Minimal Tissue Reaction after Chronic Subdural Electrode Implantation for Fully Implantable Brain–Machine Interfaces
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
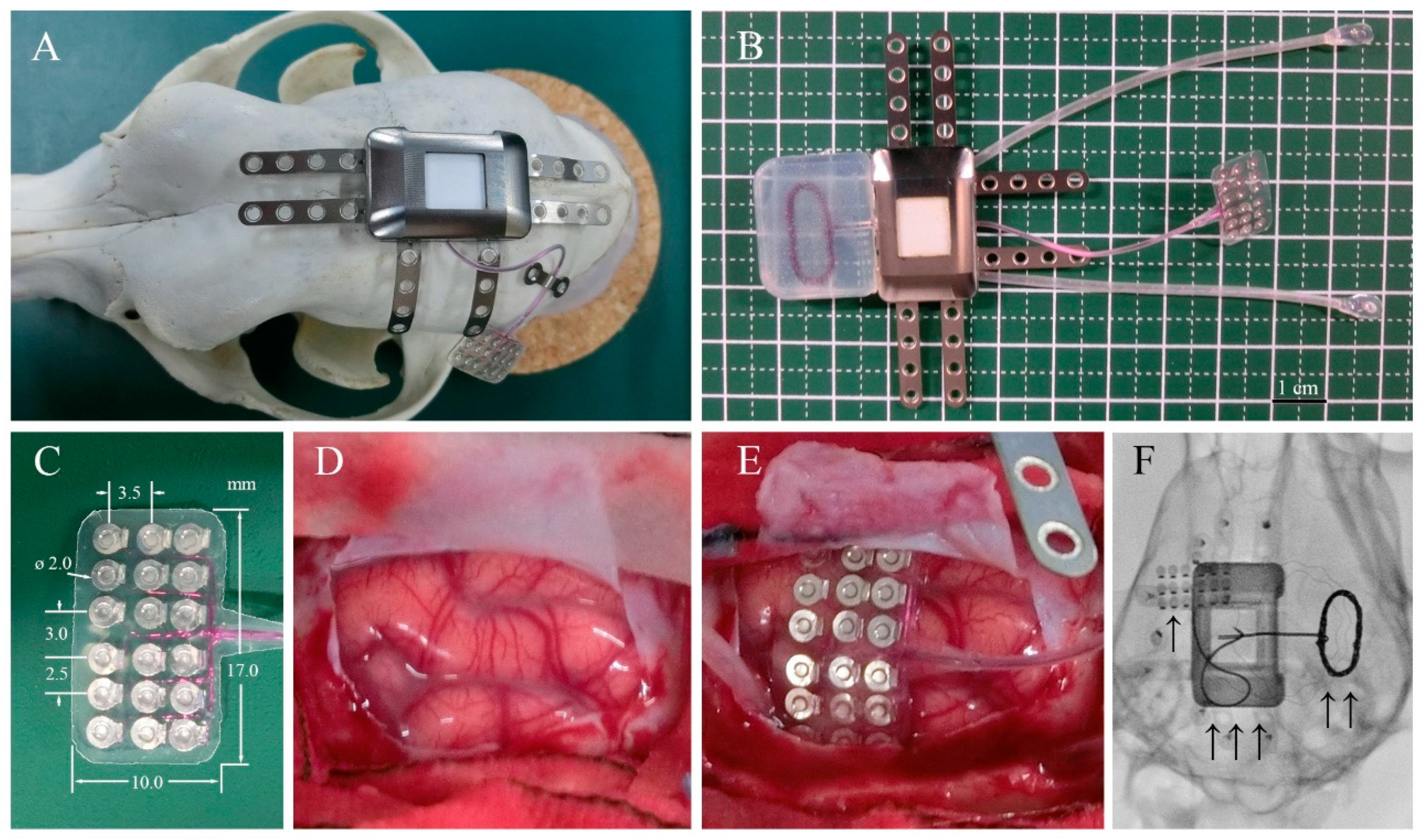
2.1. Implanted Device
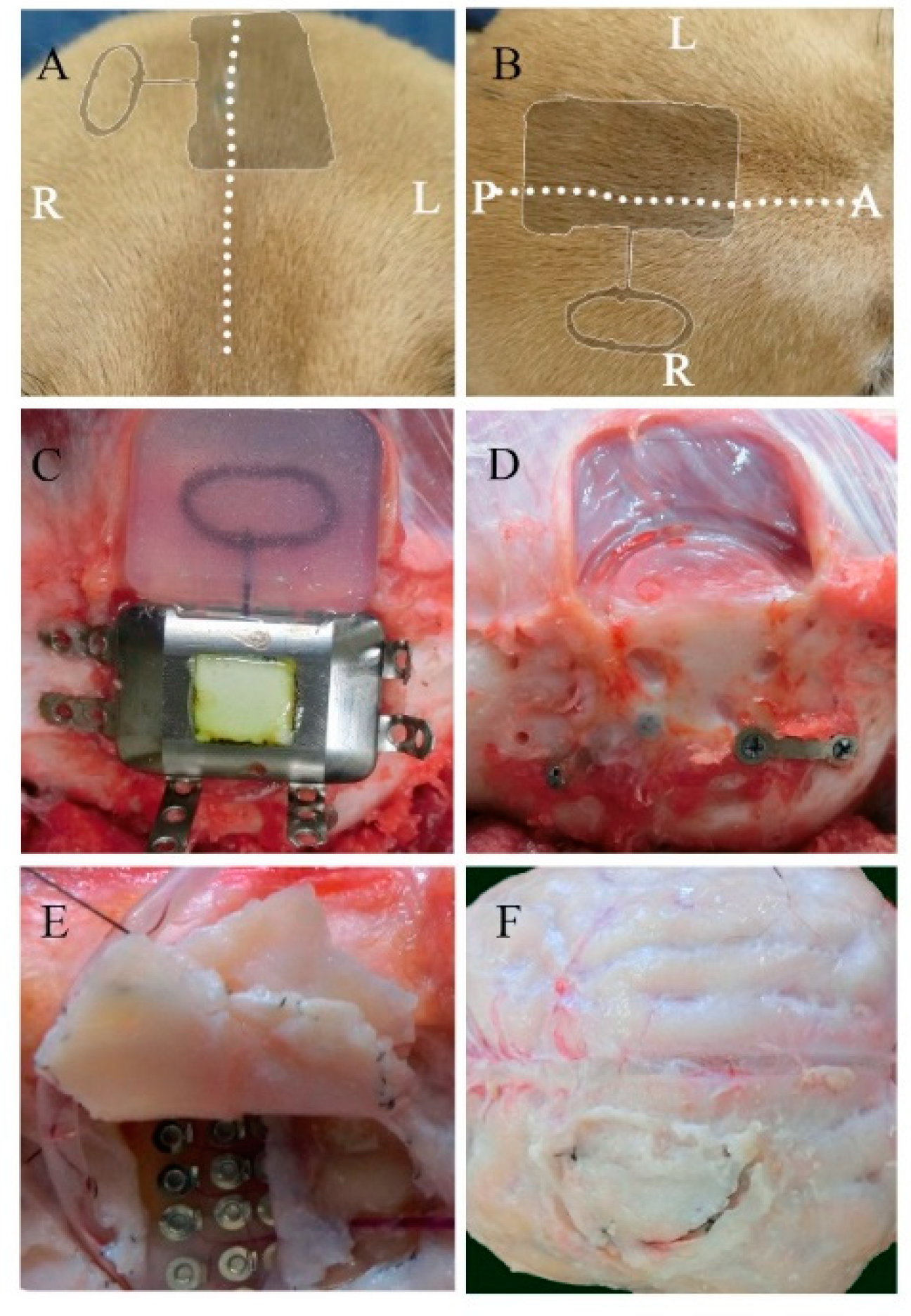
2.2. Implantation
2.3. Behavioral Observation after Implantation
2.4. Removal
2.5. Histological Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Biocompatibility
4.2. Half-Sized Device and Beagle Model
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moran, D. Evolution of brain-computer interface: Action potentials, local field potentials and electrocorticograms. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2010, 20, 741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adewole, D.O.; Serruya, M.D.; Harris, J.P.; Burrell, J.C.; Petrov, D.; Chen, H.I.; Wolf, J.A.; Cullen, D.K. The evolution of neuroprosthetic interfaces. Crit. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2016, 44, 123–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.; Collinger, J.L.; Degenhart, A.D.; Tyler-Kabara, E.C.; Schwartz, A.B.; Moran, D.W.; Weber, D.J.; Wodlinger, B.; Vinjamuri, R.K.; Ashmore, R.C. An electrocorticographic brain interface in an individual with tetraplegia. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hiremath, S.V.; Chen, W.; Wang, W.; Foldes, S.; Yang, Y.; Tyler-Kabara, E.C.; Collinger, J.L.; Boninger, M.L. Brain computer interface learning for systems based on electrocorticography and intracortical microelectrode arrays. Front. Integr. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McConnell, G.C.; Rees, H.D.; Levey, A.I.; Gutekunst, C.-A.; Gross, R.E.; Bellamkonda, R.V. Implanted neural electrodes cause chronic, local inflammation that is correlated with local neurodegeneration. J. Neural Eng. 2009, 6, 056003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collinger, J.L.; Wodlinger, B.; Downey, J.E.; Wang, W.; Tyler-Kabara, E.C.; Weber, D.J.; McMorland, A.J.; Velliste, M.; Boninger, M.L.; Schwartz, A.B. High-performance neuroprosthetic control by an individual with tetraplegia. Lancet 2012, 381, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barrese, J.C.; Rao, N.; Paroo, K.; Triebwasser, C.; Vargas-Irwin, C.; Franquemont, L.; Donoghue, J.P. Failure mode analysis of silicon-based intracortical microelectrode arrays in non-human primates. J. Neural Eng. 2013, 10, 066014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata, M.; Matsushita, K.; Suzuki, T.; Yoshida, T.; Sato, F.; Morris, S.; Yanagisawa, T.; Goto, T.; Kawato, M.; Yoshimine, T. A fully-implantable wireless system for human brain-machine interfaces using brain surface electrodes: W-herbs. IEICE Trans. Commun. 2011, E94b, 2448–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Degenhart, A.D.; Collinger, J.L.; Vinjamuri, R.; Kelly, J.; Tyler-Kabara, E.C.; Wang, W. Classification of hand posture from electrocorticographic signals recorded during varying force conditions. In Proceedings of the 2011 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Boston, MA, USA, 30 August–3 September 2011; p. 5782. [Google Scholar]
- Pei, X.; Barbour, D.L.; Leuthardt, E.C.; Schalk, G. Decoding vowels and consonants in spoken and imagined words using electrocorticographic signals in humans. J. Neural Eng. 2011, 8, 046028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Shin, D.; Watanabe, H.; Nakanishi, Y.; Kambara, H.; Yoshimura, N.; Nambu, A.; Isa, T.; Nishimura, Y.; Koike, Y. Decoding grasp force profile from electrocorticography signals in non-human primate sensorimotor cortex. Neurosci. Res. 2014, 83, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotson, G.; McMullen, D.P.; Fifer, M.S.; Johannes, M.S.; Katyal, K.D.; Para, M.P.; Armiger, R.; Anderson, W.S.; Thakor, N.V.; Wester, B.A. Individual finger control of a modular prosthetic limb using high-density electrocorticography in a human subject. J. Neural Eng. 2016, 13, 026017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Anumanchipalli, G.K.; Chartier, J.; Chang, E.F. Speech synthesis from neural decoding of spoken sentences. Nature 2019, 568, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, A.; Wu, C. Chronically implanted intracranial electrodes: Tissue reaction and electrical changes. Micromachines 2018, 9, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sillay, K.A.; Rutecki, P.; Cicora, K.; Worrell, G.; Drazkowski, J.; Shih, J.J.; Sharan, A.D.; Morrell, M.J.; Williams, J.; Wingeier, B. Long-term measurement of impedance in chornically implanted depth and subdural electrodes during responsive neurostimulation in humans. Brain Stimul. 2013, 6, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schendel, A.A.; Eliceiri, K.W.; Williams, J.C. Advanced materials for neural surface electrodes. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2014, 18, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaiju, T.; Doi, K.; Yokota, M.; Watanabe, K.; Inoue, M.; Ando, H.; Takahashi, K.; Yoshida, F.; Hirata, M.; Suzuki, T. High spatiotemporal resolution ecog recording of somatosensory evoked potentials with flexible micro-electrode arrays. Front. Neural Circuits 2017, 11, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nurse, E.S.; John, S.E.; Freestone, D.R.; Oxley, T.J.; Ung, H.; Berkovic, S.F.; O’Brien, T.J.; Cook, M.J.; Grayden, D.B. Consistency of long-term subdural electrocorticography in humans. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 65, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergamasco, L.; Accatino, A.; Priano, L.; Neiger-Aeschbacher, G.; Cizinauskas, S.; Jaggy, A. Quantitative electroencephalographic findings in beagles anaesthetized with propofol. Vet. J. 2003, 166, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.; Kim, D.; Been, J.; Cho, H.; Jun, S.C. Oscillatory brain activity changes by anodal tdcs—An ecog study on anesthetized beagles. In Proceedings of the 2016 38th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Orlando, FL, USA, 16–20 August 2016; pp. 5258–5261. [Google Scholar]
- Slutzky, M.W.; Jordan, L.R.; Krieg, T.; Chen, M.; Mogul, D.J.; Miller, L.E. Optimal spacing of surface electrode arrays for brain-machine interface applications. J. Neural Eng. 2010, 7, 26004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mestais, C.S.; Charvet, G.; Sauter-Starace, F.; Foerster, M.; Ratel, D.; Benabid, A.L. Wimagine: Wireless 64-channel ecog recording implant for long term clinical applications. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2015, 23, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitale, F.; Shen, W.; Driscoll, N.; Burrell, J.C.; Richardson, A.G.; Adewole, O.; Murphy, B.; Ananthakrishnan, A.; Oh, H.; Wang, T.; et al. Biomimetic extracellular matrix coatings improve the chronic biocompatibility of microfabricated subdural microelectrode arrays. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0206137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degenhart, A.D.; Eles, J.; Dum, R.; Mischel, J.L.; Smalianchuk, I.; Endler, B.; Ashmore, R.C.; Tyler-Kabara, E.C.; Hatsopoulos, N.G.; Wang, W. Histological evaluation of a chronically-implanted electrocorticographic electrode grid in a non-human primate. J. Neural Eng. 2016, 13, 046019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sauter-Starace, F.; Ratel, D.; Cretallaz, C.; Foerster, M.; Lambert, A.; Gaude, C.; Costecalde, T.; Bonnet, S.; Charvet, G.; Aksenova, T.; et al. Long-term sheep implantation of wimagine®, a wireless 64-channel electrocorticogram recorder. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henle, C.; Raab, M.; Cordeiro, J.; Doostkam, S.; Schulze-Bonhage, A.; Stieglitz, T.; Rickert, J. First long term in vivo study on subdurally implanted micro-ecog electrodes, manufactured with a novel laser technology. Biomed. Microdevices 2011, 13, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schendel, A.A.; Thongpang, S.; Brodnick, S.K.; Richner, T.J.; Lindevig, B.D.; Krugner-Higby, L.; Williams, J.C. A cranial window imaging method for monitoring vascular growth around chronically implanted micro-ecog devices. J. Neurosci. Methods 2013, 218, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lynn, A.D.; Blakney, A.K.; Kyriakides, T.R.; Bryant, S.J. Temporal progression of the host response to implanted poly (ethylene glycol)-based hydrogels. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2011, 96, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nunamaker, E.A.; Kipke, D.R. An alginate hydrogel dura mater replacement for use with intracortical electrodes. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2010, 95, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Preul, M.C.; Bichard, W.D.; Muench, T.R.; Spetzler, R.F. Toward optimal tissue sealants for neurosurgery: Use of a novel hydrogel sealant in a canine durotomy repair model. Neurosurgery 2003, 53, 1189–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayama, C.M.; Sorour, M.; Schmidt, R.H. Dural adhesion to porous cranioplastic implant: A potential safety concern. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2014, 5, 19. [Google Scholar]
- Saxena, T.; Karumbaiah, L.; Gaupp, E.A.; Patkar, R.; Patil, K.; Betancur, M.; Stanley, G.B.; Bellamkonda, R.V. The impact of chronic blood-brain barrier breach on intracortical electrode function. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 4703–4713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polikov, V.S.; Tresco, P.A.; Reichert, W.M. Response of brain tissue to chronically implanted neural electrodes. J. Neurosci. Methods 2005, 148, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karumbaiah, L.; Norman, S.E.; Rajan, N.B.; Anand, S.; Saxena, T.; Betancur, M.; Patkar, R.; Bellamkonda, R.V. The upregulation of specific interleukin (il) receptor antagonists and paradoxical enhancement of neuronal apoptosis due to electrode induced strain and brain micromotion. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 5983–5996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romanelli, P.; Piangerelli, M.; Ratel, D.; Gaude, C.; Costecalde, T.; Puttilli, C.; Picciafuoco, M.; Benabid, A.; Torres, N. A novel neural prosthesis providing long-term electrocorticography recording and cortical stimulation for epilepsy and brain-computer interface. J. Neurosurg. 2018, 130, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roth, T.L.; Nayak, D.; Atanasijevic, T.; Koretsky, A.P.; Latour, L.L.; McGavern, D.B. Transcranial amelioration of inflammation and cell death after brain injury. Nature 2014, 505, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, F.T.; Morrell, M.J. The rns system: Responsive cortical stimulation for the treatment of refractory partial epilepsy. Expert Rev. Med Devices 2014, 11, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borton, D.A.; Yin, M.; Aceros, J.; Nurmikko, A. An implantable wireless neural interface for recording cortical circuit dynamics in moving primates. J. Neural Eng. 2013, 10, 026010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Romanelli, P.; Valiante, T.A.; Seri, S.; Puttilli, C.; Picciafuoco, M.; Jakobs, M.; Lozano, A. A wireless neuroprosthesis for patients with drug-refractory epilepsy: A proof-of-concept study. Cureus 2019, 11, e5868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fong, J.S.; Alexopoulos, A.V.; Bingaman, W.E.; Gonzalez-Martinez, J.; Prayson, R.A. Pathologic findings associated with invasive eeg monitoring for medically intractable epilepsy. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2012, 138, 506–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salam, M.T.; Gélinas, S.; Desgent, S.; Duss, S.; Turmel, F.B.; Carmant, L.; Sawan, M.; Nguyen, D.K. Subdural porous and notched mini-grid electrodes for wireless intracranial electroencephalographic recordings. J. Multidiscip. Healthc. 2014, 7, 573. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmadi, E.; Katnani, H.A.; Daftari Besheli, L.; Gu, Q.; Atefi, R.; Villeneuve, M.Y.; Eskandar, E.; Lev, M.H.; Golby, A.J.; Gupta, R.; et al. An electrocorticography grid with conductive nanoparticles in a polymer thick film on an organic substrate improves ct and mr imaging. Radiology 2016, 280, 595–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnet, S.; Rubeck, C.; Agache, V.; Bourgerette, A.; Fuchs, O.; Gharbi, S.; Sauter-Starace, F.; Maciejasz, P.; Divoux, J.L.; Bourquin, N. Selective eng recordings using a multi-contact cuff electrode. In Proceedings of the 2013 6th International IEEE/EMBS Conference on Neural Engineering (NER), San Diego, CA, USA, 6–8 November 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Błaszczyk, J.W.; Dobrzecka, C. Effects of unilateral somatosensory cortex lesion upon locomotion in dogs. Acta Neurobiol. Exp. 1995, 55, 133–140. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, D., Jr.; Gorska, T.; Dutkiewicz, K. Corticostriate projections from the primary motor cortex in the dog. Brain Res. 1981, 209, 287–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Site | Cells/mm2 | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NeuN | Impl | 649.5 ± 125.5 | 0.41 |
| Ctl | 612.0 ± 100.8 | ||
| Iba 1 | Impl | 102.2 ± 52.0 | 0.12 |
| Ctl | 77.2 ± 13.0 | ||
| GFAP | Impl | 254.5 ± 48.8 | 0.40 |
| Ctl | 225.5 ± 52.0 |
| Device | RNS | Brown University MEA 1 | WIMAGINE | Real Size Model of This Study |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| use | epilepsy treatment | BMI | BMI | BMI |
| electrode location | Intra-cortical/subdural | Intra-cortical | Epidural | Subdural |
| Recording channel | 4 | 100 | 64 | 64 |
| Stimulation channel | 4 | - | - | - |
| Size | 60 × 27.5 × 7.5 mm | 50 × 40 × 10 mm | 50 × 50 × 10 mm | 50 × 30 × 10 mm |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, T.; Kameda, S.; Suzuki, K.; Kaiju, T.; Inoue, M.; Suzuki, T.; Hirata, M. Minimal Tissue Reaction after Chronic Subdural Electrode Implantation for Fully Implantable Brain–Machine Interfaces. Sensors 2021, 21, 178. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21010178
Yan T, Kameda S, Suzuki K, Kaiju T, Inoue M, Suzuki T, Hirata M. Minimal Tissue Reaction after Chronic Subdural Electrode Implantation for Fully Implantable Brain–Machine Interfaces. Sensors. 2021; 21(1):178. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21010178
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Tianfang, Seiji Kameda, Katsuyoshi Suzuki, Taro Kaiju, Masato Inoue, Takafumi Suzuki, and Masayuki Hirata. 2021. "Minimal Tissue Reaction after Chronic Subdural Electrode Implantation for Fully Implantable Brain–Machine Interfaces" Sensors 21, no. 1: 178. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21010178
APA StyleYan, T., Kameda, S., Suzuki, K., Kaiju, T., Inoue, M., Suzuki, T., & Hirata, M. (2021). Minimal Tissue Reaction after Chronic Subdural Electrode Implantation for Fully Implantable Brain–Machine Interfaces. Sensors, 21(1), 178. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21010178





