Influences of Probe’s Morphology for Metal Ion Detection Based on Light-Addressable Potentiometric Sensors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
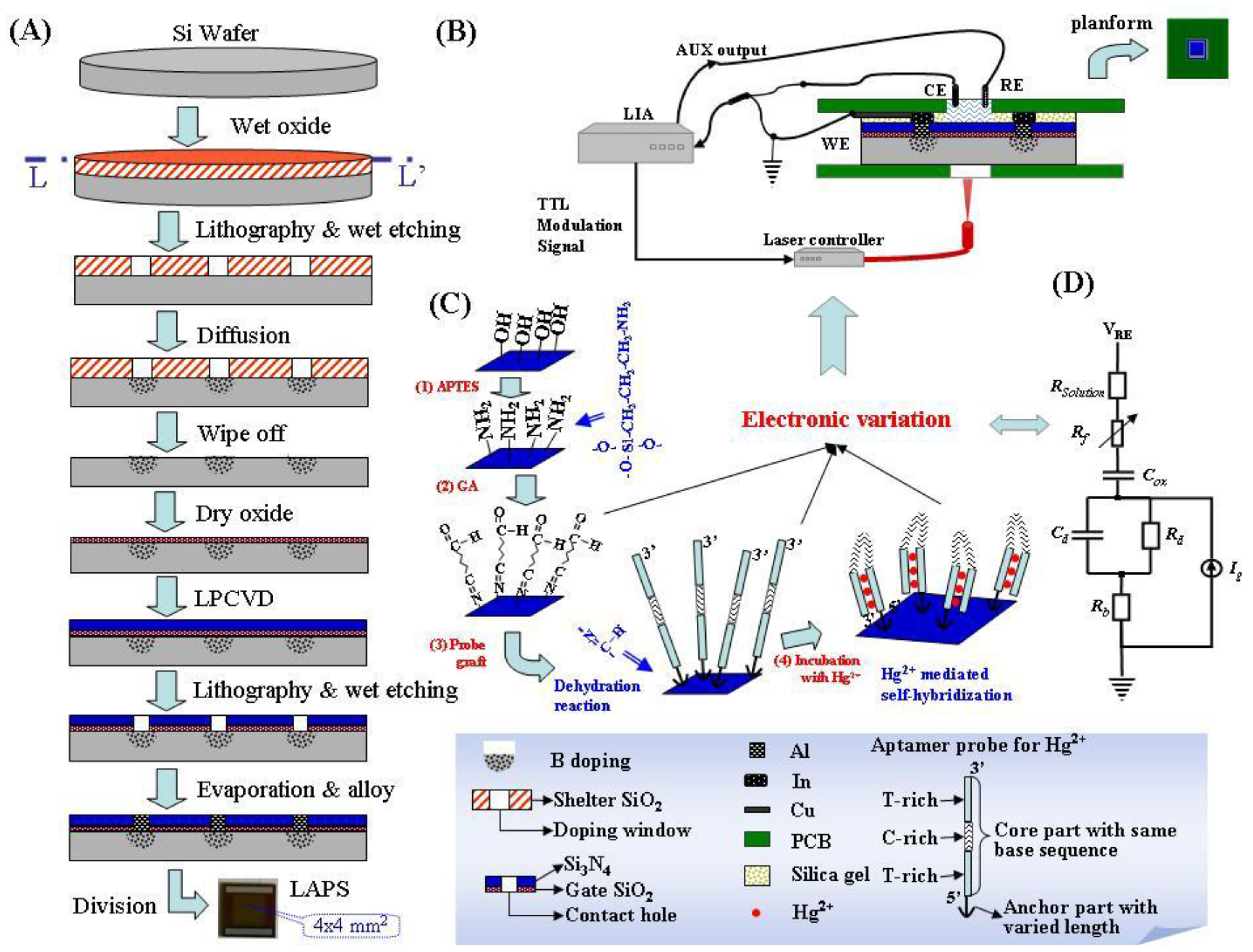
2.2. Preparation of the LAPS Chip
2.3. LAPS Detection System
2.4. Surface Modification and LAPS Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Electronic Characteristics of BLANK LAPS
3.2. Influences of Grafted Probes on LAPS
3.3. Hg2+ Detection by Aptamer LAPS
3.4. Response of Apta-LAPS to Other Metal Ions
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hafeman, D.G.; Parce, J.W.; McConnell, H.M. Light-addressable potentiometric sensor for biochemical systems. Science 1988, 240, 1182–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ermolenko, Y.E.; Yoshinobu, T.; Mourzina, Y.G. Laser-scanned silicon transducer (LSST) as a multisensor system. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2004, 103, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoning, M.J.; Wanger, T.; Wang, C.; Otto, R.; Yoshinobu, T. Development of a handheld 16 channel pen-type LAPS for electrochemical sensing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2005, 108, 808–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshinobu, T.; Schoning, M.J.; Otto, R.; Furuichi, K.; Mourzina, Y.; Ermolenko, Y.; Iwasaki, H. Portable light-addressable potentiometric sensor (LAPS) for multisensor applications. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2003, 95, 352–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, P.; Parak, W.J.; George, M.; Zhang, G. A novel design of multi-light LAPS based on digital compensation of frequency domain. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2001, 73, 152–156. [Google Scholar]
- Sawada, K.; Mimura, S.; Tomita, K.; Nakanishi, T.; Tanabe, H.; Ishida, M.; Ando, T. Novel CCD-based pH imaging sensor. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 1999, 46, 1846–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, D.; Hu, N.; Wu, C.X.; Kirsanov, D.; Legin, A.; Khaydukova, M.; Wang, P. Novel structured light-addressable potentiometric sensor array based on PVC membrane for determination of heavy metals. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 174, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, H.; Ha, D.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, H.; Wang, X.; Sun, Q.; Wang, P. Design of a novel hybrid sensor with microelectrode array and LAPS for heavy metal determination using multivariate nonlinear calibration. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 192, 755–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, L.B.; Han, J.H.; Qui, D.F.; Zhang, H. The Research of Light Addressable Potentiometric Sensor on Detection of Alpha Feto-protein. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2005, 33, 17–21. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Y.F.; Gao, C.Y.; He, J.; Feng, D.F.; Xing, K.L.; Wu, M.; Liu, Y.; Cai, W.S.; Feng, X.Z. Unlabeled multi tumor marker detection system based on bioinitiated light addressable potentiometric sensor. Analyst 2012, 137, 3806–3813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y.; Ju, C.; Li, Y.; Shang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Jia, Y.; Niu, Y. Detection of circulating tumor cells in prostate cancer based on carboxylated graphene oxide modified light addressable potentiometric sensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 66, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Y.; Qin, M.; Zhang, H.; Niu, W.; Li, X.; Wang, L.; Li, X.; Bai, Y.; Cao, Y.; Feng, X. Label-free biosensor: A novel phage-modified Light Addressable Potentiometric Sensor system for cancer cell monitoring. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 22, 3261–3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Y.; Yin, X.B.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, S.; Song, M.; Xing, K.L. Graphene oxide modified light addressable potentiometric sensor and its application for ssDNA monitoring. Analyst 2012, 137, 5866–5873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuerk, C.; Gold, L. Systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment: RNA ligands to bacteriophage T4 DNA polymerase. Science 1990, 249, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellington, A.D.; Szostak, J.W. In vitro selection of RNA molecules that bind specific ligands. Nature 1990, 346, 818–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyake, Y.; Togashi, H.; Tashiro, M.; Yamaguchi, H.; Oda, S.; Kudo, M.; Tanaka, Y.; Kondo, Y.; Sawa, R.; Fujimoto, T.; et al. MercuryII-Mediated Formation of Thymine-HgII-Thymine Base Pairs in DNA Duplexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 2172–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tombelli, S.; Minunni, M.; Mascini, M. Analytical applications of aptamers. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2005, 20, 2424–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, M.; Xu, L.; Zhang, X.; Xiao, R.; Wang, Y. Ag(I)-coordinated hairpin DNA for homogenous electronic monitoring of hepatitis C virus accompanying isothermal cycling signal amplification strategy. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 73, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Sullivan, C.K. Aptasensors-the future of biosensing? Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2002, 372, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, S.; Wang, L.; Li, J.; Fan, C.; Zhao, J. Aptamer-based biosensors. Trend. Anal. Chem. 2008, 27, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandimalla, V.B.; Ju, H. New Horizons with A Multi Dimensional Tool for Applications in Analytical Chemistry—Aptamer. Anal. Lett. 2004, 37, 2215–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Kim, Y.R.; Oh, J.W.; Kim, T.H.; Mahajan, R.K.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, H. A regenerative electrochemical sensor based on oligonucleotide for the selective determination of mercury (II). Analyst 2009, 134, 1857–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, R.M.; Zhang, X.B.; Zhang, L.L.; Jin, X.Y.; Huan, S.Y.; Shen, G.L.; Yu, R.Q. An ultrasensitive electrochemical “turn-on” label-free biosensor for Hg2+ with AuNP-functionalized reporter DNA as a signal amplifier. Chem. Comm. 2009, 37, 5633–5635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ono, A.; Togashi, H. Highly Selective Oligonucleotide-Based Sensor for Mercury (II) in Aqueous Solutions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 4300–4302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zeng, G.M.; Tang, L.; Chen, J.; Zhu, Y.; Xiao, X.H.; He, Y. Electrochemical Sensor Based on Electrodeposited Graphene-Au Modified Electrode and NanoAu Carrier Amplified Signal Strategy for Attomolar Mercury Detection. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 989–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.P.; Song, Z.G.; Fang, Y.; Mei, J.; Jia, L.; Qin, A.J.; Sun, J.Z.; Ji, J.; Tang, B.Z. Label-free fluorescence detection of mercury (II) and glutathione based on Hg2+-DNA complexes stimulating aggregation-induced emission of a tetraphenylethene derivative. Analyst 2010, 135, 3002–3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, D.; He, Y.; Xing, X.; Zhao, Y.; Tang, H.; Pang, D. Aptamer functionalized gold nanoparticles based fluorescent probe for the detection of mercury (II) ion in aqueous solution. Talanta 2013, 113, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, W.Y.; Huang, W.T.; Luo, H.Q.; Li, N.B. CTAB-capped Mn-doped ZnS quantum dots and label-free aptamer for room-temperature phosphorescence detection of mercury ions. Analyst 2012, 137, 4651–4653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.N.; Liu, D.J.; Wang, Z.X. Gold Nanoparticle-Based Dynamic Light Scattering Assay for Mercury Ion Detection. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2014, 42, 332–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Kang, M.; Yan, F.; Peng, D.; Yang, Y.; He, L.; Wang, M.; Fang, S.; Zhang, Z. Electrochemical DNA Biosensor Based on Microspheres of Cuprous Oxide and Nano-chitosan for Hg(II) Detection. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 160, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Li, X.; Kraatz, H.B. Impedimetric Immobilized DNA-Based Sensor for Simultaneous Detection of Pb2+, Ag+, and Hg2+. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 6896–6901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Sun, C.; Wu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, J.; Shen, G.; Yu, R. Label-Free Electrochemical Biosensor of Mercury Ions Based on DNA Strand Displacement by Thymine-Hg(II)-Thymine Complex. Electroanalysis 2010, 22, 2110–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronder, T.; Wu, C.S.; Poghossian, A.; Werner, C.F.; Keusgen, M.; Schöning, M.J. Label-free Detection of DNA Hybridization with Light-addressable Potentiometric Sensors: Comparison of Various DNA-immobilization Strategies. Proced. Eng. 2014, 87, 755–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Liu, H.; Zou, B.; Tian, D.; Huang, H. A fishnet electrochemical Hg2+ sensing strategy based on gold nanoparticle-bioconjugate and thymine-Hg2+-thymine coordination chemistry. Analyst 2012, 137, 309–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Cai, W.; Gao, X.M.; Wang, P. Mercury ion selective light addressable potentiometric sensor based on PVC membrane. J. Zhejiang. Univ. Sci. B 2010, 44, 1231–1236. [Google Scholar]




© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shao, C.; Zhou, S.; Yin, X.; Gu, Y.; Jia, Y. Influences of Probe’s Morphology for Metal Ion Detection Based on Light-Addressable Potentiometric Sensors. Sensors 2016, 16, 701. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16050701
Shao C, Zhou S, Yin X, Gu Y, Jia Y. Influences of Probe’s Morphology for Metal Ion Detection Based on Light-Addressable Potentiometric Sensors. Sensors. 2016; 16(5):701. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16050701
Chicago/Turabian StyleShao, Chen, Shuang Zhou, Xuebo Yin, Yajun Gu, and Yunfang Jia. 2016. "Influences of Probe’s Morphology for Metal Ion Detection Based on Light-Addressable Potentiometric Sensors" Sensors 16, no. 5: 701. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16050701
APA StyleShao, C., Zhou, S., Yin, X., Gu, Y., & Jia, Y. (2016). Influences of Probe’s Morphology for Metal Ion Detection Based on Light-Addressable Potentiometric Sensors. Sensors, 16(5), 701. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16050701




