A Novel Approach to Double the Sensitivity of Polarization Maintaining Interferometric Fiber Optic Gyroscope
Abstract
1. Introduction
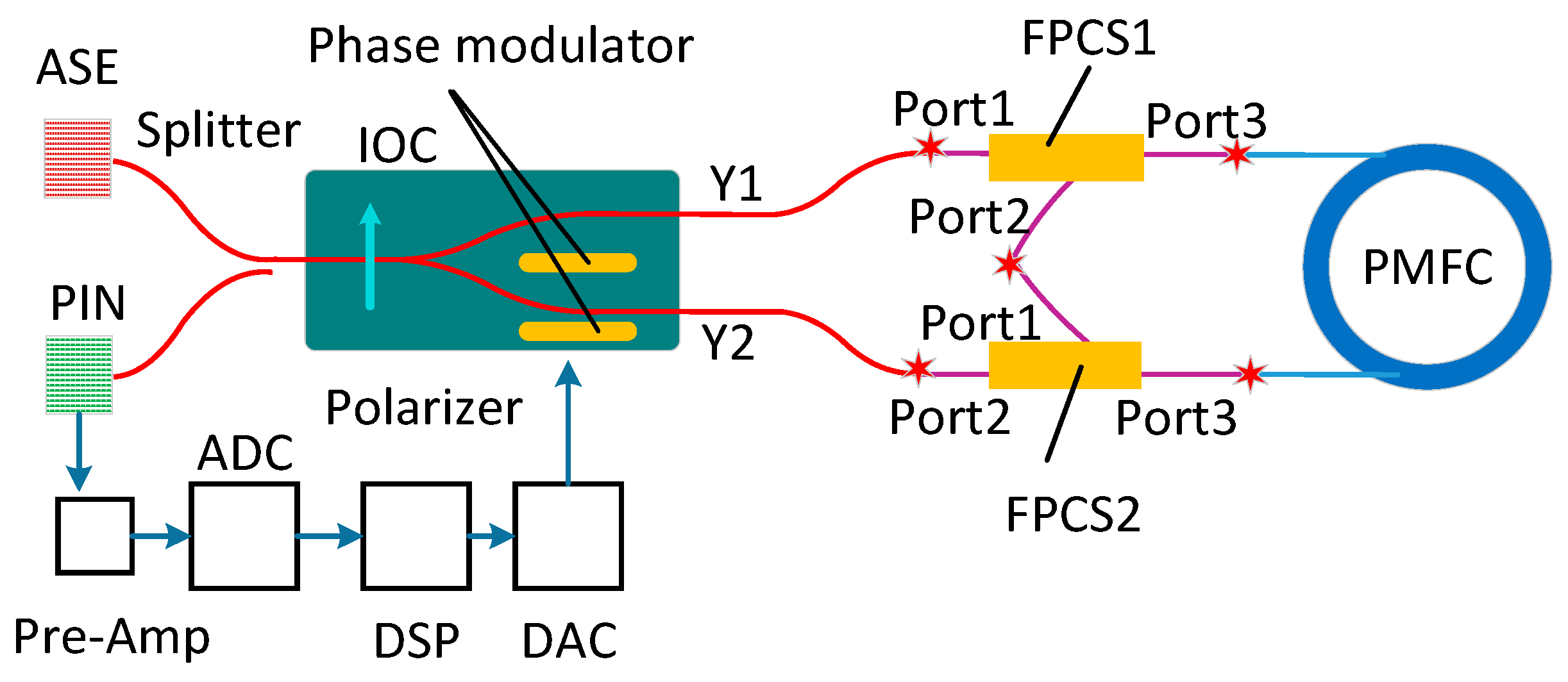
2. Working Principle
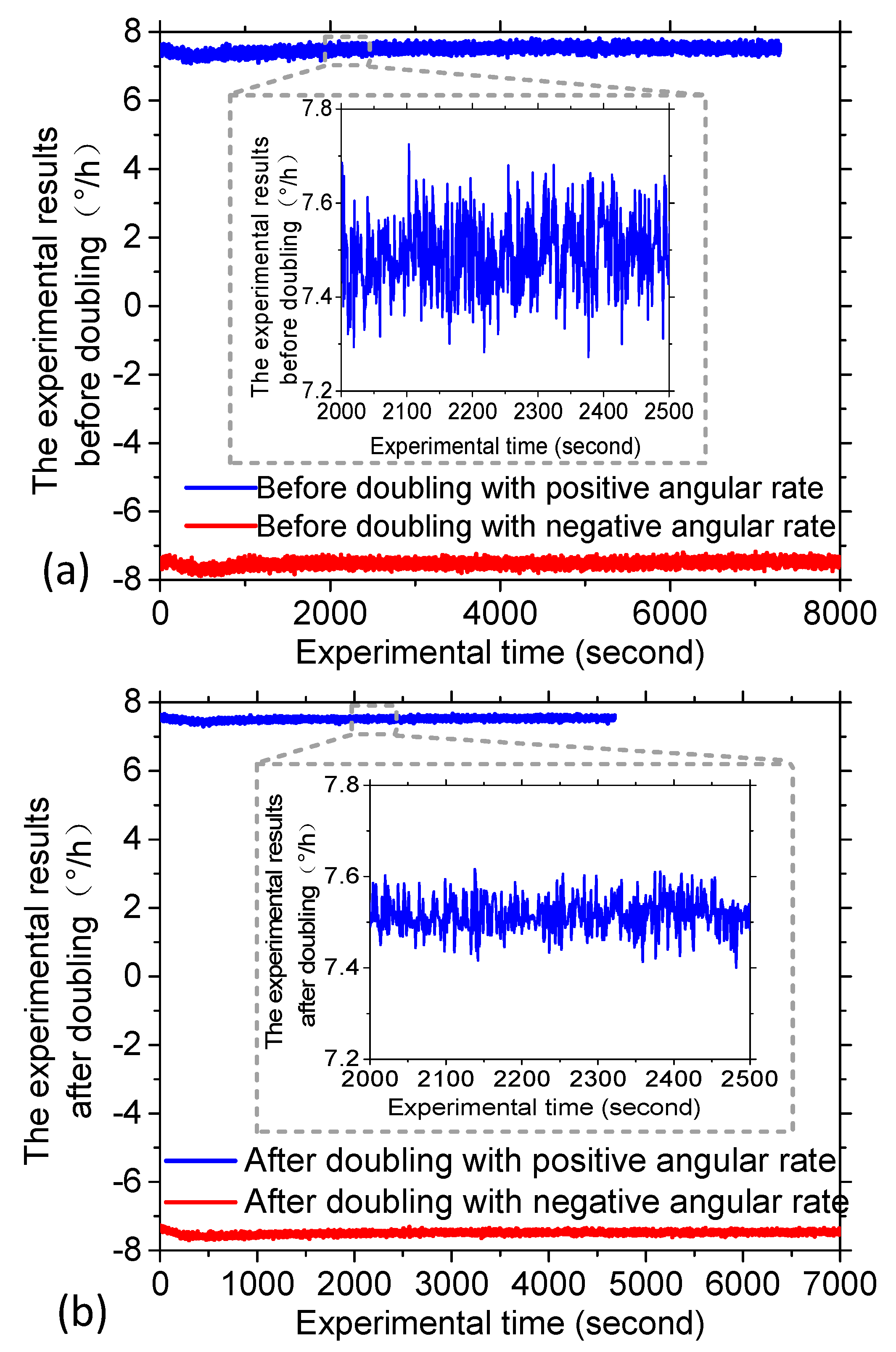
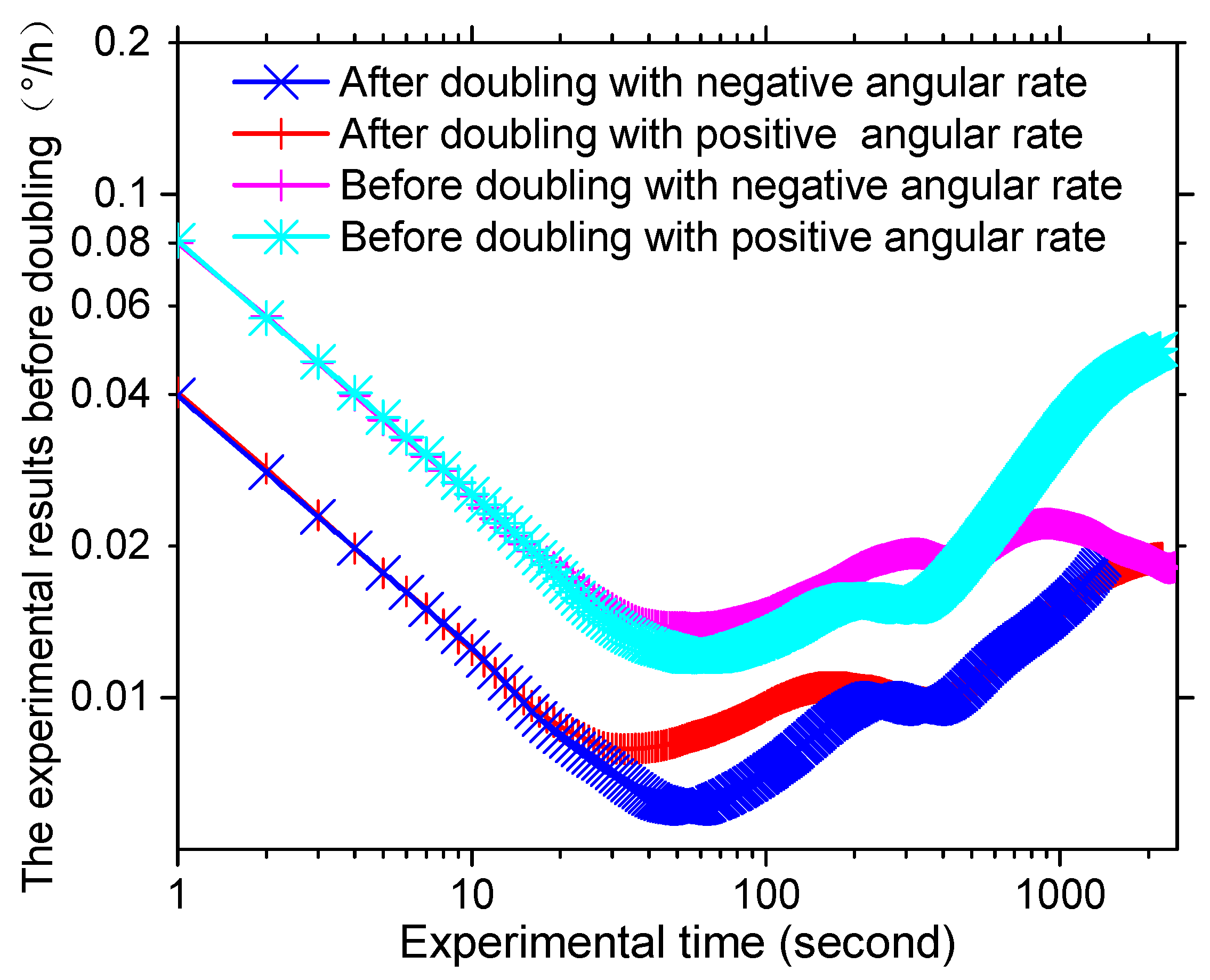
3. Experimental Verification
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Groves, P.D. Principles of GNSS, Inertial, and Multi-sensor Integrated Navigation Systems. Ind. Robot 2013, 3, 191–192. [Google Scholar]
- King, A.D. Inertial Navigation—Forty Years of Evolution. GEC Rev. 1998, 3, 140–149. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Z.; Chen, X.; Tang, X. A Novel Linear Model Based on Code Approximation for GNSS/INS Ultra-Tight Integration System. Sensors 2020, 20, 3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, L.; Hu, B.; Li, A.; Qin, F. Strapdown inertial navigation system alignment based on marginalised unscented Kalman filter. IET Sci. Meas. Technol. 2013, 2, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaneda, N.; Lamy-Perbal, S. An improved shoe-mounted inertial navigation system. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation, Zurich, Switzerland, 15–17 September 2010; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Braden, K.; Browning, C.; Gelderloos, H.; Smith, F.; Marttila, C.; Vallot, L. Integrated inertial navigation system/Global Positioning System (INS/GPS) for manned return vehicle autoland application. In Proceedings of the IEEE Symposium on Position Location and Navigation. A Decade of Excellence in the Navigation Sciences, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 20 March 1990; pp. 74–82. [Google Scholar]
- Tucek, J.; Kardos, M.; Tomastik, J. First experience with pedestrian Inertial Navigation System application under forest conditions. Zpravy Lesnickeho Vyzkumu 2016, 3, 203–212. [Google Scholar]
- Stelkens-Kobsch, T.H. Further Development of a High Precision Two-Frame Inertial Navigation System for Application in Airborne Gravimetry. In Observation of the Earth System from Space; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 479–494. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.G.; Williams, T.C. Strategic inertial navigation systems—High-accuracy inertially stabilized platforms for hostile environments. Control Syst. IEEE 2008, 1, 65–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrens, S.; Levine, D.; Andrews, G.; How, J.P. Vision-based guidance and control of a hovering vehicle in unknown, GPS-denied environments. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Kobe, Japan, 12–17 May 2009; pp. 2643–2648. [Google Scholar]
- Shkel, A.M. Precision navigation and timing enabled by microtechnology: Are we there yet? In Proceedings of the IEEE Sensors 2010 Conference, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 1–4 November 2011; pp. 5–9. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Lai, J.; Guo, X.; Yang, J. A research on all source navigation and positioning and its critical technology. In Proceedings of the 6th China Satellite Navigation Conference, Xi’an, China, 13–15 May 2015; pp. 801–808. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, C. Modeling of FOG and application in inertial navigation system. J. Chin. Inert. Technol. 2006, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, W.; Fu, W.; Liu, C.; Shu, X.; Che, S. A software-compensation method to orthogonal magnetic field drift in a depolarized fiber-optic gyroscope. Optik 2014, 11, 2565–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dranitsyna, E.V.; Egorov, D.A.; Untilov, A.A.; Deineka, G.B.; Sharkov, I.A.; Deineka, I.G. Reducing the effect of temperature variations on FOG output signal. Gyrosc. Navig. B 2013, 2, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.S.; Nan, S.Z.; Jin, J. Research on modeling and compensation technology for temperature errors of FOG. J. Astronaut. 2006, 5, 939–941. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Shen, C. Study on temperature error processing technique for fiber optic gyroscope. Optik 2013, 9, 784–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moslehi, B.; Yahalom, R.; Oblea, L.; Faridian, F.; Black, R.J.; Ha, J.C.; Berarducci, M. Low-cost and compact fiber-optic gyroscope with long-term stability. In Proceedings of the 2011 Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, MO, USA, 5–12 May 2011; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Su, H.C.; Wang, L.A. A highly efficient polarized superfluorescent fiber source for fiber-optic gyroscope applications. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2003, 10, 1357–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Zhang, R.P.; Wu, L.; Zhang, Y.G. Suppression for light source intensity noise in high-precision FOG. J. Chin. Inert. Technol. 2010, 18, 600–603. [Google Scholar]
- Kintner, E.C. Polarization control in optical-fiber gyroscopes. Opt. Lett. 1981, 3, 154–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yang, J.H.; Zhou, Y.L.; Shu, X. The application of low-noise DC-DC power source in fiber-optic gyroscope system. Opto-Electron. Eng. 2018, 1, 170517. [Google Scholar]
- Toyama, K.; Fesler, K.A.; Kim, B.Y.; Shaw, H.J. Digital integrating fiber-optic gyroscope with electronic phase tracking. Opt. Lett. 1991, 15, 1207–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Yang, C.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z. All-digital signal-processing open-loop fiber-optic gyroscope with enlarged dynamic range. Opt. Lett. 2013, 24, 5422–5425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shupe, D.M. Thermally induced nonreciprocity in the fiber-optic interferometer. Appl. Opt. 1980, 5, 654–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohr, F. Thermooptically induced bias drift in fiber optical Sagnac interferometers. J. Lightwave Technol. 2002, 1, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotate, K.; Tabe, K. Drift of an optical fiber gyroscope caused by the Faraday effect: Influence of the earth’s magnetic field. Appl. Opt. 1986, 7, 1086–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Li, X.; Guang, X.; Li, G.; Guan, L. Bias Error Caused by the Faraday Effect in Fiber Optical Gyroscope with Double Sensitivity. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2017, 15, 1273–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotate, K.; Saida, T. General formula describing drift of interferometer fiber-optic gyro due to Faraday effect: Reduction of the drift in twin-depo-I-FOG. J. Lightwave Technol. 1999, 2, 222. [Google Scholar]
- Song, N. Analysis of vibration error in digital closed-loop fiber optic gyroscope. J. Beijing Univ. Aeronaut. Astronaut. 2004, 8, 702–704. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, C.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, Y.; Shu, X.; Che, S.; Liu, C. Coupling effect of a single-mode fiber coil under time-varying temperature and magnetic field. J. Lightwave Technol. 2019, 13, 3208–3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Pan, S.; Liu, S.; Hu, K. Fiber gyroscope with a double sensitivity employing a polarization splitter. Opt. Lett. 2013, 8, 1337–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Zhou, K.; Lu, C.; Xian, T. Open-loop fiber-optic gyroscope with a double sensitivity employing a polarization splitter and Faraday rotator mirror. Opt. Lett. 2018, 23, 5861–5864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Board, I. IEEE Standard Specification Format Guide and Test Procedure for Single-Axis Interferometric Fiber Optic Gyros; IEEE Std.: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]




| Positive before Improvement | Negative before Improvement | Positive after Improvement | Negative after Improvement | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Theoretical data (°/h) | 7.5 | −7.5 | 7.5 | −7.5 |
| Average data acquired (°/h) | 7.4895 | −7.5105 | 7.5126 | −7.4874 |
| Angle random walk () | 0.0013 | 0.0013 | 0.0007 | 0.0007 |
| Bias stability (°/h) | 0.0182 | 0.0208 | 0.0091 | 0.0120 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, D.; Liang, C.; Li, N. A Novel Approach to Double the Sensitivity of Polarization Maintaining Interferometric Fiber Optic Gyroscope. Sensors 2020, 20, 3762. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20133762
Zhang D, Liang C, Li N. A Novel Approach to Double the Sensitivity of Polarization Maintaining Interferometric Fiber Optic Gyroscope. Sensors. 2020; 20(13):3762. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20133762
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Dengwei, Cui Liang, and Nan Li. 2020. "A Novel Approach to Double the Sensitivity of Polarization Maintaining Interferometric Fiber Optic Gyroscope" Sensors 20, no. 13: 3762. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20133762
APA StyleZhang, D., Liang, C., & Li, N. (2020). A Novel Approach to Double the Sensitivity of Polarization Maintaining Interferometric Fiber Optic Gyroscope. Sensors, 20(13), 3762. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20133762







