Optimal Geostatistical Methods for Interpolation of the Ionosphere: A Case Study on the St Patrick’s Day Storm of 2015
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
- IDW = 0.45 × RMSE (100% data) + 0.05 × ME (100% data) + 0.45 × RMSE (90% data) + 0.05 × ME (90% data);
- GPI = 0.45 × RMSE (100% data) + 0.05 × ME (100% data) + 0.45 × RMSE (90% data) + 0.05 × ME (90% data);
- OK = 0.45 × RMSE (100% data) + 0.05 × ME (100% data) + 0.45 × RMSE (90% data) + 0.05 × ME (90% data).
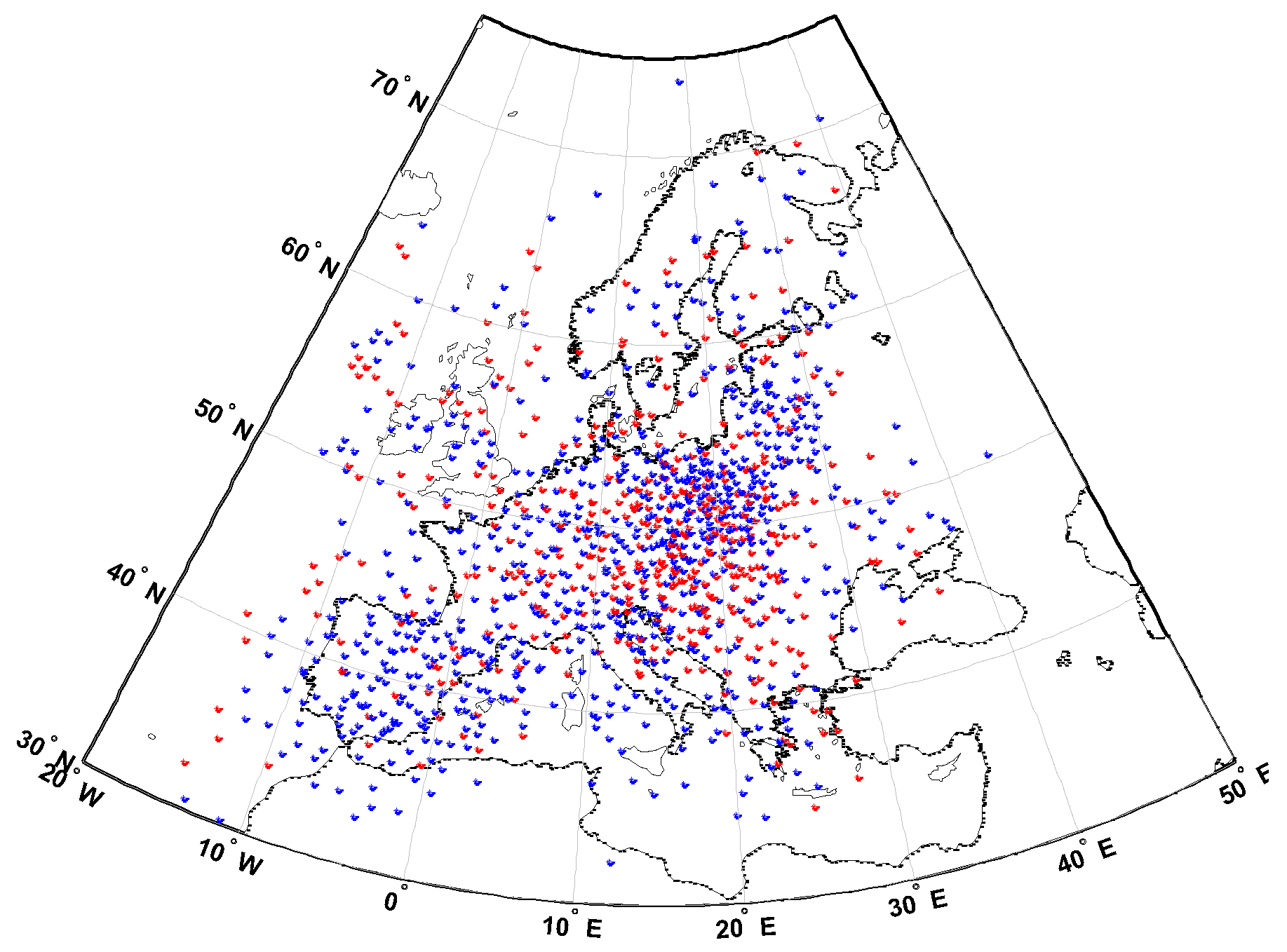
3. Experiment
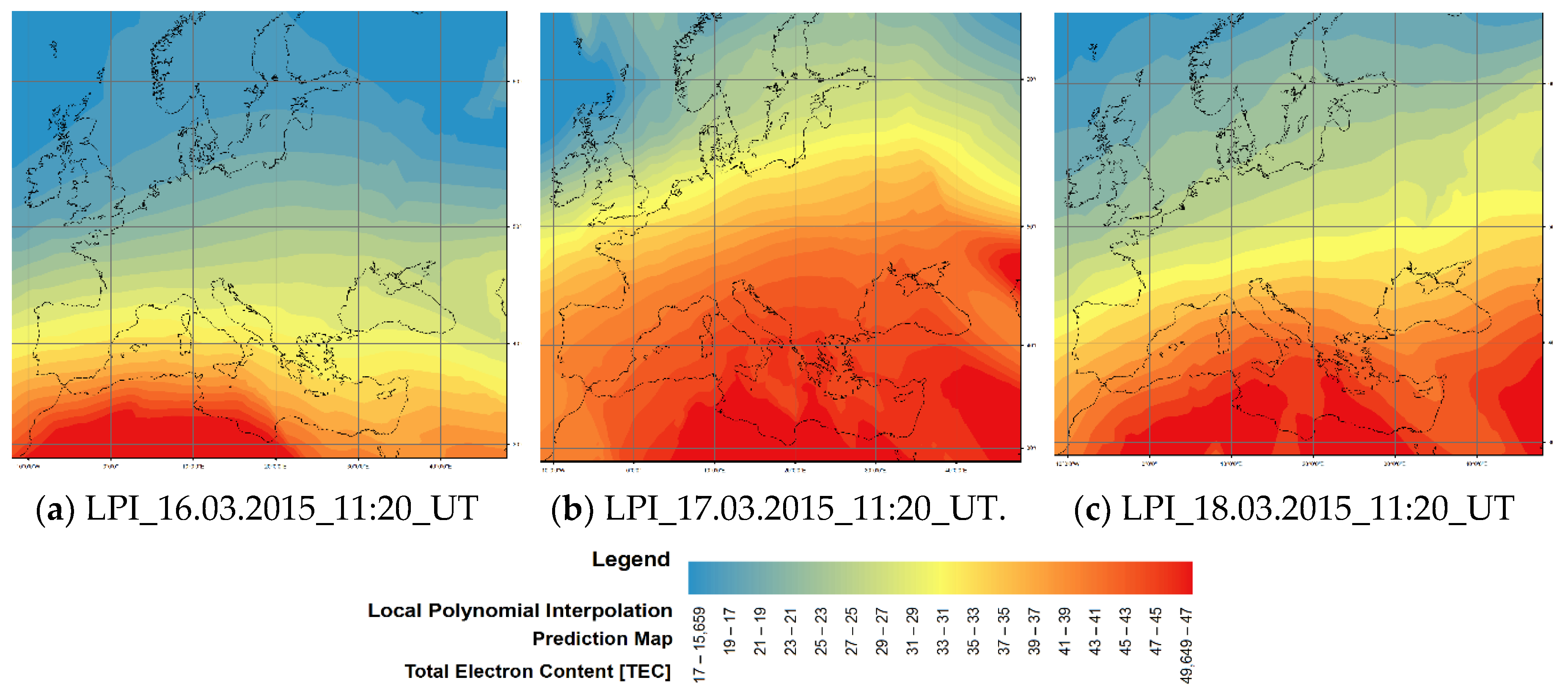
- 16 March is characterised by a regular state of the ionosphere with ƩKp = 19;
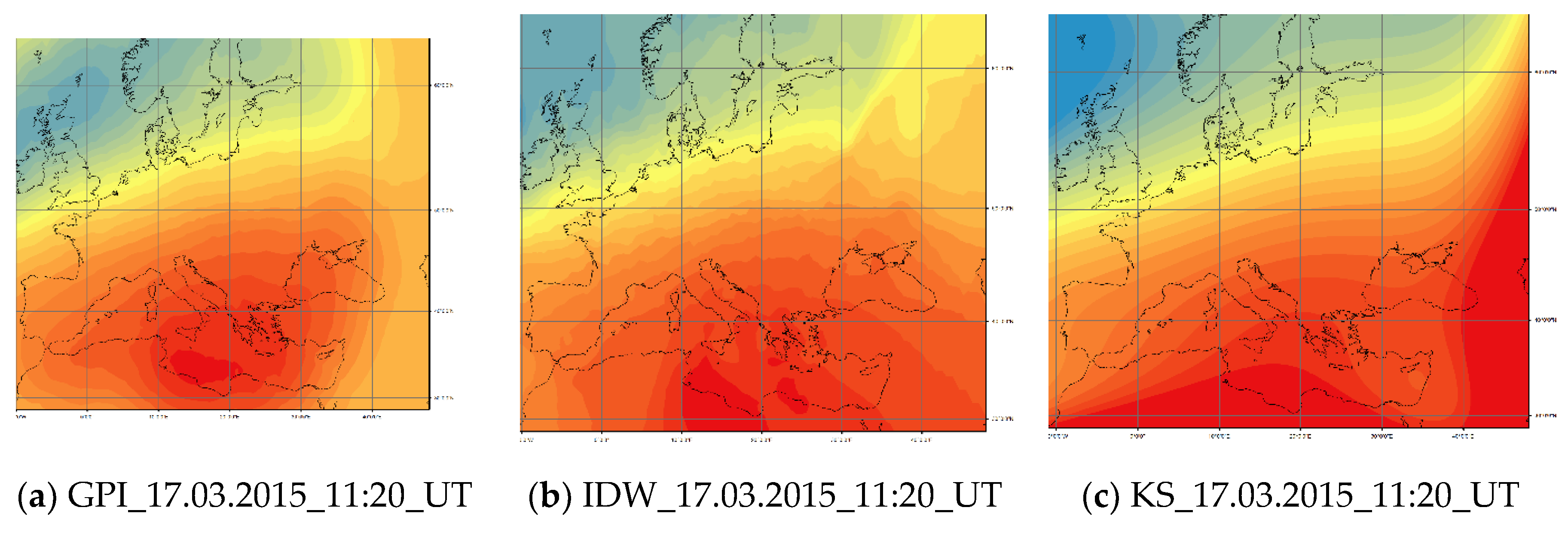
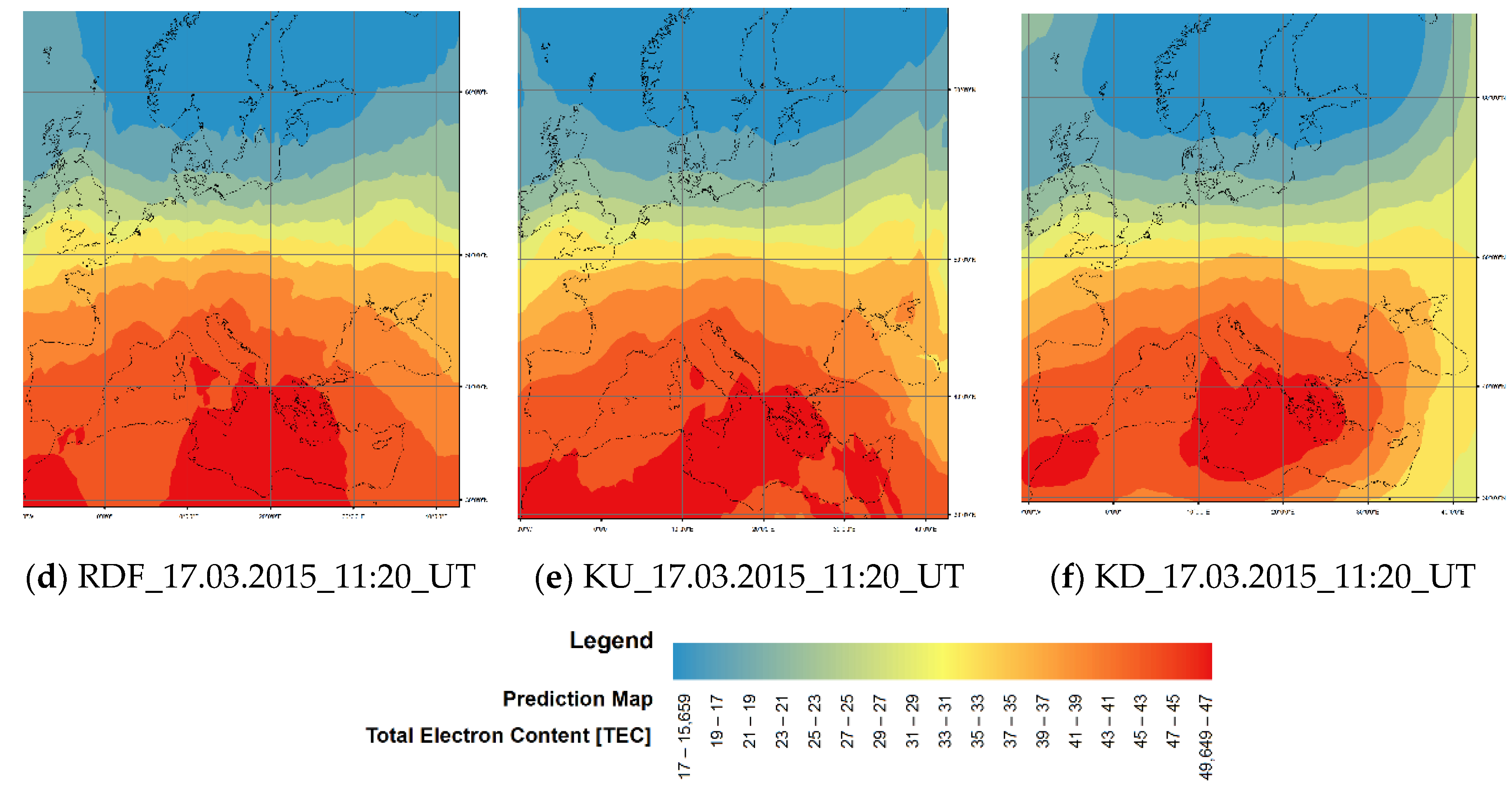
- 17 March is a stormy day with dynamic TEC variations and a clear increase over Europe with ƩKp = 48 [16];
- 18 March presents the recovery phase of the storm, with low TEC value and ƩKp = 39. The observational dataset included:
- Dual-frequency carrier phase and pseudorange GPS + GLONASS data from:
- ○
- 50 GNSS stations of the Polish ASG-EUPOS network,
- ○
- 200 GNSS stations of the EPN network,
- Sampling interval: 60 s,
- Data elevation cut-off: 30 degrees.
4. Validation
- Stage 1: Preliminary data analysis;
- Stage 2: Mapping by different interpolation methods;
- Stage 3: Execution of validation;
- Stage 4: Comparison of estimation assessment parameters;
- Stage 5: Selection of the optimal geostatistical method.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hofmann-Wellenhof, B.; Lichtenegger, H.; Wasle, E. GNSS—Global Navigation Satellite Systems; Springer: Vienna, Austria, 2008; ISBN 978-3-7091-6199-9. [Google Scholar]
- Leick, A.; Rapoport, L.; Tatarnikov, D. GPS Satellite Surveying; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; ISBN 978-1-118-67557-1. [Google Scholar]
- Bosy, J. Data processing of local gps network located in a mountain area. Acta Geodyn. Geomater. 2005, 2, 43–47. [Google Scholar]
- Odijk, D. Weighting ionospheric corrections to improve fast GPS positioning over medium distances. In Proceedings of the ION GPS, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 19–22 September 2000; pp. 1113–1123. [Google Scholar]
- Paziewski, J.; Wielgosz, P. Assessment of the multi-frequency Galileo and integrated GPS + Galileo single-epoch precise positioning supported with network corrections. GPS Solut. 2014, 18, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, T.; Böhm, J.; Wijaya, D.D.; Tresch, A.; Nafisi, V.; Schuh, H. Path Delays in the Neutral Atmosphere. In Atmospheric Effects in Space Geodesy, Springer Atmospheric Sciences; Böhm, J., Schuh, H., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2013; pp. 73–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krypiak-Gregorczyk, A. Ionosphere response to three extreme events occurring near spring equinox in 2012, 2013 and 2015, observed by regional GNSS-TEC model. J. Geod. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Cardellach, E.; Xie, F. GNSS Remote Sensing: Theory, Methods and Applications; Springer Netherlands: New Delhi, India, 2014; ISBN 9789400774810. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández-Pajares, M.; Roma-Dollase, D.; Krankowski, A.; García-Rigo, A.; Orús-Pérez, R. Methodology and consistency of slant and vertical assessments for ionospheric electron content models. J. Geod. 2017, 91, 1405–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovira-Garcia, A.; Juan, J.M.; Sanz, J.; González-Casado, G.; Ibáñez, D. Accuracy of ionospheric models used in GNSS and SBAS: Methodology and analysis. J. Geod. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, M.M.; Schuh, H.; Todorova, S.; Schmidt, M. (2011) Global ionosphere maps of VTEC from GNSS, satellite altimetry, and formosat-3/COSMIC data. J. Geod. 2016, 85, 975–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orus, M.; Hernandez-Pajares, M.; Juan, J.M.; Sanz, J. Improvement of global ionospheric VTEC maps by using kriging interpolation technique. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2005, 67, 1598–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanislawska, I.; Juchnikowski, G.; Cander, L.; Ciraolo, L.; Bradley, P.A.; Zbyszyński, Z.; Swiatek, A. The kriging method of TEC instantaneous mapping. Adv. Space Res. 2002, 29, 945–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deviren, M.; Arikan, F. IONOLAB-MAP: An automatic spatial interpolation algorithm for total electron content. Turk. J. Electr. Eng. Comput. Sci. 2018, 26, 1933–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, A.K.; Nagori, N.; Das, S.; Jain, N.; Sivaraman, M.R.; Bandyopadhyay, K. Statistical Comparison of Various Interpolation Algorithms for GridBased Single Shell Ionospheric Model over Indian Region. J. Glob. Position Syst. 2008, 7, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astafyeva, E.; Zhakarenkova, I.; Forster, M. Ionospheric response to the 2015 St. Patrick’s Day Storm: A global multi-instrumental overview. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2015, 120, 9023–9037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krypiak-Gregorczyk, A.; Wielgosz, P. Carrier phase bias estimation of geometry-free linear combination of GNSS signals for ionospheric TEC modeling. GPS Solut. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krivoruchko, K. Using ArcGIS Geostatistical Analyst; Esri: Redlands, CA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Matheron, G. Traité de Géostatistique Appliquée. Volume I; Technip: Paris, France, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Matheron, G. Traité de Géostatistique Appliquée. 2. Le krigeage; Volume II; Technip: Paris, France, 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Krige, D.G. A statistical approach to some basic mine valuation problems on the Witwatersrand. J. Chem. Metall. Min. Soc. South. Afr. 1951, 52, 119–139. [Google Scholar]
- Krige, D.G. A statistical analysis of some of the borehole values in the Orange Free State goldfield. J. Chem. Metall. Min. Soc. South. Afr. 1952, 53, 47–64. [Google Scholar]
- Hengl, T. A Practical Guide to Geostatistical Mapping of Environmental Variables; Office for Official Publications of the European Communities: Ispra (VA), Italy, 2011; ISBN 9789279069048.
- Sarma, D.D. Geostatistics with Applications in Earth Sciences; Springer Netherlands: New Delhi, India, 2009; ISBN 9781402093791. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, F.; Guo, H.-C.; Ho, Y.-S.; Wu, C.-Z. Scientometric analysis of geostatistics using multivariate methods. Scientometrics 2007, 73, 265–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cressie, N. Statistics for Spatial Data; John Willy and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1993; ISBN 978-1-119-11461-1. [Google Scholar]
- Stach, A. Analiza Struktury Przestrzennej i Czasoprzestrzennej Maksymalnych Opadów Dobowych w Polsce w latach 1956–1980; Uniwersytet im. Adama Mickiewicza w Poznaniu Seria Geografia Nr 85: Poznań, Poland, 2009; ISBN 9788323219880. [Google Scholar]
- Isaaks, E.H.; Srivastava, R.M. Applied Geostatistics; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1989; ISBN 9780195050134. [Google Scholar]
- Goovaerts, P. Geostatistics for Natural Resources Evaluation; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1997; ISBN 0-19-511538-4. [Google Scholar]
- Krivoruchko, K. Spatial Statistical Data Analysis for GIS Users; Esri Press: Redlands, CA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Matheron, G. Les Variables Régionalisées et Leur Estimation: Une Application de la Théorie des Fonctions Aléatoires aux Sciences de la Nature; Masson et CIE: Paris, France, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Ogryzek, M. When AI does spatial planning and data management, in the monograph. In AI: LAW, PHILOSOPHY & GEOINFORMATICS; Geo&IP Series: Warsaw, Poland, 2015; pp. 153–169. ISBN 978-83-64611-88-9. [Google Scholar]
- Ogryzek, M. Parametric evaluation of the quality of estimation of maps developed by geostatistical methods. Stud. Pr. WNEiZ 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogryzek, M.; Kurowska, K. Geostatystyczne metody opracowywania map średnich cen transakcyjnych gruntów rolnych niezabudowanych. Stud. Pr. WNEiZ 45/1 2016, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bosy, J.; Oruba, A.; Graszka, W.; Leonczyk, M.; Ryczywolski, M. ASG-EUPOS Densification of EUREF Permanent Network on the Territory of Poland; Warsaw Univ. of Techn.: Warsaw, Poland, 2008; pp. 105–111. ISBN 978-83-85287-84-1. [Google Scholar]
- Schaer, S. Mapping and Predicting the Earth’s Ionosphere Using the Global Positioning System. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Berne, Bern, Switzerland, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Krypiak-Gregorczyk, A.; Wielgosz, P.; Jarmołowski, W. A new TEC interpolation method based on the least squares collocation for high accuracy regional ionospheric maps. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krypiak-Gregorczyk, A.; Wielgosz, P.; Borkowski, A. Ionosphere model for European region based on multi-GNSS data and TPS interpolation. Remote Sens. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| 100% of Data | 90% of Data | ||||
| Day 75_6 am | ME | RMSE | ME | RMSE | MPQE |
| Inverse distance weighting | 0.013 | 0.545 | 0.0121 | 0.551 | 0.494 |
| Global polynomial interpolation | 0.001 | 0.999 | 0.001 | 1.013 | 0.905 |
| Radial basic functions | 0.005 | 0.587 | 0.003 | 0.627 | 0.546 |
| Local polynomial interpolation | −0.015 | 0.472 | −0.016 | 0.478 | 0.429 |
| Kriging ordinary | −0.001 | 0.476 | −0.002 | 0.479 | 0.430 |
| Kriging simple | −0.029 | 0.530 | −0.030 | 0.535 | 0.482 |
| Kriging universal | −0.001 | 0.476 | −0.002 | 0.479 | 0.430 |
| Empirical Bayesian kriging | 0.001 | 0.487 | 0.001 | 0.489 | 0.439 |
| 100% of Data | 90% of Data | ||||
| Day 76_6 am | ME | RMSE | ME | RMSE | MPQE |
| Inverse distance weighting | 0.006 | 0.540 | 0.005 | 0.547 | 0.490 |
| Global polynomial interpolation | 0.001 | 1.094 | 0.000 | 1.103 | 0.989 |
| Radial basic functions | 0.002 | 0.517 | 0.001 | 0.524 | 0.469 |
| Local polynomial interpolation | 0.001 | 0.470 | −0.001 | 0.478 | 0.426 |
| Kriging ordinary | −0.001 | 0.474 | −0.001 | 0.481 | 0.430 |
| Kriging simple | 0.169 | 0.573 | 0.174 | 0.590 | 0.540 |
| Kriging universal | −0.001 | 0.474 | −0.001 | 0.481 | 0.430 |
| Kriging disjunctive | −0.002 | 0.489 | −0.001 | 0.496 | 0.443 |
| 100% of Data | 90% of Data | ||||
| Day 77_6 am | ME | RMSE | ME | RMSE | MPQE |
| Inverse distance weighting | −0.023 | 0.359 | −0.025 | 0.369 | 0.330 |
| Global polynomial interpolation | −0.001 | 1.635 | −0.000 | 1.614 | 1.4624 |
| Radial basic functions | −0.006 | 0.355 | −0.005 | 0.359 | 0.322 |
| Local polynomial interpolation | 0.039 | 0.255 | 0.029 | 0.257 | 0.234 |
| Kriging ordinary | 0.006 | 0.249 | 0.006 | 0.255 | 0.227 |
| Kriging simple | 0.388 | 0.673 | 0.392 | 0.691 | 0.653 |
| Kriging universal | 0.006 | 0.249 | 0.006 | 0.255 | 0.227 |
| Kriging disjunctive | 0.004 | 0.258 | 0.003 | 0.263 | 0.235 |
| Date | Data Samples | Method | MPQE [TECU] |
|---|---|---|---|
| 16.03.2015 | 19,650 | LPI | 0.51 |
| OK | 0.52 | ||
| RBF | 0.57 | ||
| UK | 0.58 | ||
| IDW | 0.60 | ||
| DK | 0.61 | ||
| SK | 0.65 | ||
| GPI | 0.71 | ||
| 17.03.2015 | 18,900 | LPI | 0.80 |
| OK | 0.81 | ||
| IDW | 0.91 | ||
| UK | 0.94 | ||
| DK | 1.02 | ||
| RBF | 1.08 | ||
| SK | 1.39 | ||
| GPI | 1.44 | ||
| 18.03.2015 | 21,350 | LPI | 0.28 |
| OK | 0.34 | ||
| IDW | 0.38 | ||
| RBF | 0.44 | ||
| UK | 0.44 | ||
| KD | 0.45 | ||
| GPI | 0.57 | ||
| SK | 0.60 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ogryzek, M.; Krypiak-Gregorczyk, A.; Wielgosz, P. Optimal Geostatistical Methods for Interpolation of the Ionosphere: A Case Study on the St Patrick’s Day Storm of 2015. Sensors 2020, 20, 2840. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20102840
Ogryzek M, Krypiak-Gregorczyk A, Wielgosz P. Optimal Geostatistical Methods for Interpolation of the Ionosphere: A Case Study on the St Patrick’s Day Storm of 2015. Sensors. 2020; 20(10):2840. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20102840
Chicago/Turabian StyleOgryzek, Marek, Anna Krypiak-Gregorczyk, and Paweł Wielgosz. 2020. "Optimal Geostatistical Methods for Interpolation of the Ionosphere: A Case Study on the St Patrick’s Day Storm of 2015" Sensors 20, no. 10: 2840. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20102840
APA StyleOgryzek, M., Krypiak-Gregorczyk, A., & Wielgosz, P. (2020). Optimal Geostatistical Methods for Interpolation of the Ionosphere: A Case Study on the St Patrick’s Day Storm of 2015. Sensors, 20(10), 2840. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20102840






