Reliable UHF Long-Range Textile-Integrated RFID Tag Based on a Compact Flexible Antenna Filament
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. RFID Tag Design
2.1. Chip Selection
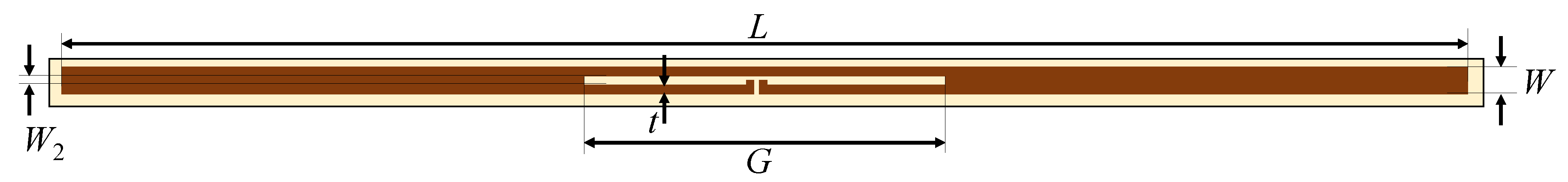
2.2. Antenna Design
3. Tag Fabrication and Encapsulation
3.1. Tag Fabrication
- A standard positive photoresist, S-1813, is spin-coated onto the Si wafers as an adhesive followed by attaching the copper coated Kapton disc onto the Si carrier.
- Photoresist is then spin-coated onto the copper layer and cured at 110 C for 3 min.
- The photoresist is UV exposed through the photomask for 30 s
- The UV-decomposed photoresist is developed using a 1:4 solution of AZ 400K developer and DI water.
- The copper is etched for 9 min using a standard PCB bubble etch tank.
- The remaining resist is removed and the exposed copper cleaned using acetone.
- The bare RFID IC is mounted using a standard soldering process.
3.2. Tag Encapsulation
- Insert 50 m-thick Kapton filament into the trench in the bottom tool piece.
- Locate the top tool piece thereby sandwiching the Kapton filament.
- Place the sandwich into an oven at 360 C for 60 s to soften the Kapton.
- Clamp the bottom and top inserts together to deform the Kapton into the shape of the RFID IC.
- Allow to cool before detaching the Kapton.
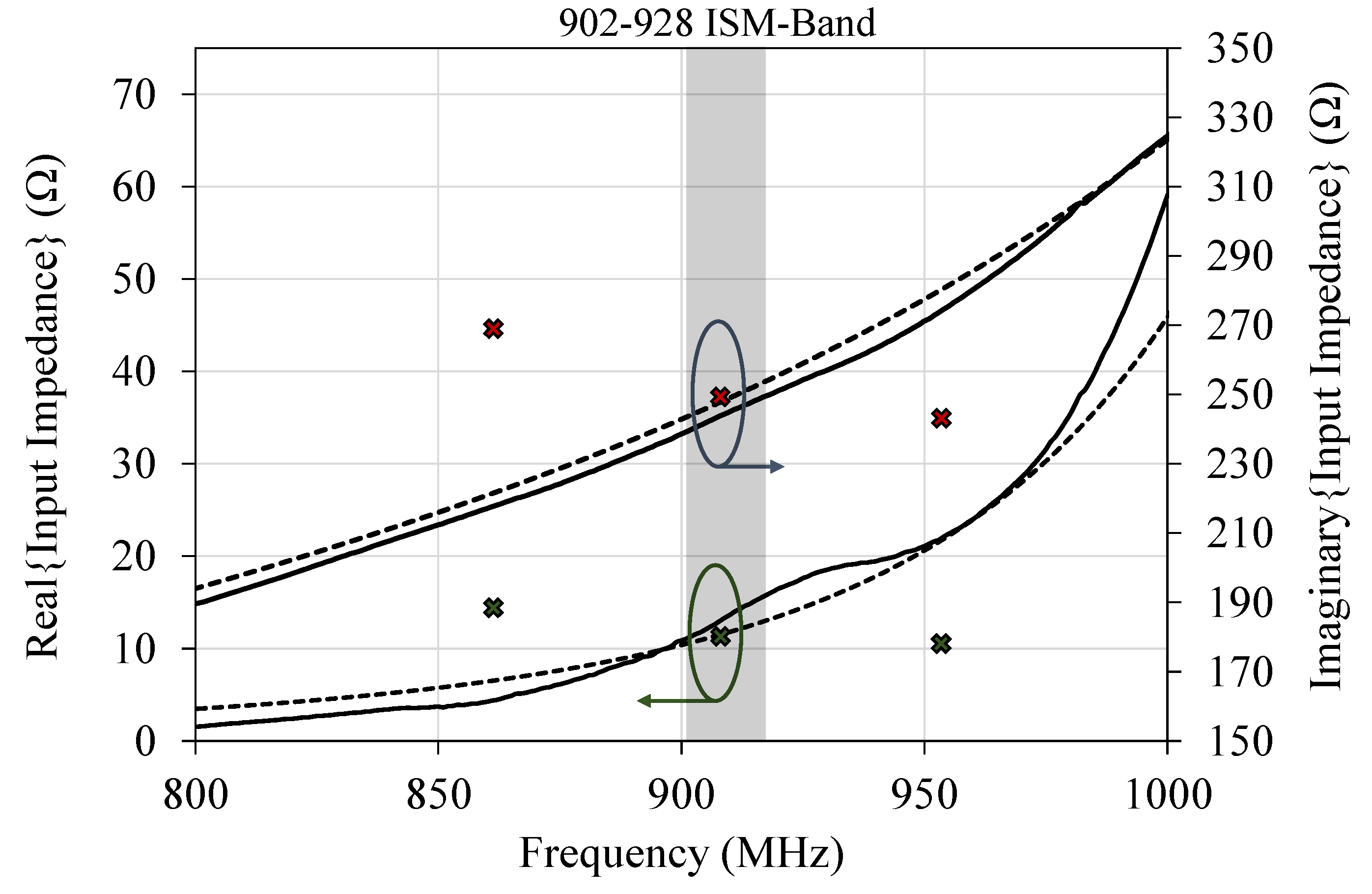
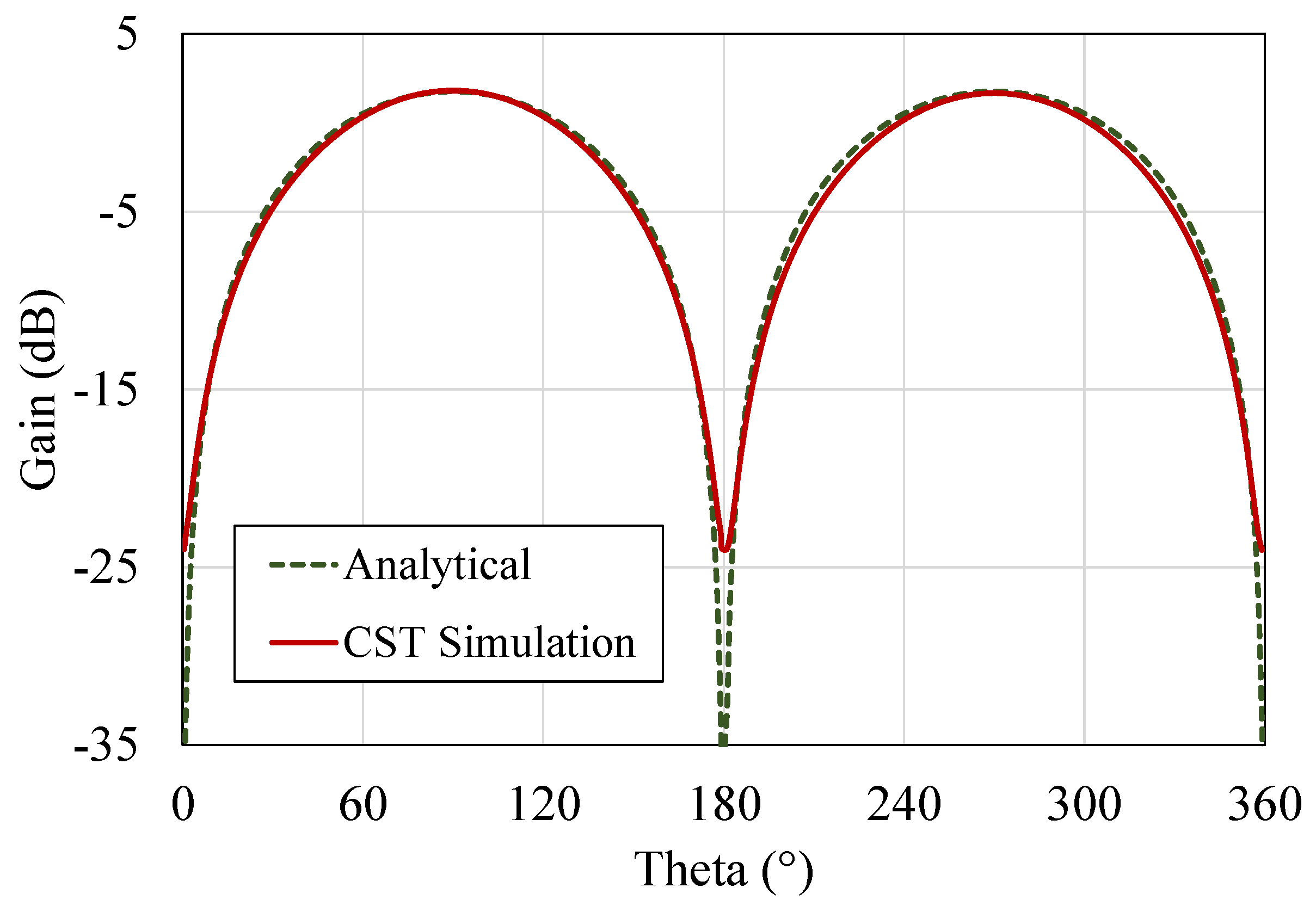
4. Antenna Simulation and Measurements
5. RFID Tag Testing and Evaluation
5.1. Tag Read-Range Test
5.2. Practical Reliability Testing Tests
5.3. Washing Test
6. Conclusions
Datasets
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Post, E.R.; Orth, M.; Russo, P.R.; Gershenfeld, N. E-broidery: Design and fabrication of textile-based computings. IBM Syst. J. 2000, 39, 840–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komolafe, A.; Torah, R.; Wei, Y.; Nunesmatos, H.; Li, M.; Hardy, D.; Dias, T.; Tudor, M.; Beeby, S. Integrating Flexible Filament Circuits for E-Textile Applications. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2019, 4, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rao, K.; Nikitin, P.; Lam, S. Antenna design for UHF RFID tags: A review and a practical application. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2005, 53, 3870–3876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrocco, G. The art of UHF RFID antenna design: Impedance-matching and size-reduction techniques. IEEE Antennas Propag. Mag. 2008, 50, 66–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Škiljo, M.; Šolić, P.; Blažević, Z.; Perković, T. Analysis of Passive RFID Applicability in a Retail Store: What Can We Expect? Sensors 2020, 20, 2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- El Khamlichi, M.; Melcon, A.A.; Mrabet, O.E.; Ennasar, M.A.; Hinojosa, J. Flexible UHF RFID Tag for Blood Tubes Monitoring. Sensors 2019, 19, 4903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Strangfeld, C.; Johann, S.B.M. Smart RFID Sensors Embedded in Building Structures for Early Damage Detection and Long-Term Monitoring. Sensors 2019, 19, 5514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cui, L.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, N.; Meng, Z.; Li, Z. Radio Frequency Identification and Sensing Techniques and Their Applications—A Review of the State-of-the-Art. Sensors 2019, 19, 4012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sample, A.P.; Yeager, D.J.; Powledge, P.S.; Mamishev, A.V.; Smith, J.R. Design of an RFID-Based Battery-Free Programmable Sensing Platform. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2008, 57, 2608–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, N.; Mirzavad, R.; Saghlatoon, H.; Honari, M.M.; Mousavi, P. A Three-Port Zero-Power RFID Sensor Architecture for IoT Applications. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 66888–66897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paracha, K.N.; Rahim, S.K.A.; Soh, P.J.; Khalily, M. Wearable Antennas: A Review of Materials, Structures, and Innovative Features for Autonomous Communication and Sensing. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 56697–56712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casula, G.A.; Montisci, G.; Rogier, H. A Wearable Textile RFID Tag Based on an Eighth-Mode Substrate Integrated Waveguide Cavity. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 11116–11123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simorangkir, R.B.V.B.; Le, D.; Björninen, T.; Sayem, A.S.M.; Zhadobov, M.; Sauleau, R. Washing Durability of PDMS-Conductive Fabric Composite: Realizing Washable UHF RFID Tags. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2019, 18, 2572–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Qureshi, S.T.; Sydänheimo, L.; Ukkonen, L.; Björninen, T. Comparison of Wearable E-Textile Split Ring Resonator and Slotted Patch RFID Reader Antennas Embedded in Work Gloves. IEEE J. Radio Freq. Identif. 2019, 3, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajin, M.A.S.; Levitt, A.S.; Liu, Y.; Knittel, C.E.; Schauer, C.L.; Dion, G.; Dandekar, K.R. On the Effect of Sweat on Sheet Resistance of Knitted Conductive Yarns in Wearable Antenna Design. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2020, 19, 542–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; He, H.; Khan, Z.; Sydänheimo, L.; Ukkonen, L.; Virkki, J. Textile-Based Batteryless Moisture Sensor. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2020, 19, 198–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Gonzalez, L.; Ver-Hoeye, S.; Vazquez-Antuna, C.; Fernandez-Garcia, M.; Andres, F.L.H. Multifunctional Fully Textile-Integrated RFID Tag to Revolutionize the Internet of Things in Clothing [Wireless Corner]. IEEE Antennas Propag. Mag. 2019, 61, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagih, M. Direct-Write Dispenser Printing for Rapid Antenna Prototyping on Thin Flexible Substrates. In Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation, Copenhagen, Denmark, 15–20 March 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Abutarboush, H.F.; Shamim, A. A Reconfigurable Inkjet-Printed Antenna on Paper Substrate for Wireless Applications. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2018, 17, 1648–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittow, W.G.; Chauraya, A.; Vardaxoglou, J.C.; Li, Y.; Torah, R.; Yang, K.; Beeby, S.; Tudor, J. Inkjet-Printed Microstrip Patch Antennas Realized on Textile for Wearable Applications. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2014, 13, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wagih, M.; Wei, Y.; Beeby, S. Flexible 2.4 GHz Sensor Node for Body Area Networks with a Compact High-Gain Planar Antenna. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2018, 17, 49–53. [Google Scholar]
- Wagih, M.; Weddell, A.S.; Beeby, S. Millimeter-Wave Textile Antenna for On-Body RF Energy Harvesting in Future 5G Networks. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Wireless Power Transfer Conference (WPTC), London, UK, 17–23 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Chahat, N.; Zhadobov, M.; Muhammad, S.A.; Coq, L.L.; Sauleau, R. 60-GHz Textile Antenna Array for Body-Centric Communications. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2013, 61, 1816–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Seet, B.C.; Joseph, F.; Li, E. Flexible Fractal Electromagnetic Bandgap for Millimeter-Wave Wearable Antennas. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2018, 17, 1281–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, G.; Islam, S.U.; Shahid, M.; Akhunzada, A.; Jabbar, S.; Khan, M.K.; Riaz, M.; Han, K. Rigorous Analysis and Evaluation of Specific Absorption Rate (SAR) for Mobile Multimedia Healthcare. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 29602–29610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patron, D.; Mongan, W.; Kurzweg, T.P.; Fontecchio, A.; Dion, G.; Anday, E.K.; Dandekar, K.R. On the Use of Knitted Antennas and Inductively Coupled RFID Tags for Wearable Applications. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2016, 10, 1047–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byondi, F.K.; Chung, Y. Longest-Range UHF RFID Sensor Tag Antenna for IoT Applied for Metal and Non-Metal Objects. Sensors 2019, 19, 5460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wagih, M.; Weddell, A.S.; Beeby, S. Sub-1 GHz Flexible Concealed Rectenna Yarn for High-Efficiency Wireless-Powered Electronic Textiles. In Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation, Copenhagen, Denmark, 15–20 March 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Tudor, J.; Liu, J.; Torah, R.; Komolafe, A.; Beeby, S. Novel Electronic Packaging Method for Functional Electronic Textiles. IEEE Trans. Components Packag. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 9, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- NXP. SL3S1204 UCODE 7, Datasheet. Available online: https://www.nxp.com/docs/en/data-sheet/SL3S1204.pdf (accessed on 16 June 2020).
- Wagih, M.; Weddell, A.S.; Beeby, S. Rectennas for RF Energy Harvesting and Wireless Power Transfer: A Review of Antenna Design. IEEE Antennas Propag. Mag. 2019, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Khaleel, H.R. Design and Fabrication of Compact Inkjet Printed Antennas for Integration within Flexible and Wearable Electronics. IEEE Trans. Components Packag. Manuf. Technol. 2014, 4, 1722–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, K.; van Rooyen, M. Simple broadband measurements of balanced loads using a network analyzer. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2006, 55, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stoumpos, C.K.; Anagnostou, D.E.; Chryssomallis, M.T. Experimental characterization of the impedance of balanced UHF RFID tag antennas. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2017, 59, 3127–3134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrank, H.; Mahony, J. Approximations to the radiation resistance and directivity of circular-loop antennas. IEEE Antennas Propag. Mag. 1994, 36, 52–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, B.A.; Boswell, A.; Perks, M.A. Loss Mechanisms in the Electrically Small Loop Antenna [Antenna Designer’s Notebook]. IEEE Antennas Propag. Mag. 2014, 56, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yu, M.; Xu, L.; Li, Y.; Ye, T.T. Broadband Textile-Based Passive UHF RFID Tag Antenna for Elastic Material. IEEE J. Radio Freq. Identif. 2020, 4, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Kiourti, A.; Burkholder, R.J.; Volakis, J.L. Broadband Textile-Based Passive UHF RFID Tag Antenna for Elastic Material. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2015, 14, 1385–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Frequency (MHz) | Calculated Range | Measured Range |
|---|---|---|
| 868 | 10.4 m | 8.2 m |
| 915 | 18.0 m | - |
| Lit. | FoM (1/m) | A (mm) | Max. R (m) | Thickness (mm) | Substrate | Flexible | Washable |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proposed | 21,460 | 382 | 8.2 | 0.05 | Polyimide | ✓ | ✓ |
| [27] | 3095 | 8400 | 26 | 10 | PLA cavity | ✗ | ✗ |
| [12] | 680 | 6790 | 4.62 | 4 | Textile | ✓ | ✗ |
| [14] | 294 | 10,170 | 3 | 0.17 | Textile | ✓ | ✗ |
| [13] | 6840 | 1540 | 10.5 | 0.13 | PDMS | ✓ | ✓ |
| [16] | 3470 | 1876 | 6.5 | - | Textile | ✓ | ✓ |
| [38] | 2400 | 1650 | 3.96 | 1–2 | Elastic polymer | ✓ | ✗ |
| [37] | 2443 | 1023 | 2.5 | 1 | Textile | ✓ | ✗ |
| Test | Tag-Read | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Magnetic test | ✓ | A neodymium magnet is used to examine if the RIFD tag has Ferro-metals. This test checks whether the RIFD tag can be detected by the needle detector or MRI. |
| Metal strip test | ✓ | A copper foil is placed at back of RFID tag and a hand held reader is used to check whether the tag functions as expected. This test is for the food industry where the tag is used on metal cans. |
| Bending test | ✓ | A RFID tag is bent over a 2 cm diameter cylinder. The reader continuously reads starting from 0.5 m and is moved away until the tag is no longer readable. |
| Multi-stack test | ✓ | 9 tags are randomly distributed in a box and the reader reads 9 tags at the same time. |
| Water Immersing test | ✓ | A RFID tag is submerged into water and read by a hand held reader, while in water. |
| Multi-stack test (wet) | ✓ | 9 wet RFID cotton towels are stacked together and read by the reader. |
| Machine washing test and spinning | ✓ | 1 cotton towel with a RFID tag is washed at 60 C for 40 min. The tag is spun at 500 rpm for 3 min. The tag is read before, during and after washing. This test examines tag under the most harsh washing condition specified by Invengo. |
| Drying test | ✓ | 1 washed and spun cotton towel with a RFID tag is then dried at 180 C for 20 min. This test examines whether a tag can survive one drying cycle at the highest temperature specified by Invengo. |
| Parameter | Setting |
|---|---|
| Washing temperature | 60 C |
| Washing duration | 40 min |
| Number of towels washed at the same time | 3 |
| Washing detergent | Daz regular washing pod |
| Softener | Fairy fabric softener original |
| Spin speed | 600 RPM |
| Spin duration | 6 min |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wagih, M.; Wei, Y.; Komolafe, A.; Torah, R.; Beeby, S. Reliable UHF Long-Range Textile-Integrated RFID Tag Based on a Compact Flexible Antenna Filament. Sensors 2020, 20, 3435. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20123435
Wagih M, Wei Y, Komolafe A, Torah R, Beeby S. Reliable UHF Long-Range Textile-Integrated RFID Tag Based on a Compact Flexible Antenna Filament. Sensors. 2020; 20(12):3435. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20123435
Chicago/Turabian StyleWagih, Mahmoud, Yang Wei, Abiodun Komolafe, Russel Torah, and Steve Beeby. 2020. "Reliable UHF Long-Range Textile-Integrated RFID Tag Based on a Compact Flexible Antenna Filament" Sensors 20, no. 12: 3435. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20123435
APA StyleWagih, M., Wei, Y., Komolafe, A., Torah, R., & Beeby, S. (2020). Reliable UHF Long-Range Textile-Integrated RFID Tag Based on a Compact Flexible Antenna Filament. Sensors, 20(12), 3435. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20123435









