Dynamic Responses of Electrically Driven Quartz Tuning Fork and qPlus Sensor: A Comprehensive Electromechanical Model for Quartz Tuning Fork
Abstract
1. Introduction
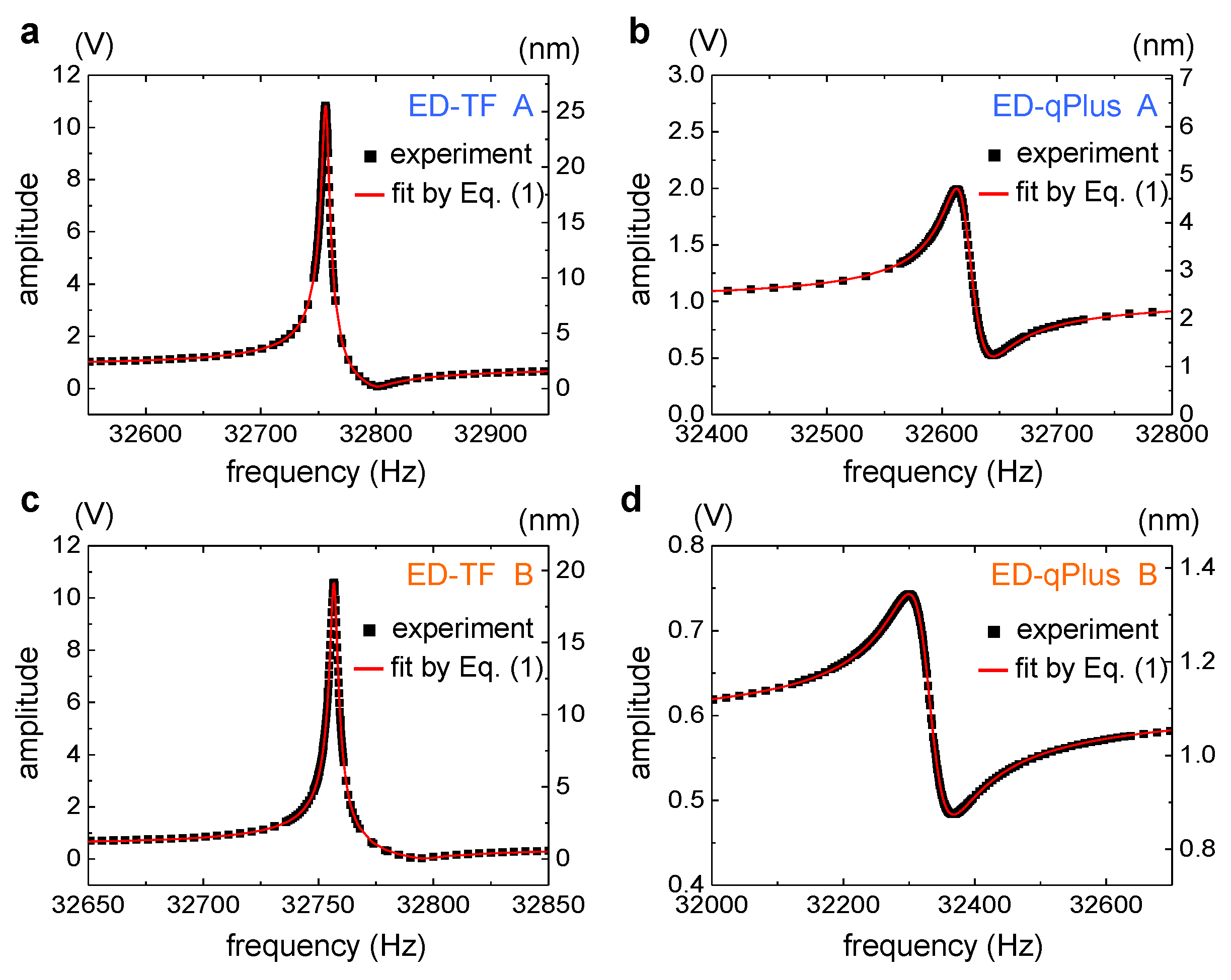
2. Experiment
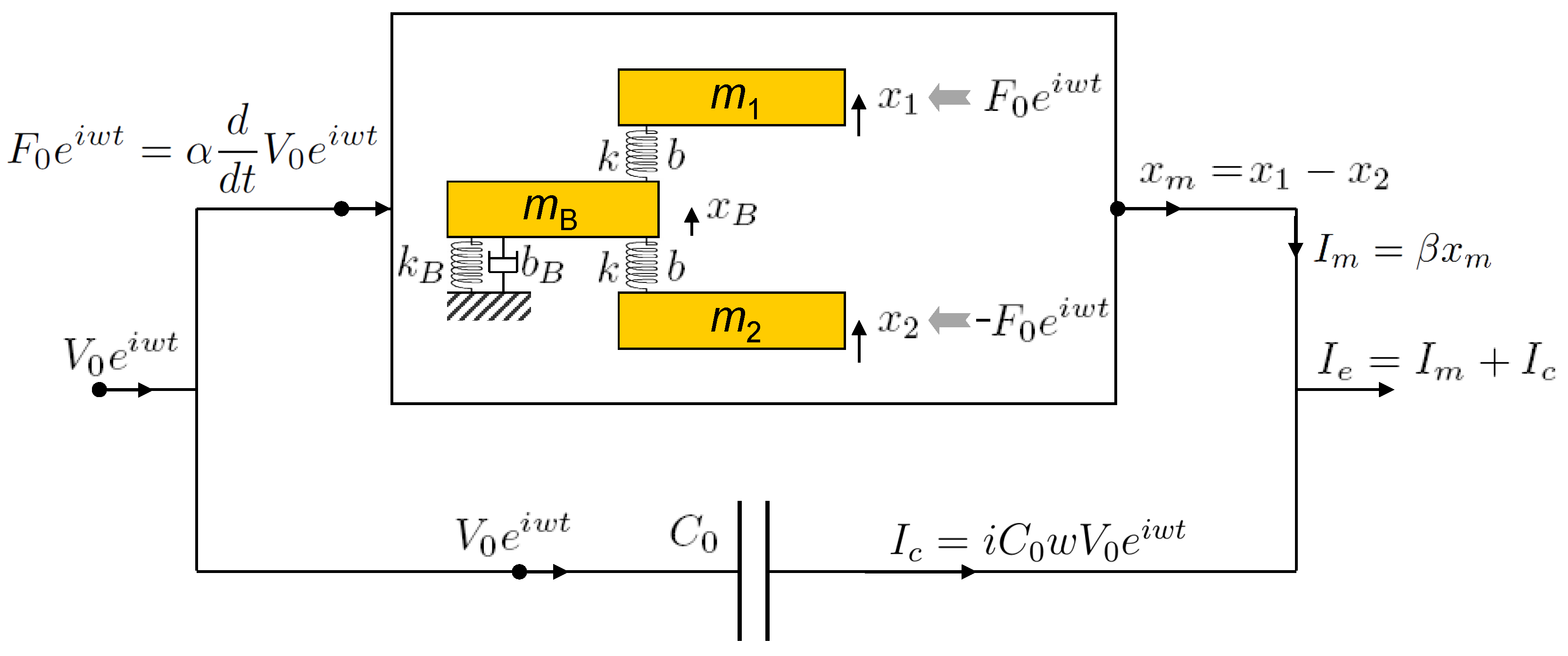
3. Theory and Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Garcia, R.; Pérez, R. Dynamic atomic force microscopy methods. Surf. Sci. Rep. 2002, 47, 197–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giessibl, F.J. Advances in atomic force microscopy. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2003, 75, 949–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Jhe, W. General theory of amplitude-modulation atomic force microscopy. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 97, 036104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voigtländer, B. Scanning Probe Microscopy; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Nony, L.; Boisgard, R.; Aimé, J.P. Nonlinear dynamical properties of an oscillating tip-cantilever system in the tapping mode. J. Chem. Phys. 1999, 111, 1615–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhushan, B.; Kawata, S.; Fuchs, H. Applied Scanning Probe Methods V. NanoScience and Technology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Thornton, S.T.; Marion, J.B. Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems, 5th ed.; Cengage Learning: Boston, MA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Lozano, J.R.; Garcia, R. Theory of multifrequency atomic force microscopy. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 100, 076102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oria, R.; Otero, J.; González, L.; Botaya, L.; Carmona, M.; Puig-Vidal, M. Finite element analysis of electrically excited quartz tuning fork devices. Sensors 2013, 13, 7156–7169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giessibl, F.J. High-speed force sensor for force microscopy and profilometry utilizing a quartz tuning fork. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1998, 73, 3956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giessibl, F.J. The qPlus sensor, a powerful core for the atomic force microscope. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2019, 90, 011101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Jahng, J.; Kim, K.; Jhe, W. Quantitative atomic force measurement with a quartz tuning fork. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 91, 023117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, S.; Giessibl, F.; Wiesendanger, R. (Eds.) Noncontact Atomic Force Microscopy; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Zelenka, J. Piezoelectric Resonators and their Applications; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Edwards, H.; Taylor, L.; Duncan, W.; Melmed, A.J. Fast, high-resolution atomic force microscopy using a quartz tuning fork as actuator and sensor. J. Appl. Phys. 1997, 82, 980–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Giessibl, F.J. Atomic resolution on Si(111)-(7x7) by noncontact atomic force microscopy with a force sensor based on a quartz tuning fork. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2000, 76, 1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karrai, K.; Grober, R.D. Piezoelectric tip-sample distance control for near field optical microscopes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1995, 66, 1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, Y.; Hwang, C.S.; Jhe, W. Electrostatic force microscopy using a quartz tuning fork. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2002, 80, 4324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Seo, Y.; Jang, H.; Chang, S.; Hong, M.-H.; Jhe, W. Shear-mode magnetic force microscopy with a quartz tuning fork in ambient conditions. Nanotechnology 2006, 17, S201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dagdeviren, O.E.; Miyahara, Y.; Mascaro, A.; Enright, T.; Grütter, P. Amplitude dependence of resonance frequency and its consequences for scanning probe microscopy. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1812.08818. [Google Scholar]
- Dagdeviren, O.E.; Miyahara, Y.; Mascaro, A.; Grütter, P. Calibration of the oscillation amplitude of electrically excited scanning probe microscopy sensors. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2019, 90, 013703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naber, A. The tuning fork as sensor for dynamic force distance control in scanning near-field optical microscopy. J. Microsc. 1999, 194, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellanos-Gomez, A.; Agrait, N.; Rubio-Bollinger, G. Force-gradient-induced mechanical dissipation of quartz tuning fork force sensors used in atomic force microscopy. Ultramicroscopy 2011, 111, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labardi, M.; Lucchesi, M. Split quartz tuning fork sensors for enhanced sensitivity force detection. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2015, 26, 035101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellanos-Gomez, A.; Agrait, N.; Rubio-Bollinger, G. Dynamics of quartz tuning fork force sensors used in scanning probe microscopy. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 215502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, G.H.; Heyde, M.; Rust, H.-P. Recipes for cantilever parameter determination in dynamic force spectroscopy: Spring constant and amplitude. Nanotechnology 2007, 18, 255503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Jahng, J.; Khan, R.M.; Park, S.; Potma, E.O. Eigenmodes of a quartz tuning fork and their application to photoinduced force microscopy. Phys. Rev. B 2017, 95, 075440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahng, J.; Potma, E.O.; Lee, E.S. Tip-enhanced thermal expansion force for nanoscale chemical imaging and spectroscopy in photoinduced force microscopy. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 11054–11061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giessibl, F.J.; Pielmeier, F.; Eguchi, T.; An, T.; Hasegawa, Y. Comparison of force sensors for atomic force microscopy based on quartz tuning forks and length-extensional resonators. Phys. Rev. B 2011, 84, 125409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melcher, J.; Stirling, J.; Shaw, G.A. A simple method for the determination of qPlus sensor spring constants. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2015, 6, 1733–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, M.; Kim, B.; An, S.; Jhe, W. Dynamic Responses of Electrically Driven Quartz Tuning Fork and qPlus Sensor: A Comprehensive Electromechanical Model for Quartz Tuning Fork. Sensors 2019, 19, 2686. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19122686
Lee M, Kim B, An S, Jhe W. Dynamic Responses of Electrically Driven Quartz Tuning Fork and qPlus Sensor: A Comprehensive Electromechanical Model for Quartz Tuning Fork. Sensors. 2019; 19(12):2686. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19122686
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Manhee, Bongsu Kim, Sangmin An, and Wonho Jhe. 2019. "Dynamic Responses of Electrically Driven Quartz Tuning Fork and qPlus Sensor: A Comprehensive Electromechanical Model for Quartz Tuning Fork" Sensors 19, no. 12: 2686. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19122686
APA StyleLee, M., Kim, B., An, S., & Jhe, W. (2019). Dynamic Responses of Electrically Driven Quartz Tuning Fork and qPlus Sensor: A Comprehensive Electromechanical Model for Quartz Tuning Fork. Sensors, 19(12), 2686. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19122686






