Review of Terahertz Pulsed Imaging for Pharmaceutical Film Coating Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Terahertz Pulsed Imaging
2.1. Instrumentation
2.2. Coating Thickness Analysis
3. Pharmaceutical Film Coatings
3.1. Off-Line Measurement
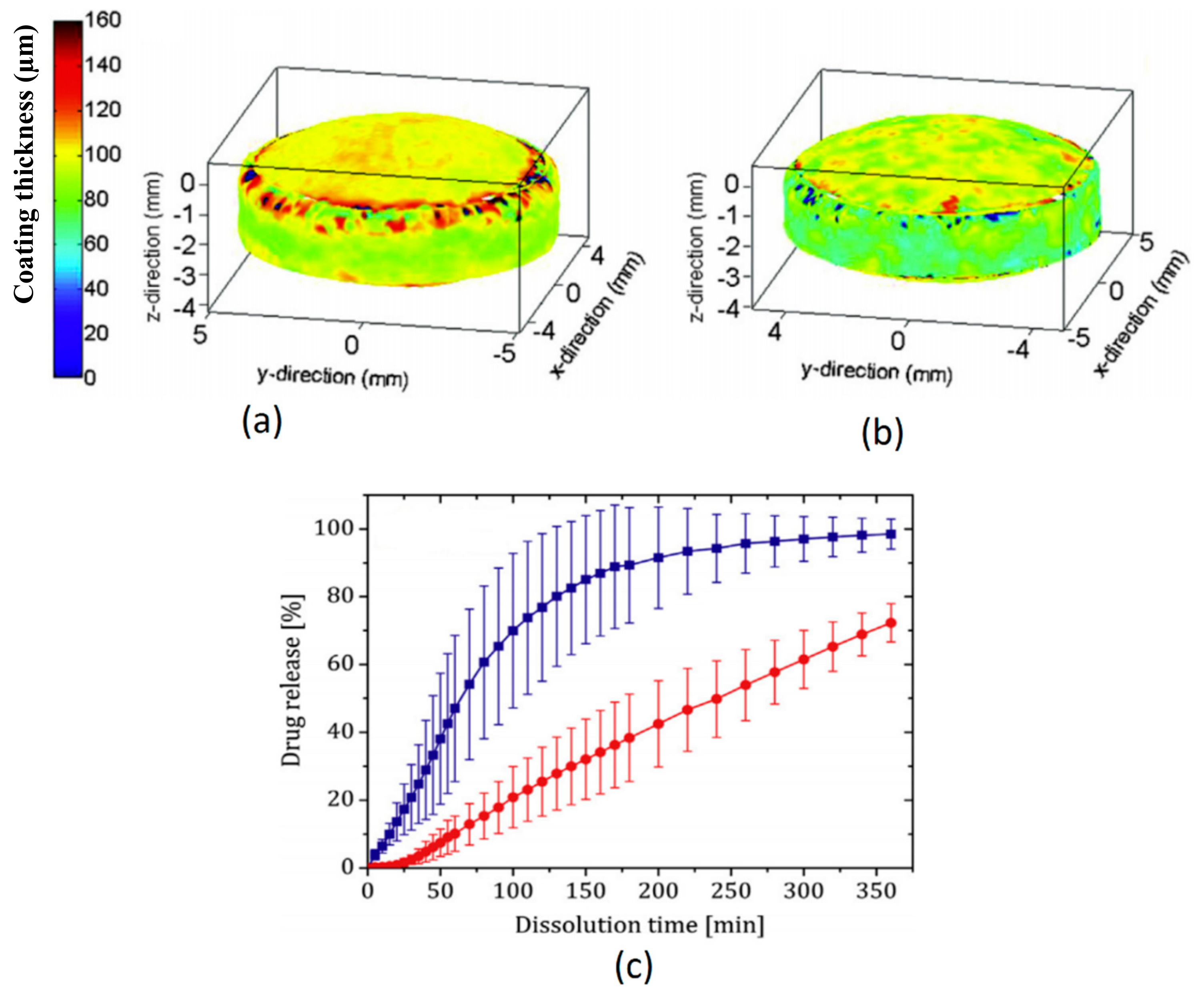
3.1.1. Coating Morphology, Density and Drug Release Performance
3.1.2. Defects Identification
3.1.3. Comparison and Calibration of PAT
3.1.4. Process Understanding
3.2. In-Line Measurement
4. Conclusions and Future Challenges
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Felton, L.A.; Porter, S.C. An update on pharmaceutical film coating for drug delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2013, 10, 421–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knop, K.; Kleinebudde, P. PAT-tools for process control in pharmaceutical film coating applications. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 457, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Remmelgas, J.; van Wachem, B.G.M.; von Corswant, C.; Johansson, M.; Folestad, S.; Rasmuson, A. Residence time distributions of different size particles in the spray zone of a Wurster fluid bed studied using DEM-CFD. Powder Technol. 2015, 280, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korasa, K.; Vrečer, F. Overview of PAT process analysers applicable in monitoring of film coating unit operations for manufacturing of solid oral dosage forms. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 111, 278–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Zhang, Z.; Markl, D.; Zeitler, J.; Shen, Y. A Review of the Applications of OCT for Analysing Pharmaceutical Film Coatings. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fitzgerald, A.J.; Cole, B.E.; Taday, P.F. Nondestructive analysis of tablet coating thicknesses using Terahertz pulsed imaging. J. Pharm. Sci. 2005, 94, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeitler, J.A.; Shen, Y.; Baker, C.; Taday, P.F.; Pepper, M.; Rades, T. Analysis of coating structures and interfaces in solid oral dosage forms by three dimensional terahertz pulsed imaging. J. Pharm. Sci. 2007, 96, 330–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auston, D.H. Picosecond optoelectronic switching and gating in silicon. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1975, 26, 101–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auston, D.H.; Cheung, K.P.; Smith, P.R. Picosecond photoconducting Hertzian dipoles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1984, 45, 284–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.C.; Taday, P.F. Development and application of terahertz pulsed imaging for nondestructive inspection of pharmaceutical tablet. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2008, 14, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Huang, S.; Pickwell-MacPherson, E. Frequency-wavelet domain deconvolution for terahertz reflection imaging and spectroscopy. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russe, I.S.; Brock, D.; Knop, K.; Kleinebudde, P.; Zeitler, J.A. Validation of terahertz coating thickness measurements using X-ray microtomography. Mol. Pharm. 2012, 9, 3551–3559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Braeuninger-Weimer, P.; Kamboj, V.S.; Jessop, D.S.; Degl’Innocenti, R.; Beere, H.E.; Ritchie, D.A.; Zeitler, J.A.; Hofmann, S. Contactless graphene conductivity mapping on a wide range of substrates with terahertz time-domain reflection spectroscopy. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cogdill, R.P.; Forcht, R.N.; Shen, Y.; Taday, P.F.; Creekmore, J.R.; Anderson, C.A.; Drennen, J.K. Comparison of terahertz pulse imaging and near-infrared spectroscopy for rapid, non-destructive analysis of tablet coating thickness and uniformity. J. Pharm. Innov. 2007, 2, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ho, L.; Müller, R.; Gordon, K.C.; Kleinebudde, P.; Pepper, M.; Rades, T.; Shen, Y.; Taday, P.F.; Zeitler, J.A. Monitoring the film coating unit operation and predicting drug dissolution using terahertz pulsed imaging. J. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 98, 4866–4876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, A.J.L. Review of near-field Terahertz measurement methods and their applications: How to achieve sub-wavelength resolution at THz frequencies. J. Infrared Millim. Terahertz Waves 2011, 32, 976–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, H.; Fumeaux, C.; Seam Yu Ung, B.; Abbott, D. Comprehensive modeling of THz microscope with a sub-wavelength source. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 5327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Fischer, B.M.; Mickan, S.P.; Abbott, D. Review of THz near-field methods. In Proceedings of the Smart Structures, Devices, and Systems III, Adelaide, Australia, 10–13 December 2006; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Su, K.; Shen, Y.C.; Zeitler, J.A. Terahertz sensor for non-contact thickness and quality measurement of automobile paints of varying complexity. IEEE Trans. Terahertz Sci. Technol. 2014, 4, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, L.; Müller, R.; Gordon, K.C.; Kleinebudde, P.; Pepper, M.; Rades, T.; Shen, Y.; Taday, P.F.; Zeitler, J.A. Applications of terahertz pulsed imaging to sustained-release tablet film coating quality assessment and dissolution performance. J. Control. Release 2008, 127, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, T.; Portieri, A.; Arnone, D.D.; Taday, P.F.; Kawanishi, T.; Hiyama, Y. Coating and density distribution analysis of commercial ciprofloxacin hydrochloride monohydrate tablets by Terahertz pulsed spectroscopy and imaging. J. Pharm. Innov. 2012, 7, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spencer, J.A.; Gao, Z.; Moore, T.; Buhse, L.F.; Taday, P.F.; Newnham, D.A.; Shen, Y.; Portieri, A.; Husain, A. Delayed release tablet dissolution related to coating thickness by terahertz pulsed image mapping. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 97, 1543–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, L.; Müller, R.; Gordon, K.C.; Kleinebudde, P.; Pepper, M.; Rades, T.; Shen, Y.; Taday, P.F.; Zeitler, J.A. Terahertz pulsed imaging as an analytical tool for sustained-release tablet film coating. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2009, 71, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, L.; Cuppok, Y.; Muschert, S.; Gordon, K.C.; Pepper, M.; Shen, Y.; Siepmann, F.; Siepmann, J.; Taday, P.F.; Rades, T. Effects of film coating thickness and drug layer uniformity on in vitro drug release from sustained-release coated pellets: A case study using terahertz pulsed imaging. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 382, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brock, D.; Zeitler, J.A.; Funke, A.; Knop, K.; Kleinebudde, P. A comparison of quality control methods for active coating processes. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 439, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brock, D.; Zeitler, J.A.; Funke, A.; Knop, K.; Kleinebudde, P. Critical factors in the measurement of tablet film coatings using terahertz pulsed imaging. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 102, 1813–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaterre, V.; Pedersen, M.; Ogorka, J.; Gurny, R.; Loggia, N.; Taday, P.F. Terahertz pulsed imaging, a novel process analytical tool to investigate the coating characteristics of push-pull osmotic systems. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2009, 74, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novikova, A.; Markl, D.; Zeitler, J.A.; Rades, T.; Leopold, C.S. A non-destructive method for quality control of the pellet distribution within a MUPS tablet by terahertz pulsed imaging. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 111, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ho, L.; Müller, R.; Römer, M.; Gordon, K.C.; Heinämäki, J.; Kleinebudde, P.; Pepper, M.; Rades, T.; Shen, Y.C.; Strachan, C.J.; et al. Analysis of sustained-release tablet film coats using terahertz pulsed imaging. J. Control. Release 2007, 119, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niwa, M.; Hiraishi, Y.; Iwasaki, N.; Terada, K. Quantitative analysis of the layer separation risk in bilayer tablets using terahertz pulsed imaging. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 452, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niwa, M.; Hiraishi, Y.; Terada, K. Evaluation of coating properties of enteric-coated tablets using terahertz pulsed imaging. Pharm. Res. 2014, 31, 2140–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niwa, M.; Hiraishi, Y. Quantitative analysis of visible surface defect risk in tablets during film coating using terahertz pulsed imaging. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 461, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vynckier, A.K.; Lin, H.; Zeitler, J.A.; Willart, J.F.; Bongaers, E.; Voorspoels, J.; Remon, J.P.; Vervaet, C. Calendering as a direct shaping tool for the continuous production of fixed-dose combination products via co-extrusion. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2015, 96, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Momose, W.; Yoshino, H.; Katakawa, Y.; Yamashita, K.; Imai, K.; Sako, K.; Kato, E.; Irisawa, A.; Yonemochi, E.; Terada, K. Applying terahertz technology for nondestructive detection of crack initiation in a film-coated layer on a swelling tablet. Results Pharma Sci. 2012, 2, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maurer, L.; Leuenberger, H. Terahertz pulsed imaging and near infrared imaging to monitor the coating process of pharmaceutical tablets. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 370, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.; Shen, Y.C.; Ho, L.; May, R.K.; Zeitler, J.A.; Evans, M.; Taday, P.F.; Pepper, M.; Rades, T.; Gordon, K.C.; et al. Non-destructive quantification of pharmaceutical tablet coatings using terahertz pulsed imaging and optical coherence tomography. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2011, 49, 361–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhong, S.; Shen, H.; Shen, Y.C.; Zeitler, J.A.; Ho, L.; Evans, M.; Taday, P.T.; Pepper, M.; Rades, T.; Gordon, K.C.; et al. Noninvasive 3D characterization of layered samples using terahertz pulsed imaging and infrared Optical Coherence Tomography. In Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Infrared, Millimeter, and Terahertz Waves, Busan, Korea, 21–25 September 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Gendre, C.; Genty, M.; Boiret, M.; Julien, M.; Meunier, L.; Lecoq, O.; Baron, M.; Chaminade, P.; Péan, J.M. Development of a Process Analytical Technology (PAT) for in-line monitoring of film thickness and mass of coating materials during a pan coating operation. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 43, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Müller, J.; Brock, D.; Knop, K.; Axel Zeitler, J.; Kleinebudde, P. Prediction of dissolution time and coating thickness of sustained release formulations using Raman spectroscopy and terahertz pulsed imaging. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2012, 80, 690–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novikova, A.; Carstensen, J.M.; Zeitler, J.A.; Rades, T.; Leopold, C.S. Multispectral UV Imaging for Determination of the Tablet Coating Thickness. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 106, 1560–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Dong, Y.; Markl, D.; Williams, B.M.; Zheng, Y.; Shen, Y.; Zeitler, J.A. Measurement of the Intertablet Coating Uniformity of a Pharmaceutical Pan Coating Process With Combined Terahertz and Optical Coherence Tomography In-Line Sensing. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 106, 1075–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, H.; Dong, Y.; Shen, Y.; Zeitler, J.A. Quantifying Pharmaceutical Film Coating with Optical Coherence Tomography and Terahertz Pulsed Imaging: An Evaluation. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 104, 3377–3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Dong, Y.; Markl, D.; Zhang, Z.; Shen, Y.; Zeitler, J.A. Pharmaceutical Film Coating Catalog for Spectral Domain Optical Coherence Tomography. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 106, 3171–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dong, Y.; Lin, H.; Abolghasemi, V.; Gan, L.; Zeitler, J.A.; Shen, Y.C. Investigating Intra-Tablet Coating Uniformity With Spectral-Domain Optical Coherence Tomography. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 106, 546–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brock, D.; Zeitler, J.A.; Funke, A.; Knop, K.; Kleinebudde, P. Evaluation of critical process parameters for intra-tablet coating uniformity using terahertz pulsed imaging. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2013, 85, 1122–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brock, D.; Zeitler, J.A.; Funke, A.; Knop, K.; Kleinebudde, P. Evaluation of critical process parameters for inter-tablet coating uniformity of active-coated GITS using Terahertz Pulsed Imaging. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2014, 88, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohi, M.; Momose, W.; Yoshino, H.; Hara, Y.; Yamashita, K.; Hakomori, T.; Sato, S.; Terada, K. Application of terahertz pulse imaging as PAT tool for non-destructive evaluation of film-coated tablets under different manufacturing conditions. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2016, 119, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haaser, M.; Naelapää, K.; Gordon, K.C.; Pepper, M.; Rantanen, J.; Strachan, C.J.; Taday, P.F.; Zeitler, J.A.; Rades, T. Evaluating the effect of coating equipment on tablet film quality using terahertz pulsed imaging. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2013, 85, 1095–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toschkoff, G.; Just, S.; Funke, A.; Djuric, D.; Knop, K.; Kleinebudde, P.; Scharrer, G.; Khinast, J.G. Spray models for discrete element simulations of particle coating processes. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2013, 101, 603–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freireich, B.; Wassgren, C. Intra-particle coating variability: Analysis and Monte-Carlo simulations. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2010, 65, 1117–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toschkoff, G.; Just, S.; Knop, K.; Kleinebudde, P.; Funke, A.; Djuric, D.; Scharrer, G.; Khinast, J.G. Modeling of an Active Tablet Coating Process. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 104, 4082–4092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freireich, B.; Kumar, R.; Ketterhagen, W.; Su, K.; Wassgren, C.; Zeitler, J.A. Comparisons of intra-tablet coating variability using DEM simulations, asymptotic limit models, and experiments. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2015, 131, 197–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boehling, P.; Toschkoff, G.; Knop, K.; Kleinebudde, P.; Just, S.; Funke, A.; Rehbaum, H.; Khinast, J.G. Analysis of large-scale tablet coating: Modeling, simulation and experiments. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 90, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- May, R.K.; Evans, M.J.; Zhong, S.; Warr, I.; Gladden, L.F.; Shen, Y.; Zeitler, J.A. Terahertz in-line sensor for direct coating thickness measurement of individual tablets during film coating in real-time. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 100, 1535–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Pei, C.; Markl, D.; Shen, Y.; Elliott, J.A.; Zeitler, J.A. Steps towards numerical verification of the terahertz in-line measurement of tablet mixing by means of discrete element modelling. IET Microw. Antennas Propag. 2018, 12, 1775–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, H.; May, R.K.; Evans, M.J.; Zhong, S.; Gladden, L.F.; Shen, Y.; Zeitler, J.A. Impact of Processing Conditions on Inter-tablet Coating Thickness Variations Measured by Terahertz In-Line Sensing. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 104, 2513–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pei, C.; Lin, H.; Markl, D.; Shen, Y.C.; Zeitler, J.A.; Elliott, J.A. A quantitative comparison of in-line coating thickness distributions obtained from a pharmaceutical tablet mixing process using discrete element method and terahertz pulsed imaging. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2018, 192, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




| Type of Coating | Coating Function |
|---|---|
| Active | Coating layer contains API |
| Sustained-release | Allows for predetermined API release rate for an extended time period using water-insoluble polymers |
| Controlled-release | API release profile is designed to ensure constant drug concentration in the body |
| Delayed-release | Aims to control the site of drug release, for example oesophagus, intestine (enteric) or colon |
| Osmotic-controlled | API is released via osmotic pressure with the aid of a semipermeable membrane |
| Enteric | Prevents dissolution or disintegration in gastric environment by incorporating polymers featuring ionisable groups |
| Soft gelatin capsule | Gelatin shell with a non-aqueous liquid filling, improves bioavailability of hydrophobic drugs |
| Excipient Material | Refractive Index a,b |
|---|---|
| Acacia spray dried | 1.71 ± 0.02 |
| Acesulfame | 2.05 ± 0.01 |
| Avicel PH101 | 1.70 ± 0.03 |
| Avicel PH102 | 1.77 ±0.03 |
| Avicel PH200 | 1.67 ± 0.03 |
| Avicel PH302 | 1.76 ± 0.02 |
| Avicel RC581 | 1.76 ± 0.01 |
| Calcium carbonate | 2.13 ± 0.03 |
| Calcium phosphate | 2.50 ± 0.01 |
| Calcium phosphate dibasic anhydrous | 3.25 ± 0.05 |
| Carboxymethyl cellulose | 1.76 ± 0.03 |
| Carboxymethyl cellulose sodium | 1.73 ± 0.01 |
| Carnuba wax | 1.77 ± 0.01 |
| Confectioners’ sugar | 1.71 ± 0.005 |
| Cornstarch | 1.62 ± 0.01 |
| Dextrose | 1.74 ± 0.01 |
| Hydroxypropyl cellulose | 1.47 ± 0.01 |
| Lactose anhydrous | 1.69 ± 0.005 |
| Magnesium hydroxide | 1.78 ± 0.01 |
| Magnesium oxide light | 1.44 ± 0.005 |
| Methyl paraben | 1.66 ± 0.02 |
| Magnesium stearate 1 | 1.37 ± 0.005 |
| Magnesium stearate 2 | 1.34 ± 0.005 |
| Magnesium stearate anhydrous | 1.34 ± 0.005 |
| Polyvinylpirrolidone K30 | 1.60 ± 0.01 |
| Povidone | 1.56 ± 0.005 |
| Pregelatinised starch | 1.65 ± 0.01 |
| Silicon dioxide colloidal | 1.26 ± 0.01 |
| Sodium bicarbonate | 1.97 ± 0.02 |
| Sodium carbonate | 2.01 ± 0.01 |
| Sodium carboxymethyl | 1.78 ± 0.01 |
| Sodium lauryl sulphate | 1.68 ± 0.01 |
| Sodium starch glycolate | 1.81 ± 0.01 |
| Stearic acid | 1.53 ± 0.02 |
| Sucrose | 1.83 ± 0.01 |
| Sugar tab | 1.70 ± 0.01 |
| Tartaric acid | 1.85 ± 0.03 |
| Titanium dioxide | 2.29 ± 0.02 |
| Xyloitol | 1.76 ± 0.03 |
| Xyloitol 300 | 1.83 ± 0.03 |
| Reference | Benchmark/Supporting Measurement | Materials | Scale | Terahertz Parameters | Additional Information |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fitzgerald et al. (2005) [6] | Optical microscopy | Film-coating | Production scale | Coating thickness | Imaging area side: 1 mm Coating thickness: 320–450 µm |
| Zeitler et al. (2007) [7] | - | Enteric-coating, sugar-coating, 3-layered controlled release tablets, soft gelatin capsules with liquid filling | Production scale | Coating thickness and distribution | Imaging acquisition time: 20–50 min Coating thickness: 38–2000 µm |
| Cogdill et al. (2007) [14] | Optical, microscopy, NIR spectroscopy, weight gain | Film-coating | Production scale | Coating thickness and distribution | Imaging acquisition time: 7 min Imaging area radius: 3.5 mm Coating thickness: 30–64 µm |
| Spencer et al. (2008) [22] | USP dissolution | Delayed release tablets | Production scale | Coating thickness and distribution | Imaging spot size: 100 µm Coating thickness: 60–110 µm |
| Ho et al. (2008) [20] | Ph. Eur. dissolution, SEM, weight gain | Sustained-release tablets | Lab (4 kg) and pilot scale (20 kg) | Coating thickness and distribution, TEFPS | Coating thickness: 50–300 µm |
| Ho et al. (2009) [23] | USP dissolution | Sustained-release tablets | Lab (4 kg) and pilot scale (20 kg) | Coating thickness, TEFPS | Imaging acquisition time: 45 min Coating thickness: 38–151 µm |
| Ho et al. (2009) [24] | SEM, stereo-microscopy imaging, USP dissolution | Sustained-release pellets | Lab scale | Coating thickness and distribution, TEFPS | Imaging area radius: 3 mm Coating thickness: 14–127 µm |
| Ho et al. (2009) [15] | USP dissolution | Sustained-release tablets | Lab scale (4 kg) | Coating thickness and distribution, TEFPS, TII | Imaging acquisition time: 45 min |
| Malaterre et al. (2009) [27] | Optical microscopy, USP dissolution | PPOS (osmotic-controlled) | Lab scale | Coating thickness and distribution | Imaging acquisition time: 15 min Coating thickness: 112–268 µm |
| Maurer et al. (2009) [35] | NIR spectroscopy, weight gain | Film-coating | Production scale | Coating thickness and distribution | Imaging acquisition time: 20–30 min Coating thickness: 22–92.5 µm |
| Gendre et al. (2011) [38] | In-line NIR sensor, weight gain | Film-coating | Lab scale (4 kg) | Coating thickness and distribution | Number of point measurements: 3200 |
| May et al. (2011) [54] | Weight gain | Film-coating | Production scale (175 kg) | Coating thickness and distribution, inter-tablet coating uniformity | In-line TPI sensor Acquisition rate: 120 Hz Coating thickness: 40–160 µm |
| Sakamoto et al. (2012) [21] | - | Film-coating | Production scale | Coating thickness and distribution, TEFPS | Imaging acquisition time: 30 min Coating thickness: 40–150 µm |
| Brock et al. (2012) [25] | HPLC, Optical microscopy | Active-coated PPOS (osmotic controlled) | Lab scale (3 kg) | Coating thickness and distribution | Imaging acquisition time: 20 min Imaging area radius: 3 mm Coating thickness: up to 500 µm |
| Russe et al. (2012) [12] | XµCT | Film-coating | - | Coating thickness and distribution | Imaging acquisition time: 45 min Coating thickness: 25–270 µm |
| Müller et al. (2012) [39] | In-line and offline Raman spectroscopy, USP dissolution | Sustained-release tablets | Lab scale (3.5 kg) | Coating thickness and distribution | System bandwidth: 0.06–3 THz Coating thickness: 40–140 µm |
| Haaser et al. (2013) [48] | SEM, UV-Vis spectrophotometry, weight gain | Delayed-release tablets | Lab scale | Coating thickness and distribution, TEFPS, TII | Imaging acquisition time: 60 min Coating thickness: up to 160 µm |
| Brock et al. (2013) [45] | - | Active-coated GITS (osmotic controlled) | Pilot scale (~40 kg) | Coating thickness and distribution, intra-tablet coating uniformity | Imaging area radius: 1.5–4 mm Coating thickness: 76–358 µm |
| Brock et al. (2014) [46] | HPLC | Active-coated GITS (osmotic controlled) | Lab (3–8 kg) and pilot scale (38–43 kg) | Coating thickness, inter-tablet coating uniformity | Imaging area radius: 1.5–4.5 mm Coating thickness: 360–500 µm |
| Niwa et al. (2014) [31] | Acid uptake, LOD, SEM, XµCT | Enteric-coating | Lab scale | Coating thickness and distribution, TEFPS, TII | Coating thickness: 50–70 µm |
| Lin et al. (2015) [42] | OCT | Sustained-release tablets | Pilot scale (20 kg) | Coating thickness and distribution, intra-tablet coating uniformity | Imaging spot size: 200 µm Coating thickness: Up to 300 µm |
| Freireich et al. (2015) [52] | DEM simulations | Film-coating | Lab scale (1 kg) | Coating thickness and distribution | Imaging acquisition time: 120 min Coating thickness: 40–100 µm |
| Lin et al. (2015) [56] | - | Film-coating | Production scale (175 kg) | Coating thickness, inter-tablet coating uniformity | In-line TPI sensor Acquisition rate: 120 Hz Coating thickness: Up to 300 µm |
| Dohi et al. (2016) [47] | - | Film-coating with hydrophilic core | Pilot (36 kg) and production scale (330 kg) | Coating thickness and distribution, TEFPS, TII | Imaging acquisition time: 20–30 min Coating thickness: 35–40 µm |
| Lin et al. (2017) [41] | In-line OCT sensor, weight gain | Sustained-release tablets | Lab scale (300 g) | Coating thickness and distribution, inter-tablet coating uniformity | In-line TPI sensor Acquisition rate: 30 Hz Coating thickness: 20–300 µm |
| Novikova et al. (2017) [40] | Multispectral UV imaging, weight gain | Film-coating | Lab scale | Coating thickness and distribution | Imaging acquisition time: 15 min Coating thickness: 50–200 µm |
| Novikova et al. (2018) [28] | XµCT | MUPS (controlled–release) | Lab scale (~400 g) | Coating thickness and distribution | Imaging acquisition time: 25 min Penetration depth: 152 µm |
| Pei et al. (2018) [57] Lin et al. (2018) [55] | DEM simulations combined with ray tracing | Film–coating | Lab scale | Coating thickness and distribution, inter and intra–tablet coating uniformity | In–line TPI sensor Acquisition rate: 30 Hz Coating thickness: Up to 100 µm |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alves-Lima, D.; Song, J.; Li, X.; Portieri, A.; Shen, Y.; Zeitler, J.A.; Lin, H. Review of Terahertz Pulsed Imaging for Pharmaceutical Film Coating Analysis. Sensors 2020, 20, 1441. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20051441
Alves-Lima D, Song J, Li X, Portieri A, Shen Y, Zeitler JA, Lin H. Review of Terahertz Pulsed Imaging for Pharmaceutical Film Coating Analysis. Sensors. 2020; 20(5):1441. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20051441
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlves-Lima, Décio, Jun Song, Xiaoran Li, Alessia Portieri, Yaochun Shen, J. Axel Zeitler, and Hungyen Lin. 2020. "Review of Terahertz Pulsed Imaging for Pharmaceutical Film Coating Analysis" Sensors 20, no. 5: 1441. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20051441
APA StyleAlves-Lima, D., Song, J., Li, X., Portieri, A., Shen, Y., Zeitler, J. A., & Lin, H. (2020). Review of Terahertz Pulsed Imaging for Pharmaceutical Film Coating Analysis. Sensors, 20(5), 1441. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20051441







