Label-Free Detection of Salivary Pepsin Using Gold Nanoparticle/Polypyrrole Nanocoral Modified Screen-Printed Electrode
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Apparatus
2.2. Fabrication of GNP/PPNCs/SPCE
2.3. Preparation of the GNP/PPNCs/SPCE-Based Immunosensors
2.4. Characterization and Electrochemical Measurements
2.5. Real Sample Test—Electrochemical Sensing of Pepsin in Saliva
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preparation and Characterization of GNP-Decorated PPNCs on SPCE
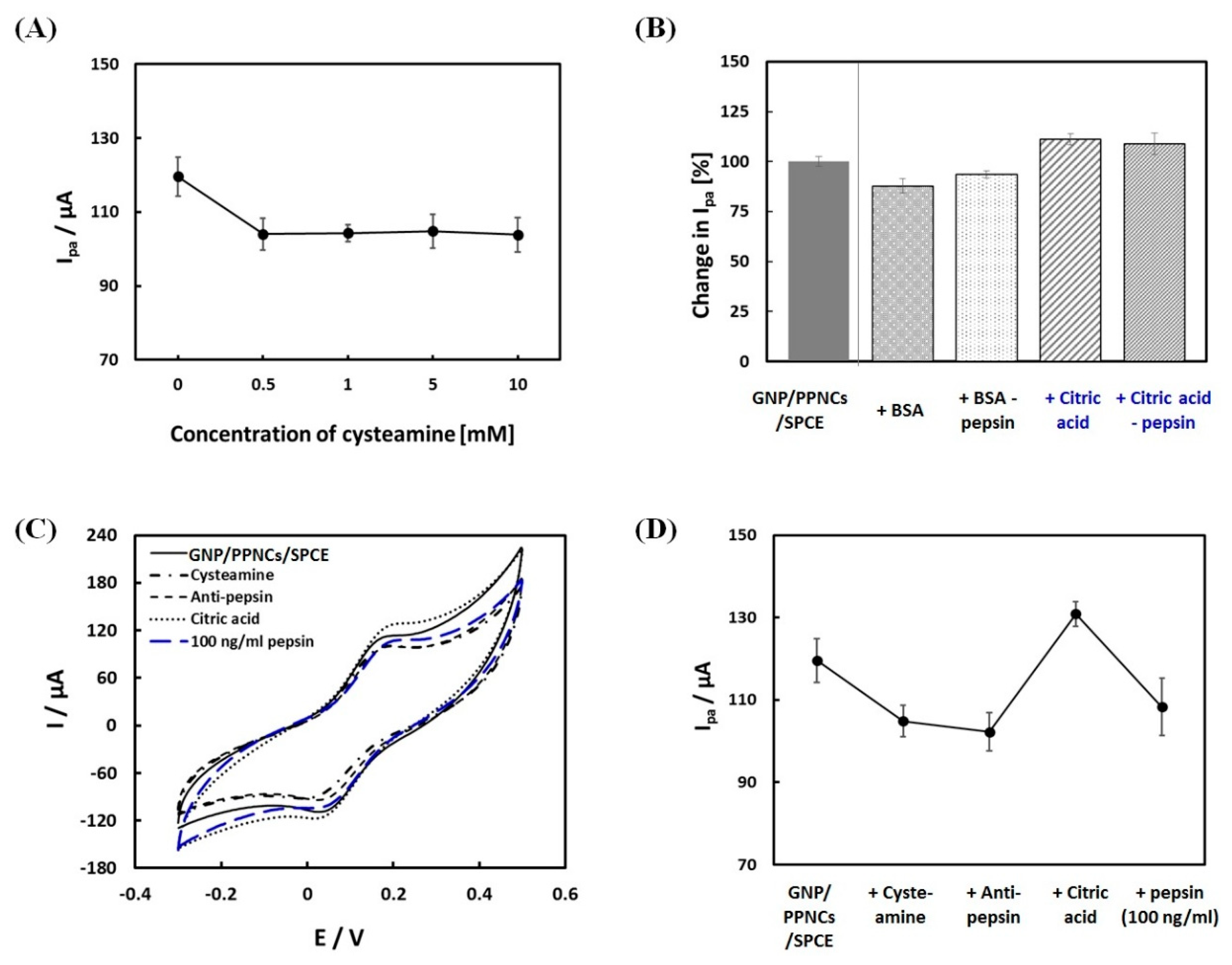
3.2. Fabrication and Electrochemical Characterization of the Immunosensor
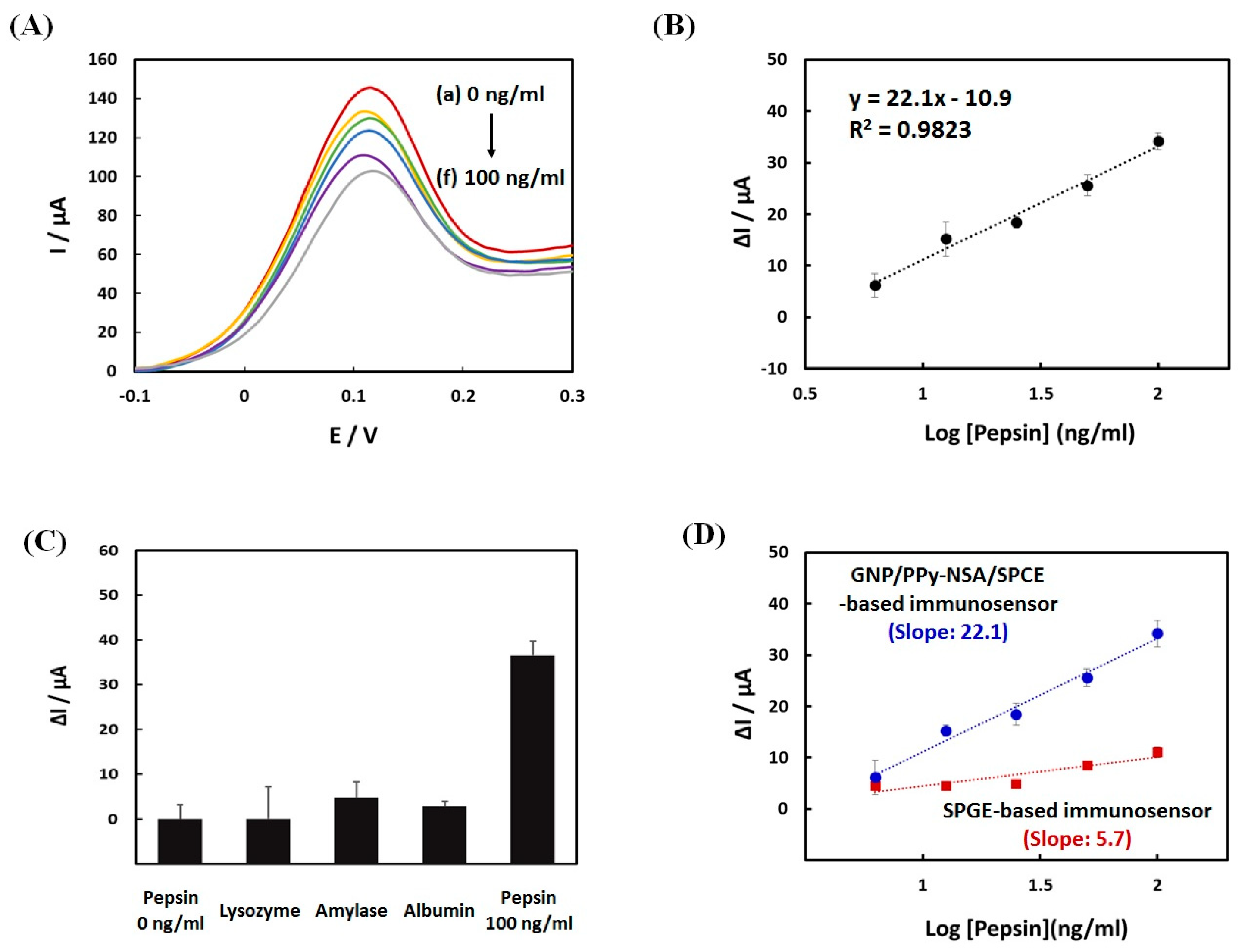
3.3. Analytical Performance of the Immunosensor
3.4. Real Sample Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Na, S.Y.; Kwon, O.E.; Lee, Y.C.; Eun, Y.G. Optimal timing of saliva collection to detect pepsin in patients with laryngopharyngeal reflux. Laryngoscope 2016, 126, 2770–2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Printza, A.; Speletas, M.; Triaridis, S.; Wilson, J. Is pepsin detected in the saliva of patients who experience pharyngeal reflux? Hippokratia 2007, 11, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hanson, D.; Conley, D.; Jiang, J.; Kahrilas, P. Role of esophageal pH recording in management chronic laryngitis: An overview. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2000, 109, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, N.; Knight, J.; Dettmar, P.W.; Lively, M.O.; Koufman, J. Pepsin and carbonic anhydrase isoenzyme III as diagnostic markers for laryngopharyngeal reflux disease. Laryngoscope 2004, 114, 2129–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, N.; Wells, C.W.; Blumin, J.H.; Toohill, R.J.; Merati, A.L. Receptor-mediated uptake of pepsin by laryngeal epithelial cells. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2007, 116, 934–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulmer, D.M.; Ali, M.S.; Brownlee, I.A.; Dettmar, P.W.; Pearson, J.P. Laryngeal mucosa: Its susceptibility to damage by acid and pepsin. Laryngoscope 2010, 120, 777–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ocak, E.; Kubat, G.; Yorulmaz, İ. Immunoserologic pepsin detection in the saliva as a non-invasive rapid diagnostic test for laryngopharyngeal reflux. Balkan Med. J. 2015, 32, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuels, T.L.; Johnston, N. Pepsin as a marker of extraesophageal reflux. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2010, 119, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knight, J.; Lively, M.O.; Johnston, N.; Dettmar, P.W.; Koufman, J.A. Sensitive pepsin immunoassay for detection of laryngopharyngeal reflux. Laryngoscope 2005, 115, 1473–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, N.; Dettmar, P.W.; Strugala, V.; Allen, J.E.; Chan, W.W. Laryngopharyngeal reflux and GERD. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2013, 1300, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortunato, J.E.; D’Agostino, R.B., Jr.; Lively, M.O. Pepsin in saliva as a biomarker for oropharyngeal reflux compared with 24-h esophageal impedance/pH monitoring in pediatric patients. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2017, 29, e12936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfaffe, T.; Cooper-White, J.; Beyerlein, P.; Kostner, K.; Punyadeera, C. Diagnostic potential of saliva: Current state and future applications. Clin. Chem. 2011, 57, 675–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farhath, S.; Aghai, Z.H.; Nakhla, T.; Saslow, J.; He, Z.; Soundar, S.; Mehta, D.I. Pepsin, a reliable marker of gastric aspiration, is frequently detected in tracheal aspirates from premature ventilated neonates: Relationship with feeding and methylxanEthine therapy. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2006, 43, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.H.; Lee, K.J.; Yeo, M.; Kim, D.K.; Cho, S.W. Pepsin detection in the sputum/saliva for the diagnosis of gastroesophageal reflux disease in patients with clinically suspected atypical gastroesophageal reflux disease symptom. Digestion 2008, 77, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farhath, S.; He, Z.; Saslow, J.; Soundar, S.; Amendolia, B.; Bhat, V.; Pyon, K.; Stahl, G.; Mehta, D.; Aghai, Z.H. Detection of pepsin in mouth swab: Correlation with clinical gastroesophageal reflux in preterm infants. J. Matern-Fetal Neonatal Med. 2013, 26, 819–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuksel, E.S.; Hong, S.K.S.; Strugala, V.; Slaughter, J.C.; Goutte, M.; Garrett, C.G.; Dettmar, P.W.; Vaezi, M.F. Rapid salivary prpein test: Blinded assessment of test performance in gastroesophareal reflux disease. Laryngoscope 2012, 122, 1312–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydemir, N.; Malmström, J.; Travas-Sejdic, J. Conducting polymer based electrochemical biosensors. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 8264–8277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramanavicius, A.; Ramanaviciene, A.; Malinauskas, A. Electrochemical sensors based on conducting polymer-polypyrrole. Electrochim. Acta 2006, 51, 6025–6037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanaviciene, A.; Ramanavicius, A. Application of polypyrrole for the creation of immunosensors. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2002, 32, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepshikha; Basu, T. A review on synthesis and characterization of nanostructured conducting polymers (NSCP) and application in biosensors. Anal. Lett. 2011, 44, 1126–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Quan, B.; Liu, M.; Wei, A.; Jiang, L. Conducting polypyrrole conical nanocontainers: Formation mechanism and voltage switchable property. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2008, 29, 1335–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Song, W.; Liu, Z. Controllable synthesis of conducting polypyrrole nanostructures. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 1158–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, M.; Jacobs, M.J.; Selvam, A.P.; Craven, J.E.; Prasad, S. Antibody-conjugated gold nanoparticle-based immunosensor for ultra-sensitive detection of troponin-T. J. Lab. Autom. 2014, 19, 546–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jazayeri, M.H.; Amani, H.; Pourfatollah, A.A.; Pazoki-Toroudi, H.; Sedighimoghaddam, B. Various methods of gold nanoparticles (GNPs) conjugation to antibodies. Sens. Biosens. Res. 2016, 9, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, W.J.; Li, L.; Yang, Y.; Mao, L.G.; Peng, Z. A label-free electrochemical immunosensor based on gold nanoparticles for direct detection of atrazine. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 191, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, F.; Sánchez Baeza, F.; Marco, M.P. Nanogold probe enhanced surface plasmon resonance immunosensor for improved detection of antibiotic residues. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 34, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mani, V.; Chikkaveeraiah, B.V.; Patel, V.; Gutkind, J.S.; Rusling, J.F. Ultrasensitive immunosensor for cancer biomarker proteins using gold nanoparticle film electrodes and multienzyme-particle amplification. Anal. Chem. 2009, 3, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.W.; Shumaker-Parry, J.S. Structural study of citrate layers on gold nanoparticles: Role of intermolecular interactions in stabilizing nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 1907–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beykal, B.; Herzberg, M.; Oren, Y.; Mauter, M.S. Influence of surface charge on the rate, extent, and structure of adsorbed Bovine Serum Albumin to gold electrodes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 460, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radecka, H.; Radecki, J. Label-free electrochemical immunosensors for viruses and antibodies detection—Review. J. Mex. Chem. Soc. 2015, 59, 269–275. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. 62 FR 27464-International Conference on Harmonisation; Guideline on the Validation of Analytical Procedures: Methodology; Availability. Fed. Regist. 1997, 62, 27464–27467. [Google Scholar]
- Hayat, J.O.; Gabieta-Somnez, S.; Yazaki, E.; Kang, J.Y.; Woodcock, A.; Dettmar, P.; Mabary, J.; Knowles, C.H.; Sifrim, D. Pepsin in saliva for the diagnosis of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. Gut 2015, 64, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Gao, Z.; Su, R.; Qi, W.; Wang, L.; He, Z. Scissor-based fluorescent detection of pepsin using lysozyme-stabilized Au nanoclusters. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 6789–6795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, M.L.; Lawi, W.; Snyder, S.T.; Wong, P.K.; Liao, J.C.; Gau, V. Matrix effects—a challenge toward automation of molecular analysis. J. Assoc. Lab. Autom. 2010, 15, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunyakul, N.; Baeumner, A.J. Combining electrochemical sensors with miniaturized sample preparation for rapid detection in clinical samples. Sensors 2015, 15, 547–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yee, E.H.; Lathwal, S.; Shah, P.P.; Sikes, H.D. Detection of biomarkers of periodontal disease in human saliva using stabilized, vertical flow immunoassays. ACS Sens. 2017, 2, 1589–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Detection Method | Linear Range (ng/mL) | Lower Detection Limit (ng/mL) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| ELISA (O.D. 450 nm) | 0.1–10 | 0.1 | [23] |
| Enzymatic assay with a fluorescent substrate | 12.5–400 | - | [24] |
| Colorimetric analysis—LFD 1 | - | 16 | [32] |
| Fluorescence sensor based on AuNCs@Lyz 2 | 1000–100,000 | 256 | [33] |
| Electrochemical immunosensor | 6.25–100 | 2.2 | In this work |
| Human Saliva Samples No. | Proposed Method (ng/mL) | ELISA Method (ng/mL) | Relative Error (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4.3 | 4.0 | 7.5 |
| 2 | 10.3 | 9.2 | 12.0 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, D.; Lee, Y.J.; Eun, Y.-G.; Lee, G.-J. Label-Free Detection of Salivary Pepsin Using Gold Nanoparticle/Polypyrrole Nanocoral Modified Screen-Printed Electrode. Sensors 2018, 18, 1685. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18061685
Lee D, Lee YJ, Eun Y-G, Lee G-J. Label-Free Detection of Salivary Pepsin Using Gold Nanoparticle/Polypyrrole Nanocoral Modified Screen-Printed Electrode. Sensors. 2018; 18(6):1685. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18061685
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Doyeon, Young Ju Lee, Young-Gyu Eun, and Gi-Ja Lee. 2018. "Label-Free Detection of Salivary Pepsin Using Gold Nanoparticle/Polypyrrole Nanocoral Modified Screen-Printed Electrode" Sensors 18, no. 6: 1685. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18061685
APA StyleLee, D., Lee, Y. J., Eun, Y.-G., & Lee, G.-J. (2018). Label-Free Detection of Salivary Pepsin Using Gold Nanoparticle/Polypyrrole Nanocoral Modified Screen-Printed Electrode. Sensors, 18(6), 1685. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18061685




