Low-Frequency Noise of Magnetic Sensors Based on the Anomalous Hall Effect in Fe–Pt Alloys
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
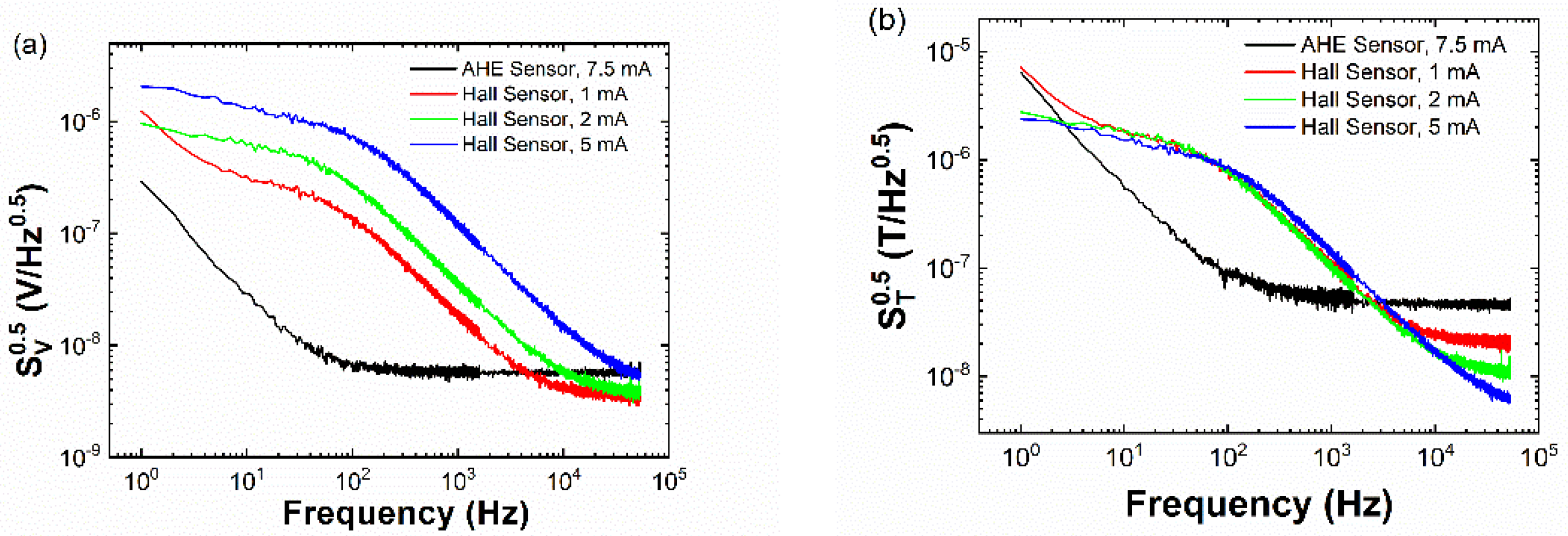
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nagaosa, N.; Sinova, J.; Onoda, S.; MacDonald, A.H.; Ong, N.P. Anomalous Hall effect. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2010, 82, 1539–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moritz, J.; Rodmacq, B.; Auffret, S.; Dieny, B. Extraordinary Hall effect in thin magnetic films and its potential for sensors, memories and magnetic logic applications. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2008, 41, 135001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canedy, C.; Gong, G.; Wang, J.; Xiao, G. Large magnetic Hall effect in ferromagnetic Fex Pt100− x thin films. J. Appl. Phys. 1996, 79, 6126–6128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Canedy, C.L.; Li, X.W.; Xiao, G. Large magnetic moment enhancement and extraordinary Hall effect in Co/Pt superlattices. Phys. Rev. B 2000, 62, 508–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Zheng, R.; Liu, H.; Tian, Y.; Li, Z. Large extraordinary Hall effect and anomalous scaling relations between the Hall and longitudinal conductivities in ε-Fe3N nanocrystalline films. Phys. Rev. B 2009, 80, 174412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fergen, I.; Seemann, K.; von der Weth, A.; Schuppen, A. Soft ferromagnetic thin films for high frequency applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2002, 242, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Nlebedim, I.; Jiles, D.C. Ultrahigh Sensitivity of Anomalous Hall Effect Sensor Based on Cr-Doped Bi2Te3 Topological Insulator Thin Films. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2016, 52, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satake, Y.; Fujiwara, K.; Shiogai, J.; Seki, T.; Tsukazaki, A. Fe-Sn nanocrystalline films for flexible magnetic sensors with high thermal stability. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilanova Vidal, E.; Stryganyuk, G.; Schneider, H.; Felser, C.; Jakob, G. Exploring Co2MnAl Heusler compound for anomalous Hall effect sensors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 99, 132509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Q.; Chen, W.Z.; Wang, S.T.; Xiao, G. Anomalous Hall effect and magnetic properties of FexPt100-x alloys with strong spin-orbit interaction. J. Appl. Phys. 2017, 122, 033901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, G.X.; Xiao, G. Giant Hall resistance in Pt-based ferromagnetic alloys. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 85, 73–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Cai, J.W. Ultrahigh sensitivity Hall effect in magnetic multilayers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 90, 012104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M.; Masumoto, T. Extraordinary Hall effect in Fe–Pt alloy thin films and fabrication of micro Hall devices. Thin Solid Films 2002, 405, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haned, N.; Missous, M. Nano-tesla magnetic field magnetometry using an InGaAs–AlGaAs–GaAs 2DEG Hall sensor. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2003, 102, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heremans, J.; Partin, D.L.; Thrush, C.M.; Green, L. Narrow-Gap Semiconductor Magnetic-Field Sensors and Applications. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 1993, 8, S424–S430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-S.; Ahn, K.-H.; Jeong, Y.-H.; Kim, D.M. Quantum-well Hall devices in Si-delta-doped Al/sub 0.25/Ga/sub 0.75/As/GaAs and pseudomorphic Al/sub 0.25/Ga/sub 0.75/As/In/sub 0.25/Ga/sub 0.75/As/GaAs heterostructures grown by LP-MOCVD: Performance comparisons. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 1996, 43, 1665–1670. [Google Scholar]
- Sampietro, M.; Fasoli, L.; Ferrari, G. Spectrum analyzer with noise reduction by cross-correlation technique on two channels. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1999, 70, 2520–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.W.; Liu, C.; Li, L.; Jones, P.; Chantrell, R.W.; Weller, D. Nonmagnetic shell in surfactant-coated FePt nanoparticles. J. Appl. Phys. 2004, 95, 6810–6812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicks, C.; Luan, L.; Moler, K.; Zeldov, E.; Shtrikman, H. Noise characteristics of 100 nm scale Ga As/Alx Ga1−x As scanning Hall probes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 90, 133512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Hao, Q.; Xiao, G. Low-Frequency Noise of Magnetic Sensors Based on the Anomalous Hall Effect in Fe–Pt Alloys. Sensors 2019, 19, 3537. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19163537
Zhang Y, Hao Q, Xiao G. Low-Frequency Noise of Magnetic Sensors Based on the Anomalous Hall Effect in Fe–Pt Alloys. Sensors. 2019; 19(16):3537. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19163537
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yiou, Qiang Hao, and Gang Xiao. 2019. "Low-Frequency Noise of Magnetic Sensors Based on the Anomalous Hall Effect in Fe–Pt Alloys" Sensors 19, no. 16: 3537. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19163537
APA StyleZhang, Y., Hao, Q., & Xiao, G. (2019). Low-Frequency Noise of Magnetic Sensors Based on the Anomalous Hall Effect in Fe–Pt Alloys. Sensors, 19(16), 3537. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19163537




