Compact Current Reference Circuits with Low Temperature Drift and High Compliance Voltage
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Circuit Description
2.1. SGA-Based Current Divider Circuit Analysis
2.2. 92 nA Current Reference Analysis
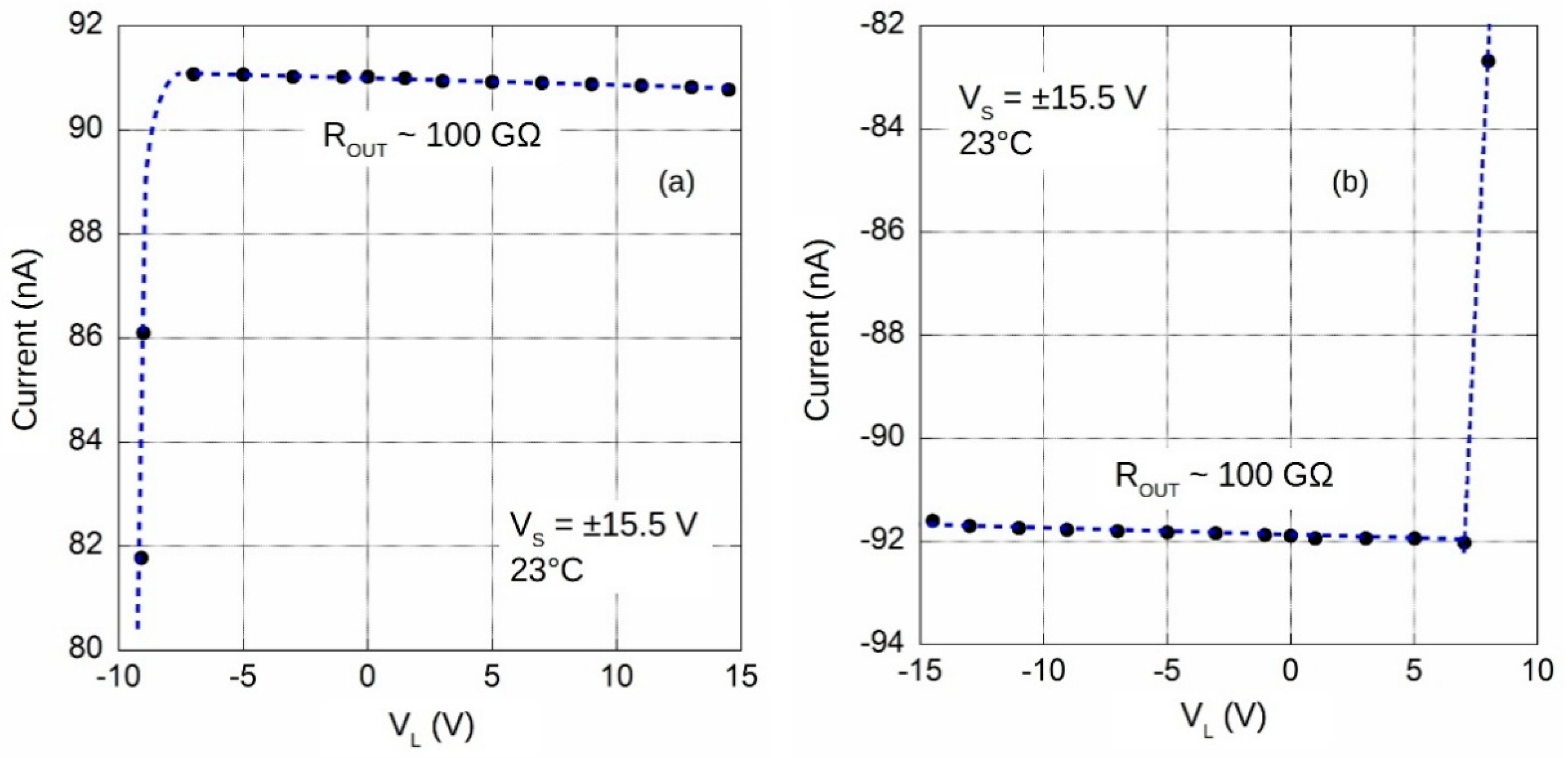
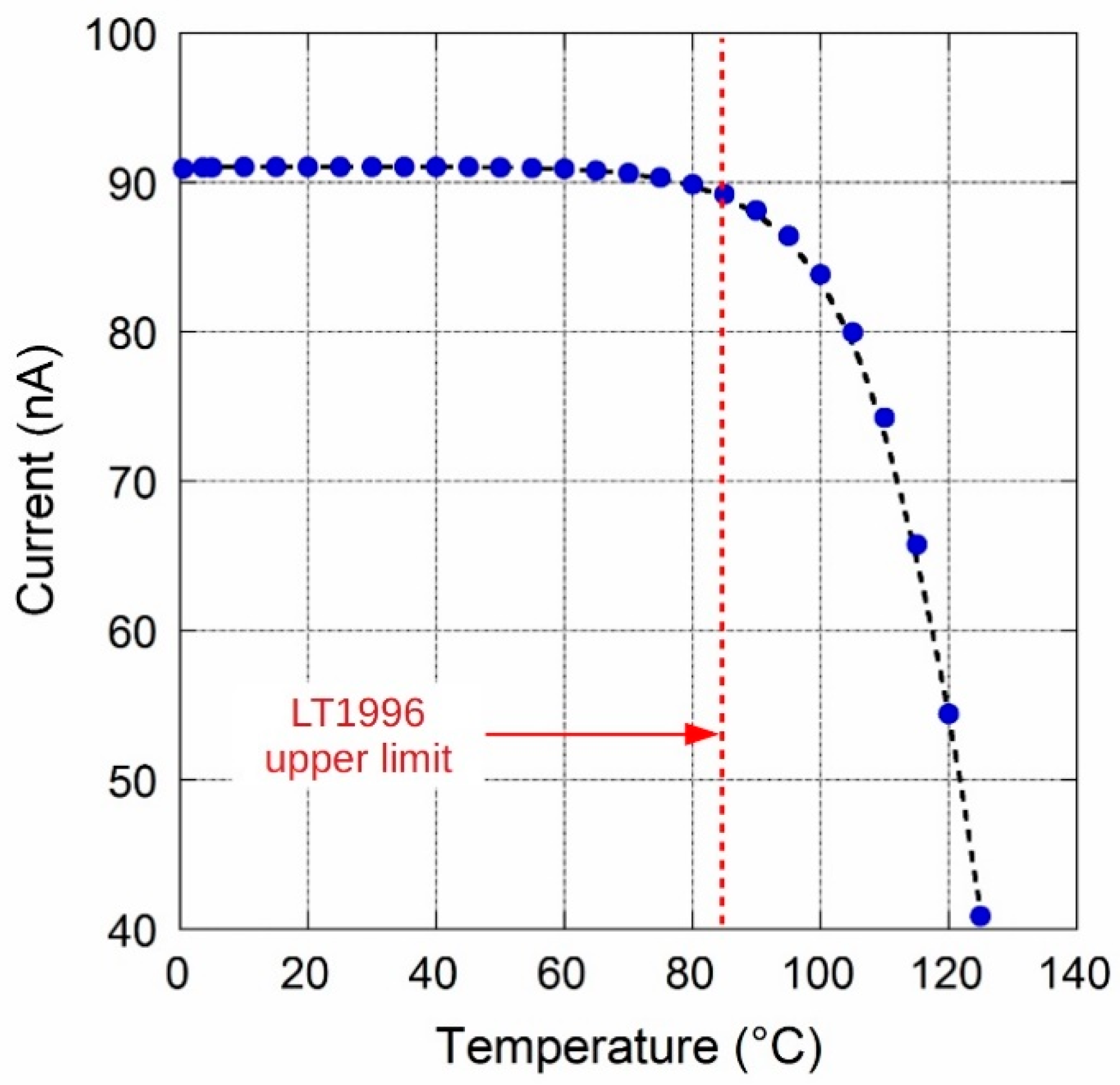
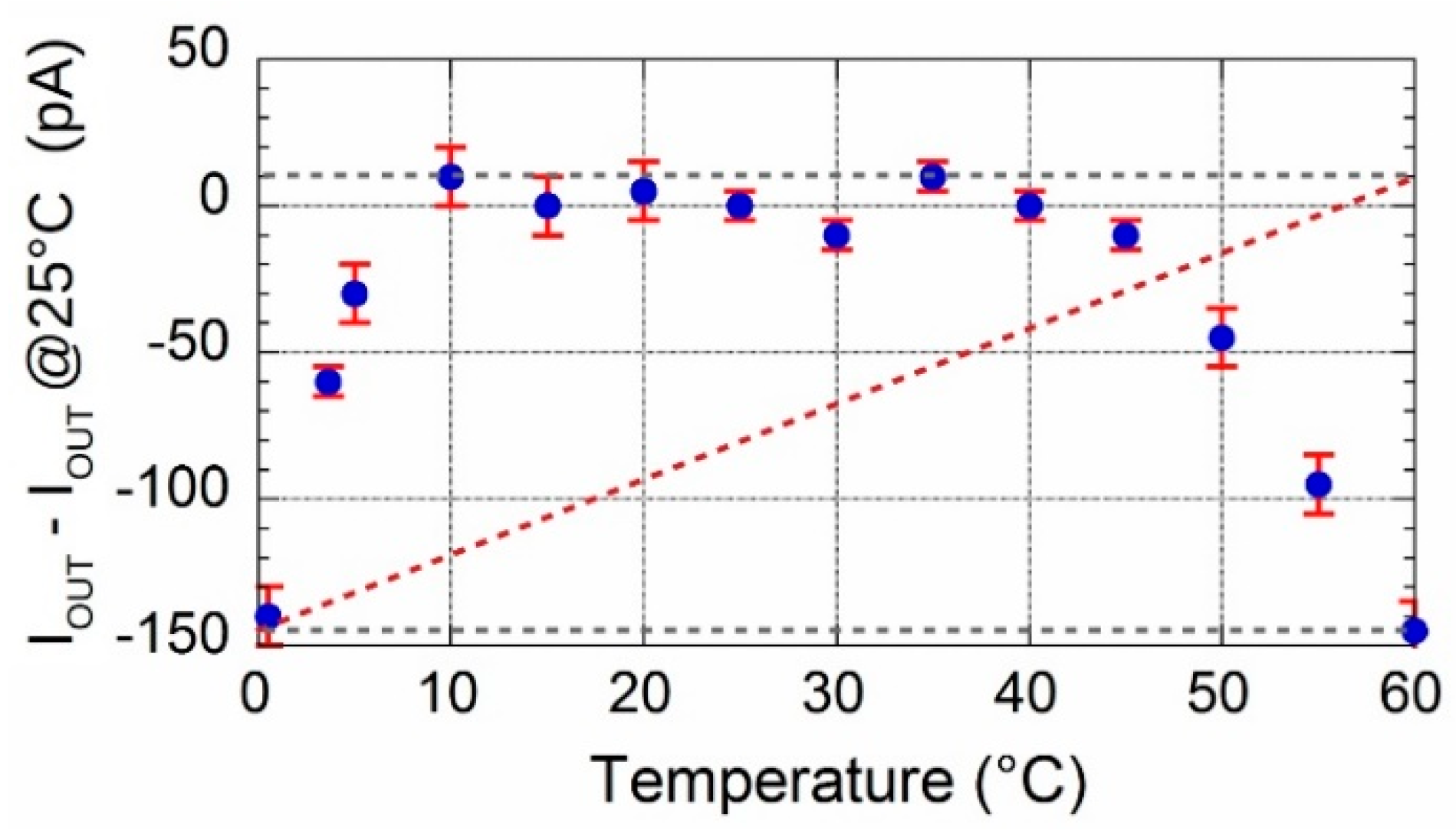
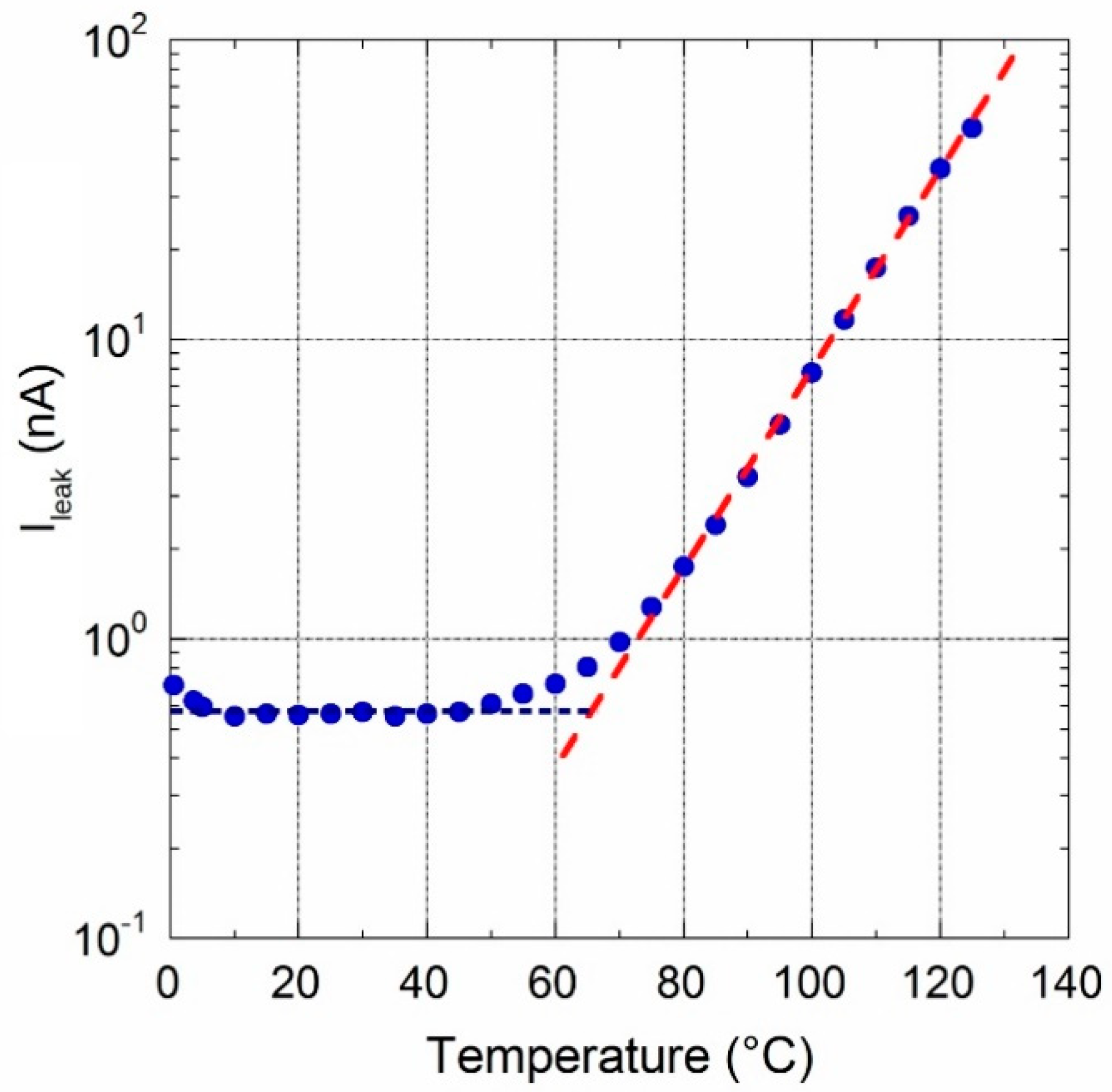
3. Prototype Characterization
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gray, P.R.; Hurst, P.J.; Lewis, S.H.; Meyer, R.G. Analysis and Design of Analog Integrated Circuits, 5th ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2009; Ch. 4. [Google Scholar]
- Murnane, M. Current Sources: Options and Circuits, AN-968, Analog Devices, Inc. 2008. Available online: https://www.analog.com/media/en/technical-documentation/application-notes/AN-968.pdf (accessed on 5 July 2020).
- Keithley Instruments Inc. Ultra-sensitive Current Sources. Available online: https://www.tek.com/keithley-low-level-sensitive-and-specialty-instruments/keithley-ultra-sensitive-current-sources-seri (accessed on 5 July 2020).
- TDK-Lambda Inc. Uses for Constant Current Power in Industrial Applications. Available online: https://www.emea.lambda.tdk.com/uk/KB/Uses-for-constant-current-power-in-Industrial-Applications.pdf (accessed on 5 July 2020).
- van Treeck, D.; Ledig, J.; Scholz, G.; Lähnemann, J.; Musolino, M.; Tahraoui, A.; Brandt, O.; Waag, A.; Riechert, H.; Geelhaar, L. Electroluminescence and current–voltage measurements of single-(In,Ga)N/GaN-nanowire light-emitting diodes in a nanowire ensemble. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 1177–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacios-Berraquero, C.; Barbone, M.; Kara, D.M.; Chen, X.; Goykhman, I.; Yoon, D.; Ott, A.K.; Beitner, J.; Watanabe, K.; Taniguchi, T.; et al. Atomically thin quantum light-emitting diodes. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flammini, A.; Marioli, D.; Taroni, A. A low-cost interface to high-value resistive sensors varying over a wide range. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2004, 53, 1052–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depari, A.; Falasconi, M.; Flammini, A.; Marioli, D.; Rosa, S.; Sberveglieri, G.; Taroni, A. A new low-cost electronic system to manage resistive sensors for gas detection. IEEE Sens. J. 2007, 7, 1073–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoon, K.; Chung, W.S.; Kim, H.J.; Son, S.H. A resistance deviation-to-pulsewidth converter for resistive sensors. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2009, 58, 397–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokolanski, Z.; Gavrovski, C.; Dimcev, V.; Makraduli, M. Simple interface for resistive sensors based on pulse width modulation. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2013, 62, 2983–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azhari, S.J.; Kaabi, H. AZKA cell, the current-mode alternative of Wheatstone bridge. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Fundam. Theory Appl. 2000, 47, 1277–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan Ramanathan, P.; George, B.; Kumar, V.J. A linearizing digitizer for wheatstone bridge based signal conditioning of resistive sensors. IEEE Sens. J. 2017, 17, 1696–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, K.F. The new current loop: An instrumentation and measurement circuit topology. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 1997, 46, 1061–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishore, K.; Malik, S.; Baghini, M.S.; Akbar, M.S. A Dual-Differential Subtractor-Based Auto-Nulling Signal Conditioning Circuit for Wide-Range Resistive Sensors. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 3047–3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Song, F.; Fang, X.; Guo, Z.-X.; Liang, S. A practical vacuum sensor based on a ZnO nanowire array. Nanotechnology 2010, 21, 475502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polese, D.; Mattoccia, A.; Giorgi, F.; Pazzini, L.; Ferrone, A.; Di Giamberardino, L.; Maiolo, L.; Pecora, A.; Convertino, A.; Fortunato, G.; et al. Layered Double Hydroxides intercalated with Chlorine used as low temperature gas sensors. Procedia Eng. 2015, 120, 1175–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Iacovo, A.; Venettacci, C.; Bruno, S.; Colace, L. Lead Sulphide Colloidal Quantum Dots for Sensing Applications. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Photonics, Optics and Laser Technology (PHOTOPTICS 2019), Prague, Czech Republic, 25–27 February 2019; pp. 235–240, ISBN 978-989-758-364-3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marcellis, A.; Ferri, G.; Mantenuto, P. A novel 6-decades fully-analog uncalibrated Wheatstone bridge-based resistive sensor interface. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 189, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marcellis, A.; Depari, A.; Ferri, G.; Flammini, A.; Sisinni, E. A CMOS integrated low-voltage low-power time-controlled interface for chemical resistive sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 179, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depari, A.; Flammini, A.; Marioli, D.; Sisinni, E.; De Marcellis, A.; Ferri, G.; Stornelli, V. A new and fast-readout interface for resistive chemical sensors. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2010, 59, 1276–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depari, A.; Flammini, A.; Sisinni, E.; de Marcellis, A.; Ferri, G.; Mantenuto, P. Fast, versatile, and low-cost interface circuit for electrochemical and resistive gas sensor. IEEE Sens. J. 2014, 14, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantenuto, P.; Ferri, G.; De Marcellis, A. Uncalibrated automatic bridge-based CMOS integrated interfaces for wide-range resistive sensors portable applications. Microelectron. J. 2014, 45, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Texas Instruments. REF200, “Dual, 100-µA Current Sink/Source”. Available online: http://www.ti.com/product/REF200 (accessed on 5 July 2020).
- Harrisson, L.T. Current Sources & Voltage References; Newnes-Elesevier: Oxford, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Callegaro, L.; D’Elia, V.; Trinchera, B. A current source for picoammeter calibration. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2007, 56, 1198–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Antonio, E.; Salvatori, S.; Oliva, P.; Patanè, F.; Girolami, M.; Trucchi, D.M. High Precision Integrator for CVD-Diamond Detectors for Dosimetric Applications. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Symposium on Medical Measurements and Applications (MeMeA), Rome, Italy, 11–13 June 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandiev, I.M. Analysis and design of voltage-controlled current sources for a grounded load. Int. J. Circ. Theor. Appl. 2015, 43, 756–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheingold, D.H. Impedance and Admittance Transformations Using Operational Amplifiers. Lightning Empiricist 1964, 12, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Pelcia, M.M.; dos Reis Filho, C.A. Fully Integrated Programmable Howland Current Source for Sensors Excitation. In Proceedings of the Fourth IEEE International Caracas Conference on Devices, Circuits and Systems 2002, Oranjestad, Aruba, Dutch Caribbean, 17–19 April 2002. C028–CI-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poletto, C.J.; Van Doren, C.L. A High Voltage, Constant Current Stimulator for Electrocutaneous Stimulation through Small Electrodes. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1999, 46, 929–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Xu, Z.; Ren, C.; Wang, W.; Zhao, D.; Zhang, H. Study of Voltage Control Current Source in Electrical Impedance Tomography System. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Bioinforrnatics and Biomedical Engineering (iCBBE) 2010, Chengdu, China, 18–20 June 2010; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; Oh, T.I.; Paek, S.M.; Lee, J.S.; Woo, E.J. Precision Constant Current Source for Electrical Impedance Tomography. In Proceedings of the 25th Annual International Conference of the IEEE EMBS, Cancun, Mexico, 17–21 September 2003; pp. 1066–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Obaidi, A.A.; Meribout, M. A New Enhanced Howland Voltage Controlled Current Source for EIT Applications. In Proceedings of the IEEE GCC Conference and Exhibition (GCC), Dubai, UAE, 19–22 February 2011; pp. 327–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Malik, R.; Liao, W. Difference Amplifier Forms Heart of Precision Current Sources. Analog Dialogue 2009, 43, 22–24. [Google Scholar]
- Salvatori, S. Gain-selectable IC yields voltage-to-current converter. EDN Eur. 2015, 7, 30–32. [Google Scholar]
- Salvatori, S.; Rossi, M.C.; Girolami, M. High-precision voltage-to-current converters based on single-chip gain-selectable amplifiers. Analog Integr. Circuits Signal Process. 2019, 99, 491–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvatori, S.; Masarone, N.; Di Nucci, G.; Conte, G. Compact front-end electronics for low-level current sensor measurements. Electron. Lett. 2006, 42, 682–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettinato, S.; Orsini, A.; Girolami, M.; Trucchi, D.M.; Rossi, M.C.; Salvatori, S. A High-Precision Gated Integrator for Repetitive Pulsed Signals Acquisition. Electronics 2019, 8, 1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettinato, S.; Orsini, A.; Rossi, M.C.; Tagnani, D.; Girolami, M.; Salvatori, S. A Compact Gated Integrator for Conditioning Pulsed Analog Signals. In Applications in Electronics Pervading Industry, Environment and Society; Saponara, S., De Gloria, A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brisebois, G.; Munson, J. Versatile Op Amps Need No Resistors. Linear Technol. J. 2004, 14, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Analog Devices. LT1991, Precision, 100μA Gain Selectable Amplifier. Available online: https://www.analog.com/media/en/technical-documentation/data-sheets/1991fh.pdf (accessed on 5 July 2020).
- Analog Devices. LT1996, Precision, 100μA Gain Selectable Amplifier. Available online: https://www.analog.com/media/en/technical-documentation/data-sheets/1996f.pdf (accessed on 5 July 2020).
- Texas Instruments. OPA189 Single, 14MHz, MUX-Friendly, Low-Noise, Zero-Drift, RRO, CMOS Precision Operational Amplifier. Available online: https://www.ti.com/lit/gpn/opa189 (accessed on 5 July 2020).
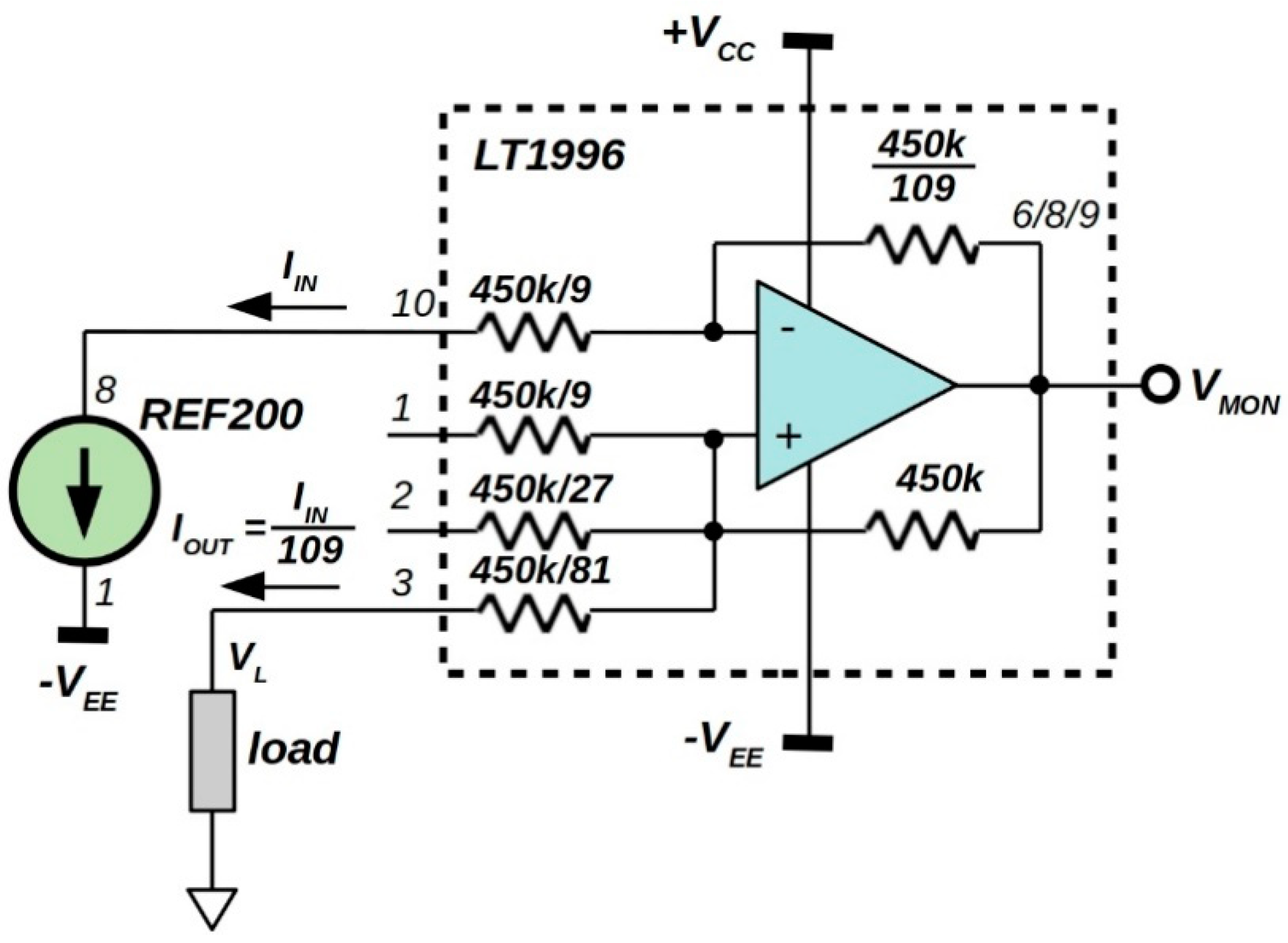
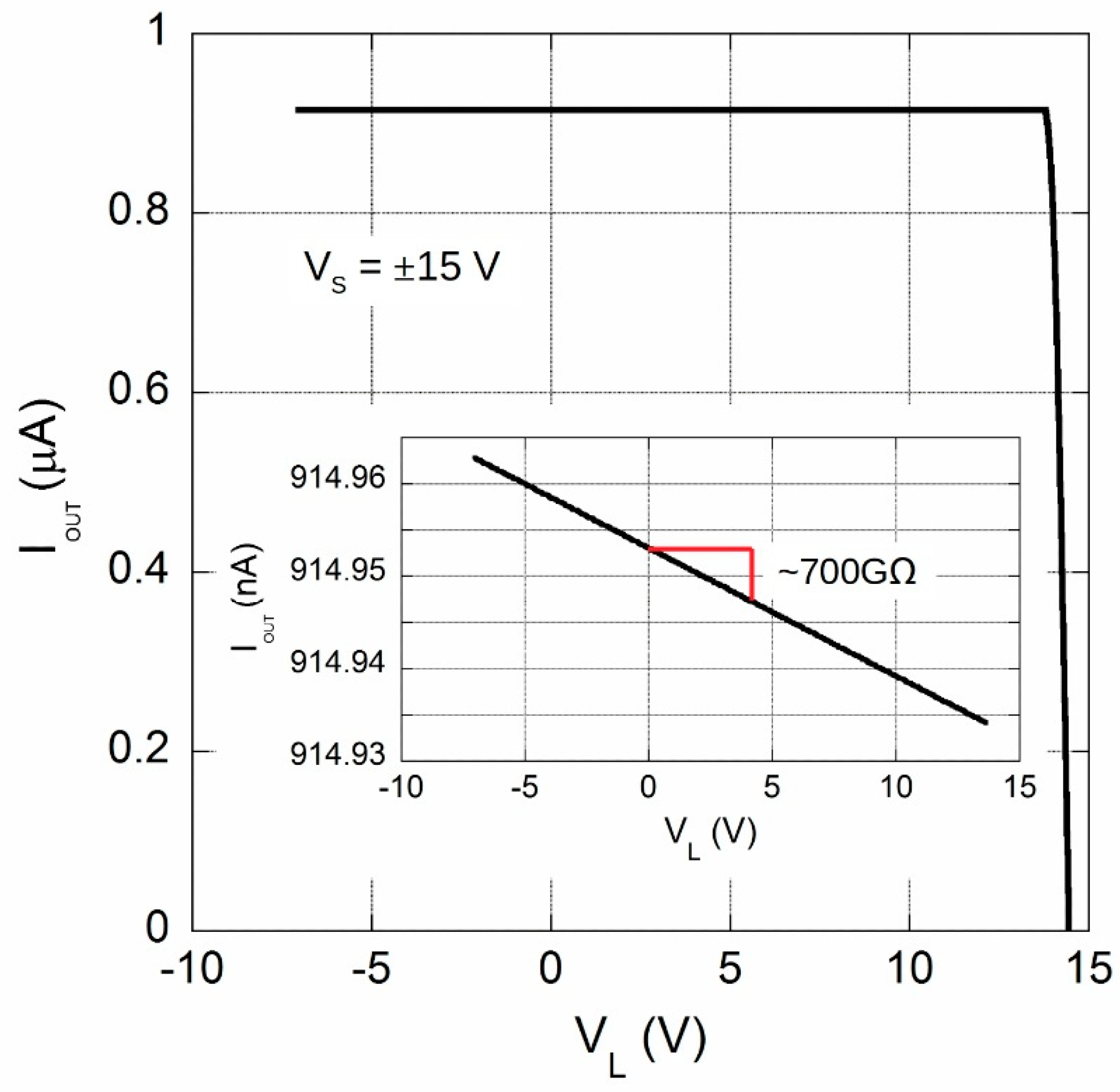
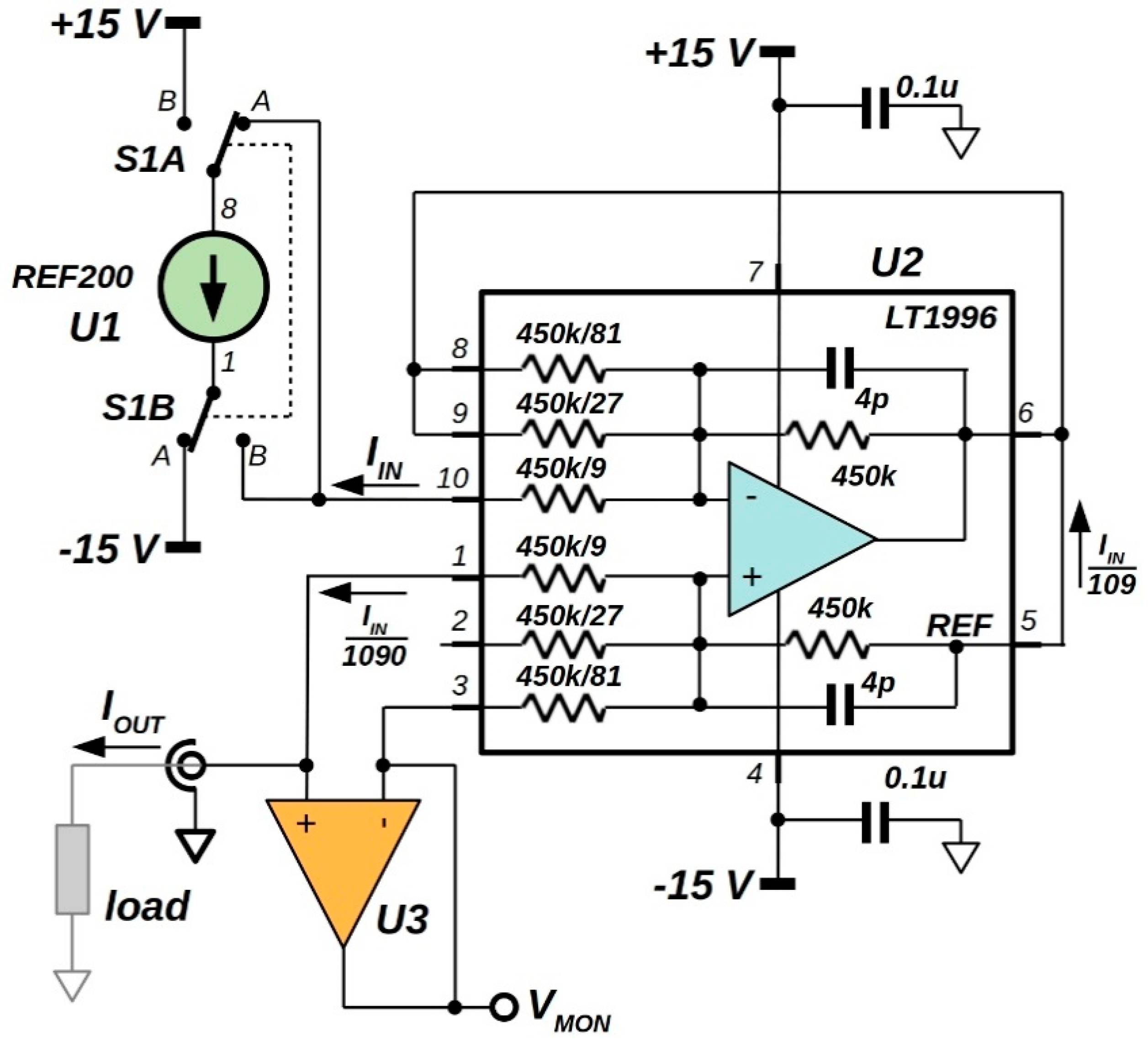
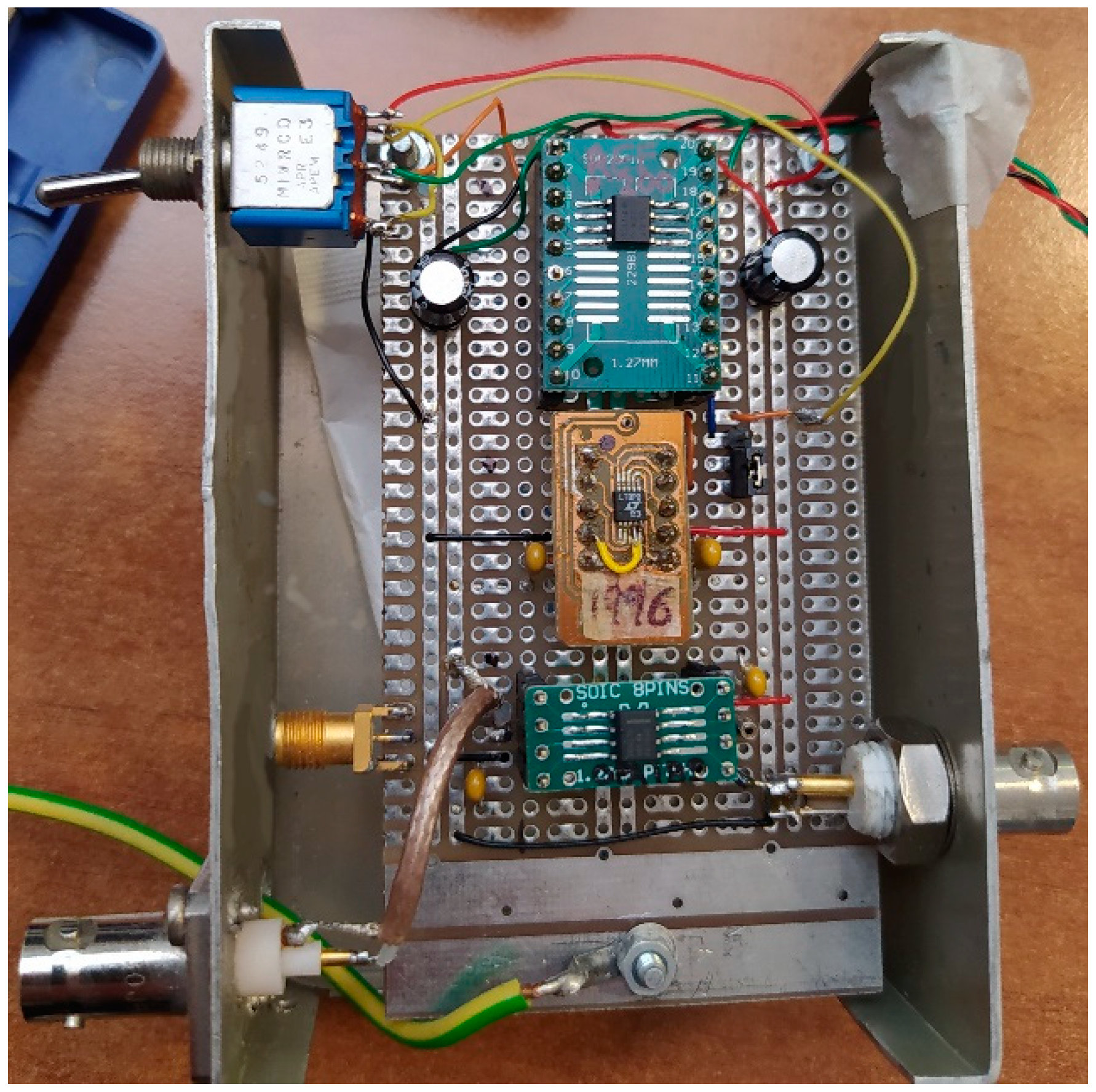



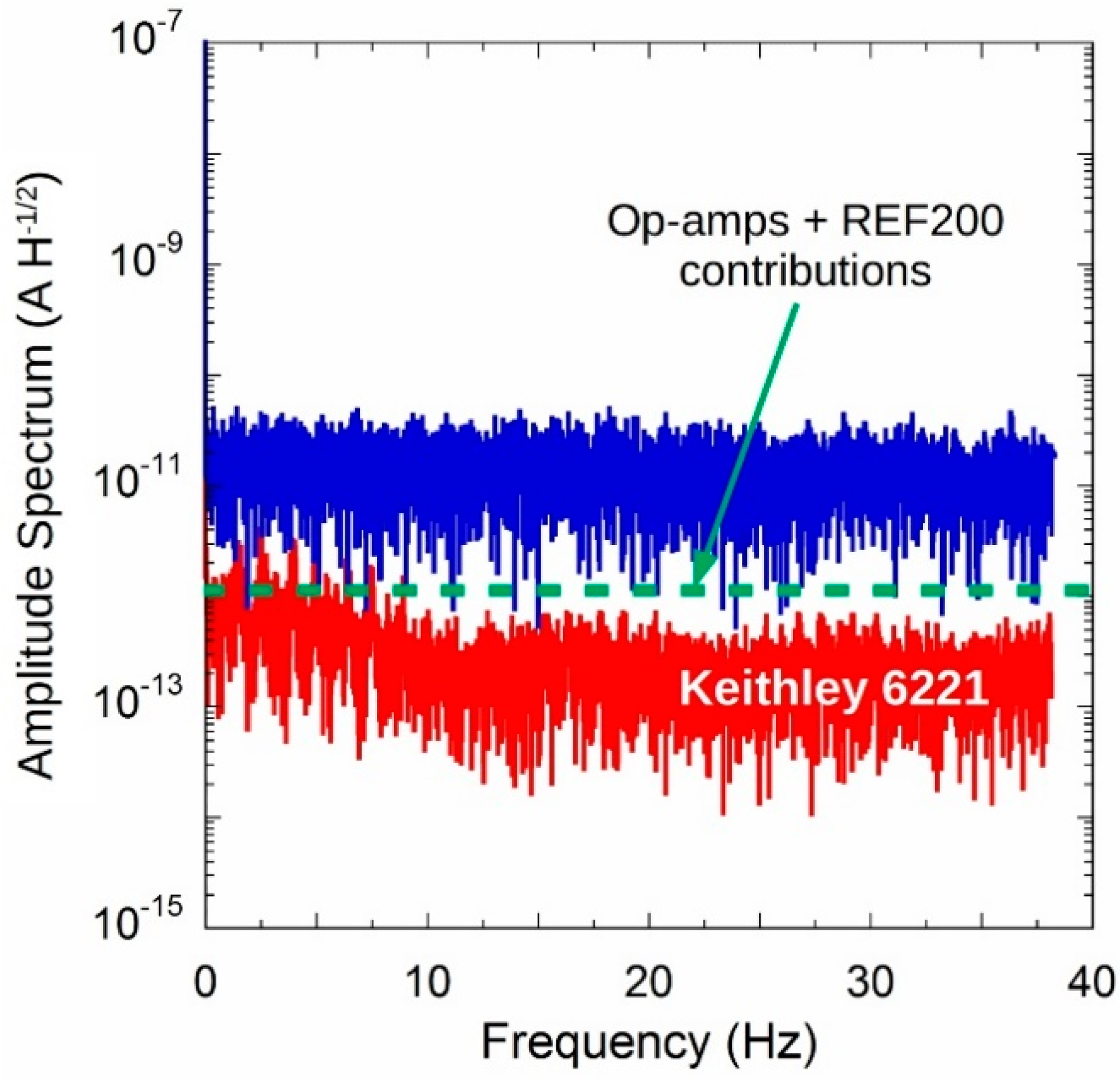
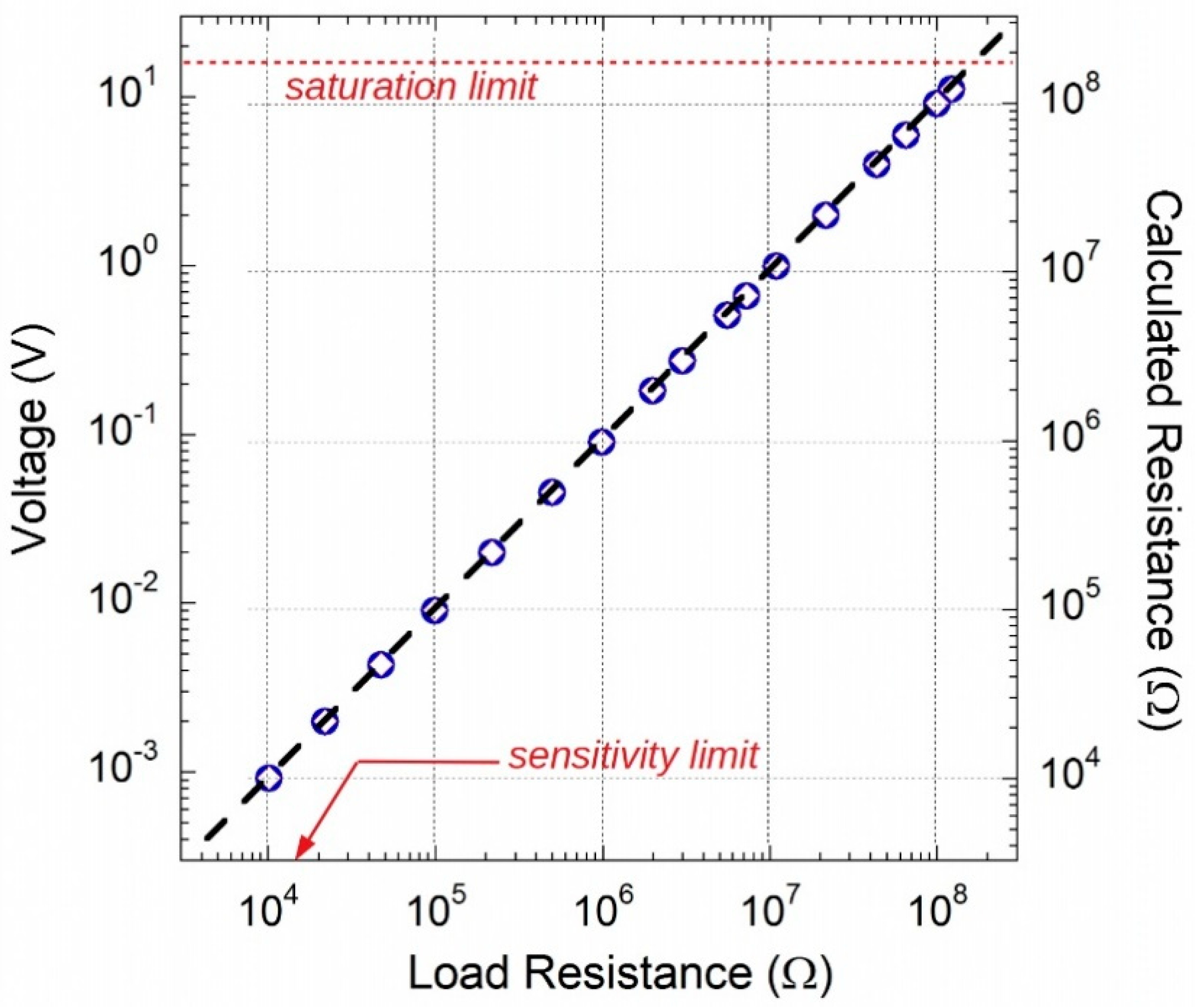
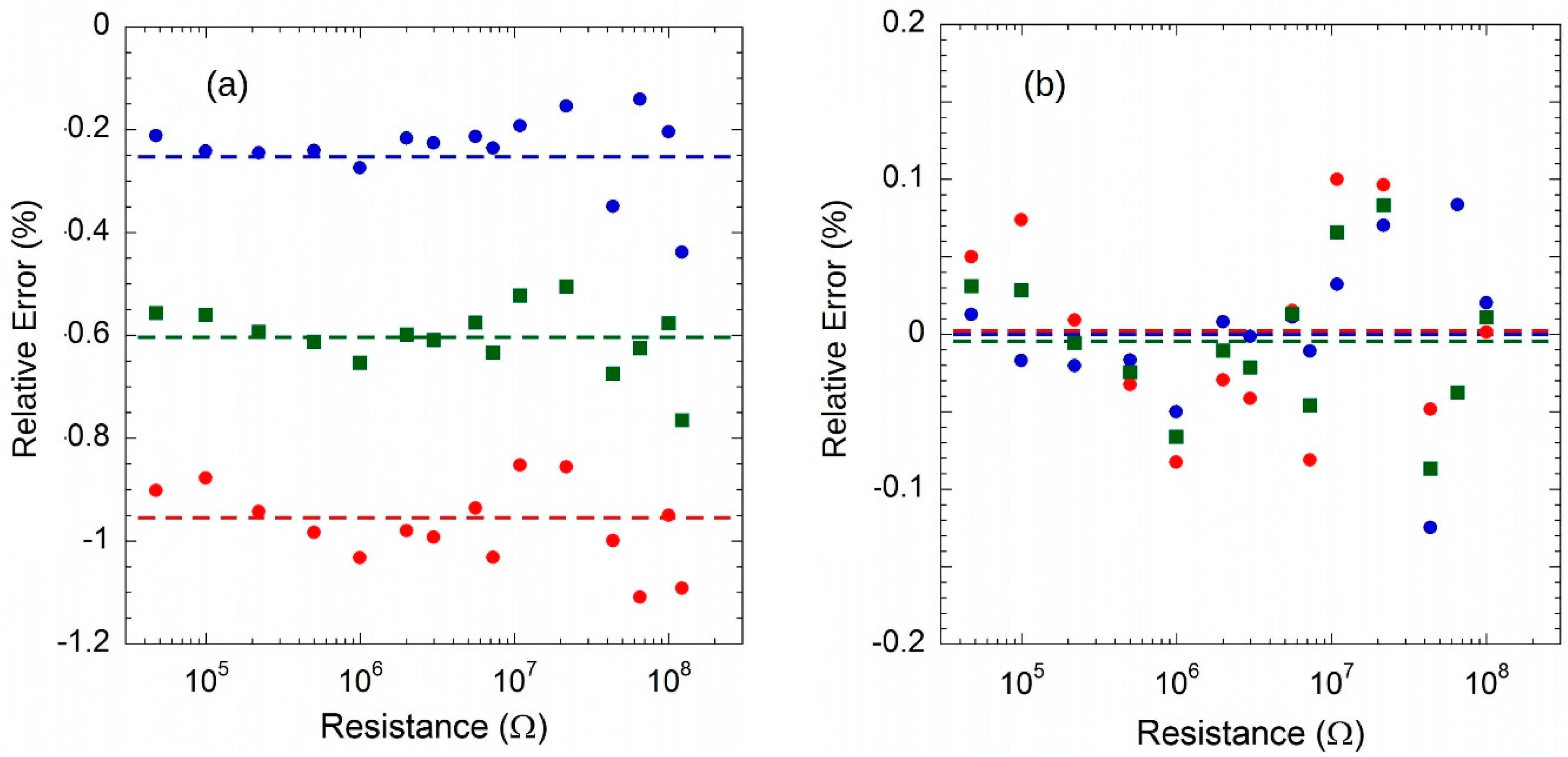
| Min | Typ | Max | Unit | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Current Value (nominal) | 917.4 | nA | ||
| Current Accuracy | ±0.54% | ±1.55% | ||
| Temperature Drift | 95 | ppm/°C | ||
| Output Impedance | 500 | 700 | 900 | GΩ |
| Voltage Compliance (source) | −VEE + 8 V | VCC − 1.2 V | ||
| Voltage Compliance (sink) | −VEE + 1.2 V | VCC − 8 V | ||
| Supply Voltage | ±20 | V |
| U3 | IB (nA) | VOS (µV) | TCOS (µV/°C) | CMRR (dB) | IOUT_SOURCE (nA) | IOUT_SINK (nA) | ROUT (GΩ) | IB (nA) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OP07 | 4 | 75 | 1.3 | 120 | 91.495 | −91.991 | 38.7 | −0.248 |
| OP27 | 80 | 100 | 0.6 | 120 | 91.495 | −91.991 | 5.7 | −0.248 |
| OP1177 | 3.8 | 61 | 2.2 | 126 | 93.488 | −89.998 | 3.1 | 1.745 |
| OPA189 | 0.3 | 3 | 0.005 | 168 | 91.430 | −92.056 | 270 | −0.313 |
| OP191 | 65 | 500 | 1.1 | 90 | 120.01 | −63.475 | 10.7 | 28.27 |
| LTC1022 | 0.15 | 1000 | 3 | 92 | 91.495 | −91.991 | 22 | −0.248 |
| LTC2054 | 0.003 | 10 | 0.1 | 130 | 91.496 | −91.990 | 258 | −0.247 |
| Min | Typ | Max | Unit | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supply Voltage (±VS) | 8 | 20 | V | |
| Current Value (source) | 91.06 | nA | ||
| Current Value (sink) | −92.183 | nA | ||
| Initial accuracy | −0.74 | +0.48 | % | |
| Temperature drift | ppm/°C | |||
| 10–40 °C | 10 | |||
| 0–70 °C | 30 | |||
| Output Resistance | 100 | GΩ | ||
| Voltage Compliance (source) | −7.5 | 14.5 | V | |
| Voltage Compliance (sink) | −14.5 | 7.3 | V | |
| Noise Current (f < 3 Hz) | 60 | pAP-P | ||
| 10 | pArms | |||
| Noise Current BW = 0.1 Hz to 40 Hz | 30 | pA/√Hz | ||
| Current Value (source) | 916.6 | nA | ||
| Current Value (sink) | −915.8 | nA | ||
| Initial accuracy | −0.09 | −0.2 | % | |
| Temperature drift 0–85 °C | 10 | ppm/°C | ||
| Voltage Compliance (source) | −7.5 | 14.5 | V | |
| Voltage Compliance (sink) | −14.5 | 7.5 | V |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pettinato, S.; Orsini, A.; Salvatori, S. Compact Current Reference Circuits with Low Temperature Drift and High Compliance Voltage. Sensors 2020, 20, 4180. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20154180
Pettinato S, Orsini A, Salvatori S. Compact Current Reference Circuits with Low Temperature Drift and High Compliance Voltage. Sensors. 2020; 20(15):4180. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20154180
Chicago/Turabian StylePettinato, Sara, Andrea Orsini, and Stefano Salvatori. 2020. "Compact Current Reference Circuits with Low Temperature Drift and High Compliance Voltage" Sensors 20, no. 15: 4180. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20154180
APA StylePettinato, S., Orsini, A., & Salvatori, S. (2020). Compact Current Reference Circuits with Low Temperature Drift and High Compliance Voltage. Sensors, 20(15), 4180. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20154180







