A Wireless High-Sensitivity Fetal Heart Sound Monitoring System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Structure of the Fetal Heart Sound Monitoring System
3. Fetal Heart Sound Collection
3.1. Fetal Heart Sound Sensor
3.2. Fetal Heart Sound Collection Module
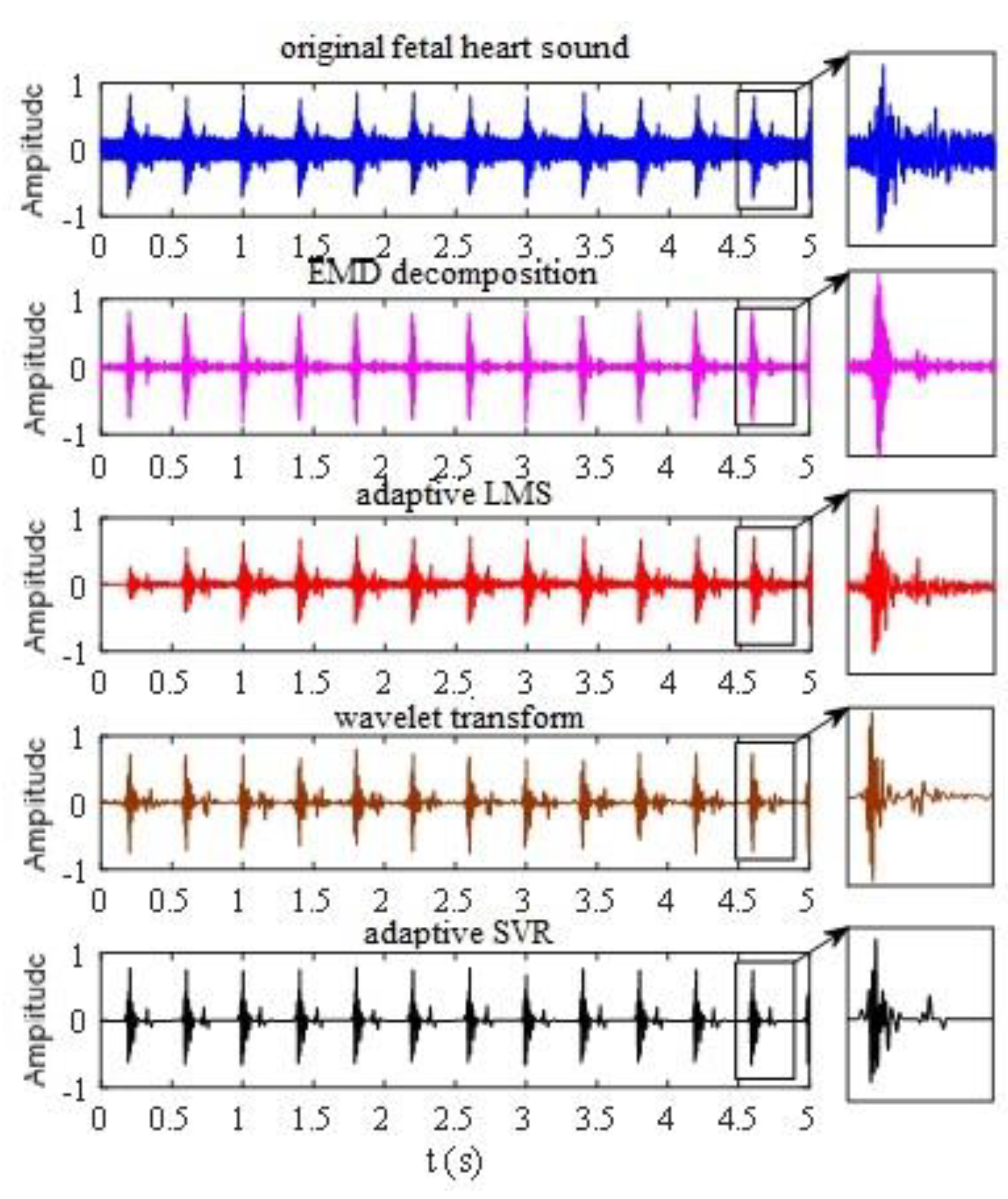
4. Adaptive Noise Reduction of the Fetal Heart Sound
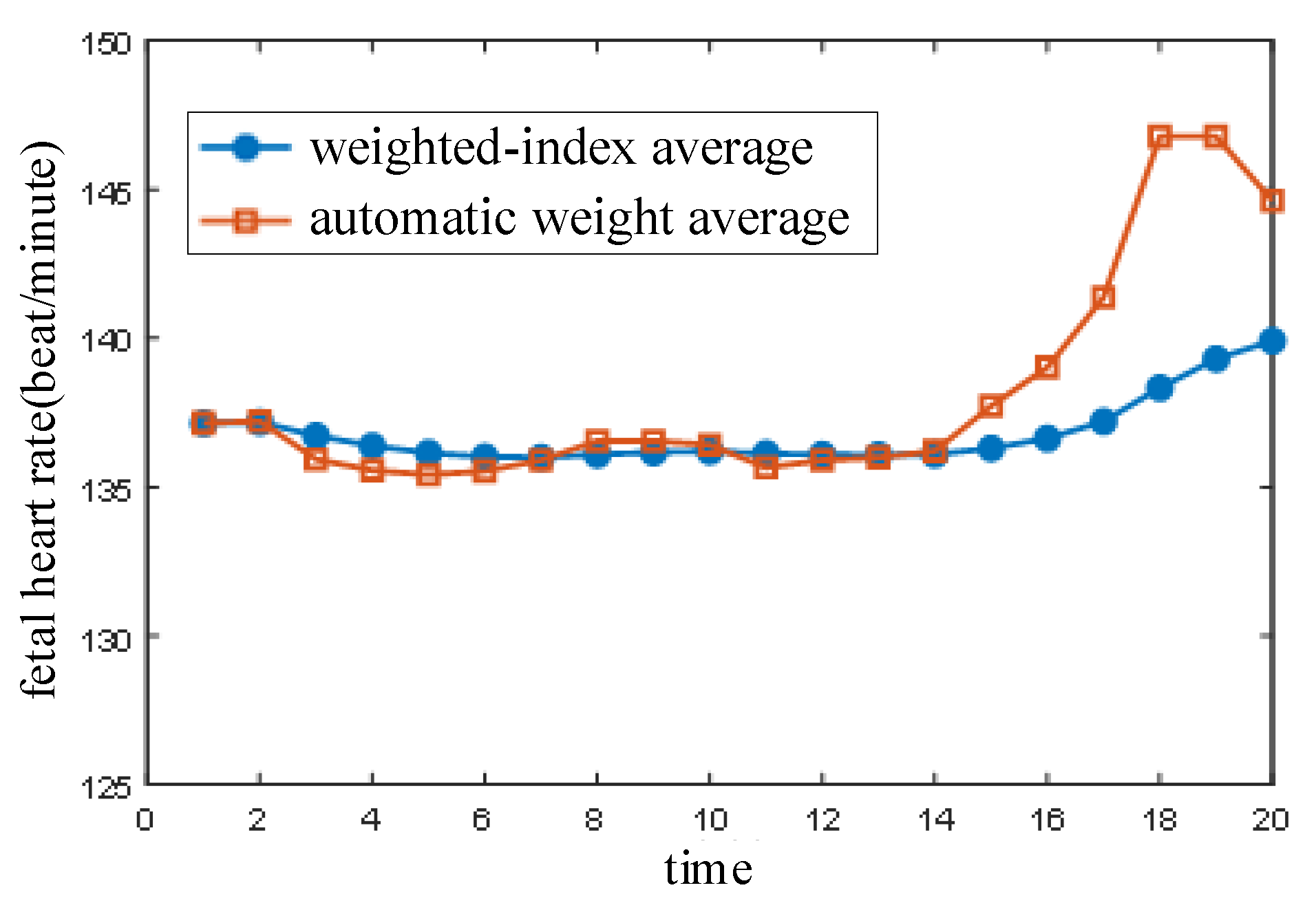
5. Extraction of Fetal Heart Rate
| Algorithm 1: Proposed Fetal Heart Rate Extraction Algorithm |
|
Input: D, fetal heart sound data with the time of T seconds, H, peak margin matrix, F0 = 0, t = 0, w = 4. 1. the fetal heart sound data were obtained from t to t + w in D; 2. sampling down, from 8 k to 1 k; 3. find out the position of m peaks; 4. calculate the interval of m−1 peak and sort them by size (largest to smallest) to obtain matrix P; 5. calculate the time difference of m−2 peak interval and obtain matrix E; 6. find out the index i, correspond to the minimum in E; 7. set , put P(i) and P(i + 1) into matrix H; 8. repeat step 5 and 6 until ; 9. calculate the mean of element in matrix H, At = mean(H); 10. calculate the fetal heart rate in window: ft = 60/At; 11. modify the fetal heart rate ; 12. move window backward: t = t + 1; 13. repeat 1–11 until t + w > T; Output: F0, F1, L, Ft−1. |
6. Experiment Result
6.1. Realization of the Collection Module
6.2. Experiment of Adaptive Noise Reduction
6.3. Fetal Heart Rate Extraction Experiment
7. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hamelmann, P.; Mischi, M.; Vullings, R.; Kolen, A.F.; Schmitt, L.; Joshi, S.; van Laar, J.O.E.H.; Bergmans, J.W.M. Flexible sensor matrix with dynamic channel weighting for improved estimation of the fetal heart rate by doppler ultrasound. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium (IUS), Washington, DC, USA, 6–9 September 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Khandoker, A.H.; Alangari, H.M.; Marzbanrad, F.; Kimura, Y. Investigating fetal myocardial function in heart anomalies by Doppler myocardial performance indices. In Proceedings of the 39th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Seogwipo, Korea, 11–15 July 2017; pp. 2197–2200. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, H.; Yoshimura, K.; Nakamoto, H.; Ishibashi, D.; Nakata, Y.; Yaginuma, Y.; Masui, S. 19.2 cm3 flexible fetal heart rate sensor for improved quality of pregnancy life. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Biomedical Circuits and Systems Conference (BioCAS), Shanghai, China, 17–19 October 2016; pp. 140–143. [Google Scholar]
- Andreotti, F.; Grasser, F.; Malberg, H.; Zaunseder, S. Non-Invasive Fetal ECG Signal Quality Assessment for Multichannel Heart Rate Estimation. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 64, 2793–2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovacs, F.; Goda, M.A.; Hosszu, G.; Telek, T. A Proposed Phonography-Based Measurement of Fetal Breathing Movement Using Segmented Structures with Frequency Splitting. In Proceedings of the 2020 42nd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 July 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Lakshmi, G.S.; Bhaskaran, A.; Bharadwaj, S.U.; Arora, M. Effect of Contact Force on Foetal Heart Sound Recordings. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Electronics, Computing and Communication Technologies (CONECCT), Bangalore, India, 2–4 July 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Eiríksdóttir, D.H.; Sæderup, R.G.; Riknagel, D.; Zimmermann, H.; Plocharski, M.; Hansen, J.; Struijk, J.J.; Schmidt, S.E. Quality Assessment of Maternal and Fetal Cardiovascular Sounds Recorded from the Skin Near the Uterine Arteries during Pregnancy. In Proceedings of the 2019 Computing in Cardiology (CinC), Singapore, 8–11 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Shengwei, W.; Yanni, L.; Jiayu, Z.; Jiajia, L. Agricultural price fluctuation model based on SVR. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Modelling, Identification and Control (ICMIC), Kunming, China, 10–12 July 2017; pp. 545–550. [Google Scholar]
- Mesquita, D.P.; Freitas, L.A.; Gomes, J.P.; Mattos, C.L. LS-SVR as a Bayesian RBF Network. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2020, 31, 4389–4393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ni, L.; Li, J.; Lin, S.; Xin, D. A method of noise optimization for Hardware Trojans detection based on BP neural network. In Proceedings of the 2nd IEEE International Conference on Computer and Communications (ICCC), Chengdu, China, 14–17 October 2016; pp. 2800–2804. [Google Scholar]
- Isogawa, K.; Ida, T.; Shiodera, T.; Takeguchi, T. Deep Shrinkage Convolutional Neural Network for Adaptive Noise Reduction. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2018, 25, 224–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Ma, J.; Zhang, X. User space transformation in deep learning based recommendation. J. Syst. Eng. Electron. 2020, 31, 674–684. [Google Scholar]
- Daryanavard, S.; Porr, B. Closed-Loop Deep Learning: Generating Forward Models with Backpropagation. Neural Comput. 2020, 32, 2122–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Wang, W.; Leung, R. SAR Target Classification Based on Radar Image Luminance Analysis by Deep Learning. IEEE Sens. Lett. 2020, 4, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, M.; Iuppariello, L.; D’Addio, G.; Clemente, F.; Amato, F.; Cesarelli, M. Computerised simulation of fetal heart rate signals. In Proceedings of the 2017 E-Health and Bioengineering Conference (EHB), Sinaia, Romania, 22–24 June 2017; pp. 185–188. [Google Scholar]
- Fuentealba, P.; Illanes, A.; Ortmeier, F. Cardiotocographic Signal Feature Extraction through CEEMDAN and Time-Varying Autoregressive Spectral-Based Analysis for Fetal Welfare Assessment. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 159754–159772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurun, G.; Zahorian, J.S.; Sisman, A.; Karaman, M.; Hasler, P.E.; Degertekin, F.L. An Analog Integrated Circuit Beamformer for High-Frequency Medical Ultrasound Imaging. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2012, 6, 454–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sbrollini, A.; Strazza, A.; Caragiuli, M.; Mozzoni, C.; Tomassini, S.; Agostinelli, A.; Morettini, M.; Fioretti, S.; Di Nardo, F.; Burattini, L. Fetal Phonocardiogram Denoising by Wavelet Transformation: Robustness to Noise. In Proceedings of the 2017 Computing in Cardiology (CinC), Rennes, France, 24–27 September 2017; Volume 44, pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Kahankova, R.; Martinek, R. Comparison of Fetal Phonocardiogram Wavelet Denoising Methods. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Signal Processing in Medicine and Biology Symposium (SPMB), Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1 December 2018; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Wei, J.; Li, X. Adaptive SVR Denoising Algorithm for Fetal Monitoring System. In Proceedings of the 2018 10th International Conference on Wireless Communications and Signal Processing (WCSP), Hangzhou, China, 18–20 October 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, J.; Wang, Z.; Xing, X. A Wireless High-Sensitivity Fetal Heart Sound Monitoring System. Sensors 2021, 21, 193. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21010193
Wei J, Wang Z, Xing X. A Wireless High-Sensitivity Fetal Heart Sound Monitoring System. Sensors. 2021; 21(1):193. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21010193
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Jianjun, Zhenyuan Wang, and Xinpeng Xing. 2021. "A Wireless High-Sensitivity Fetal Heart Sound Monitoring System" Sensors 21, no. 1: 193. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21010193
APA StyleWei, J., Wang, Z., & Xing, X. (2021). A Wireless High-Sensitivity Fetal Heart Sound Monitoring System. Sensors, 21(1), 193. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21010193



