl-tRNA synthesis. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2000, 69, 617–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Lee, S.W.; Choi, E.C.; Choi, S.Y. Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases and their inhibitors as a novel family of antibiotics. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2003, 61, 278–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forrest, A.K.; Jarvest, R.L.; Mensah, L.M.; O'Hanlon, P.J.; Pope, A.J.; Sheppard, R.J. Aminoalkyl adenylate and aminoacyl sulfamate intermediate analogues differing greatly in affinity for their cognate staphylococcus aureus aminoacyl tRNA synthetases. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2000, 10, 1871–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kang, S.U.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, S.E.; Job, Y.J.; Kim, S. Vanilloid and isovanilloid analogues as inhibitors of methionyl-tRNA and isoleucyl-tRNA synthetases. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2001, 11, 965–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kang, S.U.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, S.E.; Kang, M.K.; Jo, Y.J.; Kim, S. Ester and hydroxamate analogues of methionyl and isoleucyl adenylates as inhibitors of methionyl-tRNA and isoleucyl-tRNA synthetases. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2001, 11, 961–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, S.E.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, S.Y.; Kang, S.U.; Seo, S.H.; Chun, M.W.; Kang, T.; Choi, S.Y.; Kim, H.O. N-Alkoxysulfamide, N-hydroxysulfamide, and sulfamate analogues of methionyl and isoleucyl adenylates as inhibitors of methionyl-tRNA and isoleucyl-tRNA synthetases. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2003, 13, 1087–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, P.; Richardson, C.M.; Mensah, L.M.; O’Hanlon, P.J.; Osborne, N.F.; Pope, A.J.; Walker, G. Molecular recognition of tyrosinyl adenylate analogues by prokaryotic tyrosyl tRNA synthetases. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 1999, 7, 2473–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balg, C.; Blais, S.P.; Bernier, S.; Huot, J.L.; Couture, M.; Lapointe, J.; Chenevert, R. Synthesis of beta-ketophosphonate analogs of glutamyl and glutaminyl adenylate, and selective inhibition of the corresponding bacterial aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2007, 15, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, M.J.; Mensah, L.M.; Doyle, M.L.; Broom, N.J.; Osbourne, N.; Forrest, A.K.; Richardson, C.M.; O'Hanlon, P.J.; Pope, A.J. Rational design of femtomolar inhibitors of isoleucyl tRNA synthetase from a binding model for pseudomonic acid-A. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 6003–6011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadakh, B.; Smaers, S.; Rozenski, J.; Froeyen, M.; Van Aerschot, A. 5′-(N-aminoacyl)-sulfonamido-5′-deoxyadenosine: Attempts for a stable alternative for aminoacyl-sulfamoyl adenosines as aaRS inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 93, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, M.; Schimmel, P. Structural analyses clarify the complex control of mistranslation by tRNA synthetases. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2012, 22, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, J.; Schimmel, P. Inhibitors of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases as novel anti-infectives. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2000, 9, 1767–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; Khaybullin, R.; Fu, J.; Goncalves, K.; Xia, A.; Qi, X. Genetic code expansion using aminoacylated orthogonal tRNAs in conjunction with aminoacyl sulfamides. Int. J. Recent Technol. Eng. 2015, 3, 78–82. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, J.M.; Kluge, A.F. Aminoacyl Sulfamides for the Treatment of Hyperproliferative Disorders. U.S. Patent 5824657, 20 October 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Kolb, M.; Danzin, C.; Barth, J.; Claverie, N. Synthesis and biochemical properties of chemically stable product analogues of the reaction catalyzed by S-adenosyl-l-methionine decarboxylase. J. Med. Chem. 1982, 25, 550–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, X.; Khaybullin, R.N.; Liang, X. Sulfamide Adenosine Derivatives and Uses Thereof. U.S. Patent Provisional Application No.: 62/174,362, 2015. [Google Scholar]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khaybullin, R.N.; Liang, X.; Qi, X. (S)-N-(N-(((2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-Amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-3,4-dihydroxytetrahydrofuran-2-yl)methyl)sulfamoyl)-5-oxopyrrolidine-2-carboxamide. Molbank 2015, 2015, M864. https://doi.org/10.3390/M864
Khaybullin RN, Liang X, Qi X. (S)-N-(N-(((2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-Amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-3,4-dihydroxytetrahydrofuran-2-yl)methyl)sulfamoyl)-5-oxopyrrolidine-2-carboxamide. Molbank. 2015; 2015(2):M864. https://doi.org/10.3390/M864
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhaybullin, Ravil N., Xiao Liang, and Xin Qi. 2015. "(S)-N-(N-(((2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-Amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-3,4-dihydroxytetrahydrofuran-2-yl)methyl)sulfamoyl)-5-oxopyrrolidine-2-carboxamide" Molbank 2015, no. 2: M864. https://doi.org/10.3390/M864
APA StyleKhaybullin, R. N., Liang, X., & Qi, X. (2015). (S)-N-(N-(((2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-Amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-3,4-dihydroxytetrahydrofuran-2-yl)methyl)sulfamoyl)-5-oxopyrrolidine-2-carboxamide. Molbank, 2015(2), M864. https://doi.org/10.3390/M864