Resolving Position Ambiguity of IMU-Based Human Pose with a Single RGB Camera
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. IMU-Based Motion Capture
2.2. Image-Based Motion Capture
2.3. Motion Capture Fusing IMUs and Other Sensors
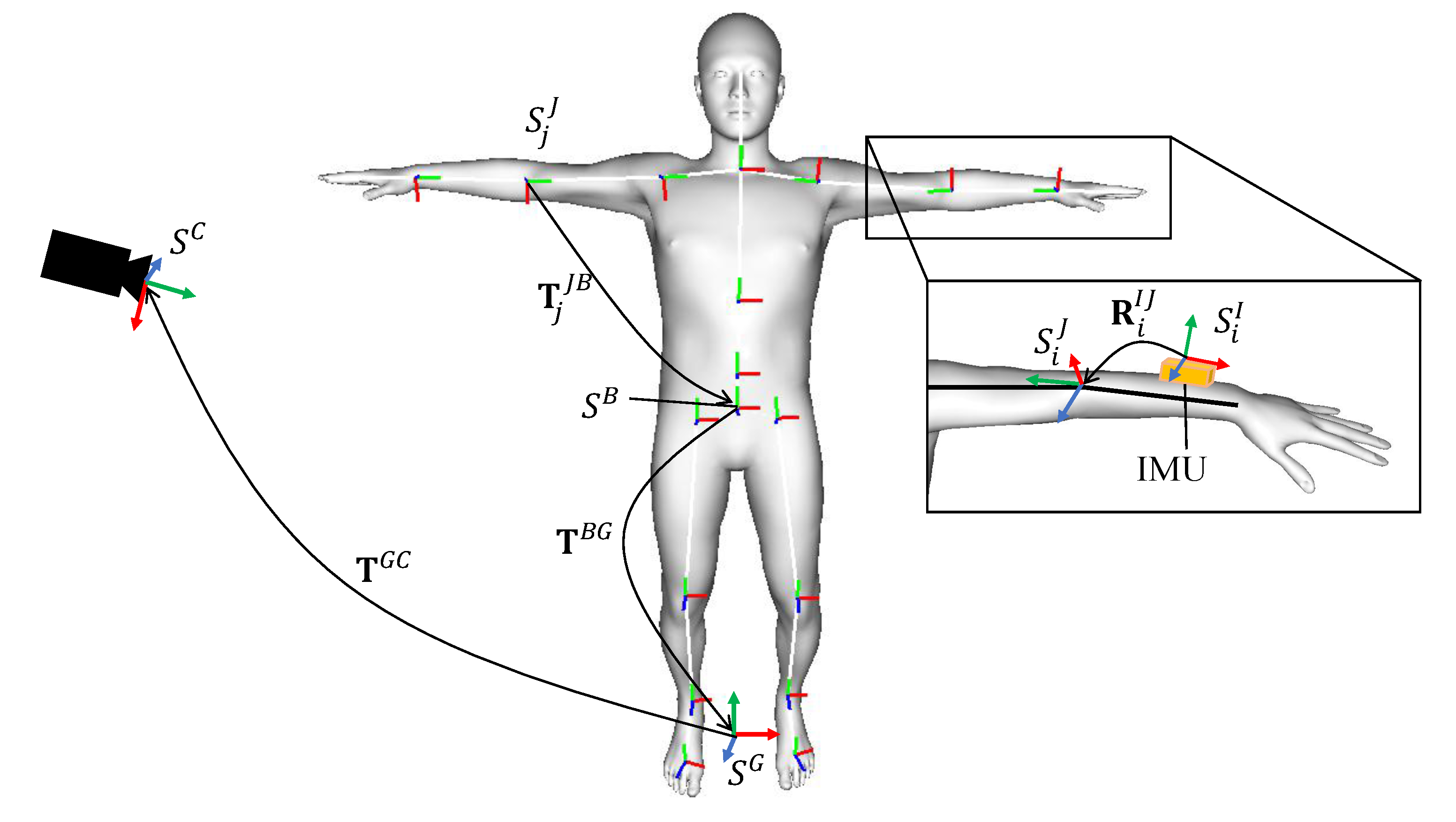
3. Methods
3.1. Pose Parameterization and Calibration
3.2. Full-Body Pose Optimization
3.2.1. IMU-Based Constraints
3.2.2. Image-Based Constraints
4. Evaluation
4.1. Dataset
4.2. Implementation Details
4.3. Contribution of the Proposed Cost Terms
4.4. The Number of IMUs
5. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, Y.; Kaufmann, M.; Aksan, E.; Black, M.J.; Hilliges, O.; Pons-Moll, G. Deep inertial poser: Learning to reconstruct human pose from sparse inertial measurements in real time. ACM Trans. Graph. TOG 2018, 37, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Marcard, T.; Rosenhahn, B.; Black, M.J.; Pons-Moll, G. Sparse inertial poser: Automatic 3D human pose estimation from sparse IMUs. In Computer Graphics Forum; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; Volume 36, pp. 349–360. [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama, T.; Tada, M.; Toda, H. Riding Motion Capture System Using Inertial Measurement Units with Contact Constraints. Int. J. Autom. Technol. 2019, 13, 506–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, B.; Wu, H.; Wei, Y. Simple baselines for human pose estimation and tracking. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 466–481. [Google Scholar]
- Luvizon, D.C.; Tabia, H.; Picard, D. Human pose regression by combining indirect part detection and contextual information. Comput. Graph. 2019, 85, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Simon, T.; Wei, S.E.; Sheikh, Y. Realtime multi-person 2D pose estimation using part affinity fields. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 7291–7299. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, G.; Sun, J. Cascaded pyramid network for multi-person pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7103–7112. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, K.; Xiao, B.; Liu, D.; Wang, J. Deep High-Resolution Representation Learning for Human Pose Estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Barbosa, J.J.; García-Ramírez, T.; Salas, J.; Hurtado-Ramos, J.B. Optimal camera placement for total coverage. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Kobe, Japan, 12–17 May 2009; pp. 844–848. [Google Scholar]
- Kalkbrenner, C.; Hacker, S.; Algorri, M.E.; Blechschmidt-Trapp, R. Motion Capturing with Inertial Measurement Units and Kinect. In Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies, Angers, France, 3–6 March 2014; Volume 1, pp. 120–126. [Google Scholar]
- Haynes, S.; Williams, K. Impact of seating posture on user comfort and typing performance for people with chronic low back pain. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2008, 38, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, L. Gesture recognition for human-robot collaboration: A review. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2018, 68, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousdar Ahmed, D.; Munoz Diaz, E.; García Domínguez, J.J. Automatic Calibration of the Step Length Model of a Pocket INS by Means of a Foot Inertial Sensor. Sensors 2020, 20, 2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zihajehzadeh, S.; Yoon, P.K.; Kang, B.S.; Park, E.J. UWB-aided inertial motion capture for lower body 3-D dynamic activity and trajectory tracking. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2015, 64, 3577–3587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garofalo, G.; Argones Rúa, E.; Preuveneers, D.; Joosen, W. A Systematic Comparison of Age and Gender Prediction on IMU Sensor-Based Gait Traces. Sensors 2019, 19, 2945. [Google Scholar]
- Trumble, M.; Gilbert, A.; Malleson, C.; Hilton, A.; Collomosse, J. Total Capture: 3D Human Pose Estimation Fusing Video and Inertial Sensors; BMVC: Guildford, UK, 2017; Volume 2, p. 3. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, L.; Xiong, S. Accuracy of base of support using an inertial sensor based motion capture system. Sensors 2017, 17, 2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veges, M.; Lorincz, A. Multi-Person Absolute 3D Human Pose Estimation with Weak Depth Supervision. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.03989. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez, J.; Hossain, R.; Romero, J.; Little, J. A Simple Yet Effective Baseline for 3d Human Pose Estimation. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2659–2668. [Google Scholar]
- Nibali, A.; He, Z.; Morgan, S.; Prendergast, L. 3d human pose estimation with 2d marginal heatmaps. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Waikoloa Village, HI, USA, 7–11 January 2019; pp. 1477–1485. [Google Scholar]
- Moreno-Noguer, F. 3D Human Pose Estimation From a Single Image via Distance Matrix Regression. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1561–1570. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, D.; Joo, H.; Sheikh, Y. Monocular total capture: Posing face, body, and hands in the wild. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 10965–10974. [Google Scholar]
- Arnab, A.; Doersch, C.; Zisserman, A. Exploiting temporal context for 3D human pose estimation in the wild. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 3395–3404. [Google Scholar]
- Von Marcard, T.; Pons-Moll, G.; Rosenhahn, B. Human pose estimation from video and IMUs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2016, 38, 1533–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malleson, C.; Gilbert, A.; Trumble, M.; Collomosse, J.; Hilton, A.; Volino, M. Real-time full-body motion capture from video and IMUs. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), Qingdao, China, 10–12 October 2017; pp. 449–457. [Google Scholar]
- Pons-Moll, G.; Baak, A.; Helten, T.; Müller, M.; Seidel, H.P.; Rosenhahn, B. Multisensor-fusion for 3d full-body human motion capture. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Francisco, CA, USA, 12–18 June 2010; pp. 663–670. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, C.; Qin, W.; Zeng, W. Fusing Wearable IMUs With Multi-View Images for Human Pose Estimation: A Geometric Approach. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 16–18 June 2020; pp. 2197–2206. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Z.; Yu, T.; Li, H.; Guo, K.; Dai, Q.; Fang, L.; Liu, Y. HybridFusion: Real-time performance capture using a single depth sensor and sparse IMUs. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 384–400. [Google Scholar]
- Von Marcard, T.; Henschel, R.; Black, M.J.; Rosenhahn, B.; Pons-Moll, G. Recovering accurate 3D human pose in the wild using IMUs and a moving camera. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 601–617. [Google Scholar]
- Endo, Y.; Tada, M.; Mochimaru, M. Dhaiba: Development of virtual ergonomic assessment system with human models. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Digital Human Symposium, Tokyo, Japan, 20–22 May 2014; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z. A flexible new technique for camera calibration. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2000, 22, 1330–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennis, J.E., Jr.; Moré, J.J. Quasi-Newton methods, motivation and theory. SIAM Rev. 1977, 19, 46–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggero Ronchi, M.; Perona, P. Benchmarking and error diagnosis in multi-instance pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 369–378. [Google Scholar]
- Moon, G.; Chang, J.Y.; Lee, K.M. Camera distance-aware top-down approach for 3d multi-person pose estimation from a single rgb image. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 10133–10142. [Google Scholar]



| S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | Mean | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W2 | A3 | F3 | W2 | A3 | R3 | W2 | A3 | F1 | W2 | A3 | F3 | W2 | F1 | F3 | ||
| Mean position error (cm) | ||||||||||||||||
| RGB only [34] | 52.4 | 90.1 | 22.5 | 33.3 | 22.6 | 27.4 | 51.4 | 26.9 | 24.6 | 50.4 | 53.3 | 56.1 | 57.7 | 37.1 | 43.1 | 43.3 |
| IMU only [3] | 45.0 | 42.7 | 44.2 | 144 | 63.9 | 8.91 | 34.8 | 72.3 | 62.4 | 42.3 | 221 | 39.4 | 124 | 32.9 | 81.0 | 70.6 |
| 54.4 | 41.7 | 29.4 | 142 | 63.3 | 12.2 | 33.0 | 68.8 | 68.5 | 42.8 | 224 | 39.2 | 124 | 28.2 | 78.1 | 70.0 | |
| 19.6 | 14.8 | 11.9 | 11.5 | 9.22 | 7.37 | 15.3 | 10.1 | 14.3 | 15.7 | 13.8 | 14.6 | 14.9 | 46.7 | 17.5 | 15.8 | |
| 20.2 | 15.6 | 12.2 | 12.2 | 10.2 | 7.32 | 15.2 | 12.5 | 11.1 | 16.3 | 12.3 | 14.7 | 16.0 | 10.0 | 16.9 | 13.5 | |
| Mean orientation error (degrees) | ||||||||||||||||
| IMU only [3] | 9.32 | 8.25 | 9.43 | 8.59 | 8.27 | 12.5 | 6.50 | 6.55 | 10.6 | 7.10 | 8.14 | 9.51 | 6.59 | 8.37 | 11.6 | 8.75 |
| 9.38 | 8.45 | 9.45 | 8.74 | 8.51 | 12.5 | 6.65 | 6.63 | 10.9 | 7.07 | 8.20 | 9.52 | 6.72 | 8.37 | 11.3 | 8.83 | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kaichi, T.; Maruyama, T.; Tada, M.; Saito, H. Resolving Position Ambiguity of IMU-Based Human Pose with a Single RGB Camera. Sensors 2020, 20, 5453. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20195453
Kaichi T, Maruyama T, Tada M, Saito H. Resolving Position Ambiguity of IMU-Based Human Pose with a Single RGB Camera. Sensors. 2020; 20(19):5453. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20195453
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaichi, Tomoya, Tsubasa Maruyama, Mitsunori Tada, and Hideo Saito. 2020. "Resolving Position Ambiguity of IMU-Based Human Pose with a Single RGB Camera" Sensors 20, no. 19: 5453. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20195453
APA StyleKaichi, T., Maruyama, T., Tada, M., & Saito, H. (2020). Resolving Position Ambiguity of IMU-Based Human Pose with a Single RGB Camera. Sensors, 20(19), 5453. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20195453





