Fast Screening of Whole Blood and Tumor Tissue for Bladder Cancer Biomarkers Using Stochastic Needle Sensors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Instruments
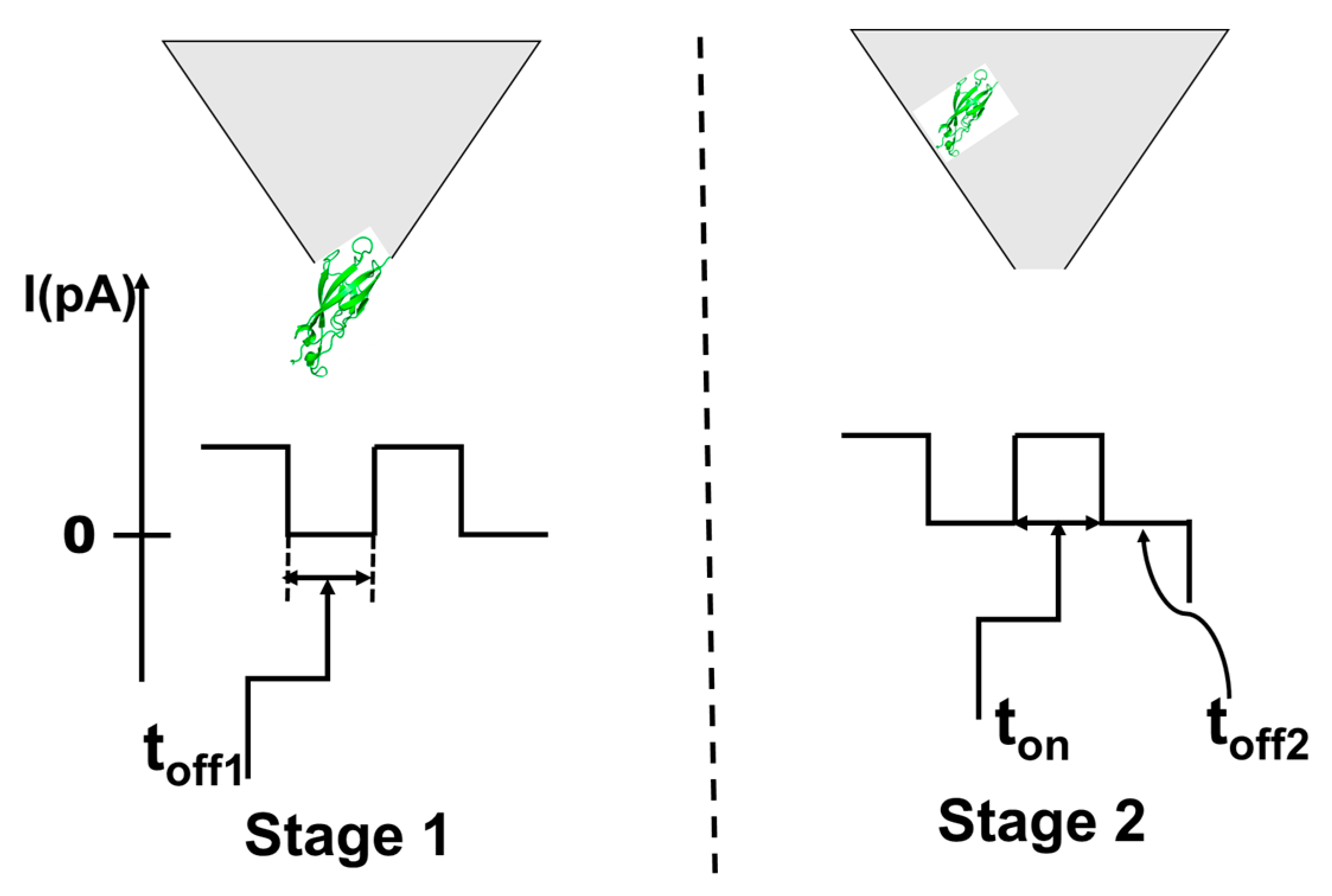
2.3. Design of the Stochastic Needle Sensors
2.4. Stochastic Mode
2.5. Samples
3. Results and Discussions
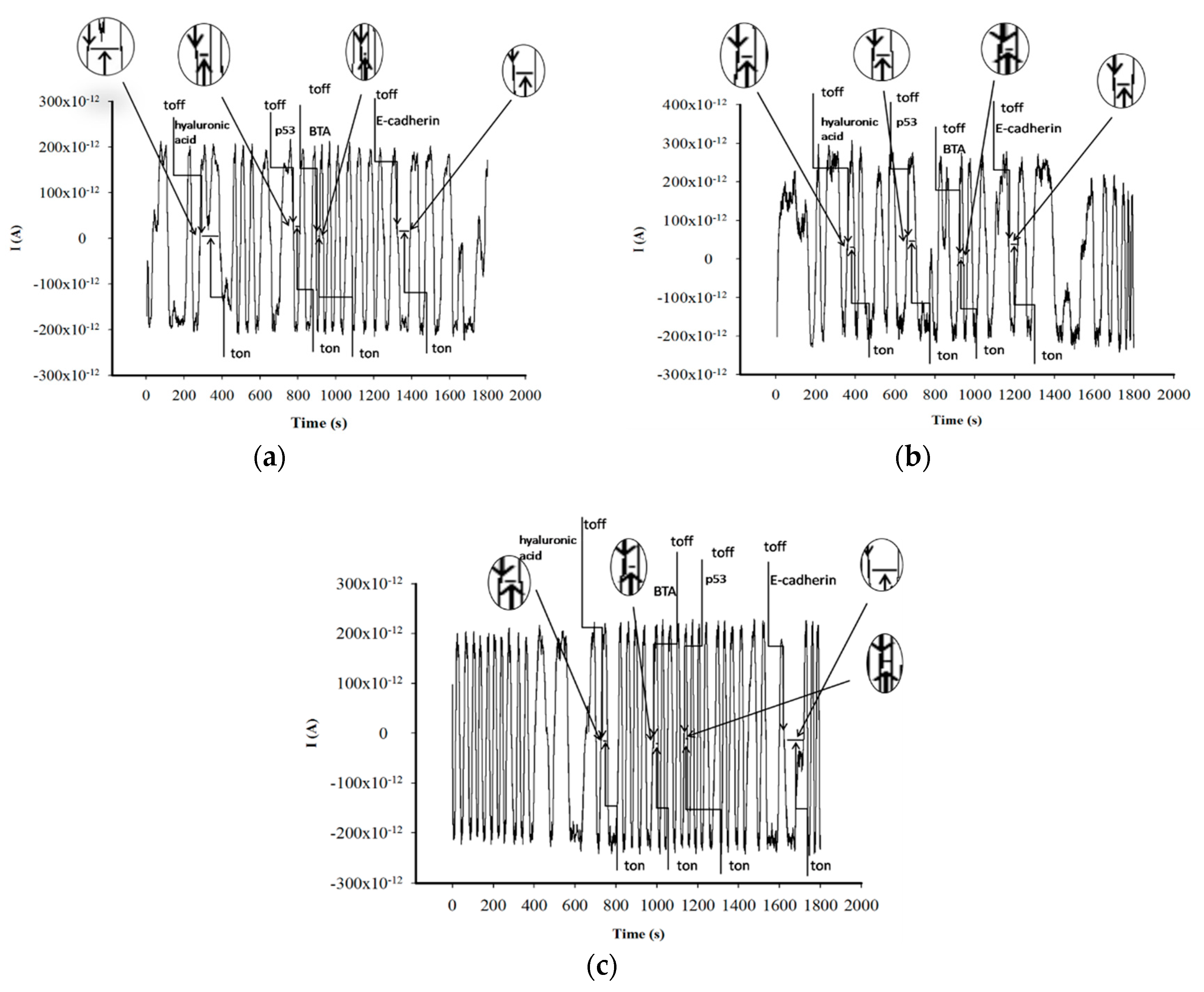
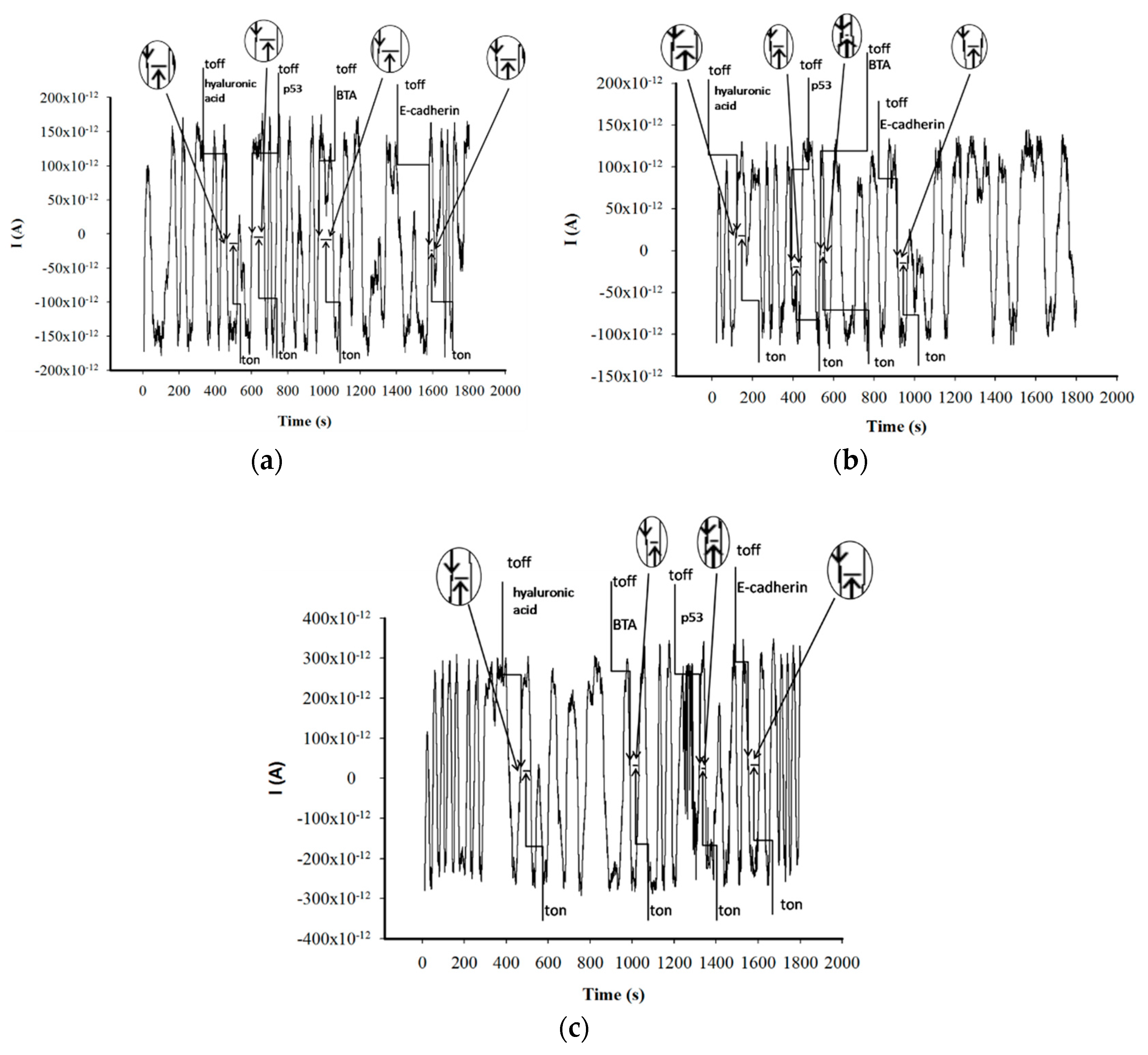
3.1. Response Characteristics of Stochastic Needle Sensors
3.2. Analytical Applications
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.; Naishadham, D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2012, 62, 10–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Cancer Research Fund. Available online: https://www.wcrf.org/dietandcancer/cancer-trends/bladder-cancer-statistics (accessed on 20 January 2020).
- Burger, M.; Catto, J.W.F.; Dalbagni, G.; Grossman, H.B.; Herr, H.; Karakiewicz, P.; Kassouf, W.; Kiemeney, L.A.; la Vecchia, C.; Shariat, S. Epidemiology and Risk Factors of Urothelial Bladder Cancer. Eur. Urol. 2012, 63, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Maturana, E.L.; Rava, M.; Anumudu, C.; Sáez, O.; Alonso, D.; Malats, N. Bladder Cancer Genetic Susceptibility. A Systematic Review. Bladder Cancer 2018, 4, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodison, S.; Rosser, C.J.; Urquidi, V. Bladder Cancer Detection and Monitoring: Assessment of Urine- and Blood-Based Marker Tests. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2013, 17, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.; Davison, D.D.; Adams, J.; Lopez-Beltran, A.; Wang, L.; Montironi, R.; Zhang, S. Biomarkers in bladder cancer: Translational and clinical implications. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2014, 89, 71–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Zhang, D. Molecular Genetic Pathology; Humana Press/Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Nives, S.-P. Tumor suppressor gene E-Cadherin and its role in normal and malignant cells. Cancer Cell Int. 2003, 3, 17. [Google Scholar]
- Gumbiner, B.M. Cell adhension: The molecular basis of tissue architecture and morphogenesis. Cell 1996, 84, 345–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malkowicz, S.B. The application of human complement factor h-related protein (BTA TRAK) in monitoring patients with bladder cancer. Urol. Clin. North Am. 2000, 27, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokeshwar, V.B.; Schroeder, G.L.; Selzer, M.G.; Hautmann, S.H.; Posey, J.T.; Duncan, R.C.; Watson, R.; Rose, L.; Markowitz, S.; Soloway, M.S. Bladder tumor markers for monitoring recurrence and screening comparison of hyaluronic acid-hyaluronidase and BTA-Stat Tests. Cancer 2002, 95, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldoveanu, I.; Stanciu-Gavan, C.; Stefan-van Staden, R.I. Molecular recognition of HER-1 in whole blood samples. J. Molec. Recogn. 2014, 27, 653–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldoveanu, I.; Stefan-van Staden, R.I. Pattern recognition of HER-2 in whole blood samples using stochastic microsensors. ESC J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 2015, 4, S3067–S3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefan-van Staden, R.I.; Ilie, R.M.; Gugoasa, L.A.; Bilasco, A.; Visan, C.A.; Streinu-Cercel, A. Molecular recognition of IL-8, IL-10, IL-12, and IL-15 in biological fluids using phthalocyanine based stochastic sensors. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 7723–7737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, E.J.; Yates, J. Single molecule characterization of metal nanoparticles using nanopore-based stochastic detection methods. Sens. Actuators B 2018, 255, 2032–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howorka, S.; Siwy, Z. Nanopore analytics: Sensing of single molecules. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 2360–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanunu, M.; Dadosh, T.; Ray, V.; Jin, J.; McReynolds, L.; Drndic, M. Rapid electronic detection of probe-specific microRNA using thin nanopore sensors. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2010, 5, 807–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayley, H.; Cremer, P.S. Stochastic sensors inspired by biology. Nature 2001, 413, 226–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, W.; Deng, M.; Liu, D.; Ma, Q.; Feng, X. Immunohistochemical determination of p53 protein overexpression for predicting p53 gene mutations in hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannetto, M.; Bianchi, M.V.; Mattarozzi, M.; Careri, M. Competitive amperometric immunosensor for determination of p53 protein in urine with carbon nanotubes/gold nanoparticles screen-printed electrodes: A potential rapid and noninvasive screening tool for early diagnosis of urinary tract carcinoma. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 991, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrero, M.; de Villena, F.J.M.; Muñoz-San Martín, C.; Campuzano, S.; Garranzo-Asensio, M.; Barderas, R.; Pingarrón, J.M. Disposable amperometric immunosensor for the determination of human p53 protein in cell lysates using magnetic micro-carriers. Biosensors 2016, 6, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-San Martín, C.; Pedrero, M.; de Villena, F.J.M.; Garranzo-Asensio, M.; Rodríguez, N.; Domínguez, G.; Barderas, R.; Campuzano, S.; Pingarrón, J.M. Disposable amperometric immunosensor for the determination of the E-cadherin tumor suppressor protein in cancer cells and human tissues. Electroanalysis 2019, 31, 309–317. [Google Scholar]
- Priolo, G.; Gontero, P.; Martinasso, G.; Mengozzi, G.; Formiconi, A.; Pelucelli, G.; Zitella, A.; Casetta, G.; Viberti, L.; Aimo, G.; et al. Bladder tumor antigen assay as compared to voided urine cytology in the diagnosis of bladder cancer. Clin. Chim. Acta 2001, 305, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepeliaev, S.; Hrudíková, R.; Jílková, J.; Pavlík, J.; Smirnou, D.; Černý, Z.; Franke, L. Colorimetric enzyme-coupled assay for hyaluronic acid determination in complex samples. Eur. Polym. J. 2017, 94, 460–470. [Google Scholar]

| Sensor Based on Graphite Paste and | Signature of the Biomarker toff (s) | Linear Concentration Range (mg/mL) | Equation of Calibration; Correlation Coefficient | Sensitivity (s−1/mg mL−1) | Limit of Quantification (mg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p53 | |||||
| Chitosan I | 0.8 | 1.17 × 10−12– 1.00 × 10−8 | 1/ton = 0.04 + 8.88 × 108 × C r = 0.9956 | 8.88 × 108 | 1.17 × 10−12 |
| Chitosan II | 1.2 | 1.17 × 10−12– 1.00 × 10−8 | 1/ton = 0.03 + 2.83 × 108 × C r = 0.9961 | 2.83 × 108 | 1.17 × 10−12 |
| Chitosan III | 1.3 | 5.28 × 10−15– 2.93 × 10−7 | 1/ton = 0.03 + 7.97 × 108 × C r = 0.9998 | 7.97 × 108 | 5.28 × 10−15 |
| E-Cadherin | |||||
| Chitosan I | 1.5 | 8.19 × 10−13– 1.00 × 10−7 | 1/ton = 0.01 + 5.88 × 109 × C r = 0.9917 | 5.88 × 109 | 8.19 × 10−13 |
| Chitosan II | 1.8 | 8.19 × 10−13– 1.00 × 10−8 | 1/ton =0.04 + 1.05 × 109 × C r = 0.9900 | 1.05 × 109 | 8.19 × 10−13 |
| Chitosan III | 2.0 | 8.19 × 10−13– 1.00 × 10−9 | 1/ton = 0.01 + 6.08 × 109 × C r = 0.9949 | 6.08 × 109 | 8.19 × 10−13 |
| BTA | |||||
| Chitosan I | 1.0 | 2.00 × 10−13– 1.00 × 10−6 | 1/ton = 0.05 + 1.89 × 109 × C r = 0.9999 | 1.89 × 109 | 2.00 × 10−13 |
| Chitosan II | 1.5 | 2.00 × 10−13– 1.00 × 10−7 | 1/ton = 0.02 + 4.62 × 108 × C r = 0.9996 | 4.62 × 108 | 2.00 × 10−13 |
| Chitosan III | 1.0 | 2.00 × 10−13– 1.00 × 10−7 | 1/ton = 0.02 + 1.59 × 109 × C r = 0.9935 | 1.59 × 109 | 2.00 × 10−13 |
| Hyaluronic acid | |||||
| Chitosan I | 0.5 | 3.00 × 10−12– 1.00 × 10−9 | 1/ton = 0.03 + 5.71 × 107 × C r = 0.9999 | 5.71 × 107 | 3.00 × 10−12 |
| Chitosan II | 1.0 | 3.00 × 10−12– 1.00 × 10−9 | 1/ton = 0.01 + 2.43 × 108 × C r = 0.9999 | 2.43 × 108 | 3.00 × 10−12 |
| Chitosan III | 0.5 | 3.00 × 10−12– 1.00 × 10−8 | 1/ton = 0.03 + 9.67 × 107 × C r = 0.9924 | 9.67 × 107 | 3.00 × 10−12 |
| Needle Sensors Based on Graphite Paste and | %, Recovery | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| p53 | E-Cadherin | BTA | Hyaluronic Acid | |
| Chitosan l | 97.47 ± 0.13 | 95.06 ± 0.11 | 99.38 ± 0.10 | 99.23 ± 0.08 |
| Chitosan ll | 99.82 ± 0.10 | 98.43 ± 0.17 | 99.69 ± 0.12 | 99.00 ± 0.15 |
| Chitosan lll | 98.49 ± 0.20 | 97.00 ± 0.24 | 97.37 ± 0.21 | 96.52 ± 0.20 |
| Sample No. | Stochastic Needle Sensors Based on Graphite Paste and | Hyaluronic Acid (pg/mL) | E-Cadherin (pg/mL) | BTA (pg/mL) | p53 (pg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Chitosan I | 171.82 ± 0.23 | 2.99 ± 0.09 | 14.30 ± 0.12 | 2.07 ± 0.08 |
| Chitosan II | 123.60 ± 0.15 | 2.53 ± 0.10 | 14.78 ± 0.11 | 2.00 ± 0.08 | |
| Chitosan III | 191.00 ± 0.14 | 2.51 ± 0.08 | 14.40 ± 0.11 | 2.78 ± 0.07 | |
| 2 | Chitosan I | 196.98 ± 0.18 | 6.29 ± 0.09 | 14.64 ± 0.10 | 2.93 ± 0.07 |
| Chitosan II | 214.00 ± 0.21 | 6.07 ± 0.08 | 15.75 ± 0.15 | 2.97 ± 0.09 | |
| Chitosan III | 191.00 ± 0.25 | 6.46 ± 0.08 | 14.50 ± 0.12 | 2.27 ± 0.10 | |
| 3 | Chitosan I | 381.03 ± 0.22 | 8.69 ± 0.07 | 14.52 ± 0.08 | 7.40 ± 0.05 |
| Chitosan II | 382.12 ± 0.12 | 8.89 ± 0.06 | 14.12 ± 0.09 | 7.32 ± 0.05 | |
| Chitosan III | 357.01 ± 0.17 | 8.74 ± 0.08 | 13.27 ± 0.09 | 7.43 ± 0.06 | |
| 4 | Chitosan I | 281.09 ± 0.12 | 10.02 ± 0.07 | 43.80 ± 0.13 | 9.20 ± 0.05 |
| Chitosan II | 298.48 ± 0.17 | 10.88 ± 0.05 | 42.45 ± 0.12 | 9.51 ± 0.09 | |
| Chitosan III | 272.02 ± 0.28 | 10.43 ± 0.09 | 44.50 ± 0.13 | 9.94 ± 0.10 | |
| 5 | Chitosan I | 228.75 ± 0.25 | 3.22 ± 0.08 | 23.10 ± 0.18 | 6.47 ± 0.03 |
| Chitosan II | 253.03 ± 0.19 | 3.88 ± 0.05 | 20.60 ± 0.18 | 6.40 ± 0.07 | |
| Chitosan III | 253.20 ± 0.20 | 3.06 ± 0.09 | 20.70 ± 0.12 | 6.03 ± 0.07 | |
| 6 | Chitosan I | 281.01 ± 0.21 | 6.07 ± 0.08 | 51.16 ± 0.13 | 6.39 ± 0.10 |
| Chitosan II | 268.20 ± 0.19 | 6.49 ± 0.08 | 51.88 ± 0.13 | 6.67 ± 0.10 | |
| Chitosan III | 255.09 ± 0.22 | 6.03 ± 0.10 | 51.30 ± 0.09 | 6.50 ± 0.08 | |
| 7 | Chitosan I | 140.30 ± 0.21 | 6.29 ± 0.07 | 64.64 ± 0.25 | 4.12 ± 0.09 |
| Chitosan II | 123.60 ± 0.15 | 6.91 ± 0.07 | 64.13 ± 0.09 | 4.12 ± 0.03 | |
| Chitosan III | 191.00 ± 0.18 | 6.42 ± 0.09 | 64.23 ± 0.09 | 4.10 ± 0.03 | |
| 8 | Chitosan I | 380.80 ± 0.27 | 3.98 ± 0.08 | 26.35 ± 0.08 | 4.06 ± 0.08 |
| Chitosan II | 389.82 ± 0.15 | 3.98 ± 0.08 | 28.19 ± 0.08 | 4.18 ± 0.06 | |
| Chitosan III | 392.20 ± 0.18 | 3.23 ± 0.09 | 27.36 ± 0.07 | 4.61 ± 0.06 | |
| 9 | Chitosan I | 129.40 ± 0.27 | 4.63 ± 0.08 | 64.40 ± 0.10 | 2.42 ± 0.10 |
| Chitosan II | 146.80 ± 0.17 | 4.00 ± 0.09 | 64.18 ± 0.10 | 2.40 ± 0.07 | |
| Chitosan III | 154.90 ± 0.23 | 4.32 ± 0.09 | 64.07 ± 0.08 | 2.47 ± 0.07 | |
| 10 | Chitosan I | 140.94 ± 0.21 | 2.88 ± 0.08 | 14.93 ± 0.07 | -* |
| Chitosan II | 137.27 ± 0.18 | 3.26 ± 0.10 | 15.80 ± 0.07 | -* | |
| Chitosan III | 153.00 ± 0.20 | 2.73 ± 0.07 | 14.40 ± 0.09 | - * |
| Sample No. | Stochastic Needle Sensors Based on Graphite Paste and | Hyaluronic Acid (pg/mL) | E-Cadherin (pg/mL) | BTA (pg/mL) | p53 (pg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Chitosan I | 281.69 ± 0.12 | 4.63 ± 0.07 | 17.40 ± 0.15 | 4.23 ± 0.10 |
| Chitosan II | 266.00 ± 0.11 | 4.56 ± 0.07 | 17.38 ± 0.17 | 4.34 ± 0.09 | |
| Chitosan III | 270.32 ± 0.11 | 4.69 ± 0.10 | 17.79 ± 0.10 | 4.30 ± 0.08 | |
| 2 | Chitosan I | 281.79 ± 0.15 | 7.01 ± 0.08 | 17.19 ± 0.08 | 7.75 ± 0.05 |
| Chitosan II | 275.43 ± 0.20 | 7.44 ± 0.07 | 17.20 ± 0.12 | 7.77 ± 0.07 | |
| Chitosan III | 279.12 ± 0.23 | 7.45 ± 0.06 | 17.31 ± 0.13 | 7.11 ± 0.08 | |
| 3 | Chitosan I | 411.00 ± 0.28 | 10.20 ± 0.08 | 28.20 ± 0.09 | 9.25 ± 0.08 |
| Chitosan II | 411.18 ± 0.24 | 10.08 ± 0.06 | 28.19 ± 0.07 | 9.40 ± 0.03 | |
| Chitosan III | 429.20 ± 0.19 | 10.50 ± 0.06 | 28.38 ± 0.07 | 9.40 ± 0.03 | |
| 4 | Chitosan I | 437.40 ± 0.11 | 13.69 ± 0.03 | 52.15 ± 0.11 | 10.20 ± 0.07 |
| Chitosan II | 437.00 ± 0.13 | 13.26 ± 0.04 | 53.00 ± 0.15 | 10.13 ± 0.07 | |
| Chitosan III | 433.59 ± 0.13 | 13.42 ± 0.04 | 52.85 ± 0.13 | 10.27 ± 0.08 | |
| 5 | Chitosan I | 502.90 ± 0.18 | 6.00 ± 0.07 | 34.85 ± 0.17 | 8.32 ± 0.02 |
| Chitosan II | 502.48 ± 0.18 | 6.59 ± 0.07 | 34.40 ± 0.15 | 8.85 ± 0.05 | |
| Chitosan III | 502.93 ± 0.23 | 6.46 ± 0.05 | 34.21 ± 0.15 | 8.59 ± 0.03 | |
| 6 | Chitosan I | 372.00 ± 0.20 | 7.56 ± 0.07 | 80.89 ± 0.18 | 10.18 ± 0.08 |
| Chitosan II | 351.20 ± 0.20 | 7.80 ± 0.07 | 80.65 ± 0.17 | 10.14 ± 0.06 | |
| Chitosan III | 369.17 ± 0.29 | 7.96 ± 0.08 | 82.14 ± 0.17 | 10.21 ± 0.05 | |
| 7 | Chitosan I | 218.20 ± 0.18 | 7.32 ± 0.05 | 75.45 ± 0.08 | 5.20 ± 0.10 |
| Chitosan II | 215.10 ± 0.19 | 7.49 ± 0.03 | 74.12 ± 0.07 | 5.66 ± 0.11 | |
| Chitosan III | 215.93 ± 0.19 | 7.01 ± 0.03 | 77.14 ± 0.07 | 5.70 ± 0.09 | |
| 8 | Chitosan I | 459.20 ± 0.18 | 6.03 ± 0.05 | 80.38 ± 0.10 | 5.32 ± 0.07 |
| Chitosan II | 475.20 ± 0.13 | 6.49 ± 0.03 | 80.66 ± 0.10 | 5.40 ± 0.07 | |
| Chitosan III | 457.07 ± 0.13 | 6.46 ± 0.03 | 80.69 ± 0.08 | 5.42 ± 0.04 | |
| 9 | Chitosan I | 357.60 ± 0.21 | 8.00 ± 0.10 | 72.23 ± 0.09 | 3.20 ± 0.08 |
| Chitosan II | 385.40 ± 0.24 | 8.64 ± 0.07 | 73.00 ± 0.08 | 3.21 ± 0.09 | |
| Chitosan III | 370.42 ± 0.24 | 8.76 ± 0.07 | 73.09 ± 0.10 | 3.15 ± 0.10 | |
| 10 | Chitosan I | 412.90 ± 0.20 | 8.82 ± 0.05 | 17.82 ± 0.05 | - * |
| Chitosan II | 413.79 ± 0.20 | 8.89 ± 0.07 | 17.03±0.07 | - * | |
| Chitosan III | 407.86 ± 0.15 | 8.75 ± 0.06 | 17.15±0.03 | - * |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stefan-van Staden, R.-I.; Gheorghe, D.-C.; Jinga, V.; Sima, C.S.; Geanta, M. Fast Screening of Whole Blood and Tumor Tissue for Bladder Cancer Biomarkers Using Stochastic Needle Sensors. Sensors 2020, 20, 2420. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20082420
Stefan-van Staden R-I, Gheorghe D-C, Jinga V, Sima CS, Geanta M. Fast Screening of Whole Blood and Tumor Tissue for Bladder Cancer Biomarkers Using Stochastic Needle Sensors. Sensors. 2020; 20(8):2420. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20082420
Chicago/Turabian StyleStefan-van Staden, Raluca-Ioana, Damaris-Cristina Gheorghe, Viorel Jinga, Cristian Sorin Sima, and Marius Geanta. 2020. "Fast Screening of Whole Blood and Tumor Tissue for Bladder Cancer Biomarkers Using Stochastic Needle Sensors" Sensors 20, no. 8: 2420. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20082420
APA StyleStefan-van Staden, R.-I., Gheorghe, D.-C., Jinga, V., Sima, C. S., & Geanta, M. (2020). Fast Screening of Whole Blood and Tumor Tissue for Bladder Cancer Biomarkers Using Stochastic Needle Sensors. Sensors, 20(8), 2420. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20082420







