Electrochemical Paper-Based Biosensor Devices for Rapid Detection of Biomarkers
Abstract
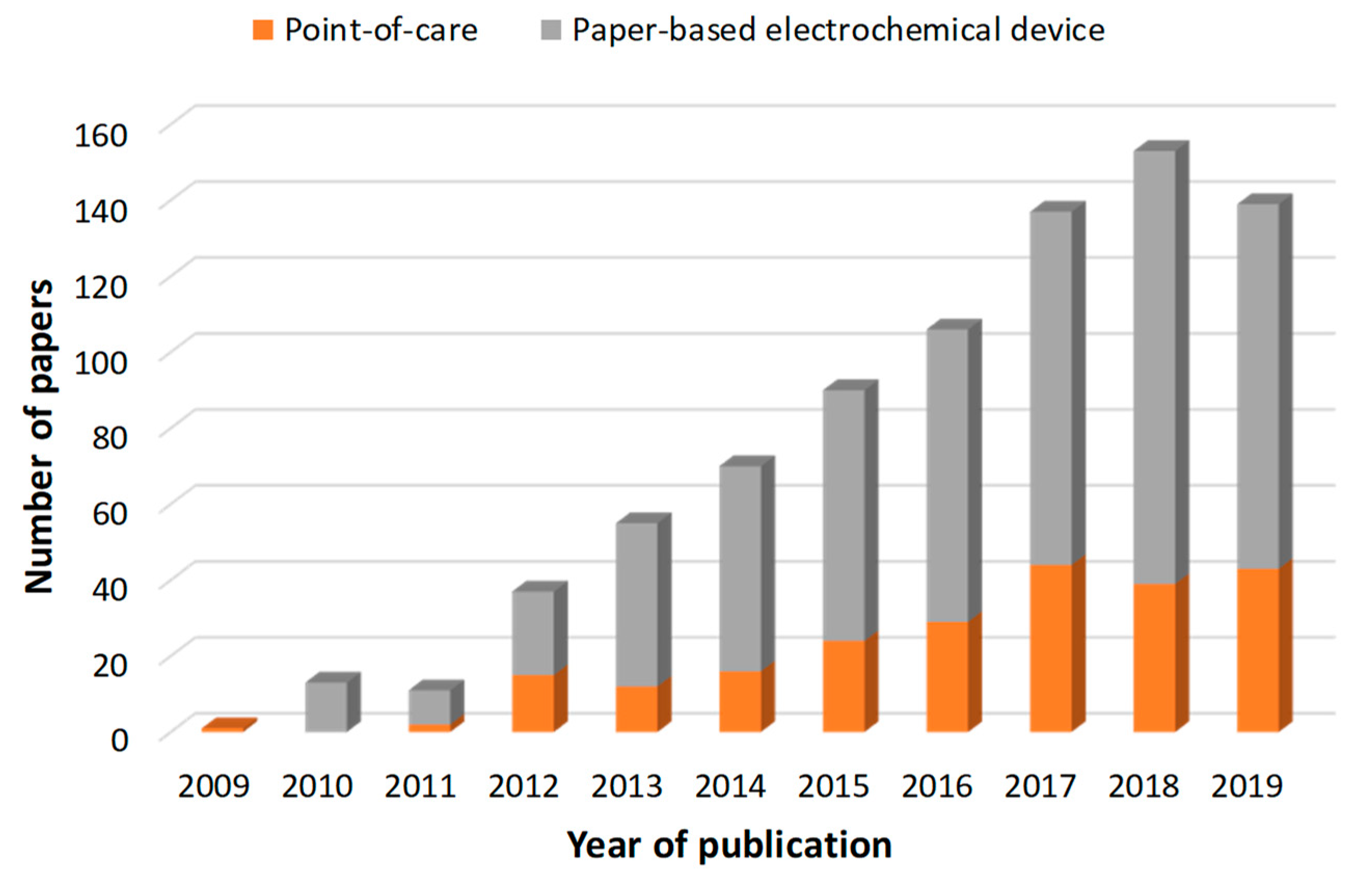
:1. Introduction
2. Paper-Based Analytical Devices (PADs) with Integrated Electrochemical Cell
3. Paper-Based Analytical Devices (PADs) with Non-Integrated Electrochemical Cell
4. Conclusions and Outlook
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dungchai, W.; Chailapakul, O.; Henry, C.S. Electrochemical Detection for Paper-Based Microfluidics. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 5821–5826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quesada-González, D.; Merkoçi, A. Nanoparticle-based lateral flow biosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 73, 47–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mahato, K.; Srivastava, A.; Chandra, P. Paper based diagnostics for personalized health care: Emerging technologies and commercial aspects. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 96, 246–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, M.M.; Sinton, D. Turning the Page: Advancing Paper-Based Microfluidics for Broad Diagnostic Application. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 8447–8480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.; Korvink, J.G.; Mager, D.; Land, K. The potential of paper-based diagnostics to meet the ASSURED criteria. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 34012–34034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Economou, A.; Kokkinos, C.; Prodromidis, M. Flexible plastic, paper and textile lab-on-a chip platforms for electrochemical biosensing. Lab Chip 2018, 18, 1812–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felix, F.; Baccaro, A.; Angnes, L. Disposable Voltammetric Immunosensors Integrated with Microfluidic Platforms for Biomedical, Agricultural and Food Analyses: A Review. Sensors 2018, 18, 4124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuss, S.; Amin, H.M.A.; Compton, R.G. Electrochemical Detection of Pathogenic Bacteria-Recent Strategies, Advances and Challenges. Chem. An Asian J. 2018, 13, 2758–2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.; Jafry, A.T.; Lee, J. Fabrication, Flow Control, and Applications of Microfluidic Paper-Based Analytical Devices. Molecules 2019, 24, 2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, R.H.; Liu, L.N.; Zhang, S.F.; He, X.C.; Li, X.J.; Xu, F.; Ni, Y.H.; Li, F. A review on advances in methods for modification of paper supports for use in point-of-care testing. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Yang, D.; Liu, G. Signal amplification strategies for paper-based analytical devices. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 136, 60–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Citartan, M.; Tang, T.-H. Recent developments of aptasensors expedient for point-of-care (POC) diagnostics. Talanta 2019, 199, 556–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Geng, Z.; Fan, Z.; Liu, J.; Chen, H. Point-of-care testing based on smartphone: The current state-of-the-art (2017–2018). Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 132, 17–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dave, V.P.; Ngo, T.A.; Pernestig, A.-K.; Tilevik, D.; Kant, K.; Nguyen, T.; Wolff, A.; Bang, D.D. MicroRNA amplification and detection technologies: Opportunities and challenges for point of care diagnostics. Lab. Investig. 2019, 99, 452–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrell, C.; Kava, A.; Nguyen, M.; Menger, R.; Munshi, Z.; Call, Z.; Nussbaum, M.; Henry, C. Beyond the lateral flow assay: A review of paper-based microfluidics. Microelectron. Eng. 2019, 206, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Yin, X.; Jin, D.; Zhang, B.; Gu, Y.; An, Y. Paper-based immunosensors: Current trends in the types and applied detection techniques. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 111, 100–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneta, T.; Alahmad, W.; Varanusupakul, P. Microfluidic paper-based analytical devices with instrument-free detection and miniaturized portable detectors. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2019, 54, 117–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noviana, E.; McCord, C.P.; Clark, K.M.; Jang, I.; Henry, C.S. Electrochemical paper-based devices: Sensing approaches and progress toward practical applications. Lab Chip 2020, 20, 9–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Pandey, C.M.; Hatamie, A.; Simchi, A.; Willander, M.; Malhotra, B.D. Nanomaterial-Modified Conducting Paper: Fabrication, Properties, and Emerging Biomedical Applications. Glob. Chall. 2019, 1900041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; He, R.; Niu, Y.; Li, F. Paper-Based Electrochemical Biosensors for Point-of-Care Testing of Neurotransmitters. J. Anal. Test. 2019, 3, 19–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Crooks, R.M. Three-Dimensional Paper Microfluidic Devices Assembled Using the Principles of Origami. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 17564–17566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruecha, N.; Shin, K.; Chailapakul, O.; Rodthongkum, N. Label-free paper-based electrochemical impedance immunosensor for human interferon gamma detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 279, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomei, M.R.; Cinti, S.; Interino, N.; Manovella, V.; Moscone, D.; Arduini, F. Paper-based electroanalytical strip for user-friendly blood glutathione detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 294, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhou, C.; Sun, X.; Jian, Y.; Kong, Q.; Cui, K.; Ge, S.; Yu, J. Polyhedral-AuPd nanoparticles-based dual-mode cytosensor with turn on enable signal for highly sensitive cell evalution on lab-on-paper device. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 117, 651–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moazeni, M.; Karimzadeh, F.; Kermanpur, A. Peptide modified paper based impedimetric immunoassay with nanocomposite electrodes as a point-of-care testing of Alpha-fetoprotein in human serum. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 117, 748–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakoh, A.; Chaiyo, S.; Siangproh, W.; Chailapakul, O. 3D Capillary-Driven Paper-Based Sequential Microfluidic Device for Electrochemical Sensing Applications. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 1211–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amatatongchai, M.; Sitanurak, J.; Sroysee, W.; Sodanat, S.; Chairam, S.; Jarujamrus, P.; Nacapricha, D.; Lieberzeit, P.A. Highly sensitive and selective electrochemical paper-based device using a graphite screen-printed electrode modified with molecularly imprinted polymers coated Fe3O4@Au@SiO2 for serotonin determination. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1077, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Luo, J.; Liu, J.; Sun, S.; Xiong, Y.; Ma, Y.; Yan, S.; Yang, Y.; Yin, H.; Cai, X. Label-free microfluidic paper-based electrochemical aptasensor for ultrasensitive and simultaneous multiplexed detection of cancer biomarkers. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 136, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Luo, J.; Liu, J.; Li, X.; Kong, Z.; Jin, H.; Cai, X. Electrochemical integrated paper-based immunosensor modified with multi-walled carbon nanotubes nanocomposites for point-of-care testing of 17β-estradiol. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 107, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Li, B.; Zhou, N.; Wang, X.; Deng, D.; Luo, L.; Chen, L. The strategy of antibody-free biomarker analysis by in-situ synthesized molecularly imprinted polymers on movable valve paper-based device. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 142, 111533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dave, K.; Pachauri, N.; Dinda, A.; Solanki, P.R. RGO modified mediator free paper for electrochemical biosensing platform. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 463, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punjiya, M.; Moon, C.H.; Matharu, Z.; Rezaei Nejad, H.; Sonkusale, S. A three-dimensional electrochemical paper-based analytical device for low-cost diagnostics. Analyst 2018, 143, 1059–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cinti, S.; Proietti, E.; Casotto, F.; Moscone, D.; Arduini, F. Paper-Based Strips for the Electrochemical Detection of Single and Double Stranded DNA. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 13680–13686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, R.; Li, Y.; Bai, J. Hierarchical assembled nanomaterial paper based analytical devices for simultaneously electrochemical detection of microRNAs. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1058, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Ren, Y.; Han, L.; Yan, Y.; Jiang, H. Three-dimensional paper based platform for automatically running multiple assays in a single step. Talanta 2019, 200, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ge, S.; Zhang, L.; Cui, K.; Zhao, P.; Yan, M.; Yu, J. Triggerable H2O2–Cleavable Switch of Paper-Based Biochips Endows Precision of Chemometer/Ratiometric Electrochemical Quantification of Analyte in High-Efficiency Point-of-Care Testing. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 10273–10281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teengam, P.; Siangproh, W.; Tuantranont, A.; Henry, C.S.; Vilaivan, T.; Chailapakul, O. Electrochemical paper-based peptide nucleic acid biosensor for detecting human papillomavirus. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 952, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-C.; Hennek, J.W.; Ainla, A.; Kumar, A.A.; Lan, W.-J.; Im, J.; Smith, B.S.; Zhao, M.; Whitesides, G.M. A Paper-Based “Pop-up” Electrochemical Device for Analysis of Beta-Hydroxybutyrate. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 6326–6333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lei, K.F.; Yang, S.-I.; Tsai, S.-W.; Hsu, H.-T. Paper-based microfluidic sensing device for label-free immunoassay demonstrated by biotin–avidin binding interaction. Talanta 2015, 134, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cánovas, R.; Parrilla, M.; Blondeau, P.; Andrade, F.J. A novel wireless paper-based potentiometric platform for monitoring glucose in blood. Lab Chip 2017, 17, 2500–2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boobphahom, S.; Ruecha, N.; Rodthongkum, N.; Chailapakul, O.; Remcho, V.T. A copper oxide-ionic liquid/reduced graphene oxide composite sensor enabled by digital dispensing: Non-enzymatic paper-based microfluidic determination of creatinine in human blood serum. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1083, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Shi, S.; Ma, J.; Guo, Y. A paper-based electrochemical immunosensor with reduced graphene oxide/thionine/gold nanoparticles nanocomposites modification for the detection of cancer antigen 125. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 135, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, B.; Mao, K.; Liu, N.; Zhang, M.; Yang, Z. Graphene nanocomposites modified electrochemical aptamer sensor for rapid and highly sensitive detection of prostate specific antigen. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 121, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, G.V.; Marques, A.C.; Fortunato, E.; Sales, M.G.F. Wax-printed paper-based device for direct electrochemical detection of 3-nitrotyrosine. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 284, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scordo, G.; Moscone, D.; Palleschi, G.; Arduini, F. A reagent-free paper-based sensor embedded in a 3D printing device for cholinesterase activity measurement in serum. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 258, 1015–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaiyo, S.; Mehmeti, E.; Siangproh, W.; Hoang, T.L.; Nguyen, H.P.; Chailapakul, O.; Kalcher, K. Non-enzymatic electrochemical detection of glucose with a disposable paper-based sensor using a cobalt phthalocyanine–ionic liquid–graphene composite. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 102, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinti, S.; Cusenza, R.; Moscone, D.; Arduini, F. Paper-based synthesis of Prussian Blue Nanoparticles for the development of whole blood glucose electrochemical biosensor. Talanta 2018, 187, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, T.; Wang, Y.; Luo, J.; Liu, J.; Sun, S.; Xing, Y.; Xiao, G.; Jin, H.; Cai, X. Folding Paper-Based Aptasensor Platform Coated with Novel Nanoassemblies for Instant and Highly Sensitive Detection of 17 beta-Estradiol. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 3186–3194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.S.; Misra, S.K.; Wang, Z.; Daza, E.; Schwartz-Duval, A.S.; Kus, J.M.; Pan, D.; Pan, D. Paper-Based Analytical Biosensor Chip Designed from Graphene-Nanoplatelet-Amphiphilic-diblock-co-Polymer Composite for Cortisol Detection in Human Saliva. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 2107–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Qian, D.; Wang, Q.; Li, Y.; Bao, N.; Gu, H.; Yu, C. Fully-drawn origami paper analytical device for electrochemical detection of glucose. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 231, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Wang, H.; Jian, Y.; Lan, F.; Zhang, L.; Liu, H.; Ge, S.; Yu, J. Ultrasensitive microfluidic paper-based electrochemical/visual biosensor based on spherical-like cerium dioxide catalyst for miR-21 detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 105, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Li, F.; Xing, Y.; Liu, Z.; You, M.; Li, Y.; Wen, T.; Qu, Z.; Li, X.L.; Xu, F. Pen-on-paper strategy for point-of-care testing: Rapid prototyping of fully written microfluidic biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 98, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fava, E.L.; Silva, T.A.; do Prado, T.M.; de Moraes, F.C.; Faria, R.C.; Fatibello-Filho, O. Electrochemical paper-based microfluidic device for high throughput multiplexed analysis. Talanta 2019, 203, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cincotto, F.H.; Fava, E.L.; Moraes, F.C.; Fatibello-Filho, O.; Faria, R.C. A new disposable microfluidic electrochemical paper-based device for the simultaneous determination of clinical biomarkers. Talanta 2019, 195, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinyorospathum, C.; Chaiyo, S.; Sae-ung, P.; Hoven, V.P.; Damsongsang, P.; Siangproh, W.; Chailapakul, O. Disposable paper-based electrochemical sensor using thiol-terminated poly(2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine) for the label-free detection of C-reactive protein. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, X.; Gao, X.; Ge, L.; Sun, X.; Li, F. A Universal Paper-Based Electrochemical Sensor for Zero-Background Assay of Diverse Biomarkers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 15381–15388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Fang, C.; Zeng, R.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, F.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, Z. A disposable paper-based microfluidic immunosensor based on reduced graphene oxide-tetraethylene pentamine/Au nanocomposite decorated carbon screen-printed electrodes. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 252, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeGregory, P.R.; Tsai, Y.-J.; Scida, K.; Richards, I.; Crooks, R.M. Quantitative electrochemical metalloimmunoassay for TFF3 in urine using a paper analytical device. Analyst 2016, 141, 1734–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Channon, R.B.; Yang, Y.; Feibelman, K.M.; Geiss, B.J.; Dandy, D.S.; Henry, C.S. Development of an Electrochemical Paper-Based Analytical Device for Trace Detection of Virus Particles. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 7777–7783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, A.W.; Phillips, S.T.; Butte, M.J.; Whitesides, G.M. Patterned Paper as a Platform for Inexpensive, Low-Volume, Portable Bioassays. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 1318–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





| Biomarker 1 | Technique 2 | Response Range | Sensitivity 3 | Limit of Detection | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IFN-γ | EIS | 5–1000 pg/mL | 33.2 kΩ/dec | 3.4 pg/mL | [22] |
| Glutathione | Amp. | 0.25–10 mM | 0.102 ± 0.005 µA/mM | 0.06 mM | [23] |
| MCF-7 line | DPV | 50–107 cells/mL | −6.8 µA/dec | 20 cells/mL | [24] |
| Serotonin | LSV | 0.01–1000 µM | 0.008 ± 0.005 µA/µM | 0.002 µM | [27] |
| α-fetoprotein | EIS | 1–104 ng/mL | - | 10 ng/mL | [25] |
| Ascorbic acid | Amp. | 0.15–0.8 mM | 7.8 µC/mM | 0.093 mM | [26] |
| Serotonin | DPV | 1–20 mM | 0.16 µA/mM | 0.15 mM | [26] |
| α-fetoprotein | EIS | 10–100 ng/mL | 10 kΩ/dec | 0.63 ng/mL | [26] |
| CEA | DPV | 0.01–500 ng/mL | −2.8 µA/dec | 0.002 ng/mL | [28] |
| NSE | DPV | 0.05–500 ng/mL | −1.4 µA/dec | 0.01 ng/mL | [28] |
| 17β-estradiol | DPV | 0.01–100 ng/mL | −1.8 µA/dec | 0.01 ng/mL | [29] |
| CEA | DPV | 1.0–500.0 ng/mL | 19.3 µA/dec | 0.32 ng/mL | [30] |
| IL-8 | Chronoamp. | 1–9 pg/mL | −1.64 µA mL/pg | 0.59 pg/mL | [31] |
| pH | Potent. | 2–12 pH | −45 mV/pH | - | [32] |
| Glucose | Chronoamp. | 5–17.5 mM | 0.34 µA/mM | - | [32] |
| Dopamine | CV | 0.01–5 mM | - | - | [32] |
| DNA targets | SWV | - | - | 3 to 7 nM | [33] |
| miR-141 | SWV | 1 fM–1 nM | - | 0.1 fM | [34] |
| miR-21 | SWV | 1 fM–1 nM | - | 0.1 fM | [34] |
| Glucose | Chronoamp. | 1–40 mM | −0.091 µA/mM | 0.32 mM | [35] |
| MCF-7 cells | DPV | 150–107 cells/mL | 0.12/dec 4 | 117 cells/mL | [36] |
| K562 cells | DPV | 220–7 × 106 cells/mL | 0.13/dec 4 | 140 cells/mL | [36] |
| Device | Biomarker | Type of Sample | Technique 1 | Response Range | Sensitivity 2 | Limit of Detection | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peptide nucleic acid biosensor | Human papillomavirus | PCR-amplified DNA from SiHa cell line | SWV | 10–200 nM | 0.004 µA/nM | 2.3 nM | [37] |
| 3D “pop-up” with commercial glucometer | Beta-hydroxybutyrate | Whole blood | Chronoamp. | 0.1–6.0 mM | - | 0.3 mM | [38] |
| Label-free immunosensor | Biotin-avidin interaction | Standard solution | Chronoamp. | Up to 500 ng/mL | 0.33 µA mL/ng | 25 ng/mL | [39] |
| Wireless potentiometric platform | Glucose | Blood | Potent. | 0.3–3 mM | -96±5 mV/dec | 0.1 mM | [40] |
| Non-enzymatic sensor | Creatinine | Human blood serum | Chronoamp. | 0.01–2.0 mM | 28 µA/cm2 mM | 0.22 µM | [41] |
| Label-free immunosensor | Cancer antigen 125 | Quality control serum | DPV | 0.1–200 U/mL | −0.37 µA mL/U | 0.01 U/mL | [42] |
| Label-free aptasensor | Prostate specific antigen | Clinical serum | DPV | 0.05–200 ng/mL | −2.0 µA/dec | 10 pg/mL | [43] |
| Voltammetric sensor | 3-nitrotyrosine | Standard solution | SWV | 0.5 µM–1 mM | - | 49.2 nM | [44] |
| Reagent-free 3D printing device | Butyrylcholinesterase activity | Serum | Chronoamp. | 1–12 IU/mL | 0.23 ± 0.01 µA mL/UI | 0.1 IU/mL | [45] |
| Disposable non-enzymatic sensor | Glucose | Human serum | Chronoamp. | 0.01–1.3 mM | 0.016 µA/µM | 0.64 µM | [46] |
| Enzymatic biosensor with pre-loaded (bio)reagents | Glucose | Whole human blood | Chronoamp. | Up to 25 mM | - | - | [47] |
| Label-free aptasensor | 17β-estradiol | Clinical serum | DPV | 0.01–500 ng/mL | −2.36 µA/dec | 5 pg/mL | [48] |
| Label-free immunosensor | Cortisol | Human saliva | EIS | 3 pg/mL–10 µg/mL | 50 Ω mL/pg | 3 pg/mL | [49] |
| Enzymatic biosensor with pre-loaded (bio)reagents | Glucose | Whole human blood | Chronoamp. | 1–12 mM | 0.9474 µA/mM | 0.05 mM | [50] |
| Enzymatic biosensor with CeO2 catalyst | miR-21 | Diluted human serum | DPV | 1.0–1000 fM | −6.22 µA/dec | 0.434 fM | [51] |
| Enzymatic biosensor with pre-loaded (bio)reagents | Glucose | Spiked human serum | Chronoamp. | 1–20 mM | - | 1 mM | [52] |
| Biomarker | Technique 2 | Response Range | Sensitivity 3 | Limit of Detection | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glucose | Chronoamp. | 0.1–40 mM | - | 0.03 mM | [53] |
| Uric acid | SWV | 0.010–3.0 µM | 0.08 ± 0.0024 µA/µM | 8.4 nM | [54] |
| Creatinine | SWV | 0.010–3.0 µM | 0.30 ± 0.0057 µA/µM | 3.7 nM | [54] |
| C-reactive protein | DPV | 5–5000 ng/mL | 5.51 µA/dec | 1.55 ng/mL | [55] |
| miR-21 | DPV | 1 fM–1 µM | 5.33 nA/dec | - | [56] |
| Alpha-fetoprotein | SWV | 0.01–100 ng/mL | −12.698 µA/dec | 0.005 ng/mL | [57] |
| TFF3 1 | ASV | 0.0125–3 µg/mL | - | 0.0125 µg/mL | [58] |
| West Nile virus | EIS | Up to 106 particles/mL | - | 2000 particles/mL | [59] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gutiérrez-Capitán, M.; Baldi, A.; Fernández-Sánchez, C. Electrochemical Paper-Based Biosensor Devices for Rapid Detection of Biomarkers. Sensors 2020, 20, 967. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20040967
Gutiérrez-Capitán M, Baldi A, Fernández-Sánchez C. Electrochemical Paper-Based Biosensor Devices for Rapid Detection of Biomarkers. Sensors. 2020; 20(4):967. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20040967
Chicago/Turabian StyleGutiérrez-Capitán, Manuel, Antonio Baldi, and César Fernández-Sánchez. 2020. "Electrochemical Paper-Based Biosensor Devices for Rapid Detection of Biomarkers" Sensors 20, no. 4: 967. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20040967
APA StyleGutiérrez-Capitán, M., Baldi, A., & Fernández-Sánchez, C. (2020). Electrochemical Paper-Based Biosensor Devices for Rapid Detection of Biomarkers. Sensors, 20(4), 967. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20040967






