A Pressure-Insensitive Self-Attachable Flexible Strain Sensor with Bioinspired Adhesive and Active CNT Layers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fabrication of the Pressure-Insensitive Self-Attachable Flexible Strain Sensor
2.2. Surface Analysis
2.3. Evaluation of the Adhesion Behavior of the Self-Attachable Flexible Strain Sensor
2.4. Characterization of the Piezoresistive Sensing Behavior of the Pressure-Insensitive Flexible Strain Sensor
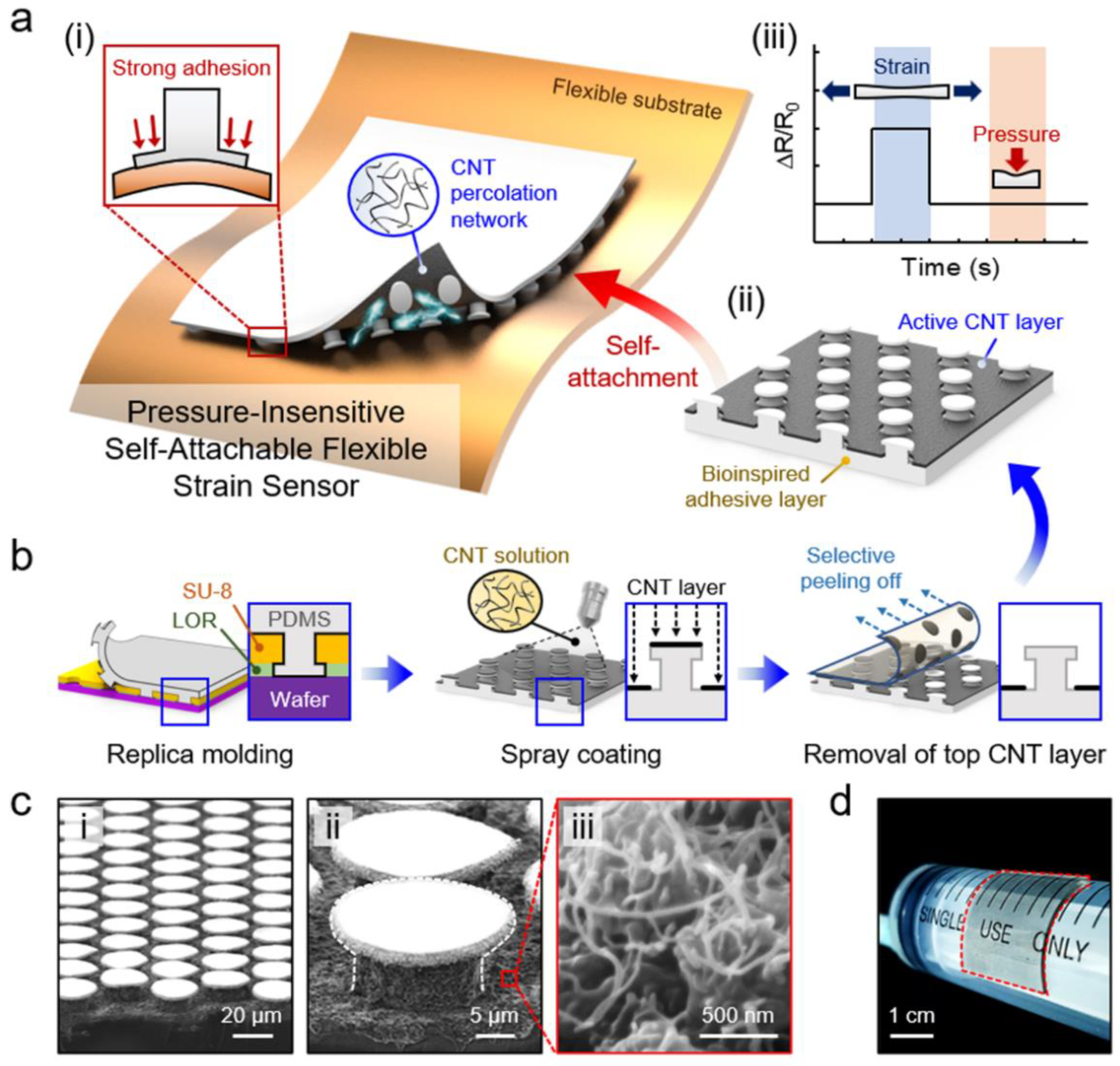
3. Design and Fabrication of the Pressure-Insensitive Self-Attachable Flexible Strain Sensor
4. Adhesion Behavior of the Self-Attachable Flexible Strain Sensor
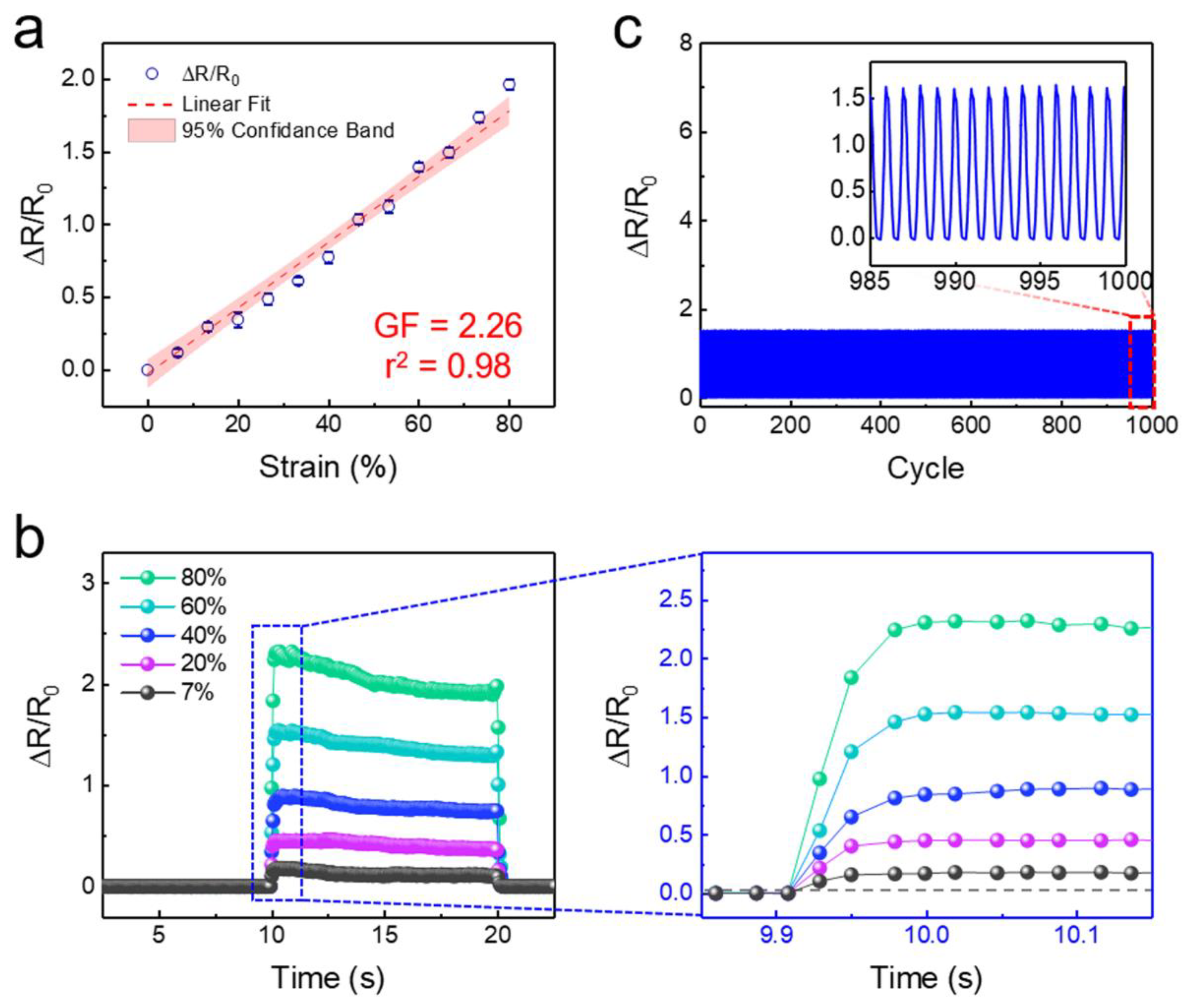
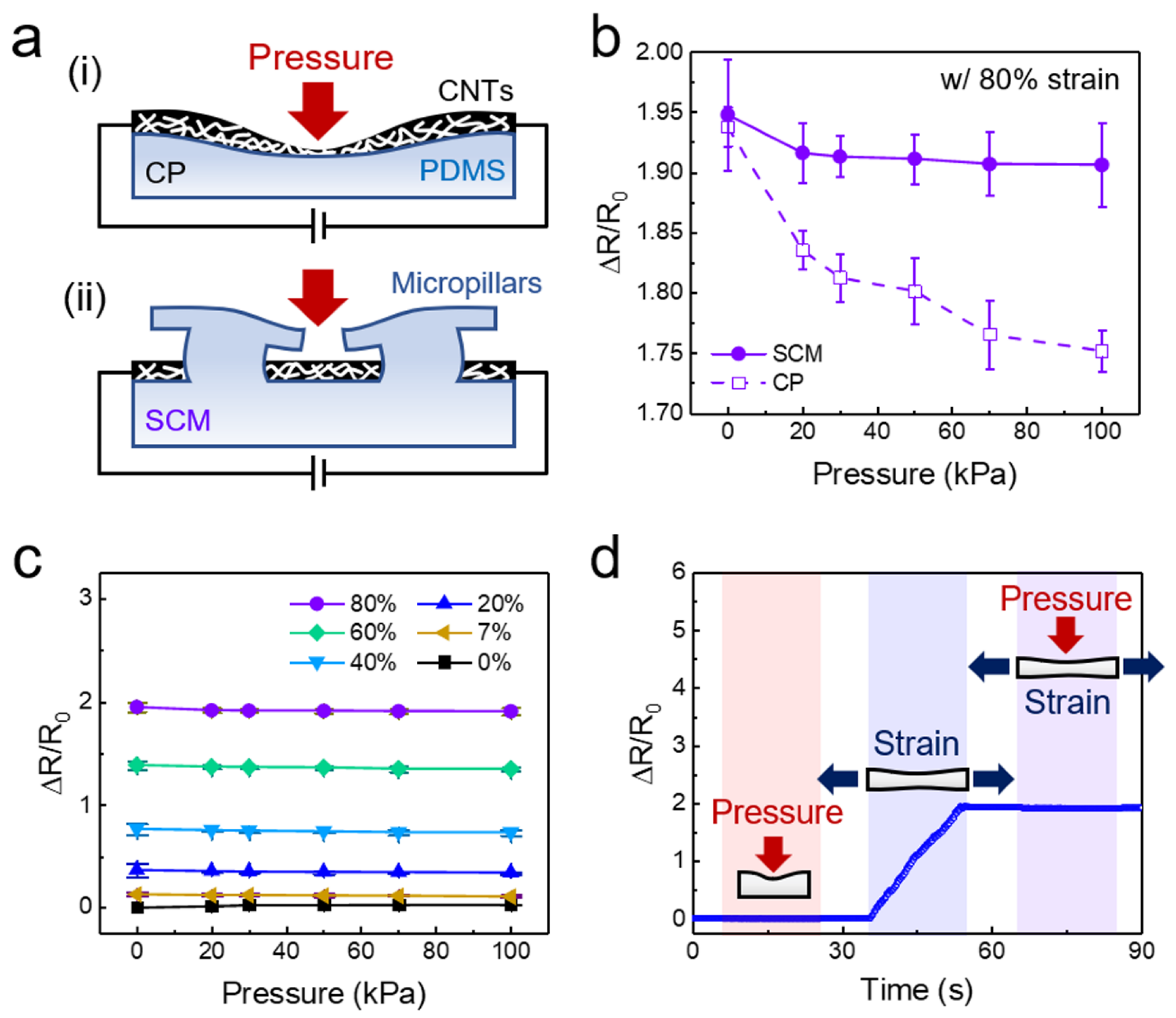
5. Sensing Behavior of the Self-Attachable Flexible Strain Sensor
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- An, T.; Anaya, D.V.; Gong, S.; Yap, L.W.; Lin, F.; Wang, R.; Yuce, M.R.; Cheng, W. Self-powered gold nanowire tattoo triboelectric sensors for soft wearable human-machine interface. Nano Energy 2020, 77, 105295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, K.; Rao, Z.; Zou, Z.; Ershad, F.; Lei, J.; Thukral, A.; Chen, J.; Huang, Q.A.; Xiao, J.; Yu, C. Metal oxide semiconductor nanomembrane-based soft unnoticeable multifunctional electronics for wearable human-machine interfaces. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaav9653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Ota, H.; Schaler, E.W.; Chen, K.; Zhao, A.; Gao, W.; Fahad, H.M.; Leng, Y.; Zheng, A.; Xiong, F.; et al. Wearable microfluidic diaphragm pressure sensor for health and tactile touch monitoring. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1701985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larson, C.; Peele, B.; Li, S.; Robinson, S.; Totaro, M.; Beccai, L.; Mazzolai, B.; Shepherd, R. Highly stretchable electroluminescent skin for optical signaling and tactile sensing. Science 2016, 351, 1071–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.; Yoon, K.; Lee, S.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, J.; Kim, D.W.; Kim, M.S.; Lee, T.; Pang, C. Conductive hierarchical hairy fibers for highly sensitive, stretchable, and water-resistant multimodal gesture-distinguishable sensor, VR applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1905808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Liu, C.; Xiao, Y.; Zhong, J.; Li, W.; Cheng, Y.; Hu, B.; Huang, L.; Zhou, J. Ultrasensitive cellular fluorocarbon piezoelectret pressure sensor for self-powered human physiological monitoring. Nano Energy 2017, 32, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.; Choi, Y.W.; Lee, T.; Lim, K.S.; Shin, J.; Kim, T.; Kim, H.K.; Koo, B.-K.; Kim, H.B.; Lee, J.-G.; et al. Nature-inspired rollable electronics. NPG Asia Mater. 2019, 11, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, M.; Shim, H.J.; Ghaffari, R.; Cho, H.R.; Son, D.; Jung, Y.H.; Soh, M.; Choi, C.; Jung, S.; et al. Stretchable silicon nanoribbon electronics for skin prosthesis. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Man, Q.; Hu, C.; Asghar, W.; Li, F.; Yu, Z.; Shang, J.; Liu, G.; et al. A skin-inspired tactile sensor for smart prosthetics. Sci. Robot. 2018, 3, eaat0429. [Google Scholar]
- Lou, Z.; Chen, S.; Wang, L.; Jiang, K.; Shen, G. An ultra-sensitive and rapid response speed graphene pressure sensors for electronic skin and health monitoring. Nano Energy 2016, 23, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Fang, Y.; He, H.; Zhang, L.; Li, C.; Ouyang, J. Wearable stretchable dry and self-adhesive strain sensors with conformal contact to skin for high-quality motion monitoring. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 2007495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Miao, L.; Su, Z.; Song, Y.; Han, M.; Chen, X.; Cheng, X.; Chen, D.; Zhang, H. Fingertip-inspired electronic skin based on triboelectric sliding sensing and porous piezoresistive pressure detection. Nano Energy 2017, 40, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bari, B.; Lee, J.; Jang, T.; Won, P.; Ko, S.H.; Alamgir, K.; Arshad, M.; Guo, L.J. Simple hydrothermal synthesis of very-long and thin silver nanowires and their application in high quality transparent electrodes. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 11365–11371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, K.; Lee, W.; Kang, K.; Kim, I.; Kang, D.; Oh, D.K.; Kim, M.C.; Choi, H.; Kim, K.; Kim, M.; et al. Low-temperature large-area fabrication of ZnO nanowires on flexible plastic substrates by solution-processible metal-seeded hydrothermal growth. Nano Converg. 2020, 7, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; Mun, J.; Bae, D.; Jeon, G.; Go, M.C.; Rho, J.; Kim, J.K. Accordion-like plasmonic silver nanorod array exhibiting multiple electromagnetic responses. NPG Asia Mater. 2018, 10, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Wen, X.; Wang, Z.L. Taxel-addressable matrix of vertical-nanowire piezotronic transistors for active and adaptive tactile imaging. Science 2013, 340, 952–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Luo, W.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Xie, B.; Wang, G.; Han, M. An ultrahigh resolution pressure sensor based on percolative metal nanoparticle arrays. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.; Im, J.; Shin, M.; Min, Y.; Park, J.; Cho, H.; Park, S.; Shim, M.B.; Jeon, S.; Chung, D.Y.; et al. Highly stretchable electric circuits from a composite material of silver nanoparticles and elastomeric fibres. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2012, 7, 803–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, H.; Park, H.-H.; Byeon, H.; Kang, M.; Ryu, J.; Sung, H.J.; Lee, S.J.; Jeong, H.E. Undulatory topographical waves for flow-induced foulant sweeping. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaax8935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, L.; Cui, F.; Yu, Y.; Khanarian, G.; Eaton, S.W.; Yang, Q.; Resasco, J.; Schildknecht, C.; Schierle-Arndt, K.; Yang, P. Solution-processed copper/reduced-graphene-oxide core/shell nanowire transparent conductors. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 2600–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.H.; Park, J.B.; Ahn, S.; Grigoropoulos, C.P. Laser-induced direct graphene patterning and simultaneous transferring method for graphene sensor platform. Small 2013, 9, 4269–4275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, M.; Kim, J.; Jang, B.; Chae, Y.; Kim, J.H.; Ahn, J.H. Graphene-based three-dimensional capacitive touch sensor for wearable electronics. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 7950–7957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Hong, S.; Lee, J.; Suh, Y.D.; Kwon, J.; Moon, H.; Kim, H.; Yeo, J.; Ko, S.H. Highly stretchable and transparent supercapacitor by Ag-Au core-shell nanowire network with high electrochemical stability. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 15449–15458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Li, J.; Che, L.; Chen, S.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, X. Toward large-scale fabrication of triboelectric nanogenerator (TENG) with silk-fibroin patches film via spray-coating process. Nano Energy 2017, 41, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Jeong, Y.R.; Yun, J.; Hong, S.Y.; Jin, S.; Lee, S.J.; Zi, G.; Ha, J.S. Stretchable array of highly sensitive pressure sensors consisting of polyaniline nanofibers and Au-coated polydimethylsiloxane micropillars. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 9974–9985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, C.; Ko, H.; Kim, H.T.; Sun, K.; Kwon, T.H.; Jeong, H.E.; Park, Y.B. Bioinspired, high-sensitivity mechanical sensors realized with hexagonal microcolumnar arrays coated with ultrasonic-sprayed single-walled carbon nanotubes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 18813–18822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Lee, Y.; Hong, J.; Ha, M.; Jung, Y.D.; Lim, H.; Kim, S.Y.; Ko, H. Giant tunneling piezoresistance of composite elastomers with interlocked microdome arrays for ultrasensitive and multimodal electronic skins. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 4689–4697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, H.H.; Nguyen, A.; Chortos, A.; To, J.W.; Lu, C.; Mei, J.; Kurosawa, T.; Bae, W.G.; Tok, J.B.; Bao, Z. A chameleon-inspired stretchable electronic skin with interactive colour changing controlled by tactile sensing. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Lee, Y.H.; Phang, I.Y.; Lee, C.K.; Ling, X.Y. Hierarchical 3D SERS substrates fabricated by integrating photolithographic microstructures and self-assembly of silver nanoparticles. Small 2014, 10, 2703–2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Chen, J.; Zhang, M.; Hong, J.-D.; Shi, G. Highly conductive stretchable electrodes prepared by in situ reduction of wavy graphene oxide films coated on elastic tapes. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2016, 2, 1600022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Ko, H.; Park, H.-H.; Seong, M.; Lee, S.H.; Yi, H.; Park, H.W.; Kim, T.I.; Pang, C.; Jeong, H.E. Hybrid architectures of heterogeneous carbon nanotube composite microstructures enable multiaxial strain perception with high sensitivity and ultrabroad sensing range. Small 2018, 14, e1803411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, J.W.; Yeo, W.H.; Akhtar, A.; Norton, J.J.; Kwack, Y.J.; Li, S.; Jung, S.Y.; Su, Y.; Lee, W.; Xia, J.; et al. Materials and optimized designs for human-machine interfaces via epidermal electronics. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 6839–6846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Reuveny, A.; Reeder, J.; Lee, S.; Jin, H.; Liu, Q.; Yokota, T.; Sekitani, T.; Isoyama, T.; Abe, Y.; et al. A transparent bending-insensitive pressure sensor. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2016, 11, 472–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, I.; Seong, M.; Yi, H.; Ko, H.; Park, H.-H.; Yeo, J.; Bae, W.G.; Park, H.W.; Jeong, H.E. Low-resistant electrical and robust mechanical contacts of self-attachable flexible transparent electrodes with patternable circuits. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2000458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, S.; Kwon, Y.T.; Kim, Y.S.; Lim, H.R.; Mahmood, M.; Yeo, W.H. Skin-conformal, soft material-enabled bioelectronic system with minimized motion artifacts for reliable health and performance monitoring of athletes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 151, 111981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.-L.; Jung, C.-W.; Oh, Y.-J.; Kim, D.-E. A highly flexible transparent conductive electrode based on nanomaterials. NPG Asia Mater. 2017, 9, e438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruth, S.R.A.; Beker, L.; Tran, H.; Feig, V.R.; Matsuhisa, N.; Bao, Z. Rational design of capacitive pressure sensors based on pyramidal microstructures for specialized monitoring of biosignals. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 30, 1903100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.; Nag, A.; Simorangkir, R.; Afsarimanesh, N.; Liu, H.; Mukhopadhyay, S.C.; Xu, Y.; Zhadobov, M.; Sauleau, R. Multifunctional flexible sensor based on laser-induced graphene. Sensors 2019, 19, 3477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aygun, L.E.; Kumar, V.; Weaver, C.; Gerber, M.; Wagner, S.; Verma, N.; Glisic, B.; Sturm, J.C. Large-area resistive strain sensing sheet for structural health monitoring. Sensors 2020, 20, 1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atalay, O.; Kennon, W.R.; Demirok, E. Weft-knitted strain sensor for monitoring respiratory rate and its electro-mechanical modeling. IEEE Sens. J. 2015, 15, 110–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabiri Ameri, S.; Ho, R.; Jang, H.; Tao, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Schnyer, D.M.; Akinwande, D.; Lu, N. Graphene electronic tattoo sensors. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 7634–7641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, I.; Kim, H.N.; Seong, M.; Lee, S.H.; Kang, M.; Yi, H.; Bae, W.G.; Kwak, M.K.; Jeong, H.E. Multifunctional smart skin adhesive patches for advanced health care. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2018, 7, e1800275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Zhao, M.; Cai, Y.; Zimniewska, M.; Li, D.; Wei, Q. A dual-mode wearable sensor based on bacterial cellulose reinforced hydrogels for highly sensitive strain/pressure sensing. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2019, 6, 1900934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.C.; Kim, J.O.; Oh, J.; Kwon, S.Y.; Sim, J.Y.; Kim, D.W.; Choi, H.B.; Park, S. Microstructured porous pyramid-based ultrahigh sensitive pressure sensor insensitive to strain and temperature. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 19472–19480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, J.; Yang, J.C.; Kim, J.O.; Park, H.; Kwon, S.Y.; Lee, S.; Sim, J.Y.; Oh, H.W.; Kim, J.; Park, S. Pressure insensitive strain sensor with facile solution-based process for tactile sensing applications. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 7546–7553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.-R.; Kim, J.-H.; Park, J.-W. Wearable and transparent capacitive strain sensor with high sensitivity based on patterned Ag nanowire networks. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 26407–26416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drotlef, D.M.; Amjadi, M.; Yunusa, M.; Sitti, M. Bioinspired composite microfibers for skin adhesion and signal amplification of wearable sensors. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1701353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Xie, J.; Zheng, Y.; Wei, D.; Yao, D.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, T. Antibacterial, self-adhesive, recyclable, and tough conductive composite hydrogels for ultrasensitive strain sensing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 22225–22236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.; Kang, M.; Kwak, M.K.; Jeong, H.E. Simple and reliable fabrication of bioinspired mushroom-shaped micropillars with precisely controlled tip geometries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 22671–22678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munzer, A.M.; Heimgreiter, M.; Melzer, K.; Weise, A.; Fabel, B.; Abdellah, A.; Lugli, P.; Scarpa, G. Back-gated spray-deposited carbon nanotube thin film transistors operated in electrolytic solutions: An assessment towards future biosensing applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 3797–3802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.J.; Shin, D.W.; Kim, J.-Y.; Park, S.H.; Han, I.t.; Yoo, J.B. The production of a flexible electroluminescent device on polyethylene terephthalate films using transparent conducting carbon nanotube electrode. Carbon 2009, 47, 3461–3465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, W.G.; Kim, H.N.; Kim, D.; Park, S.H.; Jeong, H.E.; Suh, K.Y. 25th anniversary article: Scalable multiscale patterned structures inspired by nature: The role of hierarchy. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 675–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, H.J.; Yao, H.M. Shape insensitive optimal adhesion of nanoscale fibrillar structures. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 7851–7856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boesel, L.F.; Greiner, C.; Arzt, E.; del Campo, A. Gecko-inspired surfaces: A path to strong and reversible dry adhesives. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 2125–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.; Kim, G.; Cho, Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Minsky, H.; Turner, K.T.; Gianola, D.S.; Yang, S. Orthogonal control of stability and tunable dry adhesion by tailoring the shape of tapered nanopillar arrays. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 7788–7793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, H.E.; Lee, J.K.; Kim, H.N.; Moon, S.H.; Suh, K.Y. A nontransferring dry adhesive with hierarchical polymer nanohairs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 5639–5644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Sitti, M. Biologically inspired polymer microfibers with spatulate tips as repeatable fibrillar adhesives. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 89, 261911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Autumn, K.; Liang, Y.A.; Hsieh, S.T.; Zesch, W.; Chan, W.P.; Kenny, T.W.; Fearing, R.; Full, R.J. Adhesive force of a single gecko foot-hair. Nature 2000, 405, 681–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.; Seong, M.; Sun, K.; Hwang, I.; Lee, K.; Cha, C.; Kim, T.-i.; Jeong, H.E. Wet-responsive, reconfigurable, and biocompatible hydrogel adhesive films for transfer printing of nanomembranes. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1706498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, H.Z.; Kim, K.K.; So, K.P.; Lee, Y.S.; Chang, Y.; Lee, Y.H. Effect of acid treatment on carbon nanotube-based flexible transparent conducting films. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 7758–7759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, I.D.; McCluskey, D.K.; Tan, C.K.L.; Tracey, M.C. Mechanical characterization of bulk Sylgard 184 for microfluidics and microengineering. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2014, 24, 035017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, R.; Servati, P. Effects of inter-tube distance and alignment on tunnelling resistance and strain sensitivity of nanotube/polymer composite films. Nanotechnology 2012, 23, 055703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alamusi; Hu, N.; Fukunaga, H.; Atobe, S.; Liu, Y.; Li, J. Piezoresistive strain sensors made from carbon nanotubes based polymer nanocomposites. Sensors 2011, 11, 10691–10723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Lim, M.; Yoon, J.; Kim, M.S.; Choi, B.; Kim, D.M.; Kim, D.H.; Park, I.; Choi, S.J. Transparent, flexible strain sensor based on a solution-processed carbon nanotube network. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 26279–26285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, A.; Bogdanovich, A.E.; Bradford, P.D. Aligned carbon nanotube sheet piezoresistive strain sensors. Smart Mater. Struct. 2015, 24, 095004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, K.-P.; Lim, L.-T.; Min, N.-K.; Lee, M.J.; Lee, C.J.; Park, C.-W. Novel resistive-type humidity sensor based on multiwall carbon nanotube/polyimide composite films. Sens. Actuator B-Chem. 2010, 145, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Tian, H.; Tao, L.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Deng, N.; Yang, Y.; Ren, T.L. Flexible, highly sensitive, and wearable pressure and strain sensors with graphene porous network structure. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 26458–26462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, D.; Lee, J.; Qiao, S.; Ghaffari, R.; Kim, J.; Lee, J.E.; Song, C.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, D.J.; Jun, S.W.; et al. Multifunctional wearable devices for diagnosis and therapy of movement disorders. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2014, 9, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeqi, A.; Nejad, H.R.; Alaimo, F.; Yun, H.; Punjiya, M.; Sonkusale, S. Washable smart threads for strain sensing fabrics. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 18, 9137–9144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vertuccio, L.; Guadagno, L.; Spinelli, G.; Lamberti, P.; Tucci, V.; Russo, S. Piezoresistive properties of resin reinforced with carbon nanotubes for health-monitoring of aircraft primary structures. Compos. Pt. B-Eng. 2016, 107, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Seong, M.; Hwang, I.; Lee, J.; Jeong, H.E. A Pressure-Insensitive Self-Attachable Flexible Strain Sensor with Bioinspired Adhesive and Active CNT Layers. Sensors 2020, 20, 6965. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20236965
Seong M, Hwang I, Lee J, Jeong HE. A Pressure-Insensitive Self-Attachable Flexible Strain Sensor with Bioinspired Adhesive and Active CNT Layers. Sensors. 2020; 20(23):6965. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20236965
Chicago/Turabian StyleSeong, Minho, Insol Hwang, Joosung Lee, and Hoon Eui Jeong. 2020. "A Pressure-Insensitive Self-Attachable Flexible Strain Sensor with Bioinspired Adhesive and Active CNT Layers" Sensors 20, no. 23: 6965. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20236965
APA StyleSeong, M., Hwang, I., Lee, J., & Jeong, H. E. (2020). A Pressure-Insensitive Self-Attachable Flexible Strain Sensor with Bioinspired Adhesive and Active CNT Layers. Sensors, 20(23), 6965. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20236965




