Mapping Soil Alkalinity and Salinity in Northern Songnen Plain, China with the HJ-1 Hyperspectral Imager Data and Partial Least Squares Regression
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
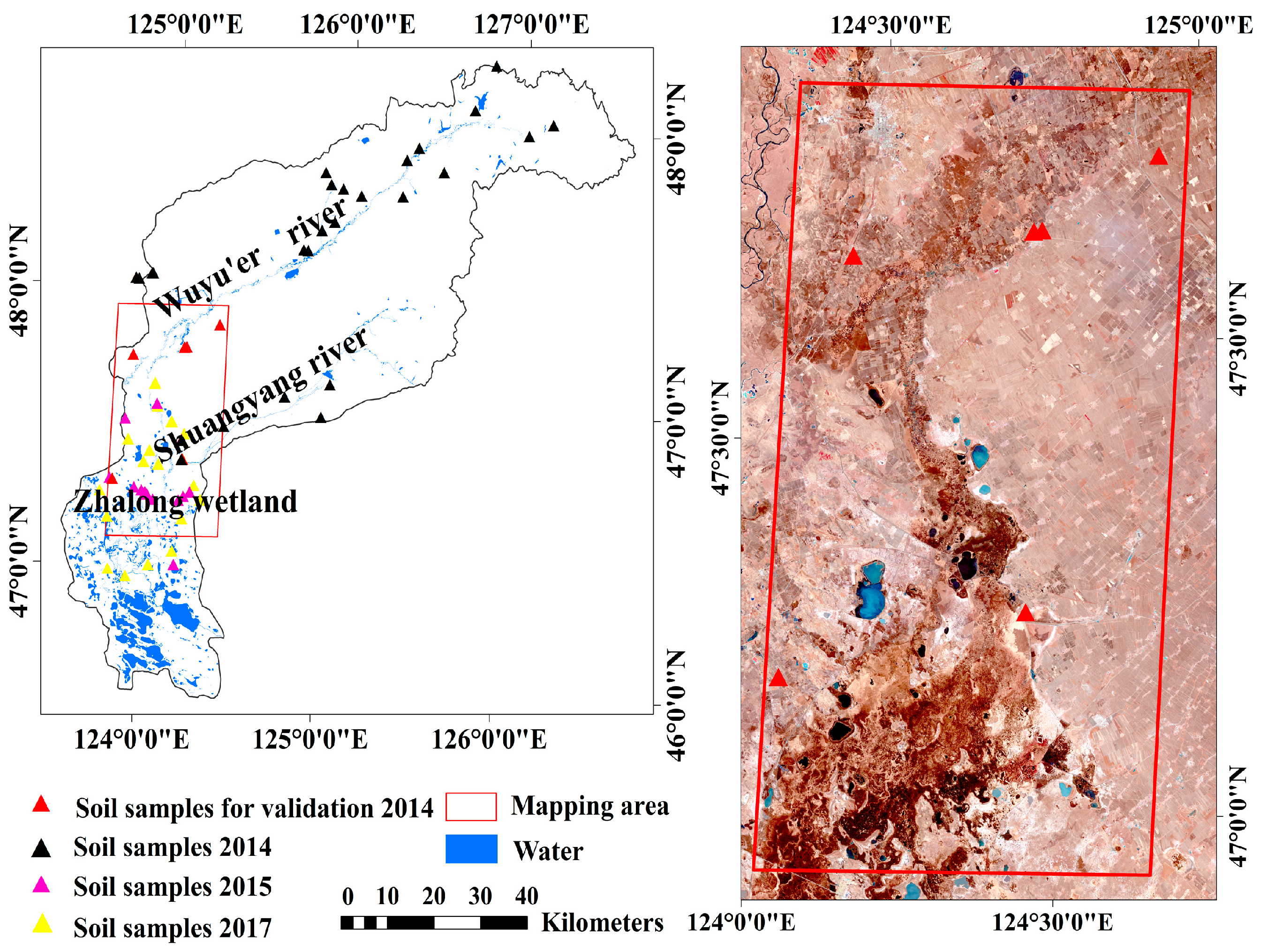
2.1. Selection of Study Area
2.2. Soil Sampling and Laboratory Measurements
2.2.1. Soil Sampling
2.2.2. Laboratory Measurements
2.3. Hyperspectral Imagery and Preprocessing
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Statistics of Soil Physical and Chemical Properties
3.2. Quantitative Estimation of Soil pH and EC
3.3. PLSR Models for Estimating Soil pH and EC with HSI-Resampled Spectra
3.3.1. Prediction Performances Using HSI-Resampled Spectra
3.3.2. HSI-Like Band Contribution to PLSR Model
3.3.3. PLSR Model Inversion Using HSI Images
4. Discussion
4.1. Soil Characteristics of Study Area
4.2. Spectral Sensitivity of HSI Image to Soil Alkalinity and Salinity
4.3. Uncertainties of HSI Image Inversion
4.4. Geographical Consideration of Affected Areas with Soil Alkalinity and Salinity
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Metternicht, G.I.; Zinck, J.A. Remote sensing of soil salinity: Potentials and constraints. Remote Sens Environ. 2003, 85, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghassemi, F.; Jakeman, A.J.; Nix, H.A. Salinisation of Land and Water Resources: Human Causes, Extent, Management and Case Studies; University of New South Wales Press Ltd.: Canberra, Australia, 1999; pp. 5–7. ISBN 13 978-0868401980. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.L.; Huang, X.J.; Zhong, T.Y. Review on sustainable utilization of salt-affected land. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2011, 66, 673–684. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Seki, K.; Miyazaki, T.; Ishihama, Y. The causes of soil alkalinization in the Songnen Plain of Northeast China. Paddy Water Environ. 2009, 7, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.J. The Alkili-saline land and agricultural sustainable development of the Western Songnen Plain in China. Sci. Geogr. Sin 2000, 20, 51–55. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lin, N.F.; Bounlom, V.; Tang, J.; Bian, J.M. Study on the relation between the formation of saline-alkali soil and the neotectonic movement. Glob. Geol. 2005, 24, 282–288. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.Z.; Li, Q.S. Research of mechanism of saline desertification in Western Songnen Plain. Soil Water Conserv. 2003, 17, 79–81. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.Z.; Gao, Q.; Chen, Q. Effects of climatic change on biomass and biomass allocation in Leymuschinensis (Poaceae) along the North-east China Transect (NECT). J. Arid Environ. 2003, 54, 653–665. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.S.; Tian, Z.C. The groundwater effect in the process of soil salinization of the Songnen plain, Jilin province. Jilin Geol. 2002, 21, 79–87. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Rao, B.R.M.; Dwivedi, R.S.; Venkataratnam, L.; Ravishankar, T.; Thammappa, S.S.; Bhargawa, G.P.; Singh, A.N. Mapping the magnitude of sodicity in part of the Indo-Gangetic Plains of Uttar Pradesh, Northern India using Landsat-TM data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1991, 12, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.S.; Liu, Z.L. Remote sensing and mapping of saline sodic land based on spectral characteristics for Da’an city. Syst. Sci. Compr. Stud. Agric. 2007, 23, 178–182. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Metternicht, G.I. Categorical fuzziness: A comparison between crisp and fuzzy class boundary modelling for mapping salt-affected soils using Landsat TM data and a classification based on anion ratios. Ecol. Model. 2003, 168, 371–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farifteh, J.; Farshad, A.; George, R.J. Assessing salt-affected soils using remote sensing, solute modeling, and geophysics. Geoderma 2006, 130, 191–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehaan, R.L.; Taylor, G.R. Image-derived spectral endmembers as indicators of salinization. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 24, 775–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannari, A.; Guedon, A.M.; El-Harti, A.; Cherkaoui, F.; El-Ghmari, A. Characterization of slightly and moderately saline and sodic soils in irrigated agriculture land using simulated data of advanced land imaging (EO-1) sensor. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant. Anal. 2008, 39, 2795–2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Wang, C.Z.; Zang, S.Y.; Zhang, Y.H.; Hao, Q.N.; Wu, Y.X. Remote Sensing of Soil Alkalinity and Salinity in the Wuyu’er-Shuangyang River Basin, Northeast China. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.I. Hyperspectral Imaging: Techniques for Spectral Detection and Classification; Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2003; pp. 15–35. [Google Scholar]
- McCarty, G.W.; Reeves, J.B., III; Reeves, V.B.; Follett, R.F.; Kimble, J.M. Mid-infrared and near-infrared diffuse reflectance spectroscopy for soil carbon management. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2002, 66, 640–646. [Google Scholar]
- McCarty, G.W.; Reeves, J.B., III. Comparison of near infrared and mid infrared diffuse reflectance spectroscopy forfield-scale measurement of soil fertility parameters. Soil Sci. 2006, 171, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vohland, M.; Ludwig, M.; Thiele-Bruhn, S.; Ludwig, B. Determination of soil properties with visible to near- and mid-infrared spectroscopy: Effects of spectral variable selection. Geoderma 2014, 223–225, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, G.R.; Salisbury, J.W. Visible and Near–infrared Spectra of Minerals and Rocks: II. Carbonates. Modern Geol. 1971, 2, 23–30. [Google Scholar]
- Mashimbye, Z.E.; Cho, M.A.; Nell, J.P.; DeClercq, W.P.; VanNiekerk, A.; Turner, D.P. Model-Based Integrated Methods for Quantitative Estimation of Soil Salinity from Hyperspectral Remote Sensing Data: A Case Study of Selected South African Soils. Pedosphere 2012, 22, 640–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Y.L.; Gong, P.; Zhu, Z.L. A spectral index for estimating soil salinity in the Yellow River Delta Region of China using EO-1 Hyperion data. Pedosphere 2010, 20, 378–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wold, H. Soft modelling by latent variables; the nonlinear iterative partial least squares approach. In Perspectives in Probability and Statistics. Papers in Honour of M. S. Barlett; Gani, J., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1975; pp. 117–142. [Google Scholar]
- Martens, H.; Izquierdo, L.; Thomassen, M. Partial least-squares regression on design variables as an alternative to analysis of variance. Anal. Chim. Acta 1986, 191, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrascal, L.M.; Galvan, I.; Gordo, O. Partial least squares regression as an alternative to current regression methods used in ecology. Oikos 2009, 118, 681–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farifteh, J.; Meer, F.V.D.; Atzberger, C.; Carranza, E.J.M. Quantitative analysis of salt-affected soil reflectance spectra: A comparison of two adaptive methods (PLSR and ANN). Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 110, 59–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubert, M.; Branden, K.V. Robust methods for partial least squares regression. J. Chemom. 2003, 17, 537–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.W.; Wu, Z.B.; Meng, J. Partial Least-Squares Regression-Linear and Nonlinear Methods; National Defense Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2006; pp. 38–40. ISBN 9787118044966. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wold, S.; SjÖstrÖm, M.; Eriksson, L. PLS-regression: A basic tool of chemometrics. Chemometr. Intell. Lab. 2001, 58, 109–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasques, G.M.; Grunwald, S.; Sickman, J.O. Comparison of multivariate methods for inferential modeling of soil carbon using visible/near-infrared spectra. Geoderma 2008, 146, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ViscarraRossel, R.A.; Behrens, T. Using data mining to model and interpret soil diffuse reflectance spectra. Geoderma 2010, 158, 46–54. [Google Scholar]
- FallahShamsi, S.R.; Zare, S.; Abtahi, S.A. Soil salinity characteristics using moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer (MODIS) images and statistical analysis. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2013, 59, 471–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoner, F.R. Physicochemical, Site, and Bidirectional Reflectance Factor Characteristics of Uniformly Moist Soils. Ph.D. Thesis, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, X.Z.; Aspandiar, M.; Oldmeadow, D. Using hyperspectral data and PLSR modelling to assess acid sulphate soil in subsurface. J. Soil Sediments 2014, 14, 904–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhoades, J.D. Soluble Salts; ASA and SSSA: Madison, WI, USA, 1982; pp. 167–179. [Google Scholar]
- China Centre for Resources Satellite Data and Application. Available online: http://219.143.215.28:8080/zywx/login.jsp (accessed on 4 May 2015).
- Adler-Golden, S.M.; Matthew, M.W.; Bernstein, L.S.; Levine, R.Y.; Berk, A.; Richtsmeier, S.C.; Acharya, P.K.; Anderson, G.P.; Felde, G.; Gardner, J.; et al. Atmospheric correction for shortwave spectral imagery based on MODTRAN4. Proc. SPIE 1999, 3753, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.Y.; Cai, H.J.; Yao, F.Q.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, Z.J. Applicability of vegetation indices to estimate fractional vegetation coverage. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2015, 46, 231–239. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Z. Research on Several Key Technologies of Partial Least Squares Regression in Chemistry and Chemical Process Modeling. Ph.D. Thesis, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China, 2005; pp. 20–25. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Bellon-Maurel, V.; Fernandez-Ahumada, E.; Palagos, B.; Roger, J.M.; McBratney, A. Critical review of chemometric indicators commonly used for assessing the quality of the prediction of soil attributes by NIR spectroscopy. Trends Anal. Chem. 2010, 29, 1073–1081. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.Y. Detection in Near-Infrared Spectroscopy of Soils; Chemistry Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2013; pp. 97–98. ISBN 9787122193414. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chorom, M.; Rengasamy, P. Carbonate chemistry, pH, and physical properties of an alkaline sodic soil asaffected by various amendments. Aust. J. Soil Res. 1997, 35, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metternicht, G.; Zinck, J.A. Spatial discrimination of salt- and sodium-affected soil surfaces. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1997, 18, 2571–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.J.; Zhang, B.; Wang, Z.M.; Song, K.S.; Hu, M.G.; Duan, H.T. Soil saline-alkalization evaluation basing on spectral reflectance characteristics. J. Infrared Millim. Waves 2008, 27, 138–142. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menenti, M. Physical Aspects and Determination of Evaporation in Desert, Applying Remote Sensing Technique. Ph.D. Thesis, Institute Land and Water Management Res, Wageningen, The Netherlands, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Song, X.F.; Zhang, Y.H.; Han, D.M.; Tang, C.Y. Hydrochemical characteristics and water quality assessment of surface water and groundwater in Songnen plain, Northeast China. Water Res. 2012, 6, 2737–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bear, F.E. Chemistry of the Soil, 2nd ed.; Reinhold Publication Corporation: New York, NY, USA, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Lillesand, M.T.; Kiefer, W.R. Remote Sensing and Image Interpretation, 6th ed.; Wiley: Noida, India, 2011; pp. 545–546. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.; Liu, M.; Du, B.; Wang, Z.; Hu, L.; Zhang, B. Mapping Soil Salinity/Sodicity by using Landsat OLI Imagery and PLSR Algorithm over Semiarid West Jilin Province, China. Sensors 2018, 18, 1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, C.C.H.; Cudahy, T.J. Mapping contaminated soils: Using remotely-sensed hyperspectral data to predict pH. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2014, 65, 897–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Granados, F.; Jurado-Expósito, M.; Peña-Barragán, J.M.; García-Torres, L. Using geoestatistical and remote sensing approaches for mapping soil properties. Eur. J. Agron. 2005, 23, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tøndel, K.; Vik, J.O.; Martens, H. Hierarchical multivariate regression-based sensitivity analysis reveals complex parameter interaction patterns in dynamic models. Chemometr. Intell. Lab. 2013, 120, 25–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, X.Z.; Lau, I.C.; Aspandiar, M. Comparison of PLSR modeling and indicative mineral mapping of airborne hyperspectral imagery for acid sulphate soil assessment. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 1309–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.J.; Zhang, B.; Liu, Z.M.; Song, K.S.; Wang, Z.M.; Duan, H.T. Specctral analysis of soils in Songnen Plain, northeastern China. J. Grad. Sch. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2007, 24, 439–445. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Stoner, E.R.; Baumgardner, M.F. Characteristics variations in reflectance of surface soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1981, 45, 1161–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Liu, Y.; Tao, J.; Weng, Y. Soil Salinity Retrieval from Advanced Multi-Spectral Sensor with Partial Least Square Regression. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 488–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nawar, S.; Buddenbaum, H.; Hill, J.; Kozak, J. Modeling and Mapping of Soil Salinity with Reflectance Spectroscopy and Landsat Data Using Two Quantitative Methods (PLSR and MARS). Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 10813–10834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kruse, A.F. Comparison of ATREM, ACORN, and FLAASH atmospheric corrections using low-altitude AVIRIS data of Boulder, CO. In Proceedings of the Summaries of 13th JPL Airborne Geoscience Workshop, Pasadena, CA, USA, 31 March–2 April 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, L.; Tiyip, T.; Ding, J.L. Soil Salinization Information Extraction by Using Hyperspectral Data of HJ-1A HSI: A case study in the Oasis of Ugan and Kuqu, Xingjang, China. J. Desert Res. 2013, 33, 1104–1109. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Metternicht, G.I. Analysing the relationship between ground based reflectance and environmental indicators of salinity processes in the Cochabamba Valleys (Bolivia). Int. J. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 1998, 24, 359–370. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, B.R.M.; Sharma, R.C.; Sankar, T. Spectral behaviour of salt-affected soils. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1995, 16, 2125–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metternicht, G.I. Detecting and Monitoring Land Degradation Features and Processes in the Cochabamba Valleys, Bolivia: A Synergistic Approach; ITC Publication: Enschede, The Netherlands, 1996; Volume 36, p. 390. [Google Scholar]
- David, J.D.; Gregory, P.A.; Roger, D. New Directions in Earth Observing: Scientific Applications of Multiangle Remote Sensing. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1999, 80, 2209–2228. [Google Scholar]
- Sommer, S.; Hillb, J.; Megier, J. The potential of remote sensing for monitoring rural land use changes and their effects on soil conditions. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 1998, 67, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.M.; Lv, K.Y.; Lou, B.J. Economic analysis on the impact of agricultural production on soil salinization. Resour. Environ. Yangtae Basin 2009, 18, 131–138. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]



| Mean | Maximum | Minimum | Standard Deviation | Median | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 8.43 | 10.86 | 5.34 | 1.91 | 9.48 |
| EC (dS/m) | 5.22 | 153.00 | 0.05 | 19.64 | 0.78 |
| TOC (%) | 1.82 | 5.71 | 0.25 | 1.40 | 1.44 |
| HCO3− (mg/L) | 1247.95 | 4515.00 | 55.57 | 1408.92 | 788.14 |
| CO32− (mg/L) | 1017.96 | 12,436.00 | 0 | 2406.44 | 224.55 |
| pH | EC | TOC | HCO3− | CO32− | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 1 | ||||
| EC | 0.74 | 1 | |||
| TOC | –0.61 | –0.48 | 1 | ||
| HCO3− | 0.19 | 0.25 | –0.07 | 1 | |
| CO32− | 0.87 | 0.85 | –0.58 | 0.16 | 1 |
| pH-EC Levels | Characteristics | Geographical Background | pH | EC (dS/m) | TOC (%) | CO32− (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strongly alkaline and strongly saline | Sporadic small patches salt crust | Margins of playas and pools | 10.48 | 17.80 | 0.45 | 8366.70 |
| Strongly alkaline and moderately saline | White color | Margins of playas and pools | 10.46 | 9.42 | 0.57 | 2450.54 |
| Strongly alkaline and slightly saline | Grey white color | Margins of playas and pools | 10.29 | 5.64 | 0.53 | 977.08 |
| Strongly alkaline and non-saline | Grey color | Margins of playas and pools | 10.11 | 1.39 | 0.69 | 296.60 |
| Moderately alkaline and non-saline | Brown color | flats near playas and pools | 8.65 | 0.29 | 1.19 | 0 |
| Slightly alkaline and non-saline | Dark color | flats | 7.94 | 0.23 | 2.34 | - |
| Non-affected soils | Dark color | flats | 5.91 | 0.14 | 3.22 | - |
| Calibration | Validation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bands | R2 | Constant | Components | RMSE | RPIQ | RMSE | |
| pH | Band 21-band 115 | 0.77 | 3.60 | 3 | 0.95 | 3.84 | 1.06 |
| EC | Band 21-band 115 | 0.48 | –38.39 | 3 | 17.92 | 0.14 | 18.92 |
| pH | Band 21, band 76, band 108 | 0.74 | 2.31 | 2 | 1.01 | 4.02 | 1.26 |
| EC | Band 21, band 73, band 109 | 0.36 | –55.51 | 1 | 19.63 | 0.13 | 18.96 |
| Map Inversion | Validation | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum | Minimum | RMSE | |
| pH | 14.65 | 1.78 | 1.09 |
| EC (dS/m) | 35.72 | −55.09 | 17.30 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bai, L.; Wang, C.; Zang, S.; Wu, C.; Luo, J.; Wu, Y. Mapping Soil Alkalinity and Salinity in Northern Songnen Plain, China with the HJ-1 Hyperspectral Imager Data and Partial Least Squares Regression. Sensors 2018, 18, 3855. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18113855
Bai L, Wang C, Zang S, Wu C, Luo J, Wu Y. Mapping Soil Alkalinity and Salinity in Northern Songnen Plain, China with the HJ-1 Hyperspectral Imager Data and Partial Least Squares Regression. Sensors. 2018; 18(11):3855. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18113855
Chicago/Turabian StyleBai, Lin, Cuizhen Wang, Shuying Zang, Changshan Wu, Jinming Luo, and Yuexiang Wu. 2018. "Mapping Soil Alkalinity and Salinity in Northern Songnen Plain, China with the HJ-1 Hyperspectral Imager Data and Partial Least Squares Regression" Sensors 18, no. 11: 3855. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18113855
APA StyleBai, L., Wang, C., Zang, S., Wu, C., Luo, J., & Wu, Y. (2018). Mapping Soil Alkalinity and Salinity in Northern Songnen Plain, China with the HJ-1 Hyperspectral Imager Data and Partial Least Squares Regression. Sensors, 18(11), 3855. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18113855







