A Method for Monitoring the Working States of Drainage Tubes Based on the Principle of Capacitance Sensing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
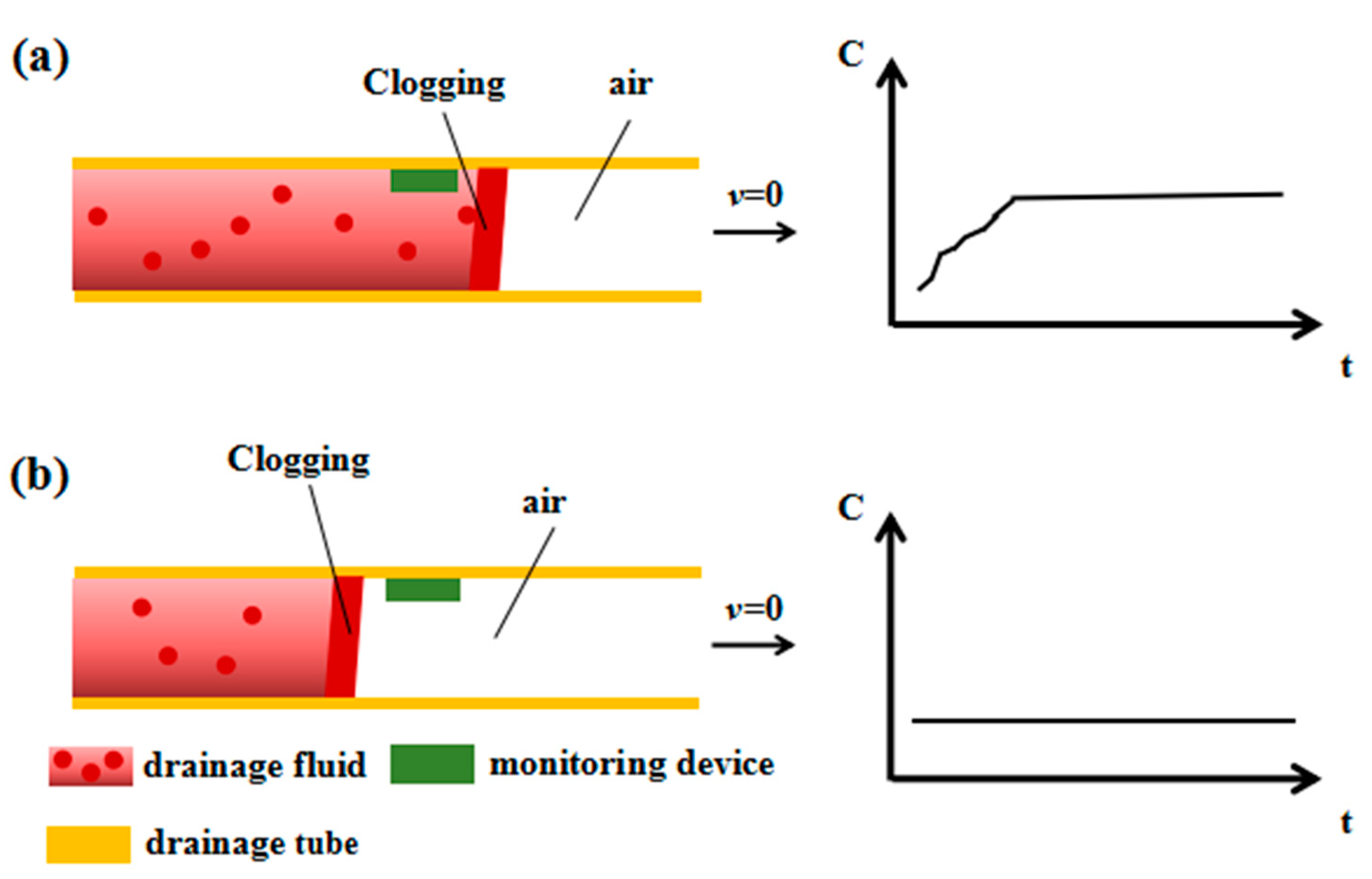
2. Principle and Method
3. Design and Fabrication of the Interdigital Capacitance Device for Drainage Monitoring
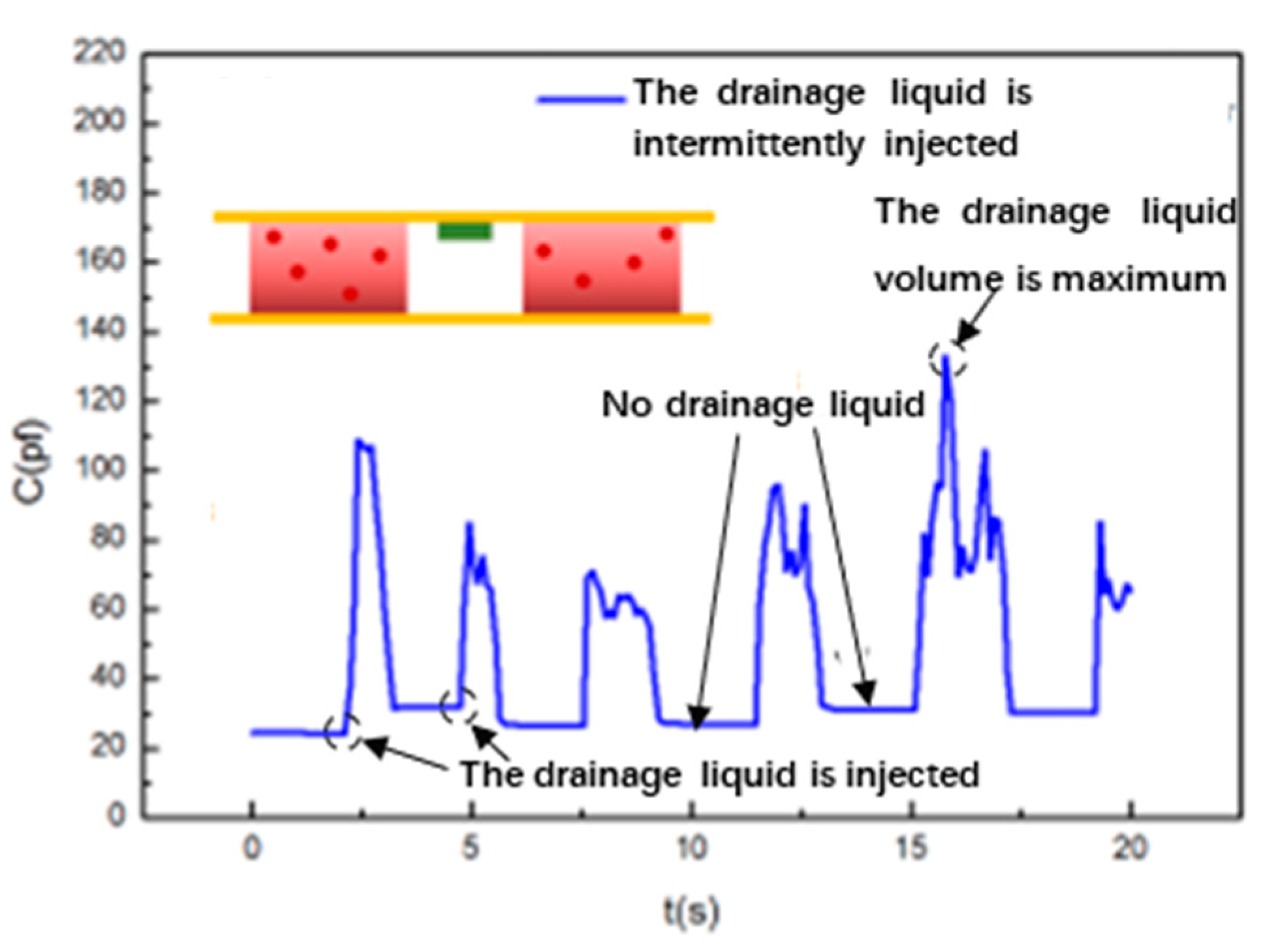
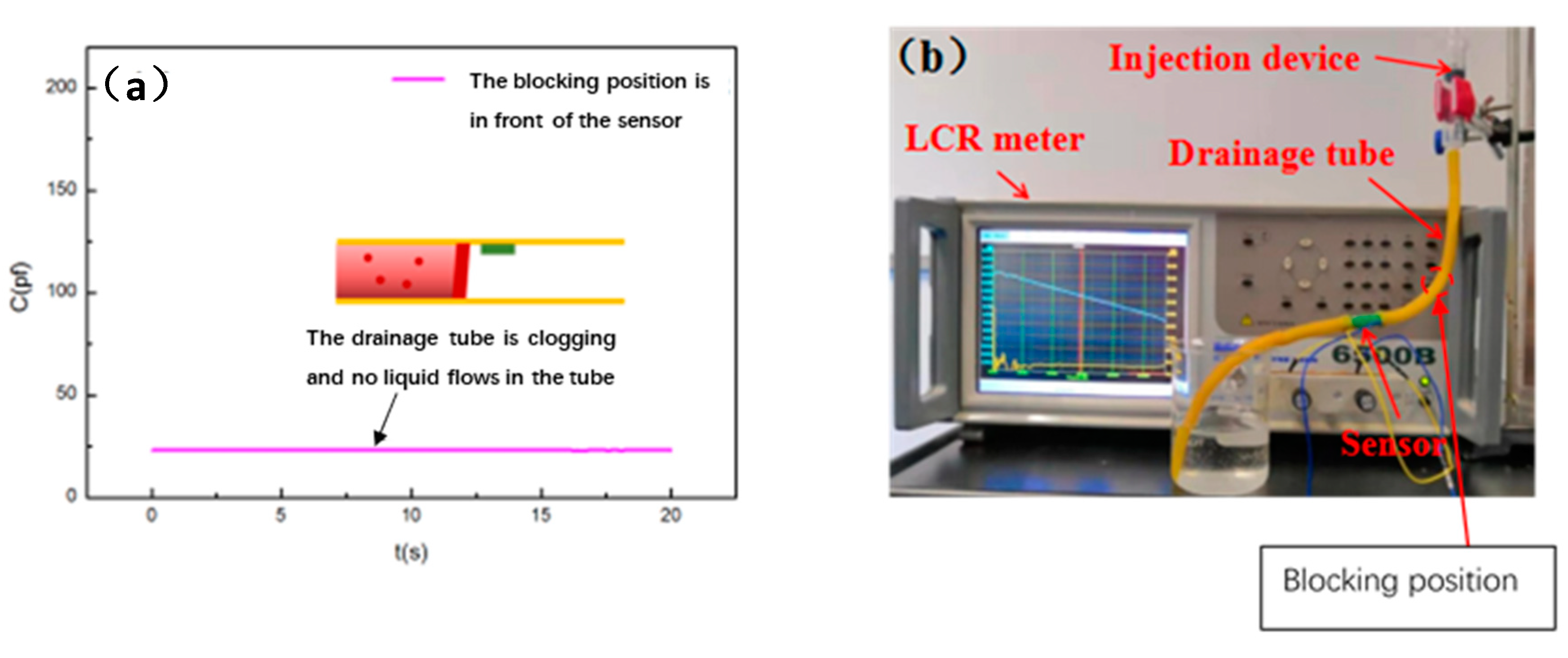
4. Experiment and Result Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Robinson, J.O. Surgical drainage: An historical perspective. Br. J. Surg. 1986, 73, 422–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durai, R.; Mownah, A.; Philip, C.H.N. Use of drains in surgery: A review. J. Perioper. Pract. 2009, 19, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyerson, J.M. A brief history of two common surgical drains. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2016, 77, 4–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eric vanSonnenberg, M.D.; Gerhard, R.; Wittich, M.D.; Brian, W.; Goodacre, M.D.; Giovanna Casola, M.D.; Horacio, B.; D’Agostino, M.D. Percutaneous abscess drainage: Update. World J. Surg. 2001, 25, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shalli, S.; Saeed Diyar, F.K.; Gillinov, A.M.; Cohn, W.E.; Perrault, L.P.; Boyle, E.M. Chest Tube Selection in Cardiac and Thoracic Surgery: A Survey of Chest Tube-Related Complications and Their Management. J. Card. Surg. 2009, 24, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiose, A.; Takaseya, T.; Fumoto, H.; Arakawa, Y.; Horai, T.; Boyle, E.M.; Gillinov, A.M.; Fukamachi, K. Improved drainage with active chest tube clearance. Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2010, 10, 685–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carruthers, K.H.; Eisemann, B.S.; Lamp, S.; Kocak, E. Optimizing the closed suction surgical drainage system. Plast. Surg. Nurs. 2013, 33, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boyacıoğlu, K.; Kalender, M.; Özkaynak, B.; Mert, B.; Kayalar, N.; Erentuğ, V. A new use of Fogarty catheter: Chest tube clearance. Heart Lung Circ. 2014, 23, e229–e230. [Google Scholar]
- Shalli, S.; Boyle, E.M.; Saeed, D.; Fukamachi, K.; Cohn, W.E.; Gillinov, A.M. The Active Tube Clearance System a Novel Bedside Chest-Tube Clearance Device. Innovations 2010, 5, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durai, R.; Ng, P.C.H. Surgical vacuum drains: Types, uses, and complications. AORN J. 2010, 91, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, Y. Management of chest drainage tubes after lung surgery. Gen. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2016, 64, 305–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zisis, C.; Tsirgogianni, K.; Lazaridis, G.; Lampaki, S.; Baka, S.; Mpoukovinas, I.; Karavasilis, V.; Kioumis, I.; Pitsiou, G.; Katsikogiannis, N.; et al. Chest drainage systems in use. Ann. Transl. Med. 2015, 3, 43. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- O′Neill, B.R.; Velez, D.A.; Braxton, E.E.; Whiting, D.; Oh, M.Y. A survey of ventriculostomy and intracranial pressure monitor placement practices. Surg. Neurol. 2008, 70, 268–273. [Google Scholar]
- Sirch, J.; Ledwon, M.; Püski, T.; Boyle, E.M.; Pfeiffer, S.; Fischlein, T. Active clearance of chest drainage catheters reduces retained blood. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2016, 151, e2–e838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karimov, J.H.; Gillinov, A.M.; Schenck, L.; Cook, M.; Kosty, S.D.; Boyle, E.M.; Fukamachi, K. Incidence of chest tube clogging after cardiac surgery: A single-Centre prospective observational study. Eur. J. Cardio-Thorac. Surg. 2013, 44, 1029–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, K.H.; Han, J.K.; Kim, K.G.; Byun, Y.; Yoon, C.J.; Kim, S.J.; Choi, B.I. Clogging of drainage catheters: Quantitative and longitudinal assessment by monitoring intracatheter pressure in catheters and rabbits. Radiology 2003, 227, 833–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.H.; Liu, T.P.; Chang, H.; Huang, T.S.; Liu, H.C.; Chen, C.H. A chest drainage system with a real-Time pressure monitoring device. J. Thorac. Dis. 2015, 7, 1119. [Google Scholar]
- Linsler, S.; Schmidtke, M.; Steudel, W.I.; Kiefer, M.; Oertel, J. Automated intracranial pressure-controlled cerebrospinal fluid external drainage with LiquoGuard®. Acta Neurochir. 2013, 155, 1589–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Sivaramakrishnan, S.; Sezen, A.S.; Rajamani, R. A novel real-Time capacitance estimation methodology for battery-Less wireless sensor systems. IEEE Sens. J. 2010, 10, 1647–1657. [Google Scholar]
- Laville, C.; Pellet, C.; N′Kaoua, G. Interdigitated humidity sensors for a portable clinical microsystem. In 1st Annual International IEEE-EMBS Special Topic Conference on Microtechnologies in Medicine and Biology; Proceedings (Cat. No. 00EX451); IEEE transactions on bio-medical engineering (United States): Lyon, France, 2000; pp. 572–577. [Google Scholar]
- Radke, S.M.; Alocilja, E.C. Design and fabrication of a microimpedance biosensor for bacterial detection. IEEE Sens. J. 2004, 4, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radke, S.M.; Alocilja, E.C. A microfabricated biosensor for detecting foodborne bioterrorism agents. IEEE Sens. J. 2005, 5, 744–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varshney, M.; Li, Y. Interdigitated array microelectrodes based impedance biosensors for detection of bacterial cells. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 24, 2951–2960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, W.; Purnendu, P.; Erwin, A.V.; Timothy, M.R.; Akhlesh, L. Thickness-Controlled hydrophobicity of fibrous Parylene-C films. Mater. Lett. 2010, 64, 1063–1065. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, X.; Crum, B.P.; Li, W. Super Hydrophobic Parylene-C Produced by Consecutive O2 and SF6 Plasma Treatment. J. Microelectromechanical Syst. 2013, 23, 628–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trantidou, T.; Prodromakis, T.; Toumazou, C. Oxygen plasma induced hydrophilicity of Parylene-C thin films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 261, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.M.; Reinhoudt, D.; Crego-Calama, M. What do we need for a superhydrophobic surface? A review on the recent progress in the preparation of superhydrophobic surfaces. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2007, 36, 1350–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, K.; Shi, W.; Chen, Y.; Wang, B.; Yao, J.; Yang, X. A Method for Monitoring the Working States of Drainage Tubes Based on the Principle of Capacitance Sensing. Sensors 2020, 20, 2087. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20072087
Luo K, Shi W, Chen Y, Wang B, Yao J, Yang X. A Method for Monitoring the Working States of Drainage Tubes Based on the Principle of Capacitance Sensing. Sensors. 2020; 20(7):2087. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20072087
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Kai, Wenpu Shi, Yinghao Chen, Bo Wang, Jialin Yao, and Xing Yang. 2020. "A Method for Monitoring the Working States of Drainage Tubes Based on the Principle of Capacitance Sensing" Sensors 20, no. 7: 2087. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20072087
APA StyleLuo, K., Shi, W., Chen, Y., Wang, B., Yao, J., & Yang, X. (2020). A Method for Monitoring the Working States of Drainage Tubes Based on the Principle of Capacitance Sensing. Sensors, 20(7), 2087. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20072087




