Abstract
The Knoevenagel reaction is an essential synthetic tool in the organic and medicinal chemistry of thiazolidin-4-one derivatives. In the present work, the application of ethylenediamine diacetate (EDDA) as an effective catalyst for the interaction of 2-thioxothiazolidin-4-one with 4-(tert-butyl)cyclohexanone is proposed. The structure of novel synthesized 5-[4-(tert-butyl)cyclohexylidene]-2-thioxothiazolidin-4-one (yield 61%) was confirmed by 1H-, 13C-NMR, LC-MS, IR, and UV spectra. Drug-like properties of the synthesized compound were evaluated in silico using the SwissAdme, and their potential antimicrobial activity against 15 strains of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria as well as yeasts was evaluated in vitro. The synthesized compound possesses satisfactory drug-like parameters and promising antimicrobial properties and presents interest as a prospective intermediate for the forthcoming design of biologically active small molecules.
1. Introduction
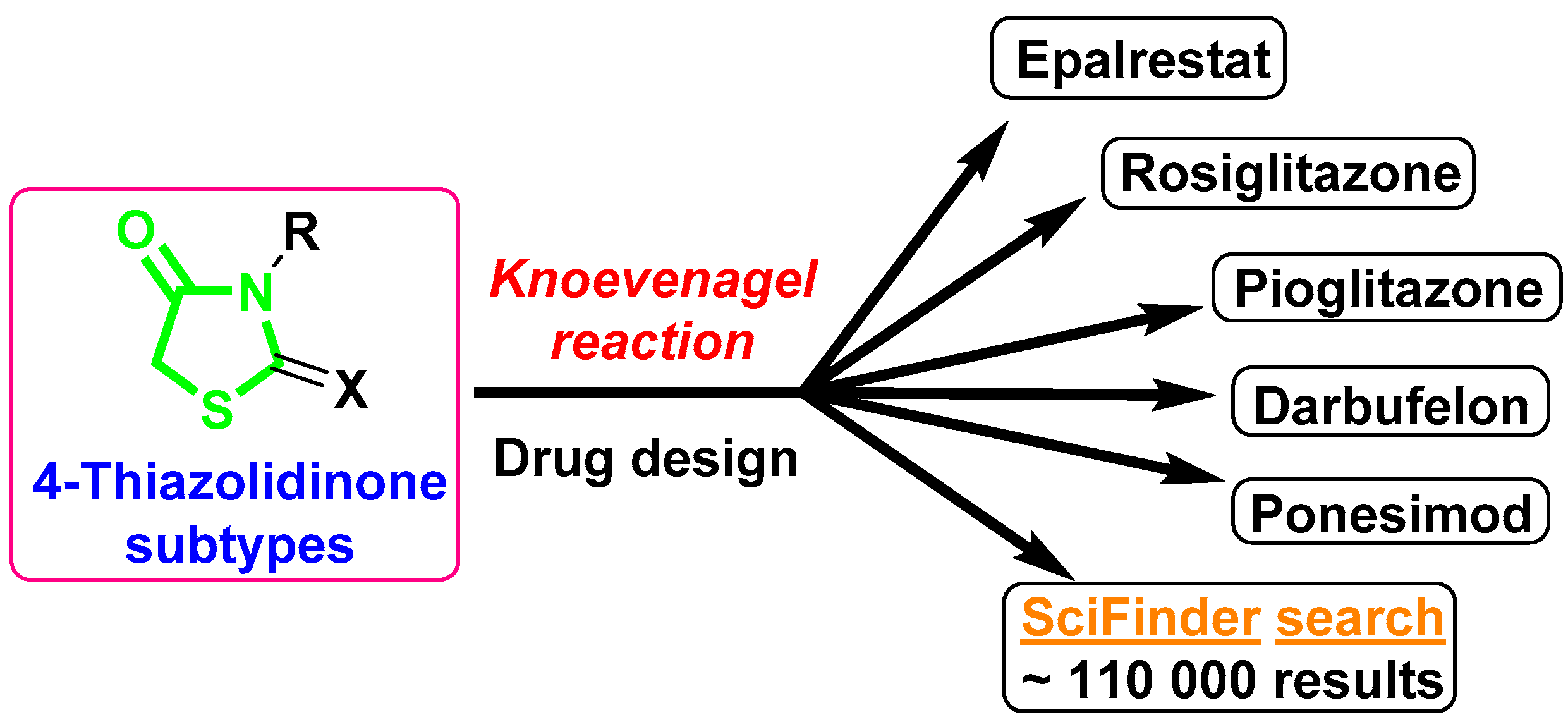
The Knoevenagel reaction plays an important role in the organic and medicinal chemistry of thiazolidin-4-one derivatives. This type of transformation is a key step in the synthetic pathways for thiazolidin-4-one-bearing drugs glitazones [1], Epalrestat [2], Darbufelone [3], and Ponesimod (Ponvory) [4,5], as well as being a convenient synthetic tool for the design of potential pharmacological agents among thiazolidin-4-one-based molecules [6,7,8,9] (Figure 1). Although there have been many conditions and variations developed and described for synthetic protocols with carbonyl substrates and aromatic/heteroaromatic aldehydes in the Knoevenagel condensation with thiazolidin-4-one derivatives, the current state of applications for aliphatic/alicyclic ketones especially is considered a synthetic “challenge’’ for medicinal chemists. Such a situation could be explained by the lower reactivity of certain types of reaction and is usually associated with difficulties in isolating target products from the reaction mixture, low yields, and long reaction time. It should be noted that choosing conditions/catalysts for specific cases of structural features of thiazolidin-4-one scaffolds often requires using completely different approaches and could be complicated even with a minor structure difference. If we analyze the reaction conditions within thiazolidin-4-one subtypes, for the interaction of 2-thioxothiazolidin-4-ones (rhodanines) with alicyclic ketones, the most common method is the Girard method [10,11] along with its modification by fusion of the reagents in the presence of CH3COONH4 [12], and the application of ionic liquids [13] is also described. However, the mentioned examples are limited and only represent the interaction of rhodanine with unsubstituted cyclopentanone, cyclhexanone, and cycloheptanone. Meanwhile, the introduction of such ketones in the ring, especially bulky or strong electron-releasing/withdrawing groups, could significantly impact the synthetic process, and requires investigation and the use of special reaction conditions.
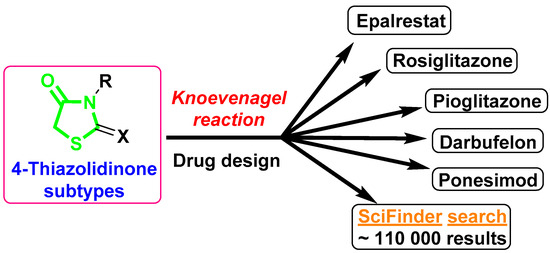
Figure 1.
The application of the Knoevenagel reaction in the medicinal chemistry of thiazolidin-4-ones.
In the present work, we describe an example of the application of ethylenediamine diacetate (EDDA) as an effective catalyst for the Knoevenagel reaction for the interaction of rhodanine with 4-(tert-butyl)cyclohexanone as a convenient and straightforward pathway for the tuning of the thiazolidin-4-one core with an sp3-rich fragment (Scheme 1). Despite that described herein, compound 3 can be purchased from numerous suppliers (PubChem CID 45923513), no reported procedure for its synthesis, nor any details on its spectroscopy, are reported in the literature. Further perspectives for the application of compound 3 in drug design were evaluated using drug-like properties studied in silico, and the estimation of antimicrobial potency in vitro was carried out.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthesis of the Title Compound 3
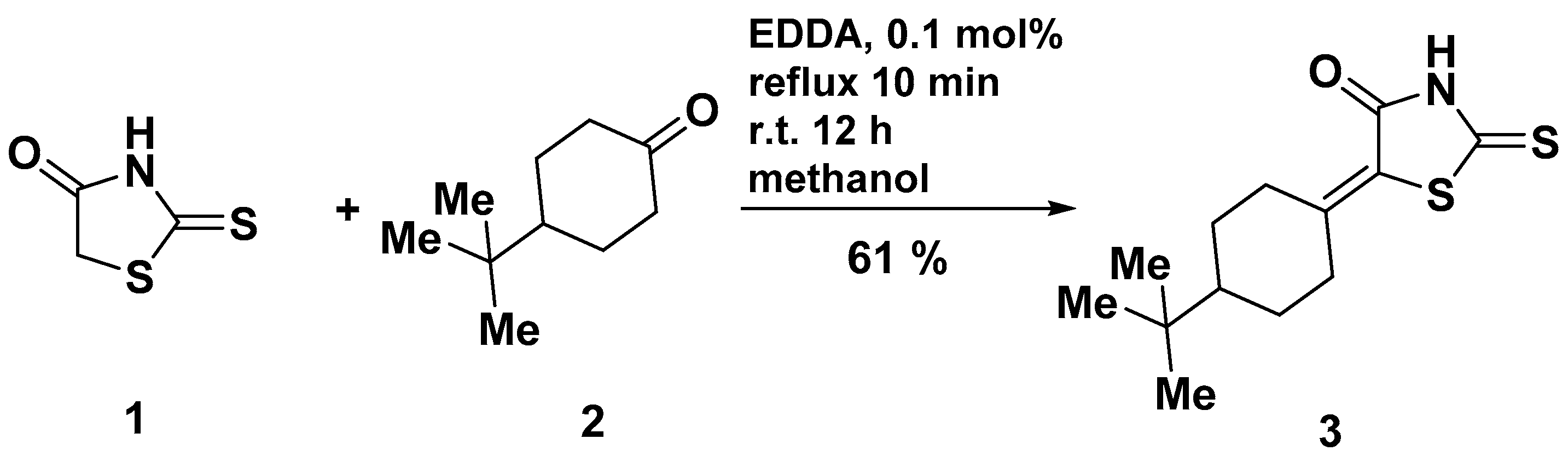
The title compound 3 was synthesized following the convenient synthetic protocol (Scheme 1) using ethylenediamine diacetate (EDDA) as a catalyst. The equimolar amounts of 2-thioxothiazolidin-4-one (1) and 4-tert-butylcyclohexanone (2) in the presence of a catalytic amount (0.1 mol%) of EDDA were refluxed for 10 min in methanol. Then, the resulting solution was left overnight (~12 h) at room temperature and the obtained precipitate of target derivative 3 was filtered off. It was synthesized in such a way that compound 3 possessed a good level of purity but could be recrystallized from glacial acetic acid.
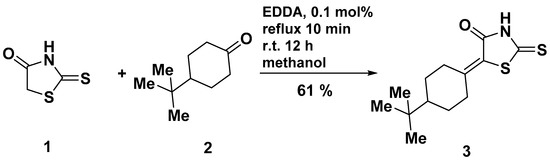
Scheme 1.
Synthesis of title compound 3. Reagent and conditions: Rhodanine (1) (10 mmol), 4-tert-butylcyclohexanone (2) (10 mmol), EDDA (10 µmol), methanol (10 mL), reflux, 10 min; r.t. 12 h.
The structure of compound 3 was characterized by 1H-, 13C-NMR, and LC-MS spectra (copies of spectra are presented in Supplementary). In the 1H- and 13C-NMR spectra, all atom signals were presented in the corresponding regions as expected. The signal of the N-H proton was observed as a singlet at 13.36 ppm. The signals of cyclohexylidene moiety protons were characterized by a complex coupling pattern and resonated as a multiplet at 4.06–4.14 ppm, a triplet of doublets at 2.33, a doublet at 2.17, a multiplet at 1.88–2.04, a triplet of doublets at 1.32, and a doublet of a quartet of doublets at 1.14 ppm, respectively. The multiplet signal at 4.06–4.14 ppm was attributed to one of the protons of the CH2-group bound to the ethylene fragment (H-13a,b), and such a shift in the low-field could be explained, first of all, due to steric adjustment by the carbonyl group of the thiazolidin-4-one ring as well as by the additional impact of the double bound. The methyl protons resonated as a strong singlet at 0.83 ppm.
In the 13C-NMR spectrum, the signals of carbon atoms in the thiocarbonyl (C=S, C-2) and the carbonyl (C=O, C-4) groups appeared at 195.1 and 167.1 ppm, respectively. The signal of the C-5 carbon atom appeared at 120.2 ppm. The six carbon atoms of the hexylidene moiety gave a set of five signals at 158.3 (C-8), 46.7 (C-11), 32.6, 29.3 (C-9, C-13), and 28.5 (C-10, C-12) ppm, respectively. The carbons of the tert-butyl-group are characterized by a signal at 37.4 ppm for C-14 and a strong signal at 27.3 ppm for methyl groups (C-15, C-16, and C-17).
The molecular ion peak observed at an m/z value of 270.0 [M + H]+ in the positive ionization mode in the mass spectrum confirmed the formation of the title compound 3.
The absorption bands at 1682 and 1614 cm−1 are assigned to the C=O and C=C stretching vibrations in the IR spectrum, respectively. In the UV spectrum, three maximums were observed at 335, 276, and 226 nm.
2.2. Evaluation of Physicochemical and Drug-like Properties In Silico of Compound 3
Physicochemical and drug-like properties of compound 3 were evaluated in silico using the SwissAdme of the Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics website [14] and the obtained results are presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Predicted physicochemical properties and drug-like parameters of compound 3.
The title compound 3 possesses satisfactory physicochemical and drug-like parameters and has no violations according to the Lipinski and Veber rules. The high level of gastrointestinal absorption and lack of blood–brain barrier permeability were both predicted for compound 3.
2.3. Antimicrobial Activity Evaluation In Vitro of Compound 3
Compound 3 was prescreened for its potential antimicrobial activity against 15 strains of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria as well as yeasts (Table 2). The antimicrobial activity was evaluated in terms of the diameter of the inhibition zone of microbial growth and minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs).

Table 2.
In vitro antimicrobial activity of compound 3 (zone of growth inhibition at conc. 1 mg/mL after 24–48 h).
Compound 3 showed selective antimicrobial activity against both tested M. luteus clinical strains and non-significant activity against S. aureus clin N 23 (Table 2).
MIC to M. luteus N 43 was in the range of 250–500 μg/mL (≥929 mmol). Determined in the same conditions, MIC for vancomycin was >4 μg/mL against M. luteus, which means M. luteus N 43 is more resistant to vancomycin.
The compound’s selective antimicrobial activity against M. luteus may represent possible higher hydrophobicity of the compound [15], but the mechanism of action needs to be studied in more detail. Nevertheless, we assume that compound 3 may act similarly to meropenem (bacterial cell wall synthesis inhibition) [16] because both M. luteus strains were sensitive only to meropenem and resistant to other antibiotics from different groups. Thus, it could be a reasonable basis for further docking analysis.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Information and Compound 3 Synthesis
Melting points were measured in open capillary tubes on a BÜCHI B-545 melting point apparatus (BÜCHI Labortechnik AG, Flawil, Switzerland) and are uncorrected. The elemental analyses (C, H, N) were performed using the Perkin–Elmer 2400 CHN analyzer (PerkinElmer, Waltham, MA, USA) and were within ±0.4% of the theoretical values. The 400 MHz-1H and 126 MHz-13C spectra were recorded on the Varian Unity Plus 400 (400 MHz) spectrometer (Varian Inc., Paulo Alto, CA, USA). All spectra were recorded at room temperature except when indicated otherwise and were referenced internally to solvent reference frequencies. Chemical shifts (δ) are quoted in ppm and coupling constants (J) are reported in Hz. LC–MS spectra were obtained on a Finnigan MAT INCOS-50 (Thermo Finnigan LLC, San Jose, CA, USA). The reaction mixture was monitored by thin-layer chromatography (TLC) using commercial glass-backed TLC plates (Merck Kieselgel 60 F254). Solvents and reagents (ethylenediamine diacetate (EDDA), CAS number: 38734-69-9; 4-tert-butylcyclohexanone, CAS number: 98-53-3) that are commercially available were used without further purification. The 2-thioxothiazolidin-4-one (CAS number: 141-84-4) (1) was prepared according to the protocol described in [17].
5-[4-(tert-Butyl)cyclohexylidene]-2-thioxothiazolidin-4-one (3): To a stirred solution of 2-thioxothiazolidin-4-one (1) (1.33 g, 10 mmol) and 4-tert-butylcyclohexanone (2) (1.54 g, 10 mmol) in MeOH (10 mL) at ca. 20 °C, ethylenediamine diacetate (EDDA) (1.8 mg, 10 µmol) was added and the mixture was then heated to reflux for 10 min and left overnight at room temperature. The resultant yellow solid of compound 3 was collected by filtration, washed with methanol (5–10 mL) and diethyl ether, and crystallized from glacial acetic acid.
Yellow crystals, yield 61 % (1.64 g), Rf (DCE) = 0.70, mp 164–166 °C (AcOH). 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6, δ): 13.36 (s, 1H), 4.06–4.14 (m, 1H), 2.33 (td, J = 13.5, 4.8 Hz, 1H), 2.17 (d, J = 14.0 Hz, 1H), 1.88–2.04 (m, 3H), 1.32 (dd, J = 8.9, 5.9 Hz, 1H), 1.14 (dqd, J = 28.7, 12.5, 4.2 Hz, 2H), 0.83 (s, 9H).13C-NMR (126 MHz, DMSO-d6, δ): 195.1 (C=S, C-2), 167.1 (C=O, C-4), 158.3 (C=C, C-8), 120.2 (C=C, C-5), 46.7 (C-11), 37.4 (C-14), 32.6, 29.3 (C-9, C-13), 28.5 (C-10, C-12), 27.3 (C-15, C-16, C-17). IR (KBr): 3140, 3034 (NH), 1682 (C=O), 1614 (C=C) cm−1. UV–Vis (acetone) λmax (ε, L·mol−1·cm−1): 335 (2.57), 276 (1.73), 226 (1.11) nm.
LCMS (ESI+) m/z 270.0 (100%, [M + H]+).
Anal. calc. for C13H19NOS2: C, 57.96%; H, 7.11%; N, 5.20%. Found: C, 58.10%; H, 7.30%; N, 5.40%.
3.2. Antimicrobial Activity
The synthesized compound 3 was tested in vitro for its antibacterial and antifungal activity using the agar diffusion and resazurin-based microdilution assays [18,19]. Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and vancomycin were used as a control. Reference and clinical microbial strains were used, previously identified by the MALDI TOF system (Bruker, Bremen, Germany) and 16S rRNA gene sequences. All clinical strains were multidrug-resistant with different antibiotic resistance patterns for the prediction of a possible compound mechanism of action. M. luteus strains were extensively drug resistant. Clinical strains were isolated from a patient with healthcare-associated infections from regional hospitals. All testing was repeated in triplicate.
4. Conclusions
In the present work, the application of ethylenediamine diacetate as an effective catalyst for the synthesis of 5-[4-(tert-butyl)cyclohexylidene]-2-thioxothiazolidin-4-one in the Knoevenagel reaction using the interaction of rhodanine with 4-(tert-butyl)cyclohexanone is described. Synthesized compound 3 possesses satisfactory predicted physicochemical and drug-like parameters calculated in silico as well as promising antimicrobial properties evaluated in vitro and presents interest as a prospective intermediate for forthcoming optimization/transformation to potential biologically active small molecules.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online. Figures S1–S4: NMR and LC-MS spectra of compound 3. Figure S5: IR spectrum of compound 3. Figure S6: UV spectrum of compound 3.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization was done by S.H., A.L., Y.K., and R.L.; methodology and experimental works were done by S.H., A.L., Y.K., and Y.S.; data analysis was done by S.H., A.L., and Y.K.; writing, review, and editing of the paper were done by S.H., A.L., Y.K., and R.L.; project administration and supervision was done by R.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The research leading to these results received funding from the Ministry of Healthcare of Ukraine (0121U100690), and the National Research Foundation of Ukraine (2020.02/0035).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in this article.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Danylo Halytsky Lviv National Medical University, which is gratefully acknowledged.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sharma, V.K.; Barde, A.; Rattan, S. A short review on synthetic strategies toward glitazone drugs. Synth. Commun. 2021, 51, 57–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terashima, H.; Hama, K.; Yamamoto, R.; Tsuboshima, M.; Kikkawa, R.; Hatanaka, I.; Shigeta, Y. Effects of a new aldose reductase inhibitor on various tissues in vitro. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1984, 229, 226–230. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Unangst, P.C.; Connor, D.T.; Cetenko, W.A.; Sorenson, R.J.; Kostlan, C.R.; Sircar, J.C.; Wright, C.D.; Schrier, D.J.; Dyer, R.D. Synthesis and biological evaluation of 5-[[3,5-bis(1,1-dimethylethyl)-4-hydroxyphenyl]methylene]oxazoles, -thiazoles, and -imidazoles: Novel dual 5-lipoxygenase and cyclooxygenase inhibitors with antiinflammatory activity. J. Med. Chem. 1994, 37, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolli, M.H.; Abele, S.; Binkert, C.; Bravo, R.; Buchmann, S.; Bur, D.; Gatfield, J.; Hess, P.; Kohl, C.; Mangold, C.; et al. 2-Imino-thiazolidin-4-one derivatives as potent, orally active S1P1 receptor agonists. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 4198–4211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markham, A. Ponesimod: First Approval. Drugs 2021, 81, 957–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sklyarova, Y.; Fomenko, I.; Lozynska, I.; Lozynskyi, A.; Lesyk, R.; Sklyarov, A. Hydrogen sulfide releasing 2-mercaptoacrylic acid-based derivative possesses cytoprotective activity in a small intestine of rats with medication-induced enteropathy. Sci. Pharm. 2017, 85, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Golota, S.; Sydorenko, I.; Surma, R.; Karpenko, O.; Gzella, A.; Lesyk, R. Facile one-pot synthesis of 5-aryl/heterylidene-2-(2-hydroxyethyl- and 3-hydroxypropylamino)-thiazol-4-ones via catalytic aminolysis. Synth. Commun. 2017, 47, 1071–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishchenko, M.; Shtrygol, S.; Lozynskyi, A.; Khomyak, S.; Novikov, V.; Karpenko, O.; Holota, S.; Lesyk, R. Evaluation of Anticonvulsant Activity of Dual COX-2/5-LOX Inhibitor Darbufelon and Its Novel Analogues. Sci. Pharm. 2021, 89, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holota, S.; Komykhov, S.; Sysak, S.; Gzella, A.; Cherkas, A.; Lesyk, R. Synthesis, Characterization and In Vitro Evaluation of Novel 5-Ene-thiazolo[3,2-b][1,2,4]triazole-6(5H)-ones as Possible Anticancer Agents. Molecules 2021, 26, 1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, F.C.; Bradsher, C.K.; McCallum, S.G.; Potter, M. Rhodanine derivatives of ketones. J. Org. Chem. 1950, 15, 174–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreiro, E.; Casas, J.S.; Couce, M.D.; Sánchez, A.; Sordo, J.; Varela, J.M.; Vázquez-López, E.M. The Influence of 5-Substituents on the Supramolecular Structures of Rhodanine Derivatives. Cryst. Growth Des. 2007, 7, 1964–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metwally, N.H.; Abdalla, M.A.; Mosselhi, M.A.; El-Desoky, E.A. Synthesis and antimicrobial activity of some new N-glycosides of 2-thioxo-4-thiazolidinone derivatives. Carbohydr. Res. 2010, 345, 1135–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alizadeh, A.; Khodaei, M.M.; Eshghi, A. A solvent-free protocol for the green synthesis of arylalkylidene rhodanines in a task-specific ionic liquid. Can. J. Chem. 2010, 88, 514–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SwissADME. Available online: http://www.swissadme.ch/ (accessed on 20 July 2021).
- Bauvois, C.; Huston, A.L.; Feller, G. Chapter 95—The cold-active M1 aminopeptidase from the arctic bacterium Colwellia psychrerythraea. In Handbook of Proteolytic Enzymes, 3rd ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 463–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiseman, L.R.; Wagstaff, A.J.; Brogden, R.N.; Bryson, H.M. Meropenem. A review of its antibacterial activity, pharmacokinetic properties and clinical efficacy. Drugs 1995, 50, 73–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nencki, M. Ueber die Einwirkung der Monochloressigsäure auf Sulfocyansäure und ihre Salze. J. Prakt. Chem. 1877, 16, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balouiri, M.; Sadiki, M.; Ibnsouda, S.K. Methods for in vitro evaluating antimicrobial activity: A review. J. Pharm. Anal. 2016, 6, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- EUCAST. Disk Diffusion—Manual v 9.0 (1 January, 2021). Available online: https://www.eucast.org/ast_of_bacteria/disk_diffusion_methodology/ (accessed on 20 July 2021).
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).