Virtual Torque Sensor for Low-Cost RC Servo Motors Based on Dynamic System Identification Utilizing Parametric Constraints
Abstract
:1. Introduction
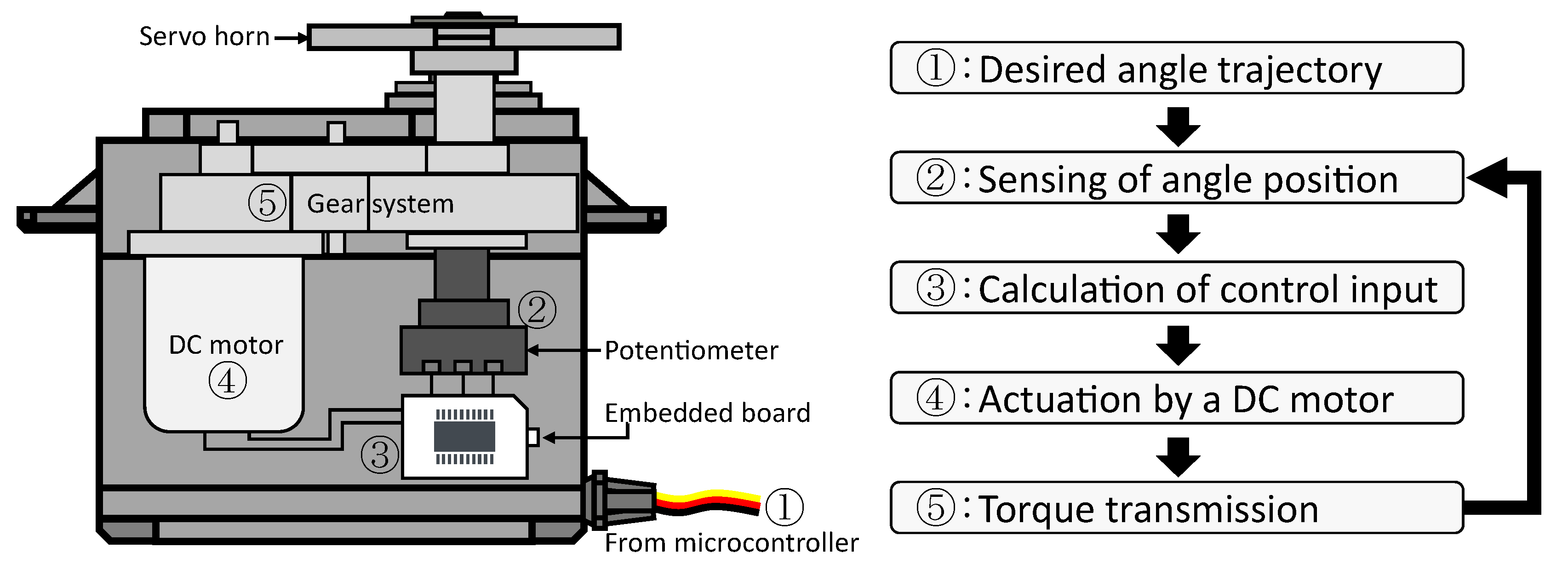
2. Virtual Torque Sensor for RC Servo Motors Using Dynamical System Model
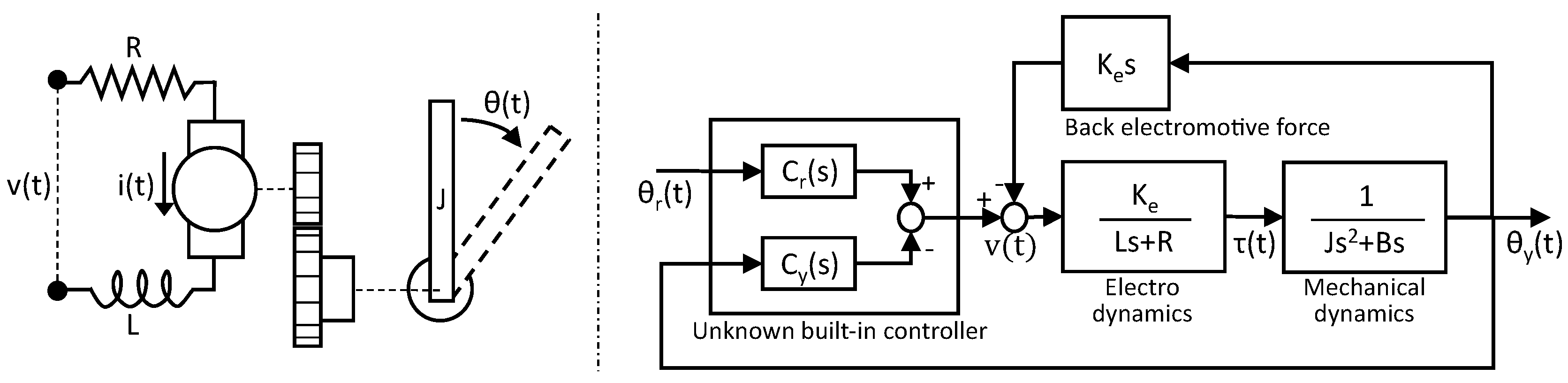
2.1. Electromechanical Model for DC Motors
2.2. Torque Estimation under Unknown Control Structure
2.3. Virtual Torque Sensor with Parametric Constraints in Independent Experiments
3. System Identification for the Proposed Virtual Torque Sensor
3.1. System Identification in the Lumped Parameters
3.2. Problem Formulation as Constrained Optimization in Frequency Domain
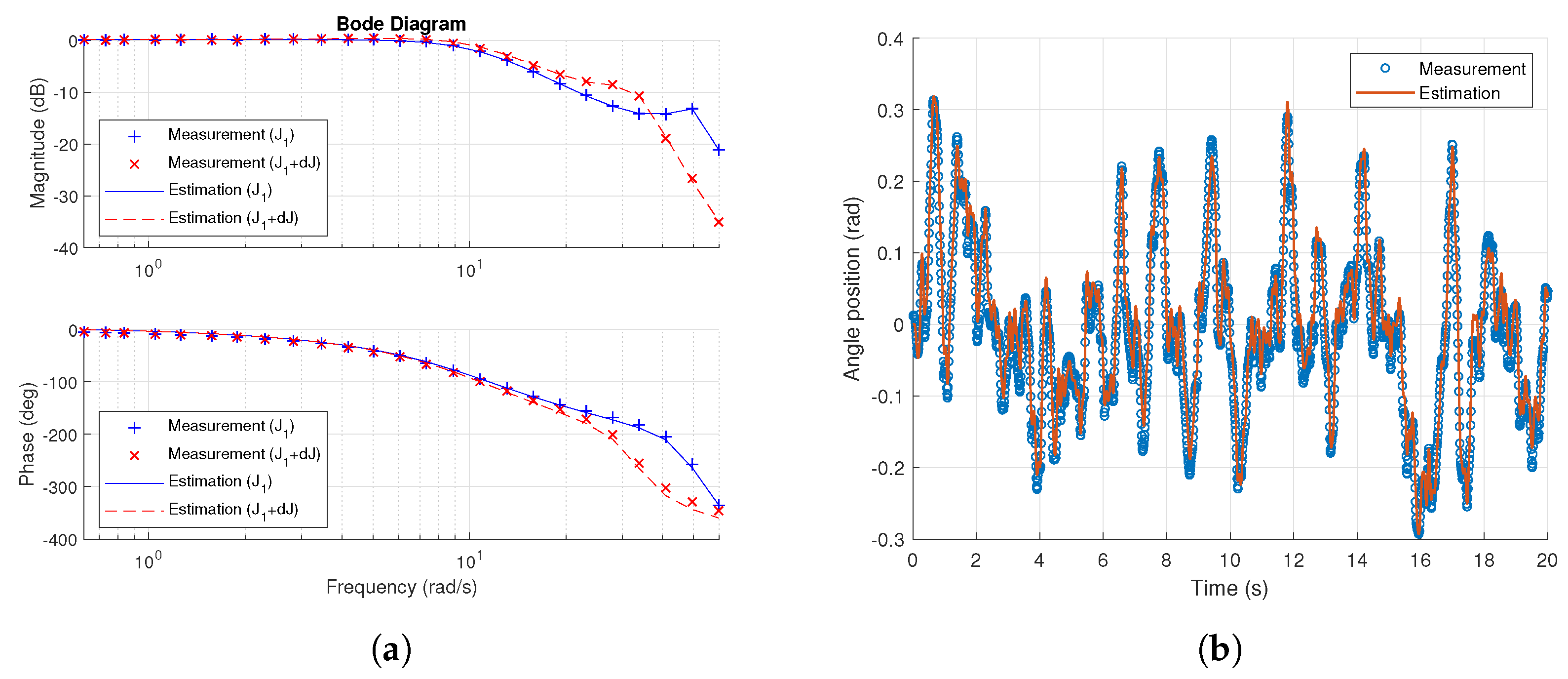
4. Experiments and Analysis
4.1. Experimental Setup
4.2. Identification of the Proposed Torque Estimator
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tadesse, Y.; Subbarao, K.; Priya, S. Realizing a humanoid neck with serial chain four-bar mechanism. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2010, 21, 1169–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, M.; Cempini, M.; Conti, R.; Meli, E.; Ridolfi, A.; Vitiello, N.; Allotta, B. Design of a Series Elastic Transmission for hand exoskeletons. Mechatronics 2018, 51, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukagoshi, H.; Watanabe, M.; Hamada, T.; Ashlih, D.; Iizuka, R. Aerial manipulator with perching and door-opening capability. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on the Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Seattle, WA, USA, 26–30 May 2015; pp. 4663–4668. [Google Scholar]
- Noorani, M.R.S.; Ghanbari, A.; Aghli, S. Design and fabrication of a worm robot prototype. In Proceedings of the 2015 3rd RSI International Conference on Robotics and Mechatronics (ICROM), Tehran, Iran, 7–9 October 2015; pp. 73–78. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, H.; Sun, R.; Hu, L.; Su, Z.; Hu, W. Control of a cheetah robot in passive bounding gait. J. Bionic Eng. 2016, 13, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, M.; Koide, Y.; Matsuhara, K.; Ushida, S.; Oku, H.; Kongprawechnon, W. Adaptive modeling and compliance control for RC servo motor. In Proceedings of the 56th Annual Conference of the Society of Instrument and Control Engineers of Japan (SICE), Kanazawa, Japan, 19–22 September 2017; pp. 664–667. [Google Scholar]
- Suarez, A.; Jimenez-Cano, A.E.; Vega, V.M.; Heredia, G.; Rodriguez-Castaño, A.; Ollero, A. Design of a lightweight dual arm system for aerial manipulation. Mechatronics 2018, 50, 30–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flacco, F.; Kheddar, A. Contact Detection and Physical Interaction for Low Cost Personal Robots. In Proceedings of the 26th IEEE International Symposium on Robot and Human Interactive Communication, Lisbon, Portugal, 27–31 August 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Staufer, P.; Gattringer, H. State estimation on flexible robots using accelerometers and angular rate sensors. Mechatronics 2012, 22, 1043–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, B.; Jeon, D. A method to accurately estimate the muscular torques of human wearing exoskeletons by torque sensors. Sensors 2015, 15, 8337–8357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Indri, M.; Trapani, S.; Lazzero, I. Development of a virtual collision sensor for industrial robots. Sensors 2017, 17, 1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bum Kim, Y.; Kim, U.; Seok, D.Y.; So, J.; Haeng Lee, Y.; Choi, H. Torque Sensor Embedded Actuator Module for Robotic Applications. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2018, 23, 1662–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.X.; Ryoo, Y.J.; Byun, K.S. Development of torque sensor with high sensitivity for joint of robot manipulator using 4-bar linkage shape. Sensors 2016, 16, 991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kara, T.; Eker, I. Nonlinear modeling and identification of a DC motor for bidirectional operation with real time experiments. Energy Convers. Manag. 2004, 45, 1087–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farnaz, A.H.Z.; Sajith, H.S.; Binduhewa, P.J.; Ekanayake, M.P.B.; Samaranayake, B. Low cost torque estimator for DC servo motors. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 10th International Conference on Industrial and Information Systems (ICIIS), Peradeniya, Sri Lanka, 18–20 December 2015; pp. 187–192. [Google Scholar]
- Villagrossi, E.; Simoni, L.; Beschi, M.; Pedrocchi, N.; Marini, A.; Tosatti, L.M.; Visioli, A. A virtual force sensor for interaction tasks with conventional industrial robots. Mechatronics 2018, 50, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beschi, M.; Villagrossi, E.; Pedrocchi, N.; Tosatti, L.M. A general analytical procedure for robot dynamic model reduction. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Hamburg, Germany, 28 September–2 October 2015; pp. 4127–4132. [Google Scholar]
- Mancisidor, A.; Zubizarreta, A.; Cabanes, I.; Portillo, E.; Jung, J.H. Virtual Sensors for Advanced Controllers in Rehabilitation Robotics. Sensors 2018, 18, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, S.; Lee, C.; Kong, K. Force control and force observer design of series elastic actuator based on its dynamic characteristics. In Proceedings of the 41st Annual Conference of the Industrial Electronics Society, Yokohama, Japan, 9–12 November 2015; pp. 4639–4644. [Google Scholar]
- Wada, T.; Ishikawa, M.; Kitayoshi, R.; Maruta, I.; Sugie, T. Practical modeling and system identification of R/C servo motors. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Control Applications, St. Petersburg, Russia, 8–10 July 2009; pp. 1378–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pintelon, R.; Schoukens, J. System Identification: A Frequency Domain Approach; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Mezura-Montes, E.; Coello, C.A.C. Constraint-handling in nature-inspired numerical optimization: Past, present and future. Swarm Evol. Comput. 2011, 1, 173–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruta, I.; Kim, T.H.; Song, D.; Sugie, T. Synthesis of fixed-structure robust controllers using a constrained particle swarm optimizer with cyclic neighborhood topology. Expert Syst. Appl. 2013, 40, 3595–3605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Coefficient | Value | Coefficient | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Equipment/Item | Model | Description |
|---|---|---|
| RC servo motor | GWS S03T 2BBMG | Max torque: 7.93 kf/cm |
| Microrotary encoder | AS5048A | Resolution: 14 bits |
| Microcontroller | Raspberry Pi 3 Model B+ | Real-time control with 1.4 GHz 64-bit |
| Analog to digital converter | Arduino Pro Mini 328 3.3 v 8 MHz | Resolution: 10 bits |
| Load cell | Force range: 0–1 kg |
| Coefficient | Value | Coefficient | Value | Coefficient | Value | Coefficient | Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −3.9949 | 4.2319 | −1.6526 | 1.7506 | ||||
| 3.2451 | 2.9589 | 1.3424 | 1.4228 | ||||
| 3.1901 | 29.4236 | 1.3196 | 27.1573 |
| Coefficient | Value | Coefficient | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hwang, Y.; Minami, Y.; Ishikawa, M. Virtual Torque Sensor for Low-Cost RC Servo Motors Based on Dynamic System Identification Utilizing Parametric Constraints. Sensors 2018, 18, 3856. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18113856
Hwang Y, Minami Y, Ishikawa M. Virtual Torque Sensor for Low-Cost RC Servo Motors Based on Dynamic System Identification Utilizing Parametric Constraints. Sensors. 2018; 18(11):3856. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18113856
Chicago/Turabian StyleHwang, Yoonkyu, Yuki Minami, and Masato Ishikawa. 2018. "Virtual Torque Sensor for Low-Cost RC Servo Motors Based on Dynamic System Identification Utilizing Parametric Constraints" Sensors 18, no. 11: 3856. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18113856
APA StyleHwang, Y., Minami, Y., & Ishikawa, M. (2018). Virtual Torque Sensor for Low-Cost RC Servo Motors Based on Dynamic System Identification Utilizing Parametric Constraints. Sensors, 18(11), 3856. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18113856





