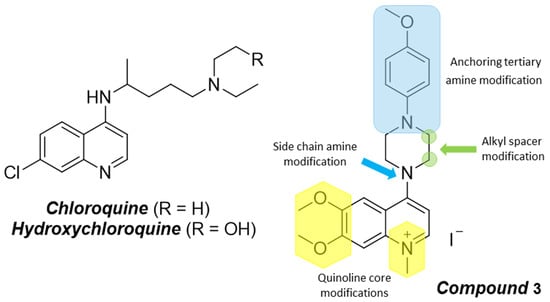
Ultrasonic Synthesis and Preliminary Evaluation of Anticoronaviral Activity of 6,7-Dimethoxy-4-(4-(4-methoxyphenyl)piperazin-1-yl)-1-methylquinolin-1-ium Iodide
Abstract
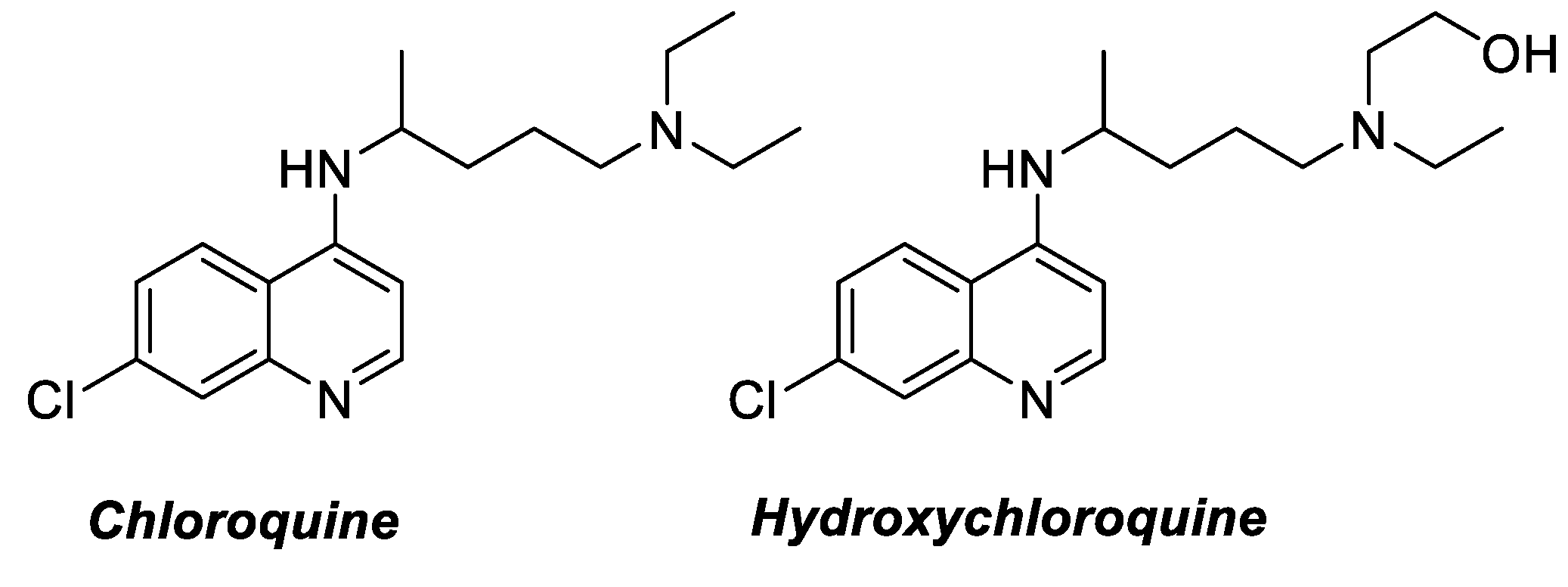
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthesis
2.2. Cytotoxicity and Antiviral Assays
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General
3.2. Synthesis
3.2.1. Synthesis of 4-Chloro-6,7-dimethoxy-1-methylquinolin-1-ium Iodide (2a)
3.2.2. Synthesis of 6,7-Dimethoxy-4-(4-(4-methoxyphenyl)piperazin-1-yl)-1-methylquinolin-1-ium Iodide (3)
3.3. Cytotoxicity Assay and Antiviral Assay against Human Coronavirus OC-43 (HCoV-OC43) (ATCC: VR-1558)
3.3.1. Cytotoxicity Assay
3.3.2. Anticoronaviral Assay
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- O’Neill, P.M.; Barton, V.E.; Ward, S.A.; Chadwick, J. 4-Aminoquinolines: Chloroquine, Amodiaquine and Next-Generation Analogues. In Treatment and Prevention of Malaria; Staines, H.M., Krishna, S., Eds.; Springer: Basel, Switzerland, 2012; pp. 19–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackenzie, A.H. Antimalarial drugs for rheumatoid arthritis. Am. J. Med. 1983, 75, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Irastorza, G. Effect of antimalarials on thrombosis and survival in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 2006, 15, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsega, E.; Besrat, A.; Damtew, B.; Seyoum, E.; Landells, J.W. Chloroquine in the treatment of porphyria cutanea tarda. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1981, 75, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Bari, M.A. Chloroquine analogues in drug discovery: New directions of uses, mechanisms of actions and toxic manifestations from malaria to multifarious diseases. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2015, 70, 1608–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alani, B.G.; Al-wash, A.H.; Ibrahim, I.T. Wide Applications of Chloroquine Other Than Antimalarial. Pharmacol. Pharm. 2020, 11, 251–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, L.R.S.; Freitas, A.C.C.; Nanayakkara, D.; McChesney, J.; Walker, L. New Chloroquine Analogues as Antiviral Agents. Acta Farm. Bonaer. 2006, 25, 351–355. [Google Scholar]
- Kondaparla, S.; Manhas, A.; Dola, V.R.; Srivastava, K.; Puri, S.K.; Katti, S.B. Design, synthesis and antiplasmodial activity of novel imidazole derivatives based on 7-chloro-4-aminoquinoline. Bioorg. Chem. 2018, 80, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa-Lima, G.; Da Silveira Pinto, L.S.; Kaiser, C.R.; Wardell, J.L.; De Freitas, C.S.; Vieira, Y.R.; Marttorelli, A.; Cerbino-Neto, J.; Bozza, P.T.; Wardell, S.M.S.V.; et al. N-(2-(arylmethylimino)ethyl)-7-chloroquinolin-4-amine derivatives, synthesized by thermal and ultrasonic means, are endowed with anti-Zika virus activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 127, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasso, B.; Novelli, F.; Tonelli, M.; Barteselli, A.; Basilico, N.; Parapini, S.; Taramelli, D.; Sparatore, A.; Sparatore, F. Synthesis and Antiplasmodial Activity of Novel Chloroquine Analogues with Bulky Basic Side Chains. Chem. Med. Chem. 2015, 10, 1570–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguiar, A.C.C.; Santos, R.M.; Figueiredo, F.J.B.; Cortopassi, W.A.; Pimentel, A.S.; Meneghetti, M.R.; Krettli, A.U. Antimalarial Activity and Mechanisms of Action of Two Novel 4-Aminoquinolines against Chloroquine-Resistant Parasites. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, M.; Cao, R.; Zhang, L.; Yang, X.; Liu, J.; Xu, M.; Shi, Z.; Hu, Z.; Zhong, W.; Xiao, G. Remdesivir and chloroquine effectively inhibit the recently emerged novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in vitro. Cell Res. 2020, 30, 269–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Cao, R.; Xu, M.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Hu, H.; Li, Y.; Hu, Z.; Zhong, W.; Wang, M. Hydroxychloroquine, a less toxic derivative of chloroquine, is effective in inhibiting SARS-CoV-2 infection in vitro. Cell Discov. 2020, 6, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nimgampalle, M.; Devanathan, V.; Saxena, A. Screening of Chloroquine, Hydroxychloroquine and its derivatives for their binding affinity to multiple SARS-CoV-2 protein drug targets. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2021, 39, 4949–4961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pallaval, V.B.; Kanithi, M.; Meenakshisundaram, S.; Jagadeesh, A.; Alavala, M.; Pillaiyar, T.; Manickam, M.; Chidipi, B. Chloroquine Analogs: An Overview of Natural and Synthetic Quinolines as Broad Spectrum Antiviral Agents. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2021, 27, 1185–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, H.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Ren, S.; Xu, T.; Lai, X.; Wen, J.; Zhao, M.; Zeng, C.; Du, L.; et al. Systematic Review and Pharmacological Considerations for Chloroquine and Its Analogs in the Treatment for COVID-19. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 554172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guevara-Pulido, J.; Jiménez, R.A.; Morantes, S.J.; Jaramillo, D.N.; Acosta-Guzmán, P. Design, Synthesis, and Development of 4-[(7-Chloroquinoline-4-yl)amino]phenol as a Potential SARS-CoV-2 Mpro Inhibitor. Chem. Sel. 2022, 7, e202200125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colson, P.; Rolain, J.M.; Lagier, J.C.; Brouqui, P.; Raoult, D. Chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine as available weapons to fight COVID-19. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2020, 55, 105932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, V.R.; Hua, C.; Lee, H. Design and synthesis of chloroquine analogs with anti-breast cancer property. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 3916–3923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, V.R.; Pundir, S.; Lee, H. Examination of novel 4-aminoquinoline derivatives designed and synthesized by a hybrid pharmacophore approach to enhance their anticancer activities. Sci. Rep. Nat. 2019, 9, 6315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Borenfreund, E.; Puerner, J.A. Toxicity determined in vitro by morphological alterations and neutral red absorption. Toxicol. Lett. 1985, 24, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vasilev, A.A.; Grozdanov, P.P.; Nikolova, I.; Lozanov, V.S.; Kandinska, M.I. Ultrasonic Synthesis and Preliminary Evaluation of Anticoronaviral Activity of 6,7-Dimethoxy-4-(4-(4-methoxyphenyl)piperazin-1-yl)-1-methylquinolin-1-ium Iodide. Molbank 2022, 2022, M1400. https://doi.org/10.3390/M1400
Vasilev AA, Grozdanov PP, Nikolova I, Lozanov VS, Kandinska MI. Ultrasonic Synthesis and Preliminary Evaluation of Anticoronaviral Activity of 6,7-Dimethoxy-4-(4-(4-methoxyphenyl)piperazin-1-yl)-1-methylquinolin-1-ium Iodide. Molbank. 2022; 2022(3):M1400. https://doi.org/10.3390/M1400
Chicago/Turabian StyleVasilev, Aleksey A., Peter P. Grozdanov, Ivanka Nikolova, Valentin S. Lozanov, and Meglena I. Kandinska. 2022. "Ultrasonic Synthesis and Preliminary Evaluation of Anticoronaviral Activity of 6,7-Dimethoxy-4-(4-(4-methoxyphenyl)piperazin-1-yl)-1-methylquinolin-1-ium Iodide" Molbank 2022, no. 3: M1400. https://doi.org/10.3390/M1400
APA StyleVasilev, A. A., Grozdanov, P. P., Nikolova, I., Lozanov, V. S., & Kandinska, M. I. (2022). Ultrasonic Synthesis and Preliminary Evaluation of Anticoronaviral Activity of 6,7-Dimethoxy-4-(4-(4-methoxyphenyl)piperazin-1-yl)-1-methylquinolin-1-ium Iodide. Molbank, 2022(3), M1400. https://doi.org/10.3390/M1400