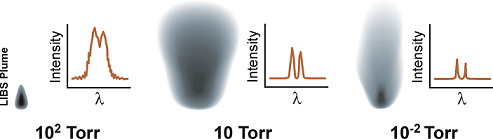
Effect of Atmospheric Conditions on LIBS Spectra
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Influence of Pressure
2.1. Low Pressure, <760 Torr
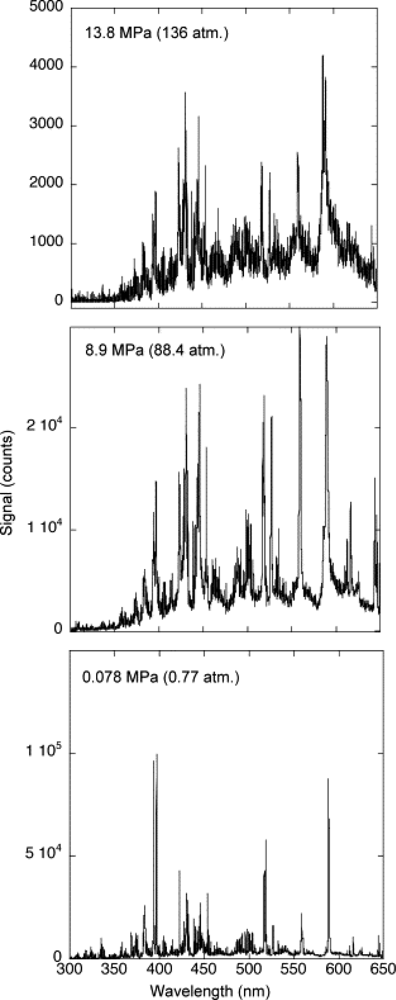
2.2. High Pressure, >760 Torr
3. Influence of Atmospheric Composition (e.g., He, N2, Ar & CO2)
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Harmon, R.S.; Remus, J.; McMillan, N.J.; McManus, C.; Collins, L.; Gottfried, J.L.; DeLucia, F.C.; Miziolek, A.W. LIBS analysis of geomaterials: Geochemical fingerprinting for the rapid analysis and discrimination of minerals. Appl. Geochem 2009, 24, 1125–1141. [Google Scholar]
- Gondal, M.A.; Hussain, T.; Yamani, Z.H.; Baig, M.A. On-line monitoring of remediation process of chromium polluted soil using LIBS. J. Hazard. Mater 2009, 163, 1265–1271. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, T.; Gondal, M.A. Monitoring and assessment of toxic metals in gulf war oil spill contaminated soil using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Environ. Monit. Assess 2008, 136, 391–399. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, T.; Specht, Z.G.; Vary, P.S.; Lin, C.T. Spectral fingerprints of bacterial strains by laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 5477–5482. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Celis, E.M.; Gornushkin, I.B.; Heitmann, U.M.; Almirall, J.R.; Smith, B.W.; Winefordner, J.D.; Omenetto, N. Laser induced breakdown spectroscopy as a tool for discrimination of glass for forensic applications. Anal. Bioanal. Chem 2008, 391, 1961–1968. [Google Scholar]
- Baudelet, M.; Guyon, L.; Yu, J.; Wolf, J.P.; Amodeo, T.; Frejafon, E.; Laloi, P. Femtosecond time-resolved laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy for detection and identification of bacteria: A comparison to the nanosecond regime. J. Appl. Phys 2006, 99, 084701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suliyanti, M.M.; Sardy, S.; Kusnowo, A.; Pardede, M.; Hedwig, R.; Kurniawan, K.H.; Lie, T.J.; Kurniawan, D.P.; Kagawa, K. Preliminary analysis of c and H in a “Sangiran” Fossil using laser-induced plasma at reduced pressure. J. Appl. Phys 2005, 98, 093307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osticioli, I.; Wolf, M.; Anglos, D. An optimization of parameters for application of a laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy microprobe for the analysis of works of art. Appl. Spectrosc 2008, 62, 1242–1249. [Google Scholar]
- Aragon, C.; Aguilera, J.A. Characterization of laser induced plasmas by optical emission spectroscopy: A review of experiments and methods. Spectrosc. Acta Pt. B-Atom. Spectr 2008, 63, 893–916. [Google Scholar]
- Capitelli, M.; Casavola, A.; Colonna, G.; De Giacomo, A. Laser-induced plasma expansion: Theoretical and experimental aspects. Spectrosc. Acta Pt. B-Atom. Spectr 2004, 59, 271–289. [Google Scholar]
- Cremers, D.A.; Radziemski, L.J. Handbook of Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy; Wiley: West Sussex, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Cremers, D.A.; Radziemski, L.J. Laser plasmas for chemical analysis. In Laser Spectroscopy and Its Applications; Radziemski, L.J., Solarz, R.W., Paisner, J.A., Eds.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1987; Chapter 5. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.-I.; Song, K.; Sneddon, J. Laser induced plasmas for analytical atomic spectroscopy. In Lasers in Analytical Atomic Spectroscopy; Sneddon, J., Thiem, T.L., Lee, Y.-I., Eds.; Wiley-VCH: New York, NY, USA, 1997; Chapter 5. [Google Scholar]
- Knight, A.K.; Scherbarth, N.L.; Cremers, D.A.; Ferris, M.J. Characterization of laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) for application to space exploration. Appl. Spectrosc 2000, 54, 331–340. [Google Scholar]
- Salle, B.; Cremers, D.A.; Maurice, S.; Wiens, R.C. Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy for space exploration applications: Influence of the ambient pressure on the calibration curves prepared from soil and clay samples. Spectrosc. Acta Pt. B-Atom. Spectr 2005, 60, 479–490. [Google Scholar]
- Shu, R.; Qi, H.X.; Lu, G.; Ma, D.M.; He, Z.P.; Xue, Y.Q. Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy based detection of lunar soil simulants for moon exploration. Chin. Opt. Lett 2007, 5, 58–59. [Google Scholar]
- Wiens, R.C.; Maurice, S. Chemcam’s cost a drop in the Mars bucket. Science 2008, 322, 1464–1464. [Google Scholar]
- Arp, Z.A.; Cremers, D.A.; Wiens, R.C.; Wayne, D.M.; Salle, B.A.; Maurice, S. Analysis of water ice and water ice/soil mixtures using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy: Application to Mars polar exploration. Appl. Spectrosc 2004, 58, 897–909. [Google Scholar]
- Brennetot, R.; Lacour, J.L.; Vors, E.; Rivoallan, A.; Vailhen, D.; Maurice, S. Mars analysis by laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (MALIS): Influence of Mars atmosphere on plasma emission and study of factors influencing plasma emission with the use of doehlert designs. Appl. Spectrosc 2003, 57, 744–752. [Google Scholar]
- Colao, F.; Fantoni, R.; Lazic, V.; Paolini, A. LIBS application for analyses of martian crust analogues: Search for the optimal experimental parameters in air and CO2 atmosphere. Appl. Phys. A-Mater 2004, 79, 143–152. [Google Scholar]
- Colao, F.; Fantoni, R.; Lazic, V.; Paolini, A.; Fabbri, F.; Ori, G.G.; Marinangeli, L.; Baliva, A. Investigation of LIBS feasibility for in situ planetary exploration: An analysis on martian rock analogues. Planet. Space Sci 2004, 52, 117–123. [Google Scholar]
- Salle, B.; Cremers, D.A.; Maurice, S.; Wiens, R.C.; Fichet, P. Evaluation of a compact spectrograph for in-situ and stand-off laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy analyses of geological samples on Mars missions. Spectrosc. Acta Pt. B-Atom. Spectr 2005, 60, 805–815. [Google Scholar]
- Salle, B.; Lacour, J.L.; Mauchien, P.; Fichet, P.; Maurice, S.; Manhes, G. Comparative study of different methodologies for quantitative rock analysis by laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy in a simulated martian atmosphere. Spectrosc. Acta Pt. B-Atom. Spectr 2006, 61, 301–313. [Google Scholar]
- Salle, B.; Lacour, J.L.; Vors, E.; Fichet, P.; Maurice, S.; Cremers, D.A.; Wiens, R.C. Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy for Mars surface analysis: Capabilities at stand-off distances and detection of chlorine and sulfur elements. Spectrosc. Acta Pt. B-Atom. Spectr 2004, 59, 1413–1422. [Google Scholar]
- Radziemski, L.; Cremers, D.A.; Benelli, K.; Khoo, C.; Harris, R.D. Use of the vacuum ultraviolet spectral region for laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy-based martian geology and exploration. Spectrosc. Acta Pt. B-Atom. Spectr 2005, 60, 237–248. [Google Scholar]
- Wiens, R.C.; Arvidson, R.E.; Cremers, D.A.; Ferris, M.J.; Blacic, J.D.; Seelos, F.P.; Deal, K.S. Combined remote mineralogical and elemental identification from rovers: Field and laboratory tests using reflectance and laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. J. Geophys. Res.-Planets 2002, 107, 8003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clegg, S.M.; Wiens, R.C.; Lawerence, D.J.; Barefield, J.E. Lunar elemental analysis with remote laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS). Proceedings of Lunar Science Workshop, Tempe, AZ, USA, February, 2007.
- Qi, H.X.; Pan, M.Z.; Lv, G.; He, Z.P.; Yan, Z.X.; Shu, R. Feasibility study on the application of laser induced breakdown spectroscopy to lunar exploration. J. Infrared Millim. Waves 2009, 28, 93–96. [Google Scholar]
- Arp, Z.A.; Cremers, D.A.; Harris, R.D.; Oschwald, D.M.; Parker, G.R.; Wayne, D.M. Feasibility of generating a useful laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy plasma on rocks at high pressure: Preliminary study for a Venus mission. Spectrosc. Acta Pt. B-Atom. Spectr 2004, 59, 987–999. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, C.A.; Martinez, M.A.; Veirs, D.K.; Cremers, D.A. Pu-239/Pu-240 isotope ratios determined using high resolution emission spectroscopy in a laser-induced plasma. Spectrosc. Acta Pt. B-Atom. Spectr 2002, 57, 929–937. [Google Scholar]
- Chinni, R.C.; Cremers, D.A.; Radziemski, L.J.; Bostian, M.; Navarro-Northrup, C. Detection of uranium using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Appl. Spectrosc 2009, 63, 1238–1250. [Google Scholar]
- Pietsch, W.; Petit, A.; Briand, A. Isotope ratio determination of uranium by optical emission spectroscopy on a laser-produced plasma-basic investigations and analytical results. Spectrosc. Acta Pt. B-Atom. Spectr 1998, 53, 751–761. [Google Scholar]
- Kurniawan, K.H.; Kagawa, K. Hydrogen and deuterium analysis using laser-induced plasma spectroscopy. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev 2006, 41, 99–130. [Google Scholar]
- Song, K.; Lee, Y.I.; Sneddon, J. Applications of laser-induced breakdown spectrometry. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev 1997, 32, 183–235. [Google Scholar]
- Glumac, N.; Elliott, G. The effect of ambient pressure on laser-induced plasmas in air. Opt. Lasers Eng 2007, 45, 27–35. [Google Scholar]
- Cowpe, J.S.; Astin, J.S.; Pilkington, R.D.; Hill, A.E. Temporally resolved laser induced plasma diagnostics of single crystal silicon - effects of ambient pressure. Proceedings of 4th Euro Mediterranean Symposium on Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy, Paris, France, September 11–13, 2007; pp. 1066–1071.
- Cowpe, J.S.; Astin, J.S.; Pilkington, R.D.; Hill, A.E. Application of response surface methodology to laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy: Influences of hardware configuration. Spectrosc. Acta Pt. B-Atom. Spectr 2007, 62, 1335–1342. [Google Scholar]
- Cowpe, J.S.; Pilkington, R.D. Swagelok Ultra-Torr based feed-through design for coupling optical fibre bundles into vacuum systems. Vacuum 2008, 82, 1341–1343. [Google Scholar]
- Dreyer, C.B.; Mungas, G.S.; Thanh, P.; Radziszewski, J.G. Study of sub-mJ-excited laser-induced plasma combined with Raman spectroscopy under Mars atmosphere-simulated conditions. Spectrosc. Acta Pt. B-Atom. Spectr 2007, 62, 1448–1459. [Google Scholar]
- Vadillo, J.M.; Romero, J.M.F.; Rodriguez, C.; Laserna, J.J. Depth-resolved analysis by laser-induced breakdown spectrometry at reduced pressure. Surf.Interface Anal 1998, 26, 995–1000. [Google Scholar]
- Vadillo, J.M.; Romero, J.M.F.; Rodriguez, C.; Laserna, J.J. Effect of plasma shielding on laser ablation rate of pure metals at reduced pressure. Surf. Interface Anal 1999, 27, 1009–1015. [Google Scholar]
- Corsi, M.; Cristoforetti, G.; Hidalgo, M.; Iriarte, D.; Legnaioli, S.; Palleschi, V.; Salvetti, A.; Tognoni, E. Effect of laser-induced crater depth in laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy emission features. Appl. Spectrosc 2005, 59, 853–860. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, D.J.; Jeon, H.; Grigoropoulos, C.P.; Yoo, J.; Russo, R.E. Femtosecond laser ablation induced plasma characteristics from submicron craters in thin metal film. Appl. Phys. Lett 2007, 91, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Pardede, M.; Lie, T.J.; Kurniawan, K.H.; Niki, H.; Fukumoto, K.; Maruyama, T.; Kagawa, K.; Tjia, M.O. Crater effects on H and D emission from laser induced low-pressure helium plasma. J. Appl. Phys 2009, 106, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Yalcin, S.; Tsui, Y.Y.; Fedosejevs, R. Pressure dependence of emission intensity in femtosecond laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. J. Anal. Atomic Spectrom 2004, 19, 1295–1301. [Google Scholar]
- Margetic, V.; Pakulev, A.; Stockhaus, A.; Bolshov, M.; Niemax, K.; Hergenroder, R. A comparison of nanosecond and femtosecond laser-induced plasma spectroscopy of brass samples. Spectrosc. Acta Pt. B-Atom. Spectr 2000, 55, 1771–1785. [Google Scholar]
- Vors, E.; Gallou, C.; Salmon, L. Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy of carbon in helium and nitrogen at high pressure. Spectrosc. Acta Pt. B-Atom. Spectr 2008, 63, 1198–1204. [Google Scholar]
- Owens, M.; Majidi, V. Effects of high-pressure buffer gases on emission from laser-induced plasmas. Appl. Spectrosc 1991, 45, 1463–1467. [Google Scholar]
- Iida, Y. Effects of atmosphere on laser vaporization and excitation processes of solid samples. Spectrosc. Acta Pt. B-Atom. Spectr 1990, 45, 1353–1367. [Google Scholar]
- Young, M.; Hercher, M. Dynamics of laser-induced breakdown in gases. J. Appl. Phys 1967, 38, 4393–4400. [Google Scholar]
- Aguilera, J.A.; Aragon, C. A comparison of the temperatures and electron densities of laser-produced plasmas obtained in air, argon, and helium at atmospheric pressure. Appl. Phys. A-Mater 1999, 69, S475–S478. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.I.; Song, K.; Cha, H.K.; Lee, J.M.; Park, M.C.; Lee, G.H.; Sneddon, J. Influence of atmosphere and irradiation wavelength on copper plasma emission induced by excimer and Q-switched Nd:YAG laser ablation. Appl. Spectrosc 1997, 51, 959–964. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, X.L.; Chan, W.T.; Shannon, M.A.; Russo, R.E. Plasma shielding during picosecond laser sampling of solid materials by ablation in He versus Ar atmosphere. J. Appl. Phys 1993, 74, 4915–4922. [Google Scholar]














© 2010 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an Open Access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Effenberger, A.J., Jr.; Scott, J.R. Effect of Atmospheric Conditions on LIBS Spectra. Sensors 2010, 10, 4907-4925. https://doi.org/10.3390/s100504907
Effenberger AJ Jr., Scott JR. Effect of Atmospheric Conditions on LIBS Spectra. Sensors. 2010; 10(5):4907-4925. https://doi.org/10.3390/s100504907
Chicago/Turabian StyleEffenberger, Andrew J., Jr., and Jill R. Scott. 2010. "Effect of Atmospheric Conditions on LIBS Spectra" Sensors 10, no. 5: 4907-4925. https://doi.org/10.3390/s100504907
APA StyleEffenberger, A. J., Jr., & Scott, J. R. (2010). Effect of Atmospheric Conditions on LIBS Spectra. Sensors, 10(5), 4907-4925. https://doi.org/10.3390/s100504907