Recent Progress on Cellulose-Based Electro-Active Paper, Its Hybrid Nanocomposites and Applications
Abstract
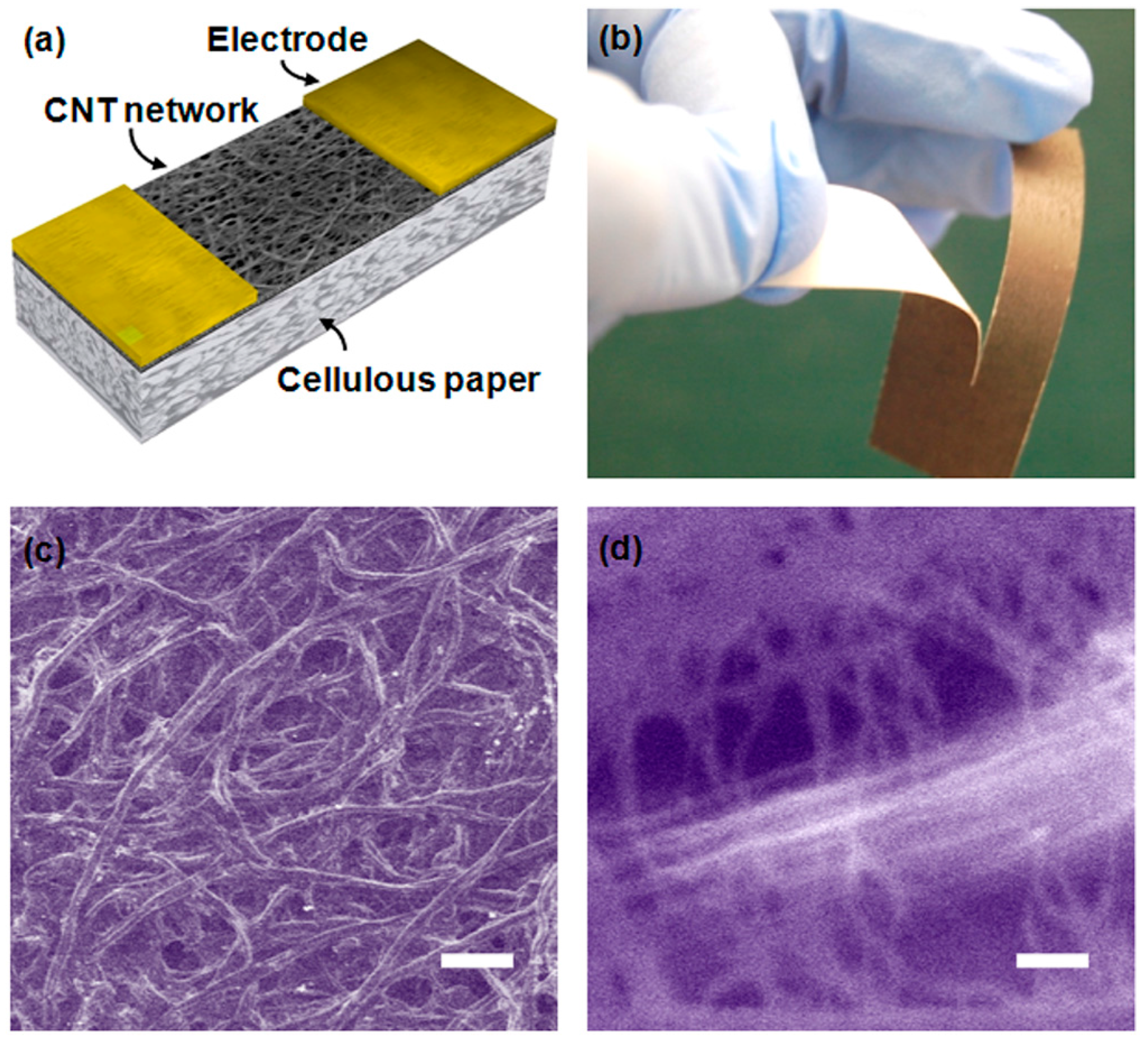
:1. Introduction
2. Cellulose EAPap
2.1. Actuation Mechanism
2.2. Mechanical Properties
2.3. Electromechanical Behavior and Direct Piezoelectricity
3. Cellulose Hybrid Nanocomposites
3.1. Cellulose-SWNT/MWNT EAPap
3.2. Cellulose-Chitosan Blended EAPap
3.3. Metal Oxide Cellulose Nanocomposites
3.4 Cellulose-Graphene Nanocomposites
4. Applications
4.1. Cellulose EAPap Actuators
4.2. EAPap Vibration Transducers
4.3. Cellulose-Nanocomposite Biosensors
4.4. Cellulose Based Gas and pH Sensors
4.5. Cellulose Based Paper Transistors
4.6. Humidity and Temperature Sensors
4.7. Acoustic Applications
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PVDF | polyvinylidene fluoride |
| EAPap | electro-active paper |
| SWNT | single walled carbon nanotube |
| MWNT | multi walled carbon nanotube |
| PEO-PEG | poly(ethylene oxide)-poly(ethylene glycol) |
| CNT | carbon nanotube |
| CPIL | cellulose-polypyrrole-ionic liquid |
| PPy | polypyrrole |
| PCB | poly carboxybetaine |
| CTM | cellulose-TiO2-MWNT |
| SPCE | screen printed carbon electrode |
| IDT | inter-digit transducer |
| IL | ionic liquid |
| GNP | gold nanoparticle |
| RFID | radio-frequency identification |
| NCC | nanocrystal cellulose |
| CNC | cellulose nanocrystals |
| GnP | graphene nanoplatelets |
| CMC | carboxymethylcellulose |
References
- Klemm, D.; Heublein, B.; Fink, H.P.; Bohn, A. Cellulose: Fascinating biopolymer and sustainable raw material. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 3358–3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukada, E. Piezoelectricity of wood. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 1955, 10, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazhenov, V.A. Piezoelectric Properties of Woods; Consultants Bureau: New York, NY, USA, 1961. [Google Scholar]
- Fukada, E. History and recent progress in piezoelectric polymers. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2000, 47, 1277–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawai, H. The piezoelectricity of poly (vinylidene fluoride). Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1969, 8, 975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Seo, Y.B. Electro-Active paper actuators. Smart Mater. Struct. 2002, 11, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, S.D.; Kim, J.; Yun, S.R. Studies on conducting polymer electroactive paper actuators: Effect of humidity and electrode thickness. Smart Mater. Struct. 2005, 14, 876–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, S.D.; Kim, J.; Yun, S.R. New electro-active paper actuator using conducting polypyrrole: Actuation behaviour in liclo(4) acetonitrile solution. Synth. Met. 2005, 149, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Yun, S.; Lee, S.K. Cellulose smart material: Possibility and challenges. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2008, 19, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresha, K.M.; Yang, S.Y.; Lee, M.H.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J. Actuator, sensor and mems devices based on regenerated cellulose. Compos. Interfaces 2008, 15, 679–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Yun, S.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J. Fabrication of piezoelectric cellulose paper and audio application. J. Bionic Eng. 2009, 6, 18–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.; Jang, S.D.; Yun, G.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J. Paper transistor made with covalently bonded multiwalled carbon nanotube and cellulose. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 95, 104102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Bae, S.H.; Lim, H.G. Micro transfer printing on cellulose electro-active paper. Smart Mater. Struct. 2006, 15, 889–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.; Kim, J. Covalently bonded multi-walled carbon nanotubes-cellulose electro-active paper actuator. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2009, 154, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.; Kim, H.S. Piezoelectricity of wet drawn cellulose electro-active paper. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2009, 154, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.W.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.; Kim, H.S. Characterization and sensor application of cellulose electro-active paper (eapap). Chin. Sci. Bull. 2009, 54, 2703–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, G.Y.; Yun, K.J.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J. Electrical and mechanical characterization of nanoscale-layered cellulose-based electro-active paper. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2011, 11, 570–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalia, S.; Boufi, S.; Celli, A.; Kango, S. Nanofibrillated cellulose: Surface modification and potential applications. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2014, 292, 5–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, N.; Gatenholm, P. Bacterial cellulose-based materials and medical devices: Current state and perspectives. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 91, 1277–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciechanska, D. Multifunctional bacterial cellulose/chitosan composite materials for medical applications. Fibres Text. East. Eur. 2004, 12, 69–72. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, W.C.; Lien, C.C.; Yeh, H.J.; Yu, C.M.; Hsu, S.H. Bacterial cellulose and bacterial cellulose-chitosan membranes for wound dressing applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 94, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gindl, W.; Keckes, J. All-cellulose nanocomposite. Polymer 2005, 46, 10221–10225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahadeva, S.K.; Kim, J. Hybrid nanocomposite based on cellulose and tin oxide: Growth, structure, tensile and electrical characteristics. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2011, 12, 055006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siro, I.; Plackett, D. Microfibrillated cellulose and new nanocomposite materials: A review. Cellulose 2010, 17, 459–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Gullapalli, H.; Balakrishnan, K.; Botello-Mendez, A.; Vajtai, R.; Terrones, M.; Ajayan, P.M. Flexible zno-cellulose nanocomposite for multisource energy conversion. Small 2011, 7, 2173–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakirov, A.S.; Yuldashev, S.U.; Cho, H.D.; Lee, J.C.; Kang, T.W.; Khamdamov, J.J.; Mamadalimov, A.T. Functional hybrid materials derived from natural cellulose. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 2012, 60, 1526–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Mun, S.; Ko, H.U.; Yun, G.Y.; Kim, J. Disposable chemical sensors and biosensors made on cellulose paper. Nanotechnology 2014, 25, 092001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Yun, S.; Ounaies, Z. Discovery of cellulose as a smart material. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 4202–4206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahadeva, S.K.; Kim, J.; Kang, K.S.; Kim, H.S.; Park, J.M. Effect of poly(ethylene oxide)-poly(ethylene glycol) addition on actuation behavior of cellulose electroactive paper. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 114, 847–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Kim, J.; Jung, W.; Ampofo, J.; Craft, W.; Sankar, J. Mechanical properties of cellulose electro-active paper under different environmental conditions. Smart Mater. Struct. 2008, 17, 015029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Jung, W.; Kim, H.S. In-Plane strain of electro-active paper under electric fields. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2007, 140, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Jung, W.; Jo, C.H.; Shelton, J.; Craft, W. Mechanical properties of cellulose-based electro-active paper. J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2008, 222, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Yang, C.; Kim, J. Hygrothermal behavior of electro-active paper actuator. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2009, 23, 2285–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Li, Y.; Kim, J. Electro-Mechanical behavior and direct piezoelectricity of cellulose electro-active paper. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2008, 147, 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kim, J.H.; Kang, K.; Kim, J.; Kim, H.S.; Yang, C. Characterization of micro-scale creep deformation of an electro-active paper actuator. Smart Mater. Struct. 2009, 18, 095008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahadeva, S.K.; Lee, S.W.; Kim, J. Effect of heat treatment on the structure, piezoelectricity and actuation behavior of a cellulose electroactive-paper actuator. Acta Mater. 2008, 56, 1868–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, J.N.; Chen, Y.; Yun, S.; Kim, J. Effect of Li+ ions on structure, properties, and actuation of cellulose electro-active paper actuator. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 108, 2260–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.; Chen, Y.; Nayak, J.N.; Kim, J. Effect of solvent mixture on properties and performance of electro-active paper made with regenerated cellulose. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2008, 129, 652–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahadeva, S.K.; Yang, S.Y.; Kim, J. Effects of solvent systems on its structure, properties and electromechanical behavior of cellulose electro-active paper. Curr. Org. Chem. 2013, 17, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Ampofo, J.; Craft, W.; Kim, H.S. Modeling elastic, viscous and creep characteristics of cellulose electro-active paper. Mech. Mater. 2008, 40, 1001–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.; Jang, S.; Yun, G.Y.; Kim, J. Electrically aligned cellulose film for electro-active paper and its piezoelectricity. Smart Mater. Struct. 2009, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, G.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J. Dielectric and polarization behaviour of cellulose electro-active paper (eapap). J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2009, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.E.; Guan, J.; Ricard, M.; Dubey, G.; Su, J.; Lopinski, G.; Dorris, G.; Bourne, O.; Simard, B. Multifunctional single-walled carbon nanotube-cellulose composite paper. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 2400–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, H.; Liu, J.; Mäder, E. Smart cellulose fibers coated with carbon nanotube networks. Fibers 2014, 2, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.Y.; Kim, J.; Ounaies, Z. Single-Walled carbon nanotube/polyaniline coated cellulose based electro-active paper (eapap) as hybrid actuator. Smart Mater. Struct. 2006, 15, N61–N65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.; Kim, J. A bending electro-active paper actuator made by mixing multi-walled carbon nanotubes and cellulose. Smart Mater. Struct. 2007, 16, 1471–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.; Kim, J. Characteristics and performance of functionalized MWNT blended cellulose electro-active paper actuator. Synth. Met. 2008, 158, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.; Kim, J. Mechanical, electrical, piezoelectric and electro-active behavior of aligned multi-walled carbon nanotube/cellulose composites. Carbon 2011, 49, 518–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Mun, S.C.; Kim, J. A wide range conductometric ph sensor made with titanium dioxide/multiwall carbon nanotube/cellulose hybrid nanocomposite. IEEE Sens. J. 2013, 13, 4157–4162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.; Yan, X.; Ding, J.J.; Ren, R. A simple method for preparing biocompatible composite of cellulose and carbon nanotubes for the cell sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2010, 146, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Yun, S.; Ko, H.U.; Kim, J. A flexible paper transistor made with aligned single-walled carbon nanotube bonded cellulose composite. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2013, 13, 897–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankonian, A.; Ounaies, Z.; Yang, C. Electrospinning of cellulose and SWNT-cellulose nano fibers for smart applications. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2011, 25, 2631–2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, C.M.; Shieh, Y.T.; Twu, Y.K. Preparation and characterization of cellulose/chitosan blend films. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 78, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.F.; Farnood, R.; O’Kelly, K.; Chen, B.Q. Mechanical behavior of transparent nanofibrillar cellulose-chitosan nanocomposite films in dry and wet conditions. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2014, 32, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Wang, N.; Chen, Y. Effect of chitosan and ions on actuation behavior of cellulose-chitosan laminated films as electro-active paper actuators. Cellulose 2007, 14, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.D.; Kim, J.H.; Cai, Z.J.; Kim, J. The effect of chitosan concentration on the electrical property of chitosan-blended cellulose electroactive paper. Smart Mater. Struct. 2009, 18, 015003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Chen, Y.; Kim, J. Electroactive paper actuator made with chitosan-cellulose films: Effect of acetic acid. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2007, 292, 748–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Alvarenga, E.S. Characterization and properties of chitosan. Biotechnol. Biopolym. 2011, 24, 364. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Z.J.; Kim, J.W. Characterization and electromechanical performance of cellulose-chitosan blend electro-active paper. Smart Mater. Struct. 2008, 17, 035028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Kim, J. Cellulose-Chitosan interpenetrating polymer network for electro-active paper actuator. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 114, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.D.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J. Modeling of electromechanical behavior of chitosan-blended cellulose electroactive paper (eapap). J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 105, 103510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Jang, S.-D.; Kim, J. Gas sensing properties of gallium nitride-coated cellulose nanocomposite. Sens. Lett. 2012, 10, 748–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.H.; Ramesh, S.; Kim, J.H.; Jung, D.; Kim, H.S. Cellulose-Silica/Gold nanomaterials for electronic applications. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2014, 14, 7495–7501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orts, W.J.; Shey, J.; Imam, S.H.; Glenn, G.M.; Guttman, M.E.; Revol, J.F. Application of cellulose microfibrils in polymer nanocomposites. J. Polym. Environ. 2005, 13, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halamus, T.; Wojciechowski, P.; Bobowska, I. Synthesis and characterization of (hydroxypropyl)cellulose/tio2 nanocomposite films. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2008, 19, 807–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, J.; Tercjak, A.; Algar, I.; Retegi, A.; Mondragon, I. Conductive properties of TiO2/bacterial cellulose hybrid fibres. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 377, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, M.; Mun, S.; Hyun, J.; Kim, J. Synthesis and characterization of iron oxide/cellulose nanocomposite film. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 74, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, I.; Filip, D.; Figueirinhas, J.L.; Godinho, M.H. New cellulose derivatives composites for electro-optical sensors. Carbohydr. Polym. 2007, 68, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, P.A.A.P.; Trindade, T.; Neto, C.P. Titanium dioxide/cellulose nanocomposites prepared by a controlled hydrolysis method. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2006, 66, 1038–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahadeva, S.K.; Nayak, J.; Kim, J. Hybrid composite thin films composed of tin oxide nanoparticles and cellulose. Smart Mater. Struct. 2013, 22, 075011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.P.; Li, R.; Liu, S.L.; Li, Q.; Zhang, L.Z.; Zhang, L.; Guan, J.G. Structure and magnetic properties of regenerated cellulose/fe3o4 nanocomposite films. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 111, 2477–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahadeva, S.K.; Walus, K.; Stoeber, B. Piezoelectric paper fabricated via nanostructured barium titanate functionalization of wood cellulose fibers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 7547–7553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, B.W.; Mun, S.; Ko, H.U.; Zhai, L.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J. Electromechanical behavior of green cellulose-zno hybrid nanocomposite. J. Biobased Mater. Bioenergy 2014, 8, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, L.N.; Seppälä, J. Electrically conductive nanocellulose/graphene composites exhibiting improved mechanical properties in high-moisture condition. Cellulose 2015, 22, 1799–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafy, A.; Sadasivuni, K.K.; Akther, A.; Min, S.-K.; Kim, J. Cellulose/Graphene nanocomposite as multifunctional electronic and solvent sensor material. Mater. Lett. 2015, 159, 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafy, A.; Sadasivuni, K.K.; Kim, H.-C.; Akther, A.; Kim, J. Designing flexible energy and memory storage materials using cellulose modified graphene oxide nanocomposites. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 5923–5931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen, I.; Seki, Y.; Sarikanat, M.; Cetin, L.; Gurses, B.O.; Ozdemir, O.; Yilmaz, O.C.; Sever, K.; Akar, E.; Mermer, O. Electroactive behavior of graphene nanoplatelets loaded cellulose composite actuators. Compos. Part B Eng. 2015, 69, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.S.; Jeon, J.H.; Kim, H.I.; Kee, C.D.; Oh, I.K. High-Fidelity bioelectronic muscular actuator based on graphene-mediated and tempo-oxidized bacterial cellulose. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 3560–3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdemir, O.; Karakuzu, R.; Sarikanat, M.; Seki, Y.; Akar, E.; Cetin, L.; Yilmaz, O.C.; Sever, K.; Sen, I.; Gurses, B.O. Improvement of the electromechanical performance of carboxymethylcellulose-based actuators by graphene nanoplatelet loading. Cellulose 2015, 22, 3251–3260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Drzal, L.T.; Qin, Y.; Huang, Z. Multifunctional graphene nanoplatelets/cellulose nanocrystals composite paper. Compos. Part B Eng. 2015, 79, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Song, C.S.; Yun, S.R. Cellulose based electro-active papers: Performance and environmental effects. Smart Mater. Struct. 2006, 15, 719–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.G.; Kim, J.; Chen, Y.; Yun, S.R.; Lee, S.K. Electro-Active-Paper actuator made with licl/cellulose films: Effect of licl content. Macromol. Res. 2006, 14, 624–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Yun, S.R.; Deshpande, S.D. Synthesis, characterization and actuation behavior of polyaniline-coated electroactive paper actuators. Polym. Int. 2007, 56, 1530–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Wang, N.G.; Chen, Y.; Lee, S.K.; Yun, G.Y. Electroactive-paper actuator made with cellulose/naoh/urea and sodium alginate. Cellulose 2007, 14, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Wang, N.; Chen, Y.; Yun, G.Y. An electro-active paper actuator made with lithium chloride/cellulose films: Effects of glycerol content and film thickness. Smart Mater. Struct. 2007, 16, 1564–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahadeva, S.K.; Kim, J. Effect of polyethylene oxide-polyethylene glycol content and humidity on performance of electro-active paper actuators based on cellulose/polyethylene oxide-polyethylene glycol microcomposite. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2010, 50, 1199–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahadeva, S.K.; Yun, S.; Kim, J. Dry electroactive paper actuator based on cellulose/poly(ethylene oxide)-poly(ethylene glycol) microcomposite. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2009, 20, 1141–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridley, D.R.; Williams, F.R.; Song, K.D.; Yun, S.R.; Kang, K.S.; Kim, J. Effect of electrode pattern on the actuator performance of cellulose electro-active paper. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2010, 21, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Yun, K.J.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J. Mechanical stretching effect on the actuator performance of cellulose electroactive paper. Smart Mater. Struct. 2009, 18, 055005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, G.Y.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, J.; Kim, K.; Yang, C. Effect of aligned cellulose film to the performance of electro-active paper actuator. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2008, 141, 530–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.H.; Kim, H.M.; Kim, K.S.; Chin, I.J. Preparation of electrospun cellulose membrane for eapap actuator. In Abstracts of Papers of the American Chemical Society; ACS: Washington, DC, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Yun, S.; Kim, J.; Lee, K.S. Evaluation of cellulose electro-active paper made by tape casting and zone stretching methods. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2010, 11, 987–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.; Kim, J.; Song, C. Performance of electro-active paper actuators with thickness variation. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2007, 133, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahadeva, S.K.; Yi, C.; Kim, J. Effect of room temperature ionic liquids adsorption on electromechanical behavior of cellulose electro-active paper. Macromol. Res. 2009, 17, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahadeva, S.K.; Kang, K.S.; Kim, J.; Ha, S.H.; Koo, Y.M. The effect of residual ionic liquid for cellulose based electro-active paper actuator. Soft Mater. 2010, 8, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahadeva, S.K.; Kim, J. An electro-active paper actuator made with cellulose-polypyrrole-ionic liquid nanocomposite: Influence of ionic liquid concentration, type of anion and humidity. Smart Mater. Struct. 2010, 19, 105014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, G.Y.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, J. Blocked force measurement of an electro-active paper actuator using a cantilevered force transducer. Smart Mater. Struct. 2008, 17, 025021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, G.Y.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, S.Y. Fabrication and testing of cellulose eapap actuators for haptic application. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2010, 164, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.; Yun, G.Y.; Kim, K.B.; Kang, B.W.; Kim, J.; Kim, S.Y. Film-Type haptic actuator made with cellulose acetate layers. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2014, 25, 1289–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.Y.; Mahadeva, S.K.; Kim, J. Wirelessly driven electro-active paper actuator made with cellulose-polypyrrole-ionic liquid and dipole rectenna. Smart Mater. Struct. 2010, 19, 105026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.Y.; Mahadeva, S.K.; Kim, J. Remotely powered and controlled eapap actuator by amplitude modulated microwaves. Smart Mater. Struct. 2013, 22, 017001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, H.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, J. Vibration sensor characteristics of piezoelectric electro-active paper. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2010, 21, 1123–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, H.; Kim, H.S. Beam vibration control using cellulose-based electro-active paper sensor. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2010, 11, 823–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.M.; Mandal, D. Native cellulose microfiber-based hybrid piezoelectric generator for mechanical energy harvesting utility. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 1555–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abas, Z.; Kim, H.S.; Zhai, L.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.H. Possibility of cellulose-based electro-active paper energy scavenging transducer. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2014, 14, 7458–7462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, W.S.; Chun, D.M.; Ahn, S.H. Research advancement of green technologies. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2014, 15, 973–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J. A review of piezoelectric energy harvesting based on vibration. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2011, 12, 1129–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abas, Z.; Kim, H.S.; Zhai, L.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.H. Electrode effects of a cellulose-based electro-active paper energy harvester. Smart Mater. Struct. 2014, 23, 074003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.L.; Chen, D.; Meng, X.W.; Tang, F.Q.; Du, A.M.; Zhang, L. Amperometric glucose biosensor based on a gold nanorods/cellulose acetate composite film as immobilization matrix. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2009, 72, 188–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esmaeili, C.; Abdi, M.M.; Mathew, A.P.; Jonoobi, M.; Oksman, K.; Rezayi, M. Synergy effect of nanocrystalline cellulose for the biosensing detection of glucose. Sensors 2015, 15, 24681–24697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahadeva, S.K.; Kim, J. Conductometric glucose biosensor made with cellulose and tin oxide hybrid nanocomposite. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 157, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, H.Y.; Zhang, D.W.; Jiang, J.; Cui, Y.R.; Qiu, S.A.; Zhou, Y.L.; Zhang, X.X. Fabrication of bienzymatic glucose biosensor based on novel gold nanoparticles-bacteria cellulose nanofibers nanocomposite. Electroanalysis 2010, 22, 2543–2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortunato, E.; Correia, N.; Barquinha, P.; Pereira, L.; Goncalves, G.; Martins, R. High-performance flexible hybrid field-effect transistors based on cellulose fiber paper. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2008, 29, 988–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, R.J.B.; Marques, P.A.A.P.; Barros-Timmons, A.M.; Trindade, T.; Neto, C.P. Novel SiO2/cellulose nanocomposites obtained by in situ synthesis and via polyelectrolytes assembly. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2008, 68, 1088–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahadeva, S.K.; Kim, J. Porous tin-oxide-coated regenerated cellulose as disposable and low-cost alternative transducer for urea detection. IEEE Sens. J. 2013, 13, 2223–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniruzzaman, M.; Jang, S.D.; Kim, J. Titanium dioxide-cellulose hybrid nanocomposite and its glucose biosensor application. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2012, 177, 844–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullahil, K.; Maniruzzaman, M.; Kang, B.-W.; Kim, J. Fabrication and characterization of titanium dioxide-cellulose composite and its urea biosensing behavior. Sens. Mater. 2015, 27, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.H.; Xu, X.W.; Brault, N.D.; Keefe, A.J.; Han, X.; Deng, Y.; Xu, J.Q.; Yu, Q.M.; Jiang, S.Y. Cellulose paper sensors modified with zwitterionic poly(carboxybetaine) for sensing and detection in complex media. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 2871–2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, C.S.K.; Tan, S.N.; Floresca, C.Z. A “green” cellulose paper based glucose amperometric biosensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 193, 536–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mun, S.; Maniruzzaman, M.; Ko, H.-U.; Kafy, A.; Kim, J. Preparation and characterisation of cellulose zno hybrid film by blending method and its glucose biosensor application. Mater. Technol. 2015, 30, B150–B154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.; Kim, J. Multi-Walled carbon nanotubes-cellulose paper for a chemical vapor sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2010, 150, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthigeyan, A.; Minami, N.; Iakoubovskii, K. Highly sensitive, room-temperature gas sensors prepared from cellulose derivative assisted dispersions of single-wall carbon nanotubes. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 47, 7440–7443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadasivuni, K.K.; Ponnamma, D.; Ko, H.-U.; Kim, H.C.; Zhai, L.; Kim, J. Flexible no 2 sensors from renewable cellulose nanocrystals/iron oxide composites. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 233, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mun, S.; Chen, Y.; Kim, J. Cellulose-Titanium dioxide-multiwalled carbon nanotube hybrid nanocomposite and its ammonia gas sensing properties at room temperature. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 171, 1186–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammu, S.; Surwade, S.P.; Agnihotra, S.; Phulgirkar, A.; Patel, S.; Manohar, N.; Lalli, M.; Manohar, S.K. Cellulose-Based sensors for detecting chlorine and nitrogen dioxide. In Abstracts of Papers of the American Chemical Society; ACS: Washington, DC, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.W.; Kim, B.; Li, J.; Meyyappan, M. A carbon nanotube based ammonia sensor on cellulose paper. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 549–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.S.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, Y.H.; Lee, D.D. Gan thin films as gas sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2003, 89, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, F.G.; Oliveira, G.E.; Anzai, T.; Richa, P.; Cosme, T.; Nele, M.; Rodrigues, C.H.M.; Soares, B.G.; Pinto, J.C. A sensor for acid concentration based on cellulose paper sheets modified with polyaniline nanoparticles. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2009, 294, 739–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahadeva, S.K.; Ko, H.U.; Kim, J. Investigation of cellulose and tin oxide hybrid composite as a disposable ph sensor. Z. Phys. Chem. 2013, 227, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Sadasivuni, K.K.; Kim, H.-C.; Min, S.-K.; Kim, J. Designing pH-responsive and dielectric hydrogels from cellulose nanocrystals. J. Chem. Sci. 2015, 127, 1119–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, H.; Liu, D.; Wang, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, S. pH-Responsive shape memory poly(ethylene glycol)-poly(ε-caprolactone)-based polyurethane/cellulose nanocrystals nanocomposite. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 12988–12999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.G.; Bai, X.Y.; Wang, Y.K.; Jin, W.; Zhang, X.; Hu, S.S. Inkjet printing of nanoporous gold electrode arrays on cellulose membranes for high-sensitive paper-like electrochemical oxygen sensors using ionic liquid electrolytes. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 3745–3750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, H.S.; Mader, E.; Liu, J.W. Unique water sensors based on carbon nanotube-cellulose composites. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 185, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, R.; Nathan, A.; Barros, R.; Pereira, L.; Barquinha, P.; Correia, N.; Costa, R.; Ahnood, A.; Ferreira, I.; Fortunato, E. Complementary metal oxide semiconductor technology with and on paper. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 4491–4496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortunato, E.; Barquinha, P.; Martins, R. Oxide semiconductor thin-film transistors: A review of recent advances. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 2945–2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barquinha, P.; Pimentel, A.; Marques, A.; Pereira, L.; Martins, R.; Fortunato, E. Effect of uv and visible light radiation on the electrical performances of transparent tfts based on amorphous indium zinc oxide. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2006, 352, 1756–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barquinha, P.; Goncalves, G.; Pereira, L.; Martins, R.; Fortunato, E. Effect of annealing temperature on the properties of izo films and izo based transparent tfts. Thin Solid Films 2007, 515, 8450–8454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriksson, M.; Berglund, L.A.; Isaksson, P.; Lindstrom, T.; Nishino, T. Cellulose nanopaper structures of high toughness. Biomacromolecules 2008, 9, 1579–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Zhu, H.L.; Chen, Y.C.; Preston, C.; Rohrbach, K.; Cumings, J.; Hu, L.B. Highly transparent and flexible nanopaper transistors. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 2106–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaspar, D.; Fernandes, S.N.; de Oliveira, A.G.; Fernandes, J.G.; Grey, P.; Pontes, R.V.; Pereira, L.; Martins, R.; Godinho, M.H.; Fortunato, E. Nanocrystalline cellulose applied simultaneously as the gate dielectric and the substrate in flexible field effect transistors. Nanotechnology 2014, 25, 094008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, L.; Gaspar, D.; Guerin, D.; Delattre, A.; Fortunato, E.; Martins, R. The influence of fibril composition and dimension on the performance of paper gated oxide transistors. Nanotechnology 2014, 25, 094007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ducere, V.; Bernes, A.; Lacabanne, C. A capacitive humidity sensor using cross-linked cellulose acetate butyrate. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2005, 106, 331–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sadasivuni, K.K.; Kafy, A.; Kim, H.-C.; Ko, H.-U.; Mun, S.; Kim, J. Reduced graphene oxide filled cellulose films for flexible temperature sensor application. Synth. Met. 2015, 206, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafy, A.; Akther, A.; Shishir, M.I.; Kim, H.C.; Yun, Y.; Kim, J. Cellulose nanocrystal/graphene oxide composite film as humidity sensor. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2016, 247, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimov, K.H.S.; Qasuria, T.A. Cellulose and pepc based humidity sensor for remote sensing. J. Optoelectron. Adv. Mater. 2010, 12, 1743–1746. [Google Scholar]
- Saeed, M.T.; Khalid, F.A.; Karimov, K.S.; Shah, M. Organic Cu/cellulose/PEPC/Cu humidity sensor. Optoelectron. Adv. Mater. Rapid Commun. 2010, 4, 888–892. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Geissler, A.; Standhardt, M.; Mehlhase, S.; Gallei, M.; Chen, L.; Thiele, C.M. Moisture-Responsive films of cellulose stearoyl esters showing reversible shape transitions. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.W.; Kim, B.; Li, J.; Meyyappan, M. Carbon nanotube based humidity sensor on cellulose paper. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 22094–22097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokman, A.; Batumalay, M.; Harun, S.W.; Arof, H. Humidity sensor based on tapered single mode fiber coated with a hydroxyethyl cellulose/poly-vinylidene fluoride composite. Ukr. J. Phys. Opt. 2014, 15, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahadeva, S.K.; Yun, S.; Kim, J. Flexible humidity and temperature sensor based on cellulose-polypyrrole nanocomposite. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2011, 165, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Rajamani, R.; Stelson, K.A.; Cui, T. Carbon nanotube-based transparent thin film acoustic actuators and sensors. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2006, 132, 626–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Yun, G.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, J.; Kim, J.H. Piezoelectric electro-active paper (eapap) speaker. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2011, 25, 2763–2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





















| No. | Name | Type of Blend/Coating | Chemical Nature of Coating/Blend | Applications | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Conducting polymer and SWNT coated cellulose EAPap | Composite of SWNT/polyaniline with dopants () | Inorganic | Ultra-light weight smart actuator | [45] |
| 2 | MWNTs mixed cellulose EAPap | MWNTs | Inorganic | Bending EAPap actuator | [46] |
| 3 | Functionalized-MWNTs blended cellulose EAPap | Functionalized-MWNTs | Inorganic | Micro-robot, micro-flying objects ,sensors | [47] |
| 4 | Aligned MWNT/Cellulose composite | MWCNTs covalently grafted to cellulose | Inorganic | Actuator | [48] |
| 5 | TiO2/MWNT/Cellulose hybrid nanocomposite | TiO2/MWCNTs | Inorganic | pH sensors | [49] |
| 6 | Biocompatible SWNTs/Cellulose composite | SWNTs | Inorganic | Cell sensors | [50] |
| 7 | SWNTs bonded cellulose composite | SWNTs | Inorganic | Flexible paper transistors | [51] |
| 8 | Cellulose-chitosan laminated films as EAPap | Chitosan with free ions ( and ) | Organic-inorganic composite | Humidity-less-sensitive EAPap actuator | [55] |
| 9 | Chitosan-blended cellulose EAPap | Chitosan | Organic | Blood clotting patches, artificial muscle, biomimetic pump | [56] |
| 10 | Cellulose derivative composite | hydroxypropylcellulose (HPC) and acetoxypropylcellulose (APC) | Organic | Electro-optical sensors | [68] |
| 11 | TiO2-cellulose nanocomposite mixed cellulosic fibers | TiO2 particles | Inorganic | Highly opaque papers | [69] |
| 12 | SnO2 nanoparticle loaded cellulose hybrid thin films | SnO2 nanoparticles | Inorganic | Low cost, flexible and biodegradable humidity sensors | [70] |
| 13 | Cellulose/silica and silica-gold hybrid biomaterials | Silica and Silica-gold particles | Inorganic | Electronics applications | [63] |
| 14 | LiCl/Cellulose EAPap | LiCl content | Inorganic | Humidity-less-sensitive EAPap actuator | [82] |
| 15 | Polyaniline-coated EAPap | Polyaniline-coating | Organic | actuators | [83] |
| 16 | Sodium alginate/cellulose EAPap | Sodium alginate | Organic | Humidity-less-sensitive EAPap actuator | [84] |
| 17 | Ionic liquid blended cellulose EAPap | Ionic liquids (BMIPF6, BMICL, BMIBF4) | Inorganic | Durable humidity-less-sensitive EAPap actuator | [94,95,96] |
| 18 | Cellulose acetate double membrane actuator | Cellulose acetate layers | Organic | Kinesthetic actutors for haptic devices | [99] |
| 19 | Cellulose-polypyrrole-ionic liquid nanocomposite | Polypyrrole-ionic liquid | Organic | EAPap actuators | [100] |
| 20 | Cellulose-polypyrrole-ionic liquid EAPap | Polypyrrole-ionic liquid | Organic | Biomimetic robots, remotely driven actuators, remote sensing units, portable electronics | [101] |
| 21 | Cellulose EAPap coated with gold electrodes | Gold electrodes | Inorganic | Electromechanical energy harvesting transducer | [105] |
| 22 | Gold nanorods/cellulose acetate composite film based biosensor | Gold nanorods | Inorganic | Amperometric glucose bisensor | [109] |
| 23 | Gold nanoparticles-bacterial cellulose nanocomposite | Gold nanoparticles-bacteria | Inorganic-organic composite | Biosensor for determination of glucose in human blood | [112] |
| 24 | Cellulose/tin oxide hybrid nanocomposite | Glucose oxidase (GOx)/ tin oxide (SnO2) | Organic-inorganic composite | Glucose biosensor | [111] |
| 25 | Tin-oxide coated cellulose | Porous tin-oxide (SnO2) | Inorganic | Urea detecting sensor | [115] |
| 26 | TiO2-cellulose hybrid nano composite | TiO2 nanoparticles | Inorganic | Conductometric glucose biosensor | [116] |
| 27 | Polycarboxybetaine functionalized cellulose paper | Polycarboxybetaine | Organic | glucose detection from undiluted human serum | [118] |
| 28 | Hydrophilic cellulose paper disk with immobilised glucose oxidase | Glucose oxidase (GOx) | Organic | Food processing control, biotechnological analytical devices | [119] |
| 29 | MWNTs-cellulose paper | MWNTs | Inorganic | chemical vapor sensor | [121] |
| 30 | SWNT-network-based gas sensors | SWNTs networks | Inorganic | Room-temperature gas sensors | [122] |
| 31 | Cellulose-TiO2-MWNT nanocomposite | TiO2-MWNTs | Inorganic | NH3 sensor | [124] |
| 32 | CNT-on-paper, CNT-cellulose composite | SWNTs | Inorganic | Ammonia sensor | [126] |
| 33 | Gallium nitride-coated cellulose nanocomposite | Gallium nitride | Inorganic | NH3 and NO2 gas sensor | [62] |
| 34 | Cellulose Paper Sheets with Polyaniline Nanoparticles | Polyaniline Nanoparticles | Organic | Acid concentration sensor | [128] |
| 35 | Tin oxide-cellulose hybrid composite | Tin-oxide | Inorganic | pH sensor | [129] |
| 36 | Nanoporous gold electrode arrays on cellulose membranes using ionic liquid electrolytes | Gold, ionic liquid | Inorganic | Electrochemical Oxygen Sensors | [132] |
| 37 | Cellulose-CNTs composite | CNTs | Inorganic | Water sensors | [133] |
| 38 | Regenerated cellulose-MWNTs flexible paper | MWNTs | Inorganic | Flexible paper transistor | [12] |
| 39 | Cellulose acetate butyrate cross-linked by a melamine formaldehyde resin | Melamine formaldehyde resin | Organic | Humidity and temperature sensor | [142] |
| 40 | Cellulose and poly-N-epoxypropyl-carbazole | Poly-N-epoxypropylcarbazole | Organic | Humidity sensor | [145] |
| 41 | Cellulose with carboxylic acid functionalized SWNTs | Carboxylic acid functionalized SWNTs | Inorganic | Resistor-type humidity sensors | [148] |
| 42 | Cellulose-polypyrrole nanocomposite | Nanoscaled polypyrrole (PPy) | Organic | Capacitive-type humidity and temperature sensor | [150] |
| 43 | PVDF thin film coated with compliant CNTs | CNTs | Inorganic | Acoustic actuators (speakers) and sensors (microphones) | [151] |
| 44 | Cellulose/BaTiO3 paper | BaTiO3 | Inorganic | Sensing devices | [72] |
| 45 | Cellulose/graphene nanocomposite | Functionalized graphene oxide | Inorganic | Disposable solvent sensor | [75] |
| 46 | Hybrid thin film of graphene nanoplatelets and cellulose nanocrystals | Graphene nanoplatelets | Inorganic | Packaging, electrical and heat conducting applications | [80] |
| 47 | TiO2-Cellulose composite | TiO2 | Inorganic | Urea biosensing | [117] |
| 48 | Cellulose nanocrystal/iron oxide composite | Iron oxide | Inorganic | Flexible NO2 sensor | [123] |
| 49 | Cellulose/reduced graphene oxide composite | Reduced graphene oxide | Inorganic | Temperature sensor | [143] |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khan, A.; Abas, Z.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, J. Recent Progress on Cellulose-Based Electro-Active Paper, Its Hybrid Nanocomposites and Applications. Sensors 2016, 16, 1172. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16081172
Khan A, Abas Z, Kim HS, Kim J. Recent Progress on Cellulose-Based Electro-Active Paper, Its Hybrid Nanocomposites and Applications. Sensors. 2016; 16(8):1172. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16081172
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhan, Asif, Zafar Abas, Heung Soo Kim, and Jaehwan Kim. 2016. "Recent Progress on Cellulose-Based Electro-Active Paper, Its Hybrid Nanocomposites and Applications" Sensors 16, no. 8: 1172. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16081172
APA StyleKhan, A., Abas, Z., Kim, H. S., & Kim, J. (2016). Recent Progress on Cellulose-Based Electro-Active Paper, Its Hybrid Nanocomposites and Applications. Sensors, 16(8), 1172. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16081172









