Finger-Counting-Based Gesture Recognition within Cars Using Impulse Radar with Convolutional Neural Network
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. System Overview
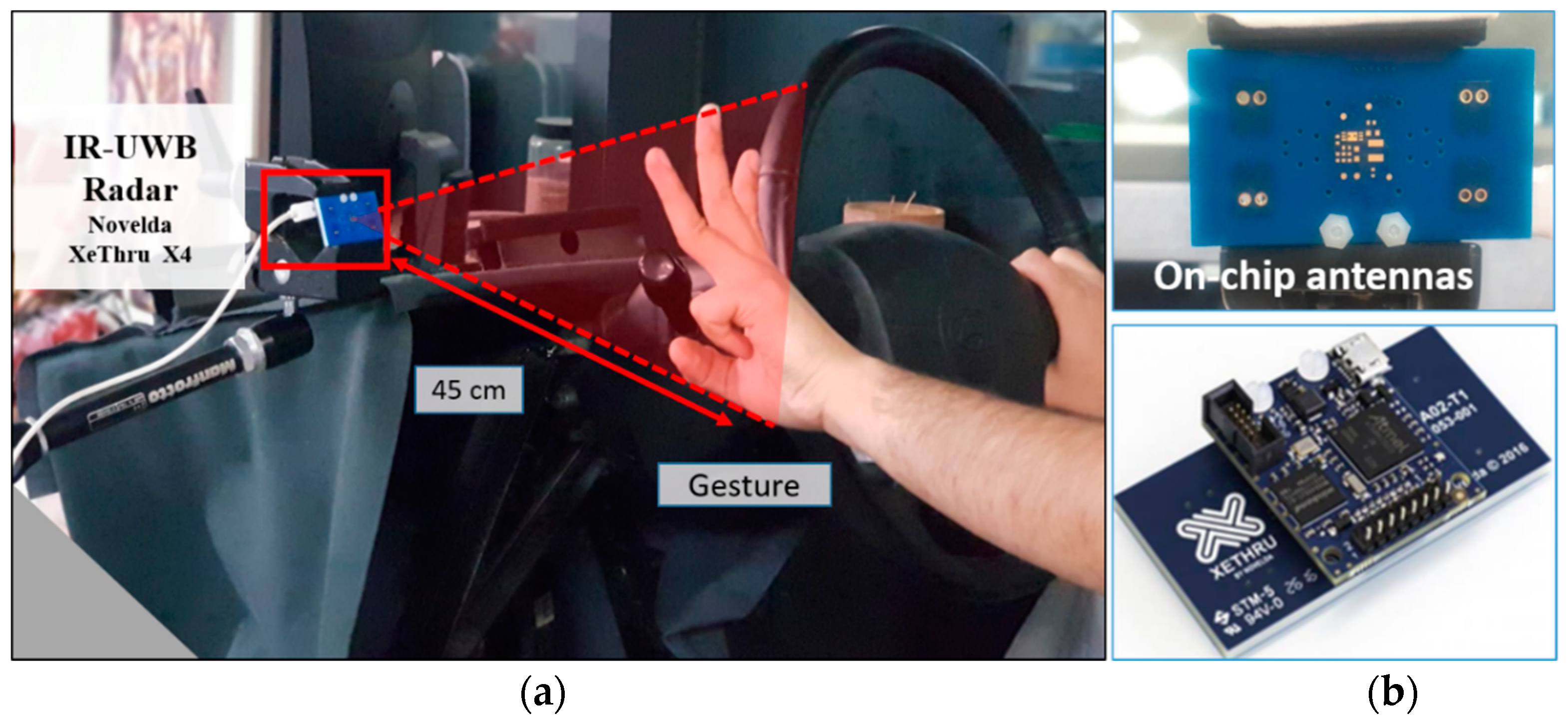
2.2. Optimul Position of Sensor within Car
2.3. Signal Preprocessing
2.4. Representation and Analysis of Gesture Data
| Algorithm 1. Transformation of radar signals into images |
|
2.5. CNN Architecture for Training and Classification
3. Experimental Setup
4. Results
4.1. Results of Clutter Removal Filter
4.2. Optimal Sensor Position
4.3. Gesture Image Patterns
4.4. Classification Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sodnik, J.; Dicke, C.; Tomazič, S.; Billinghurst, M. A user study of auditory versus visual interfaces for use while driving. Int. J. Hum. Comput. Stud. 2008, 66, 318–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kern, D.; Schmidt, A. Design space for driver-based automotive user interfaces. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Automotive User Interfaces and Interactive Vehicular Applications, Essen, Germany, 21–22 September 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Jeon, M.; Schuett, J.; Yim, J.B.; Walker, B.N. ENGIN (Exploring Next Generation IN-vehicle INterfaces): Drawing a new conceptual framework through iterative participatory processes. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Automotive User Interfaces and Interactive Vehicular Applications (AutomotiveUI’11), Salzburg, Austria, 30 November–2 December 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Parente, R.; Kock, N. An analysis of the implementation and impact of speech-recognition technology in the healthcare sector. Perspect. Health Inf. Manag. 2004, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Ryde, J.; Hillier, N. Performance of laser and radar ranging devices in adverse environmental conditions. J. Field Robot. 2009, 26, 712–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhong, L.; Chan, S.C. Superpixel-based hand gesture recognition with Kinect depth camera. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2015, 17, 2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rautaray, S.S.; Agrawal, A. Vision based hand gesture recognition for human computer interaction: A survey. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2015, 43, 1–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, S.; Chai, E.; Sundaresan, K.; Qiu, L.; Khojastepour, M.A.; Rangarajan, S. RIO: A pervasive RFID-based touch gesture interface. In Proceedings of the 23rd Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking, Snowbird, UT, USA, 16–20 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sturman, D.J.; Zeltzer, D. A survey of glove-based input. IEEE Comput. Graph. Appl. 1994, 1, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.Y.; Shin, D.K.; Shin, D. A finger counting method for gesture recognition. J. Int. Comput. Serv. 2016, 17, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Yuan, J.; Meng, J.; Zhang, Z. Robust part-based hand gesture recognition using kinect sensor. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2013, 15, 1110–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Zhang, H.; Fang, G.; Ye, S.; Gulliver, T.A. An improved algorithm for through-wall target detection using ultra-wideband impulse radar. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 22101–22118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.W.; Quan, X.; Cho, S.H. Bi-directional passing people counting system based on IR-UWB radar sensors. IEEE Internet Things J. 2018, 5, 512–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.; Cho, S.H. A detailed algorithm for vital sign monitoring of a stationary/non-stationary human through IR-UWB radar. Sensors 2017, 17, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.W.; Cho, S.H. 3D positioning algorithm based on multiple quasi-monostatic IR-UWB radar sensors. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf), Seattle, WA, USA, 8–12 May 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Seo, J. IR-UWB radar-based near-field head rotation movement sensing under fixed body motions. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Electronics, Information, and Communication, Honolulu, HI, USA, 24–27 January 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lazaro, A.; Girbau, D.; Villarino, R. Techniques for clutter suppression in the presence of body movements during the detection of respiratory activity through UWB radars. Sensors 2014, 14, 2595–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, N.; Quan, X.; Cho, S.H. Algorithm for gesture recognition using an IR-UWB radar sensor. Int. J. Comput. Commun. 2016, 4, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, S.J.; Suh, J.S.; Baek, S.H.; Hong, S.; Kim, J.H. Feature-Based Hand Gesture Recognition Using an FMCW Radar and its Temporal Feature Analysis. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 18, 7593–7602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhou, M.; Jiang, Q.; Tian, Z. TS-I3D based Hand Gesture Recognition Method with Radar Sensor. IEEE Access 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 3–6 December 2012; pp. 1097–1105. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A. Going deeper with convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Young, K.L.; Salmon, P.M. Examining the relationship between driver distraction and driving errors: A discussion of theory, studies and methods. Saf. Sci. 2012, 50, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haigney, D.E.; Taylor, R.G.; Westerman, S.J. Concurrent mobile (cellular) phone use and driving performance: Task demand characteristics and compensatory processes. Trans. Res. Part F: Traffic Psychol. Behav. 2000, 3, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassioli, D.; Win, M.Z.; Molisch, A.F. The ultra-wide bandwidth indoor channel: From statistical model to simulations. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2002, 20, 1247–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Win, M.Z.; Scholtz, R.A. Impulse radio: How it works. IEEE Commun. Lett. 1998, 2, 36–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathanson, F.E.; Reilly, J.P.; Cohen, M.N. Radar Design Principles-Signal Processing and the Environment; NASA STI/Recon Technical Report A; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, V.H.; Pyun, J.Y. Location detection and tracking of moving targets by a 2D IR-UWB radar system. Sensors 2015, 15, 6740–6762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mostafa, M.; Chamaani, S.; Sachs, J. Applying singular value decomposition for clutter reduction in heartbeat estimation using M-sequence UWB Radar. In Proceedings of the 19th International Radar Symposium (IRS), Bonn, Germany, 20–22 June 2018; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Piccardi, M. Background subtraction techniques: A review. In Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics (IEEE Cat. No. 04CH37583), Hague, The Netherlands, 10–13 October 2004; Volume 4, pp. 3099–3104. [Google Scholar]
- Gill, G.S. Ultra-wideband radar using Fourier synthesized waveforms. IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 1997, 39, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioffe, S.; Szegedy, C. Batch normalization: Accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. arXiv, 2015; arXiv:1502.03167. [Google Scholar]
- Cichy, R.M.; Khosla, A.; Pantazis, D.; Torralba, A.; Oliva, A. Comparison of deep neural networks to spatio-temporal cortical dynamics of human visual object recognition reveals hierarchical correspondence. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jaafra, Y.; Laurent, J.L.; Deruyver, A.; Naceur, M.S. A Review of Meta-Reinforcement Learning for Deep Neural Networks Architecture Search. arXiv, 2018; arXiv:1812.07995. [Google Scholar]













| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Output power | −12.6 dBm |
| Center frequency | 8.748 GHz |
| Pulse repetition frequency | 100 MHz |
| Bandwidth (−10 dB) | 2.3 GHz |
| Sampling frequency | 23 samples/s |
| Staggered PRF sequence length | 220 cycles |
| Hyperparameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Number of hidden layers in CNN | 06 |
| Convolution filter size | 03 |
| Learning rate | 0.01 |
| Epochs | 10 |
| Predicted Gesture Class | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Original Gesture Class | Gesture Class | One | Two | Three | Four | Five |
| One | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Two | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Three | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | ||
| Four | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.87 | 0.13 | |
| Five | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahmed, S.; Khan, F.; Ghaffar, A.; Hussain, F.; Cho, S.H. Finger-Counting-Based Gesture Recognition within Cars Using Impulse Radar with Convolutional Neural Network. Sensors 2019, 19, 1429. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19061429
Ahmed S, Khan F, Ghaffar A, Hussain F, Cho SH. Finger-Counting-Based Gesture Recognition within Cars Using Impulse Radar with Convolutional Neural Network. Sensors. 2019; 19(6):1429. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19061429
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhmed, Shahzad, Faheem Khan, Asim Ghaffar, Farhan Hussain, and Sung Ho Cho. 2019. "Finger-Counting-Based Gesture Recognition within Cars Using Impulse Radar with Convolutional Neural Network" Sensors 19, no. 6: 1429. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19061429
APA StyleAhmed, S., Khan, F., Ghaffar, A., Hussain, F., & Cho, S. H. (2019). Finger-Counting-Based Gesture Recognition within Cars Using Impulse Radar with Convolutional Neural Network. Sensors, 19(6), 1429. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19061429





