Comparative Study on Planetary Magnetosphere in the Solar System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Model of Solar Wind–Magnetosphere Coupling
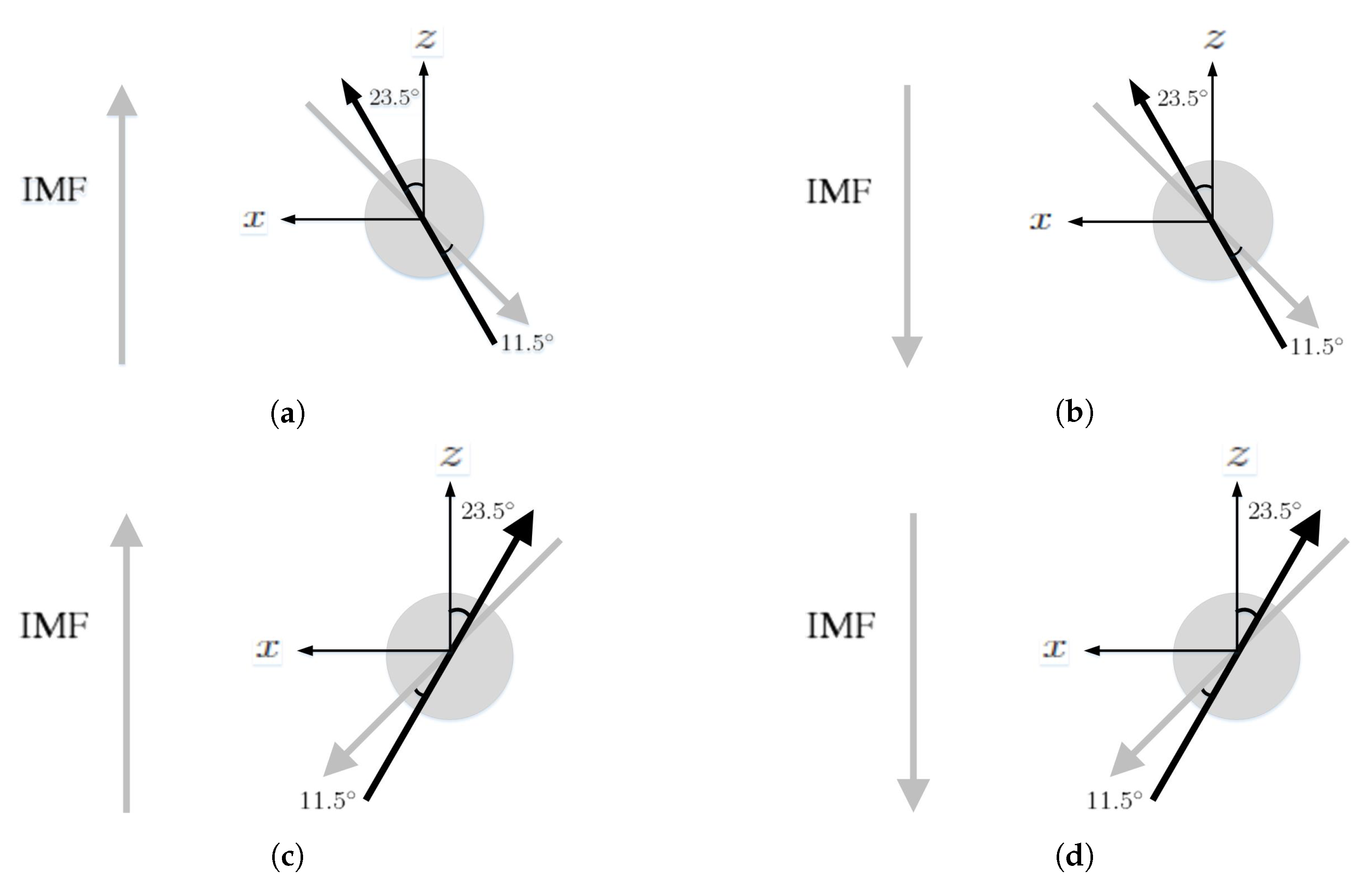
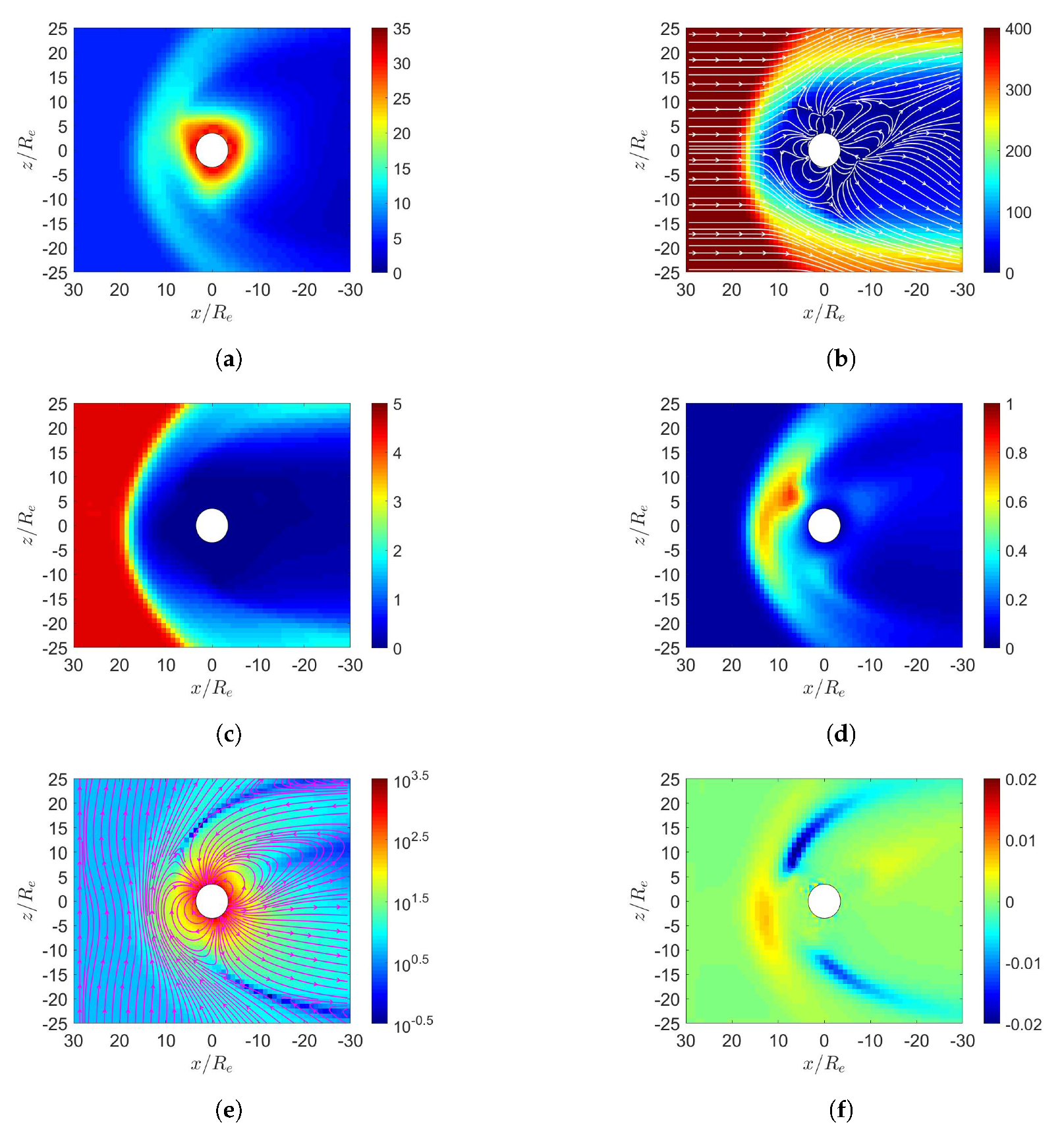
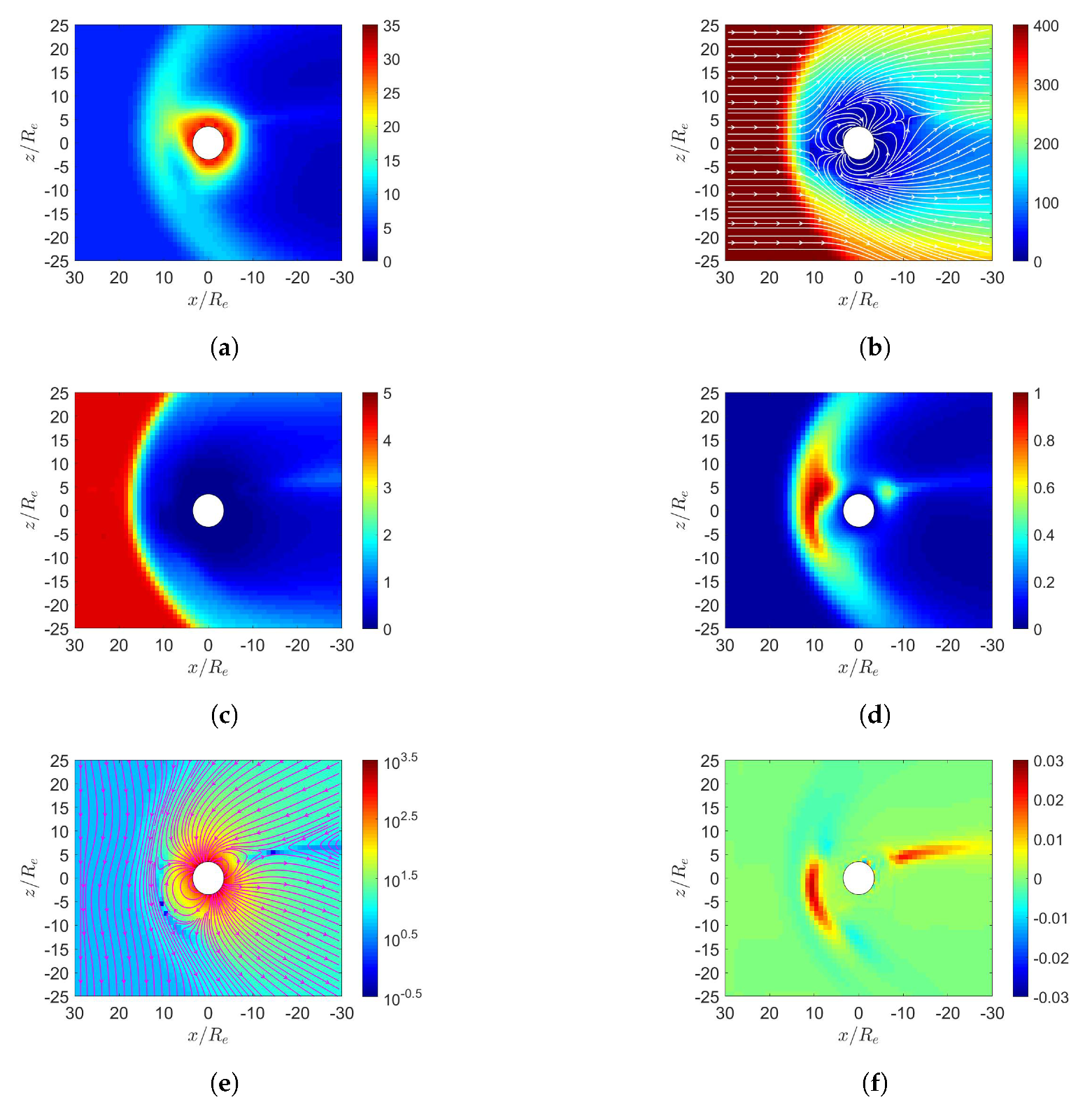
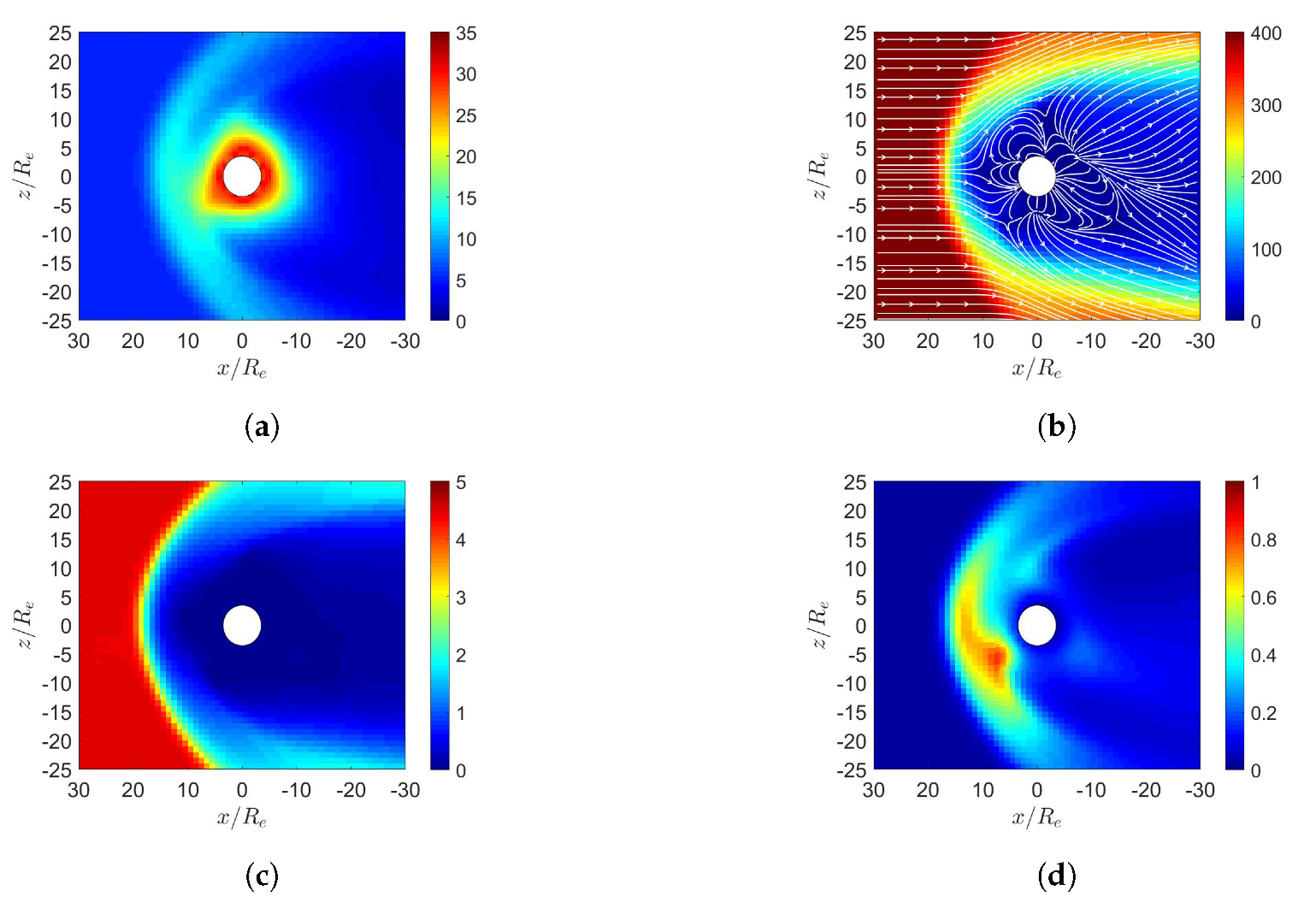
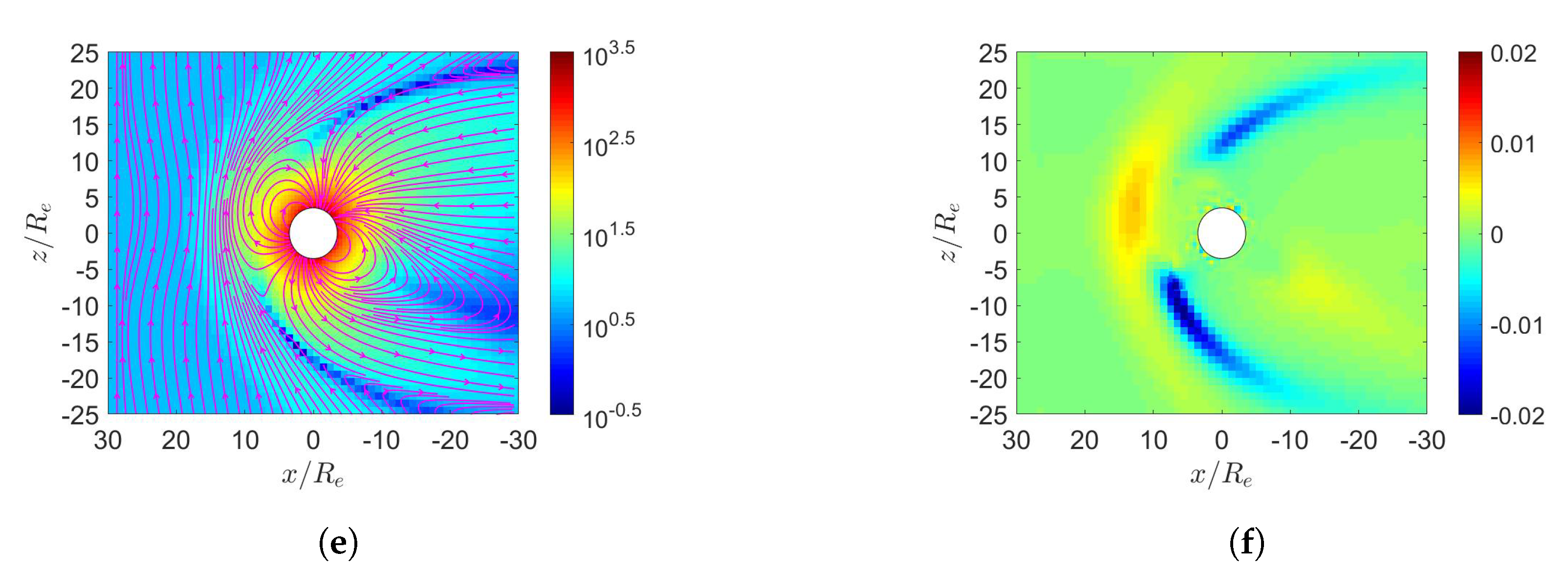
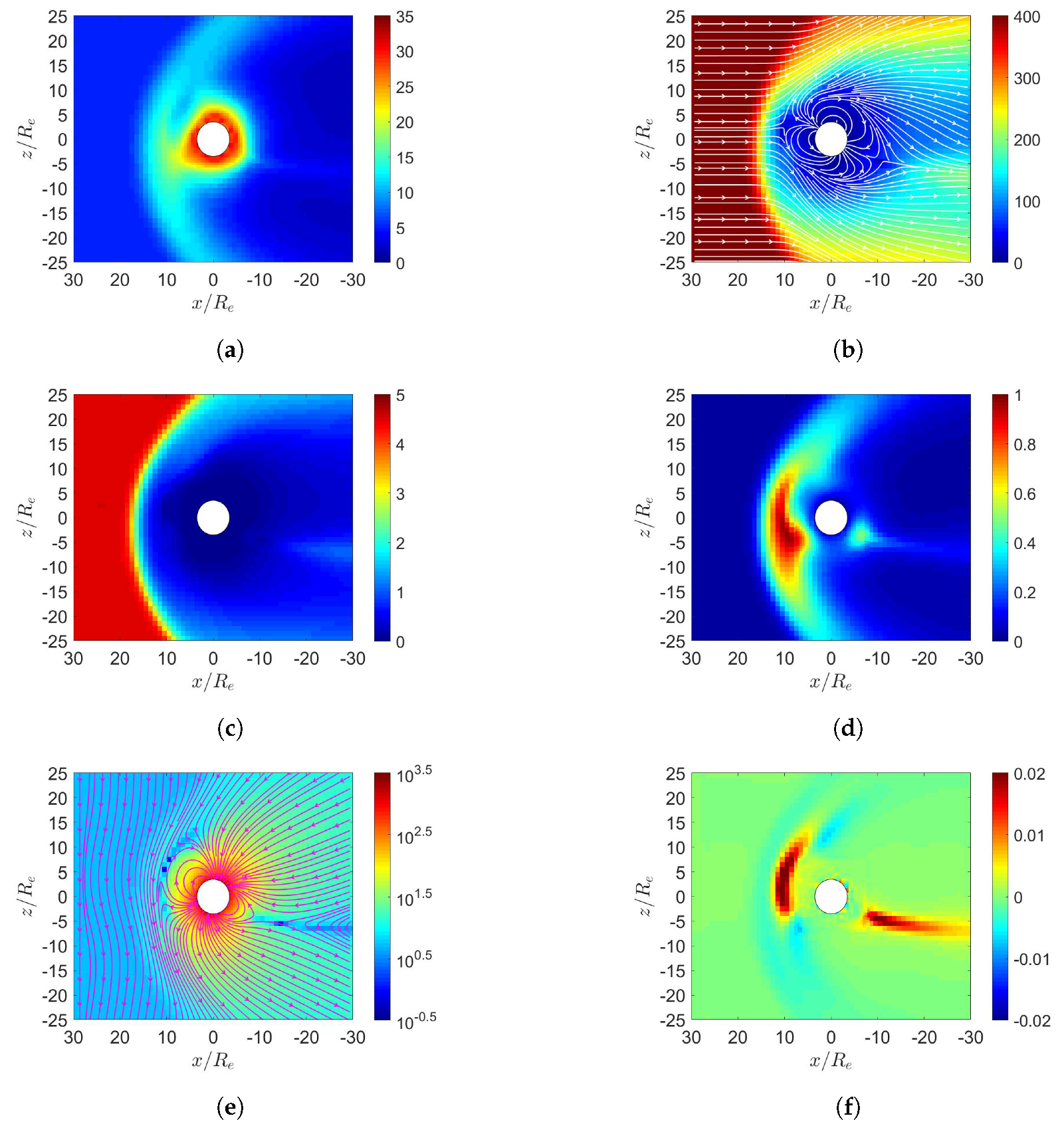
3. Simulation on Earth’s Magnetosphere
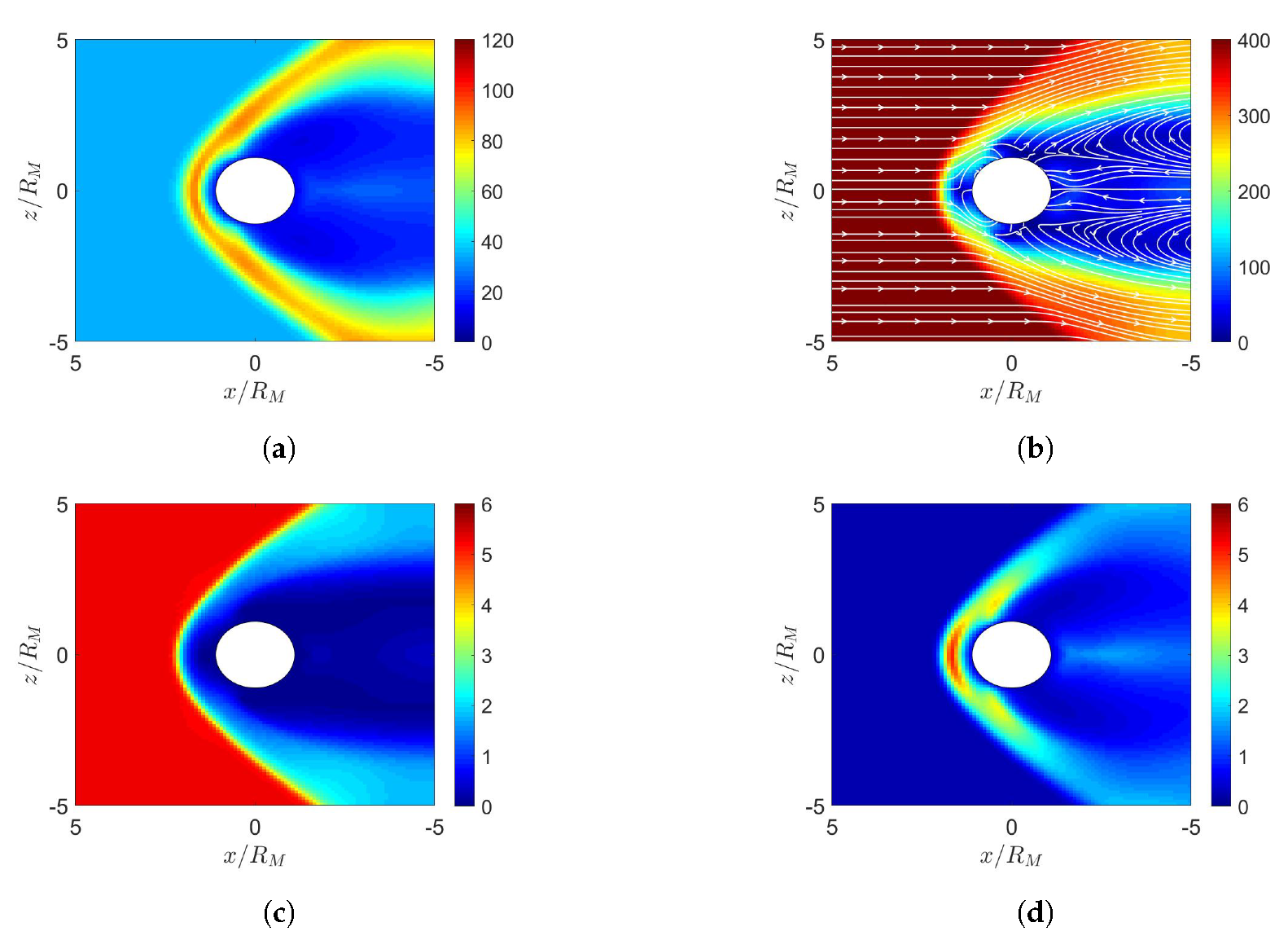
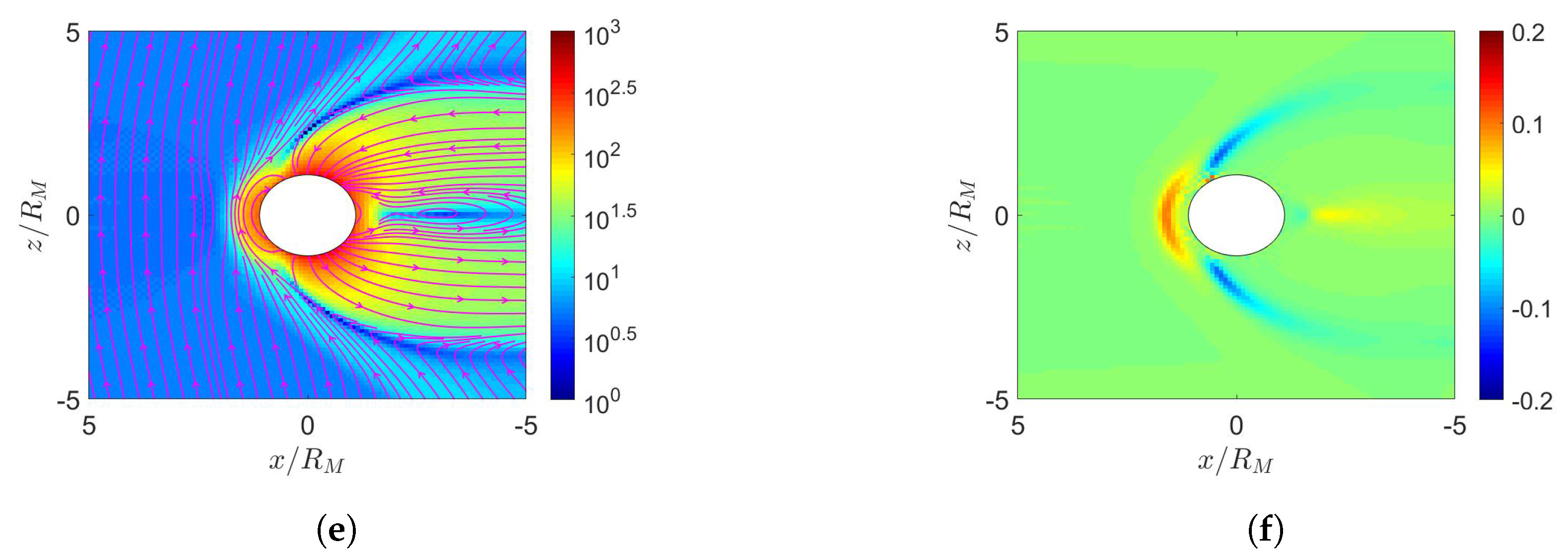
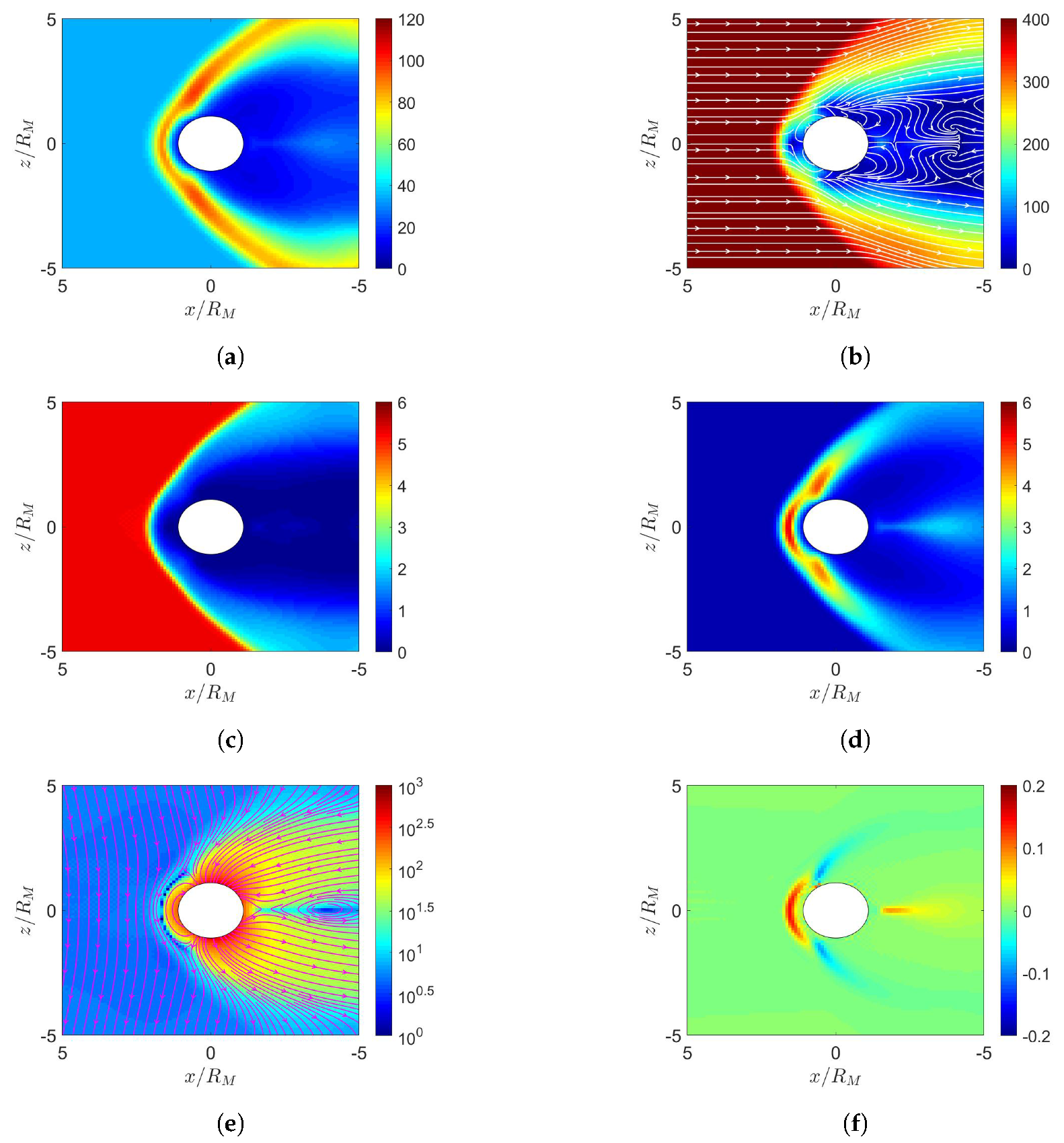
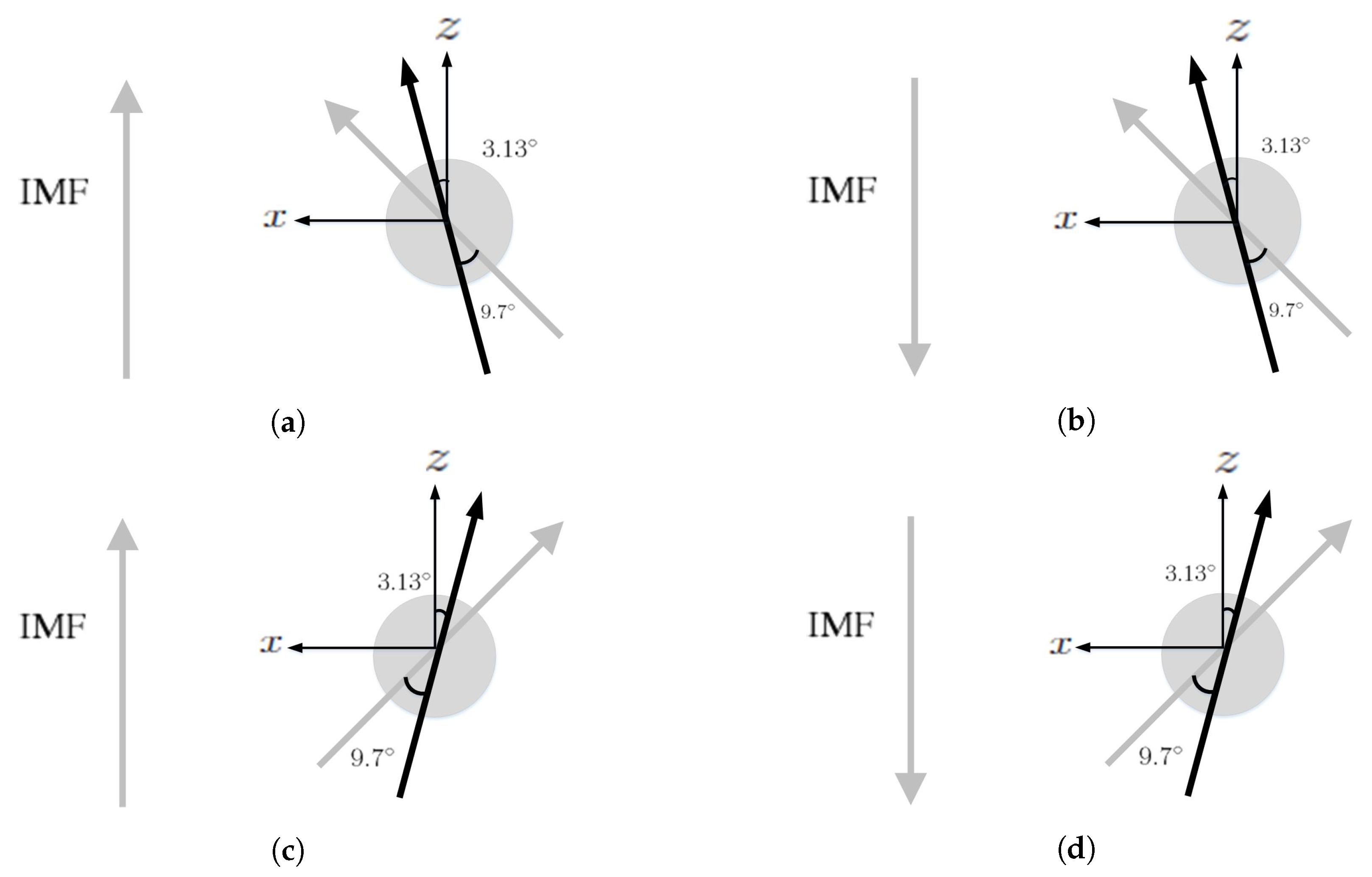
4. Simulation on Mercury’s Magnetosphere
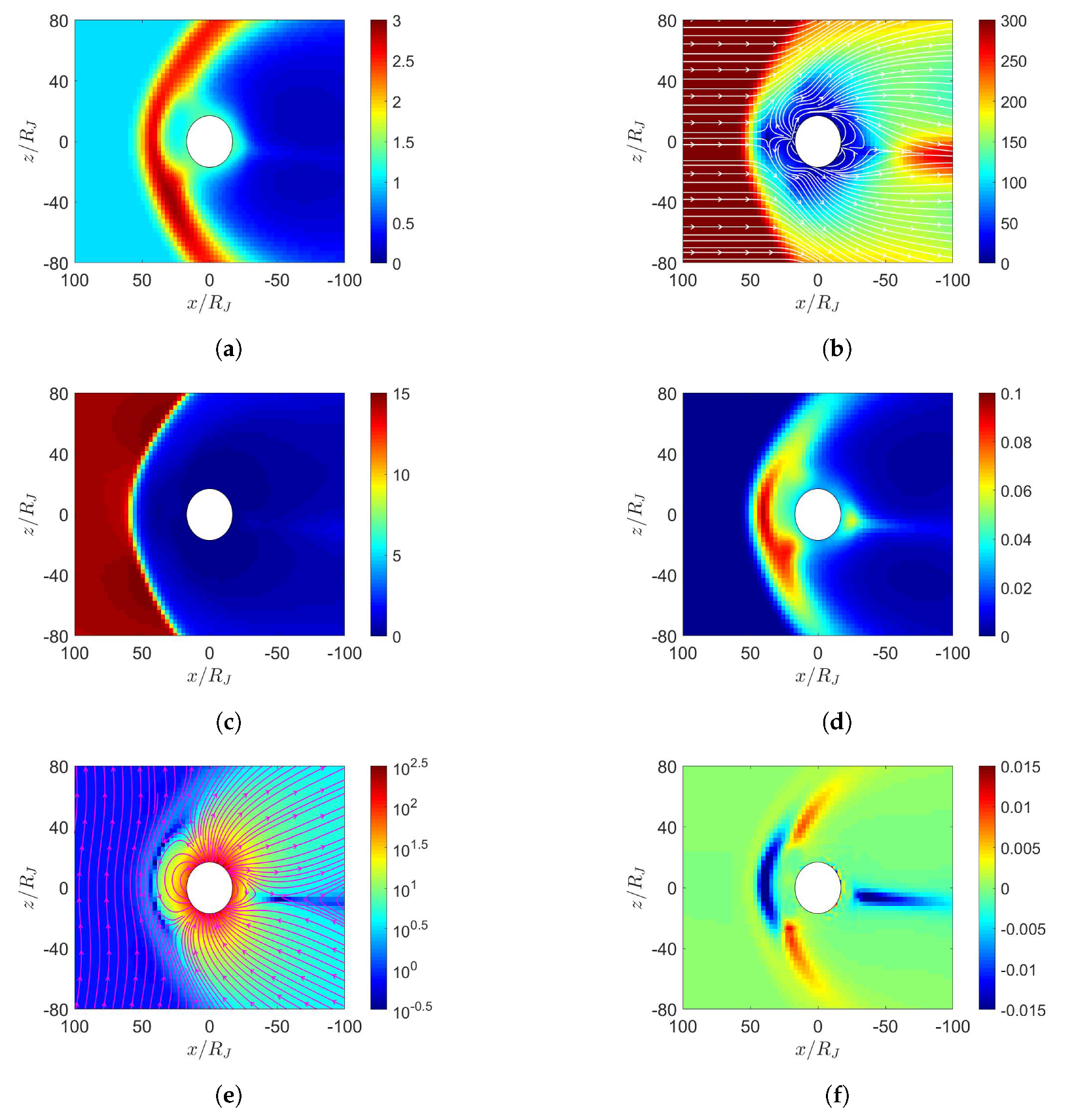
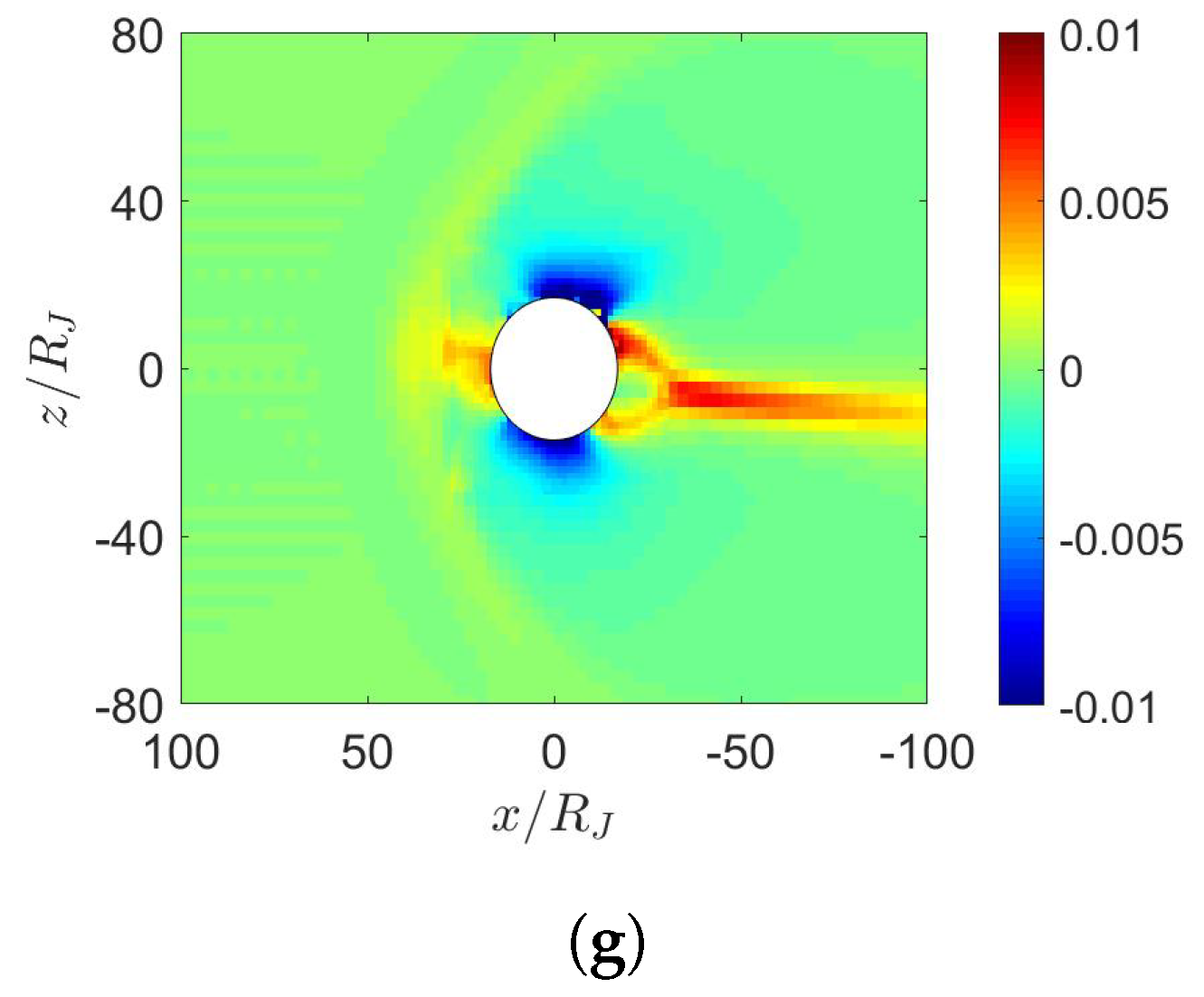
5. Simulation on Jupiter’s Magnetosphere
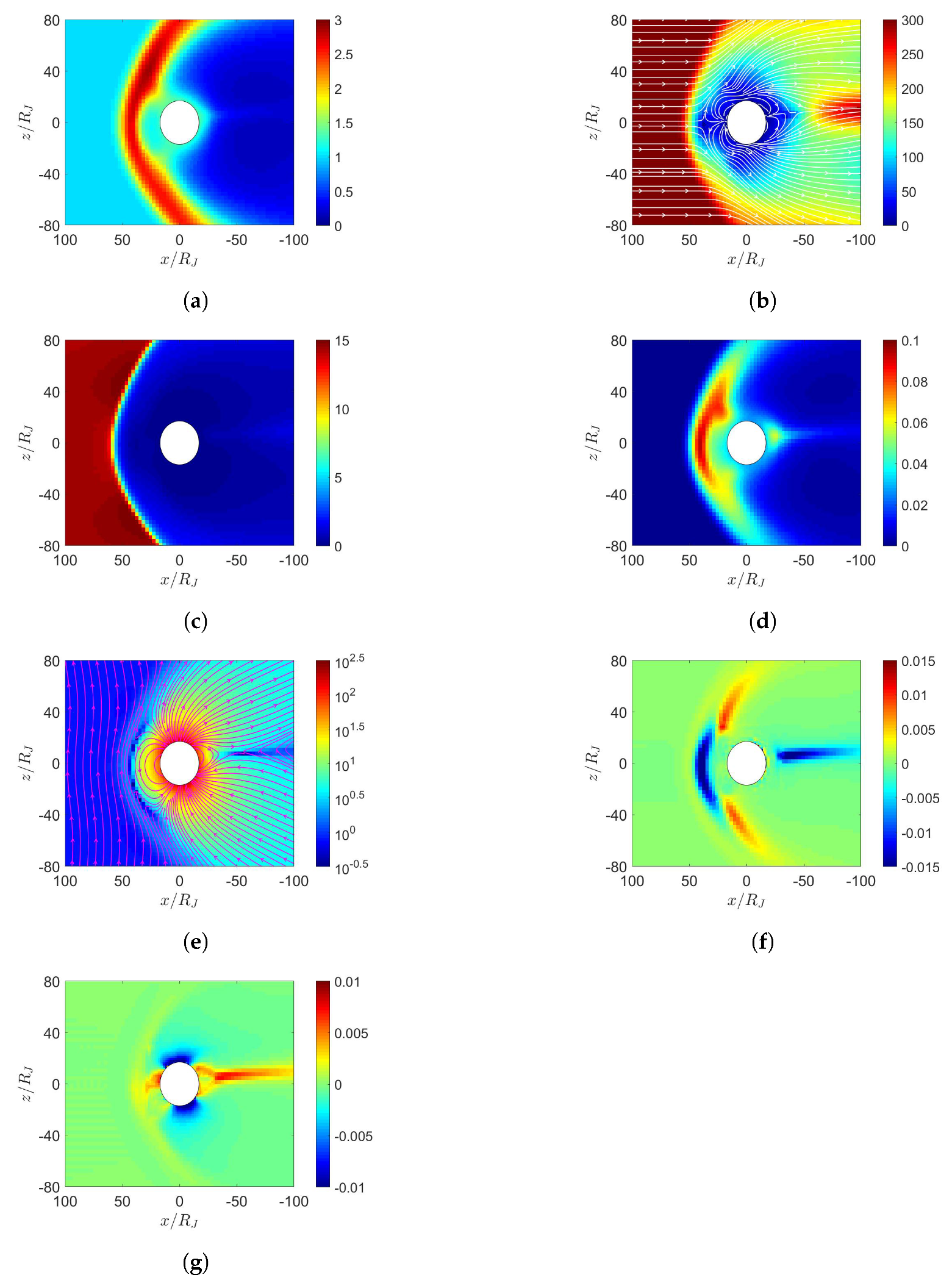
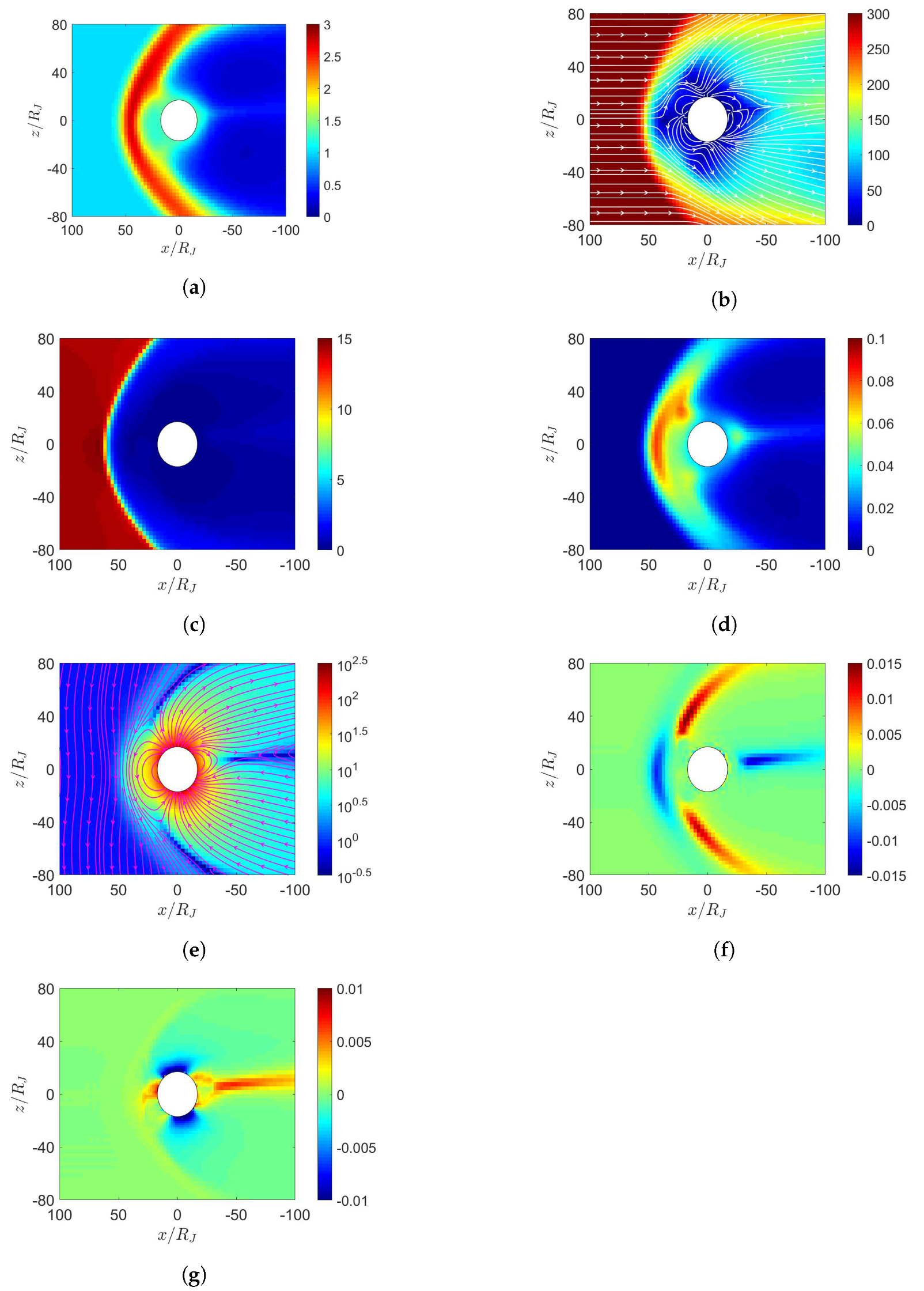
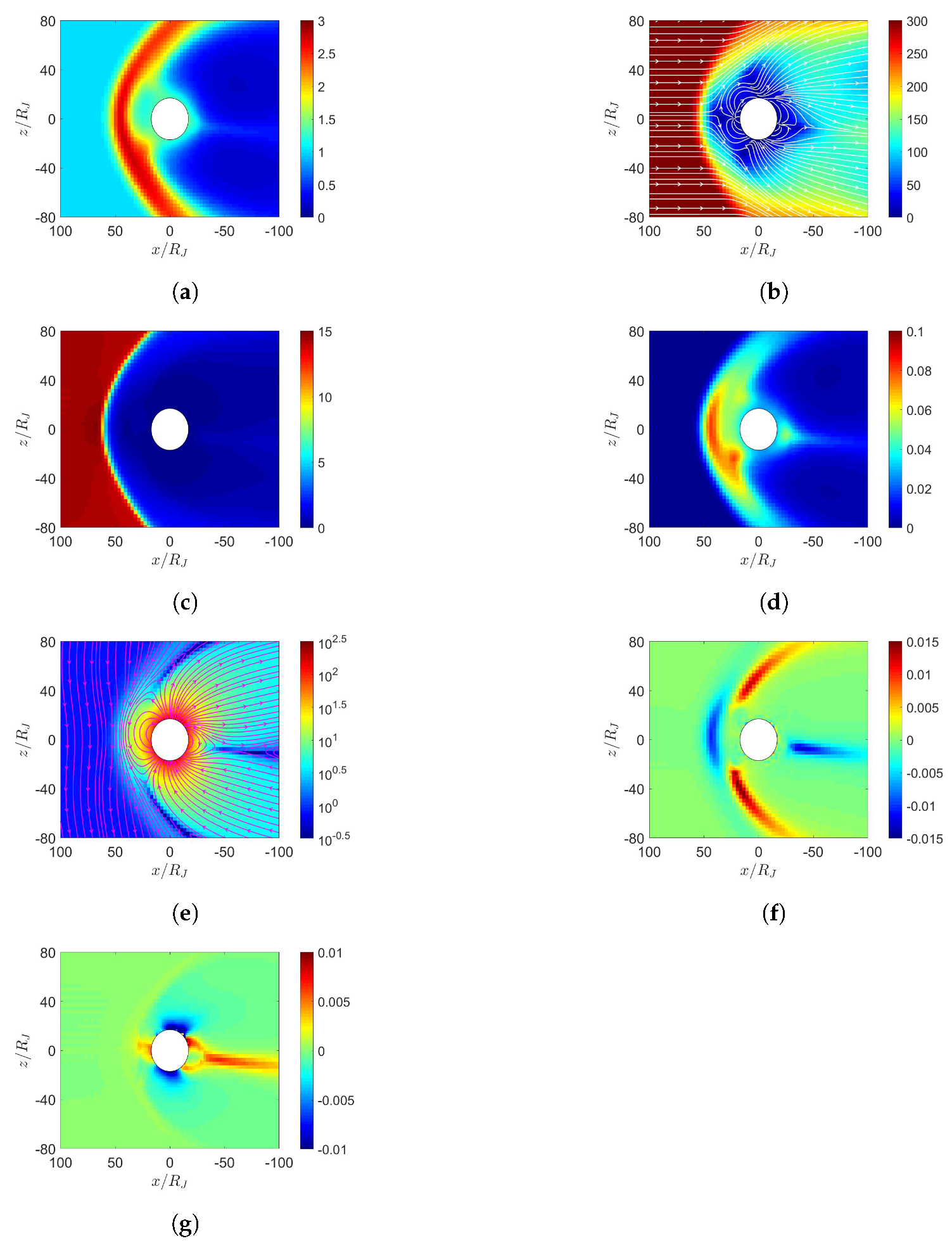
6. Simulation on Uranus’s Magnetosphere
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lazio, J.; Bastian, T.; Bryden, G.; Farrell, W.M.; Griessmeier, J.M.; Hallinan, G.; Kasper, J.; Kuiper, T.; Lecacheux, A.; Majid, W.; et al. Magnetospheric emissions from extrasolar planets. arXiv 2009, arXiv:0903.0873. [Google Scholar]
- Russell, C.T. The solar wind interaction with the Earth’s magnetosphere: A tutorial. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2000, 28, 1818–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spohn, T.; Breuer, D.; Johnson, T. Encyclopedia of the Solar System, 3rd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ogino, T. A three-dimensional MHD simulation of the interaction of the solar wind with the Earth’s magnetosphere: The generation of field-aligned currents. J. Geophys. Res. 1986, 91, 6791–6806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T. Generation mechanisms for magnetosphere-ionosphere current systems deduced from a three-dimensional MHD simulation of the solar wind–magnetosphere-ionosphere coupling processes. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1995, 100, 12057–12074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Du, A.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Ge, Y. Modeling the Earth’s magnetosphere under the influence of solar wind with due northward IMF by the AMR-CESE-MHD model. China Earth Sci. 2015, 58, 1235–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastwood, J.P.; Hietala, H.; Toth, G.; Phan, T.D.; Fujimoto, M. What controls the structure and dynamics of Earth’s magnetosphere? Space Sci. Rev. 2015, 188, 251–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Guo, X.; Tang, B.-B.; Li, W.; Wang, C. Modeling the Jovian magnetosphere under an antiparallel interplanetary magnetic field from a global MHD simulation. Earth Planet. Phys. 2018, 2, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Paty, C. Diurnal and seasonal variability of Uranus’s magnetosphere. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2017, 122, 6318–6331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tóth, G.; Kovács, D.; Hansen, K.C.; Gombosi, T. Three-dimensional MHD simulations of the magnetosphere of Uranus. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2004, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goedbloed, J.P.H.; Poedts, S. Principles of Magnetohydrodynamics: With Applications to Laboratory and Astrophysical Plasmas; Cambridge Univercity Press: Cambridge, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Raeder, J. Global magnetohydrodynamics—A tutorial. In Space Plasma Simulation; Buchner, J., Dum, C.T., Scholer, M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2003; Volume 615, pp. 212–246. [Google Scholar]
- Lyon, J.; Fedder, J.; Mobarry, C. The Lyon–Fedder–Mobarry (LFM) global MHD magnetospheric simulation code. J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys. 2004, 66, 1333–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toro, E.F. Riemann Solvers and Numerical Methods for Fluid Dynamics—A Practical Introduction, 3rd ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner, T.A.; Stone, J.M. An unsplit Godunov method for ideal MHD via constrained transport in three dimensions. J. Comput. Phys. 2008, 227, 4123–4141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kelley, M.C. The Earth’s Ionosphere: Plasma Physics and Electrodynamics, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: Burlington, MA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Goodman, M.L. A three-dimensional, iterative mapping procedure for the implementation of an ionosphere-magnetosphere anisotropic Ohm’s law boundary condition in global magnetohydrodynamics simulation. Ann. Geophys. 1995, 13, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkin, V.G.; Lyon, J.G. Effects of the low-latitude ionospheric boundary condition on the global magnetosphere. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brekke, A.; Moen, J. Observations of high latitude ionospheric conductances. J. Atmos. Terr. Phys. 1993, 55, 1493–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jardin, S. Computational Methods in Plasma Physics; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Guo, Z.; Ge, Y.S.; Du, A.; Huang, C.; Qin, P. The responses of the earth’s magnetopause and bow shock to the IMF Bz and the solar wind dynamic pressure: A parametric study using the AMR-CESE-MHD model. J. Space Weather Space Clim. 2018, 8, A41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yagi, M.; Seki, K.; Matsumoto, Y. Development of a magnetohydrodynamic simulation code satisfying the solenoidal magnetic field condition. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2009, 180, 1550–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chané, E.; Saur, J.; Poedts, S. Modeling Jupiter’s magnetosphere: Influence of the internal sources. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2013, 118, 2157–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Feng, X.; Du, A.; Ge, Y. Modeling the interaction between the solar wind and Saturn’s magnetosphere by the AMR-CESE-MHD method. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2014, 119, 9919–9930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ioannidis, G.; Brice, N. Plasma densities in the Jovian magnetosphere: Plasma slingshot or Maxwell demon? Icarus 1971, 14, 360–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, T.W. Inertial limit on corotation. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1979, 84, 6554–6558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Hansen, K.C.; Gombosi, T.I.; Kivelson, M.G.; Tóth, G.; DeZeeuw, D.L.; Ridley, A.J. Magnetospheric configuration and dynamics of Saturn’s magnetosphere: A global MHD simulation. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kivelson, M.G. The current systems of the Jovian magnetosphere and ionosphere and predictions for Saturn. Space Sci. Rev. 2005, 116, 299–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, T.W.; Dessler, A.J.; Goertz, C.K. Physics of the Jovian Magnetosphere; Cambridge Univercity Press: Cambridge, UK, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Joy, S.; Kivelson, M.G.; Walker, R.J.; Khurana, K.K.; Russell, C.T.; Ogino, T. Probabilistic models of the Jovian magnetopause and bow shock locations. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2002, 107, SMP 17-1–SMP 17-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allen, R.C.; Paranicas, C.; Bagenal, F.; Vines, S.K.; Hamilton, D.C.; Allegrini, F.; Clark, G.; Delamere, P.A.; Kim, T.K.; Krimigis, S.M.; et al. Energetic Oxygen and Sulfur Charge States in the Outer Jovian Magnetosphere: Insights From the Cassini Jupiter Flyby. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 11709–11717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Voight, G.-H.; Hill, T.W.; Dessler, A.J. The magnetosphere of Uranus—Plasma sources, convection, and field configuration. Astrophys. J. 1983, 266, 390–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lai, C.-M.; Kiang, J.-F. Comparative Study on Planetary Magnetosphere in the Solar System. Sensors 2020, 20, 1673. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20061673
Lai C-M, Kiang J-F. Comparative Study on Planetary Magnetosphere in the Solar System. Sensors. 2020; 20(6):1673. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20061673
Chicago/Turabian StyleLai, Ching-Ming, and Jean-Fu Kiang. 2020. "Comparative Study on Planetary Magnetosphere in the Solar System" Sensors 20, no. 6: 1673. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20061673
APA StyleLai, C.-M., & Kiang, J.-F. (2020). Comparative Study on Planetary Magnetosphere in the Solar System. Sensors, 20(6), 1673. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20061673




