Knocking and Listening: Learning Mechanical Impulse Response for Understanding Surface Characteristics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Surface Identification
2.2. Vibration-Based Approaches
3. Proposed System
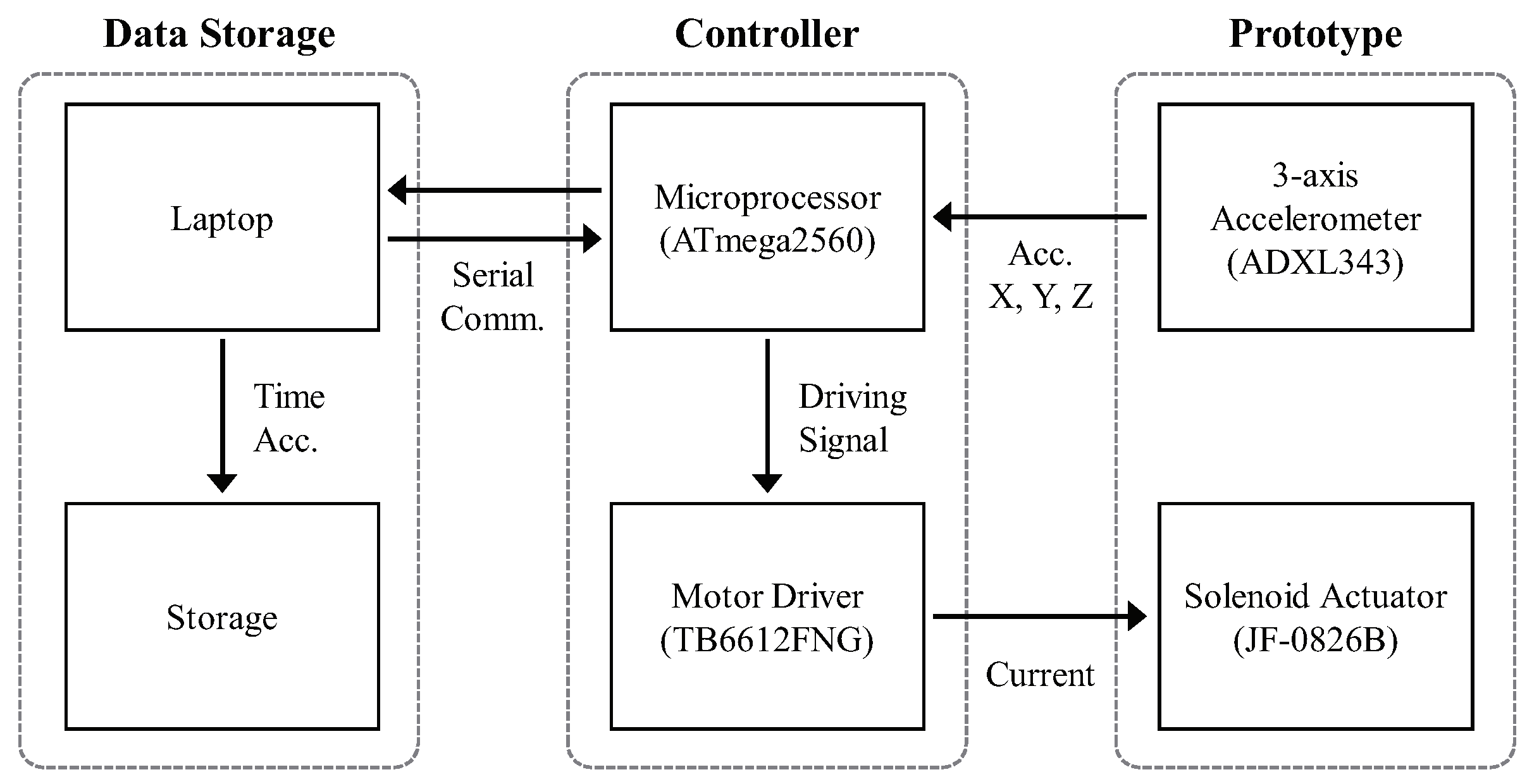
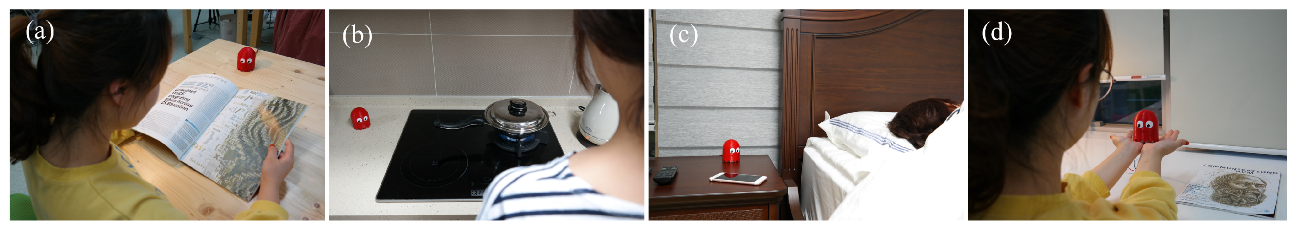
3.1. Hardware
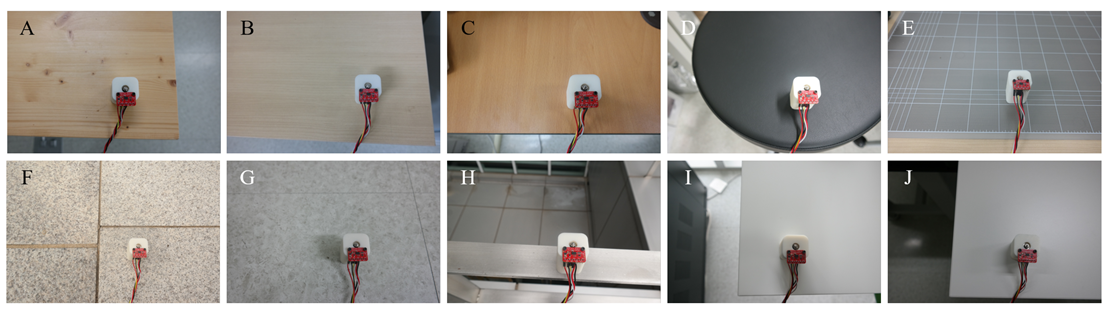
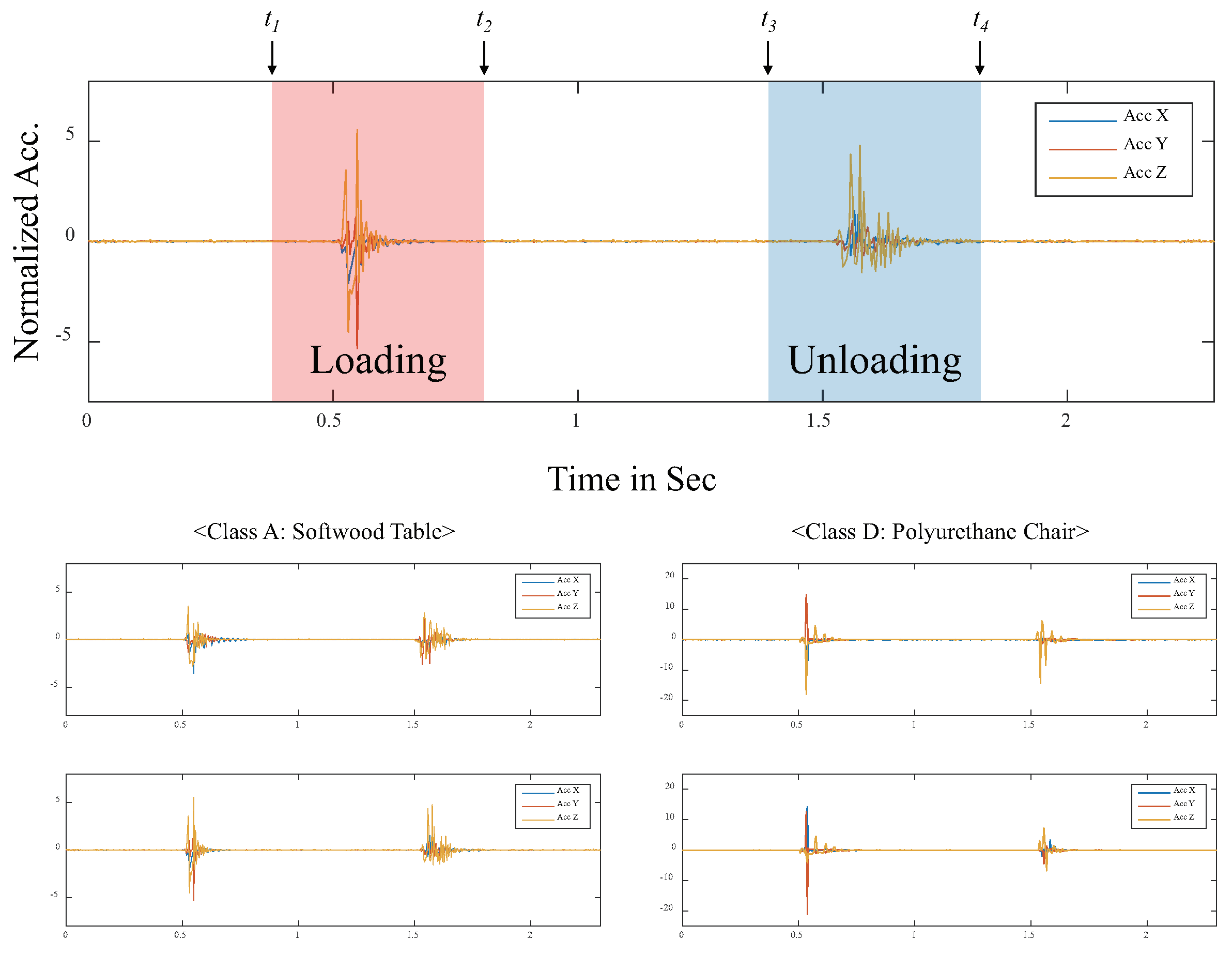
3.2. Dataset
3.3. Machine Learning
3.3.1. Baseline Classifier
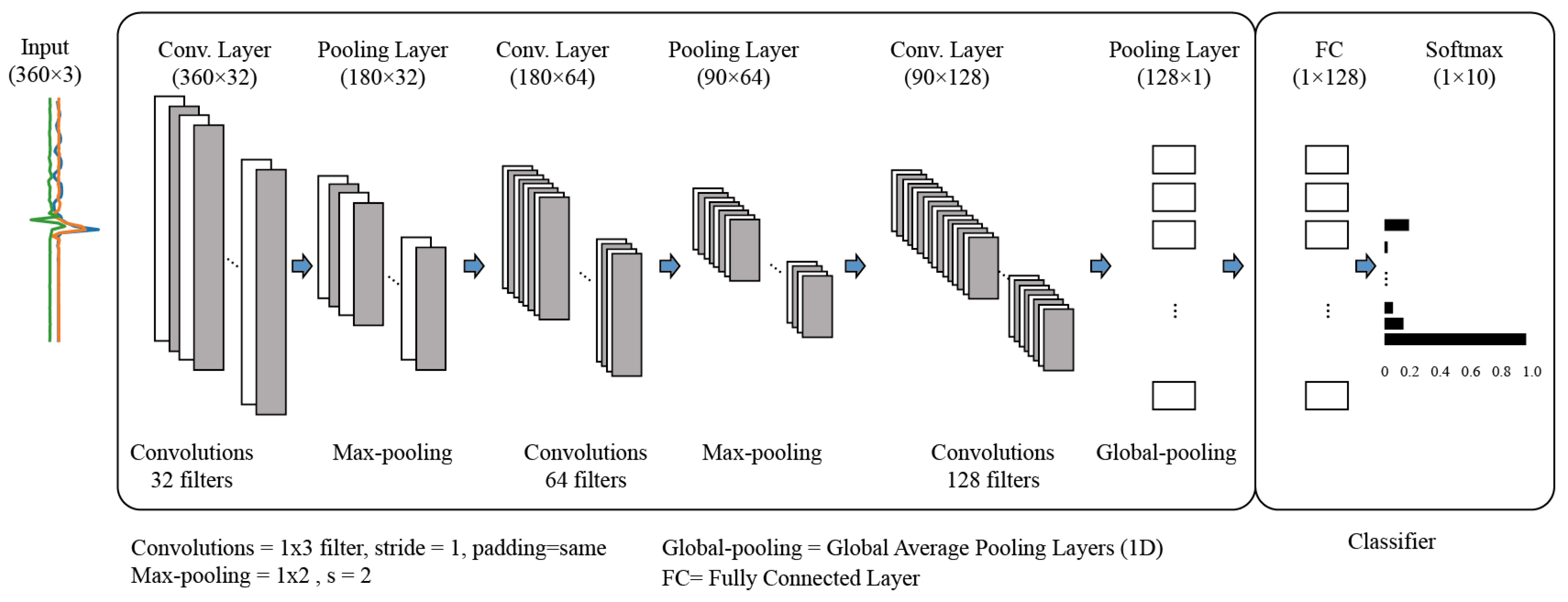
3.3.2. One-Dimensional CNN (1D-CNN) Model
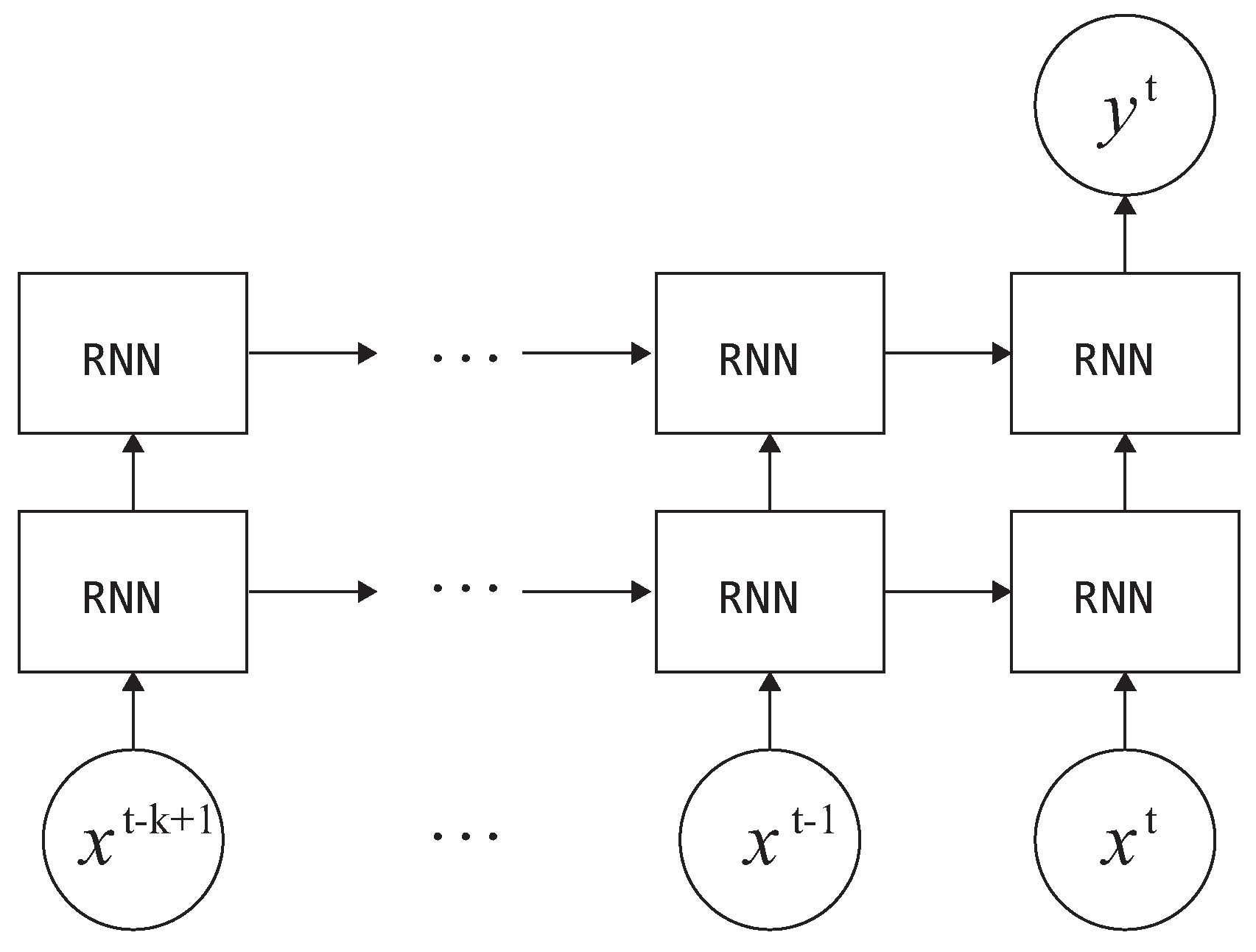
3.3.3. Gated RNNs—LSTM and GRU
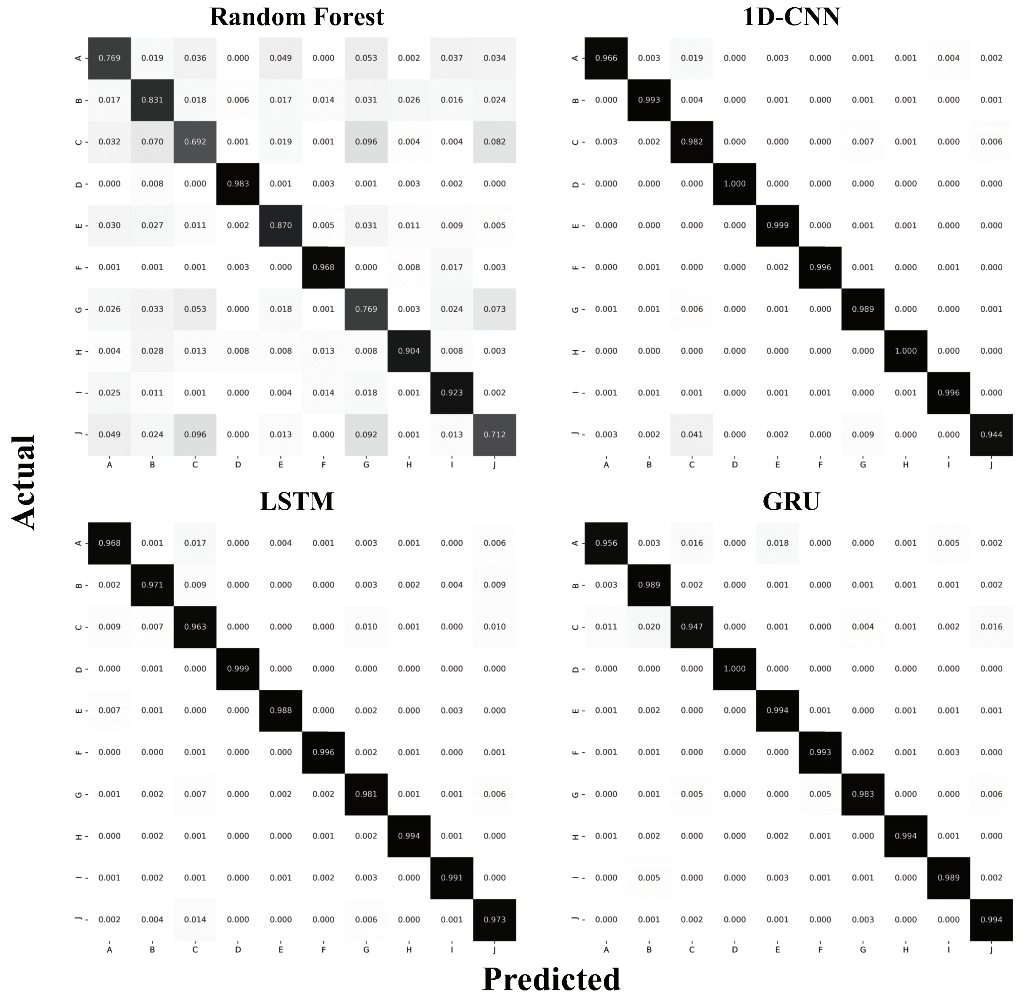
4. Evaluation
5. Discussion
5.1. General Discussion
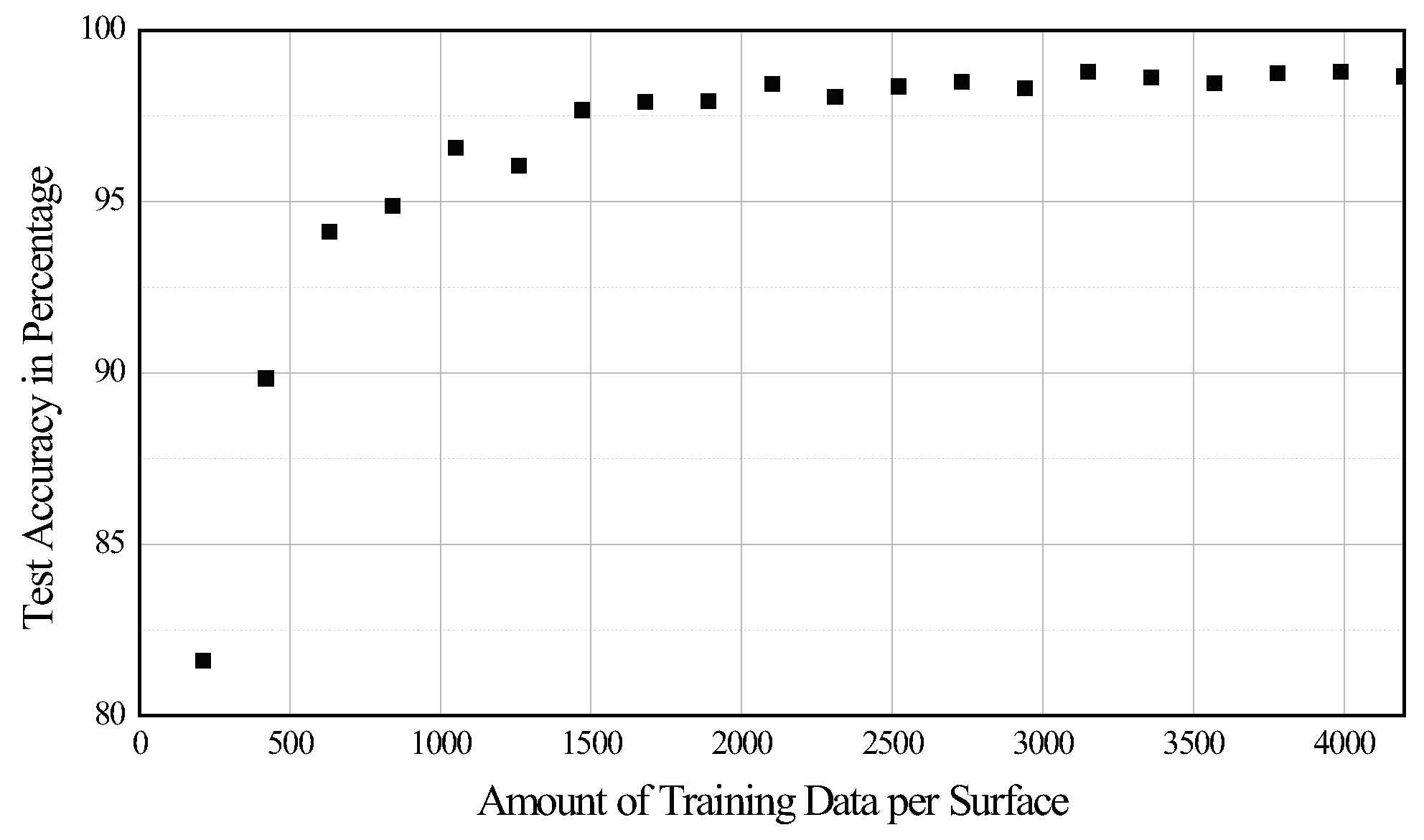
5.2. Scalability
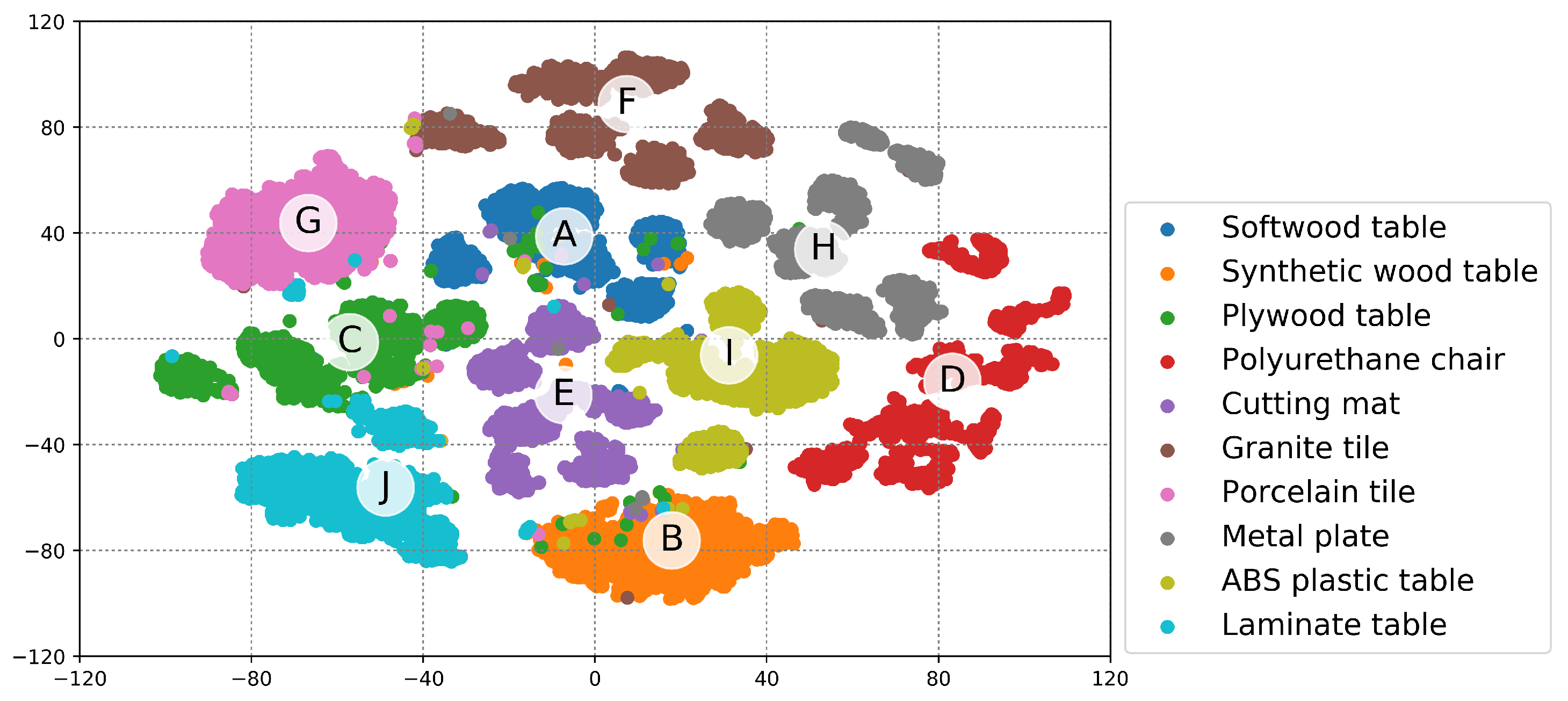
5.3. Context Understanding Based on Location
5.4. Limitations and Future Work
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Virant-Doberlet, M.; Cokl, A. Vibrational communication in insects. Neotrop. Entomol. 2004, 33, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocroft, R.B. Vibrational communication and the ecology of group-living, herbivorous insects. Am. Zool. 2001, 41, 1215–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wiley, R. Signal transmission in natural environments. New Encycl. Neurosci. 2009, 8, 827–832. [Google Scholar]
- Barth, F.G. Neuroethology of the spider vibration sense. In Neurobiology of Arachnids; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1985; pp. 203–229. [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, C.; Schwarz, J.; Hudson, S.E. TapSense: Enhancing Finger Interaction on Touch Surfaces. In Proceedings of the 24th Annual ACM Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology, New York, NY, USA, 16–19 October 2011; pp. 627–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, C.; Hudson, S.E. Scratch Input: Creating Large, Inexpensive, Unpowered and Mobile Finger Input Surfaces. In Proceedings of the 21st Annual ACM Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology, New York, NY, USA, 19–22 October 2008; pp. 205–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, S.; Lee, G. Forcetap: Extending the Input Vocabulary of Mobile Touch Screens by Adding Tap Gestures. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Human Computer Interaction with Mobile Devices and Services, New York, NY, USA, 30 August–2 September 2011; pp. 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, M.; Shizuki, B.; Tanaka, J. Touch & Activate: Adding Interactivity to Existing Objects Using Active Acoustic Sensing. In Proceedings of the 26th Annual ACM Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology, New York, NY, USA, 8–11 October 2013; pp. 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiltschi, K.; Pinz, A.; Lindeberg, T. An automatic assessment scheme for steel quality inspection. Mach. Vis. Appl. 2000, 12, 113–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, A. Neural network based detection of local textile defects. Pattern Recogn. 2003, 36, 1645–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvén, O.; Niskanen, M.; Kauppinen, H. Wood inspection with non-supervised clustering. Mach. Vis. Appl. 2003, 13, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pernkopf, F. Detection of surface defects on raw steel blocks using Bayesian network classifiers. Pattern Anal. Appl. 2004, 7, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monadjemi, A.; Mirmehdi, M.; Thomas, B. Restructured eigenfilter matching for novelty detection in random textures. Learning 2004, 5, 13. [Google Scholar]
- Tarapata, G.; Paczesny, D.; Nowak, B.; Jachowicz, R. Non-contact measurement system for the type of floor surface recognition using discrete optical methods. Elektron. Konstr. Technol. Zastos. 2015, 56, 9–11. [Google Scholar]
- Gillham, M.; Howells, G.; Spurgeon, S.; McElroy, B. Floor Covering and Surface Identification for Assistive Mobile Robotic Real-Time Room Localization Application. Sensors 2013, 13, 17501–17515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chandra, G.R.; Sathya, G.; Rajan, E.G.; Coyle, M.P. Surface Detection in 3D images using Cellular Logic Array Processing. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC), San Diego, CA, USA, 5–8 October 2014; pp. 847–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aujeszky, T.; Korres, G.; Eid, M. Thermography-based material classification using machine learning. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Symposium on Haptic, Audio and Visual Environments and Games (HAVE), Abu Dhabi, UAE, 22–23 October 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Aujeszky, T.; Korres, G.; Eid, M. Material classification with laser thermography and machine learning. Quant. Infrared Thermogr. J. 2019, 16, 181–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleyko, D.; Hostettler, R.; Birk, W.; Osipov, E. Comparison of machine learning techniques for vehicle classification using road side sensors. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 18th International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems, Las Palmas, Spain, 15–18 September 2015; pp. 572–577. [Google Scholar]
- Tarapata, G.; Paczesny, D.; Tarasiuk, Ł. Electronic system for floor surface type detection in robotics applications. In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Optical and Electronic Sensors, International Society for Optics and Photonics, Gdansk, Poland, 19–22 June 2016; Volume 10161, p. 1016111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perol, T.; Gharbi, M.; Denolle, M. Convolutional neural network for earthquake detection and location. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, e1700578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sato, M.; Poupyrev, I.; Harrison, C. Touché: Enhancing Touch Interaction on Humans, Screens, Liquids, and Everyday Objects. In Proceedings of the SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, New York, NY, USA, 5–10 May 2012; pp. 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.K.; Ryu, J.K.; Kim, S.C. Context-Aware Winter Sports Based on Multivariate Sequence Learning. Sensors 2019, 19, 3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kunze, K.; Lukowicz, P. Symbolic object localization through active sampling of acceleration and sound signatures. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Ubiquitous Computing, Innsbruck, Austria, 16–19 September 2007; pp. 163–180. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, J.; Hwang, I.; Oh, S. Vibration-based surface recognition for smartphones. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Conference on Embedded and Real-Time Computing Systems and Applications, Seoul, Korea, 19–22 August 2012; pp. 459–464. [Google Scholar]
- Laput, G.; Xiao, R.; Harrison, C. Viband: High-fidelity bio-acoustic sensing using commodity smartwatch accelerometers. In Proceedings of the 29th Annual Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology, Tokyo, Japan, 16–19 October 2016; pp. 321–333. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, L.; Ashoori, M.; Zhang, Y.; Azenkot, S. Knock knock, what’s there: converting passive objects into customizable smart controllers. In Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Human-Computer Interaction with Mobile Devices and Services, Barcelona, Spain, 3–6 September 2018; p. 31. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, T.; Cho, H.; Lee, B.; Lee, S.J. Knocker: Vibroacoustic-based Object Recognition with Smartphones. Proc. ACM Interact. Mob. Wearable Ubiquitous Technol. 2019, 3, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gislason, P.O.; Benediktsson, J.A.; Sveinsson, J.R. Random Forests for land cover classification. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 2006, 27, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levantesi, S.; Pizzorusso, V. Application of Machine Learning to Mortality Modeling and Forecasting. Risks 2019, 7, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y. Convolutional networks for images, speech, and time series. In The Handbook of Brain Theory and Neural Networks; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1995; Volume 3361, p. 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Yoon, S.M.; Cho, H. Human activity recognition from accelerometer data using Convolutional Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Big Data and Smart Computing (BigComp), Jeju, Korea, 13–16 February 2017; pp. 131–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronao, C.A.; Cho, S.B. Human activity recognition with smartphone sensors using deep learning neural networks. Expert Syst. Appl. 2016, 59, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengio, Y.; Simard, P.; Frasconi, P. Learning long-term dependencies with gradient descent is difficult. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 1994, 5, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.; Van Merriënboer, B.; Gulcehre, C.; Bahdanau, D.; Bougares, F.; Schwenk, H.; Bengio, Y. Learning phrase representations using RNN encoder-decoder for statistical machine translation. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1406.1078. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, P.; Zhou, H.; Cao, S.; Yang, P.; Xue, S. Control with Gestures: A Hand Gesture Recognition System Using Off-the-Shelf Smartwatch. In Proceedings of the 2018 4th International Conference on Big Data Computing and Communications (BIGCOM), Chicago, IL, USA, 7–9 August 2018; pp. 72–77. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, W.; Lim, S.C. Inferring interaction force from visual information without using physical force sensors. Sensors 2017, 17, 2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maaten, L.V.D.; Hinton, G. Visualizing data using t-SNE. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2008, 9, 2579–2605. [Google Scholar]


| Feature | Descriptions |
|---|---|
| mean | arithmetic mean (average) |
| median | median |
| min | minimum |
| max | maximum |
| max/min | ratio of max and min |
| std | standard deviation |
| skew | sample skewness |
| abs_min | minimum of absolute value |
| abs_max | maximum of absolute value |
| abs_mean | arithmetic mean of absolute value |
| abs_std | standard deviation of absolute value |
| Input Signals | Window | RF | 1D-CNN | LSTM | GRU |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acc. X | loading | 42.90 (0.430) | 93.10 (0.832) | 81.28 (0.813) | 79.77 (0.798) |
| Acc. Y | loading | 36.88 (0.368) | 81.39 (0.814) | 79.74 (0.798) | 76.63 (0.769) |
| Acc. Z | loading | 43.19 (0.427) | 86.00 (0.859) | 87.75 (0.877) | 85.41 (0.854) |
| Acc. X, Y | loading | 66.63 (0.666) | 92.09 (0.921) | 89.96 (0.900) | 86.86 (0.869) |
| Acc. X, Z | loading | 67.15 (0.671) | 94.52 (0.945) | 94.89 (0.949) | 93.22 (0.932) |
| Acc. Y, Z | loading | 60.32 (0.602) | 93.68 (0.937) | 95.57 (0.956) | 93.97 (0.940) |
| Acc. X, Y, Z | loading | 75.79 (0.758) | 96.38 (0.964) | 97.51 (0.975) | 96.37 (0.964) |
| Acc. X | unloading | 40.07 (0.399) | 77.58 (0.777) | 78.04 (0.781) | 77.90 (0.778) |
| Acc. Y | unloading | 34.71 (0.348) | 75.13 (0.751) | 76.38 (0.764) | 73.59 (0.738) |
| Acc. Z | unloading | 51.82 (0.516) | 87.29 (0.873) | 88.18 (0.882) | 87.83 (0.879) |
| Acc. X, Y | unloading | 63.99 (0.638) | 90.33 (0.904) | 90.59 (0.906) | 88.74 (0.887) |
| Acc. X, Z | unloading | 72.61 (0.725) | 95.26 (0.953) | 95.22 (0.952) | 94.64 (0.946) |
| Acc. Y, Z | unloading | 69.06 (0.689) | 94.62 (0.946) | 94.57 (0.946) | 93.28 (0.933) |
| Acc. X, Y, Z | unloading | 78.34 (0.782) | 96.91 (0.969) | 97.57 (0.976) | 96.82 (0.968) |
| Acc. X | both | 46.33 (0.462) | 87.82 (0.878) | 78.36 (0.785) | 86.81 (0.868) |
| Acc. Y | both | 37.77 (0.381) | 88.25 (0.882) | 78.21 (0.781) | 83.17 (0.833) |
| Acc. Z | both | 48.78 (0.482) | 95.19 (0.952) | 93.78 (0.938) | 95.28 (0.953) |
| Acc. X, Y | both | 73.04 (0.730) | 96.11 (0.961) | 93.67 (0.937) | 94.04 (0.943) |
| Acc. X, Z | both | 79.09 (0.729) | 98.39 (0.984) | 97.19 (0.972) | 98.21 (0.982) |
| Acc. Y, Z | both | 68.92 (0.689) | 98.56 (0.986) | 97.28 (0.973) | 98.07 (0.981) |
| Acc. X, Y, Z | both | 84.21 (0.842) | 98.66 (0.987) | 98.23 (0.982) | 98.39 (0.984) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ryu, S.; Kim, S.-C. Knocking and Listening: Learning Mechanical Impulse Response for Understanding Surface Characteristics. Sensors 2020, 20, 369. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20020369
Ryu S, Kim S-C. Knocking and Listening: Learning Mechanical Impulse Response for Understanding Surface Characteristics. Sensors. 2020; 20(2):369. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20020369
Chicago/Turabian StyleRyu, Semin, and Seung-Chan Kim. 2020. "Knocking and Listening: Learning Mechanical Impulse Response for Understanding Surface Characteristics" Sensors 20, no. 2: 369. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20020369
APA StyleRyu, S., & Kim, S.-C. (2020). Knocking and Listening: Learning Mechanical Impulse Response for Understanding Surface Characteristics. Sensors, 20(2), 369. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20020369





