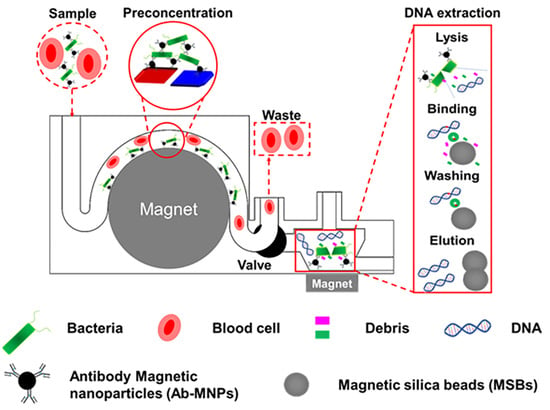
3D-Printed Modular Microfluidic Device Enabling Preconcentrating Bacteria and Purifying Bacterial DNA in Blood for Improving the Sensitivity of Molecular Diagnostics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Bacterial Culture
2.3. Synthesis of Ab-MNPs
2.4. D Printing
2.5. Estimation of the Capturing Efficiency Using Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) Analysis
2.6. Bacterial Capture by 3DpmμFD
2.7. Bacterial gDNA Purification on 3DpmμFD with a Conical Microchamber
2.8. Analysis of DNA Purity and Yield
2.9. Detection of Bacteria by PCR and qPCR
2.10. Statistical Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Microchannel Geometry on Bacterial Capturing Efficiency
3.2. Comparison of Bacterial Capturing Efficiency at Different Flow Rates in the W-Shaped Microchannel
3.3. Cross-Reactivity of the Ab-MNPs
3.4. Improvement of Bacterial gDNA Purity by Adding a Conical Microchamber into the W-Shaped Microchannel
3.5. Improvement of Amplification of Bacterial gDNA by Adding a Conical Microchamber into the W-Shaped Microchannel
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nguyen, H.B.; Rivers, E.P.; Abrahamian, F.M.; Moran, G.J.; Abraham, E.; Trzeciak, S.; Huang, D.T.; Osborn, T.; Stevens, D.; Talan, D.A. Severe sepsis and septic shock: Review of the literature and emergency department management guidelines. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2006, 48, 54.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. The immunopathogenesis of sepsis. Nature 2002, 420, 885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angus, D.C.; Van der Poll, T. Severe sepsis and septic shock. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 840–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singer, M.; Deutschman, C.S.; Seymour, C.W.; Shankar-Hari, M.; Annane, D.; Bauer, M.; Bellomo, R.; Bernard, G.R.; Chiche, J.-D.; Coopersmith, C.M. The third international consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA 2016, 315, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obara, H.; Aikawa, N.; Hasegawa, N.; Hori, S.; Ikeda, Y.; Kobayashi, Y.; Murata, M.; Okamoto, S.; Takeda, J.; Tanabe, M. The role of a real-time PCR technology for rapid detection and identification of bacterial and fungal pathogens in whole-blood samples. J. Infect. Chemother. 2011, 17, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Rothman, R.E. PCR-based diagnostics for infectious diseases: Uses, limitations, and future applications in acute-care settings. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2004, 4, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, L.E.; Hunfeld, K.-P.; Emrich, T.; Haberhausen, G.; Wissing, H.; Hoeft, A.; Stüber, F. A multiplex real-time PCR assay for rapid detection and differentiation of 25 bacterial and fungal pathogens from whole blood samples. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2008, 197, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opota, O.; Jaton, K.; Greub, G. Microbial diagnosis of bloodstream infection: Towards molecular diagnosis directly from blood. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2015, 21, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Kermekchiev, M.B.; Barnes, W.M. Direct DNA amplification from crude clinical samples using a PCR enhancer cocktail and novel mutants of Taq. J. Mol. Diagn. 2010, 12, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Soud, W.A.; Rådström, P. Purification and characterization of PCR-inhibitory components in blood cells. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hansen, W.L.; Bruggeman, C.A.; Wolffs, P.F. Evaluation of new preanalysis sample treatment tools and DNA isolation protocols to improve bacterial pathogen detection in whole blood. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2009, 47, 2629–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boardman, A.K.; Campbell, J.; Wirz, H.; Sharon, A.; Sauer-Budge, A.F. Rapid microbial sample preparation from blood using a novel concentration device. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viltrop, T.; Krjutškov, K.; Palta, P.; Metspalu, A. Comparison of DNA extraction methods for multiplex polymerase chain reaction. Anal. Biochem. 2010, 398, 260–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Lee, J.; Park, S. A 3D-printed millifluidic platform enabling bacterial preconcentration and DNA purification for molecular detection of pathogens in blood. Micromachines 2018, 9, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Anderung, C.; Persson, P.; Bouwman, A.; Elburg, R.; Götherström, A. Fishing for ancient DNA. Sci. Int. 2008, 2, 104–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogram, A.; Sayler, G.S.; Barkay, T. The extraction and purification of microbial DNA from sediments. J. Microbiol. Methods 1987, 7, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berensmeier, S. Magnetic particles for the separation and purification of nucleic acids. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 73, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitt, W.G.; Alizadeh, M.; Husseini, G.A.; McClellan, D.S.; Buchanan, C.M.; Bledsoe, C.G.; Robison, R.A.; Blanco, R.; Roeder, B.L.; Melville, M. Rapid separation of bacteria from blood—Review and outlook. Biotechnol. Prog. 2016, 32, 823–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fong, E.J.; Huang, C.; Hamilton, J.; Benett, W.J.; Bora, M.; Burklund, A.; Metz, T.R.; Shusteff, M. A microfluidic platform for precision small-volume sample processing and its use to size separate biological particles with an acoustic microdevice. JoVE 2015, e53051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Mehl, B.T.; Munshi, A.S.; Townsend, A.D.; Spence, D.M.; Martin, R.S. 3D-printed microfluidic devices: Fabrication, advantages and limitations—A mini review. Anal. Methods. 2016, 8, 6005–6012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, H.N.; Chen, Y.; Shu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Tian, Q.; Wu, H. Direct, one-step molding of 3D-printed structures for convenient fabrication of truly 3D PDMS microfluidic chips. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2015, 19, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.; Lee, J.; Kim, Y.; Kim, J.; Lee, J.; Park, S. 3D-printed microfluidic magnetic preconcentrator for the detection of bacterial pathogen using an ATP luminometer and antibody-conjugated magnetic nanoparticles. J. Microbiol. Methods 2017, 132, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.; Kwon, D.; Choi, W.; Jung, G.Y.; Au, A.K.; Folch, A.; Jeon, S. 3D-printed microfluidic device for the detection of pathogenic bacteria using size-based separation in helical channel with trapezoid cross-section. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 7717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herigstad, B.; Hamilton, M.; Heersink, J. How to optimize the drop plate method for enumerating bacteria. J. Microbiol. Methods 2001, 44, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibbal, D.; Loukiadis, E.; Kérourédan, M.; de Garam, C.P.; Ferré, F.; Cartier, P.; Gay, E.; Oswald, E.; Auvray, F.; Brugère, H. Intimin gene (eae) subtype-based real-time PCR strategy for specific detection of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli serotypes O157: H7, O26: H11, O103: H2, O111: H8, and O145: H28 in cattle feces. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 1177–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abafogi, A.T.; Kim, J.; Lee, J.; Mohammed, M.O.; van Noort, D.; Park, S. 3D-Printed Modular Microfluidic Device Enabling Preconcentrating Bacteria and Purifying Bacterial DNA in Blood for Improving the Sensitivity of Molecular Diagnostics. Sensors 2020, 20, 1202. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20041202
Abafogi AT, Kim J, Lee J, Mohammed MO, van Noort D, Park S. 3D-Printed Modular Microfluidic Device Enabling Preconcentrating Bacteria and Purifying Bacterial DNA in Blood for Improving the Sensitivity of Molecular Diagnostics. Sensors. 2020; 20(4):1202. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20041202
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbafogi, Abdurhaman Teyib, Jaewon Kim, Jinyeop Lee, Merem Omer Mohammed, Danny van Noort, and Sungsu Park. 2020. "3D-Printed Modular Microfluidic Device Enabling Preconcentrating Bacteria and Purifying Bacterial DNA in Blood for Improving the Sensitivity of Molecular Diagnostics" Sensors 20, no. 4: 1202. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20041202
APA StyleAbafogi, A. T., Kim, J., Lee, J., Mohammed, M. O., van Noort, D., & Park, S. (2020). 3D-Printed Modular Microfluidic Device Enabling Preconcentrating Bacteria and Purifying Bacterial DNA in Blood for Improving the Sensitivity of Molecular Diagnostics. Sensors, 20(4), 1202. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20041202