Design and Experiments of a Piezoelectric Motor Using Three Rotating Mode Actuators
Abstract
:1. Introduction
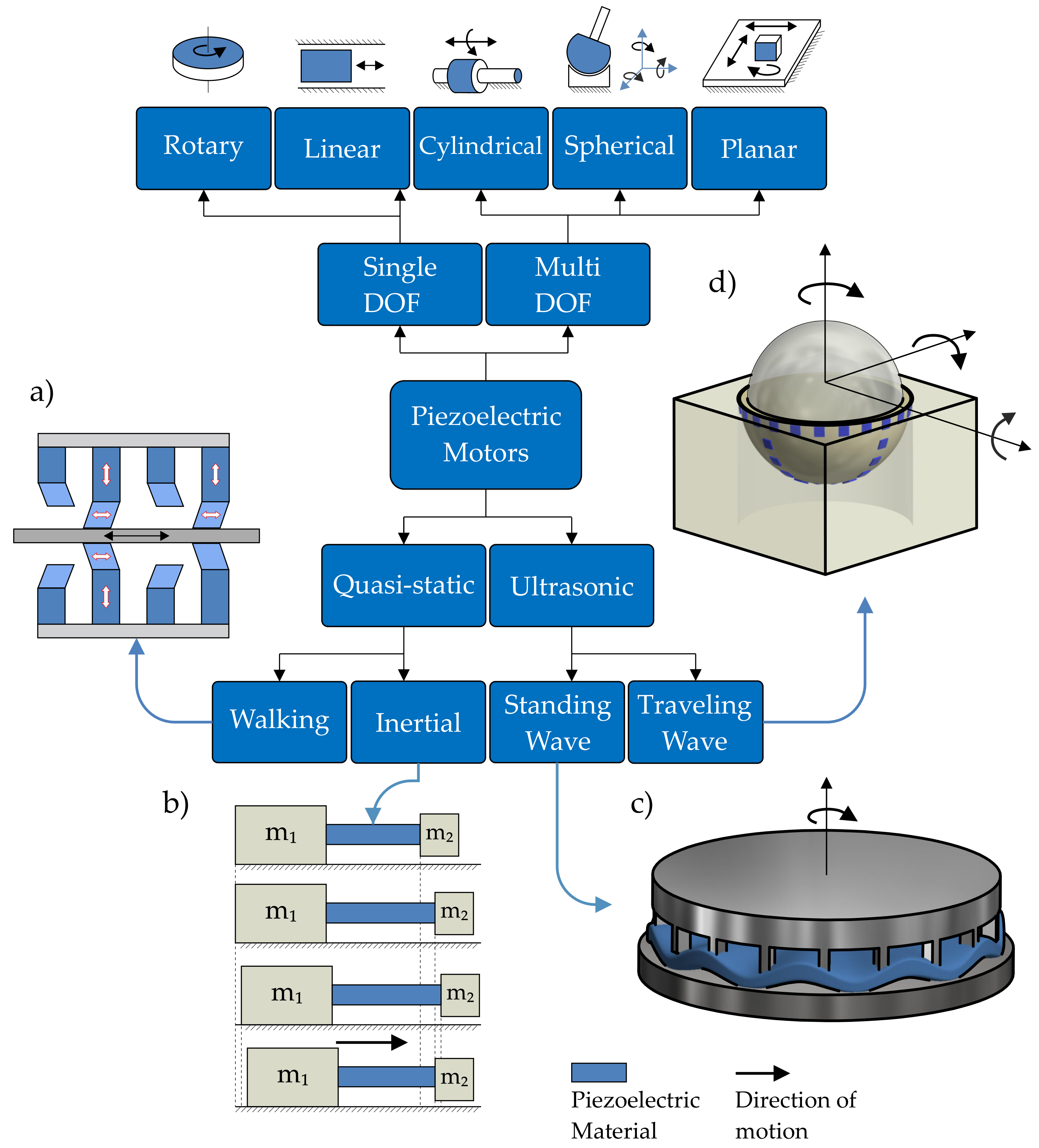
1.1. Classification of the Proposed Motor
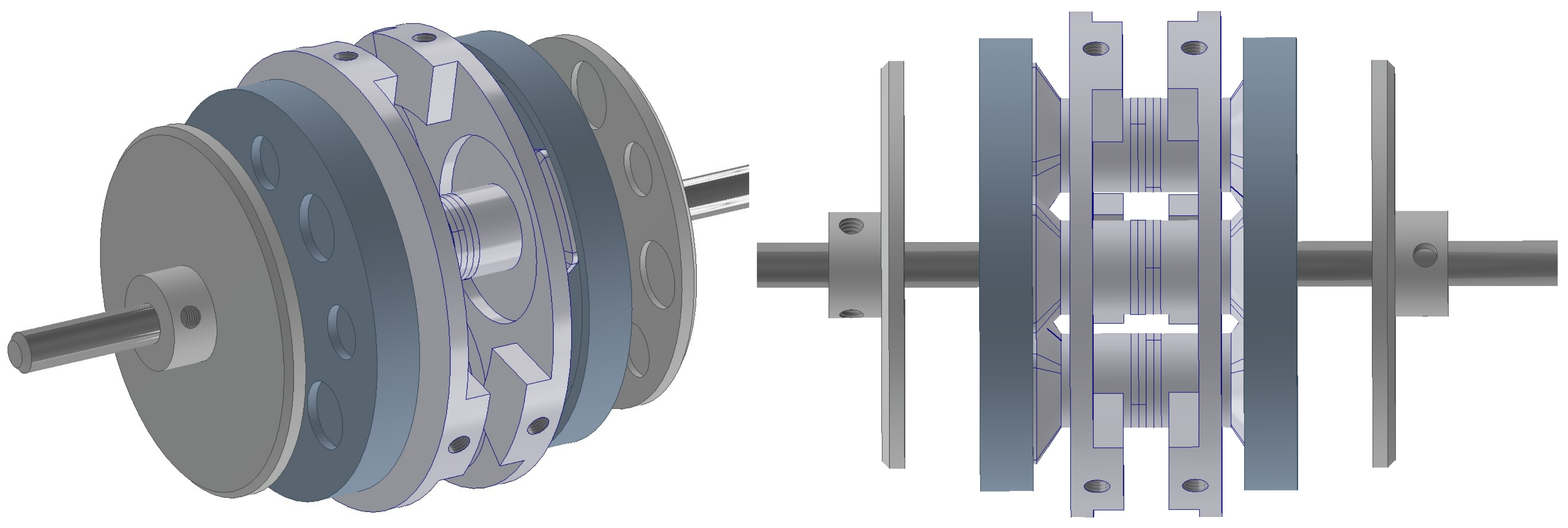
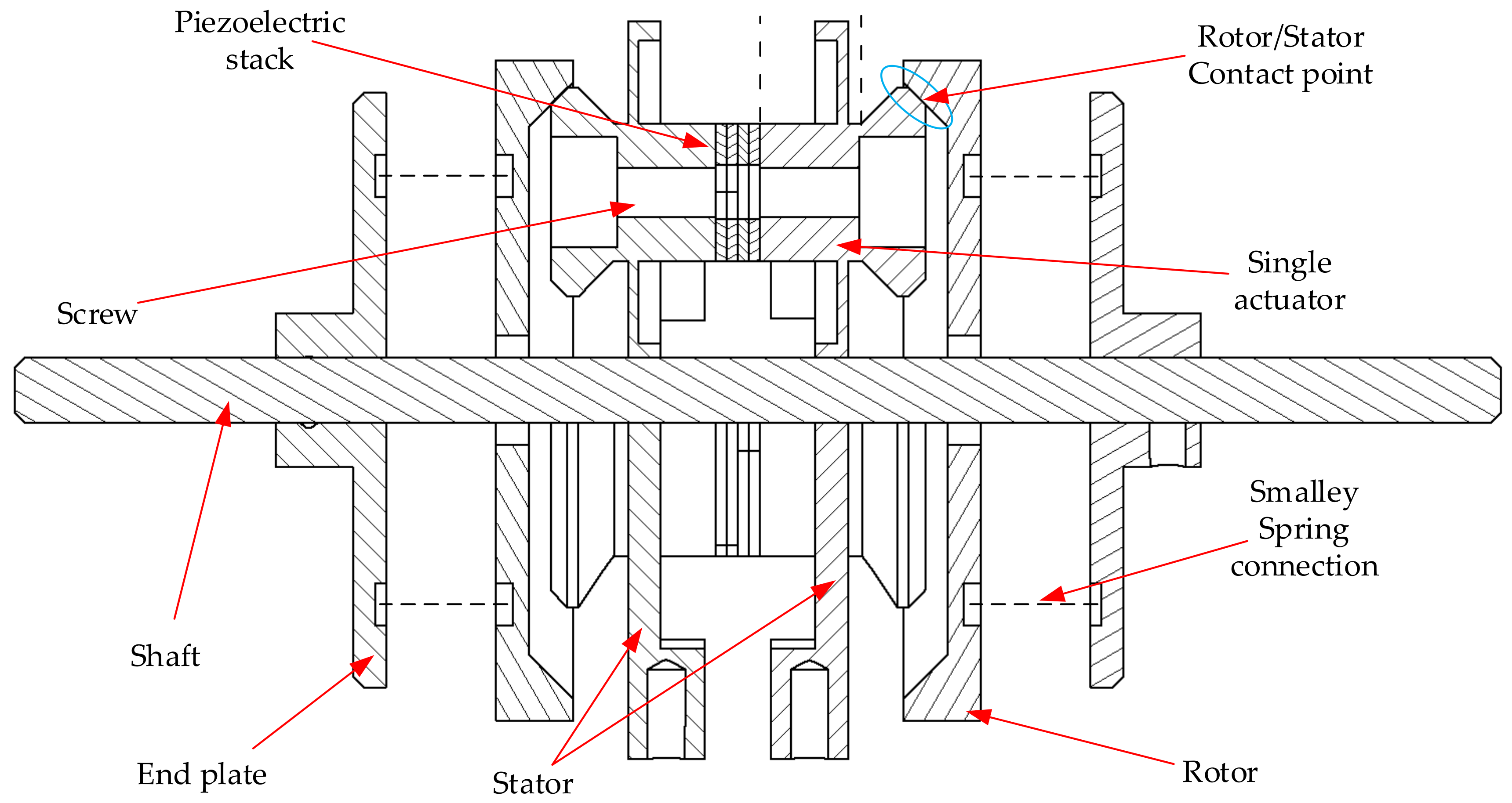
1.2. Description of the Proposed Motor
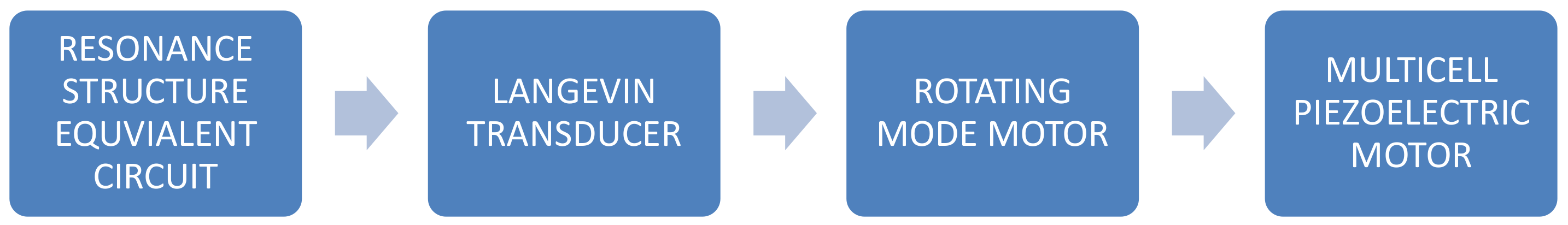
2. Analytical Models of Piezoelectric Transducers
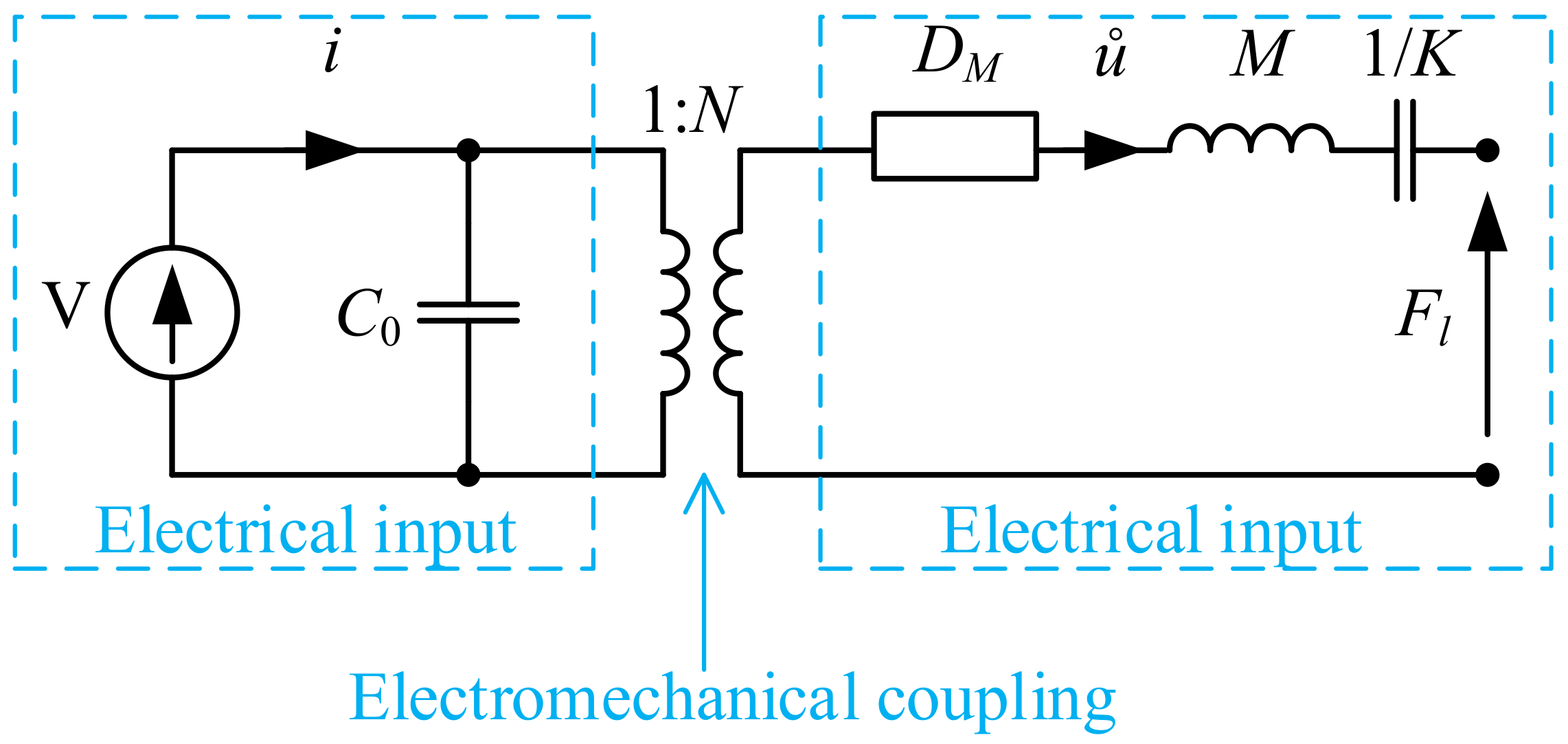
2.1. Simple Equivalent Circuit
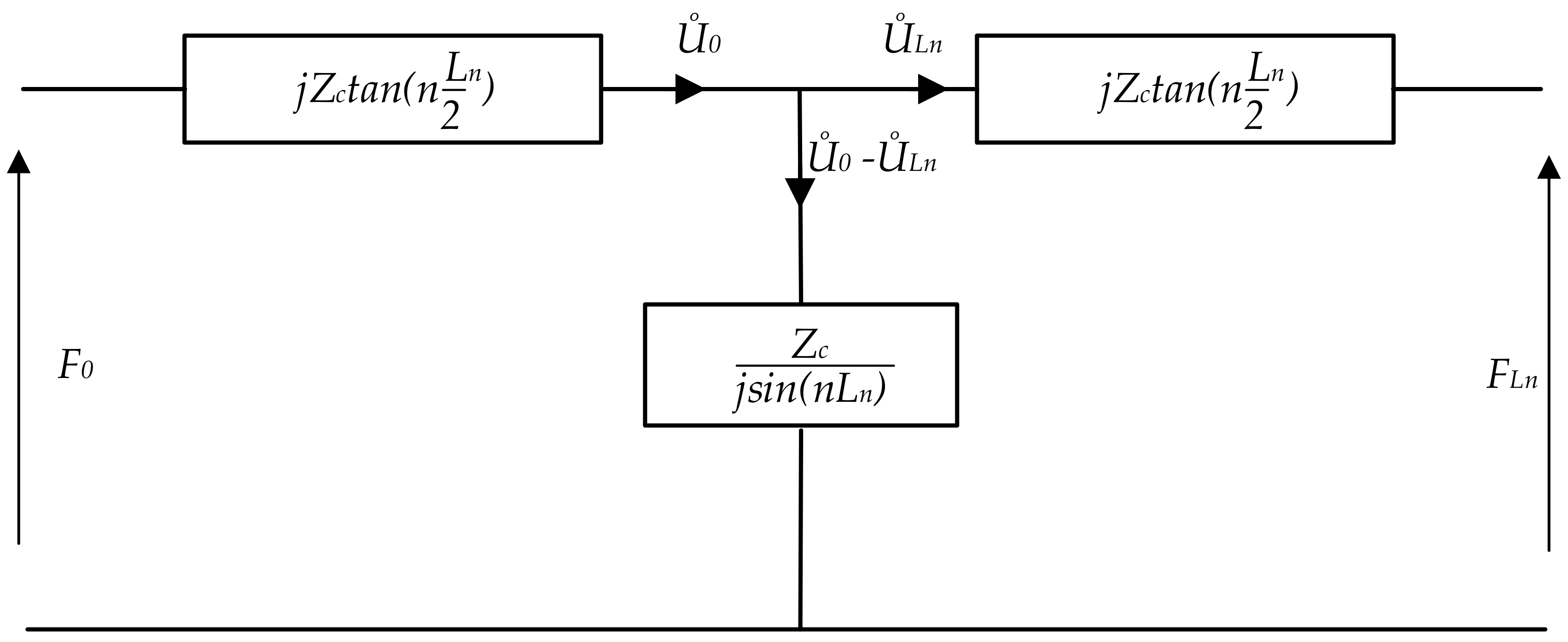
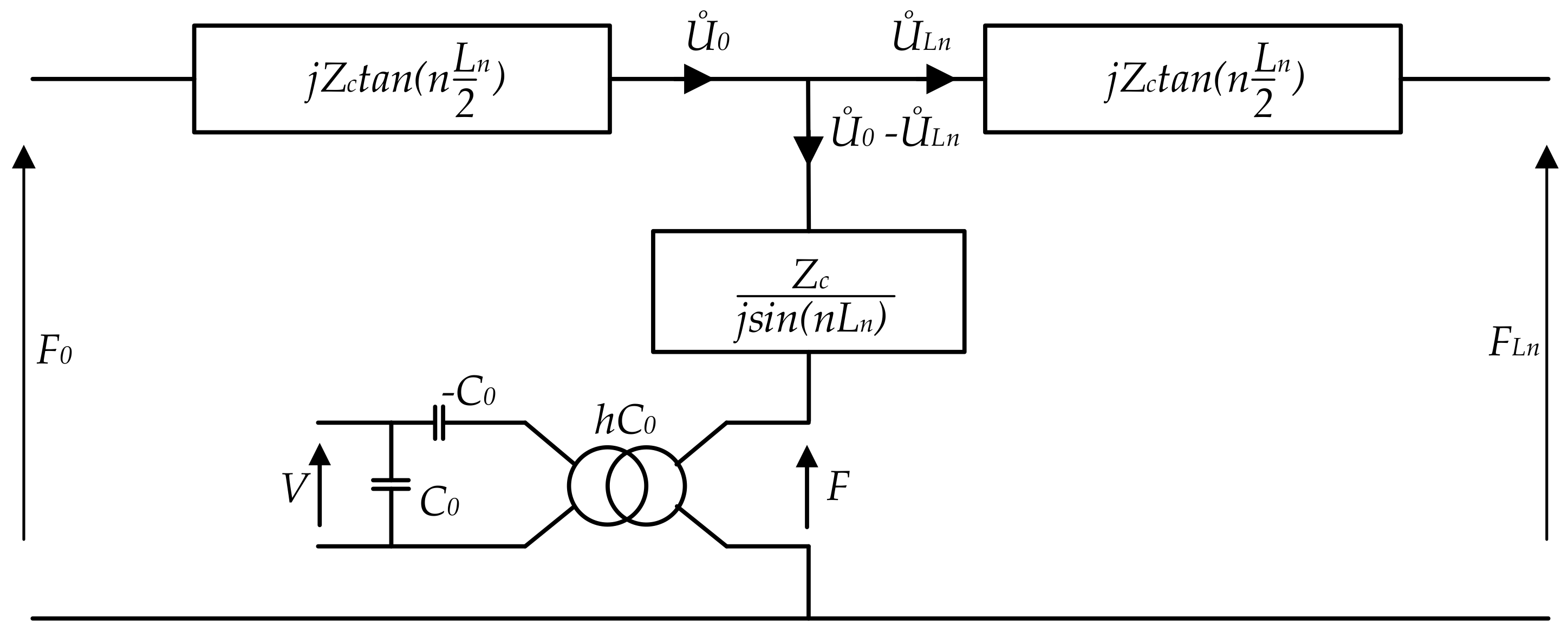
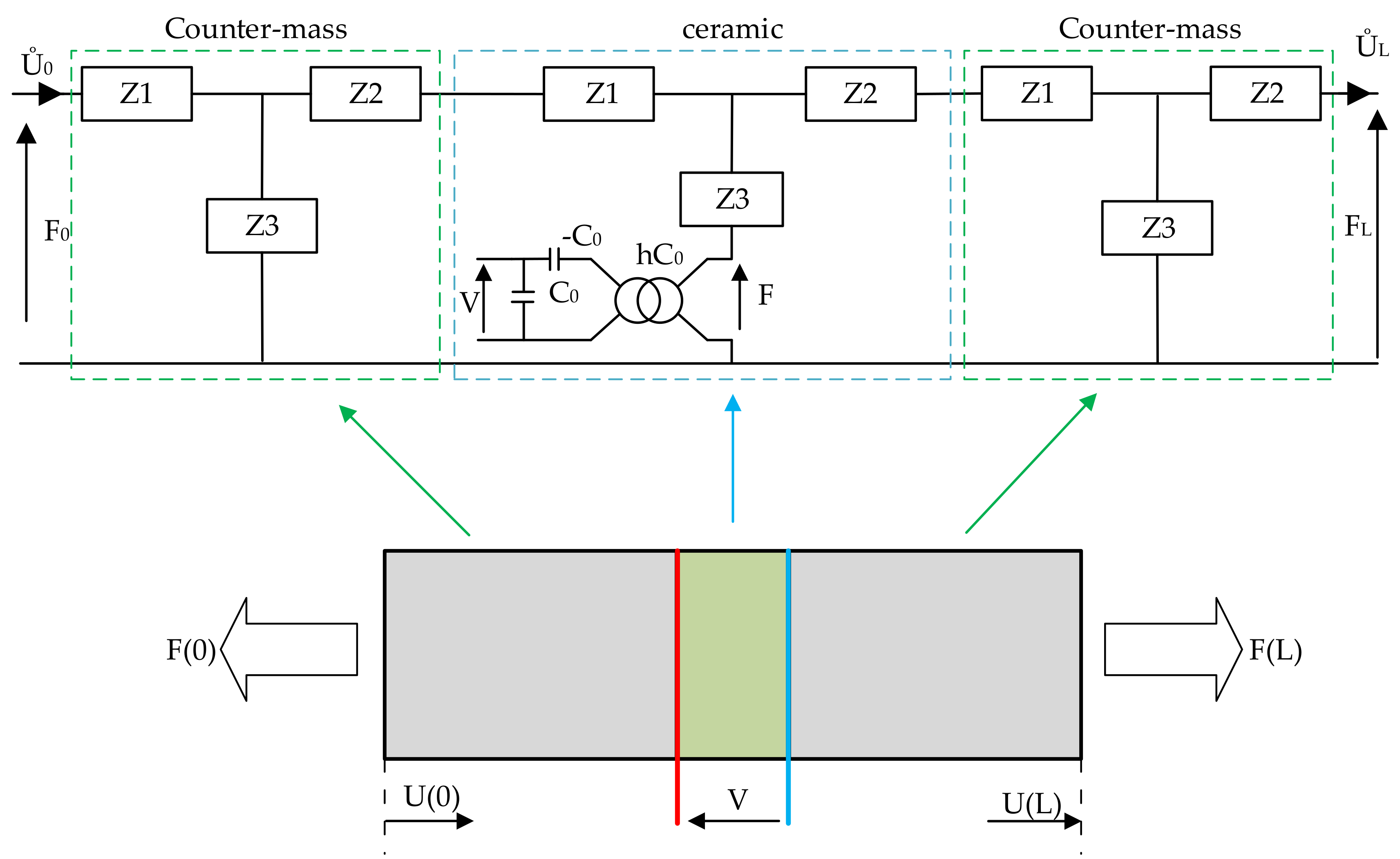
2.2. Wave Propagation in Resonance Structure
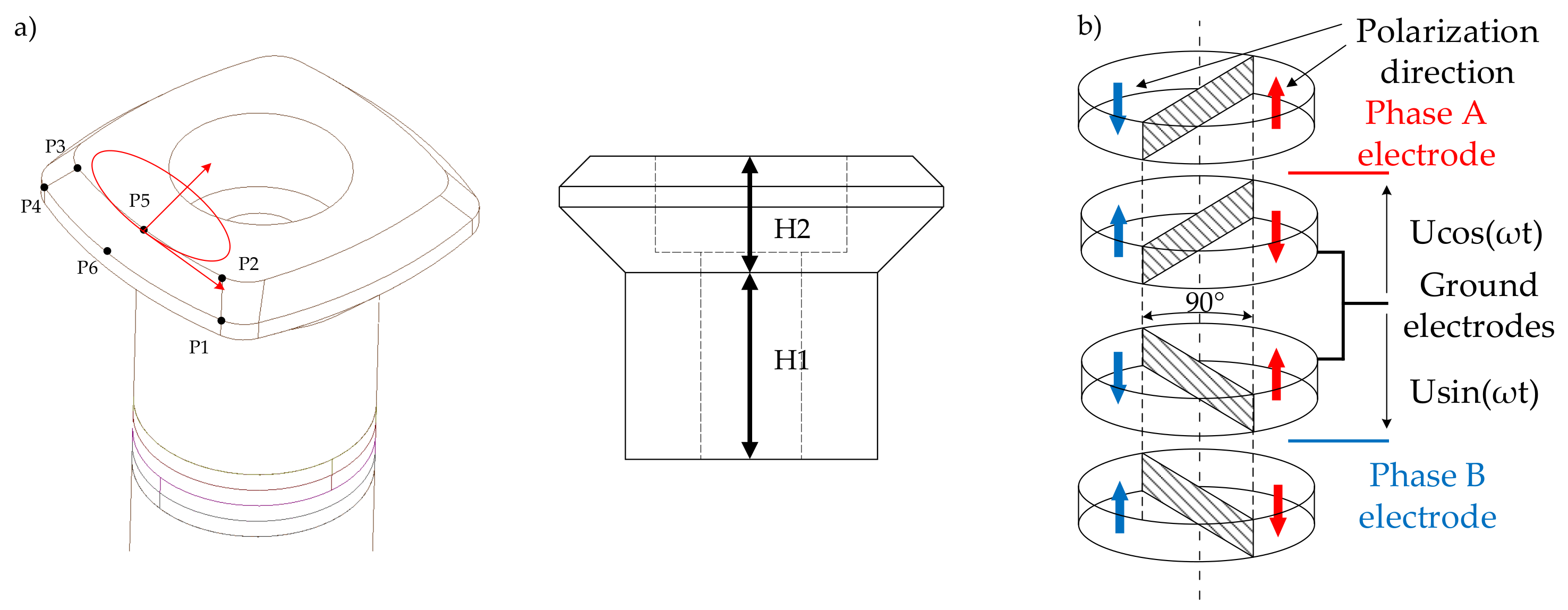
2.3. Rotating Mode Motor
3. Finite-Element Analysis
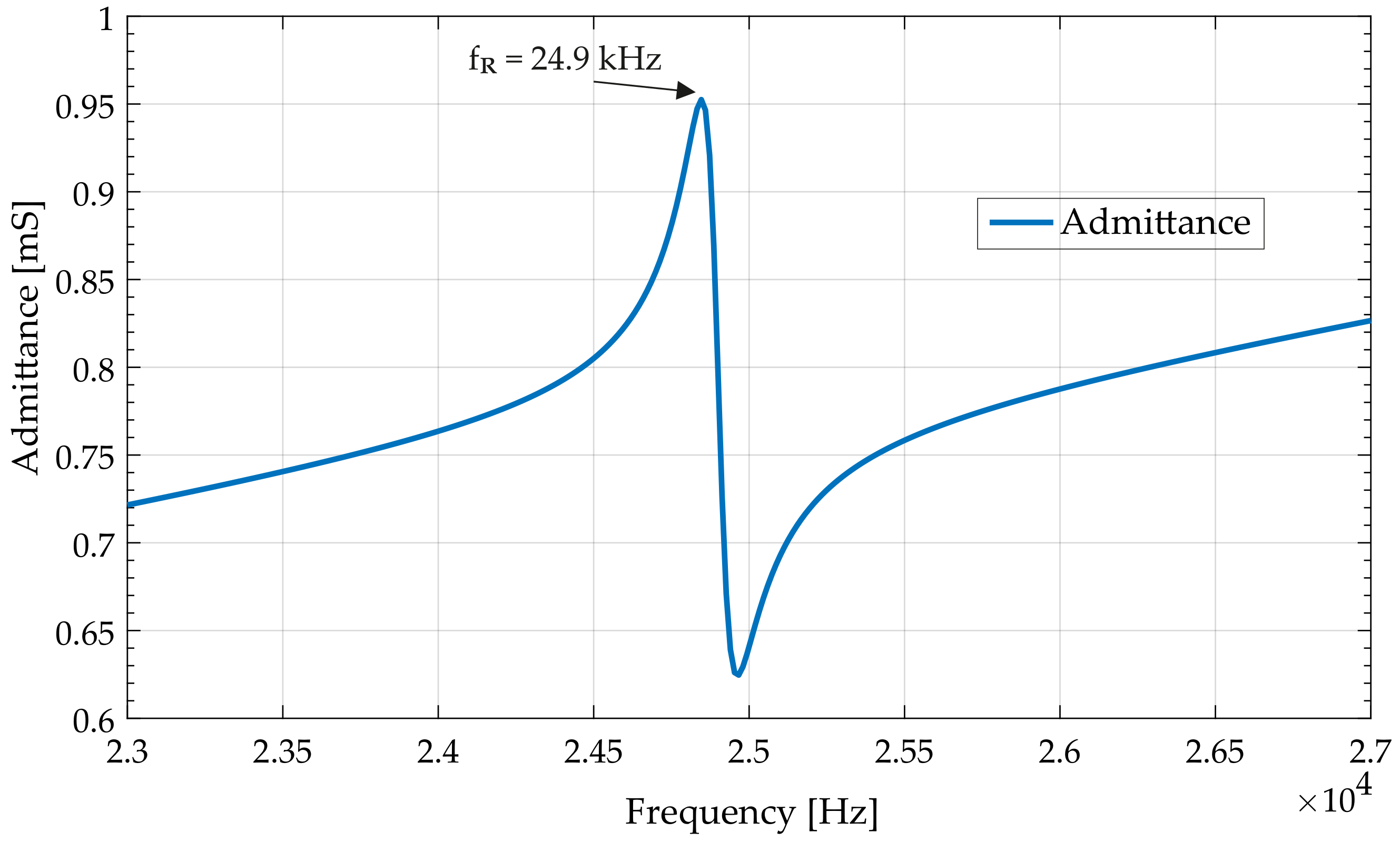
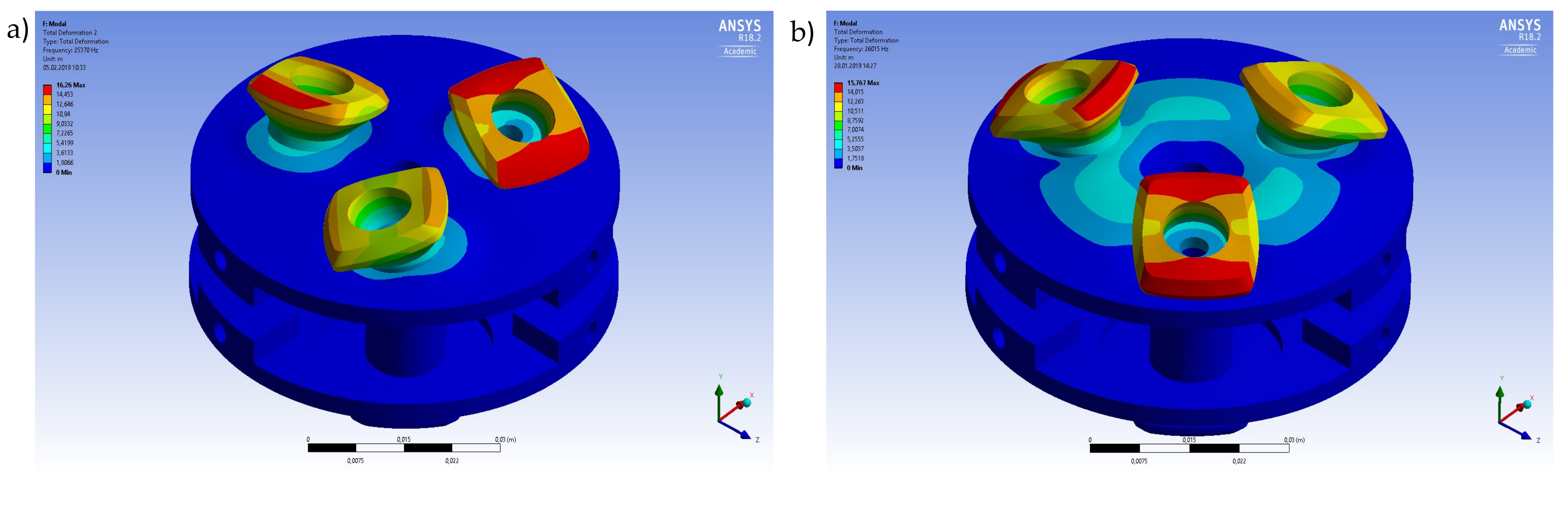
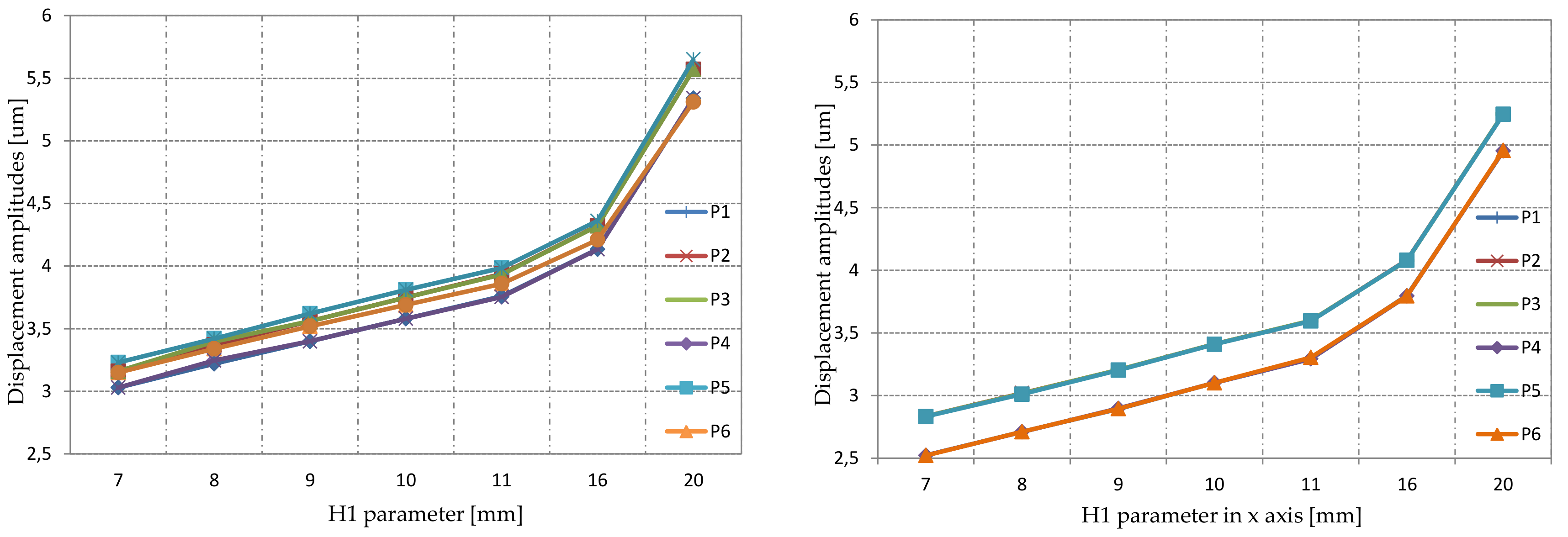
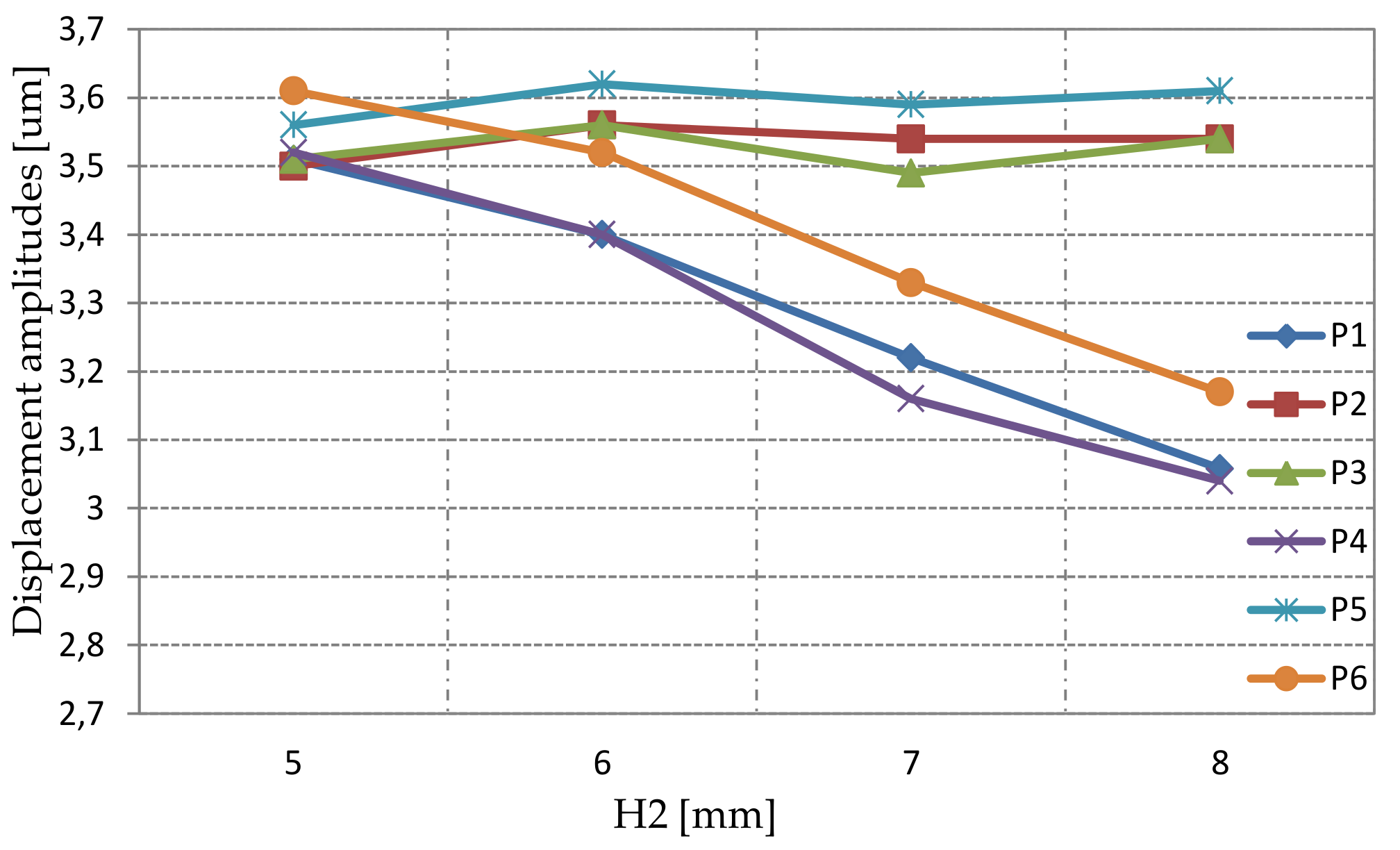
3.1. Modal Simulation
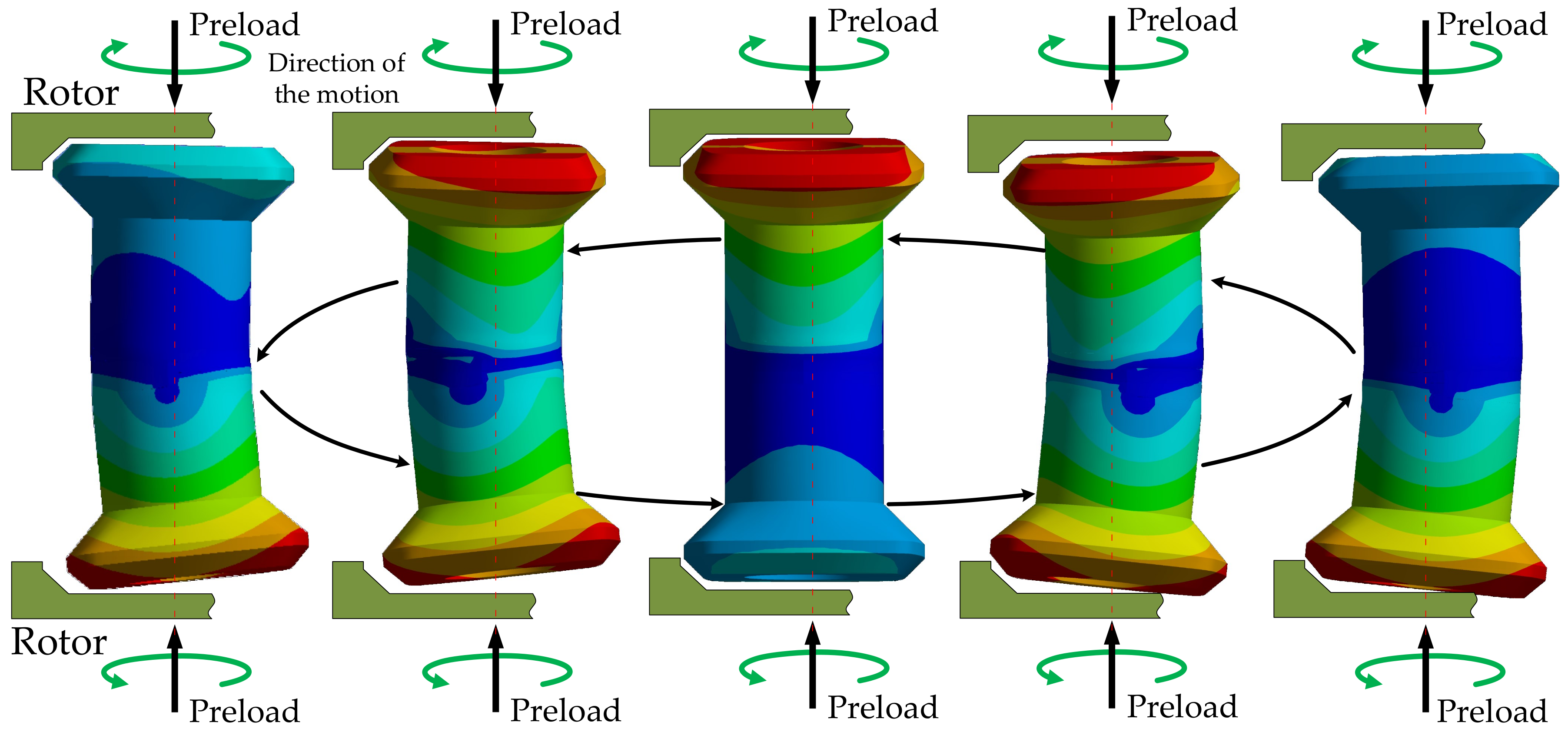
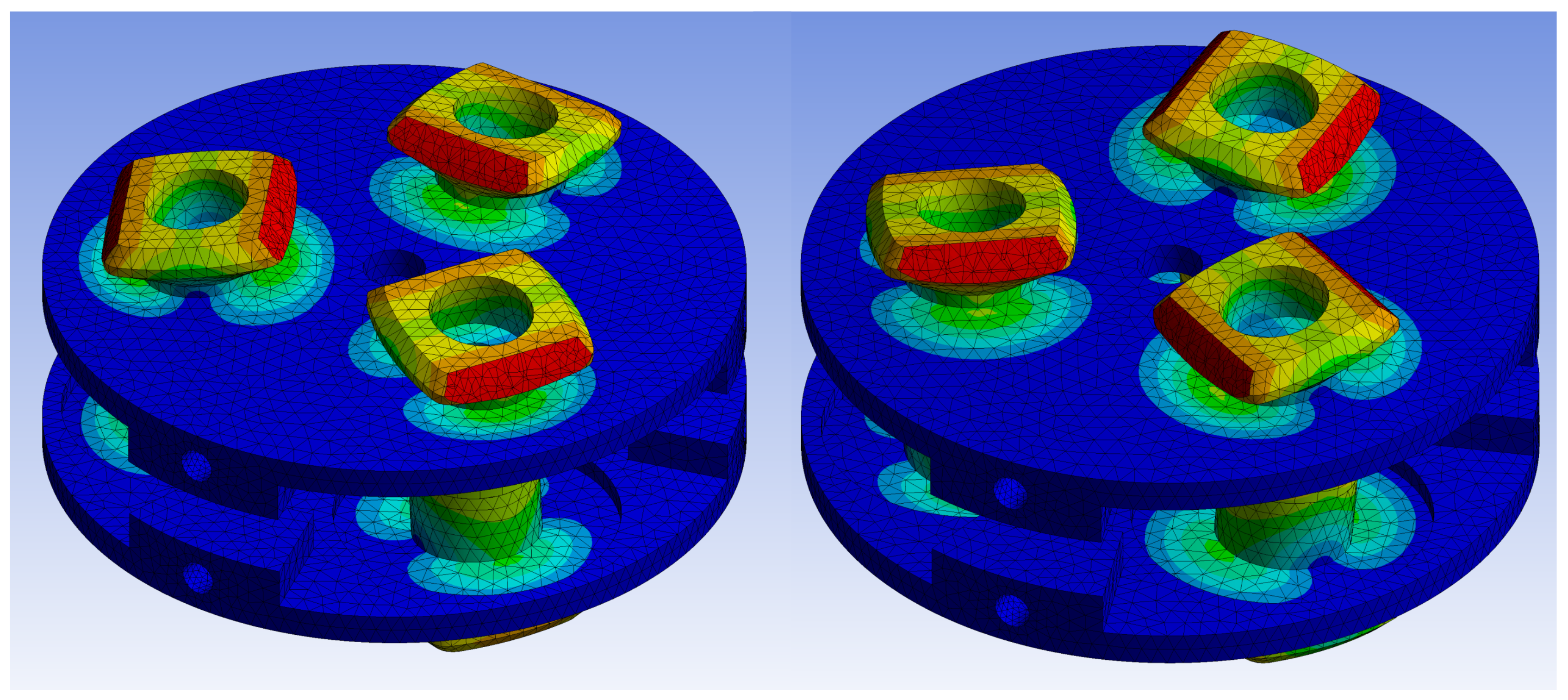
3.2. Static Simulation
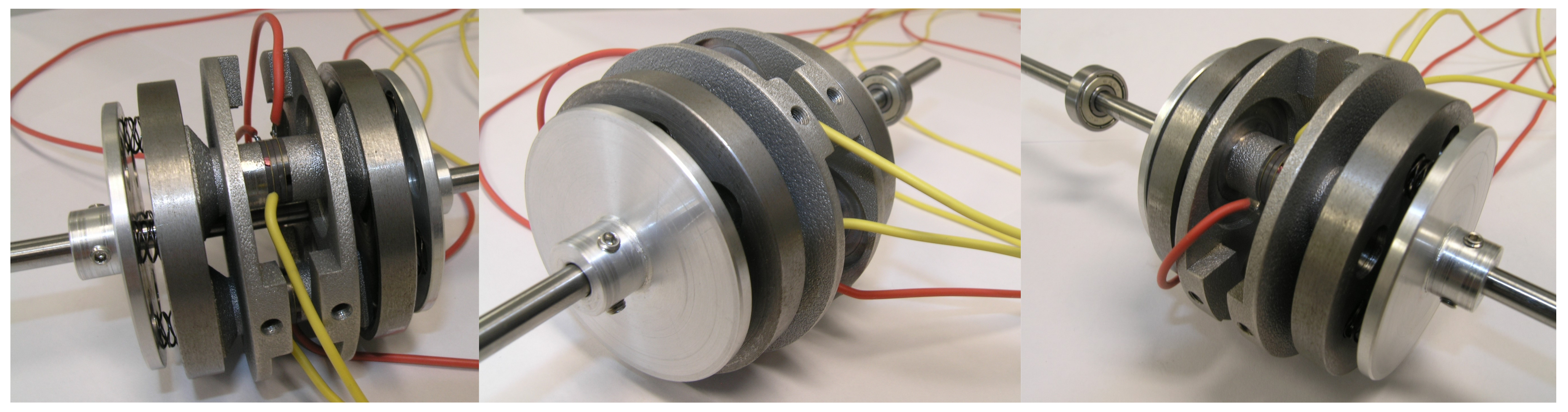
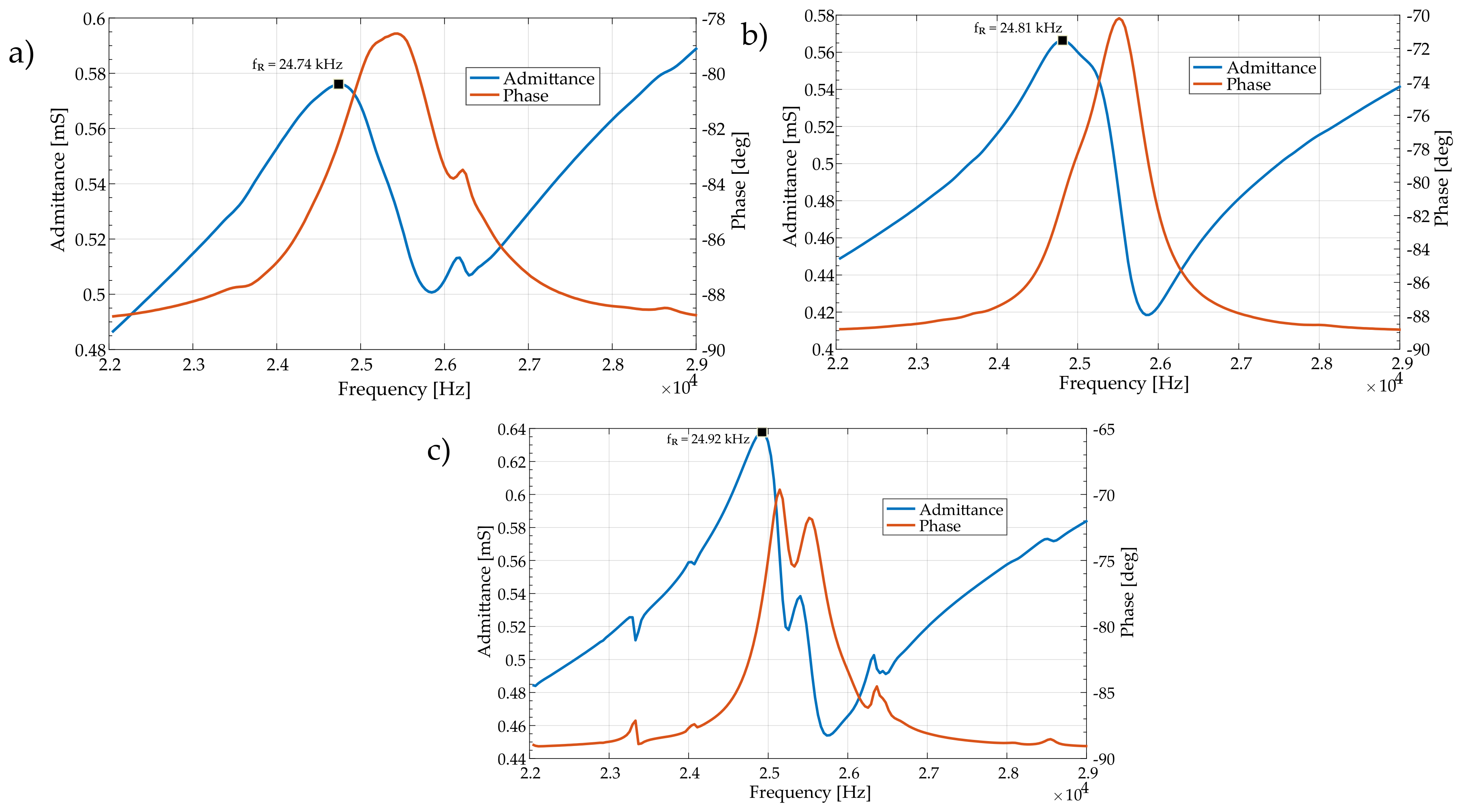
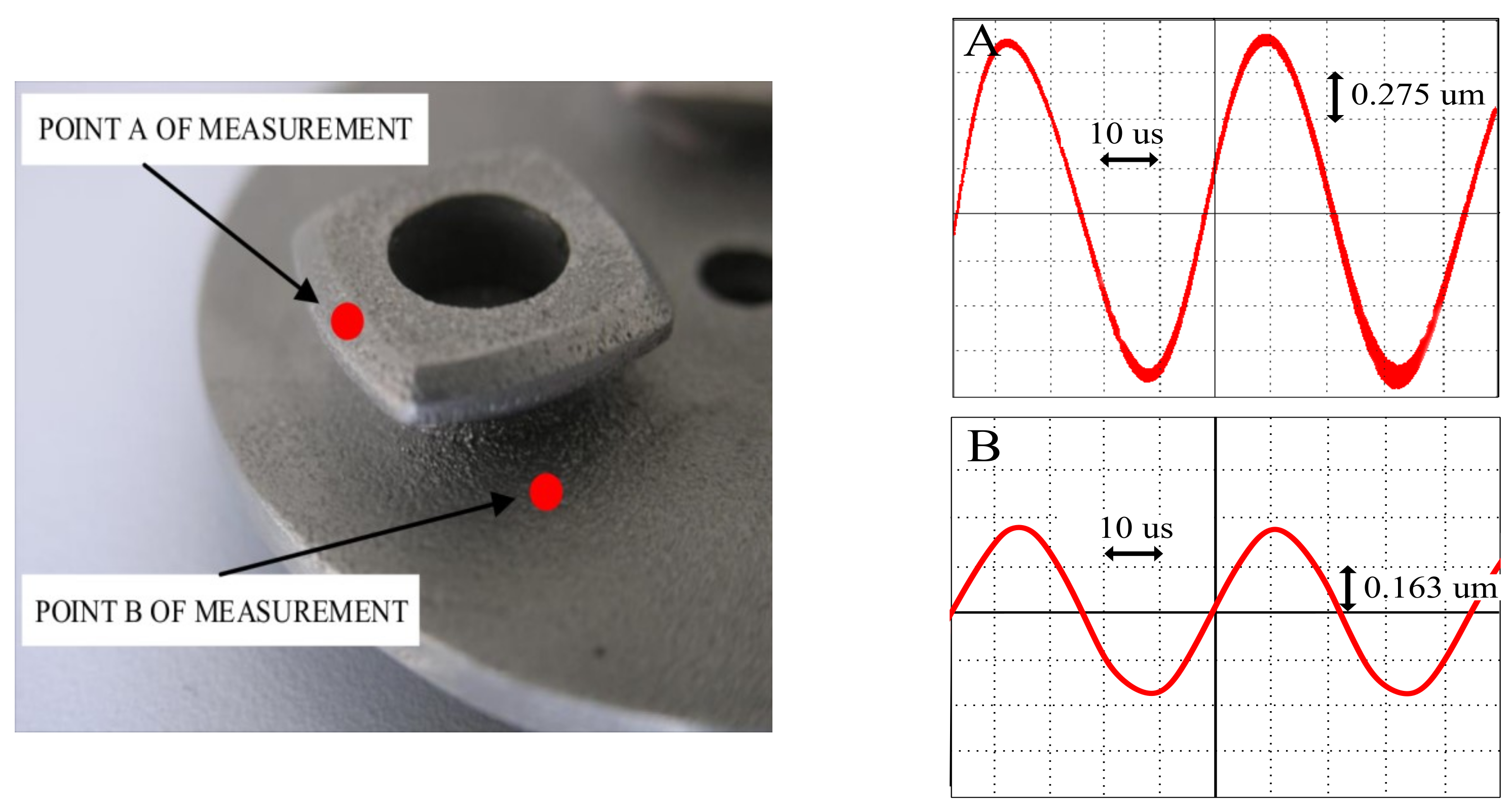
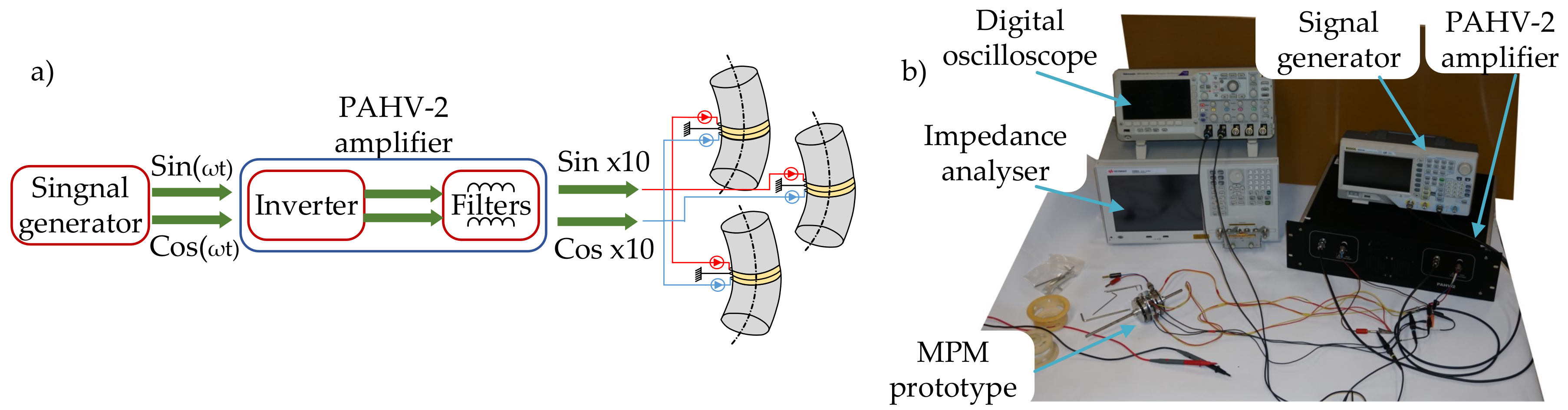
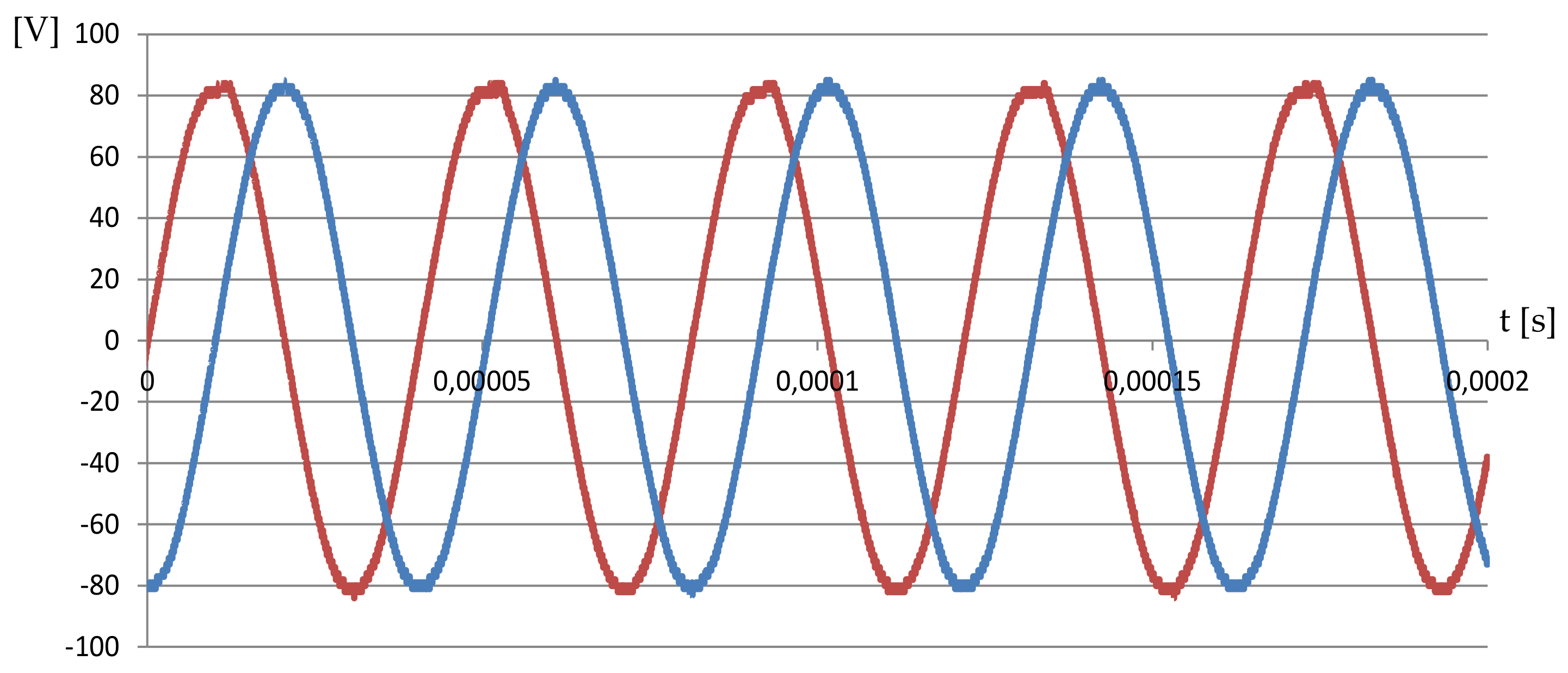
4. Experimental Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Williams, A.L.W.; Brown, W.J. Piezoelectric Motor. U.S. Patent 2,439,499, 13 April 1948. [Google Scholar]
- Sashida, T.; Kenjo, T. An Introduction to Ultrasonic Motors; Monographs in Electrical and Electronic Engineering; Oxford University Press: Oxford, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Uchino, K. Piezoelectric Actuator Renaissance. Energy Harvest. Syst. 2014, 1, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueha, S.; Tomikawa, Y.; Kurosawa, M.; Nakamura, N. Ultrasonic Motors: Theory and Applications; Oxford University Press: Oxford, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Spanner, K.; Koc, B. Piezoelectric Motors, an Overview. Actuators 2016, 5, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanner, K. Survey of the Various Operating Principles of Ultrasonic Piezomotors. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on New Actuators (ACTUATOR 2006), 14–16 June 2006; Bremen, Germany. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, C. Ultrasonic Motors: Technologies and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Katzir, S. The Beginnings of Piezoelectricity: A Study in Mundane Physics; Boston Studies in the Philosophy and History of Science; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Lang, S.B. Sourcebook of Pyroelectricity; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Heywang, W.; Lubitz, K.; Wersing, W. Piezoelectricity: Evolution and Future of a Technology; Springer Series in Materials Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa, T. Piezoelectricity and Pyroelectricity in Polymers. IEEE Trans. Electr. Insul. 1989, 24, 375–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curie, J.; Curie, P. Contractions et Dilatations Produites Par Des Tensions Dans Les Cristaux Hémièdres à Faces Inclinées; Comptes Rendus de l’Académie des Sciences: Paris, France, 1881. [Google Scholar]
- Bishop, R.H. The Mechatronics Handbook—2 Volume Set; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Duck, F. The Electrical Expansion of Quartz’ by Jacques and Pierre Curie. Ultrasound 2009, 17, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballato, A. Piezoelectricity: Old Effect, New Thrusts. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 1995, 42, 916–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tichý, J.; Erhart, J.; Kittinger, E.; Přívratská, J. Fundamentals of Piezoelectric Sensorics: Mechanical, Dielectric, and Thermodynamical Properties of Piezoelectric Materials; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 1–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballas, R.G. Piezoelectric Multilayer Beam Bending Actuators: Static and Dynamic Behavior and Aspects of Sensor Integration; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; p. 358. [Google Scholar]
- Sadl, M.; Bradesko, A.; Belavic, D.; Bencan, A.; Malic, B.; Rojac, T. Construction and functionality of a ceramic resonant pressure sensor for operation at elevated temperatures. Sensors 2018, 18, 1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunstig, M. Piezoelectric Inertia Motors A Critical Review of History, Concepts, Design, Applications, and Perspectives. Actuators 2017, 6, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogarede, B.; Henaux, C.; Rouchon, J.F.; Duhayon, E. Electroactive materials: From piezomotors to electroactive morphing. In Proceedings of the IECON Proceedings (Industrial Electronics Conference), Paris, France, 6–10 November 2006; pp. 4437–4441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Deng, J.; Su, Q. Review on Multi-Degree-of-Freedom Piezoelectric Motion Stage. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 59986–60004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Quan, Q.; Tian, X.; Li, H. Optimization and analysis of a u-shaped linear piezoelectric ultrasonic motor using longitudinal transducers. Sensors 2018, 18, 809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Kan, C.; Cheng, Y.; Chen, Z.; Ren, T. Performance evaluation of a bimodal standing-wave ultrasonic motor considering nonlinear electroelasticity: Modeling and experimental validation. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2019, 106475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morawiec, M.; Strankowski, P.; Lewicki, A.; Guzinski, J.; Wilczynski, F. Feedback Control of Multiphase Induction Machines with Backstepping Technique. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henaux, C.; Nogarede, B.; Harribey, D. A new concept of modular permanent magnet and soft magnetic compound motor dedicated to widespread application. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2012, 48, 2035–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morawiec, M. Z-Type Observer Backstepping for Induction Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 2090–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strankowski, P.; Guzinski, J.; Morawiec, M.; Lewicki, A.; Wilczynski, F. Sensorless disturbance detection for five phase induction motor with third harmonic injection. In Proceedings of the 2017 11th IEEE International Conference on Compatibility, Power Electronics and Power Engineering, CPE-POWERENG 2017, Cadiz, Spain, 4–6 April 2017; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: Cadiz, Spain, 2017; pp. 387–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merry, R.J.; de Kleijn, N.C.; van de Molengraft, M.J.; Steinbuch, M. Using a walking piezo actuator to drive and control a high-precision stage. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2009, 14, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, Y.; Tsai, Y.R.; Hou, B.K.; Lin, S.C.; Lu, C.C. Stator design of a new type of spherical piezoelectric motor. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2010, 57, 2334–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryndzionek, R.; Michna, M.; Ronkowski, M.; Rouchon, J.F. Chosen Analysis Results of the Prototype Multicell Piezoelectric Motor. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2018, 23, 2178–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, J.; Krummen, M.; Perriard, Y. Analytical and numerical modeling of an ultrasonic stepping motor using standing waves. In Proceedings of the IEEE Ultrasonics Symposium, Montreal, QC, Canada, 23–27 August 2004; Volume 2, pp. 1173–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budinger, M.; Rouchon, J.; Nogarede, B. Analytical Modeling for the Design of a Piezoelectric Rotating-Mode Motor. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2004, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Lin, S. Analysis of a cascaded piezoelectric ultrasonic transducer with three sets of piezoelectric ceramic stacks. Sensors 2019, 19, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, D.; Quan, Q.; Tang, D.; Deng, Z. Design and Experiments of a Novel Rotary Piezoelectric Actuator Using Longitudinal-Torsional Convertors. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 22186–22195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SHINSEI Corporation Products. Available online: http://www.shinsei-motor.com/English/product/ (accessed on 26 November 2019).




| Quantity | Meaning | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| PZT | piezoelectric ceramic | - |
| M | counter-mass, mechanical equivalent of Inductance (L) | kg |
| K | screw spring constant, mechanical equivalent of the inverse of Capacitance (1/C) | N/m |
| damping factor, mechanical equivalent of Resistance (R) | Ns/m | |
| Voltage, electrical equivalent of Force | V | |
| current, electrical equivalent of Velocity | A | |
| load force | N | |
| force generated by PZT | N | |
| , | position and speed of mass | m, m/s |
| N | electromechanical coupling ratio equal to | N/V |
| area of the flat surface of the PZT | m | |
| density of medium | kg/m | |
| c | compliance, mechanical equivalent of Capacitance (C) | m/N |
| angular frequency | rad/s | |
| , | coefficients depending on the boundary conditions | - |
| , | vibration speed at the extremities of the analyzed element | rad/s |
| , | force at the extremities of the analyzed element | N |
| characteristic impedance of the medium | kg/s | |
| T | stress | N/m |
| E | electric field | V/m |
| D | electric displacement | C/m |
| , | strain under constant D and E, respectively | - |
| , | stiffness under constant D and E, respectively | N/m |
| relative permittivity | - | |
| , g | piezoelectric coefficients | C/N, m/C |
| h, e | N/C, C/m |
| Parameter | Symbol | Model Value |
|---|---|---|
| Relative dielectric constant | 1020 | |
| 0.30 | ||
| Electromech. coupling factors | 0.69 | |
| 0.47 | ||
| Piezoelectric charge constant | −108 | |
| −269 | ||
| Quality factor | 1400 | |
| Density | 7730 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ryndzionek, R.; Sienkiewicz, Ł.; Michna, M.; Kutt, F. Design and Experiments of a Piezoelectric Motor Using Three Rotating Mode Actuators. Sensors 2019, 19, 5184. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19235184
Ryndzionek R, Sienkiewicz Ł, Michna M, Kutt F. Design and Experiments of a Piezoelectric Motor Using Three Rotating Mode Actuators. Sensors. 2019; 19(23):5184. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19235184
Chicago/Turabian StyleRyndzionek, Roland, Łukasz Sienkiewicz, Michał Michna, and Filip Kutt. 2019. "Design and Experiments of a Piezoelectric Motor Using Three Rotating Mode Actuators" Sensors 19, no. 23: 5184. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19235184
APA StyleRyndzionek, R., Sienkiewicz, Ł., Michna, M., & Kutt, F. (2019). Design and Experiments of a Piezoelectric Motor Using Three Rotating Mode Actuators. Sensors, 19(23), 5184. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19235184






