Molecular Fingerprints of Hemoglobin on a Nanofilm Chip
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Modification and Preparation of the NanoFilms
2.3. Characterization of the NanoFilms
2.4. Kinetic Analysis
2.5. Selectivity, Reusability and Storage Stability Analysis
3. Results and Discussions
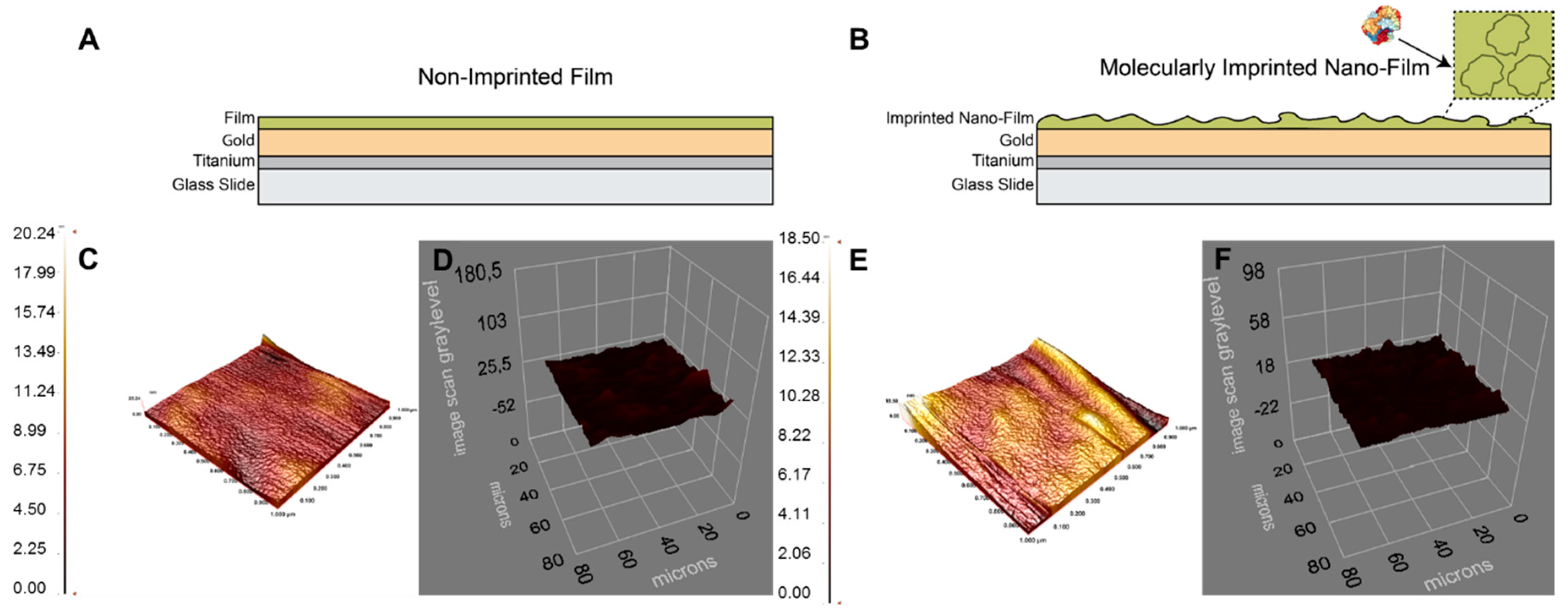
3.1. Preparation and Characterization of the NanoFilms
3.2. Kinetic Analysis
3.3. Adsorption Isotherm Models
3.4. Selectivity Analysis
3.5. Reusability and Storage Stability Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Altıntas, E.B.; Türkmen, D.; Karakoc, V.; Denizli, A. Hemoglobin binding from human blood hemolysate with poly(glycidylmethacrylate) beads. Colloid. Surf. B 2011, 85, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derazshamshir, A.; Baydemir, G.; Andac, M.; Say, R.; Galaev, I.Y.; Denizli, A. Molecularly imprinted PHEMA-based cryogel for depletion of hemoglobin from human blood. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2010, 211, 657–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angastiniotis, M.; Modell, B. Global epidemiology of hemoglobin disorders. Ann. N. Y. Sci. 1998, 850, 251–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Zhao, S.; Hao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Cui, X.; Liu, D.; Zhang, M.; Tang, Y. Synthesis of magnetic dual-template molecularly imprinted nanoparticles for the specific removal of two high-abundance proteins simultaneously in blood plasma. J. Sep. Sci. 2015, 38, 3914–3920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafiee, H.; Asghar, W.; Inci, F.; Yuksekkaya, M.; Jahangir, M.; Zhang, M.H.; Durmus, N.G.; Gurkan, U.A.; Kuritzkes, D.R.; Demirci, U. Paper and flexible substrates as materials for biosensing platforms to detect multiple biotargets. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uzun, L.; Turner, A.P. Molecularly-imprinted polymer sensors: Realising their potential. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 76, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saylan, Y.; Tamahkar, E.; Denizli, A. Recognition of lysozyme using surface imprinted bacterial cellulose nanofibers. J. Biomat. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2017, 28, 1950–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Yu, S.; Liu, W.; Fu, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, L. Molecular imprinting based hybrid ratiometric fluorescence sensor for the visual determination of bovine hemoglobin. ACS Sens. 2018, 3, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokel, O.; Yildiz, U.H.; Inci, F.; Durmus, N.G.; Ekiz, O.O.; Turker, B.; Cetin, C.; Rao, S.; Sridhar, K.; Natarajan, N.; et al. Portable microfluidic integrated plasmonic platform for pathogen detection. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saylan, Y.; Yılmaz, F.; Özgür, E.; Derazshamshir, A.; Yavuz, H.; Denizli, A. Molecular imprinting of macromolecules for sensor applications. Sensors 2017, 17, 898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.P.; Huang, L.S.; Lin, C.W.; Lee, C.K.; Chen, J.L.; Hsu, S.M.; Lin, S. Determination of binding constant of DNA-binding drug to target DNA by surface plasmon resonance biosensor technology. Curr. Drug Target 2005, 5, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Husson, S.M. Adsorption of dansylated amino acids on molecularly imprinted surfaces: A surface plasmon resonance study. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2006, 22, 336–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Samadi, A.; Husson, S.M. Synthesis and characterization of molecularly imprinted polymers for chromatographic separations. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2005, 40, 109–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamoorthy, G.; Carlen, E.T.; Van Der Berg, A.; Scasfoort, R.B. Surface plasmon resonance imaging based multiplex biosensor: Integration of biomolecular screening detection and kinetics estimation. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2010, 148, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saylan, Y.; Akgönüllü, S.; Çimen, D.; Derazshamshir, A.; Bereli, N.; Yılmaz, F.; Denizli, A. Development of surface plasmon resonance sensors based on molecularly imprinted nanofilms for sensitive and selective detection of pesticides. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 24, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umpleby, R.J.; Baxter, S.C.; Chen, Y.; Shah, R.N.; Shimizu, K.D. Characterization of molecularly imprinted polymers with the Langmuir-Freundlich isotherm. Anal. Chem. 2001, 73, 4584–4591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Sun, Y.; Yang, C.; Yan, X.; Guo, H.; Fu, G. Fabrication of surface protein-imprinted nanoparticles using a metal chelating monomer via aqueous precipitation polymerization. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 27188–27196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, M. Antibody shelf life/how to store antibodies. Mater Methods 2012, 2, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghar, W.; Yuksekkaya, M.; Shafiee, H.; Zhang, M.; Ozen, M.O.; Inci, F.; Kocakulak, M.; Demirci, U. Engineering long shelf life multilayer biologically active surfaces on microfluidic devices for point of care applications. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, B.; Ni, X.; Cao, Y.; Cao, G. Electrochemical sensor based on magnetic molecularly imprinted nanoparticles modified magnetic electrode for determination of Hb. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 91, 354–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hongzhi, L.; Shoufang, X. Functional monomer-template-QDs sandwich structure for mesoporous structured bovine hemoglobin imprinted ratiometric fluorescence sensor. Talanta 2017, 165, 482–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, R.; Luan, J.; Kharasch, E.D.; Singamaneni, S.; Morrissey, J.J. Aromatic functionality of target proteins influences monomer selection for creating artificial antibodies on plasmonic biosensors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interface 2017, 9, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Du, H.; Lan, Y.; Wang, W.; Liang, Y.; Feng, C.; Yang, M. Preparation of hemoglobin (Hb) imprinted polymer by Hb catalyzed eATRP and its application in biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 77, 894–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Wei, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Lu, K.; Li, C.; Yan, Y. Rapid and sensitive detection of hemoglobin with gold nanoparticles based fluorescence sensor in aqueous solution. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 685, 820–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Lan, Y.; Yang, L.; Kong, F.; Du, H.; Feng, C. Preparation of hemoglobin imprinted polymers based on graphene and protein removal assisted by electric potential. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 61897–61905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Chang, C.C.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Galanakis, D.K.; Levon, K.; Rafailovich, M. Design of a molecular imprinting biosensor with multi-scale roughness for detection across a broad spectrum of biomolecules. Analyst 2016, 141, 5607–5617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luan, J.; Liu, K.K.; Tadepalli, S.; Jiang, Q.; Morrissey, J.J.; Kharasch, E.D.; Singamaneni, S. PEGylated artificial antibodies: Plasmonic biosensors with improved selectivity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 23509–23516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Luo, C. Bioreceptor multi-walled carbonnanotubes@Fe3O4@SiO2–surface molecular imprinted polymer in an ultrasensitive chemiluminescent biosensor for bovine hemoglobin. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 88492–88499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Fan, L.; Dai, Y.; Kan, X. Recognition and determination of bovine hemoglobin using a gold electrode modified with gold nanoparticles and molecularly imprinted self-polymerized dopamine. Microchim. Acta 2015, 182, 2477–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Xu, S.; Luo, J.; Liu, X. Molecularly imprinted photo-sensitive polyglutamic acid nanoparticles for electrochemical sensing of hemoglobin. Microchim. Acta 2015, 182, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, F.; Xia, J.; Xia, L.; Zhang, F.; Bi, S.; Shi, G.; Xia, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; et al. An ionic liquid-modified graphene based molecular imprinting electrochemical sensor for sensitive detection of bovine hemoglobin. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 61, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; Chen, L.; Shi, H.; Li, Y.; He, X. Magnetic glass carbon electrode, modified with magnetic ferriferous oxide nanoparticles coated with molecularly imprinted polymer films for electrochemical determination of bovine hemoglobin. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2014, 734, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Jiang, S.; Liu, X. Electrochemical sensor for bovine hemoglobin based on a novel graphene-molecular imprinted polymers composite as recognition element. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 203, 782–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Qingwen, Z.; Yamin, R.; Lijing, J.; Tianxin, W. Molecularly imprinted polymer thin film based surface plasmon resonance sensor to detect hemoglobin. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 2014, 30, 42–48. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Gana, N.; Hub, F.; Li, T.; Zhou, H.; Li, X.; Zheng, L. A single antibody sandwich electrochemiluminescence immunosensor based on protein magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers mimicking capture probes. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 186, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Kang, C.; Xu, S.; Tang, Y. Selective room temperature phosphorescence sensing of target protein using Mn-doped ZnS QDs-embedded molecularly imprinted polymer. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 48, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Hong, M.; Bin, Q.; Lin, Z.; Lin, Z.; Cai, Z.; Chen, G. Highly sensitive protein molecularly imprinted electro-chemical sensor based on gold microdendrites electrode and prussian blue mediated amplification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 42, 612–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.Y.; He, X.W.; Chen, Y.; Li, W.Y.; Zhang, Y.K. Novel hybrid structure silica/CdTe/molecularly imprinted polymer: Synthesis, specific recognition, and quantitative fluorescence detection of bovine hemoglobin. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 12609–12616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, B.B.; Prasad, A.; Prasad Tiwari, M. Quantum dots-multiwalled carbon nanotubes nanoconjugate-modified pencil graphite electrode for ultratrace analysis of hemoglobin in dilute human blood samples. Talanta 2013, 109, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Equilibrium Analysis | Association Kinetic Analysis | Langmuir | Freundlich | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ΔRmax | 13 | ka, mL mg s−1 | 0.011 | ΔRmax | 5.01 | ΔRmax | 22.4 |
| KA, mL mg−1 | 12.6 | kd, s−1 | 0.001 | KD, mg mL−1 | 0.03 | 1/n | 0.67 |
| KD, mg mL−1 | 0.08 | KA, mL mg−1 | 15 | KA, mL mg−1 | 39.1 | R2 | 0.96 |
| R2 | 0.92 | KD, mg mL−1 | 0.07 | R2 | 0.99 | ||
| R2 | 0.98 | ||||||
| Protein | Molecularly Imprinted | Non-Imprinted | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| %∆R | k | %∆R | k | k′ | |
| Hb | 6.58 | 0.57 | |||
| Lyz | 4.19 | 1.57 | 1.48 | 0.39 | 4.08 |
| Rrf | 1.64 | 4.01 | 1 | 0.57 | 7.04 |
| BSA | 0.61 | 10.79 | 0.46 | 1.24 | 8.71 |
| Myb | 0.4 | 16.45 | 0.24 | 2.38 | 6.93 |
| Detection System | Base on | Detection Range | Limit of Detection | Selectivity | Reusability | Time | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electrochemical | Magnetic nanoparticles | 0.005–0.1 mg mL−1 | 0.001 mg mL−1 | Lyz, BSA, HRP | Not reported | 7 min | [20] |
| Fluorescence | Core-shell | 0.02–2.0 µM | 6.3 nM | Lyz, BSA, OB | 5 times | 15 min | [21] |
| Localized surface plasmon resonance | Artificial antibody | 0.5–20 µg mL−1 | Not reported | HSA, BSA, Lyz | Not reported | 120 min | [22] |
| Differential pulse voltametry | eATRP | 1.10−10–1.101 mg L−1 | 7.8.10−11 mg L−1 | Lyz, BSA, HSA, IgG | 3 times | 120 min | [23] |
| Fluorescence | Gold nanoparticle | 0.1–20 µmol L−1 | 0.03 µmol L−1 | BSA, BHb, Alb, CE | Not reported | Not reported | [24] |
| Differential pulse voltametry | Cryogel | 1.10−8–1.102 mg L−1 | 6.7.10−9 mg L−1 | Lyz, BSA, HSA | 3 times | 120 min | [25] |
| Electrochemical | SAM | 1–20 µg mL−1 | Not reported | Myb | Not reported | Not reported | [26] |
| Localized surface plasmon resonance | PEGlated nanorattle | 1–2500 ng mL−1 | Not reported | HSA, BSA, Myb | Not reported | Not reported | [27] |
| Chemiluminescent | Carbon nanotube | 5.10−10–7.10−7 mg mL−1 | 1.5.10−10 mg mL−1 | BSA, Lyz | Not reported | Not reported | [28] |
| Electrochemical | Gold nanoparticle | 1.10−11–1.10−2 mg mL−1 | Not reported | BSA, EA, Lyz | 5 times | Not reported | [29] |
| Electrochemical | Nanoparticle | 0.005–0.1 mg mL−1 | 25.8 ng mL−1 | Lyz, HRP | Not reported | 10 min | [30] |
| Electrochemical | Graphene-carbon electrode | 1.10−10–1.10−3 mg mL−1 | 3.09.10−11 mg mL−1 | BSA, HSA, Lyz, ATP, BI | 3 times | 120 min | [31] |
| Electrochemical | Magnetic nanoparticle | 5.10−7–1.10−5 mg mL−1 | 1.184.10−8 mg mL−1 | BSA, Lyz, Cyt C, HRP | Not reported | 70 min | [32] |
| Electrochemical | Graphene composite | 1.10−9–1.10−1 mg mL−1 | 2.10−10 mg mL−1 | BSA, Lyz, EA, Pap | Not reported | 10 min | [33] |
| Surface plasmon resonance-Electrochemical | Thin film | 0.0005–5.0 mg mL−1 | 0.000435 mg mL−1 | BSA, Lyz, Ova | Not reported | 25 min | [34] |
| Electrochemi-luminescence | Magnetic nanocomposite | 0.1–4.104 pg mL−1 | 0.023 pg mL−1 | BSA, CEA, AFP, HCG, HIgG | Not reported | 70 min | [35] |
| Phosphorescence | Quantum dot | 1.10−7–5.10−6 mol L−1 | 3.8.10−8 mol L−1 | Not reported | 11 times | 15 min | [36] |
| Electrochemical | Gold microdentrites | 0.1–4.103 µg mL−1 | 0.05 µg mL−1 | BSA, Lyz, Cyt C, Ova | 5 times | 60 min | [37] |
| Electrochemical | Quantum dot-carbon nanotube | 27.8–444 ng mL−1 | 6.73 ng mL−1 | BSA, Trp, Crp, Glu, Dop, Cys, AA, Ins | Not reported | Not reported | [38] |
| Fluorescence | Quantum dot | 0.02–2.1 µM | 9.4 nM | BSA, Lyz, OB | Not reported | 60 min | [39] |
| Surface plasmon resonance | Nanofilm | 0.0005–1.0 mg mL−1 | 0.00035 mg mL−1 | Lyz, BSA, Trf, Myb | 4 times | 23 min | This study |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saylan, Y.; Denizli, A. Molecular Fingerprints of Hemoglobin on a Nanofilm Chip. Sensors 2018, 18, 3016. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18093016
Saylan Y, Denizli A. Molecular Fingerprints of Hemoglobin on a Nanofilm Chip. Sensors. 2018; 18(9):3016. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18093016
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaylan, Yeşeren, and Adil Denizli. 2018. "Molecular Fingerprints of Hemoglobin on a Nanofilm Chip" Sensors 18, no. 9: 3016. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18093016
APA StyleSaylan, Y., & Denizli, A. (2018). Molecular Fingerprints of Hemoglobin on a Nanofilm Chip. Sensors, 18(9), 3016. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18093016






