Nano-Biosensing Platforms for Detection of Cow’s Milk Allergens: An Overview
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Analytical Standard Methods for the Milk Allergens Detection
3. Biosensors in Detecting Food Allergens
| Protein name | Buffalo | Goat | Sheep | Reindeer | Mare | Donkey | Mule | Camel | Pig |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| αS1-casein | Bub b 9 | Cap h 9 | Ovi a 9 | Not found | Equ c 9 | Not found | Not found | Cam d 9 | Sus s 9 |
| αS2-casein | Bub b 10 | Cap h 10 | Ovi a 10 | Not found.0 | Equ c 10 | Not found | Not found | Cam d 10 | Sus s 10 |
| β-casein | Bub b 11 | Cap h 11 | Ovi a 11 | Not found.0 | Equ c 11 | Not found | Not found | Cam d 11 | Sus s 11 |
| κ-casein | Bub b 12 | Cap h 12 | Ovi a 12 | Not found | Equ c 12 | Not found | Not found | Cam d 12 | Sus s 12 |
| α-Lactalbumin | Bub a 4 | Cap h 4 | Ovi a 4 | Not found .0 | Equ c ALA | Not found | Not found | Cam d 4 | Sus s 4 |
| β-Lactoglobulin | Bub a 5 | Cap h 5 | Ovi a 5 | Ran t 5 .0 | Equ c BLG | Equ as BLG | Equ mu BLG | Absent | Sus s 5 |
| BSA | Not found | Cap h 6 | Ovi a 6 | Not found | Equ c 3 a | Equ as 6 | Not found | Not found | Sus s 1 a |
| S. No. | Type | Analyte | Biosensing Platform | Transduction Mechanism | Detection Limit | Linearity Range | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Immunosensor | β-lactoglobulin | Horseradish peroxidase labeled antibody immobilized activated carboxylic-modified magnetic beads/carbon | Amperometric | 0.8 × 10−3 μg/mL | 2.8–100 × 10−3 μg/mL | [67] |
| 2 | α-lactoglobulin | Horseradish peroxidase labeled antibody immobilized activated carboxylic-modified magnetic beads/carbon | Amperometric | 11 × 10−6 μg/mL | 37–5000 × 10−6 μg/mL | [62] | |
| 3 | β-lactoglobulin | Anti-β-lactoglobulin antibody immobilized graphene/carbon | Electrochemical | 0.85 × 10−6 μg/mL | 1 × 10−6 to 100 × 10−3 μg/mL | [65] | |
| 4 | β-lactoglobulin | Anti-β -lactoglobulin antibody immobilized gold sensor chip | Surface plasmon resonance | 0.164 µg/mL | - | [68] | |
| 5 | β-lactoglobulin | Anti-β-lactoglobulin antibody immobilized streptavidin coated quantum dots/functional copolymer, copoly (DMA-NAS) coated porous alumina membrane | Polarimetry | 33.7 × 10−3 μg/mL | - | [69] | |
| 6 | β-lactoglobulin | Double-antibody sandwich immunoassay | Surface plasmon resonance | 5.54 × 10−3 μg/mL | 5–40 × 10−3 μg/mL | [70] | |
| 7 | α-lactalbumin | CdSe/ZnS quantum dots conjugated with monoclonal antibodies | Fluorescence-linked immunosorbent assay | 0.1 × 10−3 μg/mL | 0.1 to 1000 × 10−3 μg/mL | [71] | |
| 8 | Casein and Immunoglobulin G | Integrated lab-on-a-membrane foldable device using Pb- and Cd-quantum dot tags | Electrochemical | 0.04 μg/mL and 0.02 μg/mL | 0–5 µg/mL and 0–2 µg/mL | [72] | |
| 9 | Casein | Rat basophilic leukemia-immobilized graphene/carbon nanofiber/gelatin methacryloyl nanocomposites-based paper sensor | Electrochemical | 3.2 × 10-2 μg/mL | 0.1 and 3.2 μg/mL | [73] | |
| 10 | Aptasensor | β-lactoglobulin | Aptamers immobilized graphene/carbon | Electrochemical | 20 × 10−6 μg/mL | 100 × 10−6 μg/mL to 100 × 10−3 μg/mL | [64] |
| 11 | β-lactoglobulin | Aptamer functionalized Fe3O4/cDNA conjugated carbon dots | Florescence | 37 × 10−6 μg/mL | 0.25 × 10−3 to 50 × 10−3 μg/mL | [74] | |
| 12 | β-lactoglobulin | 23-nucleotide aptamer-amphiphile | Enzyme linked apta-sorbent assay | 10 nM | 5 to 0.01 µM | [75] | |
| 13 | β-lactoglobulin | Aptamer coupled poly(aniline-co-anthranilic acid)/graphite | Electrochemical | 0.053 μg/mL | 0.01 to 1.0 μg/mL | [76] | |
| 14 | Lactoferrin | Bivalent aptamer linked to fluorescein isothiocyanate dye and silver decahedral nanoparticles | Fluorescence polarization | 0.1 × 10−3 μg/mL | 0.2 × 10−3 to 25 μg/mL | [77] | |
| 15 | β-lactoglobulin | Microfluidic paper-based device with aptamer conjugated gold nanoparticles/graphene | Colorimetry | 12.4 nM | 25 nM to 1000 nM | [78] |
3.1. Immunosensors
3.2. Aptasensors
4. Commercially Available Biosensors
5. Conclusions and Future Prospects
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Minh Hiep, H.; Endo, T.; Kerman, K.; Chikae, M.; Kim, D.K.; Yamamura, S.; Takamura, Y.; Tamiya, E. A localized surface plasmon resonance based immunosensor for the detection of casein in milk. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2007, 8, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Renz, H.; Allen, K.J.; Sicherer, S.H.; Sampson, H.A.; Lack, G.; Beyer, K.; Oettgen, H.C. Food allergy. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2018, 4, 17098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Food Allergy World Allergy Organization. Available online: https://www.worldallergy.org/education-and-programs/education/allergic-disease-resource-center/professionals/food-allergy (accessed on 6 December 2019).
- Williams, P.V. The epidemiology of milk allergy in US children. Pediatrics 2013, 132, S17–S18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiocchi, A.; Schünemann, H.J.; Brozek, J.; Restani, P.; Beyer, K.; Troncone, R.; Martelli, A.; Terracciano, L.; Bahna, S.L.; Rancé, F.; et al. Diagnosis and rationale for action against Cow’s milk allergy (DRACMA): A summary report. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 126, 1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyce, J.A.; Assa’ad, A.; Burks, A.W.; Jones, S.M.; Sampson, H.A.; Wood, R.A.; Plaut, M.; Cooper, S.F.; Fenton, M.J. Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of food allergy in the United States: Report of the NIAID-sponsored expert panel. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 126, S1–S58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villa, C.; Costa, J.; Oliveira, M.B.P.P.; Mafra, I. Bovine Milk Allergens: A comprehensive review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2018, 17, 137–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hochwallner, H.; Schulmeister, U.; Swoboda, I.; Spitzauer, S.; Valenta, R. Cow’s milk allergy: From allergens to new forms of diagnosis, therapy and prevention. Methods 2014, 66, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allergome. Available online: http://www.allergome.org/script/statistic.php (accessed on 22 November 2019).
- Szépfalusi, Z.; Loibichler, C.; Pichler, J.; Reisenberger, K.; Ebner, C.; Urbanek, R. Direct evidence for transplacental allergen transfer. Pediatr. Res. 2000, 48, 404–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- D’Urbano, L.E.; Pellegrino, K.; Artesani, M.C.; Donnanno, S.; Luciano, R.; Riccardi, C.; Tozzi, A.E.; Ravà, L.; De Benedetti, F.; Cavagni, G. Performance of a component-based allergen-microarray in the diagnosis of cow’s milk and hen’s egg allergy. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2010, 40, 1561–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO/IUIS Allergen Nomenclature Home Page. Available online: http://www.allergen.org/ (accessed on 7 December 2019).
- Schulmeister, U.; Hochwallner, H.; Swoboda, I.; Focke-Tejkl, M.; Geller, B.; Nystrand, M.; Harlin, A.; Thalhamer, J.; Scheiblhofer, S.; Keller, W.; et al. Cloning, expression, and mapping of allergenic determinants of S1-casein, a major cow’s milk allergen. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 7019–7029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontopidis, G.; Holt, C.; Sawyer, L. Invited review: β-lactoglobulin: Binding properties, structure, and function. J. Dairy Sci. 2004, 87, 785–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adams, J.J.; Anderson, B.F.; Norris, G.E.; Creamer, L.K.; Jameson, G.B. Structure of bovine β-lactoglobulin (variant A) at very low ionic strength. J. Struct. Biol. 2006, 154, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wal, J.-M. Bovine milk allergenicity. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2004, 93, S2–S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares, G.M.; Croguennec, T.; Carvalho, A.F.; Bouhallab, S. Milk proteins as encapsulation devices and delivery vehicles: Applications and trends. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 37, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Neerven, R.J.J.; Knol, E.F.; Heck, J.M.L.; Savelkoul, H.F.J. Which factors in raw cow’s milk contribute to protection against allergies? J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 130, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giblin, L.; Süha Yalçın, A.; Biçim, G.; Krämer, A.C.; Chen, Z.; Callanan, M.J.; Arranz, E.; Davies, M.J. Whey proteins: Targets of oxidation, or mediators of redox protection. Free Radic. Res. 2019, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negaoui, H.; El Mecherfi, K.E.; Tadjer, S.A.; Grar, H.; Kheroua, O.; Saidi, D. Bovine lactoferrin allergenicity as studied in murine model of allergy. Food Agric. Immunol. 2016, 27, 711–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- D’Auria, E.; Salvatore, S.; Pozzi, E.; Mantegazza, C.; Sartorio, M.U.A.; Pensabene, L.; Baldassarre, M.E.; Agosti, M.; Vandenplas, Y.; Zuccotti, G. Cow’s milk allergy: Immunomodulation by dietary intervention. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- D’Auria, E.; Mameli, C.; Piras, C.; Cococcioni, L.; Urbani, A.; Zuccotti, G.V.; Roncada, P. Precision medicine in cow’s milk allergy: Proteomics perspectives from allergens to patients. J. Proteom. 2018, 188, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linhart, B.; Freidl, R.; Elisyutina, O.; Khaitov, M.; Karaulov, A.; Valenta, R. Molecular approaches for diagnosis, therapy and prevention of cow´s milk allergy. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Faisal, M.; Vasiljevic, T.; Donkor, O.N. A review on methodologies for extraction, identification and quantification of allergenic proteins in prawns. Food Res. Int. 2019, 121, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neethirajan, S.; Weng, X.; Tah, A.; Cordero, J.O.; Ragavan, K.V. Nano-biosensor platforms for detecting food allergens—New trends. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2018, 18, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croote, D.; Quake, S.R. Food allergen detection by mass spectrometry: The role of systems biology. npj Syst. Biol. Appl. 2016, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mishra, G.K.; Sharma, V.; Mishra, R.K. Electrochemical aptasensors for food and environmental safeguarding: A review. Biosensors 2018, 8, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alves, R.C.; Barroso, M.F.; González-García, M.B.; Oliveira, M.B.P.P.; Delerue-Matos, C. New trends in food allergens detection: Toward biosensing strategies. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 56, 2304–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poms, R.E.; Klein, C.L.; Anklam, E. Methods for allergen analysis in food: A review. Food Addit. Contam. 2004, 21, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acquah, C.; Agyei, D.; Obeng, E.M.; Pan, S.; Tan, K.X.; Danquah, M.K. Aptamers: An emerging class of bioaffinity ligands in bioactive peptide applications. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilolli, R.; Monaci, L.; Visconti, A. Advances in biosensor development based on integrating nanotechnology and applied to food-allergen management. TrAC-Trends Anal. Chem. 2013, 47, 12–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiocchi, A.; Schunemann, H.; Ansotegui, I.; Assa’ad, A.; Bahna, S.; Canani, R.B.; Bozzola, M.; Dahdah, L.; Dupont, C.; Ebisawa, M.; et al. The global impact of the DRACMA guidelines cow’s milk allergy clinical practice. World Allergy Organ. J. 2018, 11, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morisset, M.; Moneret-Vautrin, D.A.; Kanny, G.; Guenard, L.; Beaudouin, E.; Flabbee, J.; Hatahet, R. Thresholds of clinical reactivity to milk, egg, peanut and sesame in immunoglobulin E-dependent allergies: Evaluation by double-blind or single-blind placebo-controlled oral challenges. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2003, 33, 1046–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhoeckx, K.C.M.; Vissers, Y.M.; Baumert, J.L.; Faludi, R.; Feys, M.; Flanagan, S.; Herouet-Guicheney, C.; Holzhauser, T.; Shimojo, R.; van der Bolt, N.; et al. Food processing and allergenicity. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 80, 223–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prado, M.; Ortea, I.; Vial, S.; Rivas, J.; Calo-Mata, P.; Barros-Velázquez, J. Advanced DNA- and protein-based methods for the detection and investigation of food allergens. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 56, 2511–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holzhauser, T. Protein or no protein? Opportunities for DNA-based detection of allergenic foods. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 9889–9894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, L.; Song, S.; Zheng, Q.; Luo, P.; Wu, X.; Kuang, H. Development of a sandwich ELISA and immunochromatographic strip for the detection of shrimp tropomyosin. Food Agric. Immunol. 2019, 30, 606–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Orcajo, J.; Lavilla, M.; Martínez-de-Marañón, I. Specific and sensitive ELISA for measurement of IgE-binding variations of milk allergen β-lactoglobulin in processed foods. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1052, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samsonova, J.V.; Safronova, V.A.; Osipov, A.P. Rapid flow-through enzyme immunoassay of progesterone in whole cows’ milk. Anal. Biochem. 2018, 545, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Huang, Z.; Hu, S.; Peng, J.; Liu, D.; Xiong, Y.; Xu, H.; Wei, H.; Lai, W. Invited review: Advancements in lateral flow immunoassays for screening hazardous substances in milk and milk powder. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 1887–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Domenico, M.; Di Giuseppe, M.; Wicochea Rodríguez, J.D.; Cammà, C. Validation of a fast real-time PCR method to detect fraud and mislabeling in milk and dairy products. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Villa, C.; Costa, J.; Oliveira, M.B.P.P.; Mafra, I. Cow’s milk allergens: Screening gene markers for the detection of milk ingredients in complex meat products. Food Control 2020, 108, 106823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Zhu, P.; Pi, F.; Sun, C.; Sun, J.; Jia, M.; Ying, C.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, X. Development of a liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for simultaneous detection of the main milk allergens. Food Control 2017, 74, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montowska, M.; Fornal, E. Detection of peptide markers of soy, milk and egg white allergenic proteins in poultry products by LC-Q-TOF-MS/MS. LWT 2018, 87, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor-Vargas, C.; Maroto, A.S.; Díaz-Perales, A.; Villaba, M.; Casillas Diaz, N.; Vivanco, F.; Cuesta-Herranz, J. Sensitive detection of major food allergens in breast milk: First gateway for allergenic contact during breastfeeding. Allergy 2015, 70, 1024–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Standard Test May Miss Food Ingredients That Cause Milk Allergy-American Chemical Society. Available online: https://www.acs.org/content/acs/en/pressroom/newsreleases/2012/march/standard-test-may-miss-food-ingredients-that-cause-milk-allergy.html (accessed on 15 October 2019).
- Damodaran, S.; Li, Y. A two-step enzymatic modification method to reduce immuno-reactivity of milk proteins. Food Chem. 2017, 237, 724–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pessato, T.B.; de Carvalho, N.C.; Tavano, O.L.; Fernandes, L.G.R.; de L. Zollner, R.; Netto, F.M. Whey protein isolate hydrolysates obtained with free and immobilized Alcalase: Characterization and detection of residual allergens. Food Res. Int. 2016, 83, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thevenot, D.R.; Tóth, K.; Durst, R.A.; Wilson, G.S. Electrochemical biosensors: Recommended definitions and classification. Pure Appl. Chem. 1999, 71, 2333–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.; Nehra, M.; Kedia, D.; Dilbaghi, N.; Tankeshwar, K.; Kim, K.-H. Nanodiamonds: Emerging face of future nanotechnology. Carbon N. Y. 2019, 143, 678–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehra, M.; Dilbaghi, N.; Hassan, A.A. Carbon-Based Nanomaterials for the development of sensitive nanosensor platforms. Adv. Nanosens. Biol. Environ. Anal. 2019, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhou, J.; Du, X. Electrochemical biosensors for detection of foodborne pathogens. Micromachines 2019, 10, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saberi, R.S.; Shahrokhian, S.; Marrazza, G. Amplified electrochemical DNA sensor based on polyaniline film and gold nanoparticles. Electroanalysis 2013, 25, 1373–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, J.I.A.; Yusof, N.A. The strategies of DNA immobilization and hybridization detection mechanism in the construction of electrochemical DNA sensor: A review. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2017, 16, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilescu, A.; Nunes, G.; Hayat, A.; Latif, U.; Marty, J.L. Electrochemical affinity biosensors based on disposable screen-printed electrodes for detection of food allergens. Sensors 2016, 16, 1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Restani, P.; Gaiaschi, A.; Plebani, A.; Beretta, B.; Cavagni, G.; Fiocchi, A.; Poiesi, C.; Velonà, T.; Ugazio, A.G.; Galli, C.L. Cross-reactivity between milk proteins from different animal species. Clin. Exp. Allergy 1999, 29, 997–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehennaoui, S.; Poorahong, S.; Jimenez, G.C.; Siaj, M. Selection of high affinity aptamer-ligand for dexamethasone and its electrochemical biosensor. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Q.; Zhao, H.; Yang, Y.; He, Y.; Ding, N.; Wang, J.; Wu, Z.; Xiang, K.; Wang, G. Electrochemical immunosensor for casein based on gold nanoparticles and poly(l-Arginine)/multi-walled carbon nanotubes composite film functionalized interface. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 3469–3474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Indyk, H.E. Development and application of an optical biosensor immunoassay for α-lactalbumin in bovine milk. Int. Dairy J. 2009, 19, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indyk, H.E.; Filonzi, E.L. Determination of lactoferrin in bovine milk, colostrum and infant formulas by optical biosensor analysis. Int. Dairy J. 2005, 15, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebe Raz, S.; Liu, H.; Norde, W.; Bremer, M.G.E.G. Food allergens profiling with an imaging surface plasmon resonance-based biosensor. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 8485–8491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Valdepeñas Montiel, V.; Campuzano, S.; Torrente-Rodríguez, R.M.; Reviejo, A.J.; Pingarrón, J.M. Electrochemical magnetic beads-based immunosensing platform for the determination of α-lactalbumin in milk. Food Chem. 2016, 213, 595–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohensinner, V.; Maier, I.; Pittner, F. A “gold cluster-linked immunosorbent assay”: Optical near-field biosensor chip for the detection of allergenic β-lactoglobulin in processed milk matrices. J. Biotechnol. 2007, 130, 385–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eissa, S.; Zourob, M. In vitro selection of DNA aptamers targeting β-lactoglobulin and their integration in graphene-based biosensor for the detection of milk allergen. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 91, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eissa, S.; Tlili, C.; L’Hocine, L.; Zourob, M. Electrochemical immunosensor for the milk allergen β-lactoglobulin based on electrografting of organic film on graphene modified screen-printed carbon electrodes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 38, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Billakanti, J.M.; Fee, C.J.; Lane, F.R.; Kash, A.S.; Fredericks, R. Simultaneous, quantitative detection of five whey proteins in multiple samples by surface plasmon resonance. Int. Dairy J. 2010, 20, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Valdepeñas Montiel, V.; Campuzano, S.; Conzuelo, F.; Torrente-Rodríguez, R.M.; Gamella, M.; Reviejo, A.J.; Pingarrón, J.M. Electrochemical magnetoimmunosensing platform for determination of the milk allergen β-lactoglobulin. Talanta 2015, 131, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashley, J.; D’Aurelio, R.; Piekarska, M.; Temblay, J.; Pleasants, M.; Trinh, L.; Rodgers, T.L.; Tothill, I.E. Development of a β-Lactoglobulin sensor based on SPR for milk allergens detection. Biosensors 2018, 8, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Álvarez, J.; Sola, L.; Cretich, M.; Swann, M.J.; Gylfasson, K.B.; Volden, T.; Chiari, M.; Hill, D. Real time optical immunosensing with flow-through porous alumina membranes. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 202, 834–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, B.; Feng, Y.; He, W. Two-site antibody immunoanalytical detection of food allergens by surface plasmon resonance. Food Anal. Methods 2016, 9, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, A.; Zheng, Y.; Long, C.; Chen, H.; Liu, B.; Li, X.; Yuan, J.; Cheng, F. Fluorescent immunosorbent assay for the detection of alpha lactalbumin in dairy products with monoclonal antibody bioconjugated with CdSe/ZnS quantum dots. Food Chem. 2014, 150, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokkinos, C.; Angelopoulou, M.; Economou, A.; Prodromidis, M.; Florou, A.; Haasnoot, W.; Petrou, P.; Kakabakos, S. Lab-on-a-membrane foldable devices for duplex drop-volume electrochemical biosensing using quantum dot tags. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 6897–6904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Ge, P.; Wang, L.; Jiang, H.; Yang, M.; Yuan, L.; Ge, Q.; Fang, W.; Ju, X. A novel electrochemical mast cell-based paper biosensor for the rapid detection of milk allergen casein. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 130, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Cen, Y.; Sohail, M.; Xu, G.; Wei, F.; Ma, Y.; Xu, X.; Ma, Y.; Song, Y.; Hu, Q. Aptamer based fluorometric β-lactoglobulin assay based on the use of magnetic nanoparticles and carbon dots. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente, A.P.B.; Kuang, H.; Shabana, A.M.; Labuza, T.P.; Kokkoli, E. Design of an aptamer-amphiphile for the detection of β-lactoglobulin on a liquid crystal interface. Bioconjug. Chem. 2019, 30, 2763–2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lettieri, M.; Hosu, O.; Adumitrachioaie, A.; Cristea, C.; Marrazza, G. Beta-lactoglobulin electrochemical detection based with an innovative platform based on composite polymer. Electroanalysis 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Li, H.; Jia, W.; Liu, X.; Li, Z.; Wen, F.; Zheng, N.; Jiang, J.; Xu, D. Bivalent aptasensor based on silver-enhanced fluorescence polarization for rapid detection of lactoferrin in milk. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 5900–5908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tah, A.; Cordero, J.M.O.; Weng, X.; Neethirajan, S. Aptamer-based biosensor for food allergen determination using graphene oxide/gold nanocomposite on a paper-assisted analytical device. bioRxiv 2018, 343368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felix, F.S.; Angnes, L. Electrochemical immunosensors–A powerful tool for analytical applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 102, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, I.-H.; Lee, J.; Kim, J.; Kang, M.; Paik, J.; Ku, S.; Cho, H.-M.; Irudayaraj, J.; Kim, D.-H. Current technologies of electrochemical immunosensors: Perspective on signal amplification. Sensors 2018, 18, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rynne, N.M.; Beresford, T.P.; Kelly, A.L.; Guinee, T.P. Effect of milk pasteurization temperature and in situ whey protein denaturation on the composition, texture and heat-induced functionality of half-fat Cheddar cheese. Int. Dairy J. 2004, 14, 989–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackman, J.A.; Cho, N.J.; Nishikawa, M.; Yoshikawa, G.; Mori, T.; Shrestha, L.K.; Ariga, K. Materials Nanoarchitectonics for Mechanical Tools in Chemical and Biological Sensing. Chem.-Asian J. 2018, 13, 3366–3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, Y.; Pan, M.; Wang, L.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Gu, Y.; Yang, J.; Wang, S. Fabrication and evaluation of a label-free piezoelectric immunosensor for sensitive and selective detection of amantadine in foods of animal origin. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 5745–5753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrazza, G. Piezoelectric biosensors for organophosphate and carbamate pesticides: A review. Biosensors 2014, 4, 301–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khansili, N.; Rattu, G.; Krishna, P.M. Label-free optical biosensors for food and biological sensor applications. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 265, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Shi, Z.; Liu, Q. Smartphone-based Biosensors for Portable Food Evaluation. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2019, 28, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steglich, P.; Hülsemann, M.; Dietzel, B.; Mai, A. Optical biosensors based on silicon-on-insulator ring resonators: A review. Molecules 2019, 24, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Daems, D.; Lu, J.; Delport, F.; Mariën, N.; Orbie, L.; Aernouts, B.; Adriaens, I.; Huybrechts, T.; Saeys, W.; Spasic, D.; et al. Competitive inhibition assay for the detection of progesterone in dairy milk using a fiber optic SPR biosensor. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 950, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Qi, Q.; Wang, C.; Qian, Y.; Liu, G.; Wang, Y.; Fu, L. Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) biosensors for food allergen detection in food matrices. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 142, 111449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashley, J.; Piekarska, M.; Segers, C.; Trinh, L.; Rodgers, T.; Willey, R.; Tothill, I.E. An SPR based sensor for allergens detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 88, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Indyk, H.E.; Hart, S.; Meerkerk, T.; Gill, B.D.; Woollard, D.C. The β -lactoglobulin content of bovine milk: Development and application of a biosensor immunoassay. Int. Dairy J. 2017, 73, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarano, S.; Scuffi, C.; Mascini, M.; Minunni, M. Surface Plasmon Resonance imaging-based sensing for anti-bovine immunoglobulins detection in human milk and serum. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 707, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosaka, P.M.; Pini, V.; Ruz, J.J.; da Silva, R.A.; González, M.U.; Ramos, D.; Calleja, M.; Tamayo, J. Detection of cancer biomarkers in serum using a hybrid mechanical and optoplasmonic nanosensor. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2014, 9, 1047–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricciardi, C.; Santoro, K.; Stassi, S.; Lamberti, C.; Gabriella, M.; Arlorio, M.; Decastelli, L. Microcantilever resonator arrays for immunodetection of β-lactoglobulin milk allergen. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 254, 613–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Valdepeñas Montiel, V.; Povedano, E.; Benedé, S.; Mata, L.; Galán-Malo, P.; Gamella, M.; Reviejo, A.J.; Campuzano, S.; Pingarrón, J.M. Disposable amperometric immunosensor for the detection of adulteration in milk through single or multiplexed determination of bovine, ovine, or caprine immunoglobulins G. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 11266–11274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reverté, L.; Prieto-Simón, B.; Campàs, M. New advances in electrochemical biosensors for the detection of toxins: Nanomaterials, magnetic beads and microfluidics systems. A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 908, 8–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serafín, V.; Torrente-Rodríguez, R.M.; Batlle, M.; García de Frutos, P.; Campuzano, S.; Yáñez-Sedeño, P.; Pingarrón, J.M. Comparative evaluation of the performance of electrochemical immunosensors using magnetic microparticles and nanoparticles. Application to the determination of tyrosine kinase receptor AXL. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 4251–4258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Neuta, I.; Neumann, F.; Brightmeyer, J.; Ba Tis, T.; Madaboosi, N.; Wei, Q.; Ozcan, A.; Nilsson, M. Smartphone-based clinical diagnostics: Towards democratization of evidence-based health care. J. Intern. Med. 2019, 285, 19–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vashist, S.K.; van Oordt, T.; Schneider, E.M.; Zengerle, R.; von Stetten, F.; Luong, J.H.T. A smartphone-based colorimetric reader for bioanalytical applications using the screen-based bottom illumination provided by gadgets. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 67, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zangheri, M.; Cevenini, L.; Anfossi, L.; Baggiani, C.; Simoni, P.; Di Nardo, F.; Roda, A. A simple and compact smartphone accessory for quantitative chemiluminescence-based lateral flow immunoassay for salivary cortisol detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 64, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Liu, Q. Biosensors and bioelectronics on smartphone for portable biochemical detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 75, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosu, O.; Ravalli, A.; Lo Piccolo, G.M.; Cristea, C.; Sandulescu, R.; Marrazza, G. Smartphone-based immunosensor for CA125 detection. Talanta 2017, 166, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, G.M.S.; Bremer, M.G.E.G.; Nielen, M.W.F. Consumer-friendly food allergen detection: Moving towards smartphone-based immunoassays. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 5353–5371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shahvar, A.; Saraji, M.; Shamsaei, D. Headspace single drop microextraction combined with mobile phone-based on-drop sensing for the determination of formaldehyde. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 273, 1474–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, S.K.J.; Zhu, H.; Phillips, S.; Shiledar, A.; Feng, S.; Tseng, D.; Van Ginkel, L.A.; Nielen, M.W.F.; Ozcan, A. Cellphone-based detection platform for rbST biomarker analysis in milk extracts using a microsphere fluorescence immunoassay. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 6857–6866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludwig, S.K.J.; Tokarski, C.; Lang, S.N.; van Ginkel, L.A.; Zhu, H.; Ozcan, A.; Nielen, M.W.F. Calling biomarkers in milk using a protein microarray on your smartphone. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molinari, J.; Moina, C.; Ybarra, G. Electrochemical immunosensor for the determination of β-casein. J. Electrochem. Sci. Eng. 2015, 5, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Zhu, P.; Jiang, H.; Ji, J.; Sun, X.; Gu, W.; Zhang, G. Fluorescent magnetic bead-based mast cell biosensor for electrochemical detection of allergens in foodstuffs. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 70, 482–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelopoulou, Μ.; Botsialas, A.; Salapatas, A.; Petrou, P.S.; Haasnoot, W.; Makarona, E.; Jobst, G.; Goustouridis, D.; Siafaka-Kapadai, A.; Raptis, I.; et al. Assessment of goat milk adulteration with a label-free monolithically integrated optoelectronic biosensor. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 3995–4004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Arribas, L.N.; Benito-Peña, E.; Del Carmen Hurtado-Sánchez, M.; Moreno-Bondi, M.C. Biosensing based on nanoparticles for food allergens detection. Sensors 2018, 18, 1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Tang, S.; Zhang, W.; Cui, X.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y. A surface-enhanced Raman scattering-based lateral flow immunosensor for colistin in raw milk. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, D.S.; Cassola, A. Novel sensitive monoclonal antibody based competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the detection of raw and processed bovine beta-casein. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toh, S.Y.; Citartan, M.; Gopinath, S.C.B.; Tang, T.-H. Aptamers as a replacement for antibodies in enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 64, 392–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khedri, M.; Ramezani, M.; Rafatpanah, H.; Abnous, K. Detection of food-born allergens with aptamer-based biosensors. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 103, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jauset-Rubio, M.; El-Shahawi, M.S.; Bashammakh, A.S.; Alyoubi, A.O.; O′Sullivan, C.K. Advances in aptamers-based lateral flow assays. TrAC-Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 97, 385–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malekzad, H.; Jouyban, A.; Hasanzadeh, M.; Shadjou, N.; de la Guardia, M. Ensuring food safety using aptamer based assays: Electroanalytical approach. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 94, 77–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilescu, A.; Marty, J.-L. Electrochemical aptasensors for the assessment of food quality and safety. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 79, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassolas, A.; Blum, L.J.; Béatrice, D.L.B. Electrochemical aptasensors. Electroanalysis 2009, 21, 1237–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Li, H.; Sun, W.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, D.; He, F. Selection of aptamers against Lactoferrin based on silver enhanced and fluorescence-activated cell sorting. Talanta 2019, 193, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, H.; Jia, W.; Chen, Z.; Xu, D. Selection of aptamers based on a protein microarray integrated with a microfluidic chip. Lab Chip 2017, 17, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, Q.; Sun, M.; Zhang, J.; Mo, S.; Wang, J.; Wei, X.; Bai, J. Magnetic-assisted aptamer-based fluorescent assay for allergen detection in food matrix. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 263, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frohnmeyer, E.; Tuschel, N.; Sitz, T.; Hermann, C.; Dahl, G.T.; Schulz, F.; Baeumner, A.J.; Fischer, M. Aptamer lateral flow assays for rapid and sensitive detection of cholera toxin. Analyst 2019, 144, 1840–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Nehra, M.; Mehta, J.; Dilbaghi, N.; Marrazza, G.; Kaushik, A. Point-of-care strategies for detection of waterborne pathogens. Sensors 2019, 19, 4476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verdian, A. Apta-nanosensors for detection and quantitative determination of acetamiprid–A pesticide residue in food and environment. Talanta 2018, 176, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javidi, M.; Housaindokht, M.R.; Verdian, A.; Razavizadeh, B.M. Detection of chloramphenicol using a novel apta-sensing platform based on aptamer terminal-lock in milk samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1039, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Wang, C.; Wang, Q.; Chen, D. Resonance light scattering method for detecting kanamycin in milk with enhanced sensitivity. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 2839–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luan, Q.; Gan, N.; Cao, Y.; Li, T. Mimicking an Enzyme-Based Colorimetric Aptasensor for Antibiotic Residue Detection in Milk Combining Magnetic Loop-DNA Probes and CHA-Assisted Target Recycling Amplification. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 5731–5740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Y.; Tang, Y.; Li, B.; Gu, C.; He, M. Aptamer-based detection of melamine in milk using an evanescent wave fiber sensor. Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 4871–4878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beta-Lactoglobulin ELISA Kit II, Milk Allergen Kit | Crystal Chem. Available online: http://www.crystalchem.com/beta-lactoglobulin-elisa-kit.html (accessed on 19 October 2019).
- SENSISpec Spike Solution Beta-Lactoglobulin. Available online: https://www.eurofins-technologies.com/sensispec-spike-solution-beta-lactoglobulin.html (accessed on 19 October 2019).
- RIDASCREEN®FAST Milk (en)- Food & Feed Analysis. Available online: https://food.r-biopharm.com/products/ridascreenfast-milk/ (accessed on 22 November 2019).
- AgraStrip® Total Milk. Available online: https://www.romerlabs.com/shop/inter_en/agrastrip-r-total-milk/#theme.catalog.product.additional.information.documents.detailed (accessed on 19 October 2019).
- Reveal 3-D Food Allergen Test Strips | Food Safety | Neogen. Available online: https://foodsafety.neogen.com/en/reveal-3-d (accessed on 19 October 2019).
- Lateral Flow Milk (en)- Food & Feed Analysis. Available online: https://food.r-biopharm.com/products/lateral-flow-milk/ (accessed on 19 October 2019).
- AlerTox Sticks Total Milk: Rapid testing for Anitgens. Available online: https://emportllc.com/product/alertox-total-milk/ (accessed on 19 October 2019).
- Aller-ROSA-Charm Sciences. Available online: https://www.charm.com/products/test-and-kits/allergen-tests/aller-rosa/ (accessed on 19 October 2019).
- About Us-Sensogenic. Available online: http://www.sensogenic.com/about-us/ (accessed on 22 November 2019).
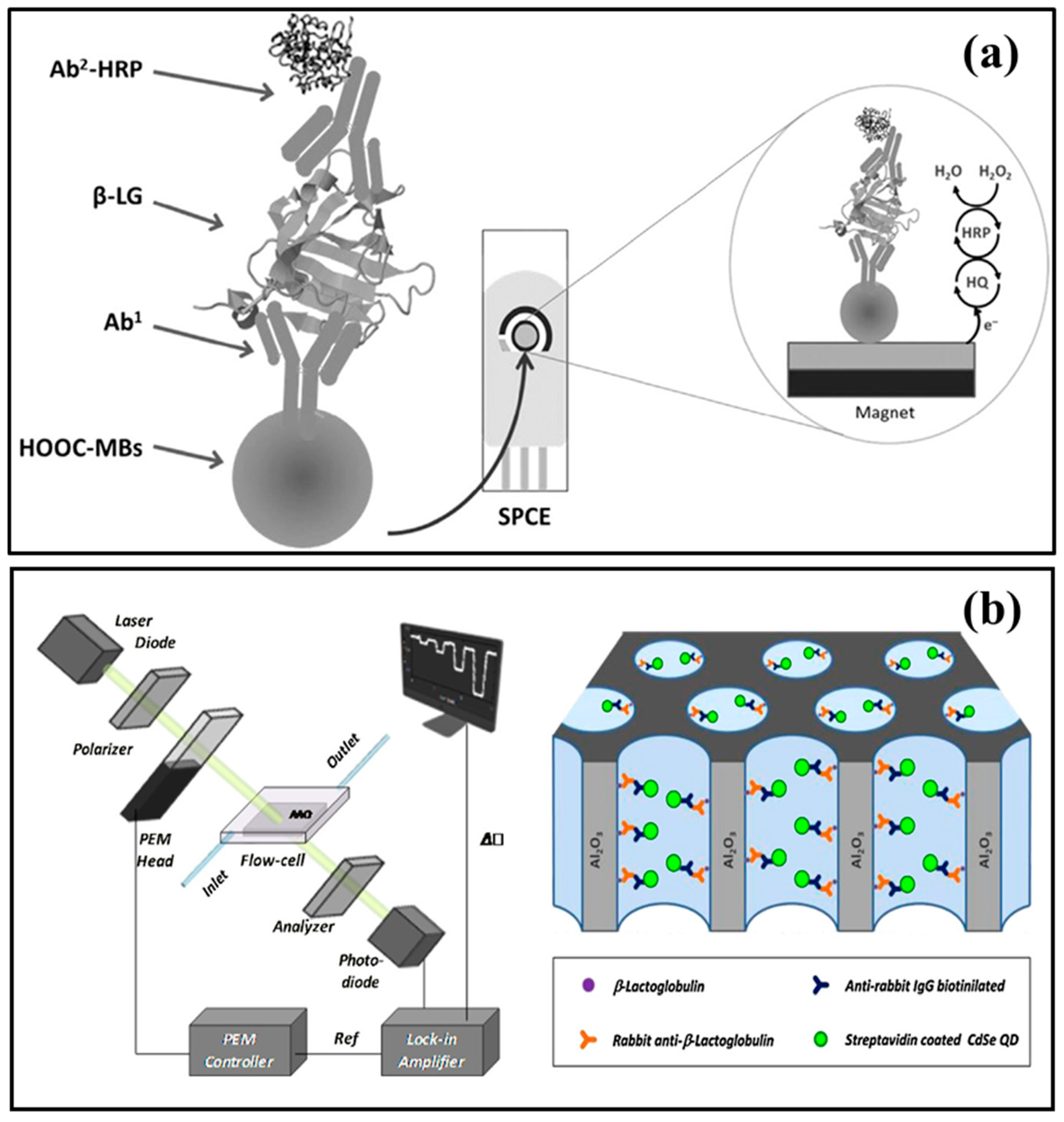

| Protein Name | Allergen Nomenclature | Conc. in Milk (g L−1) | Isoelectric Point | Number of Amino Acids/Molecules | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Casein proteins (80%) (≈5 g L−1) | αS1-casein | Bos d 9 | 12.0–15.0 | 4.9–5.0 | 199 |
| αS2-casein | Bos d 10 | 3.0–4.0 | 5.2–5.4 | 207 | |
| β-casein | Bos d 11 | 9.0–11.0 | 5.1–5.4 | 209 | |
| κ-casein | Bos d 12 | 3.0–4.0 | 5.4–5.6 | 169 | |
| Whey Proteins (20%) (≈30 g L−1) | α-Lactalbumin | Bos d 4 | 1.0–1.5 | 4.8 | 123 |
| β-Lactoglobulin | Bos d 5 | 3.0–4.0 | 5.3 | 162 | |
| BSA | Bos d 6 | 0.1–0.4 | 4.9–5.1 | 582 | |
| Immunoglobulins | Bos d 7 | 0.6–1.0 |
| S. No. | Aptamer Sequence | Affinity Constant, Kd (nM) | Targeted Milk Allergen | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CGACGATCGGACCGCAGTACCCACCCACCAGCCCCAACATCATGCCCATCCGTGTGTG | 82 ± 30 and 80 ± 26 | β-lactoglobulin A and B | [64] |
| 2 | 5′-GGGGTTGGGGTGTGGGGTTGGGG/3AmMO/-3′ | 22 ± 2 | β-lactoglobulin | [75] |
| 3 | 5′-FITC-AGGCAGGACACCGTAACCGGTGCATCTATGGCTACTAGCTCTTCCTGCCT-3′ | 28.78 ± 7.20 | lactoferrin | [77] |
| 4 | ATA CCA GCT TAT TCA ATT CGA CGA TCG GAC CGC AGT ACC CAC CCA CCA GCC CCA ACA TCA TGC CCA TCC GTG TGT GAG ATA GTA AGT GCA ATC T | -- | β-lactoglobulin | [78] |
| 5 | CGGTGCATCTATGGCTACTAGCTTTTCCTGCCTATACTAC | 1.04 ± 0.50 | lactoferrin | [120] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nehra, M.; Lettieri, M.; Dilbaghi, N.; Kumar, S.; Marrazza, G. Nano-Biosensing Platforms for Detection of Cow’s Milk Allergens: An Overview. Sensors 2020, 20, 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20010032
Nehra M, Lettieri M, Dilbaghi N, Kumar S, Marrazza G. Nano-Biosensing Platforms for Detection of Cow’s Milk Allergens: An Overview. Sensors. 2020; 20(1):32. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20010032
Chicago/Turabian StyleNehra, Monika, Mariagrazia Lettieri, Neeraj Dilbaghi, Sandeep Kumar, and Giovanna Marrazza. 2020. "Nano-Biosensing Platforms for Detection of Cow’s Milk Allergens: An Overview" Sensors 20, no. 1: 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20010032
APA StyleNehra, M., Lettieri, M., Dilbaghi, N., Kumar, S., & Marrazza, G. (2020). Nano-Biosensing Platforms for Detection of Cow’s Milk Allergens: An Overview. Sensors, 20(1), 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20010032






