Adaptive Spoofing Suppression Algorithm for GNSS Based on Multiple Antennas Array
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- An adaptive spoofing interference suppression algorithm is proposed for satellite navigation based on a multi antenna array. This algorithm improves the real-time performance of spoofing suppression and reduces the complexity of spoofing interference suppression.
- A cross-correlation model of satellite navigation spoofing signals received by multiple elements is established. The feasibility of using the spread spectrum signals received between different array elements as a cross-correlation by which to suppress spoofing interference is analyzed.
- The complexity of the implementation of the adaptive spoofing suppressor for satellite navigation based on a multi antenna array is analyzed, and the performances of the two algorithms are verified by comparing them with the algorithm that first finds the direction of a signal and then suppresses it. The location performances of the two algorithms are tested under static and dynamic conditions.
2. Spoofing Suppression Algorithm
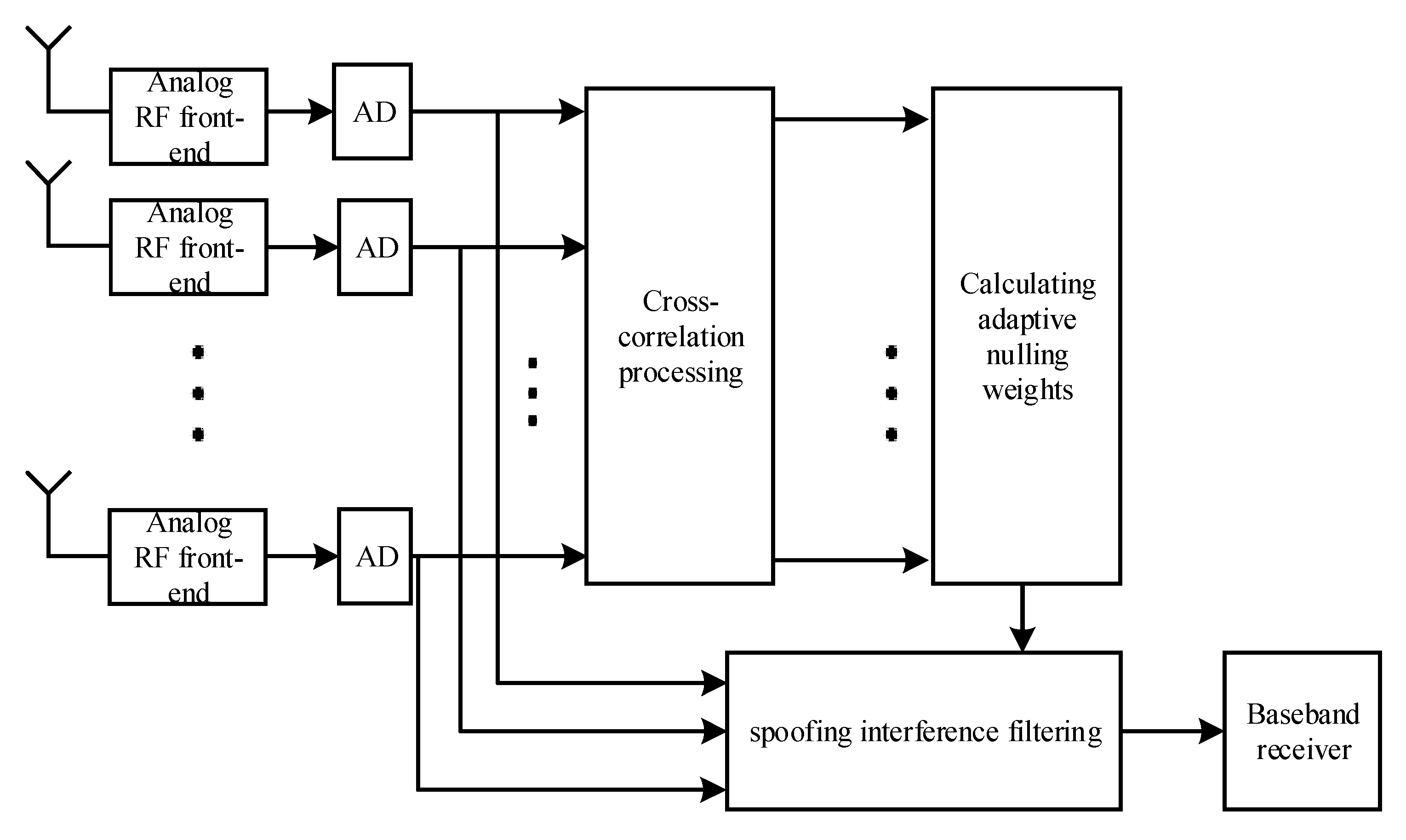
2.1. Signal Receiving Model of a Multiple Antenna Array for Spoofing
2.2. Suppressing Spoofing Based on Direction of Arrival (DOA)
| Algorithms: |
|
2.3. Adaptive Spoofing Suppression Algorithm (Assa)
| Algorithms: |
|
2.4. Complexity Analysis
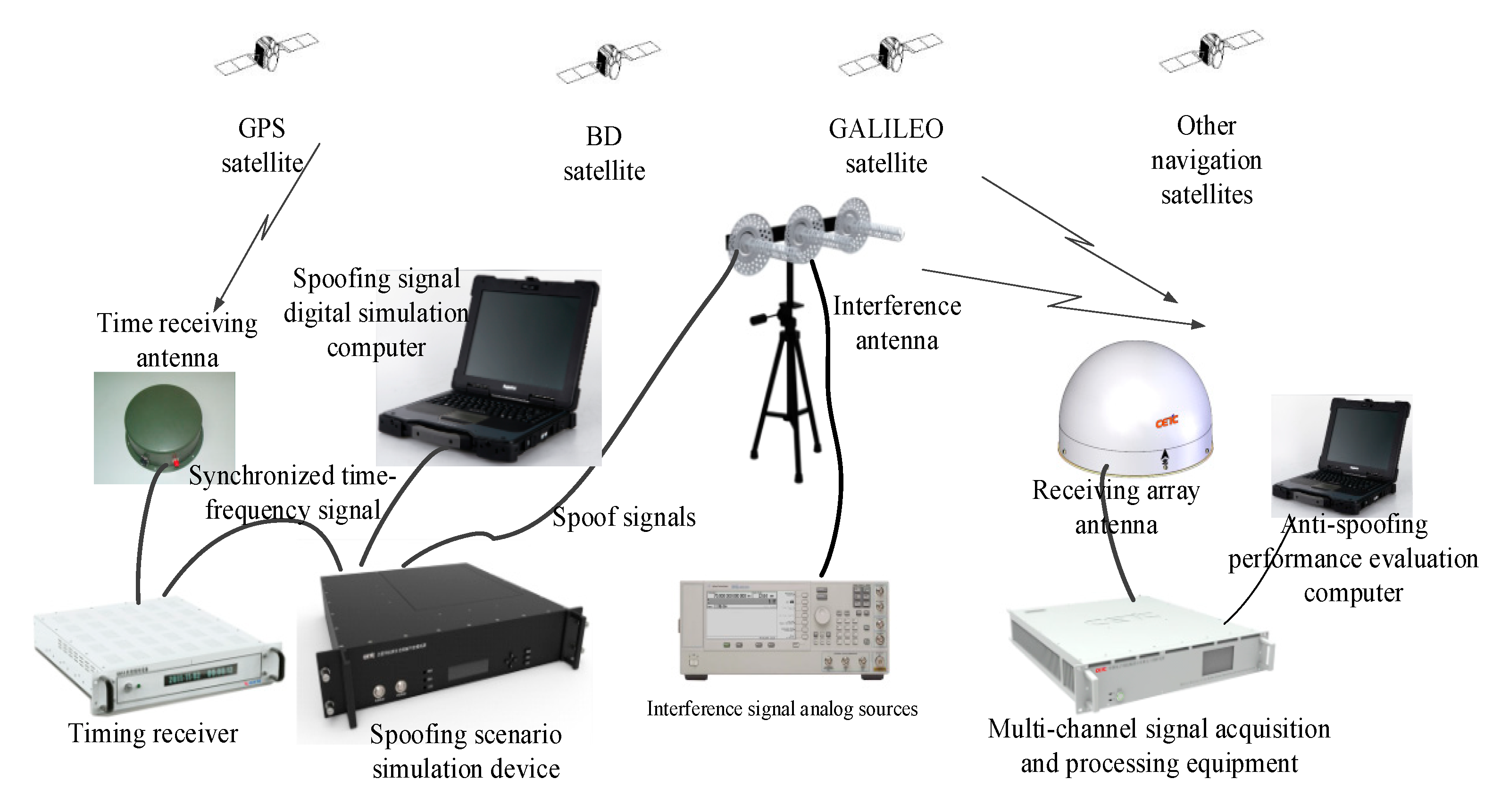
3. Implementations and Evaluation
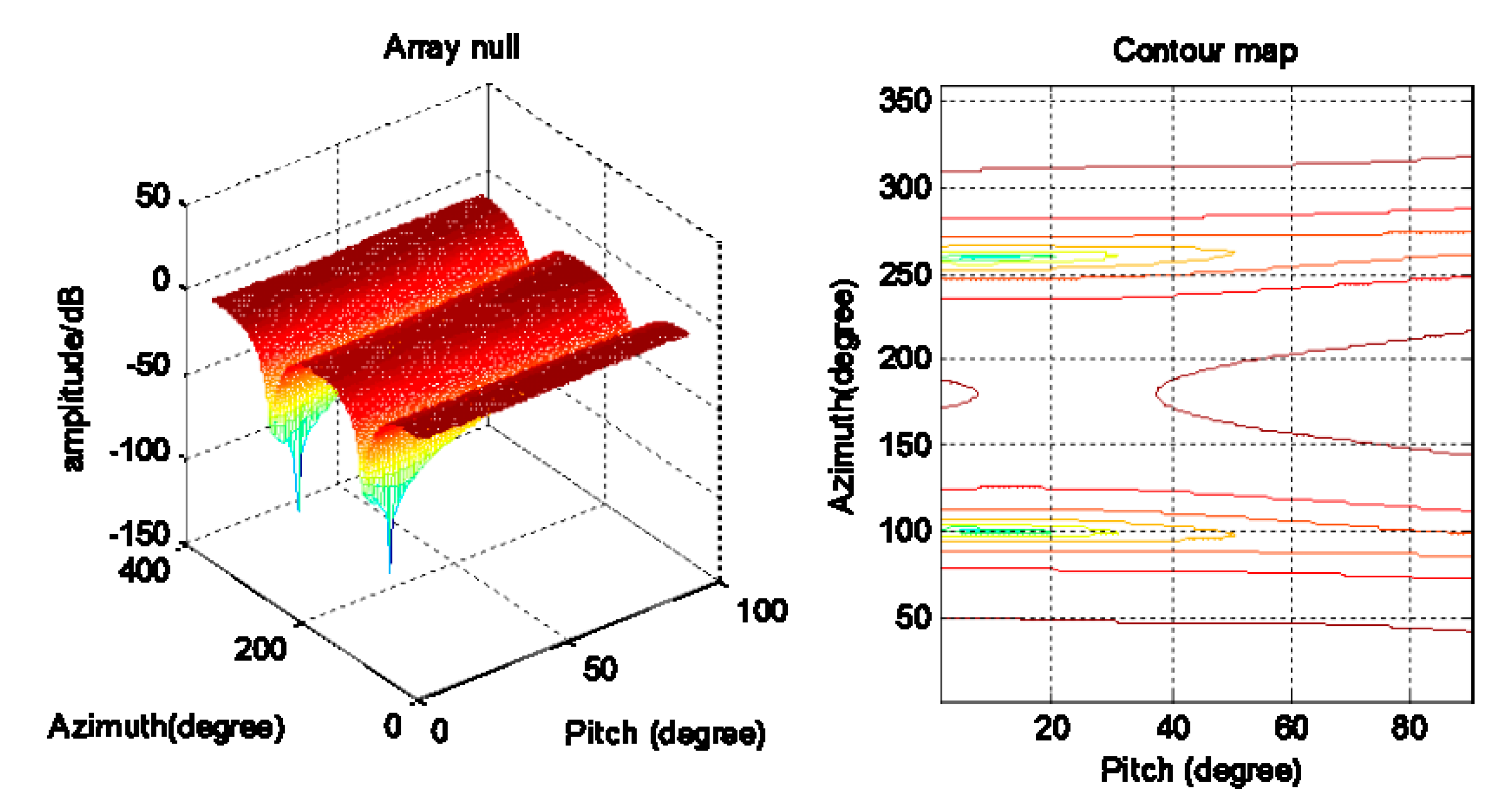
3.1. Performance Analysis
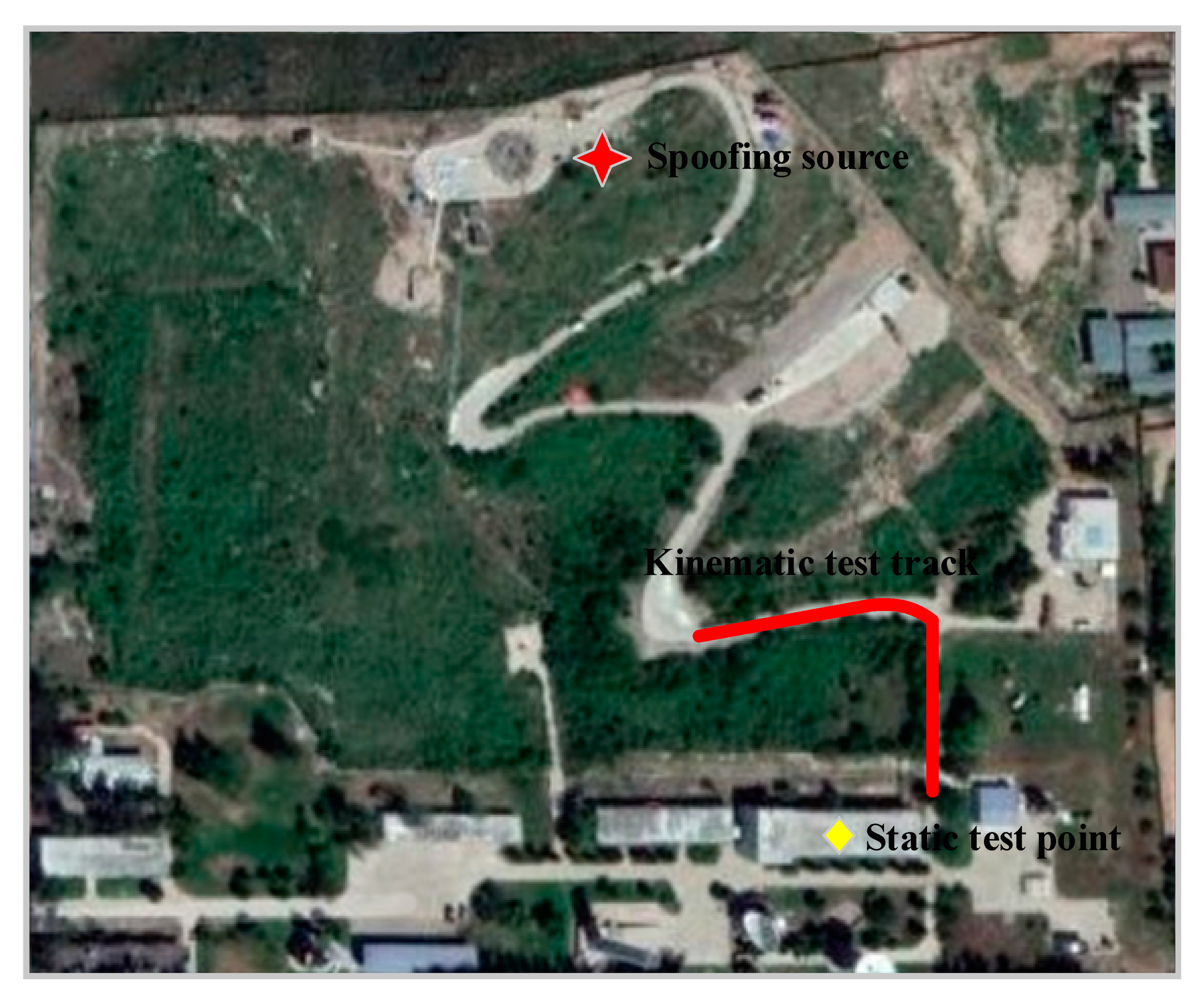
3.2. Static Test Results
3.3. Kinematic Test Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lechner, W.; Baumann, S. Global navigation satellite systems. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2000, 25, 67–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grejner-Brzezinska, D.A.; Toth, C.; Moore, T.; Raquet, J.F.; Miller, M.M.; Kealy, A. Multisensor Navigation Systems: A Remedy for GNSS Vulnerabilities? Proc. IEEE 2016, 104, 1339–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, J.V. Vulnerability Assessment of the U.S. Transportation Infrastructure that Relies on the Global Positioning System. J. Navig. 2003, 56, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpe, J.A. Vulnerability Assessment of the Transportation Infrastructure Relying on the Global Positioning System; Technical Report; National Transportation Research Center: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Naval Surface Warfare Center. Global positioning system impact to critical civil infrastructure (GICCI); Technical Report; Mission Assurance Division, Naval Surface Warfare Center: Crane, Indiana, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Psiaki, M.L.; Humphreys, T.E. GNSS Spoofing and Detection. Proc. IEEE 2016, 104, 1258–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X. A GNSS anti-spoofing technology based on Doppler shift in vehicle networking. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing Conference (IWCMC), Paphos, Cyprus, 5–9 September 2016; pp. 725–729. [Google Scholar]
- Motella, B.; Pini, M.; Fantino, M.; Mulassano, P.; Nicola, M.; Fortuny-Guasch, J.; Wildemeersch, M.; Symeonidis, D. Performance assessment of low cost GPS receivers under civilian spoofing attacks. In Proceedings of the 2010 5th ESA Workshop on Satellite Navigation Technologies and European Workshop on GNSS Signals and Signal Processing (NAVITEC), Rotterdam Netherlands, 8–10 December 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Broumandan, A.; Jafarnia-Jahromi, A.; Lachapelle, G. Spoofing detection, classification and cancelation (SDCC) receiver architecture for a moving GNSS receiver. GPS Solutions 2015, 19, 475–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, J.; Broumandan, A.; Lachapelle, G. GNSS Spoofing Detection for Single Antenna Handheld Receivers. Navig. 2011, 58, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahromi, A.J.; Broumandan, A.; Nielsen, J.; Lachapelle, G. GPS spoofer countermeasure effectiveness based on signal strength, noise power, and C/N0 measurements. Int. J. Satell. Commun. Netw. 2012, 30, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Bian, S.; Cao, K.; Ji, B. GNSS spoofing detection based on new signal quality assessment model. GPS Solutions 2018, 22, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhan, X.; Feng, S.; Ochieng, W.Y. Sensitivity analysis of the vestigial signal defence-based civil GNSS spoofing detection algorithm. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2016, 11, 861–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesson, K.D.; Gross, J.N.; Humphreys, T.E.; Evans, B.L. GNSS Signal Authentication via Power and Distortion Monitoring. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2018, 54, 739–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dobryakova, L.A.; Lemieszewski, L.S.; Ochin, E. GNSS Spoofing Detection Using Static or Rotating Single-Antenna of a Static or Moving Victim. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 79074–79081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiee, E.; Mosavi, M.R.; Moazedi, M. Detection of Spoofing Attack using Machine Learning based on Multi-Layer Neural Network in Single-Frequency GPS Receivers. J. Navig. 2017, 71, 169–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Luo, D.; Meng, W.; Li, C. Antispoofing RAIM for dual-recursion particle filter of GNSS calculation. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2016, 52, 836–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzerrouk, H.; Nebylov, A.V. Integrated Navigation System INS/GNSS Based on Joint Application of Linear and Nonlinear Filtering. IFAC Proc. Volumes 2012, 45, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanil, C.; Khanafseh, S.; Joerger, M.; Pervan, B. An INS Monitor to Detect GNSS Spoofers Capable of Tracking Vehicle Position. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2018, 54, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Merwe, J.R.; Rugamer, A.; Goicoechea, A.F.-D.; Felber, W. Blind Spoofing Detection Using a Multi-Antenna Snapshot Receiver. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Localization and GNSS (ICL-GNSS), Nuremberg, Germany, 4–6 June 2019; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, G.; Shen, F.; Amin, M.; Wang, C. DOA classification and CCPM-PC based GNSS spoofing detection technique. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/ION Position, Location and Navigation Symposium (PLANS), Monterey, CA, USA, 5–8 April 2018; pp. 389–396. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, V.H.; Falco, G.; Nicola, M.; Falletti, E. A Dual Antenna GNSS Spoofing Detector Based on the Dispersion of Double Difference Measurements. In Proceedings of the 2018 9th ESA Workshop on Satellite Navigation Technologies and European Workshop on GNSS Signals and Signal Processing (NAVITEC), Noordwijk, The Netherlands, 8–10 December 2018; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Fan, M.; Kong, M. Spoofing interference suppression using space-time process for GNSS receiver. In Proceedings of the 2012 5th International Congress on Image and Signal Processing, Chongqing, China, 22–24 October 2012; pp. 1537–1541. [Google Scholar]
- Humphreys, T.E. Detection Strategy for Cryptographic GNSS Anti-Spoofing. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2013, 49, 1073–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psiaki, M.L. Spoofing Detection for Civilian GNSS Signals. U.S. Patent 8,712,051, 29 April 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Rycroft, M.J. Understanding GPS. Principles and applications. J. Atmos. Solar-Terrestrial Phys. 1997, 59, 598–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wan, L.; Dong, M.; Ota, K.; Wang, X. Assistant Vehicle Localization Based on Three Collaborative Base Stations via SBL-Based Robust DOA Estimation. IEEE Internet Things J. 2019, 6, 5766–5777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Wen, F.; Shi, J.-P.; Gong, Z.; Xu, H. A Computationally Economic Location Algorithm for Bistatic EVMS-MIMO Radar. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 120533–120540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Shi, J.-P.; Wang, X.; Wen, F. Joint Angle and Frequency Estimation Using One-Bit Measurements. Sensors 2019, 19, 5422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Wan, L.; Huang, M.; Shen, C.; Zhang, K. Polarization Channel Estimation for Circular and Non-Circular Signals in Massive MIMO Systems. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2019, 13, 1001–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, K.; Xu, X. Spatial-spectrum estimation in a location sector. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech, Signal Process. 1990, 38, 1842–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.; Sun, L.; Kong, X.; Yuan, Y.; Sun, K.; Xia, F. Task-Driven Resource Assignment in Mobile Edge Computing Exploiting Evolutionary Computation. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2019, 26, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





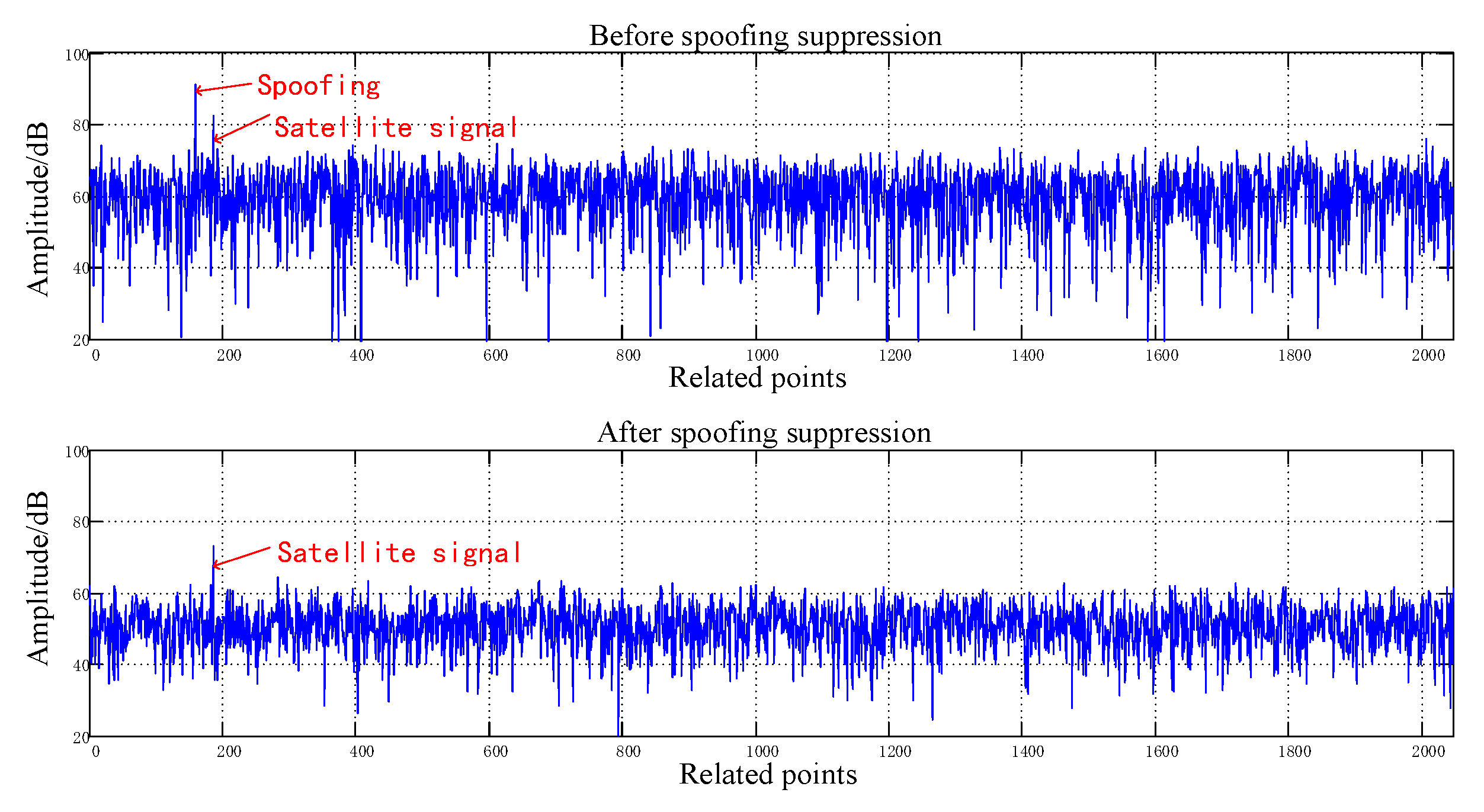

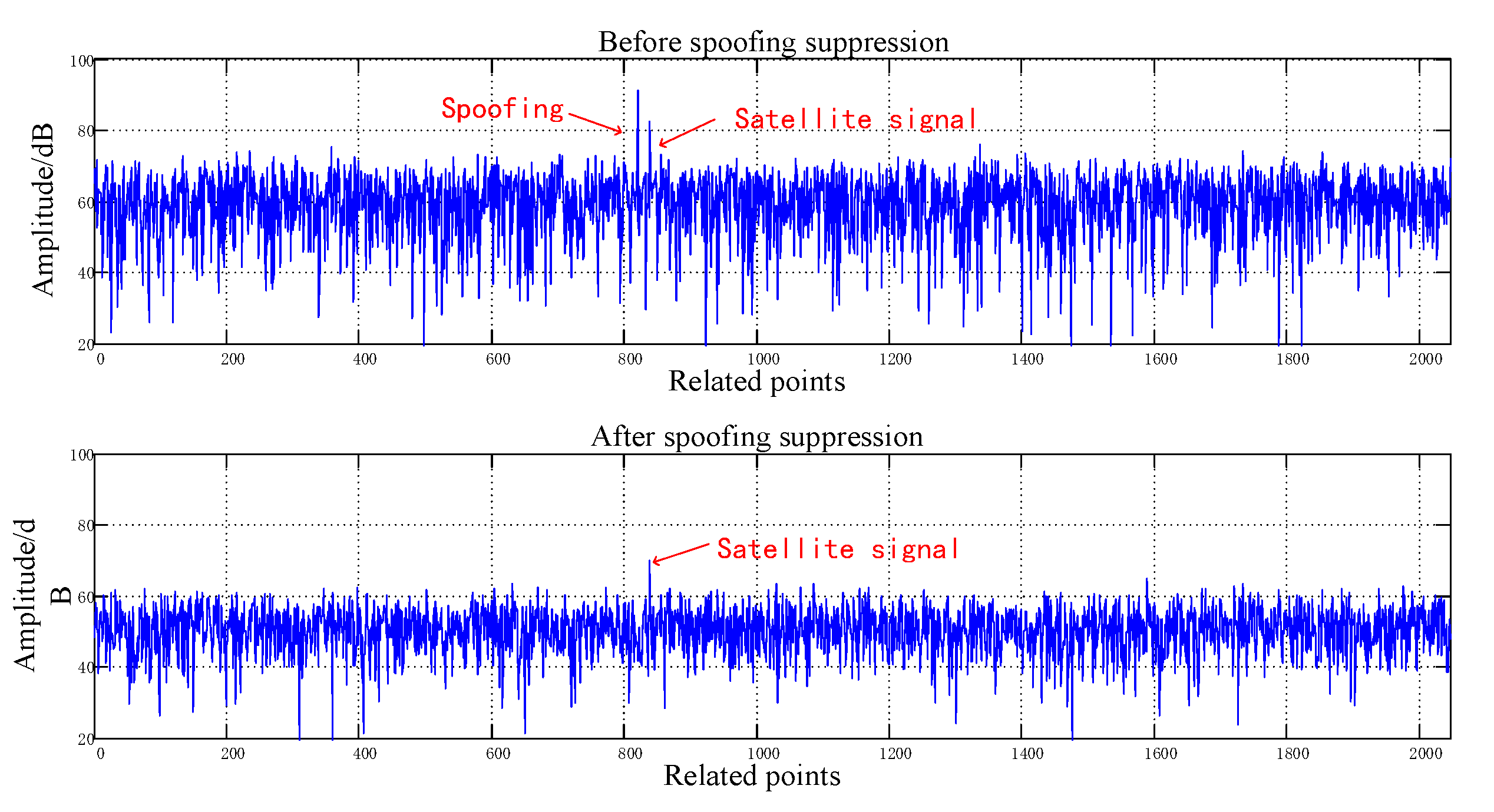
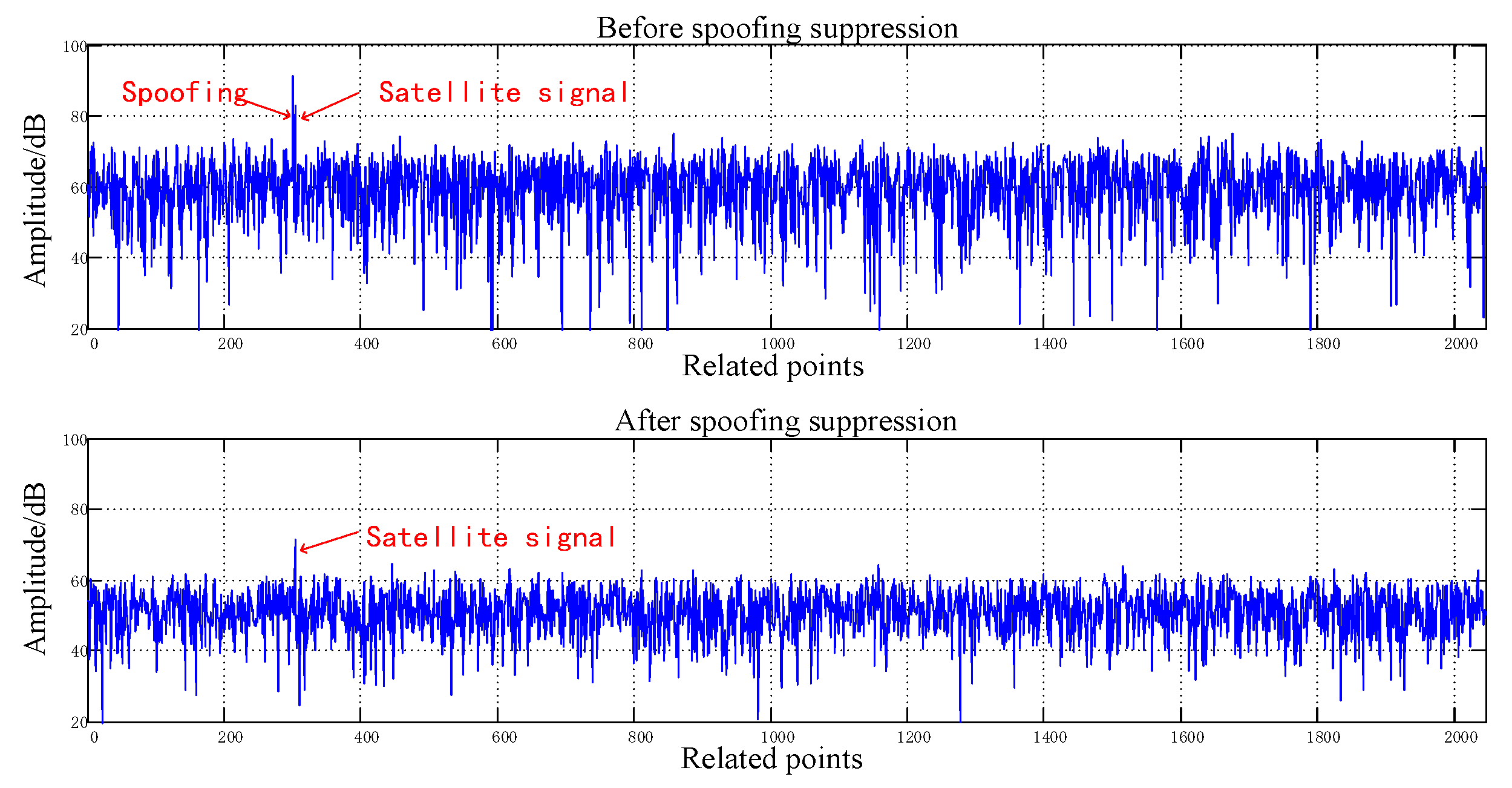

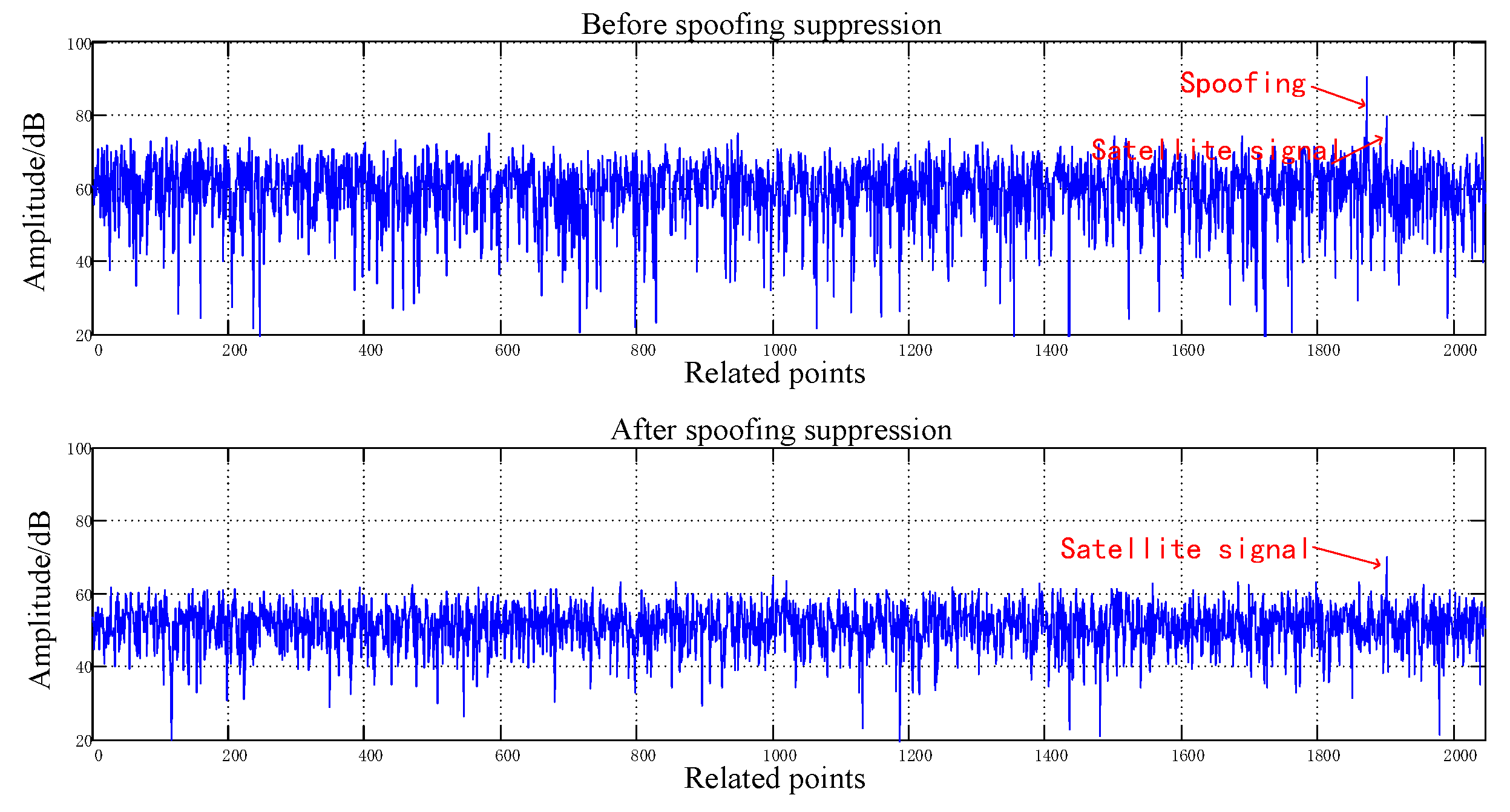
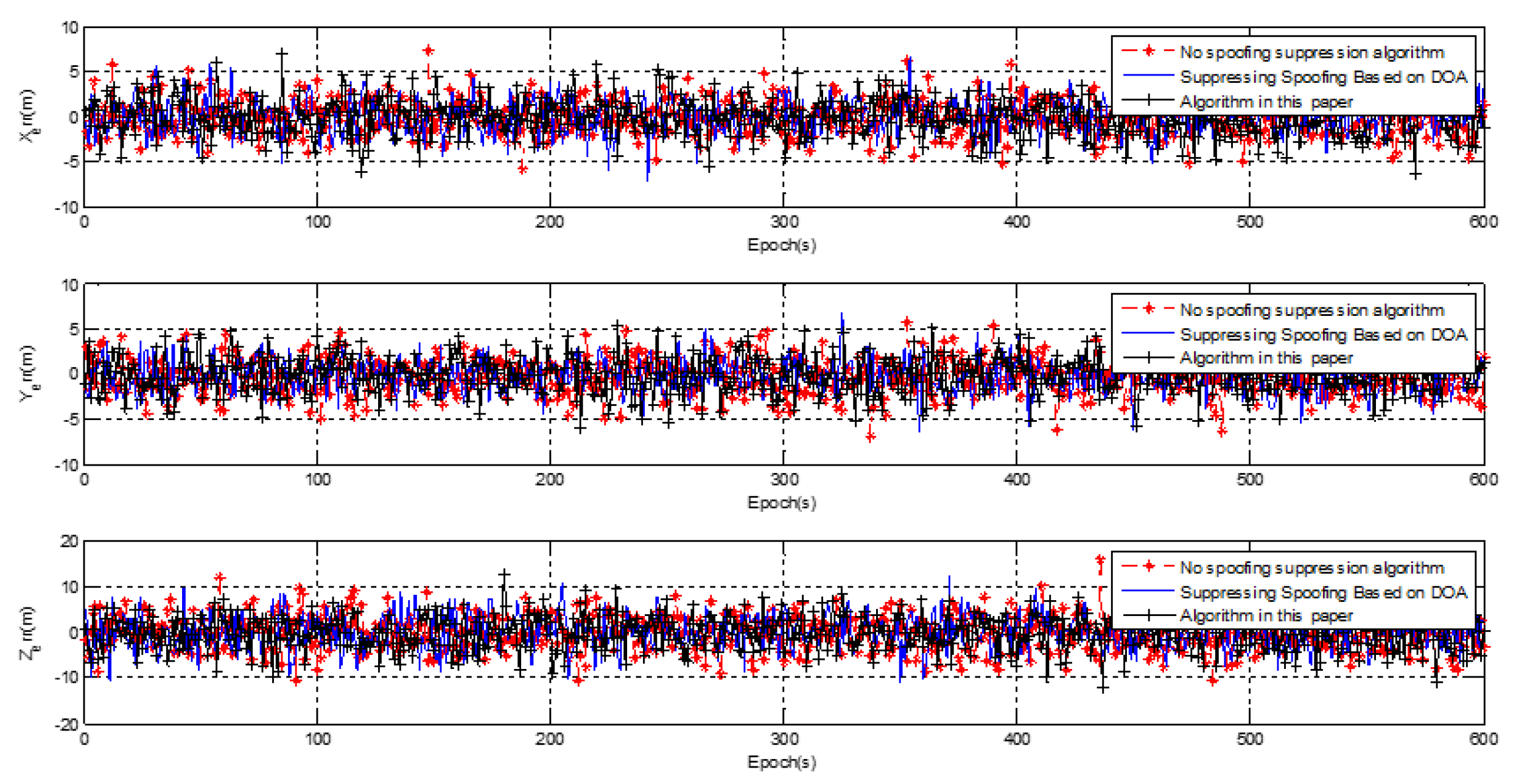

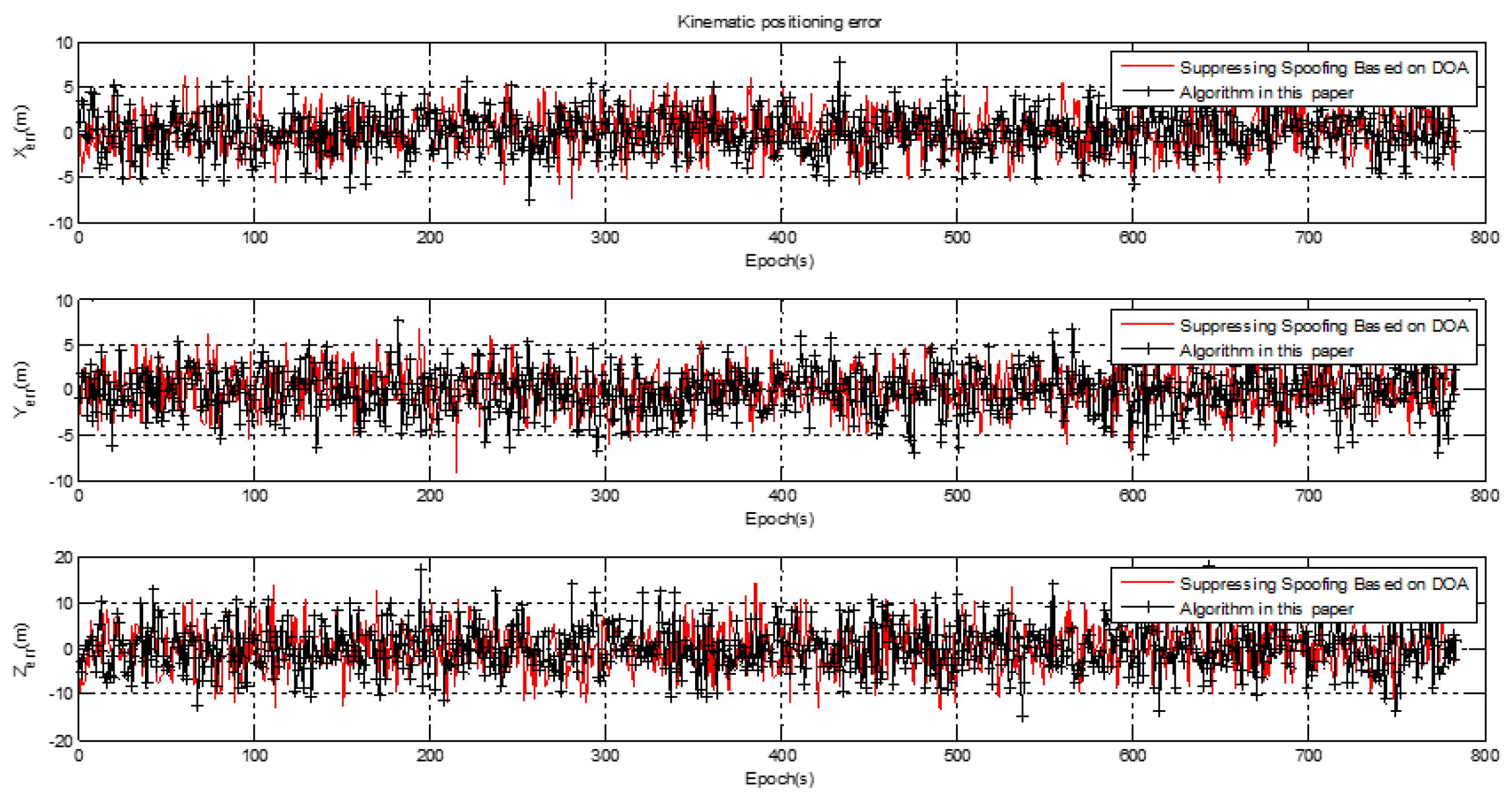
| Parameter | No Spoofing | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| No Spoofing Suppression Algorithm | Suppressing Spoofing Based on DOA | Adaptive Spoofing Suppression Algorithm(ASSA) | |
| (m) | 1.90 | 1.92 | 2.20 |
| (m) | 1.95 | 1.95 | 2.13 |
| (m) | 3.93 | 3.96 | 4.11 |
| Parameter | Spoofing | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| No Spoofing Suppression Algorithm | Suppressing Spoofing Based on DOA | Adaptive Spoofing Suppression Algorithm(ASSA) | |
| (m) | 2.14 | 2.22 | |
| (m) | 2.29 | 2.41 | |
| (m) | 4.32 | 4.43 |
| Parameter | Spoofing | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| No Spoofing Suppression Algorithm | Suppressing Spoofing Based on DOA Algorithm | Adaptive Spoofing Suppression Algorithm(ASSA) | |
| (m) | 2.38 | 2.27 | |
| (m) | 2.27 | 2.43 | |
| (m) | 4.73 | 4.64 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, G.; Gan, X.; Yu, B.; Rong, Q.; Sheng, C. Adaptive Spoofing Suppression Algorithm for GNSS Based on Multiple Antennas Array. Sensors 2020, 20, 1115. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20041115
Fan G, Gan X, Yu B, Rong Q, Sheng C. Adaptive Spoofing Suppression Algorithm for GNSS Based on Multiple Antennas Array. Sensors. 2020; 20(4):1115. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20041115
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Guangwei, Xingli Gan, Baoguo Yu, Qiang Rong, and Chuanzhen Sheng. 2020. "Adaptive Spoofing Suppression Algorithm for GNSS Based on Multiple Antennas Array" Sensors 20, no. 4: 1115. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20041115
APA StyleFan, G., Gan, X., Yu, B., Rong, Q., & Sheng, C. (2020). Adaptive Spoofing Suppression Algorithm for GNSS Based on Multiple Antennas Array. Sensors, 20(4), 1115. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20041115





