YOLO-Based Simultaneous Target Detection and Classification in Automotive FMCW Radar Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Fundamentals of FMCW Radar
2.1. How to Estimate Range and Velocity Information with Radar
2.2. How to Estimate Angle Information with Radar
3. Proposed Simultaneous Detection and Classification Method
3.1. Brief Description of YOLO
3.2. How to Combine Radar Signals with YOLO
3.3. Brief Overview of Proposed Model
4. Detection and Classification Results
4.1. Measurement Scenarios
4.2. Performance Metric
4.2.1. Detection
4.2.2. Classification
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CNN | Convolutional neural network |
| DBSCAN | Density-based spatial clustering of applications with noise |
| FCN | Fully connected neural network |
| FFT | Fast Fourier transform |
| FMCW | Frequency-modulated-continuous-wave |
| IoU | Intersection over union |
| mAP | Mean average precision |
| NMS | Non-maximum-suppression |
| OS-CFAR | Order statistic-constant false alarm rate |
| RA | Range-angle |
| RCS | Radar cross-section |
| RD | Range-Doppler |
| SVM | Support vector machine |
| YOLO | You only look once |
References
- Variant Market Research. Global Self-Driving Car Market Is Driven By Rising Investments In The Automotive Industry. 2017. Available online: https://www.openpr.com/news/783229/global-self-driving-car-market-is-driven-by-rising-investments-in-the-automotive-industry.html (accessed on 20 May 2020).
- Fleming, W.J. Overview of automotive sensors. IEEE Sens. J. 2001, 4, 296–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, M. Automotive radar-status and trends. In Proceedings of the German Microwave Conference (GeMIC), Ulm, Germany, 5–7 April 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Liaqat, S.; Khan, S.A.; Ihasn, M.B.; Asghar, S.Z.; Ejaz, A.; Bhatti, A.I. Automatic recognition of ground radar targets based on the target RCS and short time spectrum variance. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Innovations in Intelligent Systems and Applications, Istanbul, Turkey, 15–18 June 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Yoon, Y.-J.; Lee, J.-E.; Kim, S.-C. Human-vehicle classification using feature-based SVM in 77-GHz automotive FMCW radar. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2017, 10, 1589–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.; Lee, S.; Yoon, J.; Kim, S.-C. Phase-based target classification using neural network in automotive radar systems. In Proceedings of the IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf), Boston, MA, USA, 22–26 April 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Villeval, S.; Bilik, I.; Gurbuz, S.Z. Application of a 24 GHz FMCW automotive radar for urban target classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE Radar Conference, Cincinnati, OH, USA, 19–23 May 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Rytel-Andrianik, R.; Samczynski, P.; Gromek, D.; Weilgo, J.; Drozdowicz, J.; Malanowski, M. Micro-range, micro-Doppler joint analysis of pedestrian radar echo. In Proceedings of the IEEE Signal Processing Symposium (SPSympo), Debe, Poland, 10–12 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, B.K.; Kang, H.-S.; Park, S.-O. Experimental analysis of small drone polarimetry based on micro-Doppler signature. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 10, 1670–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-E.; Lim, H.-S.; Jeong, S.-H.; Kim, S.-C.; Shin, H.-C. Enhanced Iron-Tunnel Recognition for Automotive Radars. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2016, 6, 4412–4418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Lee, B.-H.; Lee, J.-E.; Kim, S.-C. Statistical characteristic-based road structure recognition in automotive FMCW radar systems. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transport. Syst. 2019, 7, 2418–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, H.; Lee, S.; Lee, B.-H.; Kim, S.-C. Road structure classification through artificial neural network for automotive radar systems. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2019, 6, 1010–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Li, H.; Wenger, F. Object detection and 3D estimation via an FMCW radar using a fully convolutional network. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1902.05394. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, B.K.; Kang, H.-S.; Park, S.-O. Drone classification using convolutional neural networks with merged Doppler images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 1, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadhrami, E.A.; Mufti, M.A.; Taha, B.; Werghi, N. Ground moving radar targets classification based on spectrogram images using convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Radar Symposium (IRS), Bonn, Germany, 20–22 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Cortes, C.; Vapnik, V. Support-vector networks. Mach. Learn. 1995, 20, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 26th Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), Stateline, NV, USA, 3–8 December 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A. Going deeper with convolutions. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.4842. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.; Wei, S.; Cui, Z.; Ding, W. YOLO-RD: A lightweight object detection network for range Doppler radar images. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 042027, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, R.; Schubert, F.; Rasshofer, R.; Biebl, E. Deep learning radar object detection and classification for urban automotive scenarios. In Proceedings of the 2019 Kleinheubach Conference, Miltenberg, Germany, 23–25 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Lee, S.; Kim, S.-C. Modulation type classification of interference signals in automotive radar systems. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2019, 6, 944–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patole, S.M.; Torlak, M.; Wang, D.; Ali, M. Automotive radars: A review of signal processing techniques. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2017, 2, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Yoon, Y.-J.; Lee, J.-E.; Sim, H.; Kim, S.-C. Two-stage DOA estimation method for low SNR signals in automotive radars. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2017, 11, 1613–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Yoon, Y.-J.; Kang, S.; Lee, J.-E.; Kim, S.-C. Enhanced performance of MUSIC algorithm using spatial interpolation in automotive FMCW radar systems. IEICE Trans. Commun. 2018, 1, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kim, S.-C. Logarithmic-domain array interpolation for improved direction of arrival estimation in automotive radars. Sensors 2019, 19, 2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. YOLOv3: An Incremental Improvement. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.02767. [Google Scholar]
- Rohling, H.; Mende, R. OS CFAR performance in a 77 GHz radar sensor for car application. In Proceedings of the International Radar Conference, Beijing, China, 8–10 October 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, S.; Lee, S.; Kim, S.-C. Clustering of detected targets using DBSCAN in automotive radar systems. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Radar Symposium (IRS), Bonn, Germany, 20–22 June 2018. [Google Scholar]

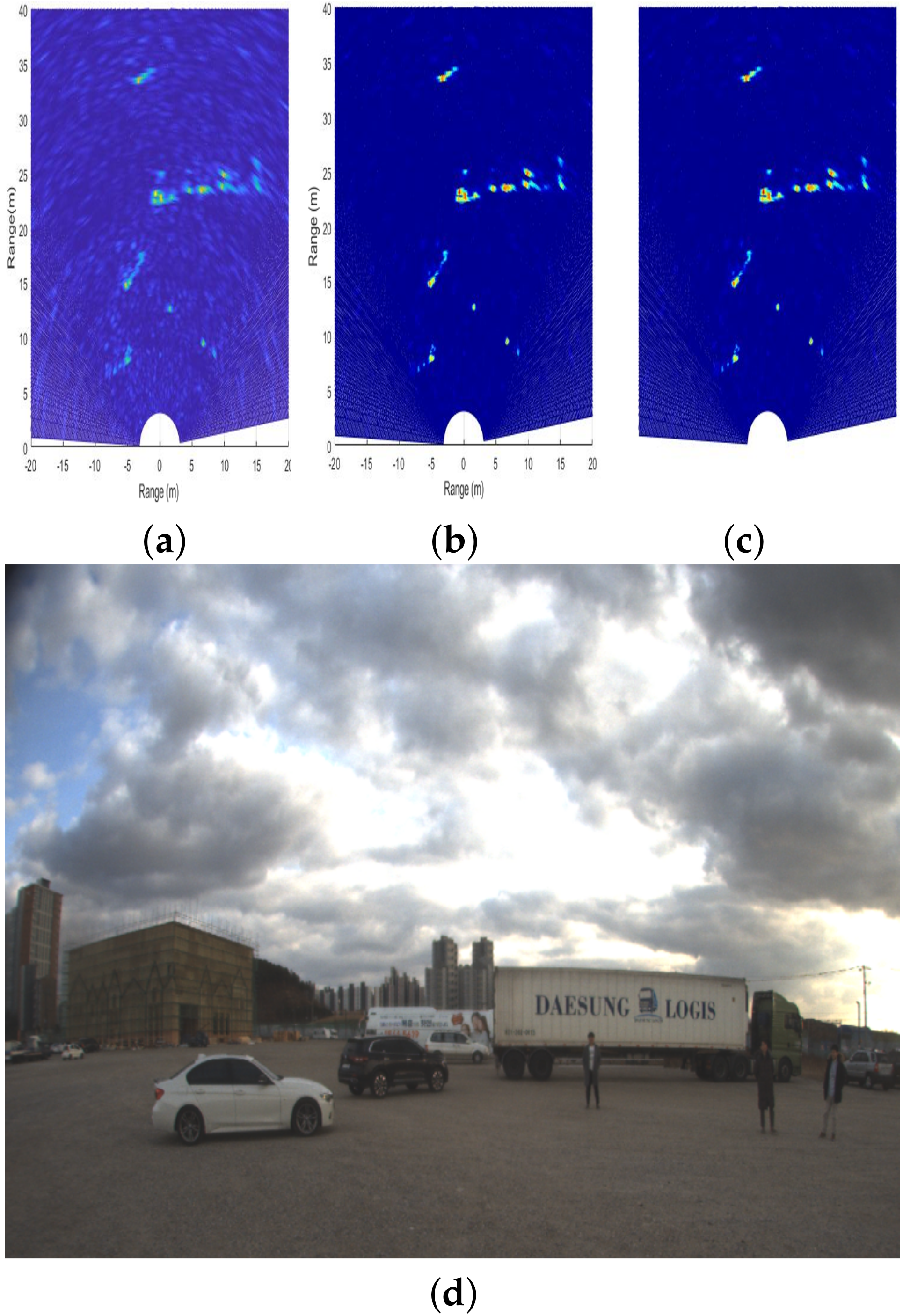





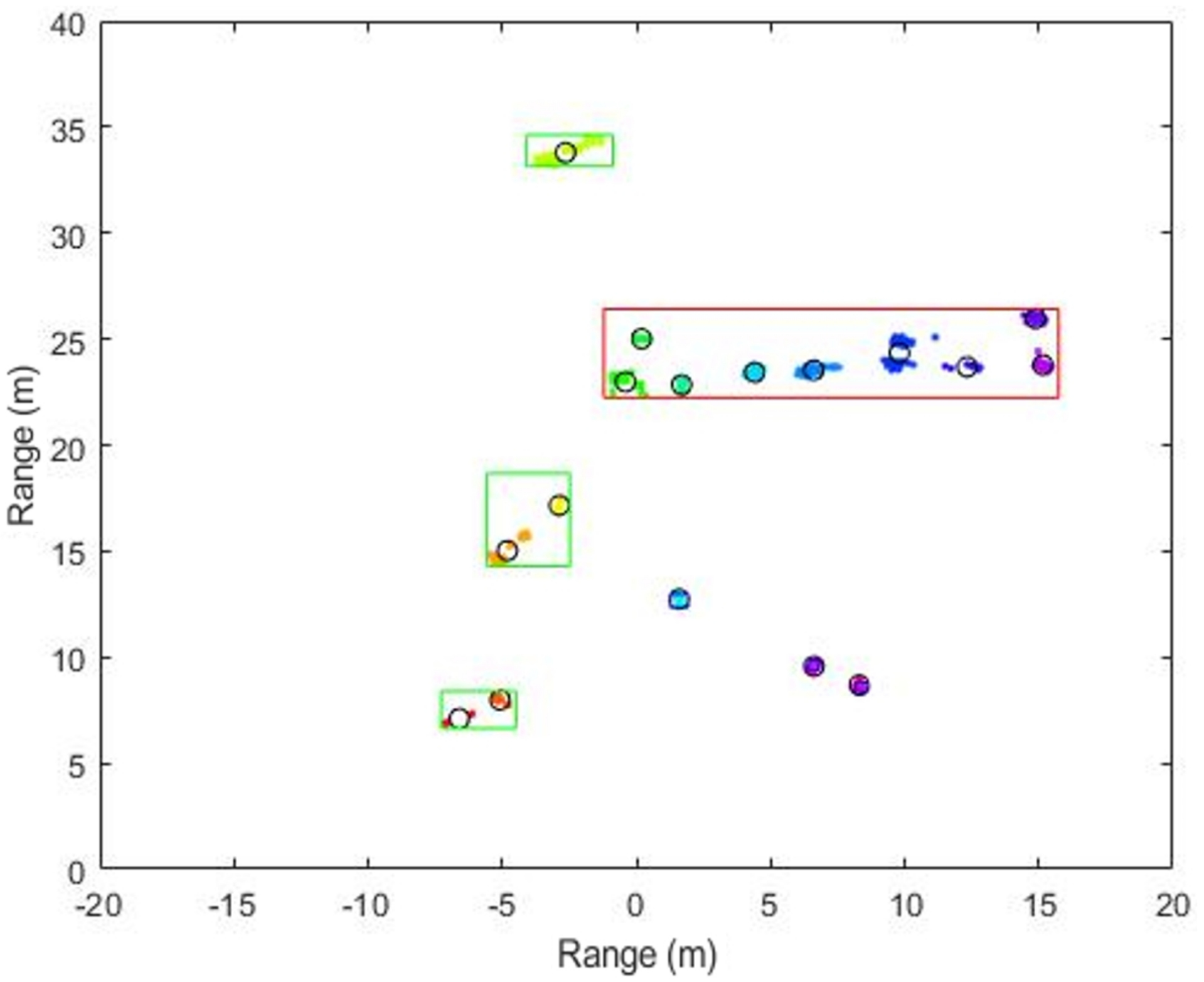
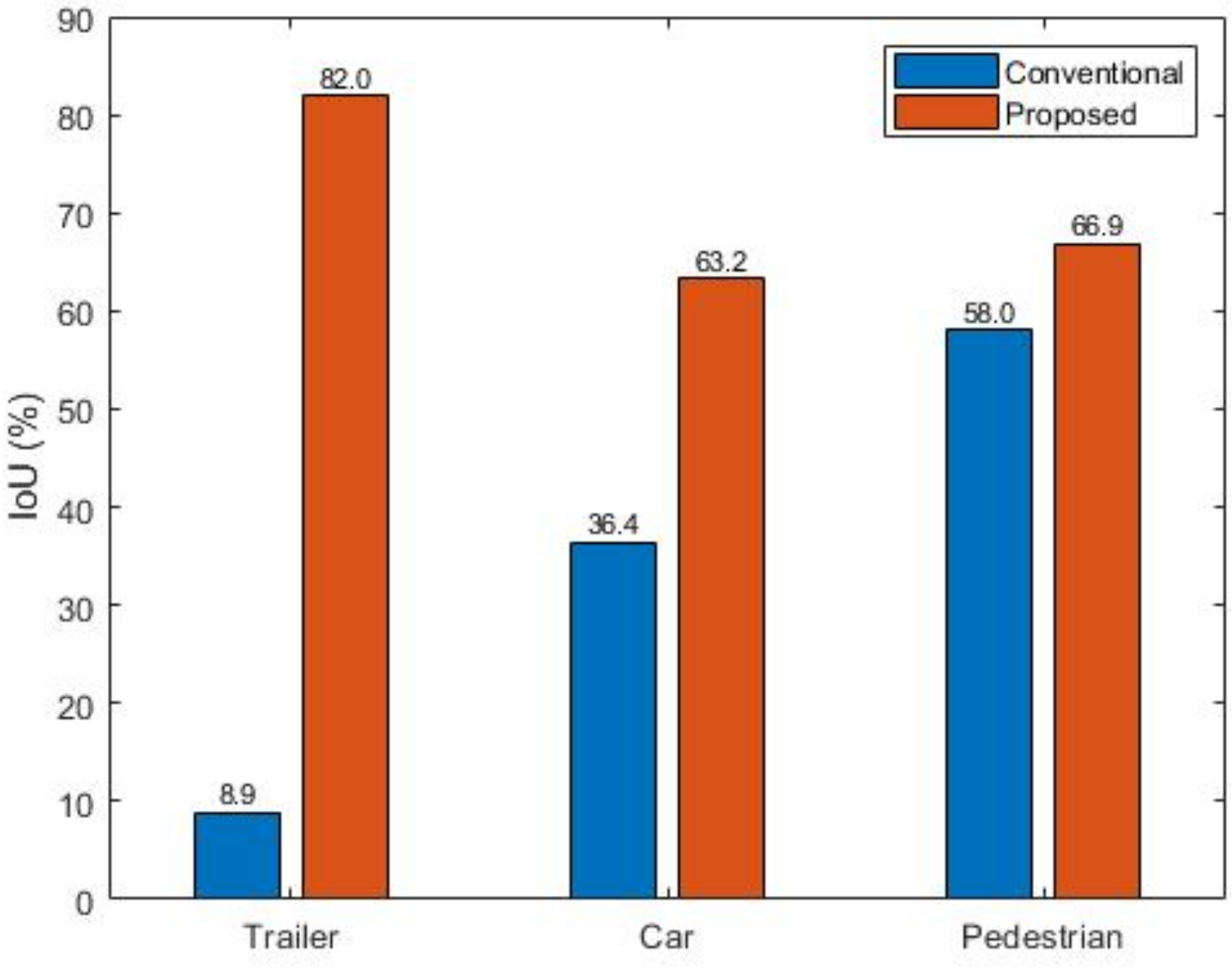
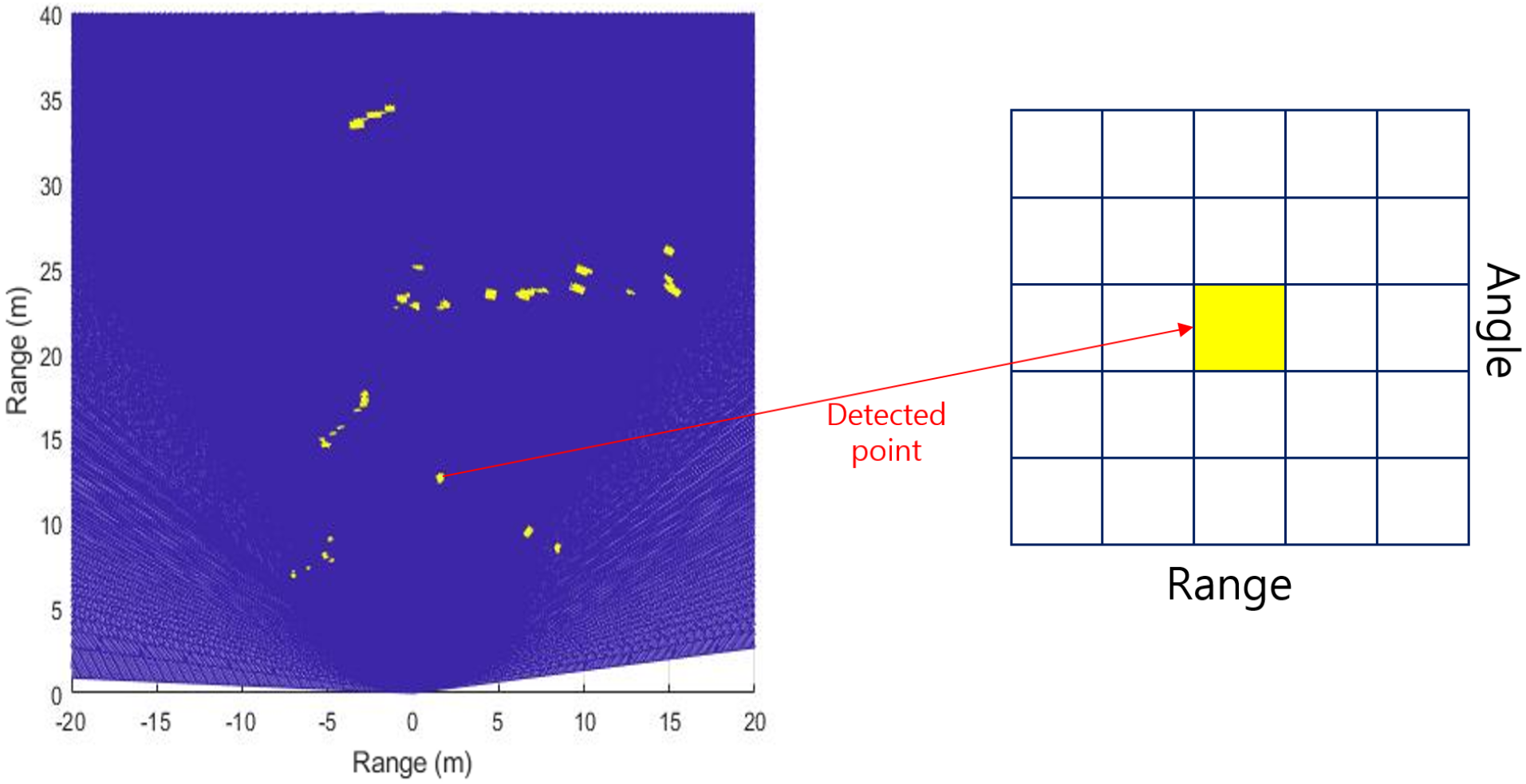

| Trailer | Truck | Car 1 | Car 2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Length (m) | 18 | 12.5 | 4.7 | 4.7 |
| Width (m) | 2.5 | 2.35 | 1.8 | 1.8 |
| Type | Dry van | Refrigerator | SUV | Sedan |
| Subject 1 | Subject 2 | Subject 3 | Subject 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Height (cm) | 175 | 179 | 184 | 185 |
| Weight (kg) | 73 | 83 | 85 | 88 |
| Parameter | Value (Unit) |
|---|---|
| Batch | 64 |
| Width | 416 (pixels) |
| Height | 416 (pixels) |
| Channels | 3 (R, G, B) |
| Max batches | 4000 |
| Burn in | 1000 (batches) |
| Policy | steps |
| Learning rate | 0.001 |
| Momentum | 0.9 |
| Steps | 3200, 3600 |
| Decay | 0.0005 |
| Scales | 0.1, 0.1 |
| SVM | 227,901 detection points |
| (125,289 points for trailer, 78,320 points for cars, 24,292 points for pedestrians) | |
| YOLO | 4028 images with 5837 ground truth |
| (1323 ground truth for trailers, 2569 ground truth for cars, 1945 ground truth for pedestrians) |
| Conventional | Proposed | |
|---|---|---|
| Processing time (ms) | 170.6 ± 10 | 20.16 |
| CPU : Intel Xeon Processor E5-2620 v4 | ||
| Spec. | GPU : NVIDIA GTX 1080 Ti GDDR5X 11GB * 8 | |
| RAM : 16GB PC4-19200 ECC-RDIMM * 8 | ||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, W.; Cho, H.; Kim, J.; Kim, B.; Lee, S. YOLO-Based Simultaneous Target Detection and Classification in Automotive FMCW Radar Systems. Sensors 2020, 20, 2897. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20102897
Kim W, Cho H, Kim J, Kim B, Lee S. YOLO-Based Simultaneous Target Detection and Classification in Automotive FMCW Radar Systems. Sensors. 2020; 20(10):2897. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20102897
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Woosuk, Hyunwoong Cho, Jongseok Kim, Byungkwan Kim, and Seongwook Lee. 2020. "YOLO-Based Simultaneous Target Detection and Classification in Automotive FMCW Radar Systems" Sensors 20, no. 10: 2897. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20102897
APA StyleKim, W., Cho, H., Kim, J., Kim, B., & Lee, S. (2020). YOLO-Based Simultaneous Target Detection and Classification in Automotive FMCW Radar Systems. Sensors, 20(10), 2897. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20102897





