Detection of Potentially Compromised Computer Nodes and Clusters Connected on a Smart Grid, Using Power Consumption Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- Detect if a node and/or a cluster is infected;
- (2)
- Differentiate between different types of applications;
- (3)
- Detect occupancy of a node and/or a cluster.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimentation Setup
2.2. Proposed Methodology
2.2.1. Preprocessing
2.2.2. Descriptive Analysis
2.2.3. Comparing Power Consumption with and without Virus
2.2.4. Implications of Three Factors
- Mean values of the observations due to one factor (presence or absence of virus) are the same.
- Mean values of the observations due to another factor (difference in applications: multimedia related, office related, idle) are the same.
- There is no interaction between the two factors (presence/absence of virus and variety of applications).
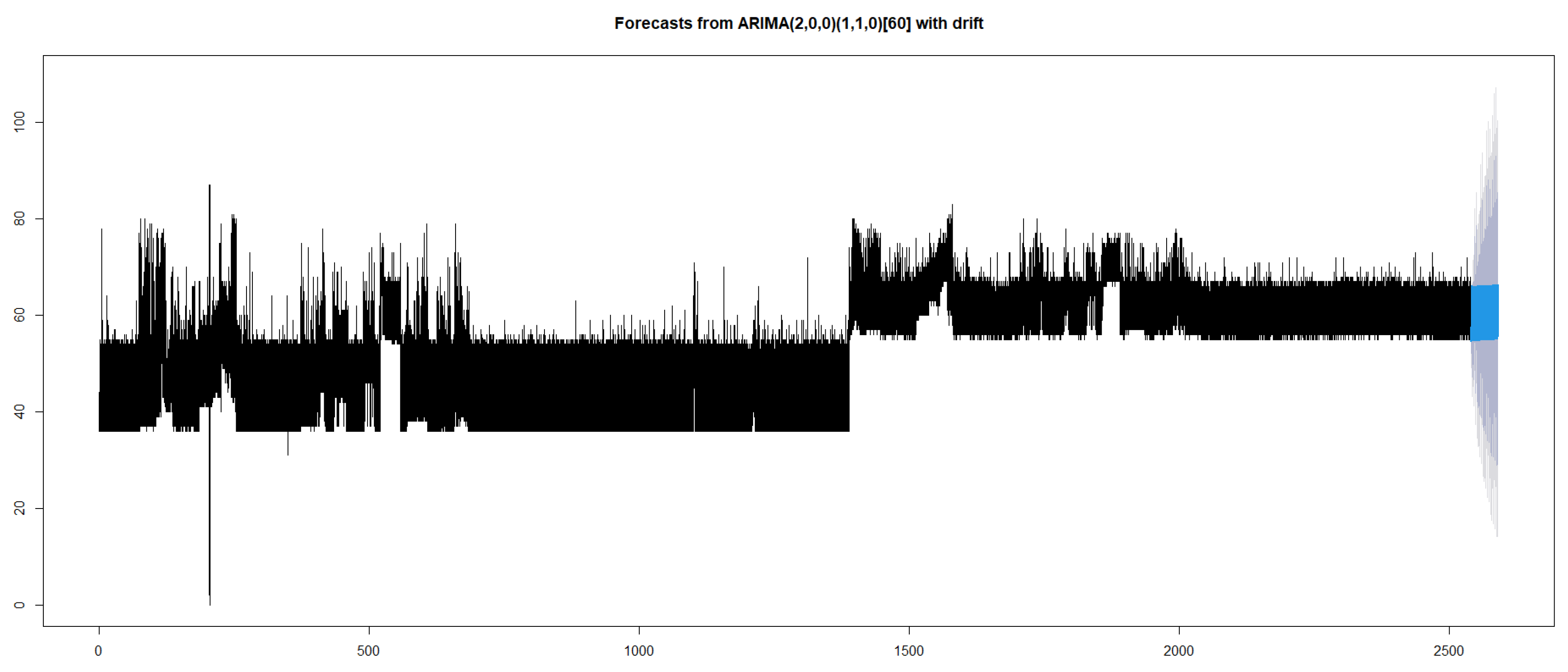
2.2.5. Time Series
- p: The number of previous/lagged Y values considered in our model for each time point. p indicates autoregressive component;
- d: The number of differences considered in our model to follow stationarity;
- q: The number of previous/lagged error values considered in our model for each time point.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preprocessing
3.2. Descriptive Analysis
3.3. Comparing Power Consumption with and without Virus
3.4. Implications of Three Factors
- Viruses have an impact on the power;
- A variety of applications impact the power consumption of the system;
- There is an interaction between the virus and the application with regards to the impact on the system.
3.5. Time Series
3.6. Outcomes from the Analysis
- Descriptive analysis: Average and standard deviation of power consumption varied while running any specific application, with or without virus;
- F-Test of two samples of variances: variances of power consumption varied with the presence or absence of virus;
- Two-way ANOVA: The interaction between the presence or absence of virus and the specific application running does impact the power consumption on the computer. Power consumption of the computer also varied due to the type of the application and whether the virus was running or not;
- Time-Series: Time series analysis on the dataset reveals that the power consumption can be represented with ARIMA model using autoregression.
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alamaniotis, M.; Bourbakis, N.; Tsoukalas, L.H. Enhancing privacy of electricity consumption in smart cities through morphing of anticipated demand pattern utilizing self-elasticity and genetic algorithms. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 46, 101426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talaat, M.; Alsayyari, A.S.; Alblawi, A.; Hatata, A.Y. Hybrid-cloud-based data processing for power system monitoring in smart grids. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 55, 102049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinakis, V.; Karakosta, C.; Doukas, H.; Androulaki, S.; Psarras, J. A building automation and control tool for remote and real time monitoring of energy consumption. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2013, 6, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roselyn, J.P.; Uthra, R.A.; Raj, A.; Devaraj, D.; Bharadwaj, P.; Krishna Kaki, S.V.D. Development and implementation of novel sensor fusion algorithm for occupancy detection and automation in energy efficient buildings. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 44, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luckett, P.; McDonald, J.T.; Glisson, W.B.; Benton, R.; Dawson, J.; Doyle, B.A. Identifying stealth malware using CPU power consumption and learning algorithms. J. Comput. Secur. 2018, 26, 589–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez Jimenez, J.; Goseva-Popstojanova, K. Malware Detection Using Power Consumption and Network Traffic Data. In Proceedings of the 2019 2nd International Conference on Data Intelligence and Security (ICDIS), South Padre Island, TX, USA, 28–30 June 2019; pp. 53–59. [Google Scholar]
- Ioaneş, A.; Tȋrnovan, R. Power Grid Health Assessment Using Machine Learning Algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2019 11th International Symposium on Advanced Topics in Electrical Engineering (ATEE), Bucharest, Romania, 28–30 March 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Mehrotra, D.; Srivastava, R.; Nagpal, R.; Nagpal, D. Multiclass classification of mobile applications as per energy consumption. J. King Saud Univ. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Android Anomaly Detection System uSing Machine Learning Classification-IEEE Conference Publication. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/7352512 (accessed on 24 August 2020).
- Zefferer, T.; Teufl, P.; Derler, D.; Potzmader, K.; Oprisnik, A.; Gasparitz, H.; Höller, A. Power Consumption-based Application Classification and Malware Detection on Android Using Machine-Learning Techniques. In Proceedings of the Future Computing 2013: The Fifth International Conference on Future Computational Technologies and Applications, IARIA, Valencia, Spain, 27 May–1 June 2013; pp. 26–31. [Google Scholar]
- Electrical Devices Identification through Power Consumption Using Machine Learning Techniques | Semantic Scholar. Available online: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Electrical-Devices-Identification-through-Power-Abeykoon-Kankanamdurage/f0ea3eabe628010a092f505b64ce26f48e82424f (accessed on 24 August 2020).
- Moon, J.; Park, J.; Hwang, E.; Jun, S. Forecasting power consumption for higher educational institutions based on machine learning. J. Supercomput. 2018, 74, 3778–3800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, M.; Wang, X.; Bu, Z.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y. Prediction of energy consumption in hotel buildings via support vector machines. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 57, 102128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajowniczek, K.; Ząbkowski, T. Two-Stage Electricity Demand Modeling Using Machine Learning Algorithms. Energies 2017, 10, 1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Markovič, R.; Gosak, M.; Grubelnik, V.; Marhl, M.; Virtič, P. Data-driven classification of residential energy consumption patterns by means of functional connectivity networks. Appl. Energy 2019, 242, 506–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, J.; Khan, M.; Talha, M.; Farman, H.; Jan, B.; Muhammad, A.; Khattak, H.A. A generic internet of things architecture for controlling electrical energy consumption in smart homes. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 43, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourdeau, M.; Zhai, X.; Nefzaoui, E.; Guo, X.; Chatellier, P. Modeling and forecasting building energy consumption: A review of data-driven techniques. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 48, 101533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croce, D.; Giuliano, F.; Tinnirello, I.; Giarré, L. Privacy-Preserving Overgrid: Secure Data Collection for the Smart Grid. Sensors 2020, 20, 2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Ji, X.; Li, Y.; Xu, W. Power-Based Non-Intrusive Condition Monitoring for Terminal Device in Smart Grid. Sensors 2020, 20, 3635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Lee, Y.S. A Low-Cost Surge Current Detection Sensor with Predictive Lifetime Display Function for Maintenance of Surge Protective Devices. Sensors 2020, 20, 2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blazakis, K.V.; Kapetanakis, T.N.; Stavrakakis, G.S. Effective Electricity Theft Detection in Power Distribution Grids Using an Adaptive Neuro Fuzzy Inference System. Energies 2020, 13, 3110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cibinskiene, A.; Dumciuviene, D.; Andrijauskiene, M. Energy Consumption in Public Buildings: The Determinants of Occupants’ Behavior. Energies 2020, 13, 3586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J. IoT-Based Smart Plug for Residential Energy Conservation: An Empirical Study Based on 15 Months’ Monitoring. Energies 2020, 13, 4035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myridakis, D.; Spathoulas, G.; Kakarountas, A.; Schinianakis, D. Smart Devices Security Enhancement via Power Supply Monitoring. Future Internet 2020, 12, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moradzadeh, A.; Sadeghian, O.; Pourhossein, K.; Mohammadi-Ivatloo, B.; Anvari-Moghaddam, A. Improving Residential Load Disaggregation for Sustainable Development of Energy via Principal Component Analysis. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahia, F.; Dey, A.R.; Masud, M.A.; Mahmud, M.S. Forecasting Electricity Consumption using ARIMA Model. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Sustainable Technologies for Industry 4.0 (STI), Dhaka, Bangladesh, 24–25 December 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, M.; Wang, Z. Prediction of the Energy Consumption Variation Trend in South Africa based on ARIMA, NGM and NGM-ARIMA Models. Energies 2020, 13, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pérez, X. Configuration of Sonoff Sensor to Espurna Firmware. Available online: https://github.com/xoseperez/espurna (accessed on 24 August 2020).
- Running on Raspberry Pi: Node-RED. Available online: https://nodered.org/docs/getting-started/raspberrypi (accessed on 24 August 2020).
- DeadLine’s Virus Maker 1.8.5. Available online: http://superhackings.blogspot.com/2015/08/deadlines-virus-maker-185free-download.html (accessed on 24 August 2020).
- Hyndman, R.J.; Khandakar, Y. Automatic Time Series Forecasting: The forecast Package for R. J. Stat. Softw. 2008, 27, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
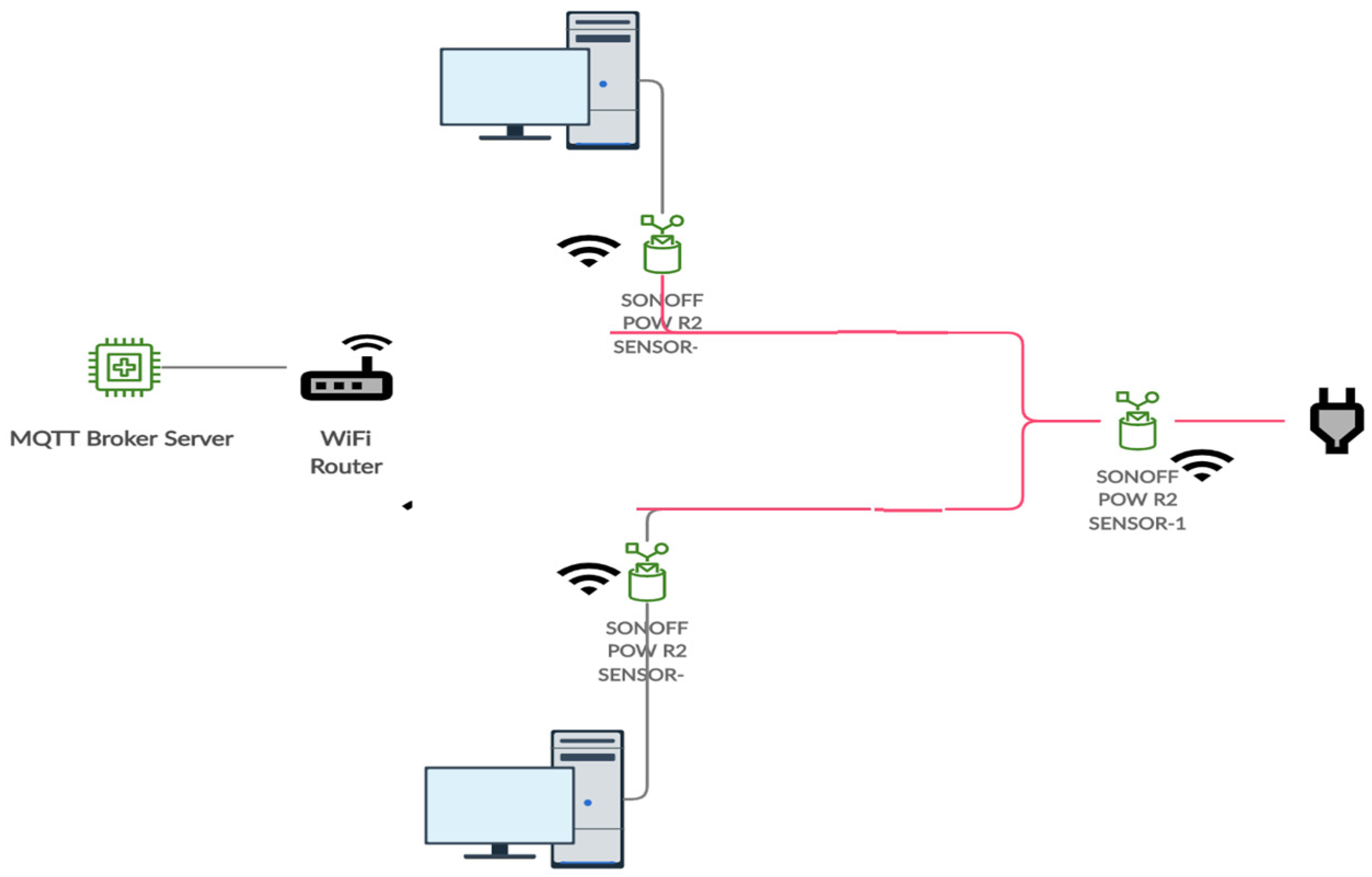

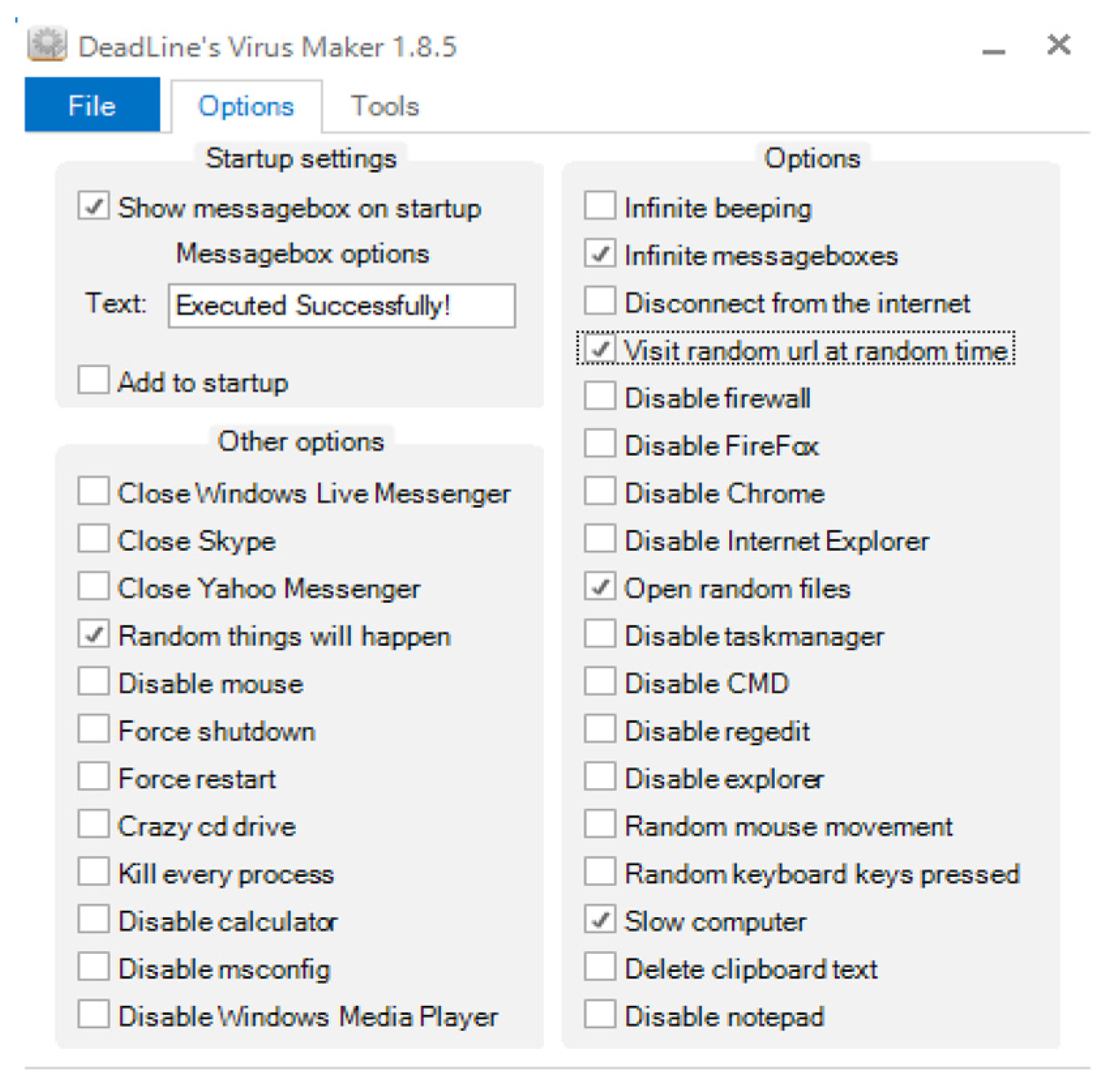


| # | Application Name/Action/Process | 1st Day | 2nd Day | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Start Time | End Time | Start Time | End Time | ||
| 1 | Start of Experiment | 05:01 | 05:35 | ||
| 2 | Open the virus on desktop 2–Sensor 2 | - | - | 08:00 | |
| 3 | NetBeans | 08:00 | 09:00 | 08:05 | 09:00 |
| 4 | Idle | 09:00 | 09:10 | 09:00 | 9:10 |
| 5 | MS Word | 9:10 | 10:00 | 9:10 | 10:00 |
| 6 | Idle | 10:00 | 10:07 | 10:00 | 10:07 |
| 7 | YouTube 240p | 10:07 | 10:20 | 10:07 | 10:20 |
| 8 | YouTube 360p | 10:21 | 10:35 | 10:21 | 10:35 |
| 9 | YouTube 1080p | 10:36 | 10:50 | 10:36 | 10:50 |
| 10 | YouTube 1440p | 10:51 | 11:15 | 10:51 | 11:15 |
| 11 | YouTube 4K | 11:15 | 11:25 | 11:15 | 11:25 |
| 12 | Idle | 11:25 | 11:30 | 11:25 | 11:30 |
| 13 | MS Excel | 11:30 | 12:00 | 11:30 | 12:00 |
| 14 | Idle | 12:00 | 13:35 | 12:00 | 13:35 |
| 15 | 3D Builder (Paint 3D) | 13:35 | 14:20 | 13:35 | 14:20 |
| 16 | Idle | 14:21 | 14:40 | 14:21 | 14:40 |
| 17 | Copy Large Files 1st Half From USB to PC | 14:40 | 15:05 | 14:40 | 15:05 |
| 18 | Idle | 15:05 | 15:40 | 15:05 | 15:40 |
| 19 | Copy Large Files 1st Half From PC to USB | 15:40 | 16:00 | 15:40 | 16:00 |
| 20 | Idle | 16:01 | 16:10 | 16:01 | 16:10 |
| 21 | Game (The great unknown Houdini’s castle) (Game Crashed at Desktop 2–Then Opened again with no issue) | 16:11 | 16:50 | 16:11 | 16:50 |
| 22 | Idle | 16:51 | 17:00 | 16:51 | 17:00 |
| 23 | Fusion 360 | 17:00 | 17:41 | 17:00 | 17:41 |
| 24 | Idle | 17:41 | 18:00 | 17:41 | 18:00 |
| 25 | MS PowerPoint | 18:00 | 18:30 | 18:00 | 18:30 |
| 26 | Idle | 18:31 | 18:35 | 18:31 | 18:35 |
| 27 | Web Browsing | 18:36 | 19:00 | 18:36 | 19:00 |
| 28 | Idle | 19:00 | 05:35 | 19:00 | 05:35 |
| 29 | End of Experiment | 05:35 | 05:35 | ||
| Original Dataset | Preprocessed Dataset | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Application ID | Inactive Virus | Active Virus | Application ID | Inactive Virus | Active Virus |
| 0 | 55,630 | 47,929 | 0 | 494 | 494 |
| 1 | 3123 | 3235 | 1 | 494 | 494 |
| 2 | 2624 | 2869 | 2 | 494 | 494 |
| 3 | 771 | 704 | 3 | 494 | 494 |
| 4 | 736 | 889 | 4 | 494 | 494 |
| 5 | 846 | 884 | 5 | 494 | 494 |
| 6 | 1216 | 1173 | 6 | 494 | 494 |
| 7 | 597 | 494 | 7 | 494 | 494 |
| 8 | 1626 | 1715 | 8 | 494 | 494 |
| 9 | 2576 | 2674 | 9 | 494 | 494 |
| 10 | 1160 | 1179 | 10 | 494 | 494 |
| 11 | 1410 | 1416 | 11 | 494 | 494 |
| 12 | 2338 | 2029 | 12 | 494 | 494 |
| 13 | 2387 | 1934 | 13 | 494 | 494 |
| 14 | 1524 | 1823 | 14 | 494 | 494 |
| 15 | 1475 | 1282 | 15 | 494 | 494 |
| 16 | 0 | 126 | |||
| Application ID | AVE (No Virus): Current | STDEV (No Virus): Current | AVE (Virus): Current | STDEV (Virus): Current | AVE (No Virus): Power | STDEV (No Virus): Power | AVE (Virus): Power | STDEV (Virus): Power |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.274250333 | 0.028103 | 0.347148 | 0.020521 | 41.65125 | 7.485862 | 60.35578 | 4.995615 |
| 1 | 0.30206212 | 0.040198 | 0.279725 | 0.032956 | 49.17003 | 10.83542 | 43.31901 | 8.913672 |
| 2 | 0.282293826 | 0.029435 | 0.351423 | 0.019544 | 43.69131 | 7.785045 | 61.7839 | 5.003486 |
| 3 | 0.294744488 | 0.027763 | 0.349382 | 0.016515 | 47.10895 | 7.176698 | 60.8821 | 4.130037 |
| 4 | 0.338485054 | 0.282622 | 0.352319 | 0.018267 | 47.13043 | 9.747805 | 61.50731 | 4.612483 |
| 5 | 0.310338061 | 0.027774 | 0.347696 | 0.017278 | 51.02364 | 7.14727 | 60.18891 | 4.235889 |
| 6 | 0.328525493 | 0.02398 | 0.351409 | 0.018236 | 55.54605 | 6.243444 | 60.99829 | 4.507483 |
| 7 | 0.336469012 | 0.045425 | 0.360682 | 0.014323 | 59.01173 | 12.08047 | 63.31984 | 3.612988 |
| 8 | 0.276551661 | 0.028898 | 0.374414 | 0.015795 | 42.26999 | 7.718847 | 66.68105 | 3.88115 |
| 9 | 0.285190606 | 0.031642 | 0.346214 | 0.017018 | 44.44293 | 8.223566 | 59.27786 | 4.086996 |
| 10 | 0.304116379 | 0.030956 | 0.355818 | 0.020229 | 49.19138 | 7.936956 | 61.79389 | 4.938064 |
| 11 | 0.299434043 | 0.029658 | 0.352472 | 0.019252 | 48.02128 | 7.655155 | 60.73729 | 4.650185 |
| 12 | 0.342401625 | 0.025261 | 0.353526 | 0.020993 | 58.9337 | 6.272336 | 61.61656 | 5.078656 |
| 13 | 0.289771261 | 0.030464 | 0.374752 | 0.023172 | 45.81232 | 8.066154 | 66.72285 | 5.671899 |
| 14 | 0.282875328 | 0.029596 | 0.350807 | 0.018327 | 43.95276 | 8.015767 | 61.19748 | 4.584067 |
| 15 | 0.300162712 | 0.035122 | 0.345573 | 0.017133 | 48.56271 | 9.288857 | 59.97738 | 4.294064 |
| Variance of Power in Idle Condition | Variance of Power with Application 3 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable 1 | Variable 2 | Variable 1 | Variable 2 | ||
| Mean | 39.93072 | 60.02728 | Mean | 58.67635 | 60.01577 |
| Variance | 112.9857 | 42.28129 | Variance | 42.94666 | 18.63846 |
| Observations | 72,354 | 72,354 | Observations | 1205 | 1205 |
| df (Degrees of Freedom) | 72,353 | 72,353 | df (Degrees of freedom) | 1204 | 1204 |
| F (F ratio) | 2.672238 | F (F ratio) | 2.304196 | ||
| P(F< = f) one-tail | 0 | P(F< = f) one-tail | 1.53 × 10−46 | ||
| F-Critical one-tail | 1.012305 | F-Critical one-tail | 1.099489 | ||
| ANOVA | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source of Variation | SS (Sum of Squares) | df (Degrees of Freedom) | MS (Mean Squares) | F (F Ratio) | p-Value | F-Critical |
| Virus | 150,880.9 | 1 | 150,880.9 | 2603.692 | 0 | 3.841753 |
| Application | 17,516,617 | 1 | 17,516,617 | 302277.3 | 0 | 3.841753 |
| Interaction | 104,200.9 | 1 | 104,200.9 | 1798.154 | 0 | 3.841753 |
| Within | 1,831,878 | 31,612 | 57.94883 | |||
| Total | 19,603,577 | 31,615 | ||||
| ANOVA | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source of Variation | SS (Sum of Squares) | df (Degrees of Freedom) | MS (Mean Squares) | F (F Ratio) | p-Value | F-Critical |
| Virus | 2429.457 | 1 | 2429.457 | 39.57663 | 3.21 × 10−10 | 3.841853 |
| Application | 17,168,455 | 1 | 17,168,455 | 279679.6 | 0 | 3.841853 |
| Interaction | 2429.457 | 1 | 2429.457 | 39.57663 | 3.21 × 10−10 | 3.841853 |
| Within | 1,448,467 | 23,596 | 61.38615 | |||
| Total | 18,621,781 | 23,599 | ||||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Almshari, M.; Tsaramirsis, G.; Khadidos, A.O.; Buhari, S.M.; Khan, F.Q.; Khadidos, A.O. Detection of Potentially Compromised Computer Nodes and Clusters Connected on a Smart Grid, Using Power Consumption Data. Sensors 2020, 20, 5075. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20185075
Almshari M, Tsaramirsis G, Khadidos AO, Buhari SM, Khan FQ, Khadidos AO. Detection of Potentially Compromised Computer Nodes and Clusters Connected on a Smart Grid, Using Power Consumption Data. Sensors. 2020; 20(18):5075. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20185075
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlmshari, Mohammed, Georgios Tsaramirsis, Adil Omar Khadidos, Seyed Mohammed Buhari, Fazal Qudus Khan, and Alaa Omar Khadidos. 2020. "Detection of Potentially Compromised Computer Nodes and Clusters Connected on a Smart Grid, Using Power Consumption Data" Sensors 20, no. 18: 5075. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20185075
APA StyleAlmshari, M., Tsaramirsis, G., Khadidos, A. O., Buhari, S. M., Khan, F. Q., & Khadidos, A. O. (2020). Detection of Potentially Compromised Computer Nodes and Clusters Connected on a Smart Grid, Using Power Consumption Data. Sensors, 20(18), 5075. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20185075






