Soft Sensing of Silicon Content via Bagging Local Semi-Supervised Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Soft Sensor Modeling Methods
2.1. Extreme Learning Machine (ELM) Regression Method
2.2. Semi-supervised Extreme Learning Machine (SELM) Regression Method
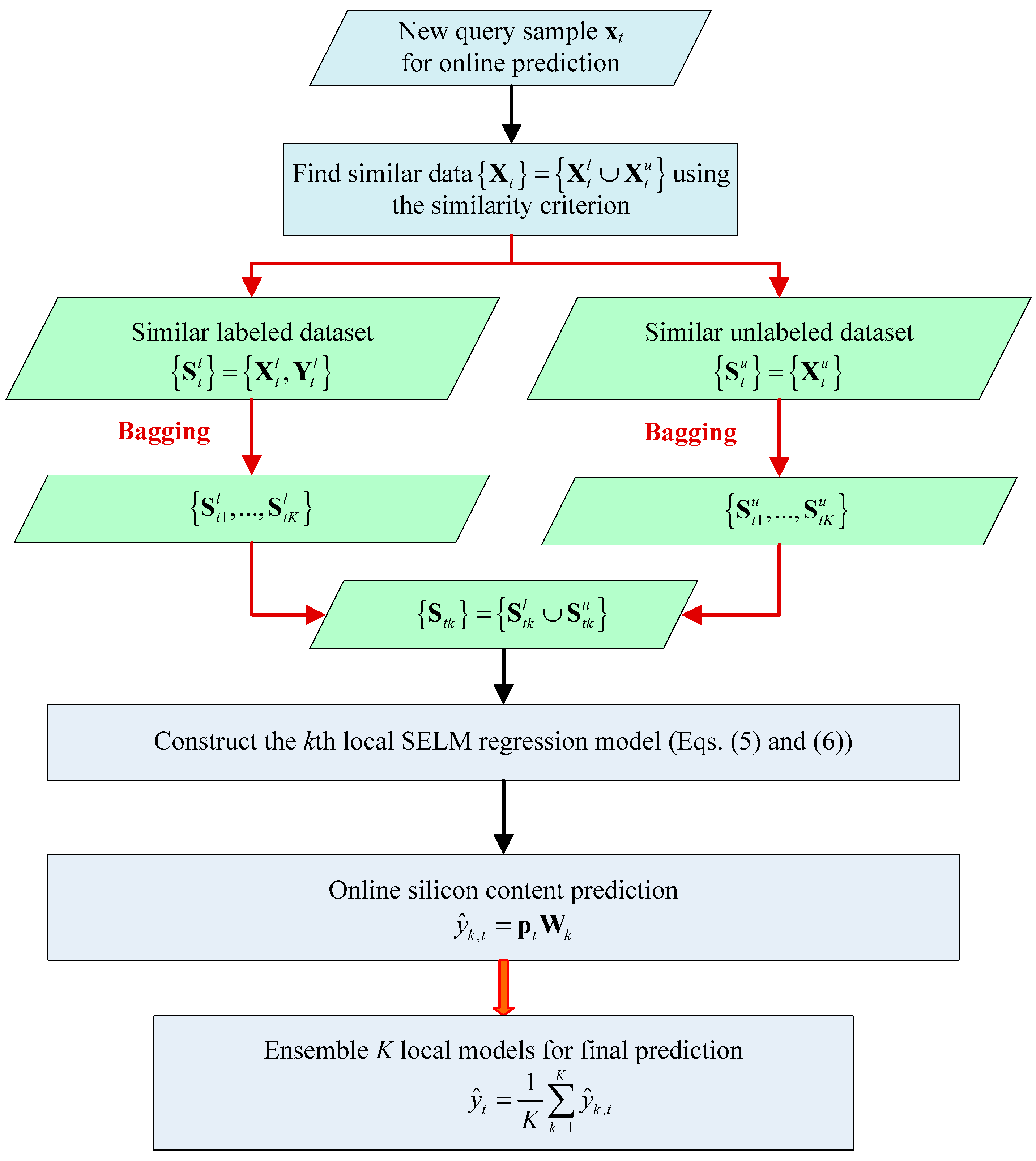
2.3. Bagging Local Semi-supervised Models (BLSM) Online Modeling Method
3. Industrial Silicon Content Online Prediction
3.1. Data Sets and Pretreatment
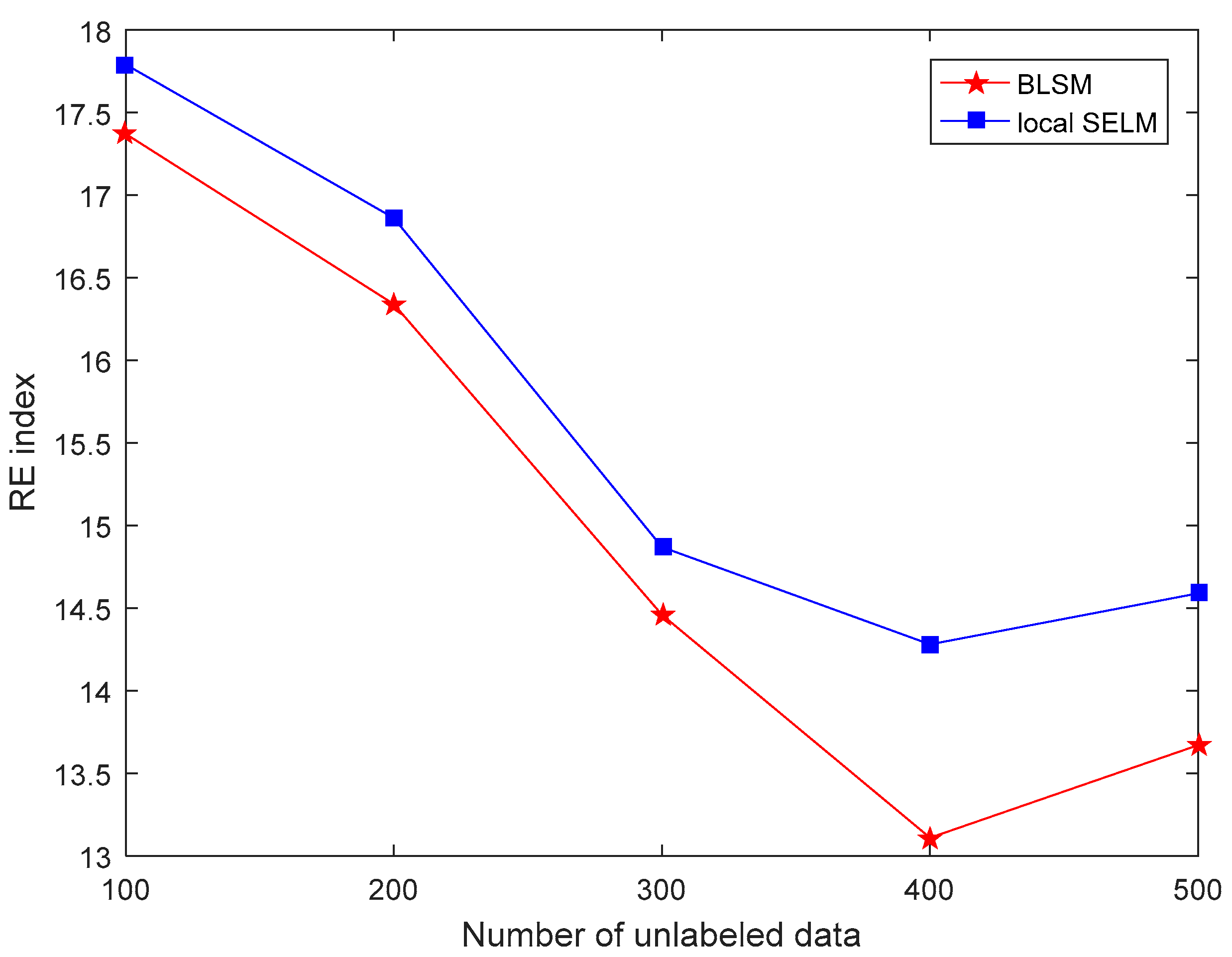
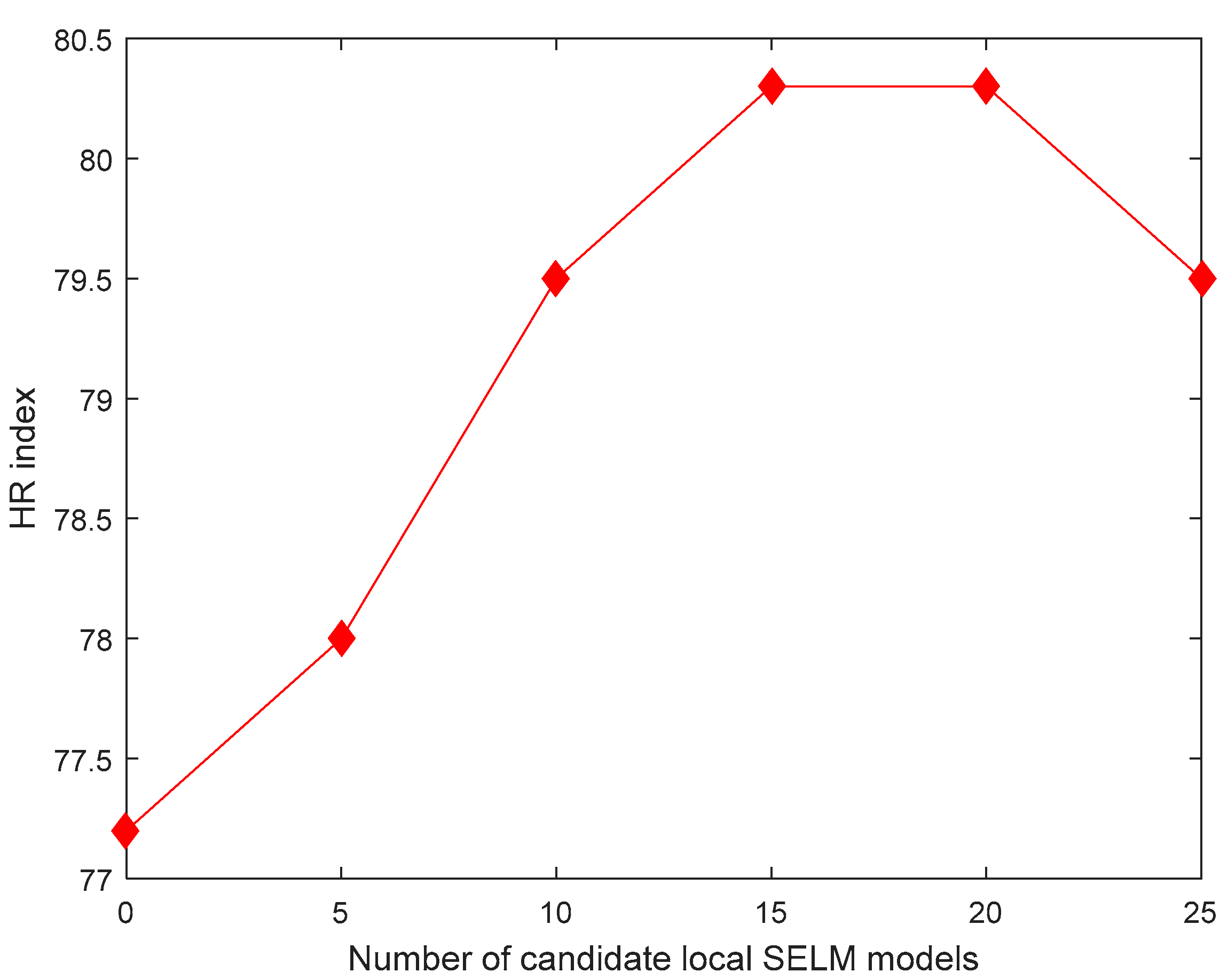
3.2. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| BLSM | bagging local semi-supervised model |
| ELM | extreme learning machine |
| JITL | just-in-time-learning |
| JLSSVR | just-in-time least squares support vector regression |
| NNs | neural networks |
| RE | relative root-mean-square error |
| RMSE | root-mean-square error |
| RELM | regularized extreme learning machine |
| SELM | semi-supervised extreme learning machine |
| SLFNs | single-hidden layer feedforward networks |
| SVR | support vector regression |
References
- Sugawara, K.; Morimoto, K.; Sugawara, T.; Dranoff, J.S. Dynamic behavior of iron forms in rapid reduction of carbon-coated iron ore. AIChE J. 1999, 45, 574–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhakrishnan, V.R.; Ram, K.M. Mathematical model for predictive control of the bell-less top charging system of a blast furnace. J. Process Control 2001, 11, 565–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogami, H.; Chu, M.; Yagi, J.I. Multi-dimensional transient mathematical simulator of blast furnace process based on multi-fluid and kinetic theories. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2005, 29, 2438–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishioka, K.; Maeda, T.; Shimizu, M. A three-dimensional mathematical modelling of drainage behavior in blast furnace hearth. ISIJ Int. 2005, 45, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, S.; Natsui, S.; Nogami, H.; Jun-Ichiro, Y.; Ariyama, T. Recent progress and future perspective on mathematical modeling of blast furnace. ISIJ Int. 2010, 50, 914–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhakrishnan, V.R.; Mohamed, A.R. Neural networks for the identification and control of blast furnace hot metal quality. J. Process Control 2000, 10, 509–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, J.; Mochon, J.; Sainz, D.A.J.; Obeso, F. Blast furnace hot metal temperature prediction through neural networks-based models. ISIJ Int. 2007, 44, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersson, F.; Chakraborti, N.; Saxén, H. A genetic algorithms based multi-objective neural net applied to noisy blast furnace data. Appl. Soft Comput. 2007, 7, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurkkala, A.; Pettersson, F.; Saxén, H. Nonlinear modeling method applied to prediction of hot metal silicon in the ironmaking blast furnace. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 9236–9248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Shen, F.; Du, G.; Shen, Y.; Xie, Z. A blast furnace prediction model combining neural network with partial least square regression. Steel Res. Int. 2005, 76, 694–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, T. Prediction of silicon content in blast furnace hot metal using partial least squares (PLS). ISIJ Int. 2005, 45, 1943–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, R.D.; Obeso, F.; Mochon, J.; Barea, R.; Jimenez, J. Hot metal temperature prediction in blast furnace using advanced model based on fuzzy logic tools. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2007, 34, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waller, M.; Saxen, H. On the development of predictive models with applications to a metallurgical process. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2000, 39, 982–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, J. Assessing the predictability for blast furnace system through nonlinear time series analysis. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2008, 47, 3037–3045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waller, M.; Saxen, H. Application of nonlinear time series analysis to the prediction of silicon content of pig iron. ISIJ Int. 2002, 42, 316–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyano, T.; Kimoto, S.; Shibuta, H.; Nakashima, K.; Ikenaga, Y.; Aihara, K. Time series analysis and prediction on complex dynamical behavior observed in a blast furnace. Physica D 2000, 135, 305–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, L.; Gao, C.; Xia, Z. A sliding-window smooth support vector regression model for nonlinear blast furnace system. Steel Res. Int. 2011, 82, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Jian, L.; Luo, S. Modeling of the thermal state change of blast furnace hearth with support vector machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2012, 59, 1134–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Chen, J.; Zeng, J.; Liu, X.; Sun, Y. A chaos-based iterated multistep predictor for blast furnace ironmaking process. AIChE J. 2009, 55, 947–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.; Gao, C. Data-based multiscale modeling for blast furnace system. AIChE J. 2014, 60, 2197–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurkkala, A.; Pettersson, F.; Saxén, H. A study of blast furnace dynamics using multiple autoregressive vector models. ISIJ Int. 2012, 52, 1763–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxén, H.; Gao, C.; Gao, Z. Data-driven time discrete models for dynamic prediction of the hot metal silicon content in the blast furnace—A review. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 9, 2213–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Liu, Y. Adaptive weighting just-in-time-learning quality prediction model for an industrial blast furnace. ISIJ Int. 2017, 57, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Liang, Y.; Gao, Z.; Liu, Y. Just-in-time correntropy soft sensor with noisy data for industrial silicon content prediction. Sensors 2017, 17, 1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kano, M.; Nakagawa, Y. Data-based process monitoring, process control, and quality improvement: Recent developments and applications in steel industry. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2008, 32, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abonyi, J.; Farsang, B.; Kulcsar, T. Data-driven development and maintenance of soft-sensors. In Proceedings of the IEEE 12th International Symposium on Applied Machine Intelligence and Informatics (SAMI), Herlany, Slovakia, 23–25 January 2014; pp. 239–244. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, C.; Liu, K.; Chen, B.; Yao, Y. Domain adaptation transfer learning soft sensor for product quality prediction. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2019, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Z.; Song, Z.; Ding, S.; Huang, B. Data mining and analytics in the process industry: The role of machine learning. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 20590–20616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Fan, Y.; Chen, J. Flame images for oxygen content prediction of combustion systems using DBN. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 8776–8783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, Q.; Fang, B.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Bao, G. Automatic pearl classification machine based on a multistream convolutional neural network. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 6538–6547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, Q.; Chen, Z.; Liu, Y.; Huang, H.; Bao, G.; Zhang, D. Multiview generative adversarial network and its application in pearl classification. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 8244–8252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Liu, Y.; Gao, Z.; Yang, J. Just-in-time semi-supervised soft sensor for quality prediction in industrial rubber mixers. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2018, 180, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Z.; Huang, B.; Song, Z. Mixture semisupervised principal component regression model and soft sensor application. AIChE J. 2014, 60, 533–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Gao, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Yang, J.; Gao, Z. Industrial Mooney viscosity prediction using fast semi-supervised empirical model. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2017, 171, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, C.; Gao, Z.; Yao, Y. Ensemble deep kernel learning with application to quality prediction in industrial polymerization processes. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2018, 174, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, H.; Arakawa, M.; Funatsu, K. Applicability domains and accuracy of prediction of soft sensor models. AIChE J. 2011, 57, 1506–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, J. Integrated soft sensor using just-in-time support vector regression and probabilistic analysis for quality prediction of multi-grade processes. J. Process Control 2013, 23, 793–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G. An insight into extreme learning machines: Random neurons, random features and kernels. Cogn. Comput. 2014, 6, 376–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, M.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, Z. SELM: Semi-supervised ELM with application in sparse calibrated location estimation. Neurocomputing 2011, 74, 2566–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Ren, J.H. Bagging for Gaussian process regression. Neurocomputing 2009, 72, 1605–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Soft Sensor Models | Brief Description | RMSE | RE (%) | HR (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BLSM | Bagging local semi-supervised learning method with ensemble learning strategy | 0.070 | 13.11 | 80.3 |
| Local SELM | Local semi-supervised learning method without ensemble learning strategy | 0.077 | 14.28 | 77.2 |
| JLSSVR [23] | Local supervised learning method | 0.091 | 17.43 | 70.9 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, X.; Ji, J.; Liu, K.; Gao, Z.; Liu, Y. Soft Sensing of Silicon Content via Bagging Local Semi-Supervised Models. Sensors 2019, 19, 3814. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19173814
He X, Ji J, Liu K, Gao Z, Liu Y. Soft Sensing of Silicon Content via Bagging Local Semi-Supervised Models. Sensors. 2019; 19(17):3814. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19173814
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Xing, Jun Ji, Kaixin Liu, Zengliang Gao, and Yi Liu. 2019. "Soft Sensing of Silicon Content via Bagging Local Semi-Supervised Models" Sensors 19, no. 17: 3814. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19173814
APA StyleHe, X., Ji, J., Liu, K., Gao, Z., & Liu, Y. (2019). Soft Sensing of Silicon Content via Bagging Local Semi-Supervised Models. Sensors, 19(17), 3814. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19173814





