Speed Sensorless Control of Linear Ultrasonic Motors Based on Stator Vibration Amplitude Compensation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Analysis
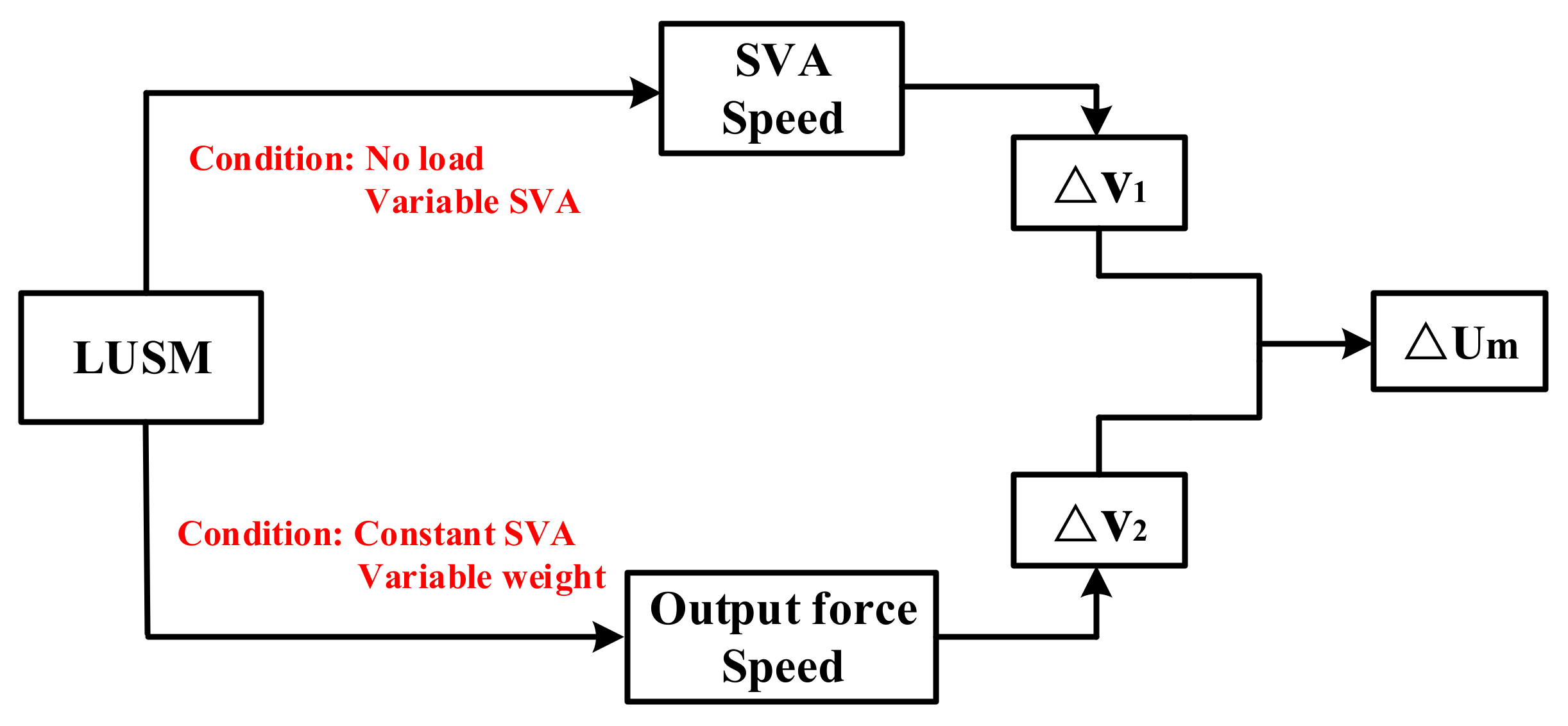
2.1. Relationship Between the Stator Vibration Amplitude and Speed, the Load and Speed of the Linear Ultrasonic Motor
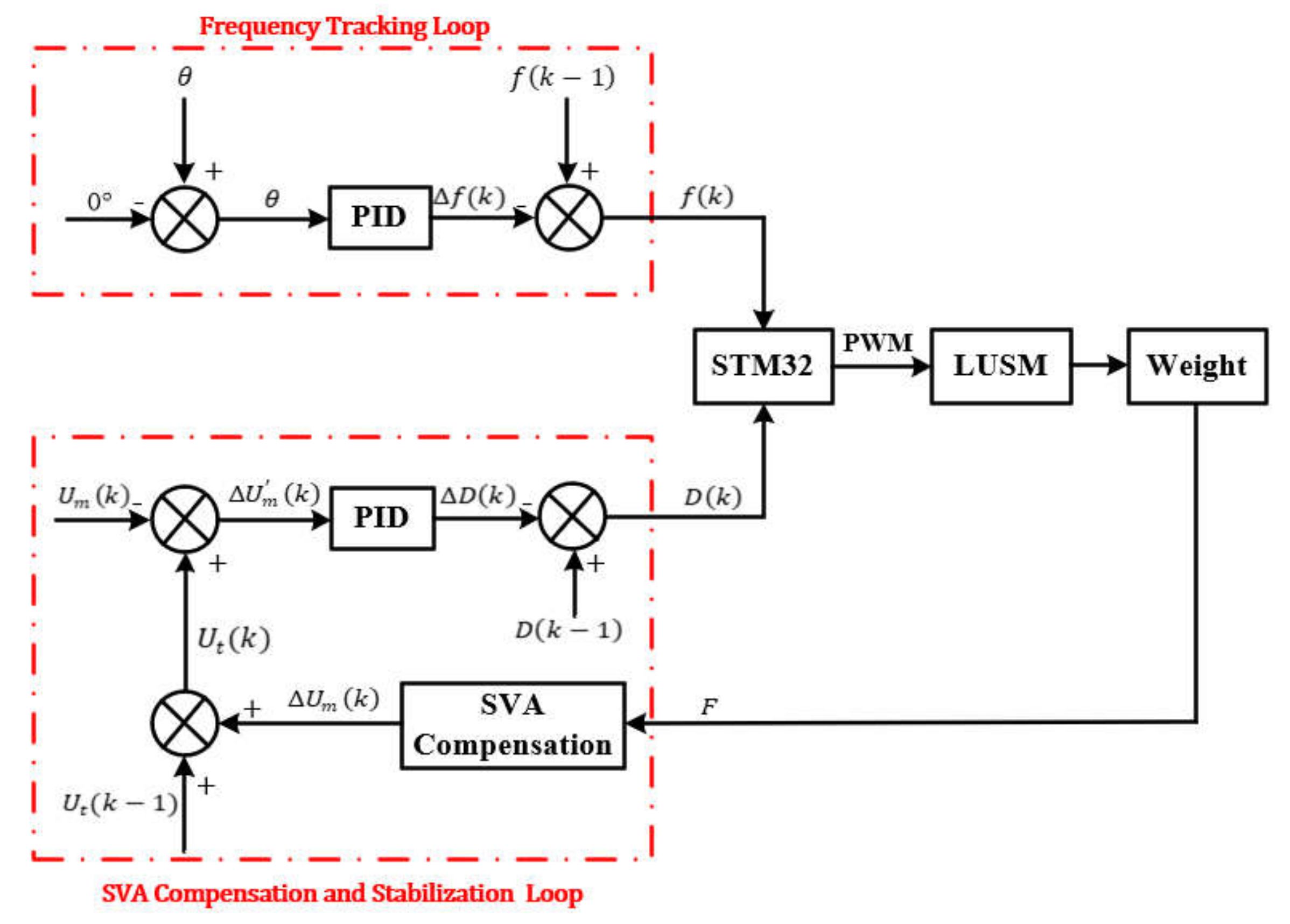
2.2. Principle of the Stator Vibration Amplitude-Based Speed Control and the Frequency Tracking
3. Specific Implementation Scheme
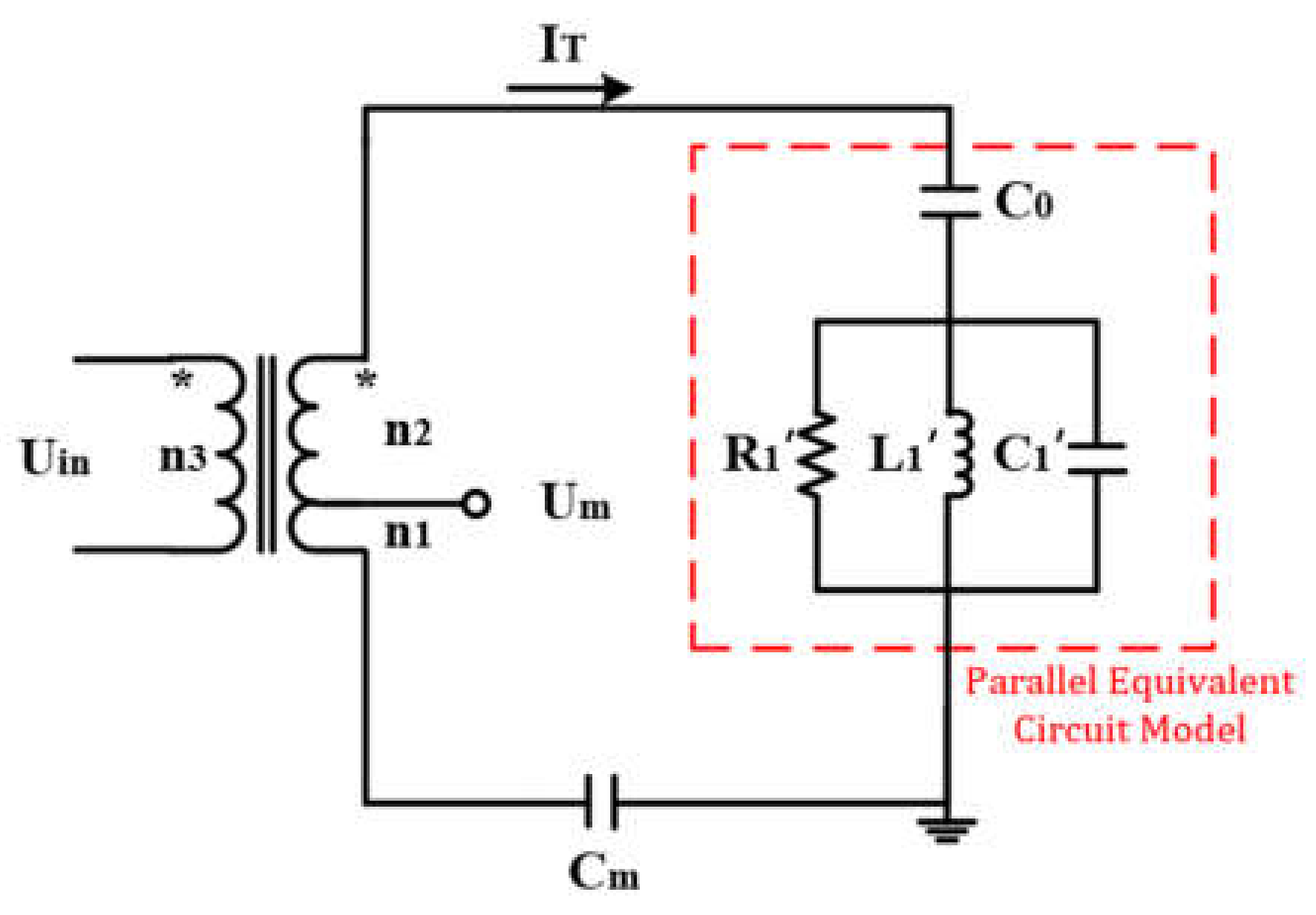
3.1. Calculation of the Stator Vibration Amplitude to Be Compensated
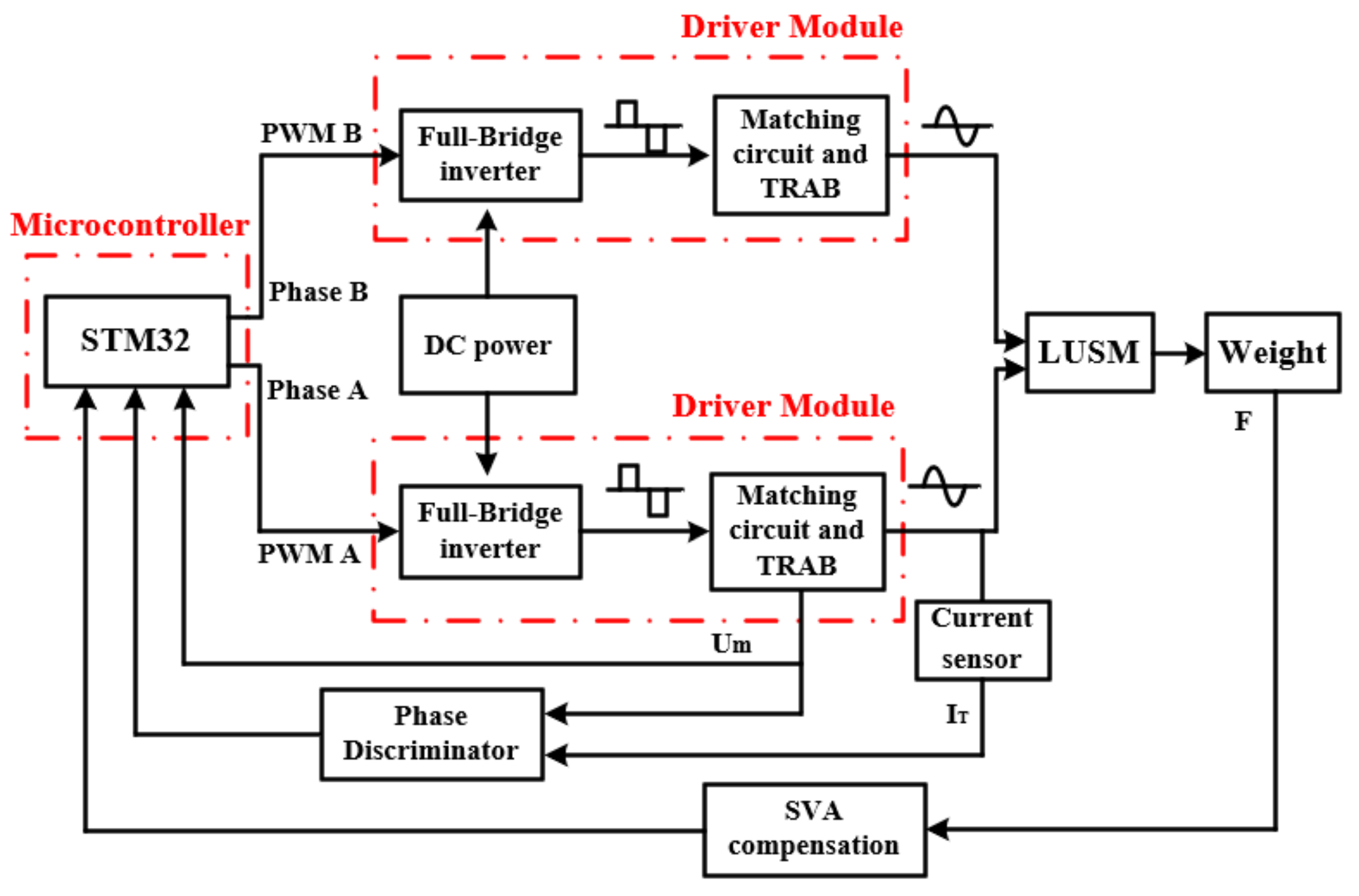
3.2. Hardware and Control Architecture
4. Experimental Results and Discussion
4.1. Experimental Settings
4.2. Stator Vibration Amplitude Control and Frequency Tracking Verification
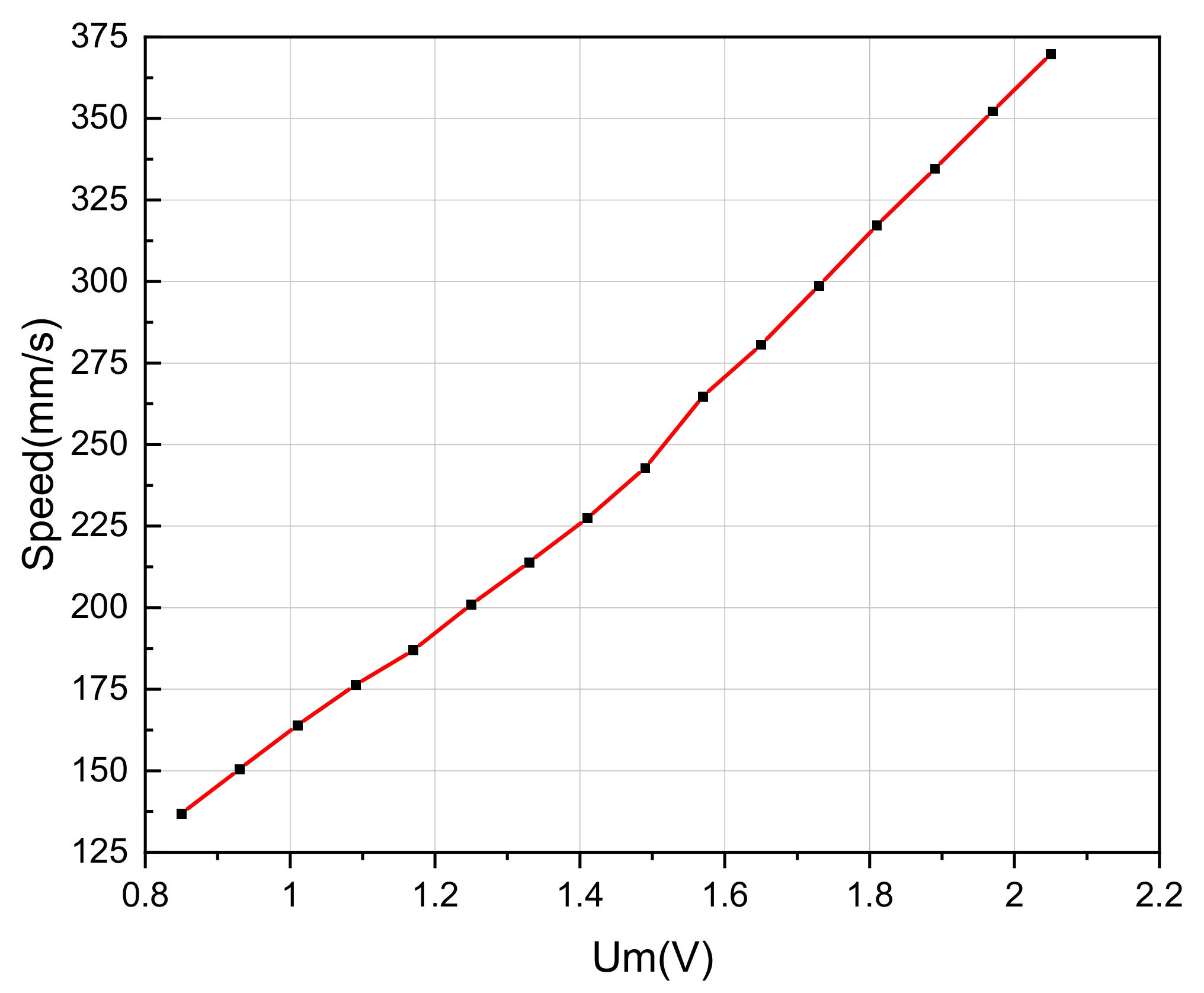
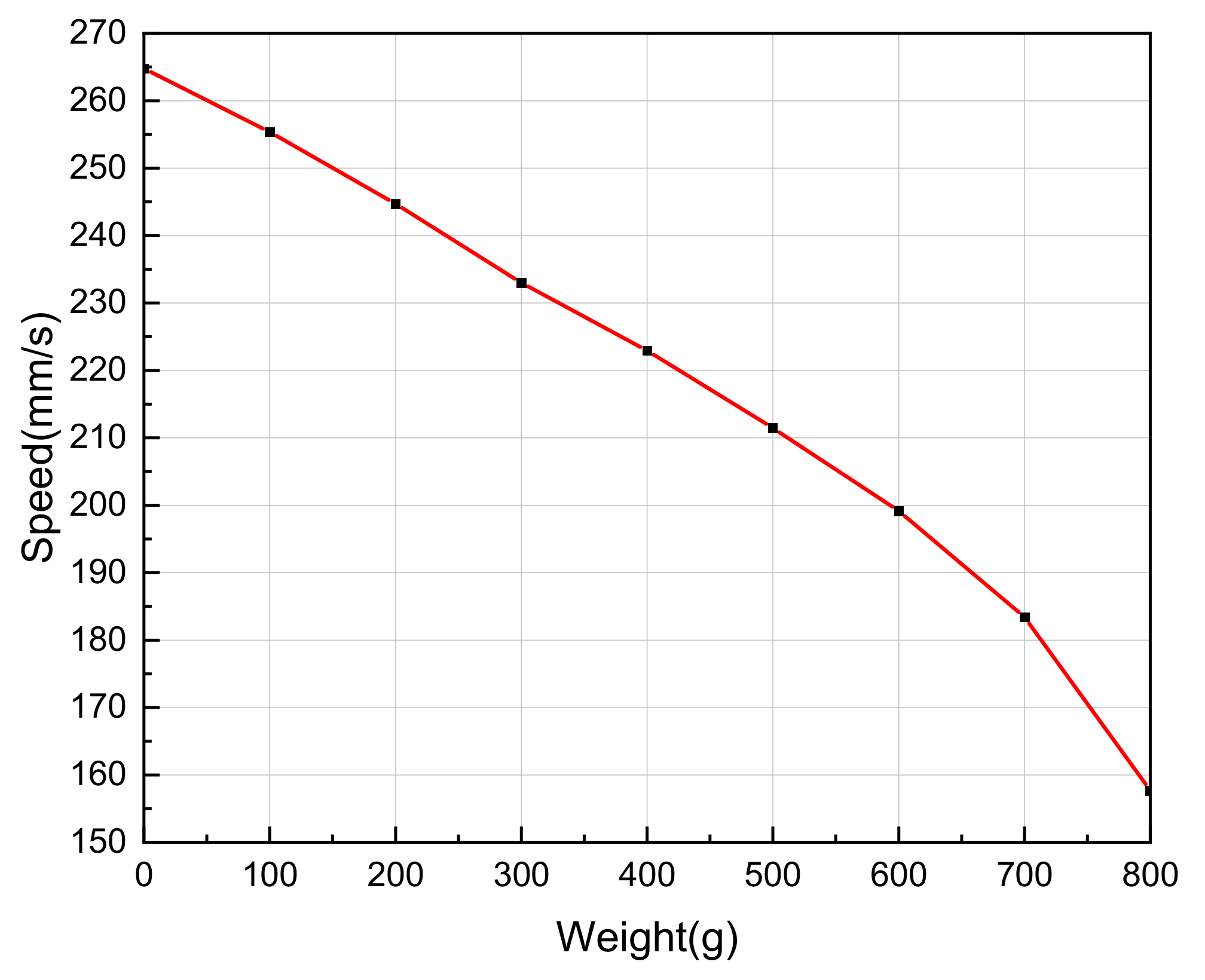
4.3. Stator Vibration Amplitude-Speed, Output Force-Speed Curve and Calculation of the Stator Vibration Amplitude to Be Compensated
4.4. Relationship between the Load and Speed After Stator Vibration Amplitude Compensation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, C. Ultrasonic Motors: Technologies and Applications; Science Press: Beijing, China; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Z.; Fu, Q.; Geng, R.; Jian, Y.; Liu, Z. Development and applications of linear ultrasonic motors. In Proceedings of the 2016 13th International Conference on Ubiquitous Robots and Ambient Intelligence (URAI), IEEE, Xian, China, 19–22 August 2016; pp. 951–954. [Google Scholar]
- Jian, Y.; Yao, Z.; Silberschmidt, V.V. Linear ultrasonic motor for absolute gravimeter. Ultrasonics 2017, 77, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tan, K.K.; Liang, W.; Pham, L.P.; Huang, S.; Gan, C.W.; Lim, H.Y. Design of a Surgical Device for Office-Based Myringotomy and Grommet Insertion for Patients with Otitis Media with Effusion. J. Med. Devices 2014, 8, 031001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Zhao, C. A new standing-wave-type linear ultrasonic motor based on in-plane modes. Ultrasonics 2011, 51, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asumi, K.; Fukunaga, R.; Fujimura, T.; Kuribayashi Kurosawa, M. High speed, high resolution ultrasonic linear motor using V-shape two bolt-clamped Langevin-type transducers. Acoust. Sci. Technol. 2009, 30, 180–186. [Google Scholar]
- Gencer, A. A new speed/position control technique for travelling wave ultrasonic motor under different load conditions. In Proceedings of the 2014 16th International Power Electronics and Motion Control Conference and Exposition, IEEE, Antalya, Turkey, 21–24 September 2014; pp. 65–70. [Google Scholar]
- Asumi, K.; Fujimura, T.; Fukunaga, R.; Kurosawa, M.K. Improvement of the low speed controllability of a V-shaped, two bolt-clamped Langevin-type transducer, ultrasonic linear motor. In Proceedings of the 2007 International Symposium on Micro-NanoMechatronics and Human Science, IEEE, Nagoya, Japan, 11–14 November 2007; pp. 377–382. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.L.; Yao, Z.Y. Research on Control Methods of Speed Stability by AR Model Based on Linear Ultrasonic Motor. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2013, 385–386, 777–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, S.; Liu, J.; Hao, M.; Song, B. Design of high precision magnetic grid displacement sensor. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation, Takamatsu, Japan, 5–8 August 2008; pp. 185–188. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, B.; Li, B. Laser Displacement Sensor in the Application of Aero-Engine Blade Measurement. IEEE Sens. J. 2016, 16, 1377–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Qi, Y.; Lu, Z. Design of a miniature grating displacement sensor with large range. In Proceedings of the 9th International Symposium on Advanced Optical Manufacturing and Testing Technologies: Micro- and Nano-Optics, Catenary Optics, and Subwavelength Electromagnetics, Chengdu, China, 26–29 June 2018; Poprawe, R., Fan, B., Li, X., Gu, M., Pu, M., Luo, X., Eds.; SPIE: Chengdu, China, 2019; p. 58. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Xu, L.; Zhang, Z. An Adaptive Sliding-Mode Observer for Induction Motor Sensorless Speed Control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2005, 41, 1039–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toso, F.; Berto, M.; Alberti, L.; Marcuzzi, F. Efficient QR Updating Factorization for Sensorless Synchronous Motor Drive Based on High Frequency Voltage Injection. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 67, 10213–10222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanpo, S.; Takahashi, R.; Ohishi, K.; Makishima, S.; Uezono, K. Online identification method of static & dynamic inductance of IPMSM for fine position sensorless control. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE 5th International Symposium on Sensorless Control for Electrical Drives, Hiroshima, Japan, 17–18 May 2014; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Senjyu, T.; Yoshida, T.; Nakamura, M.; Urasaki, N.; Funabashi, T.; Sekine, H. Position sensorless control for ultrasonic motors based on input voltage information. Electr. Eng. Jpn. 2008, 163, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.-C.; Ren, T.-J.; Lou, Y.-W. Ultrasonic motor control based on recurrent fuzzy neural network controller. In Computational Intelligence; Madani, K., Dourado, A., Rosa, A., Filipe, J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; Volume 465, pp. 291–305. [Google Scholar]
- Jahani, M.; Mojallali, H. GA-neural network based position control of traveling wave ultrasonic motor. In Proceedings of the 2010 2nd International Conference on Computer Engineering and Technology, Chengdu, China, 16–18 April 2010; pp. V6-369–V6-373. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, Z.; Yang, T.; Zhu, Y.; Li, S.; Yang, M. Velocity Control of Traveling-Wave Ultrasonic Motors Based on Stator Vibration Amplitude. Sensors 2019, 19, 5326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Tian, X.; Shen, Z.; Li, K.; Liu, Y. A low-speed linear stage based on vibration trajectory control of a bending hybrid piezoelectric ultrasonic motor. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2019, 132, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Yao, Z.; Zhou, L.; He, Y. Modeling and analysis of a linear ultrasonic motor: Consider the slider movement characteristic. Smart Mater. Struct. 2019, 28, 105028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, J. Contact analysis and modeling of standing wave linear ultrasonic motor. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. Mat. Sci. Ed. 2011, 26, 1235–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colak, I.; Yesilbudak, M.; Sagiroglu, S.; Kahraman, H.T. An intelligent approach for speed stability analysis of a travelling wave ultrasonic motor based on genetic k-NN algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2011 5th International Conference on Application of Information and Communication Technologies (AICT), Baku, Azerbaijan, 12–14 October 2011; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Furuya, S.-I.; Maruhashi, T.; Izuno, Y.; Nakaoka, M. Load-adaptive frequency tracking control implementation of two-phase resonant inverter for ultrasonic motor. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 1992, 7, 542–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ural, S.O.; Tuncdemir, S.; Zhuang, Y.; Uchino, K. Development of a High Power Piezoelectric Characterization System and Its Application for Resonance/Antiresonance Mode Characterization. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirose, S.; Takahashi, S.; Uchino, K.; Aoyagi, M.; Tomikawa, Y. Measuring Methods for High–Power Characteristics of Piezoelectric Materials. MRS Proc. 1994, 360, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, X. Frame-level bit allocation based on incremental PID algorithm and frame complexity estimation. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2009, 20, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhangfan; Chen, W.; Liu, J.; Zhao, X. Control of an ultrasonic transducer to realize low speed driven. Ultrasonics 2006, 44, e569–e574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





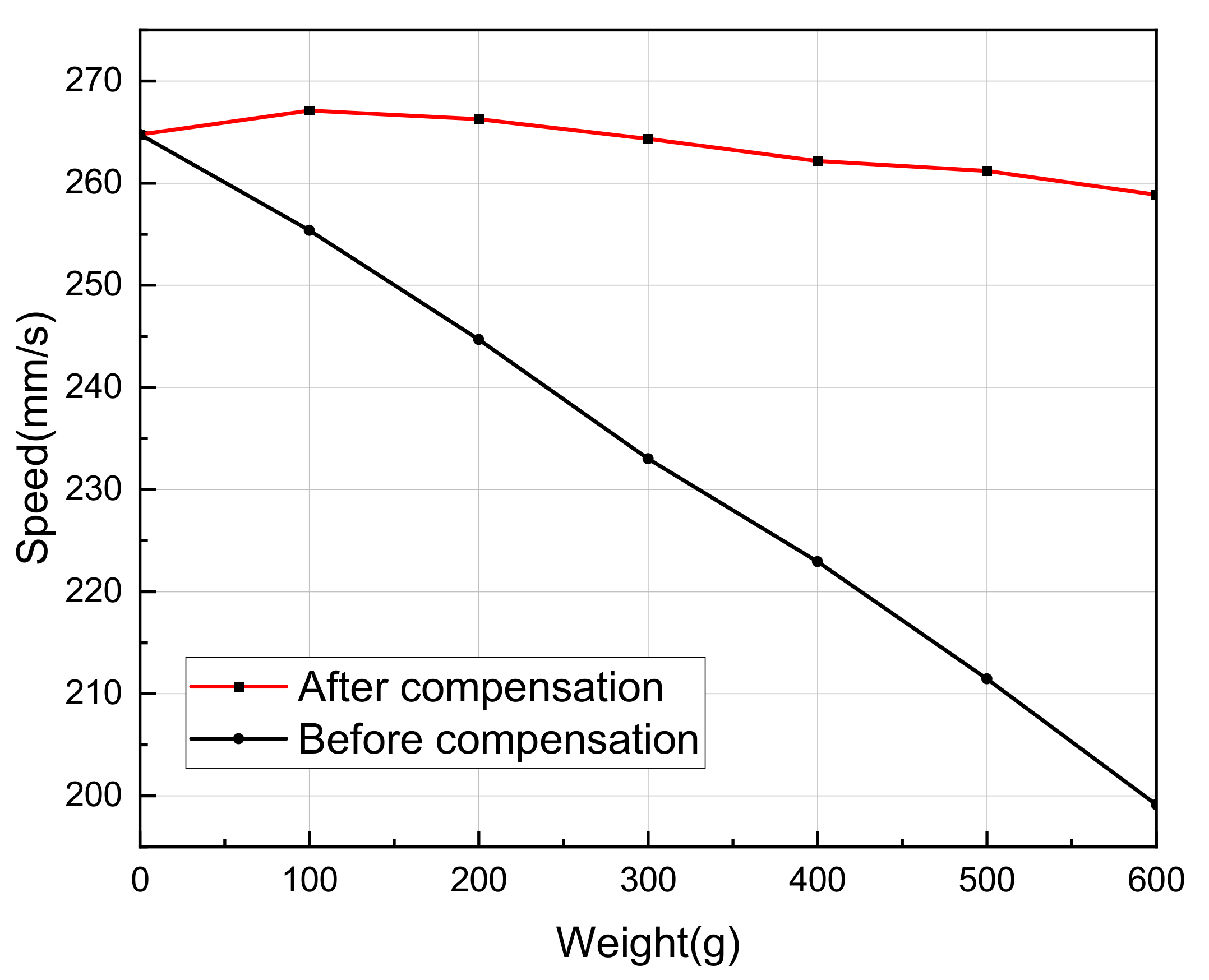
| Weight (g) | SVA after Compensation (V) |
|---|---|
| 0 | 1.57 |
| 100 | 1.626 |
| 200 | 1.682 |
| 300 | 1.738 |
| 400 | 1.794 |
| 500 | 1.85 |
| 600 | 1.906 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, Y.; Yang, M.; Yang, T.; Ye, S.; Jiang, W. Speed Sensorless Control of Linear Ultrasonic Motors Based on Stator Vibration Amplitude Compensation. Sensors 2020, 20, 6705. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20226705
Yan Y, Yang M, Yang T, Ye S, Jiang W. Speed Sensorless Control of Linear Ultrasonic Motors Based on Stator Vibration Amplitude Compensation. Sensors. 2020; 20(22):6705. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20226705
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Yuzhao, Ming Yang, Tianyue Yang, Siwei Ye, and Wanlu Jiang. 2020. "Speed Sensorless Control of Linear Ultrasonic Motors Based on Stator Vibration Amplitude Compensation" Sensors 20, no. 22: 6705. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20226705
APA StyleYan, Y., Yang, M., Yang, T., Ye, S., & Jiang, W. (2020). Speed Sensorless Control of Linear Ultrasonic Motors Based on Stator Vibration Amplitude Compensation. Sensors, 20(22), 6705. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20226705




