Multi-Pig Part Detection and Association with a Fully-Convolutional Network
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Background
3. Proposed Method
3.1. Representation of Body Part Location
3.2. Representation of Body Part Association
- Channels 1–4: Left Ear ↔ Shoulder
- Channels 5–8: Right Ear ↔ Shoulder
- Channels 9–12: Shoulder ↔ Tail
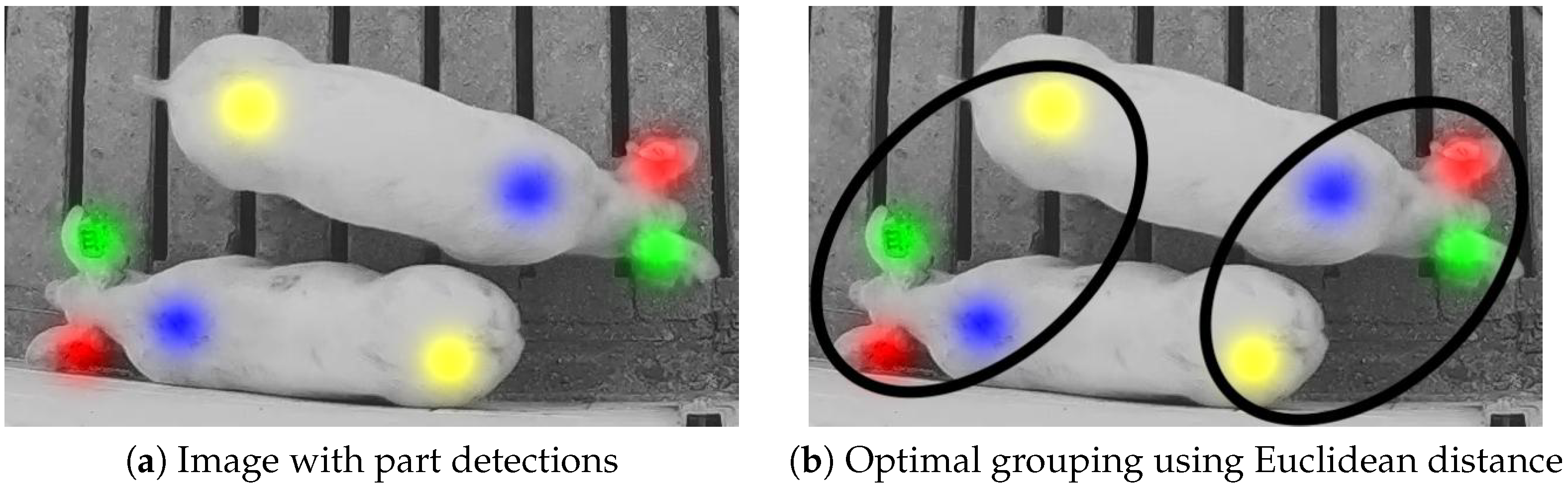
3.3. Instances from Part Detection and Association
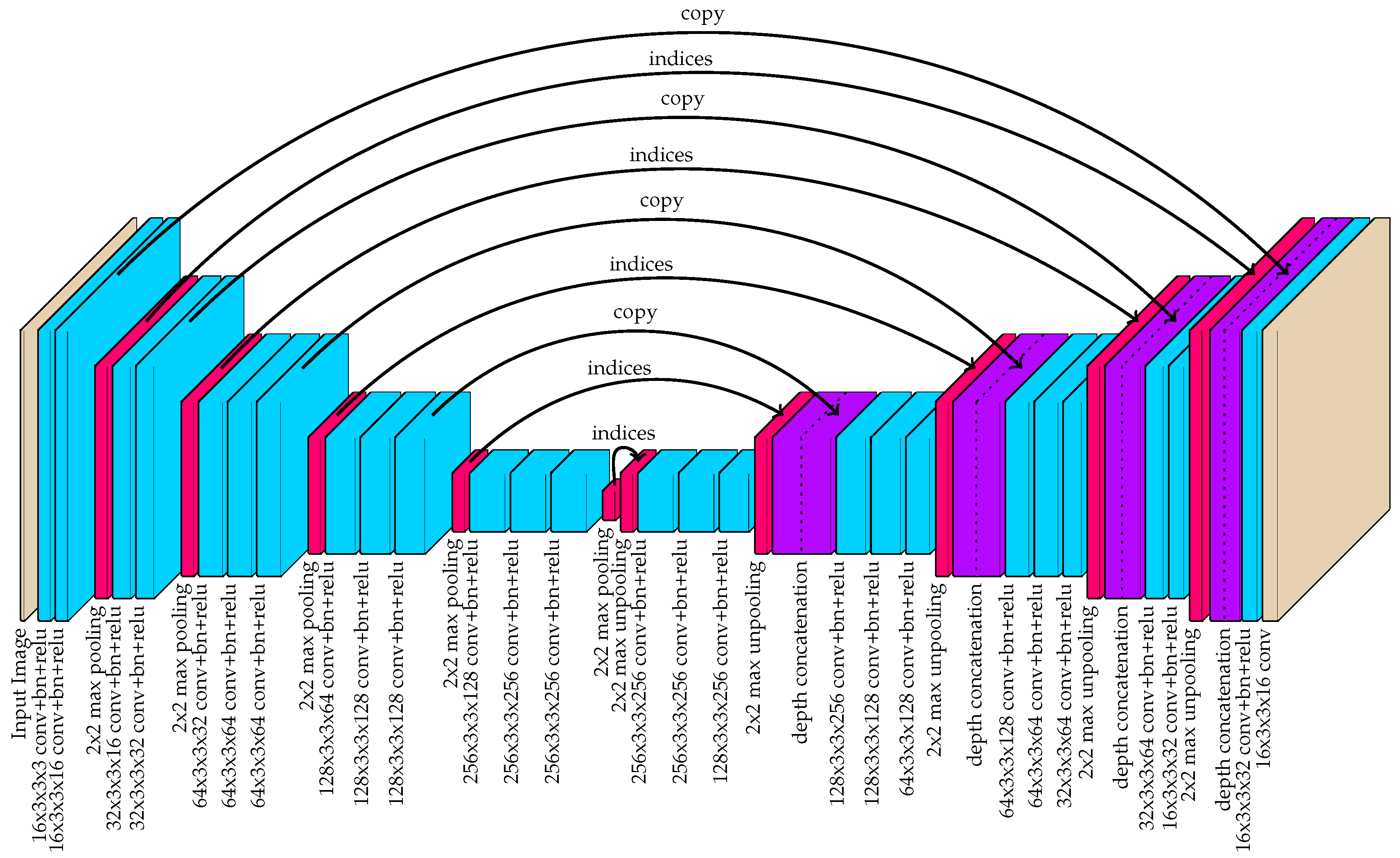
3.4. Fully-Convolution Network for Part Detection and Association Mapping
Receptive Field
4. Experimental Results
4.1. Dataset
4.2. Training Details
4.3. Processing Details
4.4. Instance Detection Performance Metric
4.5. Instance Matching Results
4.6. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Matthews, S.G.; Miller, A.L.; Clapp, J.; Plötz, T.; Kyriazakis, I. Early detection of health and welfare compromises through automated detection of behavioural changes in pigs. Vet. J. 2016, 217, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedin, M.; Baxter, E.M.; Jack, M.; Futro, A.; D’Eath, R.B. Early indicators of tail biting outbreaks in pigs. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2018, 208, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgunder, J.; Petrželková, K.J.; Modrỳ, D.; Kato, A.; MacIntosh, A.J. Fractal measures in activity patterns: Do gastrointestinal parasites affect the complexity of sheep behaviour? Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2018, 205, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PIC North America. Standard Animal Care: Daily Routines. In Wean to Finish Manual; PIC: Hendersonville, TN, USA, 2014; pp. 23–24. [Google Scholar]
- Tuyttens, F.; de Graaf, S.; Heerkens, J.L.; Jacobs, L.; Nalon, E.; Ott, S.; Stadig, L.; Van Laer, E.; Ampe, B. Observer bias in animal behaviour research: can we believe what we score, if we score what we believe? Anim. Behav. 2014, 90, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wathes, C.M.; Kristensen, H.H.; Aerts, J.M.; Berckmans, D. Is precision livestock farming an engineer’s daydream or nightmare, an animal’s friend or foe, and a farmer’s panacea or pitfall? Comput. Electron. Agric. 2008, 64, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banhazi, T.M.; Lehr, H.; Black, J.; Crabtree, H.; Schofield, P.; Tscharke, M.; Berckmans, D. Precision livestock farming: An international review of scientific and commercial aspects. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2012, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Tullo, E.; Fontana, I.; Guarino, M. Precision livestock farming: An overview of image and sound labelling. In European Conference on Precision Livestock Farming 2013:(PLF) EC-PLF; KU Leuven: Leuven, Belgium, 2013; pp. 30–38. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.H.; Kim, D.H.; Park, H.D. Animal situation tracking service using RFID, GPS, and sensors. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Second International Conference on Computer and Network Technology (ICCNT), Bangkok, Thailand, 23–25 April 2010; pp. 153–156. [Google Scholar]
- Stukenborg, A.; Traulsen, I.; Puppe, B.; Presuhn, U.; Krieter, J. Agonistic behaviour after mixing in pigs under commercial farm conditions. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2011, 129, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porto, S.; Arcidiacono, C.; Giummarra, A.; Anguzza, U.; Cascone, G. Localisation and identification performances of a real-time location system based on ultra wide band technology for monitoring and tracking dairy cow behaviour in a semi-open free-stall barn. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2014, 108, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giancola, G.; Blazevic, L.; Bucaille, I.; De Nardis, L.; Di Benedetto, M.G.; Durand, Y.; Froc, G.; Cuezva, B.M.; Pierrot, J.B.; Pirinen, P.; et al. UWB MAC and network solutions for low data rate with location and tracking applications. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE International Conference on Ultra-Wideband, Zurich, Switzerland, 5–8 September 2005; pp. 758–763. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, P.E.; Johnson, D.E.; Kniep, M.A.; Jermann, P.; Huttash, B.; Wood, A.; Johnson, M.; McGillivan, C.; Titus, K. An advanced, low-cost, GPS-based animal tracking system. Rangel. Ecol. Manag. 2006, 59, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwager, M.; Anderson, D.M.; Butler, Z.; Rus, D. Robust classification of animal tracking data. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2007, 56, 46–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, K. Cattle health monitoring using wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of the Communication and Computer Networks Conference, Cambridge, MA, USA, 8–10 November 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Garcia, L.; Lunadei, L.; Barreiro, P.; Robla, I. A Review of Wireless Sensor Technologies and Applications in Agriculture and Food Industry: State of the Art and Current Trends. Sensors 2009, 9, 4728–4750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escalante, H.J.; Rodriguez, S.V.; Cordero, J.; Kristensen, A.R.; Cornou, C. Sow-activity classification from acceleration patterns: A machine learning approach. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2013, 93, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarenga, F.A.P.; Borges, I.; Palkovič, L.; Rodina, J.; Oddy, V.H.; Dobos, R.C. Using a three-axis accelerometer to identify and classify sheep behaviour at pasture. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2016, 181, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voulodimos, A.S.; Patrikakis, C.Z.; Sideridis, A.B.; Ntafis, V.A.; Xylouri, E.M. A complete farm management system based on animal identification using RFID technology. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2010, 70, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Fu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Xu, M.; Zhang, X. Development and evaluation on a RFID-based traceability system for cattle/beef quality safety in China. Food Control 2013, 31, 314–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floyd, R.E. RFID in animal-tracking applications. IEEE Potentials 2015, 34, 32–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittek, M.; Psota, E.T.; Pérez, L.C.; Schmidt, T.; Mote, B. Health Monitoring of Group-Housed Pigs using Depth-Enabled Multi-Object Tracking. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Workshop on Visual Observation and Analysis of Vertebrate and Insect Behavior, Cancun, Mexico, 4 December 2016; pp. 9–12. [Google Scholar]
- Mittek, M.; Psota, E.T.; Carlson, J.D.; Pérez, L.C.; Schmidt, T.; Mote, B. Tracking of group-housed pigs using multi-ellipsoid expectation maximisation. IET Comput. Vis. 2017, 12, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neethirajan, S. Recent advances in wearable sensors for animal health management. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2017, 12, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schleppe, J.B.; Lachapelle, G.; Booker, C.W.; Pittman, T. Challenges in the design of a GNSS ear tag for feedlot cattle. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2010, 70, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardö, H.; Guzhva, O.; Nilsson, M.; Herlin, A.H. Convolutional neural network-based cow interaction watchdog. IET Comput. Vis. 2017, 12, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, M.; Choi, Y.; Seo, J.; Sa, J.; Lee, S.; Chung, Y.; Park, D. A Kinect-Based Segmentation of Touching-Pigs for Real-Time Monitoring. Sensors 2018, 18, 1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 3–6 December 2012; pp. 1097–1105. [Google Scholar]
- LeCun, Y.; Bottou, L.; Bengio, Y.; Haffner, P. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proc. IEEE 1998, 86, 2278–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Shelhamer, E.; Donahue, J.; Karayev, S.; Long, J.; Girshick, R.; Guadarrama, S.; Darrell, T. Caffe: Convolutional architecture for fast feature embedding. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Orlando, FL, USA, 3–7 November 2014; pp. 675–678. [Google Scholar]
- Kirk, D. NVIDIA CUDA software and GPU parallel computing architecture. In Proceedings of the 6th international symposium on Memory management, Montreal, QC, Canada, 21–22 October 2007; Volume 7, pp. 103–104. [Google Scholar]
- Everingham, M.; Eslami, S.A.; Van Gool, L.; Williams, C.K.; Winn, J.; Zisserman, A. The pascal visual object classes challenge: A retrospective. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2015, 111, 98–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.Y.; Maire, M.; Belongie, S.; Hays, J.; Perona, P.; Ramanan, D.; Dollár, P.; Zitnick, C.L. Microsoft coco: Common objects in context. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; pp. 740–755. [Google Scholar]
- Cordts, M.; Omran, M.; Ramos, S.; Rehfeld, T.; Enzweiler, M.; Benenson, R.; Franke, U.; Roth, S.; Schiele, B. The cityscapes dataset for semantic urban scene understanding. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 3213–3223. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 779–788. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. YOLO9000: Better, Faster, Stronger. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 7263–7271. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Szegedy, C.; Reed, S.; Fu, C.Y.; Berg, A.C. Ssd: Single shot multibox detector. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 8–16 October 2016; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 21–37. [Google Scholar]
- Girshick, R. Fast r-cnn. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1440–1448. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster r-cnn: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. In Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, QC, Canada, 7–12 December 2015; pp. 91–99. [Google Scholar]
- Di Stefano, L.; Bulgarelli, A. A simple and efficient connected components labeling algorithm. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Image Analysis and Processing, Venice, Italy, 27–29 September 1999; p. 322. [Google Scholar]
- Otsu, N. A threshold selection method from gray-level histograms. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1979, 9, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashiha, M.A.; Bahr, C.; Ott, S.; Moons, C.P.; Niewold, T.A.; Tuyttens, F.; Berckmans, D. Automatic monitoring of pig locomotion using image analysis. Livest. Sci. 2014, 159, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasirahmadi, A.; Richter, U.; Hensel, O.; Edwards, S.; Sturm, B. Using machine vision for investigation of changes in pig group lying patterns. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2015, 119, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrendt, P.; Gregersen, T.; Karstoft, H. Development of a real-time computer vision system for tracking loose-housed pigs. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2011, 76, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, M.; Ardö, H.; Åström, K.; Herlin, A.; Bergsten, C.; Guzhva, O. Learning based image segmentation of pigs in a pen. In Proceedings of the Visual Observation and Analysis of Vertebrate and Insect Behavior, Stockholm, Sweden, 24–28 August 2014; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Kongsro, J. Estimation of pig weight using a Microsoft Kinect prototype imaging system. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2014, 109, 32–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Ren, J.; Barclay, D.; McCormack, S.; Thomson, W. Automatic Animal Detection from Kinect Sensed Images for Livestock Monitoring and Assessment. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer and Information Technology, Ubiquitous Computing and Communications, Dependable, Autonomic and Secure Computing, Pervasive Intelligence and Computing, Liverpool, UK, 26–28 October 2015; pp. 1154–1157. [Google Scholar]
- Stavrakakis, S.; Li, W.; Guy, J.H.; Morgan, G.; Ushaw, G.; Johnson, G.R.; Edwards, S.A. Validity of the Microsoft Kinect sensor for assessment of normal walking patterns in pigs. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2015, 117, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Jin, L.; Park, D.; Chung, Y. Automatic Recognition of Aggressive Behavior in Pigs Using a Kinect Depth Sensor. Sensors 2016, 16, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lao, F.; Brown-Brandl, T.; Stinn, J.; Liu, K.; Teng, G.; Xin, H. Automatic recognition of lactating sow behaviors through depth image processing. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2016, 125, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Lee, L.; Chung, Y.; Park, D. Individual Pig Detection Using Kinect Depth Information. Kips Trans. Comput. Commun. Syst. 2016, 5, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kim, J.; Chung, Y.; Choi, Y.; Sa, J.; Kim, H.; Chung, Y.; Park, D.; Kim, H. Depth-Based Detection of Standing-Pigs in Moving Noise Environments. Sensors 2017, 17, 2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezzuolo, A.; Guarino, M.; Sartori, L.; González, L.A.; Marinello, F. On-barn pig weight estimation based on body measurements by a Kinect v1 depth camera. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2018, 148, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, A.; Dórea, J.; Fitzgerald, R.; Herring, W.; Rosa, G. A novel automated system to acquire biometric and morphological measurements, and predict body weight of pigs via 3D computer vision. J. Anim. Sci. 2018, 97, 496–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, S.G.; Miller, A.L.; PlÖtz, T.; Kyriazakis, I. Automated tracking to measure behavioural changes in pigs for health and welfare monitoring. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girshick, R.; Donahue, J.; Darrell, T.; Malik, J. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Portland, OR, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 580–587. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Gkioxari, G.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R. Mask r-cnn. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 Ocotober 2017; pp. 2980–2988. [Google Scholar]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3431–3440. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Z.; Simon, T.; Wei, S.E.; Sheikh, Y. Realtime Multi-Person 2D Pose Estimation using Part Affinity Fields. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Papandreou, G.; Zhu, T.; Chen, L.C.; Gidaris, S.; Tompson, J.; Murphy, K. PersonLab: Person Pose Estimation and Instance Segmentation with a Bottom-Up, Part-Based, Geometric Embedding Model. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Newell, A.; Yang, K.; Deng, J. Stacked hourglass networks for human pose estimation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2016; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 483–499. [Google Scholar]
- Badrinarayanan, V.; Kendall, A.; Cipolla, R. SegNet: A Deep Convolutional Encoder-Decoder Architecture for Image Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 2481–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Van Der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely connected convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the CVPR, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; Volume 1, p. 3. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 5–9 Ocotber 2015; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, W.; Li, Y.; Urtasun, R.; Zemel, R. Understanding the effective receptive field in deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 30th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Barcelona, Spain, 5–10 December 2016; pp. 4905–4913. [Google Scholar]
- MATLAB, version 9.5.0 (R2018b); The MathWorks Inc.: Natick, MA, USA, 2018.
- Deng, J.; Dong, W.; Socher, R.; Li, L.J.; Li, K.; Fei-Fei, L. Imagenet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2009), Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; pp. 248–255. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. Deeplab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected crfs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2018, 40, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.C.; Zhu, Y.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Encoder-Decoder with Atrous Separable Convolution for Semantic Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the ECCV, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, W.; Xing, J.; Milan, A.; Zhang, X.; Liu, W.; Zhao, X.; Kim, T.K. Multiple object tracking: A literature review. arXiv, 2014; arXiv:1409.7618. [Google Scholar]












| Channel | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| Encoding |
| Channel | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| Encoding | ||||||
| Channel | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 |
| Encoding |
| Layer Type | I | C | C | M | C | ⋯ | C | M | U | C | ⋯ | C | U | D | C | O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| l | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ⋯ | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | ⋯ | 37 | 38 | 39 | 40 | 41 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | ⋯ | 1 | 2 | 0.5 | 1 | ⋯ | 1 | 0.5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | ⋯ | 16 | 32 | 16 | 16 | ⋯ | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| 1 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 3 | ⋯ | 3 | 1 | 1 | 3 | ⋯ | 3 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 3 | |
| 1 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 9 | ⋯ | 181 | 181 | 181 | 213 | ⋯ | 359 | 359 | 359 | 361 | 363 |
| Part Detection Threshold | Vector Matching | Euclidean Matching | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TP | FP | FN | Recall | Precision | F-Measure | TP | FP | FN | Recall | Precision | F-Measure | |
| 0.10 | 20,217 | 27 | 525 | 0.975 | 0.999 | 0.987 | 19,170 | 1181 | 1572 | 0.924 | 0.942 | 0.933 |
| 0.15 | 20,160 | 20 | 582 | 0.972 | 0.999 | 0.985 | 19,127 | 1156 | 1615 | 0.922 | 0.943 | 0.932 |
| 0.20 | 20,092 | 17 | 650 | 0.969 | 0.999 | 0.984 | 19,058 | 1154 | 1684 | 0.919 | 0.943 | 0.931 |
| 0.25 | 19,999 | 13 | 743 | 0.964 | 0.999 | 0.981 | 18,971 | 1141 | 1771 | 0.915 | 0.943 | 0.929 |
| 0.30 | 19,865 | 10 | 877 | 0.958 | 0.999 | 0.978 | 18,851 | 1135 | 1891 | 0.909 | 0.943 | 0.926 |
| 0.35 | 19,675 | 7 | 1067 | 0.949 | 1.000 | 0.973 | 18,675 | 1162 | 2067 | 0.900 | 0.941 | 0.920 |
| 0.40 | 19,413 | 3 | 1329 | 0.936 | 1.000 | 0.967 | 18,418 | 1190 | 2324 | 0.888 | 0.939 | 0.913 |
| 0.45 | 19,029 | 2 | 1713 | 0.917 | 1.000 | 0.957 | 18,077 | 1195 | 2665 | 0.872 | 0.938 | 0.904 |
| 0.50 | 18,408 | 2 | 2334 | 0.887 | 1.000 | 0.940 | 17,526 | 1269 | 3216 | 0.845 | 0.932 | 0.887 |
| 0.55 | 17,287 | 2 | 3455 | 0.833 | 1.000 | 0.909 | 16,568 | 1281 | 4174 | 0.799 | 0.928 | 0.859 |
| 0.60 | 15,227 | 2 | 5515 | 0.734 | 1.000 | 0.847 | 14,871 | 1294 | 5871 | 0.717 | 0.920 | 0.806 |
| 0.65 | 11,929 | 0 | 8813 | 0.575 | 1.000 | 0.730 | 12,184 | 1189 | 8558 | 0.587 | 0.911 | 0.714 |
| 0.70 | 7565 | 0 | 13,177 | 0.365 | 1.000 | 0.534 | 8543 | 860 | 12,199 | 0.412 | 0.909 | 0.567 |
| 0.75 | 3261 | 0 | 17,481 | 0.157 | 1.000 | 0.272 | 4523 | 430 | 16,219 | 0.218 | 0.913 | 0.352 |
| 0.80 | 692 | 0 | 20,050 | 0.033 | 1.000 | 0.065 | 1414 | 90 | 19,328 | 0.068 | 0.940 | 0.127 |
| 0.85 | 53 | 0 | 20,689 | 0.003 | 1.000 | 0.005 | 143 | 3 | 20,599 | 0.007 | 0.979 | 0.014 |
| 0.90 | 1 | 0 | 20,741 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.000 | 5 | 0 | 20,737 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.000 |
| Evaluation Set | Vector Matching | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TP | FP | FN | Recall | Precision | F-Measure | |
| Training | 19,999 | 13 | 743 | 0.964 | 0.999 | 0.981 |
| Test: Seen | 2273 | 1 | 94 | 0.960 | 1.000 | 0.980 |
| Test: Unseen | 1150 | 112 | 573 | 0.667 | 0.911 | 0.771 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Psota, E.T.; Mittek, M.; Pérez, L.C.; Schmidt, T.; Mote, B. Multi-Pig Part Detection and Association with a Fully-Convolutional Network. Sensors 2019, 19, 852. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19040852
Psota ET, Mittek M, Pérez LC, Schmidt T, Mote B. Multi-Pig Part Detection and Association with a Fully-Convolutional Network. Sensors. 2019; 19(4):852. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19040852
Chicago/Turabian StylePsota, Eric T., Mateusz Mittek, Lance C. Pérez, Ty Schmidt, and Benny Mote. 2019. "Multi-Pig Part Detection and Association with a Fully-Convolutional Network" Sensors 19, no. 4: 852. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19040852
APA StylePsota, E. T., Mittek, M., Pérez, L. C., Schmidt, T., & Mote, B. (2019). Multi-Pig Part Detection and Association with a Fully-Convolutional Network. Sensors, 19(4), 852. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19040852




