Towards Automated 3D Inspection of Water Leakages in Shield Tunnel Linings Using Mobile Laser Scanning Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
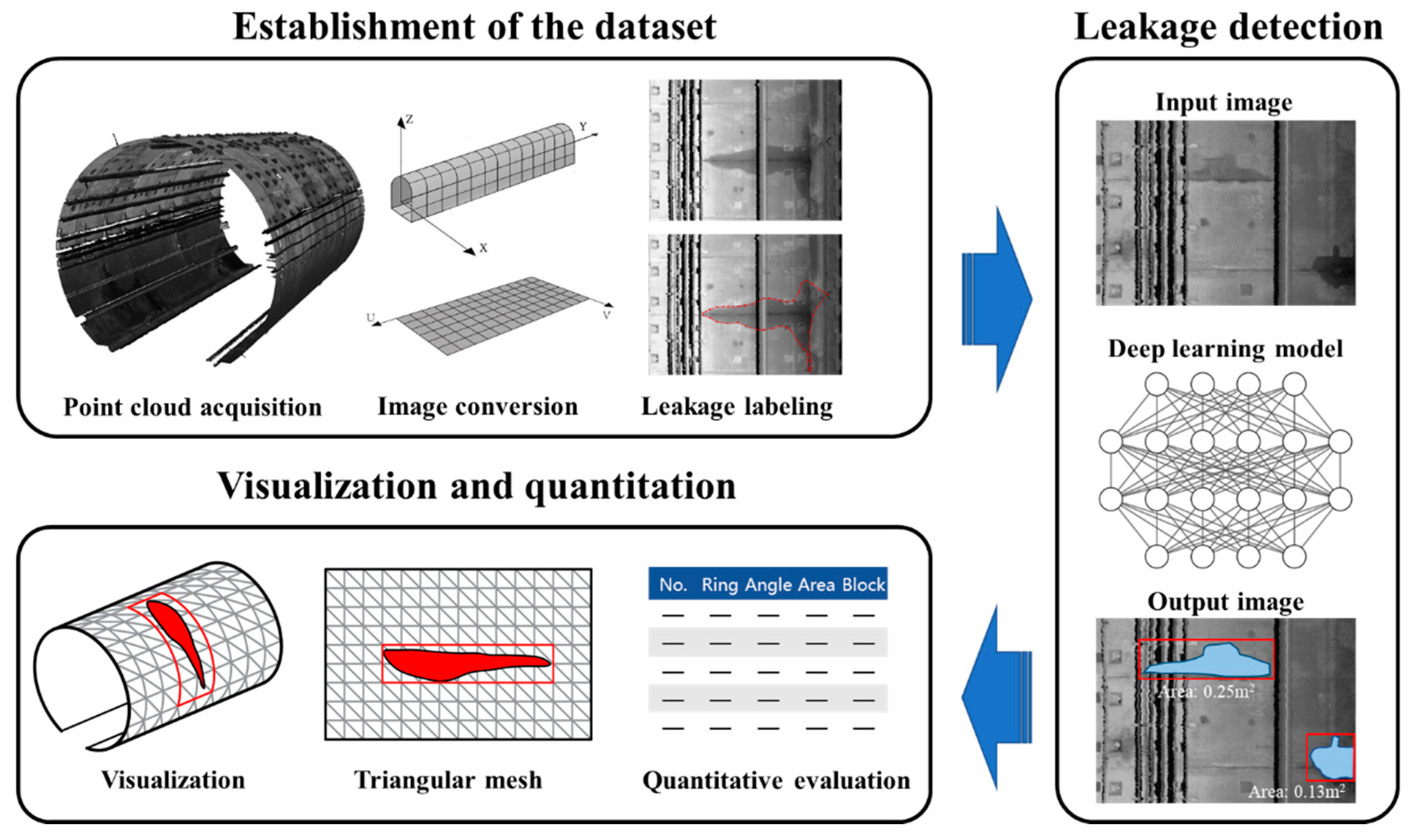
- Establishment of the water leakage dataset, which entails point cloud data acquisition, grayscale image conversion, and ground truth water leakage labeling;
- Automated water leakage detection using the Mask R-CNN algorithm, which demonstrates better accuracy and efficiency for the water leakage segmentation task than two state-of-the-art segmentation algorithms (PANet and DeepLabV3+);
- 3D visualization and quantitation of the water leakages, where a novel triangular mesh method is proposed to efficiently generate a precise 3D tunnel lining model and automatically output a 3D inspection report containing the water leakage information and its spatial information.
2. Water Leakage Dataset of Tunnel Linings
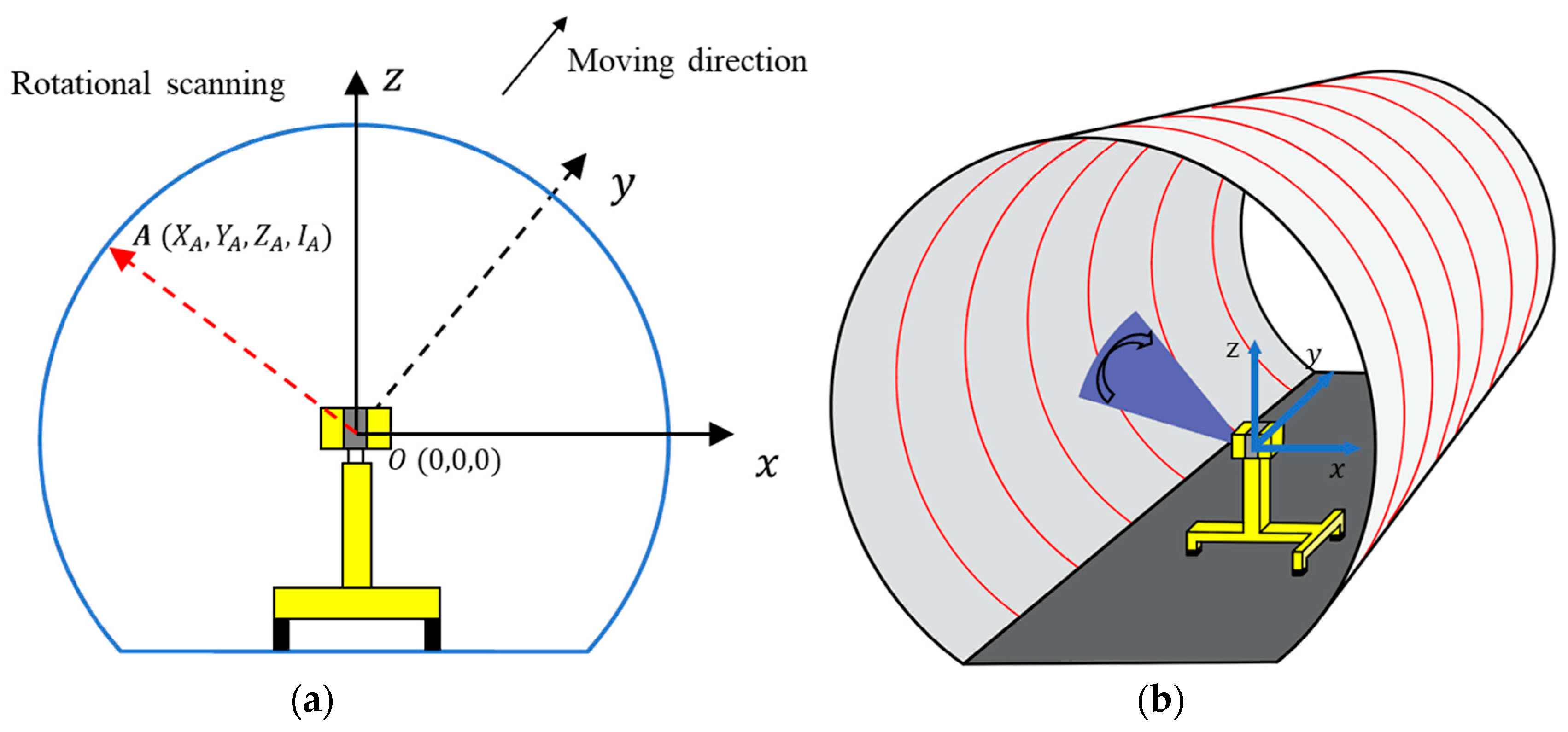
2.1. Point Cloud Data Acquisition Using MLS
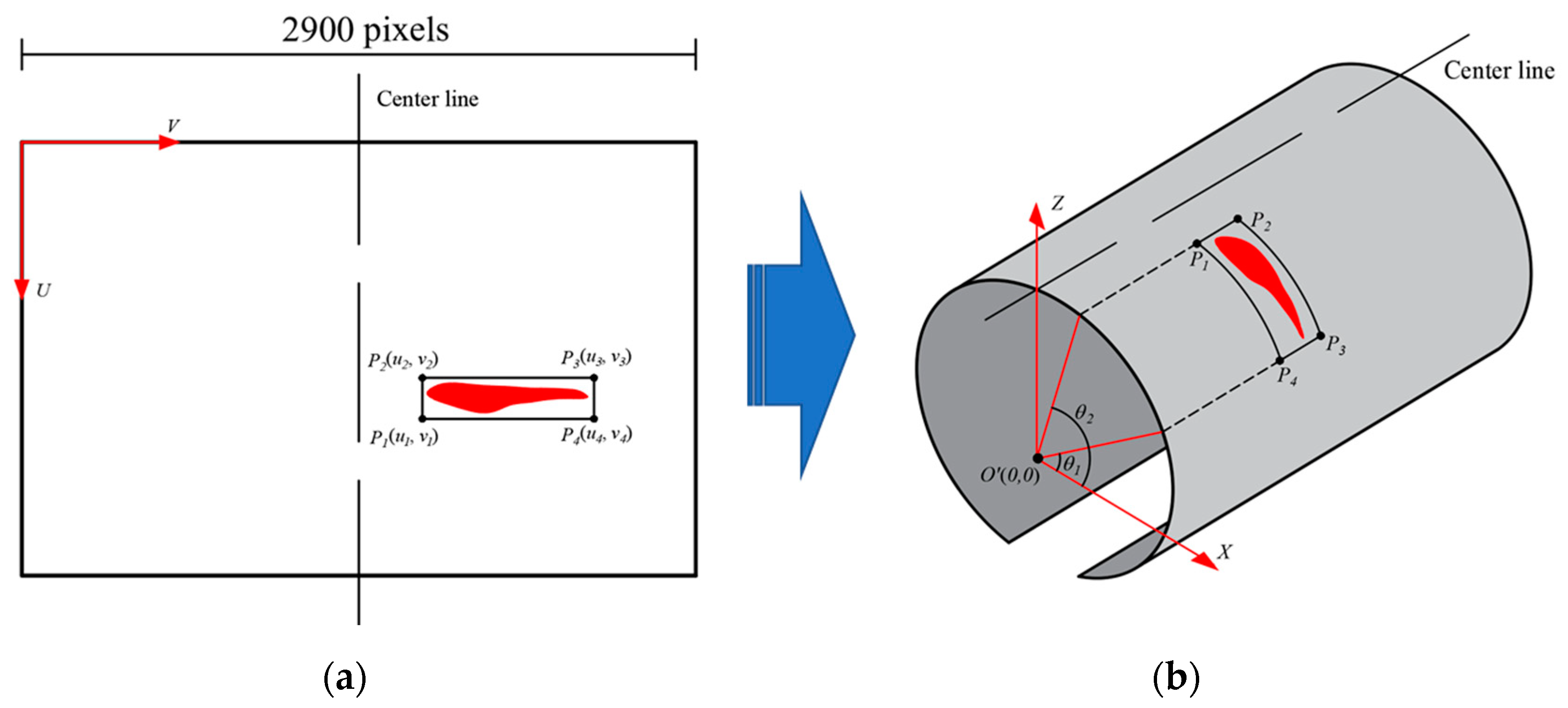
2.2. Converting 3D Point Cloud into 2D Image
2.2.1. 3D Point Cloud Unrolling
2.2.2. Generating 2D Grayscale Image
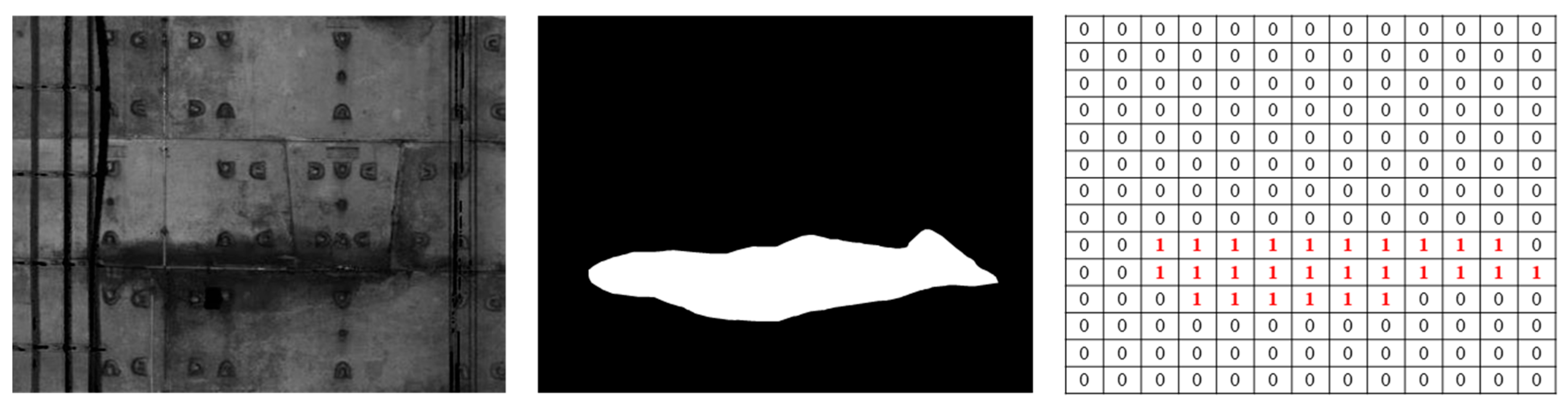
2.3. Establishment of Tunnel Leakage Image Dataset
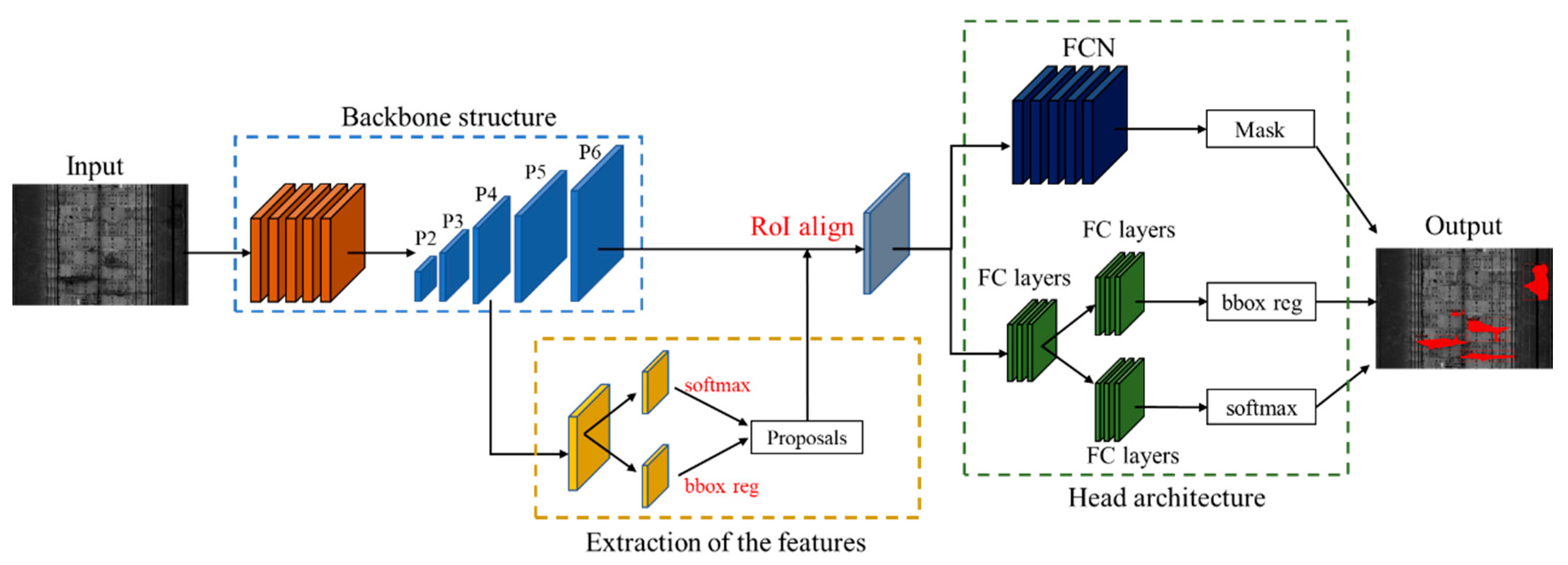
3. Automated Water Leakage Detection via Mask R-CNN
3.1. Backbone Structure
3.2. Extraction of the Features
3.3. Head Architecture
3.4. Training and Testing
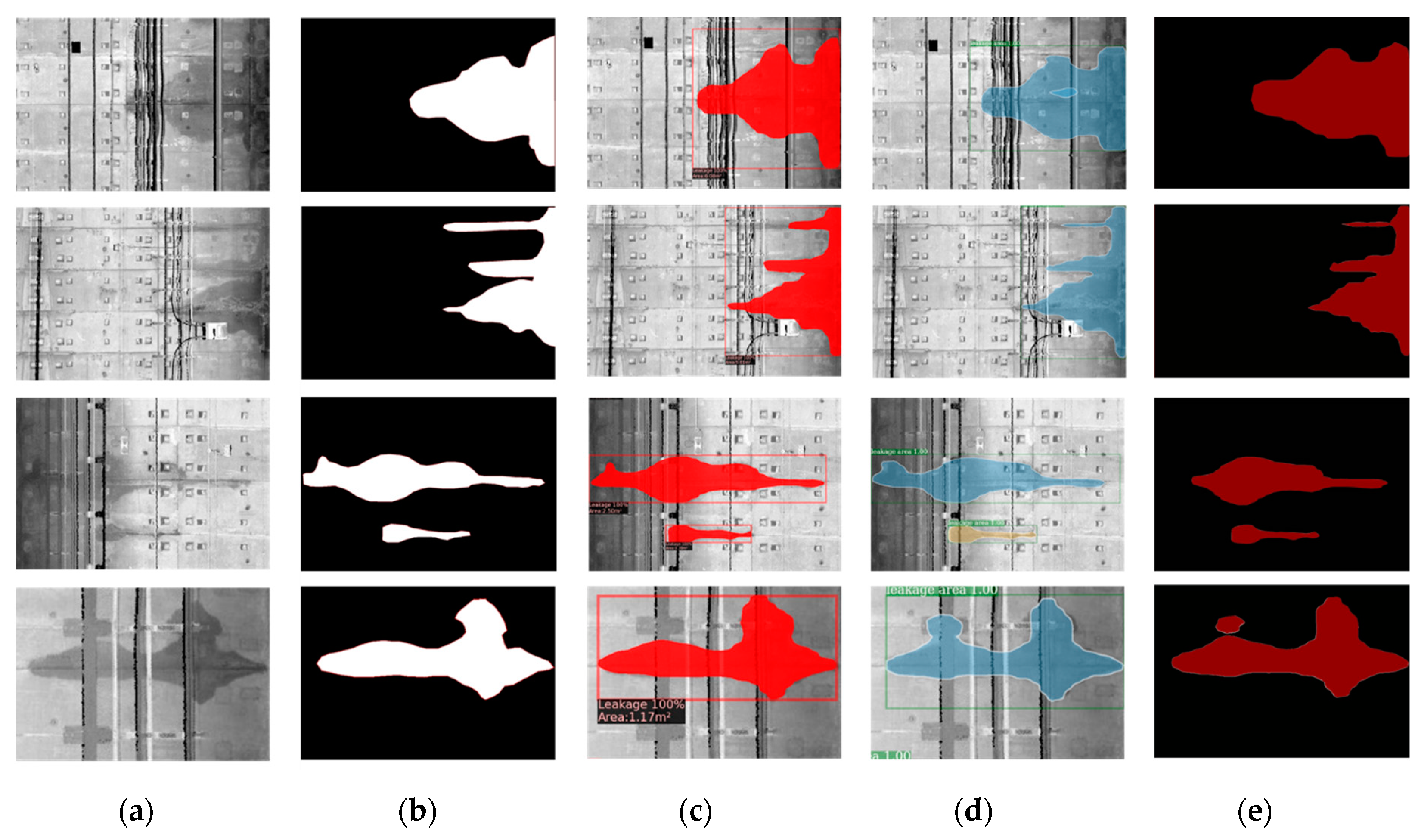
4. Automated Water Leakage Evaluation
4.1. Water Leakage Evaluation in 2D
4.2. Output Images from the Modified Mask R-CNN
4.3. Water Leakage Evaluation in 3D
5. Visualizing the Water Leakage in 3D Space
| Algorithm 1. Converting the 2D mesh to a tunnel-shaped mesh |
| Input: raw point cloud R (x, y, z); meshed plane point cloud P (x, y, 2.75) |
| Output: tunnel-shaped mesh T (x, y, z) |
| 1: R (θ, y, ρ) ← Switch Cartesian coordinates R (x, y, z) to polar coordinates |
| 2: P′ (x′, y′, z′) ← Roll up the plane data P (x, y, 2.75) to cylindrical data |
| 3: P″ (θ″, y″, ρ″) ← Switch Cartesian coordinates P′ (x′, y′, z′) to polar |
| 4: for each point P″i (θ″i, y″i, ρ″i) do |
| 5: Extract the set Nk (θ, y, ρ) from R (θ, y, ρ) ← k nearest neighbors of θ″i where | y″i − y | < m |
| 6: Compute the average ρki from Nk (θ, y, ρ) |
| 7: Ti (xi, yi, zi) ← Switch polar coordinates (θ″i, y″i, ρki) to Cartesian coordinates |
| 8: end for |
| 9: return T |
6. Comparison and Discussion
6.1. Segmentation Results Comparison
6.2. Reconstruction Results Comparison
6.3. 2D and 3D Inspection Results Comparison
7. Conclusions
- A water leakage dataset was established by collecting tunnel lining point cloud data from a 4 km metro tunnel section in Shanghai, China. The coordinates transformation and square grid partition approaches were used to achieve 2D image conversion, and data augmentation was adopted to help improve the performance of the trained model.
- Based on the dataset, the Mask R-CNN algorithm was adopted to achieve automated evaluation of the water leakage (the masks, the evaluation results, the bounding box, etc.). In comparison with two state-of-the-art segmentation algorithms (PANet and DeepLabV3+), Mask R-CNN demonstrates better accuracy and efficiency for the water leakage segmentation task.
- A novel triangular mesh method is proposed in this study to generate a precise 3D tunnel lining model with decent efficiency. The reconstruction result demonstrates sound performance for 3D visualization of the detected leakage, which retains the spatial geometric characteristics of the tunnel lining point cloud and the printed water leakage evaluation information.
- The proposed 3D inspection method provides an overall view of the detected water leakages. The water leakage information and its spatial location information (the ring number, the leakage area, the angle scope, and the lining segments) can be automatically outputted to an inspection report together with the 3D tunnel lining model.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tan, K.; Cheng, X.; Ju, Q.; Wu, S. Correction of Mobile TLS Intensity Data for Water Leakage Spots Detection in Metro Tunnels. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 13, 1711–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Bai, N.; Li, H. Analysis on tunnel accident on line 1 of Saint Petersburg Metro. Tunnel Constr. 2008, 28, 418–422. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, H.; Huang, H.; Zhang, D.; Wang, R. Case study on repair work for excessively deformed shield tunnel under accidental surface surcharge in soft clay. Chin. J. Geotech. Eng. 2016, 38, 1036–1043. [Google Scholar]
- Ai, Q.; Yuan, Y.; Bi, X. Acquiring sectional profile of metro tunnels using charge-coupled device cameras. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2016, 12, 1065–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Ren, X.; Mao, Q.; Hu, Q.; Wang, W. Shield subway tunnel deformation detection based on mobile laser scanning. Autom Constr. 2019, 106, 102889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Ayyub, B.M. Field data-based probabilistic assessment on degradation of deformational performance for shield tunnel in soft clay. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2017, 67, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panella, F.; Roecklinger, N.; Vojnovic, L.; Loo, Y.; Boehm, J. Cost-benefit analysis of rail tunnel inspection for photogrammetry and laser scanning. In Proceedings of the International Archives of Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, Nice, France, 31 August–2 September 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Attard, L.; Debono, C.J.; Valentino, G.; Di Castro, M. Tunnel inspection using photogrammetric techniques and image processing: A review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 144, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, M.; Zhu, H. Novel SfM-DLT method for metro tunnel 3D reconstruction and Visualization. Undergr. Space 2020. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2467967419300996 (accessed on 20 September 2020). [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Huang, H.; Xue, Y.; Luo, t.; Wu, C. Model test study on factors affecting image sharpness of tunnel lining. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 2017, 36 (Suppl. 2), 3915–3926. [Google Scholar]
- Du, L.; Zhong, R.; Sun, H.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Q. Cross-section positioning based on a dynamic MLS tunnel monitoring system. Photogramm. Rec. 2019, 34, 244–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Liu, S.; Zhong, R.; Du, L. Cross-Section Deformation Analysis and Visualization of Shield Tunnel Based on Mobile Tunnel Monitoring System. Sensors 2020, 20, 1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Xu, Z.; Yao, L.; Zhong, R.; Du, L.; Wu, H. Tunnel Monitoring and Measuring System Using Mobile Laser Scanning: Design and Deployment. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Sun, Y.; Xue, Y.; Wang, F. Inspection equipment study for subway tunnel defects by grey-scale image processing. Adv. Eng. Inf. 2017, 32, 188–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Li, Q.; Chen, Y.; Cao, M.; He, L.; Zhang, B. An efficient and reliable coarse-to-fine approach for asphalt pavement crack detection. Image Vision Comput. 2017, 57, 130–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Qader, I.; Abudayyeh, O.; Kelly, M.E. Analysis of edge-detection techniques for crack identification in bridges. J. Comput. Civ. Eng. 2003, 17, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Xu, L.; Li, X.; Yao, J. Detection of Water Leakage in Underground Tunnels Using Corrected Intensity Data and 3D Point Cloud of Terrestrial Laser Scanning. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 32471–32480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, CA, USA, 3–6 December 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, B.; Cho, S. Image-based concrete crack assessment using mask and region-based convolutional neural network. Struct. Contr. Health Monit. 2019, 26, e2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Gao, Y.; Sui, Q.; Jiang, P. A deep-learning-based multiple defect detection method for tunnel lining damages. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 182643–182657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, Y.J.; Choi, W.; Suh, G.; Mahmoudkhani, S.; Büyüköztürk, O. Autonomous structural visual inspection using region-based deep learning for detecting multiple damage types. Comput. Aided Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2018, 33, 731–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Shadabfar, M.; Huang, H.; Leung, Y.F.; Uchida, S. Meta-modelling of coupled thermo-hydro-mechanical behaviour of hydrate reservoir. Comput. Geotech. 2020, 128, 103848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, D.; Huang, H.; Shadabfar, M.; Zhou, M.; Yang, T. Image-based segmentation and quantification of weak interlayers in rock tunnel face via deep learning. Autom Constr. 2020, 120, 103371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yang, T.; Zhang, D.; Huang, H.; Tian, Y. Deep learning based classification of rock structure of tunnel face. Geosci. Front. 2020. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1674987120300931 (accessed on 20 September 2020). [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, S.; Girshick, R.; Dollár, P.; Tu, Z.; He, K. Aggregated residual transformations for deep neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster r-cnn: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, QC, Canada, 7–12 December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, J.; Li, Y.; He, K.; Sun, J. R-FCN: Object detection via region-based fully convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Barcelona, Spain, 5–10 December 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.; Li, Q.; Zhang, D. Deep learning based image recognition for crack and leakage defects of metro shield tunnel. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2018, 77, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Li, Y. A Fast Detection Method via Region-Based Fully Convolutional Neural Networks for Shield Tunnel Lining Defects. Comput. Aided Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2018, 33, 638–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Jian, M.; Hu, M.; Tanniru, M.; Li, S. Faster multi-defect detection system in shield tunnel using combination of FCN and faster RCNN. Adv. Struct. Eng. 2019, 22, 2907–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.-C.; Zhu, Y.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Encoder-Decoder with Atrous Separable Convolution for Semantic Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference of Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Gkioxari, G.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R. Mask r-cnn. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Hu, M.; Xu, G.; Zhou, X.; Li, Z. Detecting Leakage Water of Shield Tunnel Segments Based on Mask R-CNN. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Architecture, Construction, Environment and Hydraulics (ICACEH), Xiamen, China, 20–22 December 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, Y.; Cai, X.; Shadabfar, M.; Shao, H.; Zhang, S. Deep learning-based automatic recognition of water leakage area in shield tunnel lining. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2020, 104, 103524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Zhang, D.; Huang, H. Deep learning–based image instance segmentation for moisture marks of shield tunnel lining. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2020, 95, 103156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Qi, L.; Qin, H.; Shi, J.; Jia, J. Path Aggregation Network for Instance Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kazhdan, M.; Bolitho, M.; Hoppe, H. Poisson surface reconstruction. In Proceedings of the Fourth Eurographics Symposium on Geometry Processing, Cagliari, Italy, 26–28 June 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Ao, X.; Wu, H.; Xu, Z.; Gao, Z. Damage Extraction of Metro Tunnel Surface from Roughness Map Generated by Point Cloud. In Proceedings of the 2018 26th International Conference on Geoinformatics, Kunming, China, 28–30 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Zhong, R.; Chen, W.; Sun, H.; Ren, Y.; Lei, N. Study of Tunnel Surface Parameterization of 3-D Laser Point Cloud Based on Harmonic Map. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 17, 1623–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nojima, K.; Kawhara, M. Mesh Generation of Three-dimensional Underground Tunnels Based on the Three-Dimensional Delaunay Tetrahedration. J. Appl. Mech. 2002, 5, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stent, S.; Gherardi, R.; Stenger, B.; Soga, K.; Cipolla, R. Visual change detection on tunnel linings. Mach. Vis. Appl. 2016, 27, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coren, F.; Sterzai, P. Radiometric correction in laser scanning. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 3097–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, C.; Lu, D.; Xie, Q.; Liu, S.; Li, H.; Wei, M.; Wang, J. Hierarchical tunnel modeling from 3D raw LiDAR point cloud. Comput. Aided Des. 2019, 114, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Yang, G.; Tang, G. A fast two-dimensional median filtering algorithm. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 1979, 27, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Goel, V.; Kingsbury, B. Data augmentation for deep convolutional neural network acoustic modeling. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Brisbane, Australia, 19–24 April 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wada, K. labelme: Image Polygonal Annotation with Python. GitHub Repository. 2020. Available online: https://github.com/wkentaro/labelme (accessed on 20 September 2020).
- Lin, T.-Y.; Maire, M.; Belongie, S.; Hays, J.; Perona, P.; Ramanan, D.; Dollár, P.; Zitnick, C.L. Microsoft COCO: Common objects in context. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Alain, G.; Bengio, Y. Understanding intermediate layers using linear classifier probes. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1610.01644. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A. Going deeper with convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.-Y.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S. Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Kirillov, A.; Massa, F.; Lo, W.; Girshick, R. Detectron2. GitHub Repository. 2019. Available online: https://github.com/facebookresearch/detectron2 (accessed on 20 September 2020).
- Li, X.; Lin, X.; Zhu, H.; Wang, X.; Liu, Z. Condition assessment of shield tunnel using a new indicator: The tunnel serviceability index. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2017, 67, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Shen, S.; Chen, R.; Zhou, A. Three-dimensional numerical modelling on localised leakage in segmental lining of shield tunnels. Comput Geotech. 2020, 122, 103549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, X.; Zhu, H. Condition evaluation of urban metro shield tunnels in Shanghai through multiple indicators multiple causes model combined with multiple regression method. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2019, 85, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Shi, J.; Huang, H.; Zhang, D. Modified analytical solution of shield tunnel lining considering nonlinear bending stiffness of longitudinal joint. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2020, 106, 103625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
















| Leakage | Ring Number N | (°) | Area (m2) | Lining Segments |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| #1 | 3 | −50~−45 | 0.06 | D |
| #2 | 4 | −19~−8 | 0.05 | B2 |
| #3 | 6~9 | −54~−13 | 3.43 | B2~D |
| #4 | 9~10 | 91~112 | 0.23 | L1~L2 |
| #5 | 10~11 | 15~83 | 2.36 | L1~B2 |
| #6 | 11~12 | 84~170 | 2.13 | B1~L2 |
| #7 | 12~13 | 4~96 | 1.44 | L1~B2 |
| #8 | 14~15 | 12~83 | 2.15 | L1~B2 |
| #9 | 14~15 | −47~2 | 1.16 | L2~D |
| #10 | 14~15 | 92~120 | 0.76 | F~L2 |
| #11 | 16~17 | 8~86 | 2.05 | L1~B2 |
| #12 | 16~18 | 98~165 | 3.38 | B1~L2 |
| #13 | 17~18 | 31~90 | 0.62 | L1~B2 |
| #14 | 18~19 | 237~240 | 0.06 | D~B1 |
| #15 | 19~20 | 94~159 | 1.26 | B1~L2 |
| #16 | 22~23 | −9~86 | 1.86 | L1~B2 |
| #17 | 23~24 | 19~228 | 4.51 | D~B2 |
| #18 | 23~24 | 162~233 | 1.33 | D~L1 |
| #19 | 25~26 | 51~170 | 2.90 | B1~L2 |
| Method | MPA (%) | MIoU (%) | AIT (s/Image) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mask R-CNN | 97.18 | 77.05 | 0.093 |
| PANet | 97.57 | 77.34 | 0.112 |
| DeepLabV3+ | 95.34 | 75.84 | 0.486 |
| Algorithm | Raw Points | Reconstructed Points | Inference Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| Delaunay triangulation | 13,623,722 | 13,623,722 | 560 s |
| Poisson reconstruction | 13,623,722 | 1,669,747 | 121 s |
| Proposed method | 13,623,722 | 7,250,000 | 334 s |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, H.; Cheng, W.; Zhou, M.; Chen, J.; Zhao, S. Towards Automated 3D Inspection of Water Leakages in Shield Tunnel Linings Using Mobile Laser Scanning Data. Sensors 2020, 20, 6669. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20226669
Huang H, Cheng W, Zhou M, Chen J, Zhao S. Towards Automated 3D Inspection of Water Leakages in Shield Tunnel Linings Using Mobile Laser Scanning Data. Sensors. 2020; 20(22):6669. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20226669
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Hongwei, Wen Cheng, Mingliang Zhou, Jiayao Chen, and Shuai Zhao. 2020. "Towards Automated 3D Inspection of Water Leakages in Shield Tunnel Linings Using Mobile Laser Scanning Data" Sensors 20, no. 22: 6669. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20226669
APA StyleHuang, H., Cheng, W., Zhou, M., Chen, J., & Zhao, S. (2020). Towards Automated 3D Inspection of Water Leakages in Shield Tunnel Linings Using Mobile Laser Scanning Data. Sensors, 20(22), 6669. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20226669






